Abstract
Irrigation of calcareous soil with saline–sodic water can modify the composition of the soil solution and exchange complexes in agricultural land of arid and semi-arid regions with low water resources. The objective of this study was to monitor (medium-term) potential changes in a calcareous clay soil irrigated with two types of sodic waters without cropping. Irrigation water with two high sodium adsorption ratios (SAR = 20 and 40) and electrical conductivity (EC < 3 dS m−1) was prepared using NaCl and NaHCO3 salts. The sodic irrigation waters were applied (June–October) in three periods (1, 2, and 4; one period = five irrigations) to bare non-saline soil with drip irrigation during two growing seasons; no irrigation action was taken in the winter–spring rainy season (period 3). Sampling (0–30 cm) was made after each period to determine the changes in soil pH, EC, water-soluble Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, Cl−, and HCO3−. Relative to the control, irrigation with both sodic waters increased soil pH, EC, and water-soluble Na+ and decreased or did not change water-soluble cations (Ca2+, Mg2+). The Cl− concentration increased rapidly with NaCl-type water application, but it was leached away quickly by winter–spring rains. The HCO3− concentration increased with NaHCO3-type water application, yet it leached out slowly in the rainy period. The movement of HCO3− ions in the upper soil profile (0–30 cm) was significantly slower compared to Cl− ions. Dissolution of slightly soluble soil CaCO3 by irrigation increased the solution concentration of Ca2+ and its mobility, yet the kinetics of processes depended on water type and irrigation period. The released Ca2+ interacted with other cations in the soil, causing further significant positive physicochemical changes in the soil solution and exchange capacity (comparable with control soil) at the end of the irrigation period. The CaCO3 content in the soil would be a long-term guarantee of the Ca2+ resource in soils, even if the amount of water-soluble Ca2+ may decrease for the short-term period during irrigation. The results should be considered for rational irrigation management (with various water qualities) in semi-arid and arid regions.
1. Introduction
Almost 40% of global agricultural production comes from just 20% of the world’s irrigated farmland, showing that irrigation, along with other management, has more than doubled land productivity in arid conditions [1]. However, due to the priority given to water resources in urban areas in arid and semi-arid regions, freshwater resources suitable for irrigation rapidly decrease in these climatic regions [2]. Moreover, one-third of the world’s agricultural lands are affected by soil degradation associated with erosion and salinity [3]. Therefore, applying irrigation with lower water quality (e.g., treated wastewater, saline water, effluent, drainage, and groundwater) to agricultural land is common in such regions. However, irrigation water quality and efficiency must be considered to prevent secondary salinization in the soil and a more significant reduction in soil quality [4,5]. It is undisputed that salinity and alkalinity are the most accepted water quality parameters of concern. Salinity refers to the total concentration of dissolved salts in soil and water, whereas water quality largely depends on the composition and concentration of dissolved ions or salts [6,7,8]. Using saline irrigation water causes salt accumulation in the soil, and salts containing Na+ ions (e.g., NaCl, NaHCO3) cause salt or abiotic stress (e.g., decreased transpiration, specific toxic ion effect) to the plants and deteriorate soil structure and physical properties and quality [9,10]. However, soil degradation caused by salinization can be suppressed by the calcium carbonate (CaCO3) in the soil, especially in arid regions. Therefore, depending on water quality, management, and climatic conditions, its deteriorative effect may appear in more extended periods. This, unfortunately, enables local farmers to continue using these waters without proper consideration of affecting factors [7,8,9,10].
In arid and semi-arid regions, salts are mainly found in irrigation water in the form of chlorides (Cl−), sulfates (SO42−), and bicarbonates (HCO3−) of calcium (Ca2+), magnesium (Mg2+), sodium (Na+), and potassium (K+) [11]. Saline–sodic irrigation waters can significantly increase soil sodicity in dry regions with limited rainfall and high evaporation; for example, drip irrigation with saline–sodic water (EC = 3.0–8.5 dS m−1 and SAR = 14–26 mmol1/2 L−1/2) significantly increased soil sodicity during the short period under cotton production [12]. The electrical conductivity (EC) of the soil solution, water-soluble Na, and Cl ion content in the soil increased with the increase in the salinity of the irrigation water in two years [13]. In other studies, excessive exchangeable Na with pH > 8.5 in irrigation water caused the physical properties of soils to deteriorate and adversely affected water and air movement, soil erodibility, and plant growth [14,15,16]. Irrigation with alkaline waters (with high carbonate and bicarbonate content) caused an increase in soil pH and Na saturation of the soils. As a result, notable soil aeration and permeability reduction were noted due to soil aggregate slaking and clay dispersion and clogging soil pores [17,18]. Yet, the result was soil texture dependent [19,20]. In similar experimental conditions, crop productivity was negatively affected by soil salinity and sodicity [21,22,23].
In arid and semi-arid regions, the ion compositions are changed in the exchange complexes and soil solution after being irrigated with sodic water. Sodic water usage in non-saline soil for short periods (e.g., up to 2–3 irrigation periods) is often necessary due to water scarcity. High clay and CaCO3 content in a calcareous clay soil limit the movement of Na+ ions downwards and structure deterioration [24,25]. With the dissolution of CaCO3 during the use of saline water, there is an increase in exchangeable Ca2+ in the calcareous clay soil, which competes with the exchangeable Na+ in the soil solution, thus limiting the increase in soil exchangeable Na+ and SAR in the soil solution or solid phase [26]. Furthermore, elevated soil salinity and sodicity can affect soil hydraulics by changing the pore size distribution through clay dispersion and flocculation [9,27]. Results of numerical studies from Turkiye and foreign countries were in the same line, reporting that, along with irrigation water quality, factors such as soil and salt type, irrigation frequency and season, and soil permeability (linked to soil texture and type) should be considered in evaluating the potential of irrigation water quality on physicochemical properties and quality of soils in arid and semi-arid lands [28,29,30,31,32].
The overall water demand in Turkiye continues to increase, and it is expected that the country will suffer from water scarcity in the following decades, particularly in arid and semi-arid territories, as a result of population growth and the impact of climate change [33,34,35]. Approximately 74% of the total water supply is used for agricultural irrigation, and 11% and 15% are used for industrial and domestic purposes, respectively. Therefore, the short- and long-term contributions of water quality to soil properties and land quality must be considered as a high-priority problem to tackle in the regions with scarce water resources. The quality of water in the area where the study was conducted is mostly not suitable for irrigation, as it may contain significant amounts of sodium. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of sodic water type (quality) on the chemical properties of a calcareous clay soil in semi-arid irrigated land to monitor the potential of medium-term changes in the ion dynamics. A typical calcareous soil was chosen to prove to what extent calcium carbonate can tolerate the adverse effects of sodic water.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Location
This study was conducted as a field trial at Ankara University Research and Application Farm in Haymana, Ankara (Figure 1), in a semi-arid region of Central Anatolia over two years. The distinctive feature of the region’s soils is low organic matter content but high amounts of carbonate, mostly calcium carbonate. For latter reason, aggregate formation and relatively strong soil structure are evident. The study area is located at an average altitude of 1065 m above sea level and has a continental climate zone characterized by little precipitation and significant temperature variations. In the Haymana district, summers are warm, dry, and open, and winters are freezing, snowy, and partly cloudy. The temperature typically ranges from −6 °C to 29 °C throughout the year, rarely below −13 °C or above 33 °C. The average temperature in the province is 11.7 °C, and the annual average precipitation is 390 mm. The evaporation demand is high, especially between April and October (up to 1222 mm) [25].
