Assessment of Diesel Engine Exhaust Levels in an Underground Mine Before and After Implementing Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) and Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mine Description
2.2. Diesel Emission Control Technologies
2.3. DPM Sampling
2.4. Laboratory Analysis
2.5. Gas Detectors
2.6. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Gas Concentrations
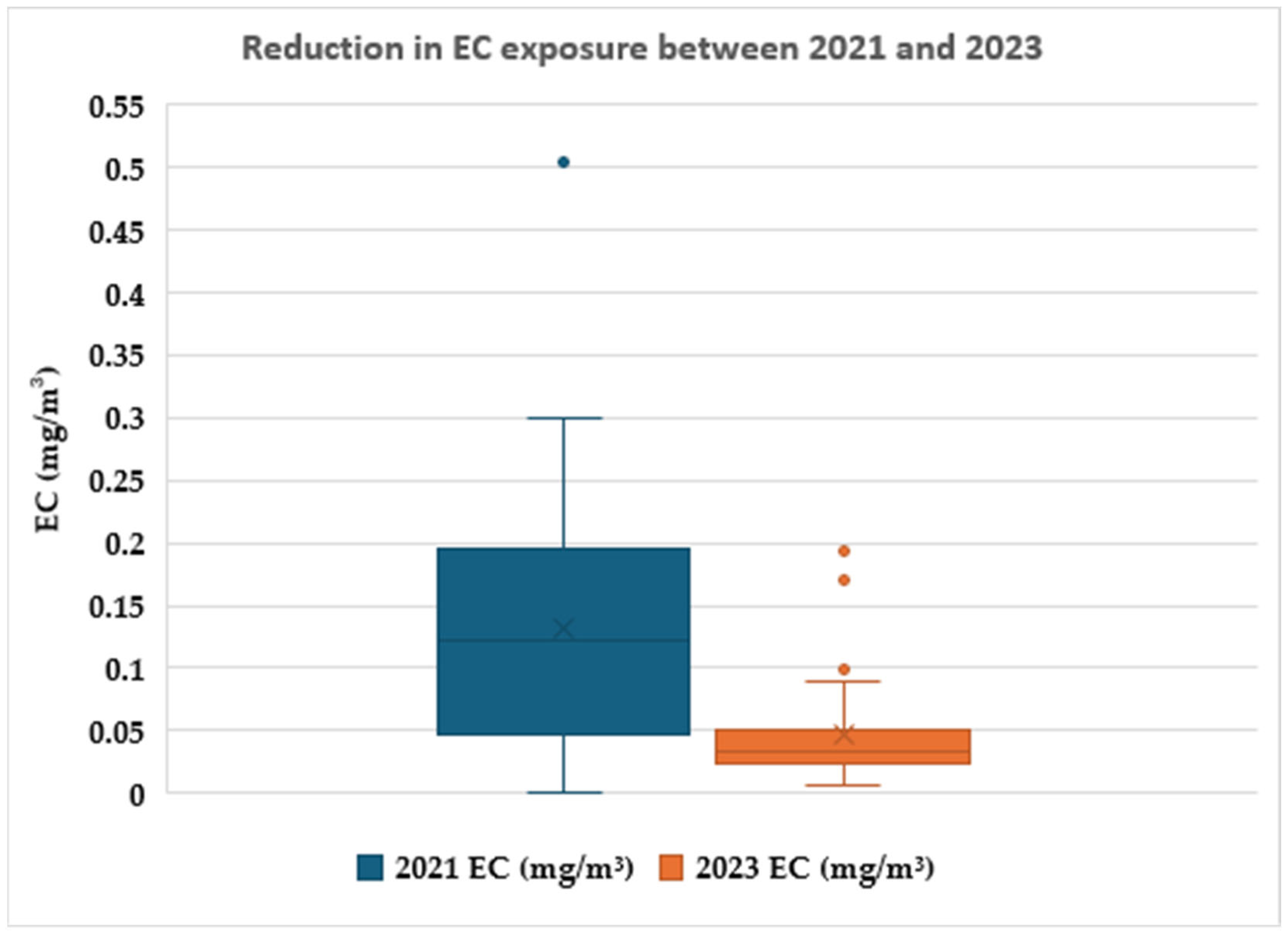
3.2. Elemental Carbon (EC) and Total Carbon (TC) Levels
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DPM | Diesel particulate matter |
| PM | Particulate matter |
| DEE | Diesel engine exhaust emissions |
| DPF | Diesel Particulate Filters |
| SCR | Selective Catalytic Reduction |
| EC | Elemental carbon |
| TC | Total carbon |
| OEL | Occupational exposure limit |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| NO2 | Nitrogen dioxide |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| PAHs | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| PN | Particle number |
| ECS | Emission control systems |
Appendix A. Mine Ventilation Layout and Key Working Zones
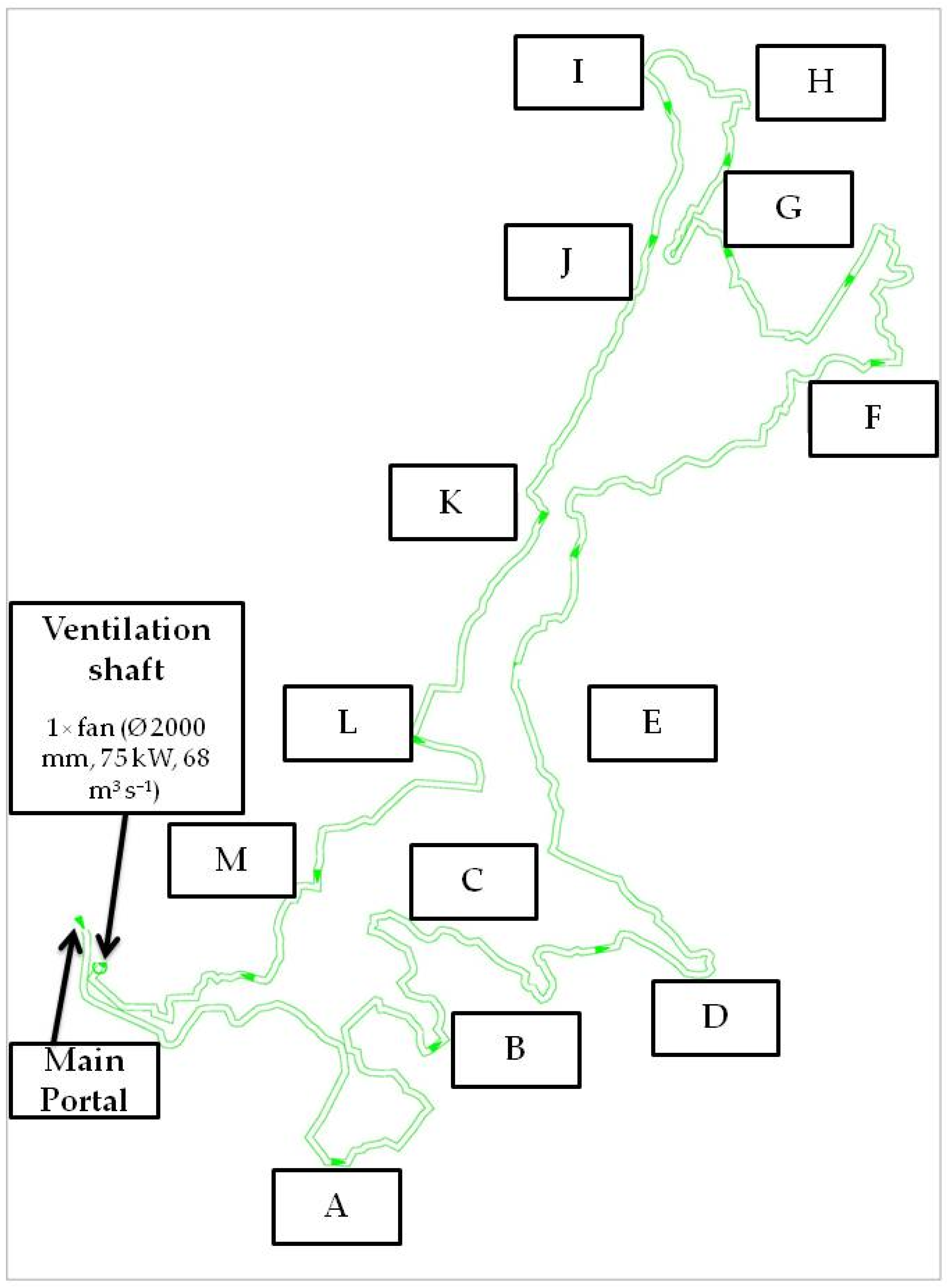
| Working Zone | Average Elevation (m) | Distance to Main Portal (m) | Distance to Ventilation Shaft (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Portal | 69 | 0 | 7780 |
| A | 40 | 790 | 6990 |
| B | 25 | 1400 | 6380 |
| C | –10 | 1720 | 6060 |
| D | 6 | 2410 | 5370 |
| E | –48 | 3020 | 4460 |
| F | –164 | 4050 | 3730 |
| G | –164 | 5120 | 2660 |
| H | –190 | 5380 | 2400 |
| I | –165 | 5575 | 2205 |
| J | –125 | 5870 | 1910 |
| K | –65 | 6270 | 1510 |
| L | –24 | 6860 | 920 |
| M | –10 | 7270 | 510 |
| Ventilation Shaft | 86 | 7780 | 0 |
Appendix B. Inventory of Underground Mining Equipment
| Equipment Type | Vehicle Model | Engine Specification | Year of Manufacture | ECS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loader | OK-L20 | DEUTZ/L20, 89 kW, 1800 rpm | 2001 | Proventia NOxBuster |
| Loader | OK-L20 | DEUTZ/L20, 89 kW, 1800 rpm | 1993 | Proventia NOxBuster |
| Loader | OK-L20 | DEUTZ/L20, 89 kW, 1800 rpm | 1992 | Proventia NOxBuster |
| Loader | OK-L20 | DEUTZ/L20, 89 kW, 1800 rpm | 1998 | Proventia NOxBuster |
| Loader | OK-L20 | DEUTZ/L20, 89 kW, 1800 rpm | 2000 | Proventia NOxBuster |
| Loader | OK-L20 | DEUTZ/L20, 89 kW, 1800 rpm | 2001 | - |
| Articulated Dumper | VOLVO A25 | VOLVO BM, 3245 kW | 1991 | Proventia NOxBuster |
| Truck | MERCEDES 2629 | MERCEDES, 59 kW/213 | 1992 | Proventia NOxBuster |
| Truck | MERCEDES 2629AK | MERCEDES, 59 kW/213 | 1992 | Proventia NOxBuster |
