Glyphosate-Based Herbicide Formulations with Greater Impact on Earthworms and Water Infiltration than Pure Glyphosate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
- Factor GBH (three levels): one-time application of Touchdown Quattro (TQ), Roundup PowerFlex (PF), or Roundup LB Plus (LB) at recommended dosages (Table 2).
- Factor AI (three levels): one-time application of diammonium salt (am), potassium salt (po), or isopropylamine salt (is) at recommended dosages (Table 2).
- Control: mechanical weeding (co) by pulling plants.
- Factor SOM (two levels): low (3.0% SOM) or high (4.1% SOM).
2.2. Planting and Earthworms
2.3. Herbicide Applications
- Factor GBH: consisted of a one-time application of Touchdown Quattro (TQ; AI 360 g L−1; Syngenta Agro GmbH; Vienna, Austria), Roundup PowerFlex (PF; AI 588 g L−1), or Roundup LB Plus (LB; AI 360 g L−1; both Bayer Agrar Austria; Vienna, Austria).
- Factor AI: consisted of a one-time application of potassium salt (AI in Roundup PowerFlex), isopropylamine salt (AI in Roundup LB Plus), or diammonium salt (AI in Touchdown Quattro).
- Control: pots were sprayed with tap water, and plants were uprooted and left on the soil surface of the pots.
2.4. Measurements
2.4.1. Plant Growth
2.4.2. Earthworm Activity
2.4.3. Litter Decomposition
2.4.4. Water Infiltration, Soil Temperature, Moisture, and Electrical Conductivity
2.5. Termination of the Experiment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
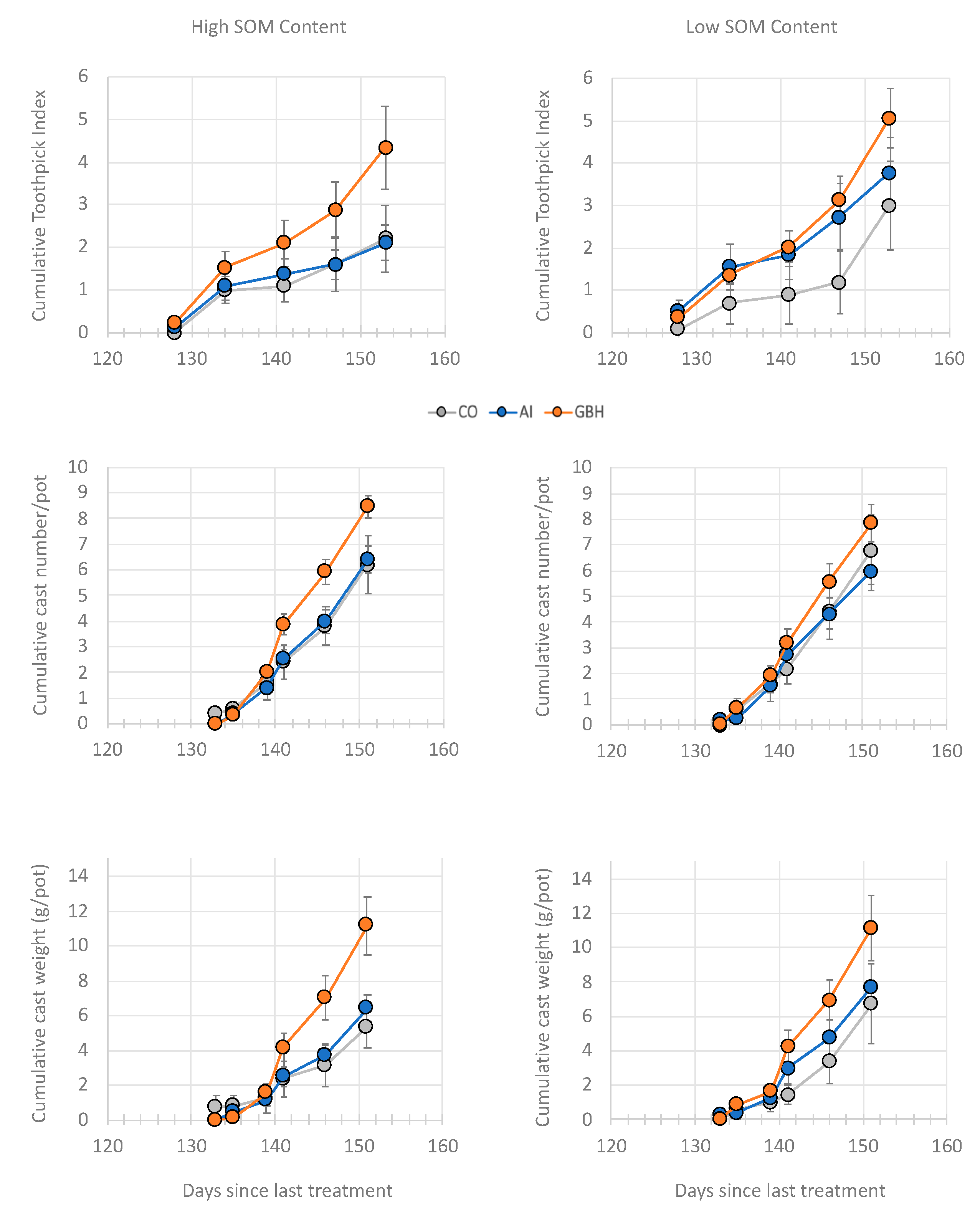
3.1. Legacy GBH/AI Effects
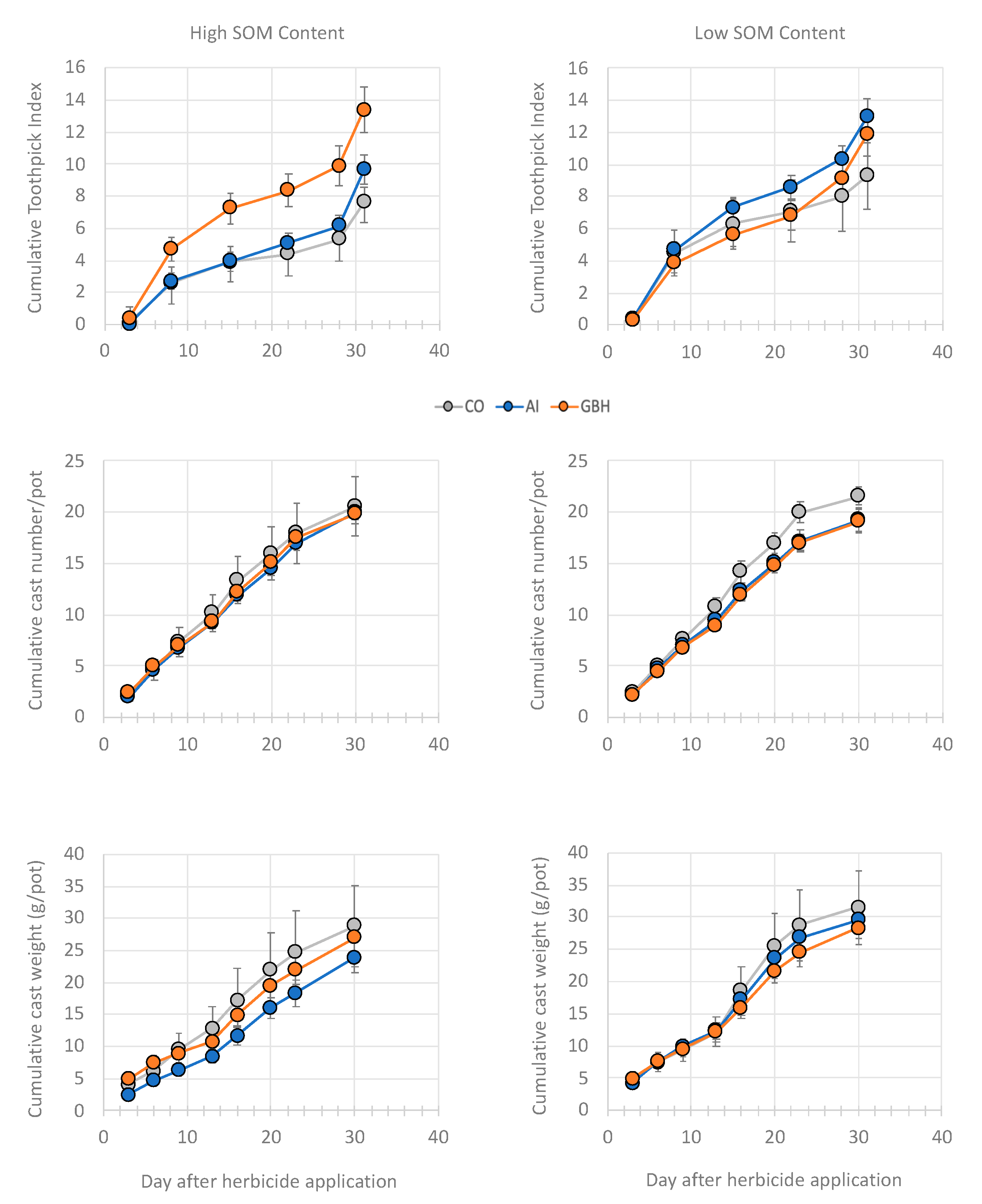
3.2. Short-Term GBH/AI Effects on Earthworm Activity
3.3. Water Infiltration and Leachate
3.4. Litter Decomposition and Soil Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Long-Term Legacy Effects
4.2. Short-Term Effects of GBHs versus AIs
4.3. Water Infiltration and Leaching
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mertens, M.; Höss, S.; Neumann, G.; Afzal, J.; Reichenbecher, W. Glyphosate, a chelating agent—Relevant for ecological risk assessment? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 5298–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Conclusion on the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance glyphosate. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A. Managing Cover Crops Profitably, 3rd ed.; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Schappert, A.; Messelhäuser, M.H.; Saile, M.; Peteinatos, G.G.; Gerhards, R. Weed Suppressive Ability of Cover Crop Mixtures Compared to Repeated Stubble Tillage and Glyphosate Treatments. Agriculture 2018, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, S.O. The history and current status of glyphosate. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesnage, R.; Benbrook, C.; Antoniou, M.N. Insight into the confusion over surfactant co-formulants in glyphosate-based herbicides. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 128, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesnage, R. Coformulants in commercial herbicides. In Herbicides: Chemistry, Efficacy, Toxicology, and Environmental Impacts; Mesnage, R., Zaller, J., Thomas, B.F., Eds.; Emerging Issues in Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 87–112. [Google Scholar]