Figure 1.
Location of the experimental plots.
2.2. Experimental Design
The experimental design of field plots (3 × 4 m and 2 m apart from each other) was randomized blocks with three replications: drip irrigation method with (i) control (fresh water, EC < 1 dS m−1) was used, and (ii) four sodic waters (NaCl SAR 20, NaCl SAR 40, NaHCO3 SAR 20 and NaHCO3 SAR 40) were applied (5 treatments × 3 replication = 15 plots). Sodic waters (EC < 3 dS m−1) with two SAR levels (20 and 40) were prepared using NaCl and NaHCO3 salts; the ion concentrations of the irrigation water were computed with the Extract Chem Software program [36]. The plots were not cultivated and not cropped. Pesticides were used for weed control. Bare plots were irrigated for two years during the June–October period. The initial soil characteristics (pH, EC, water-soluble Na+, Ca2+, Cl−, and HCO3− contents) were used as a control to evaluate the contribution of irrigation with sodic water quality on soil properties (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7). Groundwater depth was >20 m, and thus, did not affect the dynamics of soil salinity.
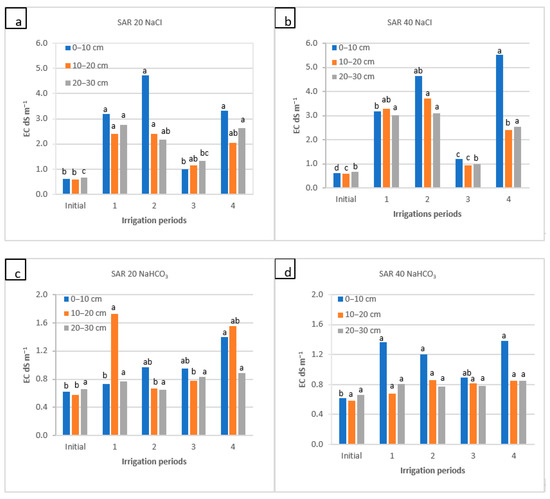
Figure 2.
Soil ECe as a function of water application during the irrigation periods (1, 2, and 4) and the rainy period (3) for four water qualities: (a) NaCl water: SAR 20; (b) NaCl water: SAR 40; (c) NaHCO3 water: SAR 20; and (d) NaHCO3 water: SAR 40. For each water quality, within each soil depth, the columns labeled with the same letter are not significantly different at p < 0.05.
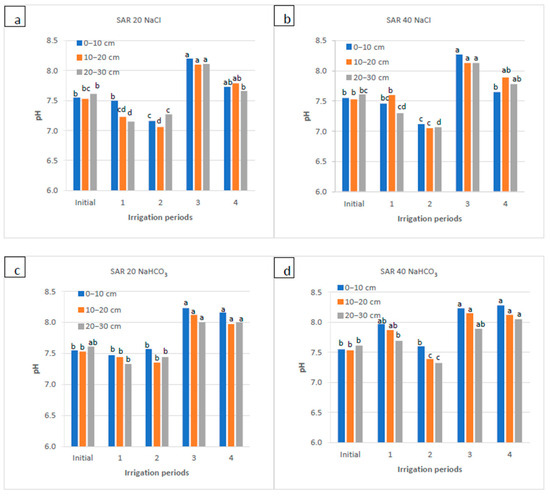
Figure 3.
Soil pH as a function of irrigation water applications during the irrigation periods (1, 2, and 4) and the rainy period (3) for four water qualities: (a) NaCl water: SAR 20; (b) NaCl water: SAR 40; (c) NaHCO3 water: SAR 20; and (d) NaHCO3 water: SAR 40. For each water quality, within each soil depth, the columns labeled with the same letter are not significantly different at p < 0.05.
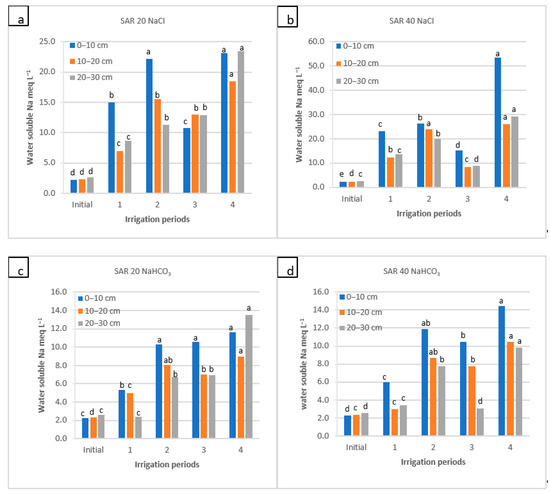
Figure 4.
Water-soluble Na+ of soil as a function of irrigation water applications during the irrigation periods (1, 2, and 4) and the rainy period (3) for four water qualities: (a) NaCl water: SAR 20; (b) NaCl water: SAR 40; (c) NaHCO3 water: SAR 20; and (d) NaHCO3 water: SAR 40. For each water quality, within each soil depth, the columns labeled with the same letter are not significantly different at p < 0.05.
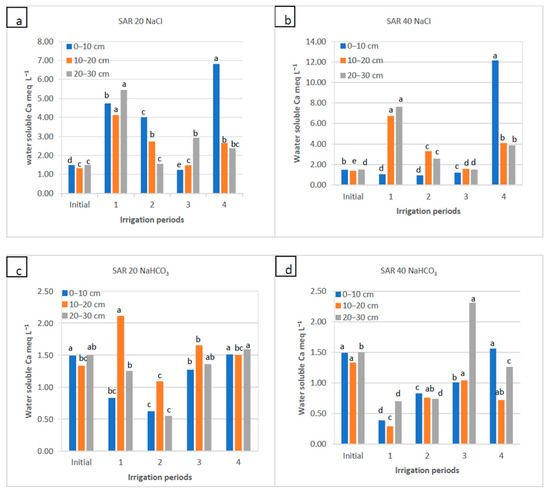
Figure 5.
