Biodegradation of Malathion in Amended Soil by Indigenous Novel Bacterial Consortia and Analysis of Degradation Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Media
2.2. Microorganisms
2.3. Identification of Malathion-Degrading Bacteria
2.4. Inoculum Preparation
2.5. Experimental Design for Pot Experiment
2.6. Estimation of Malathion and Its Metabolites
2.7. Analysis of Extracts for Malathion Estimation
2.8. Confirmation–Identification of Degradation Metabolites
2.9. Degradation Kinetics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparative Analysis of Malathion Degradation by Bacterial Species in Liquid Culture
3.2. Bioremediation Evaluation of Individual Strains and Mixed Strains Consortia
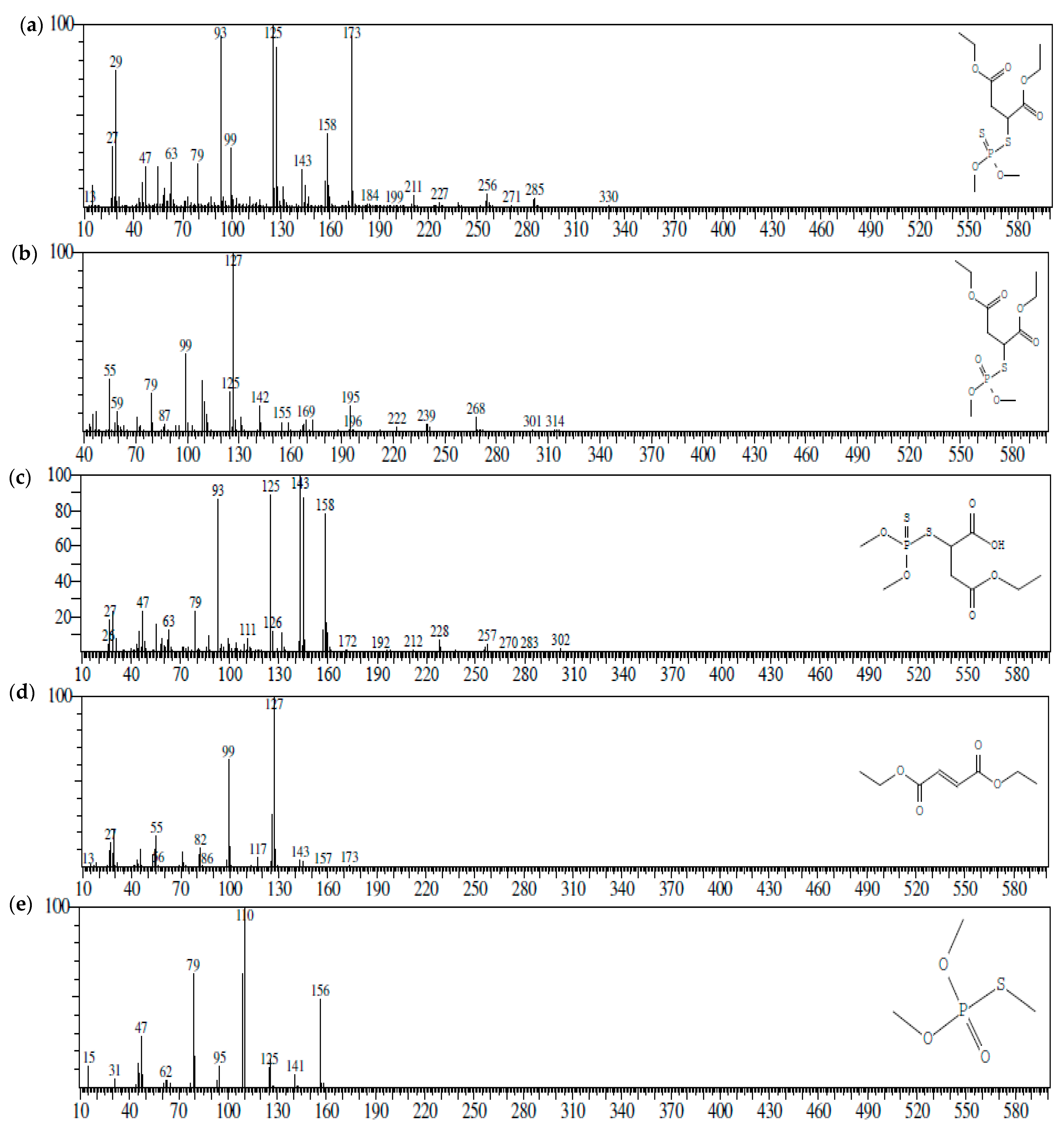
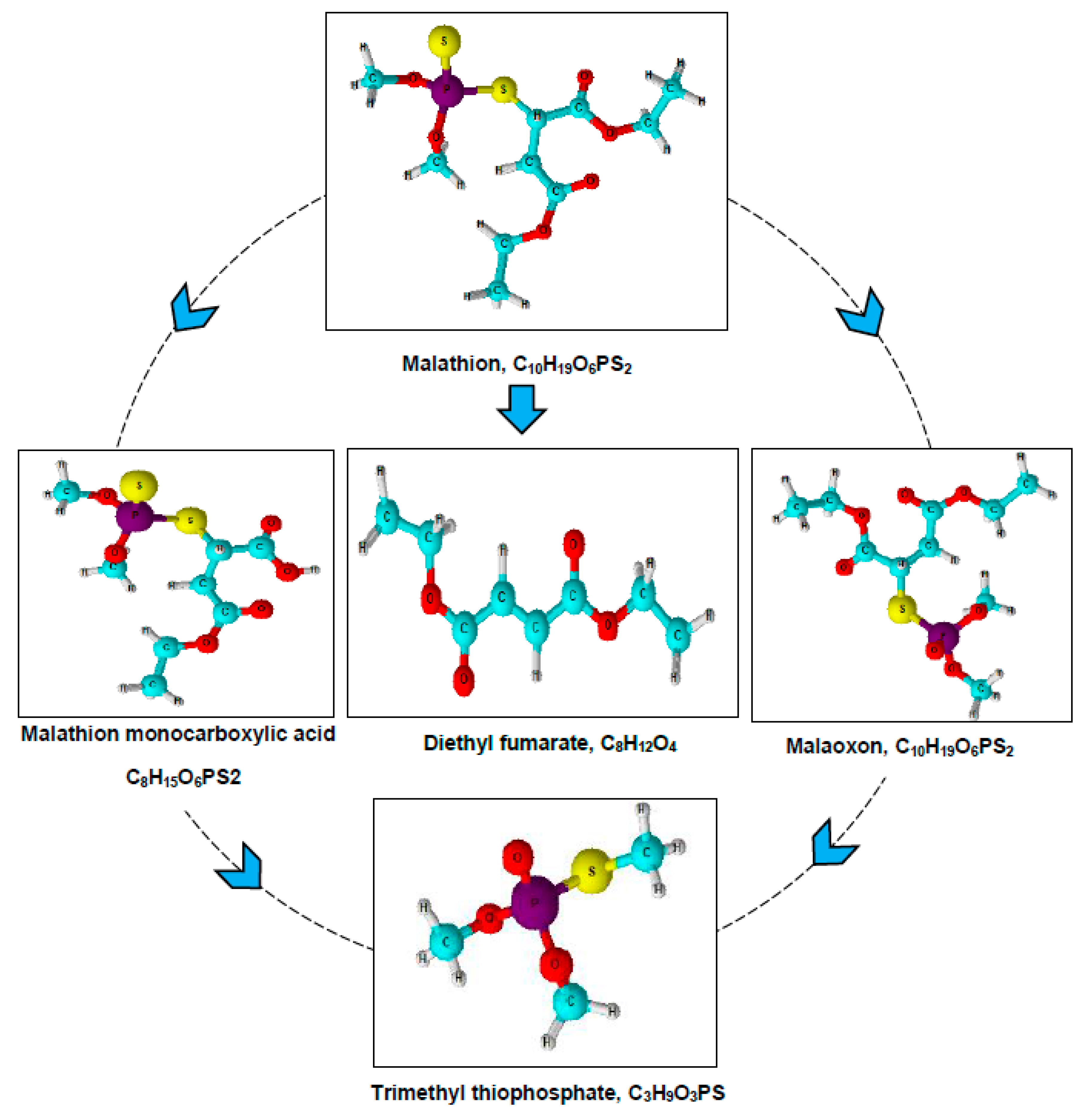
3.3. Metabolites Analysis
3.4. Kinetic Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ortiz-Hernández, M.L.; Sánchez-Salinas, E.; Dantán-González, E.; Castrejón-Godínez, M.L. Pesticide biodegradation: Mechanisms, genetics and strategies to enhance the process. Biodegrad.-Life Sci. 2013, 10, 251–287. [Google Scholar]
- Morillo, E.; Villaverde, J. Advanced technologies for the remediation of pesticide-contaminated soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 576–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, K.R.; Philip, L. Biodegradation of lindane, methyl parathion and carbofuran by various enriched bacterial isolates. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B-Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2008, 43, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dar, M.A.; Kaushik, G.; Chiu, J.F.V. Pollution status and biodegradation of organophosphate pesticides in the environment. In Abatement of Environmental Pollutants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 25–66. [Google Scholar]
- Dar, M.A.; Kaushik, G.; Villarreal-Chiu, J.F. Pollution status and bioremediation of chlorpyrifos in environmental matrices by the application of bacterial communities: A review. J Environ. Manag. 2019, 239, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dar, M.A.; Baba, Z.A.; Kaushik, G. A review on phorate persistence, toxicity and remediation by bacterial communities. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aardema, H.; Meertens, J.; Ligtenberg, J.J.M.; Peters-Polman, O.M.; Tulleken, J.E.; Zijlstra, J.G. Organophosphorus pesticide poisoning: Cases and developments. Neth. J. Med. 2008, 66, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan, R.; Bonner, M.R.; Hoppin, J.A.; Alavanja, M.C.R. Phorate exposure and incidence of cancer in the agricultural health study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.S.; Shi, T.Z.; Wu, X.W.; Ma, X.; Li, X.Q.; Hua, R.M.; Tang, X.Y.; Li, Q.X. Rapid biodegradation of organophosphorus pesticides by Stenotrophomonas sp. G1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 297, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geed, S.; Kureel, M.; Shukla, A.; Singh, R.; Rai, B. Biodegradation of malathion and evaluation of kinetic parameters using three bacterial species. Resour.-Effic. Technol. 2016, 2, S3–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, B.; Madan, V.K.; Kathpal, T.S. Status of insecticide contamination of soil and water in Haryana, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadaei, A.; Dehghani, M.H.; Nasseri, S.; Mahvi, A.H.; Rastkari, N.; Shayeghi, M. Organophosphorous Pesticides in Surface Water of Iran. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 88, 867–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harinathareddy, A.; Prasad, N.; Devi, L. Pesticide residues in vegetable and fruit samples from Andhra Pradesh, India. J. Biol. Chem. Res 2014, 31, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Sanghi, R.; Pillai, M.K.K.; Jayalekshmi, T.R.; Nair, A. Organochlorine and organophosphorus pesticide residues in breast milk from Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2003, 22, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dar, M.A.; Kaushik, G. Optimizing the malathion degrading potential of a newly isolated Bacillus sp. AGM5 based on Taguchi design of experiment and elucidation of degradation pathway. Biodegradation 2022, 33, 419–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.A.; Chanwala, J.; Meena, P.R.; Singh, A.P.; Kaushik, G. Biodegradation of malathion by Micrococcus sp. strain MAGK3: Kinetics and degradation fragments. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.A.; Kaushik, G. Phytotoxic effects and persistence of malathion on fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum), and assessment of health risks. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. World Health Organisation Staff. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 370–373. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, P.D.; Yedjou, C.G.; Tchounwou, P.B. Malathion-induced oxidative stress, cytotoxicity, and genotoxicity in human liver carcinoma (HepG2) cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2010, 25, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, K.; Minami, T.; Matsui, Y.; Magara, Y. Effects of chlorine on organophosphorus pesticides adsorbed on activated carbon: Desorption and oxon formation. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Hernandez, M.L.; Sanchez-Salinas, E. Biodegradation of the organophosphate pesticide tetrachlorvinphos by bacteria isolated from agricultural soils in mexico. Rev. Int. De Contam. Ambient. 2010, 26, 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Liu, J.X.; Li, L.; Qiao, C.L. Biodegradation of malathion by Acinetobacter johnsonii MA19 and optimization of cometabolism substrates. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Zaffar, H.; Irshad, U.; Ahmad, R.; Khan, A.R.; Shah, M.M.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, M.; Naqvi, T. Biodegradation Of Malathion By Bacillus Licheniformis Strain Ml-1. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2016, 68, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Torres, C.; Ortiz, I.; San-Martin, P.; Hernandez-Herrera, R.I. Biodegradation of malathion, α-and β-endosulfan by bacterial strains isolated from agricultural soil in Veracruz, Mexico. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2016, 51, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishag, A.S.A.; Abdelbagi, A.O.; Hammad, A.M.A.; Elsheikh, E.A.E.; Elsaid, O.E.; Hur, J.H.; Laing, M.D. Biodegradation of Chlorpyrifos, Malathion, and Dimethoate by Three Strains of Bacteria Isolated from Pesticide-Polluted Soils in Sudan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8491–8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.A.; Kaushik, G. Optimization of process parameters for biodegradation of malathion by Micrococcus aloeverae MAGK3 using Taguchi methodology and metabolic pathway analysis. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 102362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jariyal, M.; Jindal, V.; Mandal, K.; Gupta, V.K.; Singh, B. Bioremediation of organophosphorus pesticide phorate in soil by microbial consortia. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, S.; Rasool, T.; Gani, K.M. A review of interactions of pesticides within various interfaces of intrinsic and organic residue amended soil environment. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 11, 100301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Pehkonen, S.O.; Brooks, E. Pathways for the hydrolysis of phorate: Product studies by 31P NMR and GC-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3013–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, D.O.; Yellowlees, D.; Tibbett, M. Autoclaving kills soil microbes yet soil enzymes remain active. Pedobiologia 2007, 51, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Wronkowska, H. On the efficiency of soil sterilization in autoclave. Zent. Mikrobiol. 1987, 142, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevors, J. Sterilization and inhibition of microbial activity in soil. J. Microbiol. Methods 1996, 26, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K.; Walker, A. Microbial degradation of organophosphorus compounds. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 428–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpouzas, D.; Walker, A. Factors influencing the ability of Pseudomonas putida strains epI and II to degrade the organophosphate ethoprophos. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 89, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cycon, M.; Zmijowska, A.; Wojcik, M.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Biodegradation and bioremediation potential of diazinon-degrading Serratia marcescens to remove other organophosphorus pesticides from soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 117, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maya, K.; Singh, R.S.; Upadhyay, S.N.; Dubey, S.K. Kinetic analysis reveals bacterial efficacy for biodegradation of chlorpyrifos and its hydrolyzing metabolite TCP. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 2130–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Yang, C.L.; Gong, M.B.; Zhao, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, C.X.; Jiang, J.D.; Li, S.P. Adsorption and degradation of triazophos, chlorpyrifos and their main hydrolytic metabolites in paddy soil from Chaohu Lake, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpouzas, D.G.; Singh, B.K. Microbial degradation of organophosphorus xenobiotics: Metabolic pathways and molecular basis. In Advances in Microbial Physiology; Poole, R.K., Ed.; Advances in Microbial Physiology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; Volume 51, pp. 119–185. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmi, C.V.; Kumar, M.; Khanna, S. Biotransformation of chlorpyrifos and bioremediation of contaminated soil. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2008, 62, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, S.K.; Elsayed, I.E.; Khodair, T.A.; El-Sayed, W.; Mohamed, M.E. Screening for and isolation and identification of malathion-degrading bacteria: Cloning and sequencing a gene that potentially encodes the malathion-degrading enzyme, carboxylestrase in soil bacteria. Biodegradation 2010, 21, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kaur, J.; Singh, K. Transformation of malathion by Lysinibacillus sp. isolated from soil. Biotechnol. Lett. 2012, 34, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kaur, J.; Singh, K. Bioremediation of malathion in soil by mixed Bacillus culture. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Gong, L.; Chen, X.; Xie, Q.; Jin, Y.; Liu, G. Mechanism of β-cypermethrin metabolism by Bacillus cereus GW-01. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birolli, W.G.; Dos Santos, A.; Pilau, E.; Rodrigues-Filho, E. New role for a commercially available bioinsecticide: Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner biodegrades the pyrethroid cypermethrin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4792–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, W.J.; Li, J.; Ghorab, M.A.; Alansary, N.; El-Hefny, D.E.; Chen, S. Novel mechanism and degradation kinetics of allethrin using Bacillus megaterium strain HLJ7 in contaminated soil/water environments. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Ahn, J.Y.; Moon, S.H.; Lee, J. Biodegradation and detoxification of organophosphate insecticide, malathion by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp pisi cutinase. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirajuddin, S.; Khan, M.A.; Ul Qader, S.A.; Iqbal, S.; Sattar, H.; Ansari, A. A comparative study on degradation of complex malathion organophosphate using of Escherichia coli IES-02 and a novel carboxylesterase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Xue, R.; Zhou, J.; Wen, X.; Shi, Z.; Chen, M.; Xin, F.; Zhang, W.; Dong, W.; Jiang, M. Characterization of acetamiprid biodegradation by the microbial consortium ACE-3 enriched from contaminated soil. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Zhang, Z.H.; Hong, Y.F.; Li, S.P. A microcosm study on bioremediation of fenitrothion-contaminated soil using Burkholderia sp. FDS-1. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2007, 59, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cycon, M.; Wojcik, M.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Biodegradation kinetics of the benzimidazole fungicide thiophanate-methyl by bacteria isolated from loamy sand soil. Biodegradation 2011, 22, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
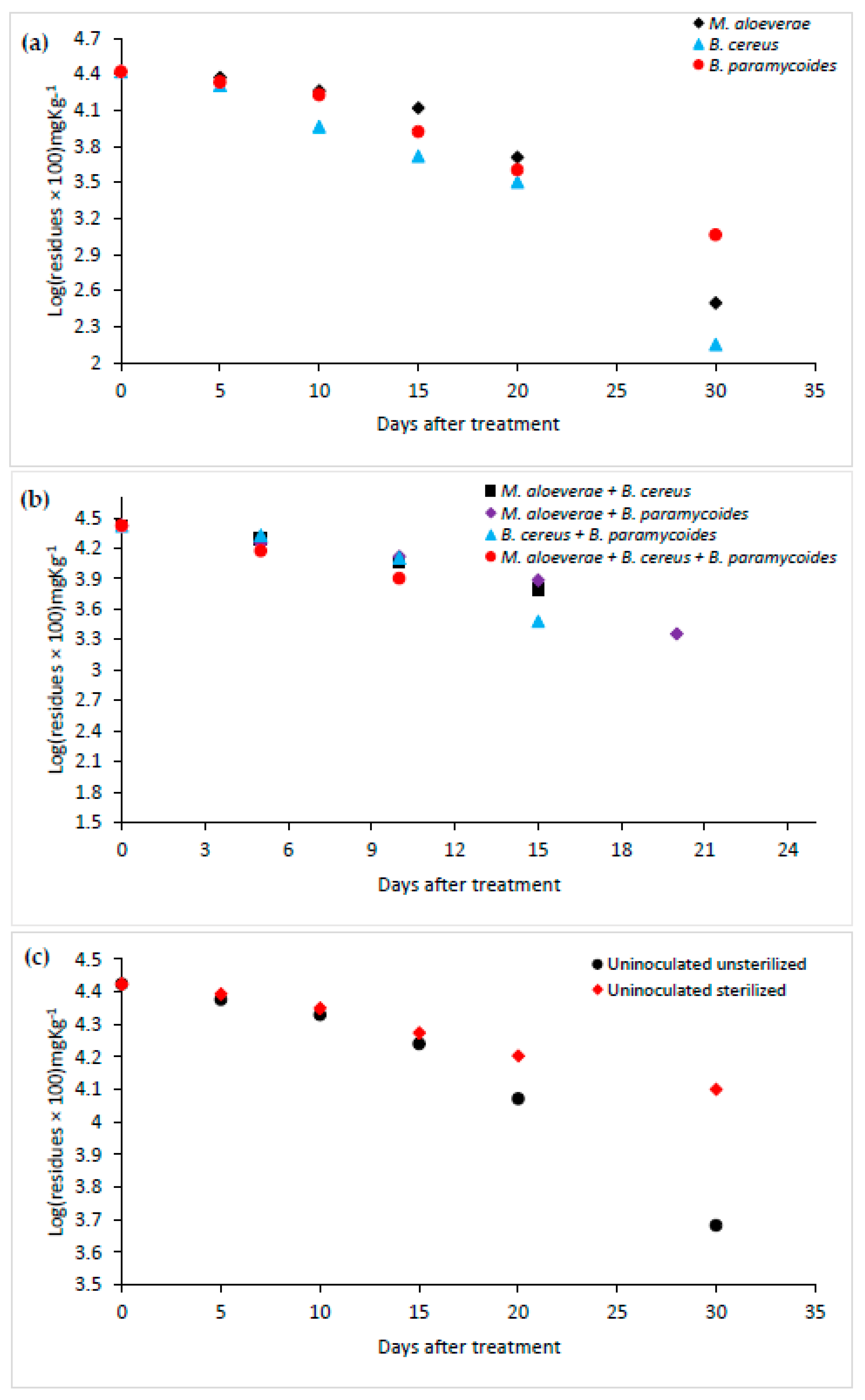
| Days after Treatment | Micrococcus aloeverae | Bacillus cereus | Bacillus paramycoides | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malathion Residues | Percent Reduction | Malathion Residues | Percent Reduction | Malathion Residues | Percent Reduction | |
| 0 | 265.127 | 0 | 265.127 | 0 | 265.127 | 0 |
| 5 | 237.440 | 10.442 | 204.796 | 22.755 | 216.877 | 18.198 |
| 10 | 184.595 | 30.374 | 92.591 | 65.076 | 168.735 | 36.356 |
| 15 | 132.147 | 50.156 | 52.690 | 80.126 | 83.582 | 68.474 |
| 20 | 51.3440 | 80.634 | 32.092 | 87.895 | 40.410 | 84.757 |
| 30 | 3.1501 | 98.811 | 1.424 | 99.462 | 11.615 | 95.618 |
| Days after Treatment | Micrococcus aloeverae + Bacillus cereus | Micrococcus aloeverae + Bacillus paramycoides | Bacillus cereus + Bacillus paramycoides | Micrococcus aloeverae + Bacillus cereus + Bacillus paramycoides | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malathion Residues | Percent Reduction | Malathion Residues | Percent Reduction | Malathion Residues | Percent Reduction | Malathion Residues | Percent Reduction | |
| 0 | 265.127 | 0 | 265.127 | 0 | 265.127 | 0 | 265.127 | 0 |
| 5 | 193.371 | 27.064 | 179.332 | 32.360 | 213.443 | 19.494 | 149.716 | 43.530 |
| 10 | 114.699 | 56.738 | 132.164 | 50.150 | 127.418 | 51.940 | 79.699 | 69.939 |
| 15 | 62.096 | 76.578 | 77.024 | 70.948 | 30.211 | 88.605 | ND | 100 |
| 20 | ND | 100 | 22.790 | 91.404 | ND | 100 | - | - |
| 30 | - | - | ND | 100 | - | - | - | - |
| Days after Treatment | Uninoculated Unsterilized | Uninoculated Sterilized | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malathion Residues | Percent Reduction | Malathion Residues | Percent Reduction | |
| 0 | 265.127 | 0 | 265.127 | 0 |
| 5 | 237.415 | 10.452 | 247.795 | 6.537 |
