Abstract
In this study, we investigated the use of functionalized deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as a medium for CO2 capture integrated with CO2 desorption and biofixation in microalgal culture, as an approach for carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS). The newly devised DES formulation—comprising choline chloride, ethylene glycol, and monoethanolamine—demonstrated a significant advancement in CO2 absorption capacity compared with conventional solvents. Effective CO2 desorption from the solvent was also achieved, recovering nearly 90% of the captured CO2. We then examined the application of the functionalized DESs to promote microalgal cultivation using a Chlorella sp. strain. The experimental results indicated that microalgae exposed to DES-desorbed CO2 exhibited heightened growth rates and enhanced biomass production, signifying the potential of DES-driven CO2 capture for sustainable microalgal biomass cultivation. This research contributes to the growing field of CCUS strategies, offering an avenue for efficient CO2 capture and conversion into valuable biomasses, thereby contributing to both environmental sustainability and bioresource use.
1. Introduction
CO2 capture using deep eutectic solvents (DESs) is a promising technology that involves the use of a low-cost and environmentally friendly solvent to selectively capture CO2 from flue gasses. A DES is a type of low-transition temperature mixture (LTTM) that is formed by mixing two or more solid and/or liquid components at a specific molar ratio to form a composition that should have a lower melting point than its individual components [1]. The lower melting point is obtained through the formation of hydrogen bonds between at least one component acting as a hydrogen bond donor (HBD) and one component acting as a hydrogen bond acceptor (HBA).
For understanding and the optimal use of DESs, it is essential to recognize their customizable nature for specific applications. These solvents offer a range of potential uses, such as effective organic solvents for reactions [2], cosmetic applications [3], and biotransformations [4]. DESs have several advantages over conventional solvents, including low volatility, high solubility, and low toxicity (depending on the nature of their components) [5]. These properties render them ideal candidates for CO2 capture [6,7,8,9,10] as they can effectively capture CO2 from flue gasses, with a lower energy cost and smaller environmental footprint. DESs can be easily regenerated; thus, they are suitable for multiple cycles of CO2 capture and release.
CO2 capture using DESs [6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17] is a promising technology that can significantly contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change. Further research and development are required to optimize the process and increase its economic feasibility for large-scale industrial applications [18].
Carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) are a set of technologies and techniques that aim to reduce CO2 emissions [19] from industrial processes and power generation by capturing CO2 and either using it for various purposes (such as enhanced oil recovery, chemical production, or concrete production) or storing it underground in geological formations [20,21]. The goal of CCUS is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change whilst maintaining energy security and supporting economic growth.
A promising application of CCUS is CO2 use for microalgal growth [18,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. This involves using CO2 as a carbon source for photosynthesis in microalgae. Microalgae convert CO2 into organic matter through photosynthesis, which can then be used as feedstock for various applications such as biofuels, animal feed, and pharmaceuticals. Microalgae are capable of capturing and fixing large amounts of CO2 from various sources, including industrial exhaust gasses, thus contributing to the mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions. Using CO2 to cultivate microalgae can reduce the cost of microalgae production because CO2 is typically a waste product in many industrial processes. CO2 use for microalgal growth is a promising approach for the sustainable production of valuable products whilst mitigating climate change.
Several drawbacks limit the application of microalgae cultivation for CO2 fixation from emissions of industrial processes [30,31]. One of these drawbacks is related to high CO2 content in industrial emissions, the presence of nitric and sulfur oxides, and limited rates of CO2 fixation by microalgae [30]. One solution to these drawbacks is to capture CO2 in a solvent and further release it for microalgae cultivation [32].
A category of solvents that could be used for such an integrated capture–desorption–biofixation process is DESs. A key advantage of DESs lies in their capacity for functionalization or customization [14,33,34,35]. Within this framework, CO2 is captured within the eutectic cage formed by hydrogen bonding between the HBA and HBD through weak physical, i.e., van der Waals, interactions [8].
Ethaline (a DES based on choline chloride (ChCl) as an HBA and ethylene glycol (EG) as an HBD at a ratio of 1:2) has demonstrated CO2 capture capacity but at high pressure (60 bar) [36,37,38]. Monoethanolamine (MEA) is known to be highly reactive with CO2, forming carbamate, but it has the drawback of being corrosive [39,40,41]. Our groups [42] and others’ groups have demonstrated that incorporating MEA into DESs significantly reduces the corrosiveness of MEA. In a previous study, it was demonstrated that mixtures of ethaline and amines such as MEA had a similar CO2 absorption capacity to aqueous solutions of amines, but at lower pressures [41]. Most of the studies investigating DESs as CO2 solubilizers have focused on the process of CO2 capturing and desorption in DESs, with less focus on the further utilization of CO2.
The objective of this study was to develop a CCUS process at a laboratory scale that involved capturing CO2 using deep eutectic solvents at a low pressure and desorbing CO2 into a bioreactor system for microalgal growth. To address the challenges of high pressure and corrosiveness, we functionalized ethaline with MEA. This functionalization involved the introduction of pure MEA as an additional HBD to ethaline (ChCl:EG 1:2) at a 1:1 molar ratio (ethaline:MEA), forming a ternary DES. The resulting functionalized solvent, abbreviated as CEM 1:2:1 (ChCl:EG:MEA 1:2:1), underwent physicochemical characterization and laboratory testing to determine its performance. The CEM 1:2:1 DES was compared with the binary solvent ChCl:MEA 1:8 (abbreviated as CM 1:8) DES for CO2 capture and microalgae growth.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The microalgae strain used was Chlorella sp. NIVA-CHL 137, obtained from the Norwegian Culture Collection of Algae (NORCCA), Norwegian Institute for Water Research (Oslo, Norway). Chlorella sp. NIVA-CHL 137 was isolated from a terrestrial habitat and was demonstrated to have a significant ability to grow in axenic conditions [43].
High-purity reagents were used in the preparation of the DESs. ChCl with +98% purity was purchased from Alfa Aesar (Ward Hill, MA, USA), and MEA and EG of 99.9% purity were procured from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). The components were mixed, characterized by their physicochemical properties, and tested.
In this study, Chlorella sp. NIVA-CHL 137 was cultivated using a BG-11 growth medium [44]. For the preparation of the BG-11 growth medium, the following reagents were acquired: sodium nitrate (NaNO3), magnesium sulfate (MgSO4 · 7H2O), calcium chloride (CaCl2 · 2H2O), iron(III) chloride, and cobalt(II) nitrate (Co(NO3)2 · 6H2O), which were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany); potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KHPO4), citric acid, boric acid (H3BO3), zinc sulfate (ZnSO4 · 7H2O), sodium molybdate (Na2MoO4 · 2H2O), and cobalt(II) nitrate (Co(NO3)2 · 6H2O), which were obtained from Scharlau (Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain); EDTA disodium salt (Na2EDTA · 2H2O), which was sourced from Honeywell Fluka (Seelze, Germany); manganese chloride (MnCl2 · 4H2O), which was procured from Carl Roth GmbH (Karlsruhe, Germany); and copper sulfate (CuSO4 · 5H2O), which was acquired from Chimopar S.A. (Bucharest, Romania). Merck (Darmstadt) supplied dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) for the chlorophyll extractions.