| Truck | MERCEDES 2629AK | MERCEDES, 59 kW/213 | 1991 | Proventia NOxBuster |
| Truck | MERCEDES 2629AK | MERCEDES, 59 kW/213 | 1990 | Proventia NOxBuster |
| Jumbo Drill | MERCURY 14IFPD6 | DEUTZ F6L912W | 1993 | Proventia NOxBuster |
| Jumbo Drill | MERCURY 1FPD6 | DEUTZ D914L06 | 1998 | Proventia NOxBuster |
| Jumbo Drill | MERCURY 14IFD | DEUTZ D914L06 | 2009 | Proventia NOxBuster |
| Excavator | CASE CX145C | ISUZU AM-4JJ1X, 74.9 kW | 2013 | Factory-installed ECS |
| Telescopic Platform | DIECI ET173 RUNNER 30.11 | IVECO D-F4GE9454A, 74 kW | 2007 | No |
| Telescopic Platform | DIECI LLM175 RUNNER 30.11 | IVECO D-F4GE9454A, 74 kW | 2011 | No |
| Telescopic Platform | DIECI LLM175 RUNNER 30.11 | IVECO D-F4GE9454A, 74 kW | 2011 | No |
| Telescopic Platform | TEREX ELELIFT 3713 ELITE | PERKINS D-2166/2300, 63.5 kW | 2005 | No |
Appendix C. Field Monitoring Data of Personal Carbon Exposures
| Year | Position | Sampling Time (min) | OC ± Uncertainty (µg C/Filter) | EC ± Uncertainty (µg C/Filter) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | Truck Driver | 334 | 169.6 ± 27.6 | 50.3 ± 9.7 |
| 2021 | Electrician | 371 | 282.9 ± 37.5 | 84.0 ± 15.5 |
| 2021 | Blaster | 370 | 132.3 ± 23.0 | 39.4 ± 8.2 |
| 2021 | Supervisor | 402 | 194.4 ± 30.5 | 84.0 ± 15.7 |
| 2021 | Jumbo operator | 393 | 257.6 ± 36.4 | 140.4 ± 24.0 |
| 2021 | Mechanic | 379 | 103.0 ± 19.0 | 39.5 ± 8.2 |
| 2021 | Truck Driver | 331 | 221.3 ± 33.8 | 91.3 ± 17.3 |
| 2021 | Rock Bolts installation | 316 | 98.5 ± 18.2 | 73.7 ± 14.1 |
| 2021 | Scaling with cherry picker | 378 | 234.3 ± 34.2 | 117.6 ± 20.9 |
| 2021 | Loader Operator | 344 | 161.3 ± 26.9 | 99.9 ± 18.5 |
| 2021 | Scaling with cherry picker | 395 | 210.9 ± 32.7 | 210.0 ± 32.6 |
| 2021 | Blaster | 401 | 256.5 ± 35.8 | 209.0 ± 32.5 |
| 2021 | Truck Driver | 337 | 292.0 ± 38.5 | 159.8 ± 26.8 |
| 2021 | Jumbo operator | 396 | 243.5 ± 35.2 | 156.5 ± 26.0 |
| 2021 | Manual Scaling | 400 | 177.9 ± 29.5 | 272.3 ± 38.0 |
| 2021 | Supervisor | 392 | 149.7 ± 26.1 | 164.8 ± 27.8 |
| 2021 | Mine Manager | 366 | 94.1 ± 17.6 | 71.4 ± 14.3 |
| 2021 | Loader Operator | 345 | 147.5 ± 25.3 | 397.1 ± 41.4 |
| 2021 | Excavator Operator | 334 | 292.2 ± 39.3 | 169.2 ± 28.8 |
| 2021 | Explosives delivery | 333 | 124.0 ± 21.7 | 115.3 ± 20.8 |
| 2023 | Electrician | 383 | 172.0 ± 31.0 | 65.6 ± 11.5 |
| 2023 | Loader Operator | 378 | 87.9 ± 16.5 | 80.0 ± 14.8 |
| 2023 | Blaster | 378 | 54.0 ± 9.9 | 42.3 ± 7.2 |
| 2023 | Scaling with cherry picker | 386 | 97.8 ± 17.6 | 59.1 ± 10.6 |