- Mesnage, R.; Defarge, N.; Vendômois, J.S.d.; Séralini, G.-E. Major Pesticides Are More Toxic to Human Cells Than Their Declared Active Principles. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 179691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Decourtye, A.; Delpuech, J.-M. The Sublethal Effects of Pesticides on Beneficial Arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedobová, J.; Skalský, M.; Ouředníčková, J.; Michalko, R.; Bartošková, A. Synergistic effects of glyphosate formulation herbicide and tank-mixing adjuvants on Pardosa spiders. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuhra, M.; Bøhn, T.; Cuhra, P. Glyphosate: Too much of a good thing? Front. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maderthaner, M.; Weber, M.; Takács, E.; Mörtl, M.; Leisch, F.; Römbke, J.; Querner, P.; Walcher, R.; Gruber, E.; Székács, A.; et al. Commercial glyphosate-based herbicides effects on springtails (Collembola) differ from those of their respective active ingredients and vary with soil organic matter content. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 17280–17289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaller, J.G.; Weber, M.; Maderthaner, M.; Gruber, E.; Takács, E.; Mörtl, M.; Klátyik, S.; Győri, J.; Römbke, J.; Leisch, F.; et al. Effects of glyphosate-based herbicides and their active ingredients on earthworms, water infiltration and glyphosate leaching are influenced by soil properties. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borggaard, O.K.; Gimsing, A.L. Fate of glyphosate in soil and the possibility of leaching to ground and surface waters: A review. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erban, T.; Stehlik, M.; Sopko, B.; Markovic, M.; Seifrtova, M.; Halesova, T.; Kovaricek, P. The different behaviors of glyphosate and AMPA in compost-amended soil. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandl, K.; Cantelmo, C.; Gruber, E.; Faber, F.; Friedrich, B.; Zaller, J.G. Effects of Glyphosate-, Glufosinate- and Flazasulfuron-Based Herbicides on Soil Microorganisms in a Vineyard. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 101, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.; Spangl, B.; Gruber, E.; Takács, E.; Mörtl, M.; Klátyik, S.; Székács, A.; Zaller, J.G. Glyphosate Effects on Earthworms: Active Ingredients vs. Commercial Herbicides at Different Temperature and Soil Organic Matter Levels. Agrochemicals 2023, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gestel, C.A.M. Soil ecotoxicology: State of the art and future directions. ZooKeys 2012, 176, 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Montanarella, L.; Jones, A.; Fernandez-Ugalde, O.; Mol, H.G.J.