Water-soluble Ca2+ of soil as a function of irrigation water applications during the irrigation periods (1, 2, and 4) and the rainy period (3) for four water qualities: (a) NaCl water: SAR 20; (b) NaCl water: SAR 40; (c) NaHCO3 water: SAR 20; and (d) NaHCO3 water: SAR 40. For each water quality, within each soil depth, the columns labeled with the same letter are not significantly different at p < 0.05.
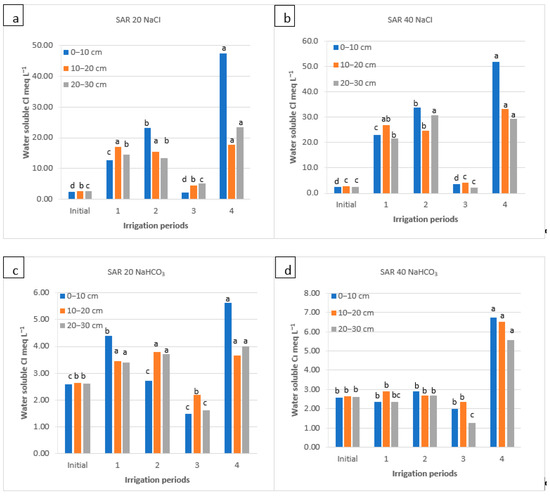
Figure 6.
Water-soluble Cl− of soil as a function of irrigation water applications during the irrigation periods (1, 2, and 4) and the rainy period (3) for four water qualities: (a) NaCl water: SAR 20; (b) NaCl water: SAR 40; (c) NaHCO3 water: SAR 20; and (d) NaHCO3 water: SAR 40. For each water quality, within each soil depth, the columns labeled with the same letter are not significantly different at p < 0.05.
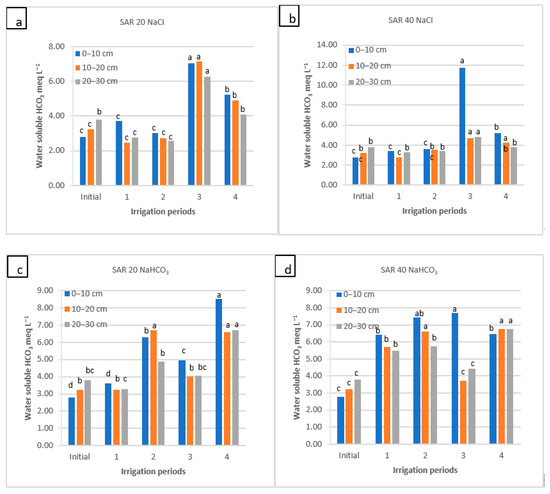
Figure 7.
Water-soluble HCO3− of soil as a function of irrigation water applications during the irrigation periods (1, 2, and 4) and the rainy period (3) for four water qualities: (a) NaCl water: SAR 20; (b) NaCl water: SAR 40; (c) NaHCO3 water: SAR 20; and (d) NaHCO3 water: SAR 40. For each water quality, within each soil depth, the columns labeled with the same letter are not significantly different at p < 0.05.
Details of irrigation with sodic water and soil sampling are provided in Table 1. The irrigations were carried out during four periods: periods 1, 2, and 4 were irrigation periods (one period = five irrigations), and period 3 was the winter–spring (October–May) precipitation period (Table 1). This is the period when the soil leaching occurred. The total precipitations that fell were 338.0, 32.2, 276.2 mm, and 190.8 mm during the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th periods, respectively. For each sodic water type’s treatment, the irrigation rate applied to the plots was based on soil moisture content and was ~10% greater than soil field capacity to avoid obstacles with potential inaccuracy and deep infiltration (based on the preliminary tests). A soil moisture sensor was used to control the soil moisture content (ECH 20 EC-5; METER Group, Inc., Pullman, WA, USA). Irrigation was repeated when the soil moisture decreased to the wilting point. During the 3rd period, no action was taken (e.g., salts were not applied to the plots by irrigation water). After the winter–spring period, the last 4th period of irrigation period (June–August) was performed, and then irrigation was terminated. After each watering period, soil samples (four replications) were taken from each plot at 0–10, 10–20, and 20–30 cm soil depths.

Table 1.
Details of irrigation schedule and sampling time.
2.3. Soil and Water Analysis
Air-dried soil samples were crushed and sieved through a 2 mm sieve and analyzed for texture with the Bouyoucos hydrometer method [37], soil pH and electrical conductivity (ECe) by saturation extract [38], organic matter by modified Walkley Black wet burning method [39], CaCO3 contents with a Scheibler calcimeter [38], and cation exchange capacity (CEC) by treatment with sodium acetate solution (pH 8.2) [40]. The water-soluble Na+, Ca2+, and K+ were determined with a flame photometer, Mg with an AAS [41], and CO32− and HCO3− in saturation extract by titration with 0.01 N H2SO4 and Cl by 0.005 N AgNO3 solution [38]. The SAR was computed by the equation of Na/(√(Ca + Mg)/2) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Selected soil and water properties before the experiment.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Data were evaluated using analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the SPSS 20.0. For each water quality and SAR level (NaCl SAR 20; NaCl SAR 40; NaHCO3 SAR 20; NaHCO3 SAR 40) comparison of means (ECe, pH, Na+, Ca2+, Cl−, HCO3−, Mg2+, K+) was made at p < 0.05 (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7; Supplementary Figures S1 and S2). Also, multivariate analysis of variance (multiple ANOVA (MANOVA)) was used to evaluate the contribution of water quality (water type), SAR level, and soil depth and their interactions on the studied soil properties (Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5). Then, multiple post hoc comparisons (water type, SAR level, and soil depth) were conducted to see where the differences originated. The variation of the mean values of the monitored soil properties by the periods was determined by one-way ANOVA, and the differences between the periods were grouped with ‘Tukey’ test at a confidence level of p < 0.05 (Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5).

Table 3.
Multiple comparison tests on the effect of SAR, water type, and soil depth and their interaction with soil properties. Differences are considered significant at the p < 0.05.

Table 4.
Effect of SAR level on soil properties.

Table 5.
Effect of the irrigation water type on soil properties.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Properties before the Experiment
The initial field soil properties (before irrigation with sodic water) and the fresh irrigation water quality parameters are provided in Table 2. The soil is generally characterized by clay texture, slight alkalinity, low organic matter, and high CaCO3 content at all depths. The variation in clay, pH, EC, and CaCO3 and most of the soluble cation’s content was mainly lower than the variation in organic matter and cation exchange capacity (CEC). Non-saline irrigation waters with very low sodicity had an alkaline reaction.
