Assessment of Sustainable Biogas Production from Co-Digestion of Jatropha De-Oiled Cake and Cattle Dung Using Floating Drum Type Digester under Psychrophilic and Mesophilic Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Feedstock for Experiments
2.2. Characterization of Feedstock
2.3. Preparation of Feed Material
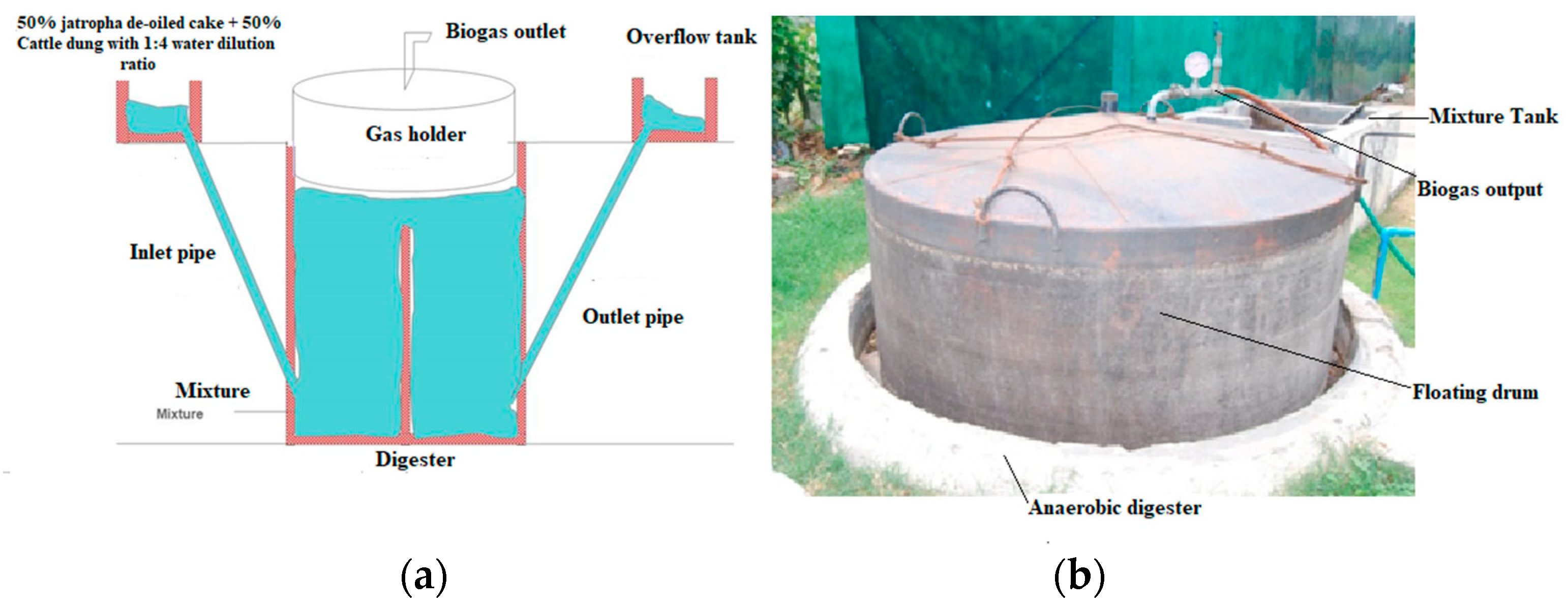
2.4. Experimental Set-Up and Consequent Processes
2.5. Biogas Production Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Jatropha De-Oiled Cake and Cattle Dung
3.2. Biogas Production from Jatropha De-Oiled Cake and Cattle Dung under Psychrophilic and Mesophilic Temperature Conditions
3.3. Specific Biogas Production Rate from Jatropha De-Oiled Cake and Cattle Dung under Psychrophilic and Mesophilic Temperature Conditions
3.4. Biogas Composition from 50% JDC + 50% CD under Psychrophilic and Mesophilic Temperatures
3.5. Specific and Cumulative Methane Production Rate from 50% JDC + 50%CD under Psychrophilic and Mesophilic Temperatures
3.6. Total Volatile Solid Mass Removal Efficiency 50% JDC + 50% CD under Psychrophilic and Mesophilic Temperatures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, A.K.; Sahoo, P.K.; Singhal, S.; Joshi, G. Exploration of upstream and downstream process for microwave assisted sustainable biodiesel production from microalgae Chlorella vulgaris. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.C.; Singh, B.; Upadhyay, S.N. Advancements in development and characterization of biodiesel: A review. Fuel 2008, 87, 2355–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Pulla, R.H.; Sahoo, P.K. Performance analysis of a medium-scale downdraft gasifier using lantana camera biomass as feeding material. Energy Sour. Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.; Pandey, J.K.; Rana, S.; Rawat, D.S. Challenges and opportunities for the application of biofuel. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Sharma, P.K.; Chintala, V.; Khatri, N.; Patel, A. Environment-friendly biodiesel/diesel blends for improving the exhaust emission and engine performance to reduce the pollutants emitted from transportation fleets. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Sharma, A.; Singh, Y.; Chen, W.H. Production of a Sustainable Fuel from Microalgae Chlorella Minutissima Grown in a 1500 L Open Raceway Ponds. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 149, 106073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodke, P.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Pandey, J.K.; Chen, W.-H.; Patel, A.; Ashokkumar, V. Pyrolysis of sewage sludge for sustainable biofuels and value-added biochar production. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Sharma, A.; Kumar Ghodke, P.; Manna, S.; Chen, W.-H. Emerging technologies for sustainable production of biohydrogen production from microalgae: A state-of-the-art review of upstream and downstream processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 342, 126057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, M.M.; Juchelkova, D.; Win, M.M.; Thu, A.M.; Puchor, T. Biomass energy: An overview of biomass sources, energy potential, and management in Southeast Asian Countries. Resources 2019, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chintala, V.; Kumar, S.; Pandey, J.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Kumar, S. Solar thermal pyrolysis of non-edible seeds to biofuels and their feasibility assessment. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 153, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havilah, P.R.; Sharma, P.K.; Sharma, A.K. Characterization, thermal and kinetic analysis of Pinusroxburghii. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 23, 8872–8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.; Sharma, V.; Mittal, S. Social entrepreneurship through forest bioresidue briquetting: An approach to mitigate forest fires in pine areas of Western Himalaya, India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabed, H.M.; Akter, S.; Yun, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, X. Biogas from microalgae: Technologies, challenges and opportunities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 117, 109503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Ghosh, P.; Kumar, M.; Sengupta, S.; Gupta, A.; Kumar, S.S.; Vijay, V.; Kumar, V.; Kumar Vijay, V.; Pant, D. Valorization of agricultural waste for biogas based circular economy in India: A research outlook. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 304, 123036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Sahoo, P.K.; Singhal, S. Comparative evolution of biomass production and lipid accumulation potential of chlorella species grown in a bubble column photobioreactor. Biofuels 2016, 7, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauen, A.; Berndes, G.; Junginger, M.; Londo, M.; Vuille, F.; Ball, R.; Bole, T.; Chudziak, C.; Faaij, A.; Mozaffarian, H. Bioenergy: A sustainable and reliable energy source. Policy Stud. 2018, 2017, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Piloto-Rodríguez, R.; Tobío, I.; Ortiz-Alvarez, M.; Díaz, Y.; Konradi, S.; Pohl, S. An approach to the use of Jatropha Curcas by-products as energy source in agroindustry. Energy Sour. Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaroiu, G.; Mihaescu, L.; Mavrodin, E.M. Combustion of Biogas Obtained by Anaerobic Fermentation of Animal Proteins; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 149–178. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves Neto, J.; Vidal Ozorio, L.; Campos de Abreu, T.C.; Ferreira dos Santos, B.; Pradelle, F. Modeling of biogas production from food, fruits and vegetables wastes using artificial Neural Network (ANN). Fuel 2021, 285, 119081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Rout, P.R.; Dubey, B.; Meena, S.S.; Pal, P.; Goel, M. A critical review on biogas production from edible and non-edible oil cakes. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 12, 949–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepanraj, B.; Senthilkumar, N.; Ranjitha, J. Effect of solid concentration on biogas production through anaerobic digestion of rapeseed oil cake. Energy Sour. Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2021, 43, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, N.V.; Kale, N.W.; Deshmukh, S.J. A study on biogas generation from Mahua (Madhuca Indica) and Hingan (Balanites Aegyaptiaca) oil seedcake. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2012, 16, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunkunle, O.; Ahmed, N.A.; Olatunji, K.O. Biogas yields variance from anaerobic co-digestion of cow dung with jatropha cake under mesophilic temperatures. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1378, 032060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Singh, S.K.; Larroche, C.; Soccol, C.R.; Pandey, A. Oil cakes and their biotechnological applications—A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2000–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raheman, H.; Mondal, S. Biogas production potential of Jatropha seed cake. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 37, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, B.; Chandra, R.; Vijay, V.K.; Subbarao, P.M.V.; Isha, A. Utilization of de-oiled rice bran as a feedstock for renewable biomethane production. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 140, 105674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.; Vijay, V.K. Comparative evaluation of raw and detoxified mahua seed cake for biogas production. Appl. Energy 2013, 102, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłoński, S.J.; Kułażyński, M.; Sikora, I.; Łukaszewicz, M. The influence of different pretreatment methods on biogas production from Jatropha Curcas oil cake. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barik, D.; Murugan, S. Assessment of sustainable biogas production from de-oiled seed cake of Karanja-an organic industrial waste from biodiesel industries. Fuel 2015, 148, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsair, A.; Cinar, S.O.; Alassali, A.; Qdais, H.A.; Kuchta, K. Operational parameters of biogas plants: A review and evaluation study. Energies 2020, 13, 3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Mandal, S.K. The utilization of non-edible oil cake along with cow dung for methane-enriched biogas production using mixed inoculum. Energy Sour. Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2011, 33, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.; Vijay, V.K.; Subbarao, P.M.V.; Khura, T.K. Production of methane from anaerobic digestion of Jatropha and Pongamia oil cakes. Appl. Energy 2012, 93, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, S.; Agarwal, S.; Singhal, N.; Sharma, R.; Sharma, R. Designing and operation of pilot scale continuous stirred tank reactor for continuous production of bio-methane from toxic waste. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2019, 38, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinbrenner, J.; Jeen, J.; Nägele, H.J.; Kirchner, S.; Bohlinger, B.; Lemmer, A. Anaerobic digestion of aqueous Jatropha seed oil extraction residues and phorbol ester degradation. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2020, 12, 100601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaiyaraju, P.; Partha, N. Biogas production from co-digestion of orange peel waste and Jatropha de-oiled cake in an anaerobic batch reactor. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 3339–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainaina, S.; Lukitawesa; Kumar Awasthi, M.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Bioengineering of anaerobic digestion for volatile fatty acids, hydrogen or methane production: A critical review. Bioengineered 2019, 10, 437–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Substrate | Crude Protein (%, wt/wt) | Carbohydrate (%, wt/wt) | Acid Detergent Fiber (%, wt/wt) | Neutral Detergent Fiber (%, wt/wt) | Lipid Content (%, wt/Volume) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jatropha de-oiled cake | 38.13 ± 2% | 23.54 + 3% | 6.54 + 1% | 8.71 + 1% | 7.2 ± 1% |
| Material Used for Feeding the Digester | Proximate Analysis of Jatropha De-oiled Cake (ASTM D3172-07a) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture Content in % | Total Solids in % | Volatile Solids in % (on Dry Basis) | Non-Volatile Solids in % (on Dry Basis) | Ash Content (in %) | |
| Cattle dung | 84.5 | 15.5 | 83.5 | 16.5 | 1.2 |
| Jatropha de-oiled cake | 6.8 ± 0.5 | 93.2 | 91.5 | 8.5 | 0.65 |
| Feed Material | Elemental Analysis | C/N Ratio | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C% | H% | N% | P% | K% | S% | ||
| Cattle dung | 34.50 | 4.45 | 1.63 | 0.79 | 1.77 | nd | 21.1 |
| Jatropha de-oiled cake | 44.51 | 6.90 | 3.69 | 2.09 | 1.68 | 0.18 | 12.06 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, A.K.; Sahoo, P.K.; Mukherjee, M.; Patel, A. Assessment of Sustainable Biogas Production from Co-Digestion of Jatropha De-Oiled Cake and Cattle Dung Using Floating Drum Type Digester under Psychrophilic and Mesophilic Conditions. Clean Technol. 2022, 4, 529-541. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol4020032
Sharma AK, Sahoo PK, Mukherjee M, Patel A. Assessment of Sustainable Biogas Production from Co-Digestion of Jatropha De-Oiled Cake and Cattle Dung Using Floating Drum Type Digester under Psychrophilic and Mesophilic Conditions. Clean Technologies. 2022; 4(2):529-541. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol4020032
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Amit Kumar, Pradeepta Kumar Sahoo, Mainak Mukherjee, and Alok Patel. 2022. "Assessment of Sustainable Biogas Production from Co-Digestion of Jatropha De-Oiled Cake and Cattle Dung Using Floating Drum Type Digester under Psychrophilic and Mesophilic Conditions" Clean Technologies 4, no. 2: 529-541. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol4020032
APA StyleSharma, A. K., Sahoo, P. K., Mukherjee, M., & Patel, A. (2022). Assessment of Sustainable Biogas Production from Co-Digestion of Jatropha De-Oiled Cake and Cattle Dung Using Floating Drum Type Digester under Psychrophilic and Mesophilic Conditions. Clean Technologies, 4(2), 529-541. https://doi.org/10.3390/cleantechnol4020032