2.2. DES Preparation
The reflux system used to prepare the DESs comprised a round-bottomed flask and an ascending condenser composed of a glass tube in the form of bubbles, surrounded by a glass jacket through which cooling water was circulated and released at the top. It was only used as a bottom-up condenser in the reflux setups. An electric heating plate and an oil bath were also used.
The reagents were accurately weighed, mixed in the round-bottomed flask, and agitated at 600 RPM to ensure even mixing. The temperature was maintained at 60 °C for approximately 2 h until a clear, homogenous liquid was obtained [45,46,47]. After cooling, the samples were transferred to airtight plastic or glass containers and stored at room temperature in a desiccator. A proper sealing system was crucial because choline chloride has a high level of hygroscopicity [48], even within an eutectic mixture.
2.3. CO2 Capture Using the DES
A system based on a vapor–liquid equilibrium (VLE) [37,49,50] was created for the absorption tests in the laboratory. It consisted of a cylinder with pure CO2 gas (99.999% purity, SIAD, Romania), a glass reactor with a ceramic bubbler for fine gas distribution, a magnetic stirrer to prolong the contact time between the gas and the DES, and an inlet and an outlet flowmeter for the manometer. The absorption temperature was constantly maintained during the measurement by placing the reactor in a thermostatic water bath. Atmospheric pressure and a temperature of 40 °C were used for the tests.
The reaction was stopped when the outflow gas flow was equal to the inflow gas flow. This indicated that the DES was completely saturated with gas. The captured CO2 was gravimetrically determined. The CO2 absorption equilibrium was considered to be reached when the increase in the DES mass was less than 10 mg between two weighing points.
2.4. CO2 Desorption from the DES
A carefully controlled procedure was implemented to initiate the CO2 desorption process [51,52]. The functionalized DESs (CEM 1:2:1 or CM 1:8) were placed within a stainless-steel container designed to withstand the conditions of the process. This container was then subjected to a temperature of 80 °C, ensuring optimal conditions for CO2 desorption. The system was set to rotate at a speed of 200 RPM to facilitate efficient desorption, thereby creating a uniform environment for CO2 release. Within the stainless-steel chamber, a full vacuum was applied to reduce the pressure to a minimum, facilitating complete desorption. The vacuum was controlled by a pump system designed to maintain the desired pressure levels. This comprehensive approach—integrating controlled temperature, rotational speed, and a vacuum system—ensured the effective desorption of CO2 from the functionalized DESs. This critical desorption step sets the stage for the subsequent biofixation within microalga photobioreactors, as illustrated in Figure 1.
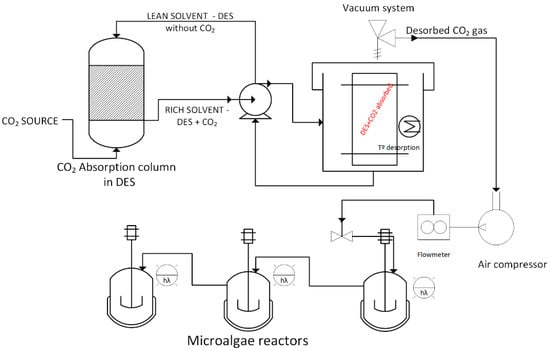
Figure 1.
Integrated CO2 capture system using a DES and biofixation using microalgae.
2.5. Experimental Model for the High-Throughput Screening of CO2 Fixation Using Microalgae
The laboratory model (Figure 1) consisted of 3 simple photobioreactors that could be extended and operated in different manners to meet the needs of the experiments, including parallel operation to select microorganisms or serial operation to develop various process utilizations. A typical photobioreactor for the laboratory experiments was produced using a Duran® GL 45 stirred bottle reactor system (DKW Life Sciences, Wertheim, Germany). The bottles had a volume of 2000 mL and were equipped with a cap that included standard magnetic stirrers as well as holes for a dissolved oxygen sensor and a pH sensor. The reactors had an inlet peristaltic pump hose and an aeration hose; they were magnetically stirred. The peristaltic pump was used to obtain the samples. The reactor was illuminated by a white LED strip (MY2250 Myria, Complet Electro Serv, Voluntari, Romania) that produced an additional 20 μmol photons m−2 s−1 of photosynthetically active light radiation during a light/dark photoperiod of 13/11 h.
2.6. Installation Workflow
CO2 was absorbed in the absorption column that contained the selected DES. The gas and liquid flows interacted in a countercurrent manner to increase the contact between the two phases, i.e., the gas flowing from below and the existent DES in the column. The CO2-rich solvent was extracted from the bottom tray and transported to the desorption unit. CO2 was desorbed using the vacuum system and by applying heat. The gas was then introduced into the microalgal cultivation reactors, which could be operated either in parallel or in series. The reactors were continuously agitated and illuminated using a white LED light source. CO2-rich air was intermittently supplied for 90 min a day to prevent excessive acidification [19,22].
2.7. Determination of CO2 Sorption and Carbon Sequestration Capacity
CO2 capture using the DESs was gravimetrically monitored [53] with an analytical balance (MS105DU, Mettler Toledo, Greifensee, Switzerland). The desorption step was monitored with a BIOGAS 5000 gas analyzer (Geotech, St. Albans, UK).
The microalgal growth was monitored through measurements of optical density and biomass accumulation after 1, 7, and 14 days of incubation [26,54]. The optical density was measured using a UV–Vis spectrometer (UV–VIS–NIR DH-2000-BAL, Ocean Optics, Duiven, The Netherlands). The biomass was gravimetrically measured using an analytical balance after centrifugation at 2535 RCF and 4 °C for 10 min using a Universal 320R centrifuge (Hettich, Tuttlingen, Germany) and drying in an oven (UE200, Memmert, Büchenbach, Germany) [55].
To assess the pigment levels, we employed the methodology outlined by Chai [56]. Initially, 2 mL of each sample underwent centrifugation at 1830 g for 3 min. A total of 2 mL of DMSO preheated to 60 °C was then added to the residual pellet, and the mixture was vortexed for 10 min. Subsequently, Eppendorf tubes were centrifuged under the same conditions mentioned above before measuring absorbance using a UV–Vis spectrophotometer (ClarioStar, BMG Labtech, Ortenberg, Germany). Measurements were obtained at three distinct wavelengths (480 nm, 649 nm, and 665 nm); these were crucial to compute the content of chlorophyll a (ChlA), chlorophyll b (ChlB), total carotenoids, and overall pigments in the samples. The calculations followed the formulas specified below.