3.2. Effect of Irrigation on Water-Soluble Ion Concentration
The results of the change in soil ECe in the soil profile are provided in Figure 2. The ECe values increased in the soil surface (primarily) and sub-surface layer during the 1st, 2nd, and 4th periods of irrigation, especially by NaCl water applications (from 0.6 to 5.5 dS m−1) rather than NaHCO3 water treatment (from 0.6 to 1.7 dS m−1). During the 3rd period, salts leached out, and ECe decreased intently to the initial values (e.g., NaCl: 1.0–1.3 dS m−1; NaHCO3: 0.8–1.0 dS m−1) or moved from the upper to the lower soil layers and accumulated there. Remarkably, both NaCI and NaHCO3 water treatments significantly contributed to soil ECe at the SAR 40, particularly at the upper layer (0–10 cm). However, the changes in ECe values were far less dynamic in the soil profile with the application of NaHCO3 water (Figure 2).
Soil pH was 7.55 at the beginning and decreased after the 1st and 2nd periods of NaCl water applications but exceeded 8.0 and 7.7 after the 3rd and 4th periods of irrigation for two SAR levels, respectively. Although the increments after 3rd period were significant, the effect of NaCl water on soil pH was insignificant for the entire experiment period. In NaHCO3 water applications, the soil pH decreased insignificantly after the 2nd period of irrigation and then increased (to 7.9–8.3) after 3rd and 4th periods of irrigation, particularly in the top layer (0–10 cm). There was a significant increase in soil pH for both SAR levels, especially for the SAR 40, and soil pH reached 8.3 in the top layer after the 4th irrigation period (Figure 3). For both water quality, water-soluble Na+ increased in the 1st, 2nd, and 4th periods in both the surface (from 2.4 to 53.5 meq L−1) and subsurface (~23 meq L−1) layers; in comparison with NaHCO3, the NaCl water applications yielded two-times higher Na+. The increases between sampling periods were significant. There was no clear trend in Na+ distribution in the soil profile, yet Na+ concentration was higher, mainly in the top layer (Figure 4).
Under irrigation, in general, water-soluble Na+ decreased the water-soluble Ca2+ concentration in the top layer of soil; water-soluble Ca2+ ions were leached from the top layer (0–10 cm) and accumulated at a depth of 10–20 cm, and depending on the water quality, some changes were also noticed in the 20–30 cm depth. Compared to the initial control value (1.5 meq L−1), water-soluble Ca2+ increased at the SAR 20 of NaCl water applications in the 1st, 2nd and 4th periods (4.7–7.0 meq L−1) in the top layer, whereas for the SAR 40 of NaCl treatment, Ca2+ decreased considerably after the 2nd or 3rd period of irrigation (0.9–1.2 meq L−1), except for the 4th period, when Ca2+ increased to 12.2 meq L−1 at the end of irrigation. It should be noted that after winter–spring precipitation (3rd period), concentrations of Ca2+ were similar to the initial values (Figure 5). Excess soil Na concentration in the NaCl SAR 40 application could be related to a rapid transport of soluble Ca2+ from the top to deeper soil layers.
In both SAR levels of NaHCO3 water applications, water-soluble Ca2+ in the soil decreased after the 1st and 2nd irrigation periods, while the trend in different depths varied notably (Figure 5). Although there was a slight increase in the 3rd period (0–20 cm) compared to the first two periods, it reached a value somewhat close to the initial value of water-soluble Ca2+ after the 4th period. For the NaHCO3 water use, the differences in soil water-soluble Ca2+ between the periods were significant (Figure 5).
The water-soluble Mg2+ in the soils showed irregular increases and decreases in the SAR 20 of NaCl water application but later displayed an apparent reduction in the 3rd period and a net increase in the 4th period of irrigation. After the 1st period, the water-soluble Mg2+ at both SAR levels of NaHCO3 water use decreased compared to the initial concentration at all depths. At the same time, it remained almost non-existent in the 2nd period. NaHCO3 water seemingly affected the water-soluble Mg2+ concentration in the soil, even at depths of 20–30 cm. Similar results were obtained at SAR 20 and SAR 40 in the 3rd and 4th periods, revealing that the water-soluble Mg increased slightly compared to the 2nd period. The changes in water-soluble Mg2+ in the NaHCO3 water treatments between the periods were not statistically significant (Supplementary Figure S1).
The water-soluble K+ first decreased with NaCl water applications at both SAR levels and increased to the control value with continuous irrigation. During the 3rd period, it fell with winter–spring rains and rose again in the 4th period, especially in the top layer. While the increase in the 4th period was significant, the changes in other periods were insignificant. At both SAR levels of NaHCO3 water use, water-soluble K+ decreased in the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd periods compared to the initial control value; however, during the 4th period, it increased, especially in the surface layer. While the changes in the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd periods for SAR 20 treatments were significant, the differences were insignificant for SAR 40 (Supplementary Figure S2).
At both SAR levels of NaCl water applications, water-soluble Cl− in the surface soil layer increased rapidly after the 1st and 2nd periods; this increase was more noticed in SAR 40 (38.0 meq L−1) water than in SAR 20 (23.2 meq L−1) water. In the 3rd period, after the winter–spring precipitation, the water-soluble Cl− in the soil decreased rapidly and increased again during the 4th period (~50 meq L−1). The changes between the periods were significant (Figure 6). For the NaHCO3 water applications, however, water-soluble Cl− in the soil surface was not increased significantly at both SAR levels until the end of the 2nd period. Values similar to the initial Cl− concentrations were noticed in the 3rd period; however, in the 4th period, Cl− increased significantly for both SAR levels (Figure 6).
The water-soluble HCO3− did not change until the end of the 1st and 2nd periods in the top layer at both SAR levels of the NaCl water applications. During the winter–spring precipitation, water-soluble HCO3− increased in the 3rd period (from ~3 to 7 and 11.7 meq L−1) and decreased again in the 4th period; the changes between the 3rd and 4th periods were significant. The NaHCO3 water use did not significantly change water-soluble HCO3− in the soil until the 2nd period for all depths (at the SAR 20). However, after the 2nd period, the water-soluble HCO3− in the soil decreased and again increased (8.5 meq L−1) significantly in the 4th period of irrigation. Similar to the NaCl application, these differences between the 3rd and 4th periods were significant (Figure 7).