| 2023 | Jumbo operator | 388 | 67.4 ± 12.3 | 56.9 ± 10.5 |
| 2023 | Jumbo operator | 388 | 251.8 ± 42.3 | 166.4 ± 29.9 |
| 2023 | Mechanic | 386 | 53.6 ± 9.7 | 19.3 ± 2.6 |
| 2023 | Truck Driver | 371 | 74.9 ± 14.1 | 37.9 ± 6.2 |
| 2023 | Loader Operator | 390 | 71.3 ± 13 2 | 60.8 ± 10.6 |
| 2023 | Loader Operator | 390 | 142.3 ± 25.5 | 83.4 ± 14.9 |
| 2023 | Truck Driver | 376 | 123.4 ± 22.9 | 62.6 ± 11.5 |
| 2023 | Loader Operator | 378 | 116.4 ± 21.2 | 51.1 ± 8.8 |
| 2023 | Truck Driver | 370 | 87.7 ± 16.0 | 41.6 ± 7.1 |
| 2023 | Excavator Operator | 498 | 106.3 ± 19.2 | 17.4 ± 2.6 |
| 2023 | Supervisor | 375 | 58.7 ± 10 5 | 42.9 ± 7.0 |
| 2023 | Mine Manager | 356 | 63.5 ± 11.5 | 30.9 ± 5.3 |
| 2023 | Blaster | 387 | 140.5 ± 25.6 | 93.7 ± 16.8 |
| 2023 | Loader Operator | 388 | 431.6 ± 59.7 | 318.5 ± 50.0 |
| 2023 | Jumbo operator | 391 | 150.4 ± 27.0 | 54.0 ± 9.9 |
| 2023 | Electrician | 386 | 215.9 ± 37.2 | 80.5 ± 15.0 |
| 2023 | Loader Operator | 411 | 204.9 ± 35.5 | 194.2 ± 33.7 |
| 2023 | Manual Scaling | 381 | 165.9 ± 30.0 | 120.9 ± 22.1 |
| 2023 | Supervisor | 387 | 90.7 ± 16.6 | 72.4 ± 13.1 |
| 2023 | Loader Operator | 385 | 194.6 ± 34.4 | 96.0 ± 17.6 |
| 2023 | Truck Driver | 379 | 97.6 ± 17.5 | 50.6 ± 9.2 |
| 2023 | Loader Operator | 399 | 136.5 ± 24.5 | 91.0 ± 16.6 |
| 2023 | Truck Driver | 368 | 130.9 ± 23.7 | 52.7 ± 9 7 |
| 2023 | Truck Driver | 385 | 143.9 ± 26.3 | 119.3 ± 21.9 |
| 2023 | Services | 382 | 129.7 ± 23.7 | 92.9 ± 16.7 |
| 2023 | Mechanic | 570 | 115.3 ± 21.3 | 340.5 ± 52.4 |
| 2023 | Surveyor | 381 | 101.3 ± 18.5 | 47.5 ± 7.9 |
| 2023 | Maintenance engineer | 362 | 68.0 ± 12.4 | 21.2 ± 2.7 |
References
- IARC. IARC Diesel Engine Exhaust Carcinogenic; IARC: Lyon, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Diesel Engine Exhaust (DEE). Stop Carcinogens at Work. Available online: https://stopcarcinogensatwork.eu/fact/diesel-engine-exhaust/ (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Azam, S.; Liu, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Zheng, S. Assessing the Hazard of Diesel Particulate Matter (DPM) in the Mining Industry: A Review of the Current State of Knowledge. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2024, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, A.; Coble, J.; Stewart, P. Occupational Exposure to Diesel Engine Exhaust: A Literature Review. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2009, 19, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, H.; Lopez-Pola, T.; Martinez-Gonzalez, D.; Alonso-Barcena, J. Assessment of NOx Levels in an Underground Hospital Car Park: Implications for Occupational and Environmental Health. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugarski, A.D.; Ritter, D.A. Advanced Diesel Powertrains for Underground Mining Mobile Equipment. Min. Metall. Explor. 2025, 42, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, S.; Bisig, C.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Diesel Exhaust: Current Knowledge of Adverse Effects and Underlying Cellular Mechanisms. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1541–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadano, Y.S.; Borillo, G.C.; Godoi, A.F.L.; Cichon, A.; Silva, T.O.B.; Valebona, F.B.; Errera, M.R.; Penteado Neto, R.A.; Rempel, D.; Martin, L.; et al. Gaseous Emissions from a Heavy-Duty Engine Equipped with SCR Aftertreatment System and Fuelled with Diesel and Biodiesel: Assessment of Pollutant Dispersion and Health Risk. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 500–501, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive (EU) 2019/130 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 January 2019 Amending Directive 2004/37/EC on the Protection of Workers from the Risks Related to Exposure to Carcinogens or Mutagens at Work (Text with EEA Relevance.); 2019; Volume 030. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32019L0130 (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- García-González, H.G.; González-Garcia, J.; Fernández-Cachon, S.G.C.; Mateos, S.P. Nitrogen Oxides Gas Levels in NATM Tunnel Construction during the Directive 2017/164/EU Transitional Period. Inf. Constr. 2022, 74, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Tato Diogo, M. European Legal Framework Related to Underground Mining and Tunnelling Concerning Commission Directive (EU) 2017/164, 31 January Establishing a Fourth List of Indicative Occupational Exposure Limit Values. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2020, 30, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, H.; Rodriguez, R.; Bascompta, M. Nitrogen Dioxide Gas Levels in TBM Tunnel Construction with Diesel Locomotives Based on Directive 2017/164/EU. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emission Standards: Europe: Nonroad Engines. Available online: https://dieselnet.com/standards/eu/nonroad.php (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Rumchev, K.; Hoang, D.V.; Lee, A. Trends in Exposure to Diesel Particulate Matter and Prevalence of Respiratory Symptoms in Western Australian Miners. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gren, L.; Krais, A.M.; Assarsson, E.; Broberg, K.; Engfeldt, M.; Lindh, C.; Strandberg, B.; Pagels, J.; Hedmer, M. Underground Emissions and Miners’ Personal Exposure to Diesel and Renewable Diesel Exhaust in a Swedish Iron Ore Mine. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2022, 95, 1369–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, P.A.; Coble, J.B.; Vermeulen, R.; Schleiff, P.; Blair, A.; Lubin, J.; Attfield, M.; Silverman, D.T. The Diesel Exhaust in Miners Study: I. Overview of the Exposure Assessment Process. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2010, 54, 728–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debia, M.; Couture, C.; Njanga, P.-E.; Neesham-Grenon, E.; Lachapelle, G.; Coulombe, H.; Hallé, S.; Aubin, S. Diesel Engine Exhaust Exposures in Two Underground Mines. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2017, 27, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, M.K.; Mensah-Darkwa, K.; Drebenstedt, C.; Annam, B.V.; Armah, E.K. Occupational Respirable Mine Dust and Diesel Particulate Matter Hazard Assessment in an Underground Gold Mine in Ghana. J. Health Pollut. 2020, 10, 200305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanatidis, S.; Ntziachristos, L.; Giechaskiel, B.; Bergmann, A.; Samaras, Z. Impact of Selective Catalytic Reduction on Exhaust Particle Formation over Excess Ammonia Events. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11527–11534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herner, J.D.; Hu, S.; Robertson, W.H.; Huai, T.; Chang, M.-C.O.; Rieger, P.; Ayala, A. Effect of Advanced Aftertreatment for PM and NOx Reduction on Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine Ultrafine Particle Emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2413–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Thomson, E.M.; Kumarathasan, P.; Guénette, J.; Rosenblatt, D.; Chan, T.; Rideout, G.; Vincent, R. Nitrogen Dioxide and Ultrafine Particles Dominate the Biological Effects of Inhaled Diesel Exhaust Treated by a Catalyzed Diesel Particulate Filter. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 135, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotek, M. Analysis of Particulate Matter Production during DPF Service Regeneration. In Proceedings of the TAE 2019-Proceeding of 7th International Conference on Trends in Agricultural Engineering, Prague, Czech Republic, 17–20 September 2019; Volume 2019, pp. 