ChlA (mg/L) = 12.47 · (OD665) − 3.62 · (OD649)
ChlB (mg/L) = 25.06 · (OD649) − 6.5 · (OD665)
Total pigments (mg/L) = (1) + (2) + (3)
2.8. Characterization of the DESs before and after CO2 Capture
The characteristics of CEM 1:2:1 and CM 1:8 were investigated using various analytical techniques. A Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) analysis was performed using an IRTracer-100 SHIMADZU spectrometer (Kyoto, Japan) to examine the molecular composition and functional groups. The pH of the DESs was determined using a Seven Compact pH meter equipped with an InLab® Viscous Pro-ISM electrode (Mettler Toledo, Greifensee, Switzerland). A density analysis was conducted using an EasyD40 densimeter (Mettler Toledo, Greifensee, Switzerland). The refractive index of the solvents was measured using an Abbe refractometer (Bausch&Lomb, Jena, Germany), enabling the assessment of their optical characteristics. A molar refraction model was used to estimate the theoretical refractive indices of the two deep eutectic solvents [57]. The expected refractive indices were calculated from the molar refractions of the individual components and their respective concentrations in the mixtures.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS 21 software package (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). The experiments were performed in triplicate and the data were analyzed in evolution. To separate treatment means within each measured parameter, a least significant difference (LSD) test was used at a significance level of p < 0.05 and p < 0.01.
3. Results
3.1. CO2 Capture Using the Functionalized DESs
In our preceding investigation [38], ethaline exhibited a significant CO2 capture capacity under heightened pressure conditions (60 bar), sequestering 4.75 g CO2/100 g ethaline or, equivalently, 0.28 mol CO2/1 mol ethaline. Conversely, when subjected to atmospheric pressure but with modest heating (40 °C), its capacity was observed to be 0.44 g CO2/100 g ethaline, corresponding with 0.026 mol CO2/1 mol ethaline. This was 11 times lower than that observed in the high-pressure test. These observations incontrovertibly underscored the role of a critical operational parameter—pressure—in governing the phenomenon of physical absorption.
Laboratory examinations were conducted on the capacity of the ternary DES CEM 1:2:1 to capture CO2 under atmospheric pressure and 40 °C conditions. The results revealed a CO2 uptake of 2.04 g/100 g CEM, equivalent to 0.29 mol/1 mol CEM. This was four times greater than the performance of ethaline.
In the case of CM 1:8, an absorption of 8.76 g CO2/100 g, equivalent to 0.65 mol CO2/1 mol CM 1:8, was obtained under the same conditions.
3.2. Characterization of the DESs before and after CO2 Capture
3.2.1. pH
Using a pH electrode for the viscous samples, the pH of CEM 1:2:1 was determined to be 10.55 ± 0.02 before CO2 absorption (Figure 2A). The presence of MEA increased the pH of ethaline, as the initial pH of ethaline was 7.90 ± 0.02. After CO2 absorption, the pH of CEM 1:2:1 decreased to 8.54 ± 0.02, indicating the formation of carbamate from the amine [58,59]. After desorption, the pH reached 9.58 ± 0.02, indicating the conversion of carbamate back to amine and the partial release of CO2.
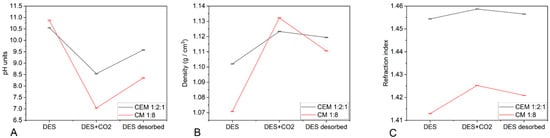
Figure 2.
Evolution of the pH (A), density (B), and refractive index (C) of CEM 1:2:1 and CM 1:8 during CO2 absorption and desorption.
The initial pH of CM 1:8 was 10.87 ± 0.02 (Figure 2A), indicating that the sample was alkaline before any CO2 interaction. The significant drop in pH to 7.04 ± 0.03 following CO2 absorption reflected the formation of carbonic acid (H2CO3) due to the dissolution of CO2 into the solvent. This decrease indicated the successful capture of CO2, resulting in the solution becoming neutral. The pH increased to 8.36 ± 0.02 after CO2 desorption, indicating the release of CO2 and a return to a more alkaline state [58,59]. This suggested that the DES effectively released the captured CO2 during desorption.
3.2.2. Density
The density of CEM 1:2:1 was 1.1020 ± 0.0002 g/cm3, which was slightly higher (12%) than the standard 30% MEA aqueous solution. The density increased to 1.1233 ± 0.0001 g/cm3 after the CO2 addition, indicating the occurrence of capture. After desorption, the density reached 1.1194 ± 0.0002 g/cm3, indicating that the CO2 was not completely released (Figure 2B).
The initial density of CM 1:8 was 1.0708 ± 0.0002 g/cm³, slightly lower than that of CEM 1:2:1 (Figure 2B). The increase in density up to 1.1322 ± 0.0002 g/cm³, higher than in the case of CEM 1:2:1 after the addition of CO2 to the solution, suggested CO2 absorption by CM 1:8. The density decreased to 1.1106 ± 0.0002 g/cm³ after CO2 desorption, indicating incomplete CO2 desorption and/or structural changes in CM 1:8 after CO2 was released.
3.2.3. Refractive Index
The refractive index is a parameter of purity. The theoretical refractive index for CEM 1:2:1 was 1.4640 ± 0.0001, and the experimental value was 1.4544 ± 0.0001. This difference was due to trace amounts of water, which was a result of the hygroscopic nature of choline chloride. The refractive index demonstrated a high degree of purity for the prepared solvent. The presence of CO2 altered the refractive index to 1.4587. It reached 1.4565 ± 0.0001 after desorption (Figure 2C).
In the case of CM 1:8, the increase in the refractive index after the CO2 addition (from 1.4129 ± 0.0002 to 1.4252 ± 0.0001) suggested CO2 absorption in the DES. The refractive index reached 1.4209 ± 0.0001 after CO2 desorption, indicating that the composition of the DES was in an intermediate state between pre- and post-CO2 absorption (Figure 2C).
3.3. CO2 Desorption from DESs: CEM 1:2:1 and CM 1:8
The functionalized DESs were subjected to the desorption of CO2 via immersion in a thermostatic oil bath set at 70 °C. Gravimetric monitoring of the samples was conducted until no detectable changes were observed. With the initial CO2 input knowledge (2.04 g CO2 absorbed by CEM 1:2:1), it was observed that approximately 89.4% of the CO2 (1.82 g) underwent desorption within an approximate total duration of 70 min. The CEM-desorbed solvent underwent the aforementioned characterization process. Although the desorption process exhibited incompleteness (as indicated by the obtained data), the rate of desorption was deemed to be satisfactory.
The gravimetric quantitation of the desorption of CO2 from CM 1:8 resulted not only in an apparent 100% desorption of the absorbed CO2 (8.76 g of CO2) but also in a significant portion of MEA (32.8 g) from the composition in the form of ammonia gas. This phenomenon could be explained by the high volatility of MEA (vapor pressure of 64 Pa at 20 °C) [41] and its significant presence in the solvent composition. The FTIR spectrum (Figure 3) confirmed the existence of such a phenomenon.
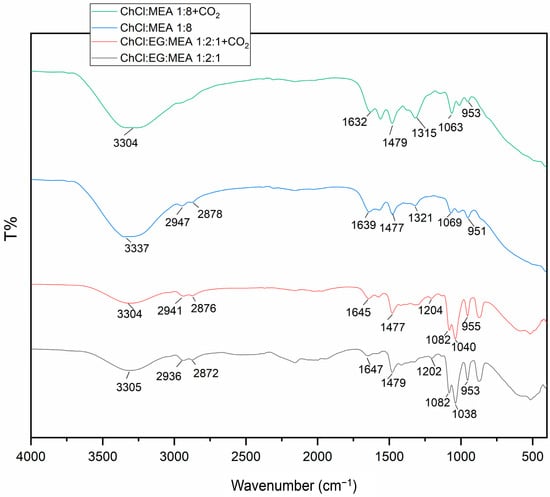
Figure 3.