3.3. Multivariate Analysis of Variance
The effects of SAR level, water type, and soil depth on soil properties (except K+, Mg2+, or pH) were significant (Table 3). Thus, the effects of SAR level, water type, and soil depth and their interactions on studied soil properties were analyzed (Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6). The interaction effects of the factors on soil properties were changeable: (i) SAR level x water type effect was significant for Na+, Ca2+, K+, and Cl−; (ii) SAR level × soil depth effect was weighty for Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, HCO3−, and Cl−; (iii) water type × soil depth effect was important for all properties, except Mg2+; and (iv) triple interaction effect was significant for Ca2+, Na+, Mg2+, Cl−, and HCO3−, i.e., for most of the ions (Table 3). While the influence of the SAR levels of irrigation waters on the mean concentration of water-soluble ions (Na+, Ca2+, Cl− and HCO3−) and soil ECe were diverse, the difference between them (control SAR 1 and SAR 20 and SAR 40) were significant (Table 4). The contributions of water types (control fresh, NaCl, and NaHCO3) were significant for water-soluble Na+, Ca2+, Cl−, and HCO3−, and also for ECe (NaCl) and pHe (NaHCO3) (Table 5). Though the effect of soil depth was significant for water-soluble ions (Na+ and Ca2+, K+, HCO3−, Cl−) and ECe, the significant difference was found at 0–10 cm depth with the highest mean of studied properties (Table 3 and Table 6).

Table 6.
Effect of irrigation on soil properties at various depths.
4. Discussion
Management practices, local meteorological events (temperature, wind, radiation, and air humidity), and soil conditions (soil texture, salinity, lime content, water content, and tillage practices) significantly affect soluble ion movement and distributions in the soil profile. The permeability of clay soil was low, affecting both the velocity of water and ion transport and the kinetics of ion exchange processes between solid and solution phases [25]. In the 1st, 2nd, and 4th periods of irrigation, ECe values on the soil surface and subsurface layers increased significantly in terms of SAR levels for both sodic water types, mostly when NaCl water was used (Figure 2). The main reasons for these differences were related to (i) the continuous addition of salts to the soil with sodic irrigation water (Table 1), (ii) the variation in the solubility of NaCl and NaHCO3 salts in the presence of high soil CaCO3, and (iii) the variation in the mobility and accumulation rate of ions at different depths in the soil profile, which was in line with the previous studies [42,43,44,45]. The salts accumulated during the first irrigation season (1st and 2nd periods) were leached out by the precipitation (from the surface towards the deeper horizons) in the 3rd period, leading to a significant decrease in soil ECe (Figure 2). Since most of the precipitation in the study area falls in the winter–spring seasons, it was established that most of the salts in the clay soil profile accumulated within the upper 0–30 cm layer and a small amount (<30%) was transported into the deeper layers. However, in the 3rd watering period, a considerable downward movement of various ions depended on their solubility and chemical properties. Many studies from arid and semi-arid regions found that the salt content of the clay soil increases during the irrigation season and decreases in the rainy season due to leaching [46,47,48]. While the ions in the soil profile are transported downwards with irrigation or rain, they move upwards by capillary forces during evaporation, particularly in clayey soils and when water with high sodium is used. The increase in ECe by irrigation that was observed in the 4th period and the upward movement of water with capillary forces were the main reasons for the rise of EC again to the soil surface [49]. Öztürk and Özkan [49] have reported that soil ECe at the soil surface after ten days of evaporation period increased to up to 31% and 46% of the pre-drying level for the clay loam and sandy clay loam soils, respectively.
This study revealed that NaCl water application did not significantly change the soil pH due to its neutral salt characteristics (Figure 3). The buffering property of the soil and the further release of Ca2+ ions from CaCO3 would have also contributed to those processes. Sreenivas [50] reported a negative relationship between the soil EC and the pH of the saturation extract; the author noted that the high NaCl salt concentration in the irrigation water prevented an increase in the soil pH. Several studies from dry regions also have shown that the salinity of irrigation water and the intervals between them do not affect soil pH [51,52,53]. On the other hand, Pessoa et al. [48] found that in salt-affected sandy and silty loamy soils, irrigation water with varying types of salt containing Cl− increased the rate of the soluble Cl− over CO32− and HCO3− concentration in the soil; thus, pH in the soil extract decreased. In the current study, the increases in the pH values after the 3rd and 4th periods in the SAR 40 level of the NaHCO3 water were significant compared to the other periods. This change, especially in NaHCO3 applications in the 3rd period, was related to the hydrolyses of exchangeable Na+ into NaOH, leaching down with winter–spring precipitation, and the formation of Na2CO3 from NaOH reacting with CO2, absorbed from the air or produced by microorganisms, and the high content of the bicarbonates in the irrigation water [54]. Saygın et al. [54] explained that a slow but steady increase in calcareous soil pH value at the end of two growing seasons with NaHCO3 irrigation waters with a SAR 20 is linked to the buffering effect of CaCO3 and the formation of NaOH. Numerous studies reported that elevated HCO3− in the irrigation water caused a rise in soil pH under a combination of rain and irrigation or irrigation alone [55,56].
With the sodic water application, the water-soluble Na+ content increased together with the ECe of soil, and subsequently, Na+ leached downwards, especially when NaCl water was used (Figure 4). Researchers from different countries have reported a highly positive relationship between soil ECe and water-soluble Na+ [48,57,58,59,60]. In a study conducted for two years, the Na+ concentration increased up to 21.6% for three different salt levels in irrigation water, and Na+ concentration was consistent with soil ECe [61]. In our study, although a similar effect was evident for NaCl water applications, these changes were not observed for NaHCO3 water type. Salts with high dissolution rates can immediately mix into the soil solution and cause the effects of these salts (such as NaCl) on soil salinity to differ from those of salts with low solubility in water [62].
The presence of a high amount of Ca2+ in the soil solution was related to the high Na+ ion concentration after the treatment of sodic irrigation water (Figure 3 and Figure 4). The soil became salinized during the SAR 20 of NaCl water application, yet it was not fully saturated with Na2+ at the end of the 1st or 2nd periods. At the beginning of irrigation, Ca2+ was the major cation in the soil solid and solution phase due to its strong bonding force, and it was associated with calcareous soil characteristics. In the SAR 40 of NaCl water application, the soil became more saturated with Na+ due to its increased concentration, which tended to increase soil pH and decrease the concentration of water-soluble Ca2+ in the surface layer compared to the initial control one; subsequently, Ca2+ moved to the lower depths due to the displacement of Na+ with Ca2+ in the soil absorption sides. It was found that Ca2+ released from the exchange complexes with NaCl applications before the rainy season (rainfall with no electrolytes) was leached downwards only during the 3rd period and thus was removed from the soil surface layer. Sodic water application in the 4th period increased the water-soluble Ca2+ concentration at the soil surface since the Ca2+ on the colloid surfaces did not have a chance to be leached out yet. In addition, the low soluble CaCO3 reacted with sodium, dissolved some of its Ca2+ ions, and released them into the soil solution environment. The excess amount of Na+ was replaced by Ca2+, which was bound to the adhesion surfaces and caused the release of Ca2+ ions into the soil solution and, finally, increased Ca2+ concentration in the leachates [26,54].