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, O.P.; Lüers, B.; Heuser, B.; Holderbaum, B.; Pischinger, S. Fuel Formulation Effects on the Soot Morphology and Diesel Particulate Filter Regeneration in a Future Optimized High-Efficiency Combustion System. Int. J. Engine Res. 2017, 18, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimaratos, A.; Giechaskiel, B.; Clairotte, M.; Fontaras, G. Impact of Active Diesel Particulate Filter Regeneration on Carbon Dioxide, Nitrogen Oxides and Particle Number Emissions from Euro 5 and 6 Vehicles under Laboratory Testing and Real-World Driving. Energies 2022, 15, 5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIOSH. Diesel Particulate Matter (as Elemental Carbon): Method 5040 Issue 4. NIOSH Man Occup. Saf. Health 2016, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Real Decreto 427/2021, de 15 de junio, por el que se modifica el Real Decreto 665/1997, de 12 de mayo, sobre la protección de los trabajadores contra los riesgos relacionados con la exposición a agentes cancerígenos durante el trabajo. Boletín Oficial del Estado (BOE) 2021, A-2021-10029, 73376–73381. Available online: https://www.boe.es/eli/es/rd/2021/06/15/427 (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- ISO/IEC 17025:2017; General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/66912.html (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- UNE-EN 16909:2018; Ambient Air—Measurement of Elemental Carbon (EC) and Organic Carbon (OC) Collected on Filters. Asociación Española de Normalización (AENOR): Madrid, Spain, 2018.
- Olkhovskiy, D.V.; Parshakov, O.S.; Bublik, S.A. Study of Gas Hazard Pattern in Underground Workings after Blasting. Min. Sci. Technol. 2023, 8, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Directive (EU) 2017/164 of 31 January 2017 Establishing a Fourth List of Indicative Occupational Exposure Limit Values Pursuant to Council Directive 98/24/EC, and Amending Commission Directives 91/322/EEC, 2000/39/EC and 2009/161/EU (Text with EEA Relevance.); 2017; Volume 027. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2017/164/oj/eng (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- Noll, J.D.; Mischler, S.; Cauda, E.; Patts, L.; Janisko, S.; Grau, R. The Effects of Passive Diesel Particulate Filters on Diesel Particulate Matter Concentrations in Two Underground Metal/Non-Metal Mines. In Proceedings of the 13th US/North American Mine Ventilation Symposium, Sudbury, ON, Canada, 13–16 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- MSHA-Tool Box Series-Practical Ways to Reduce Exposure to Diesel Exhaust in Mining. Available online: https://arlweb.msha.gov/S&HINFO/TOOLBOX/DTBFINAL.htm#13 (accessed on 4 March 2025).