FTIR spectrum of ChCl:EG:MEA 1:2:1 and ChCl:MEA 1:8 with and without absorbed CO2.
A stretching vibration of the O–H bond was observed at 3300 cm−1, which was present in all compounds (ChCl, EG, and MEA). The saturated C–H bonds at 2872–2876 and 2936–2941 cm−1 originated from ChCl, EG, and MEA [15]. Carbamate could be observed, with signals in the 1600–1100 cm−1 region, as well as asymmetric COO- between 1639 and 1650 cm−1, symmetric COO- between 1447 and 1321 cm−1, and N-COO- at 1202–1204 cm−1 [60]. The signals at 1350 cm−1 and 1063–1082 cm−1 were characteristic of carbamate [14]. Specific bands of the C-C-O- group appeared at 1069 cm−1, and the HO···HN group was observed at 953–951 cm−1.
3.4. Microalgal Cultivation
3.4.1. CEM 1:2:1
The desorbed CO2 concentration exceeded atmospheric levels as anticipated, measuring 1.4%. This was determined using the BIOGAS 5000 analyzer. The effect on microalgal growth was monitored using optical density (OD) and biomass analyses.
The results of the experiment regarding the growth of Chlorella sp. microalga using OD as a parameter are depicted in Figure 4A. The OD of the control had a consistent increase from day 1 to day 14. When applying the desorbed CO2 flow, the OD demonstrated a 12% increase at day 7, although this difference was not statistically significant, and a 24.7% statistically significant increase at day 14 compared to the control. Similar results were obtained in the case of the gravimetrically monitored biomass, but in this case, the values from both day 7 and day 14 showed statistically significant differences between the CO2 sample and the control. The cultures subjected to the CO2 flow demonstrated a 31% increase at day 7 and a 23% increase at day 14 compared with the control, according to the biomass quantification (Figure 4B).
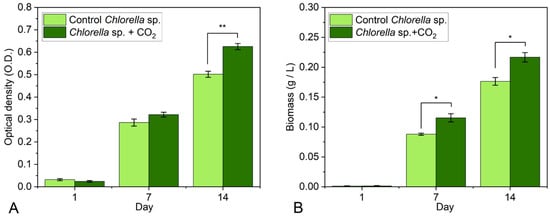
Figure 4.
The effect of CO2 desorption from CEM 1:2:1 on (A) the optical density (OD) and (B) the biomass of Chlorella sp. The values are mean ± standard error, n = 3, * when p-value < 0.05, ** when p-value < 0.01.
3.4.2. CM 1:8
The measured CO2 concentration from CM 1:8 after desorption was 0.46%, as determined by the gas analyzer. This surpassed atmospheric levels. After the initial 7 days, the control samples of the Chlorella sp. culture exhibited an OD of 0.178, whereas the CO2-desorbed samples reached an OD of 0.38 (Figure 5A). This signified a 113.5% increase in microalgal abundance compared with the control. After 14 days, the control OD reached 0.42, and the microalgae exposed to CO2 bubbling achieved an OD of 0.53, a 26% increase compared with the control (Figure 5A). The differences were statistically significant.
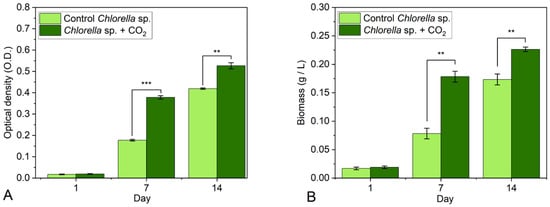
Figure 5.
The effect of CO2 desorption from CM 1:8 on (A) the OD and (B) the biomass of Chlorella sp. The values are mean ± standard error, n = 3, ** when p-value < 0.01, *** when p-value < 0.001.
Following the first week (7 days), the control group demonstrated a biomass accumulation of 0.08 g/L, whereas the CO2-rich sample was higher than 0.17 g/L, i.e., 53% higher than the control (Figure 5B). After 14 days, the biomass of the control group measured 0.173 g/L, whereas the CO2-desorbed bioreactor series yielded 0.226 g/L of biomass, i.e., 31% greater than the control. All differences between the CO2-rich samples and the corresponding controls were statistically significant.
3.4.3. Chlorophyll Content
The chlorophyll content data (Figure 6) revealed the impact of CO2 desorbed from CM 1:8 and CEM 1:2:1 in the microalgal cultures.
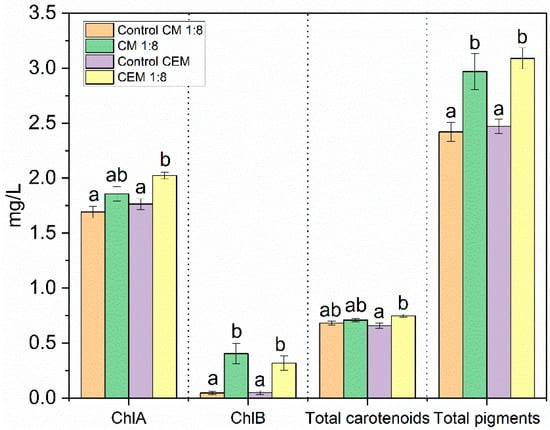
Figure 6.
Chlorophyll content in microalgae with CO2 desorbed from CM 1:8 and CEM 1:2:1, respectively. The standard error was used. The values are mean ± standard deviation, n = 3. Values with the same letter do not differ significantly for p < 0.05. The statistics were performed comparing individually the CO2-rich sample with the corresponding control for each parameter.
There was a noticeable increase in chlorophyll a (ChlA) in the CM 1:8 cultures, alongside a rise in chlorophyll b (ChlB), compared with the control. This suggested a positive influence on the chlorophyll synthesis pathways. Similarly, the CEM-treated cultures exhibited elevated levels of both ChlA and ChlB, indicating an enhancement in chlorophyll production. The total carotenoid content, indicative of microalgae health and stress response, revealed a slight increase in both cultures compared with their respective controls. Both CM 1:8 and CEM 1:2:1 demonstrated an overall rise in total pigments, reflecting a positive impact on pigment production in the microalgae due to the carbon source [61,62]. A comparative analysis suggested that the CEM 1:2:1 treatment resulted in a slightly higher increase in the ChlA content and total carotenoids compared with CM 1:8, but the difference in total pigments was not statistically significant.
3.4.4. Comparison between CM 1:8 and CEM 1:2:1
The comparison between CM 1:8 and CEM 1:2:1 in terms of the desorbed CO2 effects on the microalgal growth is presented in Figure 7. The desorbed CO2 from both the CM 1:8 and CEM 1:2:1 experimental condition resulted in a significantly higher optical density and biomass of microalgae compared with their respective control groups. CM 1:8 was more efficient at stimulating the growth of Chlorella sp. compared with CEM 1:2:1 (113.5% versus 12% after 7 days and 26% versus 24.7% after 14 days, respectively, in optical density increase).