For NaHCO3 treatment, the concentration of the water-soluble Ca2+ and Mg2+ in the soil solution decreased at all depths for SAR 20 and SAR 40 applications (Supplementary Figure S1) due to the increased concentration of water-soluble Na+ in semi-arid soils treated with sodic water; consequently, the release of Ca2+ and Mg2+ into the solution led to the decrease in their concentrations in the surface layers [63,64]. Analogous results were found in this study: the decrease in the water-soluble Mg2+ concentration, along with the salinity level and composition of the irrigation water, was associated with the increase of the Na+ concentration in the soil solution with the sodic irrigation waters. Tavakkoli et al. [65] reported that treating sandy soils with NaCl waters decreased the exchangeable Mg2+ concentration in the semi-arid region of South Australia. Moreover, Pessoa et al. [48] and Saygın et al. [53] established that using irrigation waters with different EC and SAR values decreased the exchangeable Mg2+ concentration similar to the Na+–Ca2+ shift in soil exchange complexes. The saline irrigation water did not significantly affect the change of water-soluble K+ values at the soil surface and the subsurface layers (Supplementary Figure S2). The reason could be related to the low K+ concentration in irrigation water and soil, as the high Na+ concentration in the water quickly washed away K+ from the adsorptive surfaces. Generally, K+ and P3+ were found in low concentrations in soil solutions [66].
Depending on the SAR level, the water-soluble Cl− concentration in the soil increased by NaCl water applications during the first irrigation seasons and decreased in the 3rd period when Cl− was leached out of the soil surface with rainfall with no salts (Figure 6). On the contrary, NaHCO3 water applications did not significantly affect the water-soluble Cl− concentration in the soil, except for the 4th period. It could be explained by the high Na+ and Cl− concentrations in the water and the rapid dissolution rate of these ion compounds. There is a synergistic relationship between Na+ and Cl−. Previous studies have also shown that Cl− is generally the most active ion in solute transport processes, followed by sulfate and relatively stagnant carbonate (bicarbonate) [67]. A very low Cl− concentration in the top layer after the irrigation and a sharp increase in Cl− concentration after the evaporation period was explained by the high mobility of this ion [68]. Pondkule et al. [56] found that Cl− in the soil extract before irrigation varied between 4.8 and 7.2 meq L−1, while it raised to 5.2 and 8.80 meq L−1 after irrigation. Soil texture also affects the retention of these ions in the soil. Due to their high water-holding capacity, Na+ and Cl− accumulations in fine-textured soils were higher than in coarse-textured soils [48]. In the NaHCO3 water treatments, the high soluble Cl− concentration at the soil top layer during the 4th period may be related to the moving of Cl− ions, which leached and accumulated at specific depths during the rainy season, or to the soil surface by evaporation [59].
In the NaCl water treatment, the amount of HCO3− in the soil increased after the 3rd period. This could be explained by the increased solubility of HCO3−, which has low solubility with NaCl salt (Figure 7). At the same time, it was observed that water-soluble HCO3− increased at SAR 40 in the 4th period and accumulated at lower depths due to the precipitation of Ca2+. However, it should be noted that NaHCO3 water applications (at SAR 40) increased the soil HCO3− concentration continuously, although, in the 3rd period, the concentration of HCO3− ions was expected to decrease. The difference in leaching rate or HCO3− ion distribution in soil profile can also be explained by the fact that saturated hydraulic conductivity of clay soil strongly depends on both EC of water and water salinity type [10,21]. Application of four pore volumes of NaHCO3 sodic water (EC = 3 dS m−1, SAR = 20) in similar clay soils decreased saturated hydraulic conductivity from ~0.4 cm min−1 to 0.15 cm min−1 [27,37]. Because of its low solubility and mobility characteristics in clay soils, winter–spring precipitation could not have leached HCO3− from the top layers of semi-arid soils, allowing the carbonates to accumulate in the soil profile [69]. As reported [70], the soil HCO3− concentration was strongly affected by irrigation water quality, soil depth, and sampling time. Pondkule et al. [56] stated that the HCO3− concentration in the soil extract increased from 7.3 to 8.4 meq L−1 to 7.5 to 8.9 meq L−1 at the end of the irrigation with sodic water. When the water-soluble HCO3− concentration was high, it reacted with the Ca2+ in the soil and precipitated as CaCO3. This condition led to an increase in the Na+ soil sodicity ratio in the soil [71]. In another study, a sharp decrease in NO3–, SO42−, and Cl− concentrations, but not in HCO3−, at the beginning of the leaching and, later, steady-state concentrations were observed in the collected leachates when irrigation water with NaHCO3 was used [54].
5. Conclusions
Calcium carbonate, which is generally found in the soil profile in such semi-arid areas or dry regions, plays a vital role in reducing or delaying the effects of possible problems associated with sodic water application and soil chemical and physical quality deterioration. Increasing Na+ in irrigation water increased the solubility of Ca2+ in the form of CaCO3, which has low solubility, and enhanced its leaching to lower soil depths. The released Ca2+ interacted with other cations in the soil, causing further positive physicochemical changes in the soil solution, yet the kinetics of the processes were dependent on water type. Although the amount of water-soluble Ca2+ released through ion exchange phenomena in soil exchange complexes decreased for the short-term period with sodium irrigation water application, the excess lime content in the soil can guarantee Ca2+ restoration in the long term. Results show that physical and chemical deteriorations that may occur in the soil can be prevented or limited to a certain extent, particularly when sodic water is used to balance the deficit of irrigation water. Therefore, the results of this study can be used for sustainable irrigation management plans in arid and semi-arid regions, considering site-specific conditions associated with soil properties and available irrigation water quality. Increasing water productivity and making safe use of poor-quality water in agriculture will play a vital role in easing competition for scarce water resources, preventing environmental degradation, and providing food security.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/soilsystems8010010/s1, Figure S1: Water-soluble Mg2+ of soil as a function of irrigation water applications during the irrigation periods (1, 2, and 4) and the rainy period (3) for four water qualities: (a) NaCl water: SAR 20; (b) NaCl water: SAR 40; (c) NaHCO3 water: SAR 20; and (d) NaHCO3 water: SAR 40. For each water quality, within each soil depth, the columns labeled with the same letter; Figure S2: Water-soluble K+ of soil as a function of irrigation water applications during the irrigation periods (1, 2, and 4) and the rainy period (3) for four water qualities: (a) NaCl water: SAR 20; (b) NaCl water: SAR 40; (c) NaHCO3 water: SAR 20; and (d) NaHCO3 water: SAR 40. For each water quality, within each soil depth, the columns labeled with the same letter.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.E.P. and H.S.Ö.; methodology, A.E.P. and H.S.Ö.; investigation, A.E.P.; field experiments, A.E.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.E.P., H.S.Ö. and A.I.M.; writing—review and editing, A.E.P., H.S.Ö. and A.I.M.; visualization, A.E.P. and A.I.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding. The authors thank Ankara University for the financial support.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fernández-Cirreli, A.; Arumí, J.L.; Rivera, D.; Boochs, P.W. Environmental effects of irrigation in arid and semi-arid regions. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2009, 69, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertran, J.M. Irrigation with saline water: Benefits and environmental impact. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 40, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.M.A.; Serralheiro, R.P. Soil salinity: Effect on vegetable crop growth. Management practices to prevent and mitigate soil salinization. Horticulturae 2017, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jin, M.; Ferré, T.P.; Liu, Y.; Xian, Y.; Shan, T.; Ping, X. Spatial distribution of soil moisture, soil salinity, and root density beneath a cotton field under mulched drip irrigation with brackish and fresh water. Field Crops Res. 2018, 215, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourgholam-Amijia, M.; Khoshraveshb, M.; Waqasc, M.M.; Mirzaeid, S.M.J. Study of combined magnetized water and salinity on soil permeability in North of Iran. Big Data Agric. 2020, 2, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Papazotos, P.; Koumantakis, I.; Vasileiou, E. Hydrogeochemical assessment and suitability of groundwater in a typical Mediterranean coastal area: A case study of the Marathon basin, NE Attica, Greece. HydroResearch 2019, 2, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, A.; Dell’Aquila, R. Effects of irrigation with saline waters, at different concentrations, on soil physical and chemical characteristics. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 77, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Xue, X.; Wang, T.; De Mascellis, R.; Mele, G.; You, Q.G.; Peng, F.; Tedeschi, A. Effects of saline water irrigation on soil properties in northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 63, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, G.J.; Goldstein, D.; Mamedov, A.I. Saturated hydraulic conductivity of semi—Arid soils: Combined effects of salinity, sodicity and rate of wetting. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerts, S.; Raes, D.; Garcia, M.; Condori, O.; Mamani, J.; Miranda, R.; Vacher, J. Could deficit irrigation be a sustainable practice for quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) in the Southern Bolivian Altiplano? Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheferia, B.; Seid, A. Effects of Saline Water and Irrigation Interval on Soil Physicochemical Properties. Adv. App. Sci. Res. 2021, 12, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Mantell, A.; Frenkle, H.; Meiri, A. Drip irrigation of cotton with saline sodic water. Irrig. Sci. 1985, 6, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucci, G.; Lacolla, G.; Rubino, P. Irrigation with saline-sodic water: Effects on soil chemical-physical properties. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 8, 358–365. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.K.; Manchanda, H.R. Influence of leaching with different amounts of water on desalinization and permeability behaviour of chloride and sulphate-dominated saline soils Agric. Water Manag. 1996, 31, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Gupta, M.; Pandey, A.; Pandey, V.; Singh, N.; Tewari, S.K. Effects of sodicity induced changes in soil physical properties on paddy root growth. Plant Soil Environ. 2014, 60, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashenafi, W.; Bedadi, B. Studies on soil physical properties of salt affected soil in Amibara Area, Central Rift Valley of Ethiopia. Int. J. Agric. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2016, 3, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, T.; Chen, X.; Shao, L. Effect of multiple wetting and drying cycles on the macropore structure of granite residual soil. J. Hydrol. 2022, 614, 128583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Chen, X.; Luo, Y.; Shao, L.; Niu, G. Three-dimensional pore structure characteristics of granite residual soil and their relationship with hydraulic properties under different particle gradation by X-ray computed tomography. J. Hydrol. 2023, 618, 129230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, S.R.; Oster, J.D. Use and reuse of saline-sodic waters for irrigation of crops. In Crop production in Saline Environments: Global and Integrative Perspectives; Goyal, S.S., Sharma, S.K., Rains, D.W., Eds.; Haworth Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 131–162. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, G.J.; Mamedov, A.I.; Goldstein, D. Sodicity and water quality effects on slaking of aggregates from semi-arid soils. Soil Sci. 2003, 168, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, O.P.; Josan, A.S.; Bajwa, M.S.; Kapur, M. Effect of sustained sodic and saline-sodic irrigations and application of gypsum and farmyard manure on yield and quality of sugarcane under semi-arid conditions. Field Crops Res. 2004, 87, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, P.S.; Dubey, S.K.; Sharma, D.R. Effects of soil and paddy-wheat crops irrigated with residual alkalinity. Soil Use Manag. 2007, 23, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.R.; Minhas, P.S. Strategies for managing saline/alkali waters for sustainable agriculture production in South Asia. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 78, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lado, M.; Ben-Hur, M.; Assouline, S. Effects of effluent irrigation on seal formation, infiltration, and soil loss during rainfall. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 69, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, H.S.; Saygin, S.D.; Copty, N.K.; İzci, E.; Erpul, G.; Demirel, B.; Saysel, A.K.; Babaei, M. Hydro-physical deterioration of a calcareous clay-rich soil by sodic water in Central Anatolia, Türkiye. Geoderma Reg. 2023, 33, e00649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agassi, M.; Tarchitzky, J.; Keren, R.; Chen, Y.; Goldstein, D.; Fizik, E. Effects of prolonged irrigation with treated municipal effluent on runoff rate. J. Environ. Qual. 2023, 32, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuther, F.; Schlüter, S.; Wallach, R.; Vogel, H.J. Structure and hydraulic properties in soils under long-term irrigation with treated wastewater. Geoderma 2019, 333, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajala, O.N.; Olaniyan, J.O.; Affinnih, K.; Ahamefule, H.E. Effect of Irrigation Water Quality on Soil Structure Along Asa River Bank. Ilorin Kwara State. Bulg. J. Soil. Sci. 2018, 3, 34–47. [Google Scholar]
- Javadi, A.; Mostafazadeh-Fard, B.; Shayannejad, M.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Ebrahimian, H. Soil physical and chemical properties and drain water quality as affected by irrigation and leaching managements. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 65, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, F.; Jalali, M. Long-term simulation of some soil chemical properties under continuous wheat cultivation irrigated with waters of different qualities. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 3249–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peker, A.E.; Öztürk, H.S. Sodyumlu sulama sularının toprak tuzluluk değişimine etkisi. Toprak Su Dergisi. 2020, 9, 102–115. [Google Scholar]