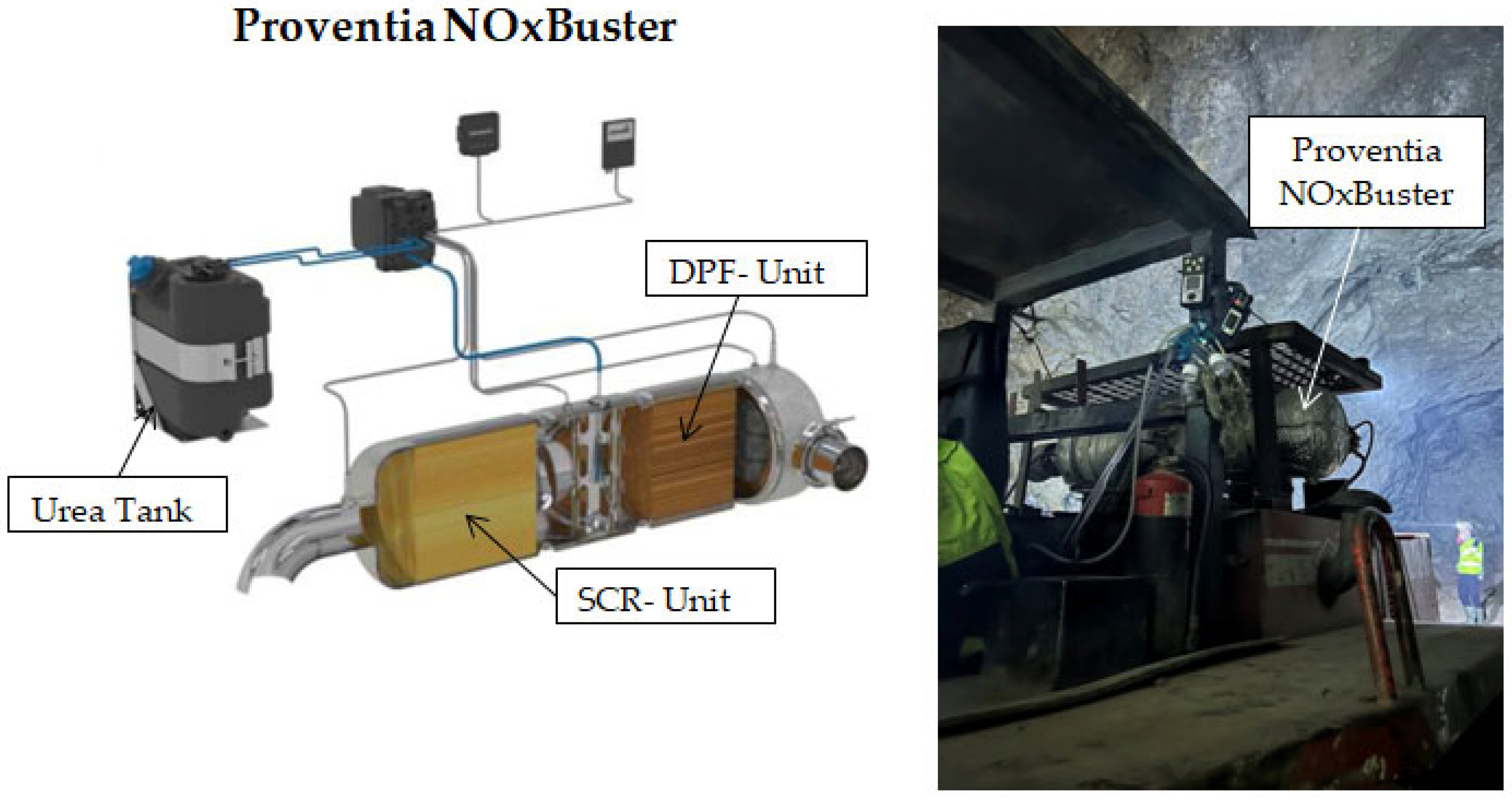

| Machine Type | Number of Units |
|---|---|
| Loaders | 6 |
| Drilling Jumbos (diesel) | 3 |
| Trucks | 7 |
| Excavators | 1 |
| Telescopic Handlers | 4 |
| Other Vehicles | 11 |
| Date | Place | NO (ppm) | NO2 (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15/12/2020 | Jumbo | 9.57 | 0.38 |
| 17/12/2020 | Jumbo | 7.45 | 0.80 |
| 22/12/2020 | Jumbo | 8.41 | 1.30 |
| 23/12/2020 | Jumbo | 1.81 | 0.03 |
| 13/01/2021 | Jumbo | 3.54 | 0.41 |
| Pred-ECS (mean) | 6.15 | 0.58 | |
| 28/11/2023 | Jumbo | 1.52 | 0.13 |
| 29/11/2023 | Jumbo | 1.24 | 0.18 |
| Post-ECS (mean) | 1.38 | 0.16 | |
| Date | Place | NO (ppm) | NO2 (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15/12/2020 | Loader | 3.06 | 0.23 |
| 16/12/2020 | Loader | 5.65 | 1.22 |
| 17/12/2020 | Loader | 5.40 | 0.41 |
| 23/12/2020 | Loader | 3.46 | 0.74 |
| 22/12/2020 | Loader | 5.70 | 0.87 |
| 13/01/2021 | Loader | 2.39 | 0.35 |
| Pre-ECS (mean) | 4.28 | 0.64 | |
| 29/11/2023 | Loader | 4.40 | 0.36 |
| 28/11/2023 | Loader | 4.28 | 0.30 |
| Post-ECS (mean) | 4.34 | 0.33 | |
| - | 2021 | 2023 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| POSITION | EC (mg/m3) | TC (mg/m3) | EC (mg/m3) | TC (mg/m3) |
| Electrician | 0.100 | 0.435 | 0.036 | 0.134 |
| Electrician | - | - | 0.044 | 0.183 |
| Blaster | 0.046 | 0.204 | 0.051 | 0.146 |
| Blaster | 0.227 | 0.505 | 0.023 | 0.046 |
| Truck Driver | 0.067 | 0.293 | 0.021 | 0.057 |
| Truck Driver | 0.210 | 0.594 | 0.023 | 0.068 |
| Truck Driver | 0.122 | 0.417 | 0.035 | 0.102 |
| Truck Driver | - | - | 0.03 | 0.119 |
| Truck Driver | - | - | 0.065 | 0.163 |
| Truck Driver | - | - | 0.028 | 0.094 |
| Loader Operator | 0.505 | 0.693 | 0.032 | 0.066 |
| Loader Operator | 0.129 | 0.336 | 0.044 | 0.123 |
| Loader Operator | - | - | 0.028 | 0.091 |
| Loader Operator | - | - | 0.171 * | 0.469 |
| Loader Operator | - | - | 0.099 | 0.233 |
| Loader Operator | - | - | 0.052 | 0.18 |
| Loader Operator | - | - | 0.048 | 0.137 |
| Loader Operator | - | - | 0.044 | 0.09 |
| Supervisor | 0.092 | 0.304 | 0.024 | 0.049 |
| Supervisor | 0.182 | 0.347 | 0.039 | 0.101 |
| Jumbo operator | 0.158 | 0.447 | 0.029 | 0.126 |
| Jumbo operator | 0.173 | 0.442 | 0.090 | 0.243 |