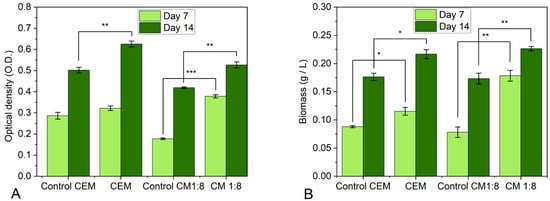
Figure 7.
Comparison between the growth of Chlorella sp. using CO2 desorbed from ChCl:MEA 1:8 (CM 1:8) and ChCl:EG:MEA 1:2:1 (CEM 1:2:1) with respect to their corresponding controls. (A) Optical density (OD); (B) gravimetrically determined biomass of Chlorella sp. The values are mean ± standard error, n = 3, * when p-value < 0.05, ** when p-value < 0.01, *** when p-value < 0.001.
4. Discussion
One of the advantages of DESs is their ability to be functionalized or customized [14,63]. Ethaline has demonstrated a good CO2 capture capacity under high pressure (60 bar) in previous research. As MEA is highly reactive with CO2, forming carbamate, it is a promising chemical for DES functionalization. In this work, we used a derived ternary DES, resulting from the combination of ethaline ingredients and MEA, to decrease the required pressure for CO2 capture in an integrated system of CO2 absorption, desorption, and biosequestration. The capture of CO2 within the ternary DES—CEM 1:2:1—occurs through two distinct mechanisms. Firstly, CO2 is physically captured through weak forces, specifically van der Waals forces, within the eutectic cage formed by the hydrogen bonds between the HBA (choline chloride) and HBDs (EG [64] and MEA [65]). MEA typically functions as an HBD because of its ability to donate a hydrogen bond. In the given context, ChCl is mentioned as the HBA, and EG and MEA are the HBDs. In the context of hydrogen bonding, the chloride anion can act as an HBA because it has a lone pair of electrons that can be involved in hydrogen bonding interactions. The positive charge on the choline cation influences its ability to accept hydrogen bonds. The physical absorption induced by the EG presence is a result of the molecular arrangement within the eutectic structure. Secondly, a chemical capture process takes place as CO2 reacts with the MEA present in the DES, forming carbamates. This chemical interaction provides an alternative mechanism for CO2 sequestration, showcasing the dual nature of the capture process within the studied DES mixture [8]. The formation of carbamate involves a reversible reaction governed by the zwitterion mechanism [51]. The electrophilic nature of the carbon atom in CO2 makes it susceptible to nucleophilic attack by primary amines, resulting in the creation of a zwitterionic transition state. This state can undergo an intramolecular proton transfer, ultimately forming a neutral carbamic acid. The subsequent reaction of this carbamic acid with a Brønsted base amine can lead to the reversible formation of carbamate, maintaining a 0.5:1 CO2:amine ratio (Equation (1)).
A second DES with a binary composition of ChCl and MEA at a ratio of 1:8 was employed for a parallel investigation with the ternary solvent.
The selection of the two DESs was based on several considerations: (i) MEA as a classic CO2 solvent. MEA is a widely recognized and extensively studied solvent for CO2 capture, particularly in 30% aqueous solutions [66,67]. Its well-established role in CO2 absorption renders it an essential benchmark for comparison [68,69]. (ii) ChCl as an HBA. ChCl serves as the primary hydrogen bond acceptor in many deep eutectic solvents [6,9,14,70,71]. Its inclusion in a binary solvent introduces an important component typically used in DES formulations. (iii) Industrial suitability. The chosen 1:8 molar ratio of ChCl:MEA aligned with industrial considerations and practices, as demonstrated in our prior research. This ratio has demonstrated applicability and feasibility in previous works, rendering it a valuable candidate for this comparative study [38].
4.1. CO2 Absorption in Deep Eutectic Solvents
The observed difference of a higher OD and a lower biomass in CO2 absorption between CEM 1:2:1 and CM 1:8 could be attributed to several factors, primarily related to the compositions and interactions within the DES. These were (a) The composition and molar ratios. CM 1:8 had a higher molar content of MEA compared with CEM 1:2:1. MEA readily reacts with CO2 to form carbamate, leading to a high CO2 absorption capacity. (b) The role of ethylene glycol. EG in CEM 1:2:1 influenced the CO2 absorption behavior [72]. It contributed to a mechanism of physical absorption that was distinct from the chemical absorption observed with MEA. This distinction could lead to variations in the overall CO2 absorption capacity of the solvent. (c) Hydrogen bonding and interactions. MEA in CM 1:8 provided more favorable hydrogen bonding interactions with the CO2 molecules, enhancing their capture within the solvent matrix. The different solvent components in CEM 1:2:1 may have resulted in various molecular arrangements that affected the accessibility and reactivity of CO2 [73,74]. (d) Eutectic formation and stability. The specific eutectic structure formed by CM 1:8 may have provided a conducive environment for CO2 absorption. The presence of EG in CEM 1:2:1 introduced a unique characteristic compared with the binary solvent CM 1:8. Unlike the binary solvent, CEM 1:2:1 incorporated an additional hydrogen bond donor (HBD) in the form of EG. This difference impacted the dynamic interactions within the deep eutectic solvent, altering its response to CO2 capture [75,76]. (e) Physical and chemical properties. Variations in properties such as viscosity, density, and polarity between the two solvents may have affected their ability to absorb and retain CO2. MEA-rich CM 1:8 exhibited more favorable physical and chemical properties for CO2 absorption than CM 1:2:1 [77,78,79].
The fourfold reduction in the CO2 absorption capacity observed in CEM 1:2:1 compared with CM 1:8 is compensated for by a lower cost and fewer corrosion effects [42].
These characteristic evolutions provide a detailed picture of how the CM 1:8 and CEM 1:2:1 DESs interacted with CO2 during the capture and release processes. The observed changes in pH, density, and refractive index provided a detailed insight into how CM 1:8 and CEM 1:2:1 dynamically interacted with CO2 during the capture and release processes. The shift in pH reflected the transformation between the carbamate formation and its subsequent release, whereas changes in the density and refractive index provided quantitative measures of the degree of CO2 absorption and desorption. These characteristics collectively contributed to our understanding of the underlying mechanisms governing the performance of CM 1:8 and CEM 1:2:1 as CO2 capture solvents.
4.2. Biofixation of Desorbed CO2 Using Chlorella sp.
Chlorella sp. is a green microalgae species. It is widely studied for its potential as biofuel feedstock due to its high lipid content and ability to capture CO2 [25,26,27,80,81,82,83]. The cells are 2–10 µm in diameter, are mostly spherical, and contain a single, cup-shaped chloroplast surrounded by a layer of cytoplasm. Chlorella sp. is often used as a source of protein for animal feed because of its high protein content [80,84,85]. Another advantage of Chlorella sp. is that it can be grown in large quantities using low-cost, non-arable land. Chlorella sp. has been effectively used in wastewater treatment [23]. It has the capacity to remove nitrogen, phosphorus, and organic pollutants (phenols and dyes) and absorbs these pollutants for growth, forming a biomass that can then be harvested and used for various purposes (biofuel, animal feed, and fertilizer). Chlorella sp. is a promising species of green microalgae with a high potential and versatility in various fields of application, from agriculture to energy and environmental remediation.