| 10 | 213.546 | 19.455 | 223.539 | 15.686 |
| 15 | 173.783 | 34.452 | 187.874 | 29.137 |
| 20 | 117.788 | 55.572 | 159.346 | 39.898 |
| 30 | 48.021 | 81.887 | 126.046 | 52.458 |
| S. No | Compound | Chemical Formula | CAS No. | Molecular Weight (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Malathion | C10H19O6PS2 | CAS:121-75-5 | 330 |
| 2 | Malaoxon | C10H19O7PS | CAS:1634-78-2 | 314 |
| 3 | Malathion monocarboxylic acid | C8H15O6PS2 | CAS:1190-29-0 | 302 |
| 4 | Diethyl fumarate | C8H12O4 | CAS:623-91-6 | 173 |
| 5 | Trimethyl thiophosphate | C3H9O3PS | CAS: 152-18-1 | 156 |
| Treatment | Regression Equation (y) | Half-Life (Days) | Correlation Coefficient (R2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Micrococcus aloeverae | −0.1438x + 0.7096 | 9.753 | 0.8472 |
| Bacillus cereus | −0.1684x + 0.5344 | 7.288 | 0.9187 |
| Bacillus paramycoides | −0.1087x + 0.3135 | 9.259 | 0.9634 |
| Micrococcus aloeverae + Bacillus cereus | −0.2305x + 0.742 | 6.225 | 0.8725 |
| Micrococcus aloeverae + Bacillus paramycoides | −0.1903x + 0.7593 | 7.631 | 0.8834 |
| Bacillus cereus + Bacillus paramycoides | −0.2153x + 0.5918 | 5.967 | 0.9013 |
| Micrococcus aloeverae + Bacillus cereus + Bacillus paramycoides | −0.2333x + 0.0648 | 3.248 | 0.8503 |
| Uninoculated unsterilized | −0.0565x + 0.2082 | 15.950 | 0.915 |
| Uninoculated sterilized | −0.0261x + 0.0422 | 28.168 | 0.9865 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dar, M.A.; Kaushik, G. Biodegradation of Malathion in Amended Soil by Indigenous Novel Bacterial Consortia and Analysis of Degradation Pathway. Soil Syst. 2023, 7, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7040081
Dar MA, Kaushik G. Biodegradation of Malathion in Amended Soil by Indigenous Novel Bacterial Consortia and Analysis of Degradation Pathway. Soil Systems. 2023; 7(4):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7040081
Chicago/Turabian StyleDar, Mohd Ashraf, and Garima Kaushik. 2023. "Biodegradation of Malathion in Amended Soil by Indigenous Novel Bacterial Consortia and Analysis of Degradation Pathway" Soil Systems 7, no. 4: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7040081
APA StyleDar, M. A., & Kaushik, G. (2023). Biodegradation of Malathion in Amended Soil by Indigenous Novel Bacterial Consortia and Analysis of Degradation Pathway. Soil Systems, 7(4), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7040081