- Saygin, S.D.; Ozturk, H.S.; Izci, E.; Menon, M.; Nick, S.M.; Erpul, G.; Mawodza, T.; Copty, N. Solute movement through undisturbed calcareous and dry region soils under differing water flow velocities. In Proceedings of the Copernicus Meetings, Online, 19–30 April 2021; p. EGU21-15203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahasan, B.C.; Pınar, M. Climate Change and Spatial Agricultural Development in Turkey. ERF Work. Pap. 2021, 27, 1699–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerli, C.; Sahin, U. An assessment of the urban water footprint and blue water scarcity: A case study for Van (Turkey). Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 82, e249745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Change Post. Fresh Water Resources-Turkey. Retrieved from Climate Change Post website. Available online: https://www.climatechangepost.com/turkey/fresh-water-resources/ (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- Suarez, D.L.; Taber, P.E. Extract Chem Numerical Software Package for Estimating Changes in Solution Composition due to Changes in Soil Water Content; Version 2.0; US Salinity Lab.: Riverside, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bouyoucus, G.L. A recalibration of the hydrometer for making mechanical analysis of soils. Agron. J. 1951, 43, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. (Ed.) Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils (No 60); US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total Carbon, Organic Carbon and Organic Matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part II, Chemical and Microbiological Properties; ASA and SSSA. Agronomy Monograph No: 9; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 539–579. [Google Scholar]
- Bower, C.A. Cation-exchange equilibria in soils affected by sodium salts. Soil Sci. 1959, 88, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis; Prentice Hall of India: New Delhi, India, 1967; pp. 38–82. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, L.; Dhankhar, R.; Chhikara, S. Soil characteristics affected by long term application of sewage wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2010, 4, 513–518. [Google Scholar]
- Alsadon, A.; Sadder, M.; Wahb-Allah, M. Responsive gene screening and exploration of genotypes responses to salinity tolerance in tomato. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Karakoç, B.; Kale, S. The Effects of Salt Levels in Irrigation Water with Various Salt Dissolubility on the Yield of Lettuce (Lactuca sativa). SDÜ J. Fac. Agric. 2016, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Alrub, I.; Marcum, K.B.; Kabir, N.; Aran, A.; Hammadi, M.A. Productivity and nutritional value of four forage grass cultivars compared to Rhodes grass irrigated with saline water. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2018, 12, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauder, T.A.; Waskom, R.M.; Sutherland, P.; Davis, J.G. Irrigation Water Quality Criteria. Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado State University, Libraries, Ford Collins, CO, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Tang, X.; Wang, H.; Shao, H.B. Proline accumulation and metabolism-related genes expression profiles in Kosteletzkya virginica seedlings under salt stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, L.G.M.; dos Santos Freire, M.B.G.; dos Santos, R.L.; Freire, F.J.; Miranda, M.F.A.; dos Santos, P.R. Saline water irrigation in semiarid region: I-effects on soil chemical properties. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2019, 13, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, H.S.; Özkan, İ. Effects of Evaporation and different flow regimes on solute distribution in soil. Transp. Porous Media 2004, 56, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivas, C.; Konda Reddy, C. Salinity-sodicity relationships of the Kalipatnam drainage pilot area, Godavari Western Delta, India. Irrig. Drain. 2008, 57, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Sheppard, C.D.; Fedler, C.B. Short-term effects of wastewater land application on soil chemical properties. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 211, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahil, M.; Hajjeh, H.; Qanadillo, A. Effect of saline water application through different irrigation intervals on tomato yield and soil properties. Open J. Soil. Sci. 2013, 3, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygin, S.D.; Özturk, H.S.; Akca, M.O.; Copty, N.K.; Erpul, G.; Demirel, B.; Saysel, A.K.; Babaei, M. Solute transport through undisturbed carbonatic clay soils in dry regions under differing water quality and irrigation patterns. Geoderma 2023, 434, 116489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedinpour, M. Assessments of saline water application and different irrigation intervals on soil and soybean yield. Azarian J. Agric. 2016, 3, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, J.L.; Aparicio, V.C. Quality assessment of irrigation water under a combination of rain and irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 159, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pondkule, R.G.; Jadhao, S.M. Impact of irrigation on soil properties in Purna valley of Vidarbha region of Maharashtra. IJCS 2020, 8, 2110–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgili, A. Spatial assessment of soil salinity in the harran Plain using multiple kriging techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 777–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.S.; Alves, D.C.; Cunha, J.C.; Lima, A.M.N.; Cavalcante, I.H.L.; da Silva, K.A.; de Melo Junior, J.C.F. Spatial analysis of soil salinity in a mango irrigated area in semi-arid climate region. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2018, 12, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, A.M.; Hellal, F.A.; Abd El-Hady, M. Water salinity impacts on some soil properties and nutrients uptake by wheat plants in sandy and calcareous soil. Aust. J. Basic. Appl. Sci. 2008, 2, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- Mojiri, A. Effects of municipal wastewater on physical and chemical properties of saline soil. J. Biol. Envıron. Sci. 2011, 5, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Asadbegi, M.; Bahmani, O.; AtlassiPak, V. Impact of saline water on some ions uptake and yield of wheat genotypes and soil salt accumulation. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2019, 50, 2787–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoorn, J.W.; Van Alpen, J.G. Salinity Control, Salt Balance and Leaching Requirement of Irrigated Soils. In 29th International Course Land Drainage; Lecture Notes; Landbouwuniversiteit: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoodabadi, M.; Yazdanpanah, N.; Sinobas, L.R. Reclamation of calcareous saline sodic soil with different amendments (I): Redistribution of soluble cations within the soil profile. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 120, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhan, X.; He, J.; Feng, H.; Kang, Y. Salt characteristics and soluble cations redistribution in an impermeable calcareous saline-sodic soil reclaimed with an improved drip irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 197, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakkoli, E.; Rengasamy, P.; McDonald, G.K. High concentrations of Na+ and Cl– ions in soil solution have simultaneous detrimental effects on growth of faba bean under salinity stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 4449–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grattan, S.; Grieve, C.M. Mineral nutrient acquisition and response by plants grown in saline environments. In Handbook of Plant and Crop Stress; Pessarakli, M., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 203–229. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wan, S. Effect of soil matric potential on the distribution of soil salt under drip irrigation on saline and alkaline land in arid regions. Trans. CSAE 2008, 24, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Öztürk, H.S.; Özkan, İ. Solute movement in large soil columns during different ponded infiltration. Aust. J. Agri. Res. 2002, 53, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Günal, H. Clay Illuviation and Calcium Carbonate Accumulation along Precipitation Gradient in Kansas. Ph.D. Thesis, Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hanifa Lu, A. The Effect of Wastewater Effluent in Ahvaz on the Physical, Hydraulic and Chemical Properties of Soil in a Short Period of Time. Master’s Thesis, Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz, Ahvaz, Iran, 2005; pp. 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Korkmaz, N.; Gündüz, M.; Aşık, Ş. Temporal variation of ground water level and quality of agricultural lands south of Gediz River. Derim 2016, 33, 263–278. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