Bioreactors in use today can be categorized into either open or closed systems [86,87,88]. A closed system is considered to be advantageous for optimal CO2 fixation and obtaining uncontaminated biomasses for biomolecule extraction. The cultivation of selected microalgae for CO2 capture and utilization can occur in various systems, including open ponds [80] or closed photobioreactors [89,90]. This allows the flexible implementation of the proposed technology, considering the specific environmental and economic conditions of the location. A promising system for use in CO2 capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) is microalgae bioreactors. CO2 emissions are passed through the reactor, converting them into useful products such as biofuels, chemicals, fertilizers, and materials.
In the present study, we demonstrated that it was feasible to efficiently integrate the capture and release of CO2 from DESs with the use of desorbed CO2 to optimize the growth of Chlorella sp. Both the OD measurements and the gravimetric analysis of the biomass revealed that the released CO2 from the DESs improved the microalgal growth and biomass accumulation. The CO2 released from CM 1:8 was more efficient at stimulating microalgal growth than the CO2 released from CEM 1:2:1.
In summary, our data underscored the significant impact of CO2 supplementation from DESs on Chlorella sp. growth and biomass production. Variations were observed between the CM 1:8 and CEM 1:2:1 condition, with respect to the effectiveness of these methods in optimizing microalgal cultivation for potential applications in biofuel production and carbon capture. Although the desorption from CM 1:8 showed a much higher stimulatory activity than CEM 1:2:1 on algal growth after 7 days, the two DESs showed almost similar effects after 14 days of algal growth. This indicates that CEM 1:2:1 is promising as starting point for optimization of alternatives to MEA-rich, corrosive solvents. The reduced difference after 14 days could be explained by accelerated transition to the stationary phase of the culture stimulated by CO2 desorbed from CM 1:8., due to more stressful conditions. The higher increase in chlorophyll b content, comparing to the increase in chlorophyll a content in the microalgae culture stimulated by CO2 desorbed from CM 1:8, suggests a rearrangement of the photosynthetic machinery and a higher oxidative stress in this culture. Similar changes in chlorophyll a/chlorophyll b ratio were reported for C. sorokiniana UTEX 1230 and C. vulgaris 211/11P strains cultivated in media supplemented with CO2 [91]. Our results demonstrated the potential of microalgal cultivation in combination with CO2 capture using DESs as a viable method for CO2 mitigation.
5. Conclusions
The distinct composition and molecular arrangements of the investigated deep eutectic solvents, i.e., CM 1:8 and CEM 1:2:1, resulted in a significant difference in the CO2 absorption capacity. The higher MEA concentration in CM 1:8 led to superior CO2 absorption compared with CEM 1:2:1. Although CEM 1:2:1 captured four times less CO2 than CM 1:8, it has the advantage of being less corrosive. This characteristic may improve the durability and longevity of equipment and materials used in CO2 capture processes.
Using the selected microalgal strain of Chlorella sp., both CM 1:8 binary solvent and the ternary solvent CEM 1:2:1 resulted in higher optical density and biomass compared with controls. After 7 days of growth, the biostimulatory effect was much higher for CM 1:8 than for CME 1:2:1, but the difference became much lower between the two solvents after 14 days of algal growth. Future optimization of CME 1:2:1 might further reduce this difference, CME 1:2:1 being a promising starting point.
This study highlighted the positive influence of desorbed CO2 from DES on Chlorella sp. microalgal growth. The bioconversion of CO2 by microalgae serves as a natural mechanism for carbon sequestration, contributing to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions as well as ecosystem preservation. Microalgae have additional potential in renewable energy production and valuable co-product generation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.O.; methodology, E.G.B. and D.G.P.; validation, E.G.B., D.G.P., D.C.-A. and C.I.M.; formal analysis, D.C.-A. and F.O.; investigation, E.G.B. and D.G.P.; resources, F.O. and C.I.M.; data curation, D.C.-A. and T.D.; writing—original draft preparation, E.G.B.; writing—review and editing, D.C.-A. and F.O.; visualization, E.G.B.; supervision, F.O. and T.D.; project administration, F.O.; funding acquisition, F.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), the Competitiveness Operational Program (POC), Axis 1, project POC-A1-A1.2.3-G-2015-P_40_352, My_SMIS 105684, “Sequential processes of closing the side streams from bioeconomy and innovative (bio)products resulting from it–SECVENT”, subsidiary project 1882/2020–Aqua-STIM and from the NO Grants 2014–2021, under Project RO-NO-2019-540 STIM 4+, contract no. 14/2020.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are included in this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Martins, M.A.R.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Insights into the Nature of Eutectic and Deep Eutectic Mixtures. J. Solut. Chem. 2019, 48, 962–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, M.D.; Mezzetta, A.; Guazzelli, L.; Scanlan, E.M. Radical-mediated thiol–ene ‘click’ reactions in deep eutectic solvents for bioconjugation. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rente, D.; Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Panić, M.; Paiva, A.; Caprin, B.; Radojčić Redovniković, I.; Duarte, A.R.C. Review of deep eutectic systems from laboratory to industry, taking the application in the cosmetics industry as an example. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 135147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tao, Y.; Masuku, M.V.; Cao, J.; Yang, J.; Huang, K.; Ge, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Kuang, Y.; et al. Effects of deep eutectic solvents on the biotransformation efficiency of ω-transaminase. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 377, 121379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira Sanches, M.; Freitas, R.; Oliva, M.; Mero, A.; De Marchi, L.; Cuccaro, A.; Fumagalli, G.; Mezzetta, A.; Colombo Dugoni, G.; Ferro, M.; et al. Are natural deep eutectic solvents always a sustainable option? A bioassay-based study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 17268–17279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboshatta, M.; Magueijo, V. A Comprehensive Study of CO2 Absorption and Desorption by Choline-Chloride/Levulinic-Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2021, 26, 5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, H.; Susanto, H.; Grisdanurak, N.; Hantoko, D.; Yoshikawa, K.; Qun, H.; Yan, M. Recent developments of deep eutectic solvent as absorbent for CO2 removal from syngas produced from gasification: Current status, challenges, and further research. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, X.; Lu, X. Choline-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 separation: Review and thermodynamic analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 97, 436–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.-N.; Pauli, G.F. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents: Properties, Applications, and Perspectives. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Sarmad, S.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Ji, X. Development of Low-Cost Deep Eutectic Solvents for CO2 Capture. Energy Procedia 2017, 142, 3320–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Dhattarwal, H.S.; Kashyap, H.K. Distinct Solvation Structures of CO2 and SO2 in Reline and Ethaline Deep Eutectic Solvents Revealed by AIMD Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 1852–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.; Lin, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Xu, X. Understanding the CO2 capture performance by MDEA-based deep eutectics solvents with excellent cyclic capacity. Fuel 2021, 293, 120466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmad, S.; Nikjoo, D.; Mikkola, J.-P. Amine functionalized deep eutectic solvent for CO2 capture: Measurements and modeling. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 309, 113159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, I.; Abu-Zahra, M.R.M.; Alnashef, I. Novel Green Solvents for CO2 Capture. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 2552–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, T.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Jeong, Y.K.; Choi, J. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Attractive Media for CO2 Capture. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 2834–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leron, R.B.; Caparanga, A.; Li, M.-H. Carbon dioxide solubility in a deep eutectic solvent based on choline chloride and urea at T=303.15–343.15K and moderate pressures. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 44, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepburn, C.; Adlen, E.; Beddington, J.; Carter, E.A.; Fuss, S.; Mac Dowell, N.; Minx, J.C.; Smith, P.; Williams, C.K. The technological and economic prospects for CO2 utilization and removal. Nature 2019, 575, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. Perspectives on microalgal CO2-emission mitigation systems—A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Teng, F.; McLellan, B.C. A critical review on deployment planning and risk analysis of carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) toward carbon neutrality. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Ashworth, P. The development of Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage (CCUS) research in China: A bibliometric perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 138, 110521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhola, V.; Swalaha, F.; Ranjith Kumar, R.; Singh, M.; Bux, F. Overview of the potential of microalgae for CO2 sequestration. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 2103–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbib, Z.; Ruiz, J.; Álvarez-Díaz, P.; Garrido-Pérez, C.; Perales, J.A. Capability of different microalgae species for phytoremediation processes: Wastewater tertiary treatment, CO2 bio-fixation and low cost biofuels production. Water Res. 2014, 49, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, W.Y.; Show, P.L.; Chang, J.-S.; Ling, T.C.; Juan, J.C. Biosequestration of atmospheric CO2 and flue gas-containing CO2 by microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 184, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Gong, S.; Chen, Z.; Xia, J.; Xiang, W. Potential microalgal strains for converting flue gas CO2 into biomass. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjamshidian, R.; Abolghasemi, H.; Esmaili, M.; Amrei, H.D.; Parsa, M.; Rezaei, S. Carbon dioxide biofixation by Chlorella sp. in a bubble column reactor at different flow rates and CO2 concentrations. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Gao, S.; Lopez, P.A.; Ogden, K.L. Effects of pH on cell growth, lipid production and CO2 addition of microalgae Chlorella sorokiniana. Algal Res. 2017, 28, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Su, Y. Process effect of microalgal-carbon dioxide fixation and biomass production: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 31, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Hende, S.; Vervaeren, H.; Boon, N. Flue gas compounds and microalgae: (Bio-)chemical interactions leading to biotechnological opportunities. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 1405–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Z. Advances in the biological fixation of carbon dioxide by microalgae. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 1475–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gu, X.; Wang, Z.; Shatner, W.; Wang, Z. Progress, challenges and solutions of research on photosynthetic carbon sequestration efficiency of microalgae. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 110, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xiao, W.; Yang, T.; Lyu, T. Optimization and Process Effect for Microalgae Carbon Dioxide Fixation Technology Applications Based on Carbon Capture: A Comprehensive Review. C 2023, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, M.; Zhang, H.; Shang, M.; Li, G.; Su, Y. CO2 absorption with diamine functionalized deep eutectic solvents in microstructured reactors. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaib, Q.; Masoumi, Z.; Aich, N.; Kyung, D. Review of the synthesis and applications of deep eutectic solvent-functionalized adsorbents for water treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Yang, D.; Qi, H. Efficient SO2 Absorption by Anion-Functionalized Deep Eutectic Solvents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 4536–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhawna; Pandey, A.; Pandey, S. Superbase–Added Choline Chloride–Based Deep Eutectic Solvents for CO2 Capture and Sequestration. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 11422–11430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, N.R.; Nicholas, N.J.; Wu, Y.; Mumford, K.A.; Kentish, S.E.; Stevens, G.W. Experiments and Thermodynamic Modeling of the Solubility of Carbon Dioxide in Three Different Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs). J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 3246–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihăilă, E.G.; Constantinescu-Aruxandei, D.; Doncea, S.M.; Oancea, F.; Dincă, C. Deep eutectic solvents for CO2 capture in post-combustion processes. Stud. UBB Chem. 2021, 65, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainar, M.; Veawab, A. Corrosion in CO2 capture process using blended monoethanolamine and piperazine. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 9299–9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Huang, A.-C.; Shu, C.-M.; Zhang, L. Thermal Decomposition and Nonisothermal Kinetics of Monoethanolamine Mixed with Various Metal Ions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahi, M.-R.; Mokbel, I.; Negadi, L.; Dergal, F.; Jose, J. Experimental solubility of carbon dioxide in monoethanolamine, or diethanolamine or N-methyldiethanolamine (30 wt%) dissolved in deep eutectic solvent (choline chloride and ethylene glycol solution). J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 289, 111062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretfeld (Mihăilă), E.G.; Oancea, F.; Dincă, C. Degradation study of deep eutectic solvents in CO2 capture technologies. U.P.B. Sci. Bull. Ser. B 2023, 85, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Halfhide, T.; Åkerstrøm, A.; Lekang, O.I.; Gislerød, H.R.; Ergas, S.J. Production of algal biomass, chlorophyll, starch and lipids using aquaculture wastewater under axenic and non-axenic conditions. Algal Res. 2014, 6, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, D.G.; Georgescu, F.; Dumitrascu, F.; Shova, S.; Constantinescu-Aruxandei, D.; Draghici, C.; Vladulescu, L.; Oancea, F. Novel Strigolactone Mimics That Modulate Photosynthesis and Biomass Accumulation in Chlorella sorokiniana. Molecules 2023, 28, 7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, A.P.R.; Mora-Vargas, J.A.; Guimarães, T.G.S.; Amaral, C.D.B.; Oliveira, A.; Gonzalez, M.H. Sustainable synthesis of natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) by different methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 293, 111452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, F.J.V.; Espino, M.; Fernández, M.A.; Silva, M.F. A Greener Approach to Prepare Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 6122–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aissaou, T. Novel Contribution to the Chemical Structure of Choline Chloride Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Pharm. Anal. Acta 2015, 6, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.C.; Fernandes, J.O. Extraction techniques with deep eutectic solvents. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.; Hadj-Kali, M.K.; Mulyono, S.; Alnashef, I. Analysis of operating conditions for CO2 capturing process using deep eutectic solvents. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2016, 47, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawsari, J.N.; Adeyemi, I.A.; Bessadok-Jemai, A.; Ali, E.; AlNashef, I.M.; Hadj-Kali, M.K. Polyethylene glycol-based deep eutectic solvents as a novel agent for natural gas sweetening. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma Maheswari, A.; Palanivelu, K. Carbon Dioxide Capture and Utilization by Alkanolamines in Deep Eutectic Solvent Medium. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 11383–11392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ma, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Qi, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Molecular Mechanism and Absorption Performance Evaluation of CO2 Capture from the PCC Process by Monoethanolamine-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torralba-Calleja, E.; Skinner, J.; Gutiérrez-Tauste, D. CO2 Capture in Ionic Liquids: A Review of Solubilities and Experimental Methods. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 473584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemmler, K.; Massimi, R.; Kirkwood, A.E. Growth and fatty acid characterization of microalgae isolated from municipal waste-treatment systems and the potential role of algal-associated bacteria in feedstock production. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.K.; Lee, K.T.; Mohamed, A.R. Current status and challenges on microalgae-based carbon capture. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2012, 10, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.; Shi, J.; Huang, T.; Guo, Y.; Wei, J.; Guo, M.; Li, L.; Dou, S.; Liu, L.; Liu, G. Characterization of Chlorella sorokiniana growth properties in monosaccharide-supplemented batch culture. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, F.; Focke, W.W.; Androsch, R.; du Toit, E. Estimating binary liquid composition from density and refractive index measurements: A comprehensive review of mixing rules. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 332, 115893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M. Effect of pH on desorption of CO2 from alkanolamine-rich solvents. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1864, 020091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.; Robinson, K.; Puxty, G.; Attalla, M. In situ Fourier Transform-Infrared (FT-IR) analysis of carbon dioxide absorption and desorption in amine solutions. Energy Procedia 2009, 1, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.; McCluskey, A.; Attalla, M.I. An ATR-FTIR study on the effect of molecular structural variations on the CO2 absorption characteristics of heterocyclic amines, part II. Chemphyschem 2012, 13, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Ferreira, V.; Sant’Anna, C. Impact of culture conditions on the chlorophyll content of microalgae for biotechnological applications. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oo, Y.Y.N.; Su, M.C.; Kyaw, K.T. Extraction and determination of chlorophyll content from microalgae. Int. J. Adv. Res. Publ. 2017, 1, 298. [Google Scholar]
- García, G.; Atilhan, M.; Aparicio, S. An approach for the rationalization of melting temperature for deep eutectic solvents from DFT. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2015, 634, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Tan, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, J.; Mao, B.; Yan, J. Effect of hydrogen bond donor molecules ethylene glycerol and lactic acid on electrochemical interfaces in choline chloride based-deep eutectic solvents. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 155, 244702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishaq, M.; Gilani, M.A.; Bilad, M.R.; Faizan, A.; Raja, A.A.; Afzal, Z.M.; Khan, A.L. Exploring the potential of highly selective alkanolamine containing deep eutectic solvents based supported liquid membranes for CO2 capture. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 340, 117274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiesen, F.A.; Haugen, G.; Hartono, A. A systematic procedure for process energy evaluation for post combustion CO2 capture: Case study of two novel strong bicarbonate-forming solvents. Appl. Energy 2018, 211, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Haugen, G.; Ditaranto, M.; Berstad, D.; Jordal, K. Impacts of exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) on the natural gas combined cycle integrated with chemical absorption CO2 capture technology. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Otto, A.; Robinius, M.; Stolten, D. A Review of Post-combustion CO2 Capture Technologies from Coal-fired Power Plants. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 650–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas, J.I.; Gomez, M.D.; Giraldo, N.; Garzón, J. CO2 Absorbing Capacity of MEA. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 965015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhotaray, P.K.; Biswal, S.K.; Pandey, S. Development of novel hybrid ionic fluids for efficient CO2 capture and cellulose dissolution. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 312, 113477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Mellado, N.; Larriba, M.; Navarro, P.; Rigual, V.; Ayuso, M.; García, J.; Rodríguez, F. Thermal stability of choline chloride deep eutectic solvents by TGA/FTIR-ATR analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 260, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Guo, B.; Han, L.; Zhu, N.; Gao, F.; Li, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, J. CO2 Fixation into Novel CO2 Storage Materials Composed of 1,2-Ethanediamine and Ethylene Glycol Derivatives. Chemphyschem 2015, 16, 2106–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehkordi, F.; Sobati, M.A.; Gorji, A.E. New molecular structure based models for estimation of the CO2 solubility in different choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents (DESs). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, Y. A novel approach based on detailed structural and molar free volume analyses to characteristics of deep eutectic solvents specialized for CO2 absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 141802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, V.; Esser, L.; Kirchner, B. How is CO2 absorbed into a deep eutectic solvent? J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 154, 094503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, G.; Atilhan, M.; Aparicio, S. A theoretical study on mitigation of CO2 through advanced deep eutectic solvents. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2015, 39, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmad, S.; Xie, Y.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Ji, X. Screening of deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as green CO2 sorbents: From solubility to viscosity. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Ji, X. Effect of Water on the Density, Viscosity, and CO2 Solubility in Choline Chloride/Urea. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2014, 59, 3344–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Gray, S. Design of Improved Deep Eutectic Solvents Using Hole Theory. Chemphyschem 2006, 7, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spennati, E.; Casazza, A.A.; Converti, A.; Padula, M.P.; Dehghani, F.; Perego, P.; Valtchev, P. Winery waste valorisation as microalgae culture medium: A step forward for food circular economy. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 293, 121088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcántara, C.; Fernández, C.; García-Encina, P.A.; Muñoz, R. Mixotrophic metabolism of Chlorella sorokiniana and algal-bacterial consortia under extended dark-light periods and nutrient starvation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 2393–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åkerström, A.M.; Mortensen, L.M.; Rusten, B.; Gislerød, H.R. Biomass production and nutrient removal by Chlorella sp. as affected by sludge liquor concentration. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 144, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanan, R.; Kannan, K.; Deshkar, A.; Yadav, R.; Chakrabarti, T. Enhanced algal CO2 sequestration through calcite deposition by Chlorella sp. and Spirulina platensis in a mini-raceway pond. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2616–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-Bashan, L.E.; Bashan, Y.; Moreno, M.; Lebsky, V.K.; Bustillos, J.J. Increased pigment and lipid content, lipid variety, and cell and population size of the microalgae Chlorella spp. when co-immobilized in alginate beads with the microalgae-growth-promoting bacterium Azospirillum brasilense. Can. J. Microbiol. 2002, 48, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, L.E.; Bashan, Y. Increased growth of the microalga Chlorella vulgaris when coimmobilized and cocultured in alginate beads with the plant-growth-promoting bacterium Azospirillum brasilense. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2000, 66, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Ergas, S.; Yuan, X.; Sahu, A.; Zhang, Q.; Dewulf, J.; Malcata, F.X.; van Langenhove, H. Enhanced CO2 fixation and biofuel production via microalgae: Recent developments and future directions. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Gonçalves, L.; Starling, M.C.V.M.; Leal, C.D.; Oliveira, D.V.M.; Araújo, J.C.; Leão, M.M.D.; Amorim, C.C. Enhanced biodiesel industry wastewater treatment via a hybrid MBBR combined with advanced oxidation processes: Analysis of active microbiota and toxicity removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 4521–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Griffin, M.; Cai, J.; Li, S.; Bulter, P.E.M.; Kalaskar, D.M. Bioreactors for tissue engineering: An update. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 109, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratomski, P.; Hawrot-Paw, M. Production of Chlorella vulgaris Biomass in Tubular Photobioreactors during Different Culture Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, B.D.; Mota, A.; Ferreira, A.; Dragone, G.; Teixeira, J.A.; Vicente, A.A. Characterization of split cylinder airlift photobioreactors for efficient microalgae cultivation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 117, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchin, M.; Paloschi, M.; Busnardo, G.; Cazzaniga, S.; Cuine, S.; Li-Beisson, Y.; Wobbe, L.; Ballottari, M. CO2 supply modulates lipid remodelling, photosynthetic and respiratory activities in Chlorella species. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 2987–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).