| Jumbo operator | - | - | 0.030 | 0.061 |
| Rock Bolts installation | 0.107 | 0.249 | - | - |
| Mechanic | 0.046 | 0.166 | 0.010 | 0.03 |
| Mechanic | - | - | 0.193 | 0.296 |
| Scaling with cherry picker | 0.137 | 0.410 | 0.032 | 0.083 |
| Scaling with cherry picker | 0.233 | 0.466 | - | - |
| Manual Scaling | 0.299 | 0.494 | 0.067 | 0.181 |
| Excavator Operator | 0.221 | 0.603 | 0.007 | 0.048 |
| Explosives delivery | 0.153 | 0.318 | - | - |
| Mine Manager | 0.083 | 0.193 | 0.018 | 0.047 |
| Services | - | - | 0.051 | 0.14 |
| Surveyor | - | - | 0.026 | 0.093 |
| Maintenance engineer | - | - | 0.012 | 0.059 |
| MEDIAN (P25-P75) | 0.145 (0.098–0.213) | 0.413 (0.301–0.473) | 0.034 (0.026–0.051) | 0.102 (0.065–0.150) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Menendez-Cabo, P.; Garcia-Gonzalez, H. Assessment of Diesel Engine Exhaust Levels in an Underground Mine Before and After Implementing Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) and Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) Systems. Clean Technol. 2025, 7, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol7040104
Menendez-Cabo P, Garcia-Gonzalez H. Assessment of Diesel Engine Exhaust Levels in an Underground Mine Before and After Implementing Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) and Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) Systems. Clean Technologies. 2025; 7(4):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol7040104
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenendez-Cabo, Pablo, and Hector Garcia-Gonzalez. 2025. "Assessment of Diesel Engine Exhaust Levels in an Underground Mine Before and After Implementing Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) and Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) Systems" Clean Technologies 7, no. 4: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol7040104
APA StyleMenendez-Cabo, P., & Garcia-Gonzalez, H. (2025). Assessment of Diesel Engine Exhaust Levels in an Underground Mine Before and After Implementing Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) and Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) Systems. Clean Technologies, 7(4), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol7040104