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Distribution of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) in agricultural topsoils of the European Union. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defarge, N.; Spiroux de Vendômois, J.; Séralini, G.E. Toxicity of formulants and heavy metals in glyphosate-based herbicides and other pesticides. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J.P.K.; Sethi, N.; Mohan, A.; Datta, S.; Girdhar, M. Glyphosate toxicity for animals. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihtmäe, M.; Blinova, I.; Künnis-Beres, K.; Kanarbik, L.; Heinlaan, M.; Kahru, A. Ecotoxicological effects of different glyphosate formulations. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 72, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.; Reichenbecher, W.; Teichmann, H.; Tappeser, B.; Lötters, S. Questions concerning the potential impact of glyphosate-based herbicides on amphibians. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaller, J.G.; Brühl, C.A. Direct herbicide effects on terrestrial nontarget organisms belowground and aboveground. In Herbicides: Chemistry, Efficacy, Toxicology, and Environmental Impacts; Mesnage, R., Zaller, J.G., Thomas, B.F., Eds.; Emerging Issues in Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 181–230. [Google Scholar]
- Brühl, C.A.; Zaller, J.G. Indirect herbicide effects on biodiversity, ecosystem functions, and interactions with global changes. In Herbicides: Chemistry, Efficacy, Toxicology, and Environmental Impacts; Mesnage, R., Zaller, J.G., Thomas, B.F., Eds.; Emerging Issues in Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 231–272. [Google Scholar]
- Zaller, J.G.; Kruse-Plaß, M.; Schlechtriemen, U.; Gruber, E.; Peer, M.; Nadeem, I.; Formayer, H.; Hutter, H.-P.; Landler, L. Pesticides in ambient air, influenced by surrounding land use and weather, pose a potential threat to biodiversity and human. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, C. Reduction of pesticide use can increase earthworm populations in wheat crops in a European temperate region. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 181, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaupp-Berghausen, M.; Hofer, M.; Rewald, B.; Zaller, J.G. Glyphosate-based herbicides reduce the activity and reproduction of earthworms and lead to increased soil nutrient concentrations. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellin, F.; Gavinelli, F.; Stevanato, P.; Concheri, G.; Squartini, A.; Paoletti, M.G. Effects of different concentrations of glyphosate (Roundup 360®) on earthworms (Octodrilus complanatus, Lumbricus terrestris and Aporrectodea caliginosa) in vineyards in the North-East of Italy. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 123, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pérez, J.A.; Alarcón-Gutiérrez, E.; Perroni, Y.; Barois, I. Earthworm communities and soil properties in shaded coffee plantations with and without application of glyphosate. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 83, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaller, J.G.; Heigl, F.; Ruess, L.; Grabmaier, A. Glyphosate herbicide affects belowground interactions between earthworms and symbiotic mycorrhizal fungi in a model ecosystem. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blouin, M.; Hodson, M.E.; Delgado, E.A.; Baker, G.; Brussard, L.; Butt, K.R.; Dai, J.; Dendooven, L.; Peres, G.; Tondoh, J.E.; et al. A review of earthworm impact on soil function and ecosystem services. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2013, 64, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurst, S.; Sonnemann, I.; Zaller, J.G. Soil macro-invertebrates-their impact on plants and associated aboveground communities in temperate regions. In Aboveground-Belowground Community Ecology; Ohgushi, T., Wurst, S., Johnson, S.N., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2018; Volume 234, pp. 175–200. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, C.A.; Bohlen, P.J. Biology and Ecology of Earthworms, 3rd ed.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Schönholzer, F.; Kohli, L.; Hahn, D.; Daniel, O.; Goez, C.; Zeyer, J. Effects of decomposition of leaves on bacterial biomass and on palatability to Lumbricus terrestris L. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaller, J.G.; Heigl, F.; Grabmaier, A.; Lichtenegger, C.; Piller, K.; Allabashi, R.; Frank, T.; Drapela, T. Earthworm-mycorrhiza interactions can affect the diversity, structure and functioning of establishing model grassland communities. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capowiez, Y.; Cadoux, S.; Bouchant, P.; Ruy, S.; Roger-Estrade, J.; Richard, G.; Boizard, H. The effect of tillage type and cropping system on earthworm communities, macroporosity and water infiltration. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 105, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackhall, M.; Raffaele, E.; Paritsis, J.; Tiribelli, F.; Morales, J.M.; Kitzberger, T.; Gowda, J.H.; Veblen, T.T. Effects of biological legacies and herbivory on fuels and flammability traits: A long-term experimental study of alternative stable states. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 1309–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaller, J.G.; Cantelmo, C.; Dos Santos, G.; Muther, S.; Gruber, E.; Pallua, P.; Mandl, K.; Friedrich, B.; Hofstetter, I.; Schmuckenschlager, B.; et al. Herbicides in vineyards reduce grapevine root mycorrhization and alter soil microorganisms and the nutrient composition in grapevine roots, leaves, xylem sap and grape juice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 23215–23226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, B.; Saikkonen, K.; Helander, M. Glyphosate-Modulated Biosynthesis Driving Plant Defense and Species Interactions. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruuskanen, S.; Fuchs, B.; Nissinen, R.; Puigbò, P.; Rainio, M.; Saikkonen, K.; Helander, M. Ecosystem consequences of herbicides: The role of microbiome. TREE 2023, 38, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keuskamp, J.A.; Dingemans, B.J.J.; Lehtinen, T.; Sarneel, J.M.; Hefting, M.M. Tea Bag Index: A novel approach to collect uniform decomposition data across ecosystems. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing—Version 3.6.1; The R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zaller, J.G.; Arnone, J.A. Earthworm and soil moisture effects on the productivity and structure of grassland communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, E.C.; Jordan, D. Temperature and soil moisture content effects on the growth of Lumbricus terrestris (Oligochaeta: Lumbricidae) under laboratory conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, C.; Barot, S.; Capowiez, Y.; Hedde, M.; Vandenbulcke, F. Pesticides and earthworms. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 199–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.A.; Tzilivakis, J.; Warner, D.J.; Green, A. An international database for pesticide risk assessments and management. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2016, 22, 1050–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, A.; Brown, G.G.; Sautter, K.D.; Ribas de Oliveira, C.M.; de Vasconcelos, E.C.; Niva, C.C.; Bartz, M.L.C.; Bedano, J.C. Toxicity of AMPA to the earthworm Eisenia andrei Bouché, 1972 in tropical artificial soil. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagner, M.; Mikola, J.; Saloniemi, I.; Saikkonen, K.; Helander, M. Effects of a glyphosate-based herbicide on soil animal trophic groups and associated ecosystem functioning in a northern agricultural field. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helander, M.; Lehtonen, T.K.; Saikkonen, K.; Despains, L.; Nyckees, D.; Antinoja, A.; Solvi, C.; Loukola, O.J. Field-realistic acute exposure to glyphosate-based herbicide impairs fine-color discrimination in bumblebees. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochron, S.T.; Mezic, M.; Byrne, S.; Sasoun, S.; Casamassima, A.; Kilic, M.; Nuzzo, A.; Beaudet, C.-E. Exposure to Roundup increases movement speed and decreases body mass in earthworms. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santadino, M.; Coviella, C.; Momo, F. Glyphosate Sublethal Effects on the Population Dynamics of the Earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny, 1826). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochron, S.; Choudhury, M.; Gomez, R.; Hussaini, S.; Illuzzi, K.; Mann, M.; Mezic, M.; Nikakis, J.; Tucker, C. Temperature and body mass drive earthworm (Eisenia fetida) sensitivity to a popular glyphosate-based herbicide. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 139, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochron, S.; Simon, L.; Mirza, A.; Littleton, A.; Sahebzada, F.; Yudell, M. Glyphosate but not Roundup® harms earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.J.G.; Ferreira, M.F.L.; Cachada, A.; Duarte, A.C.; Sousa, J.P. Pesticide application to agricultural fields: Effects on the reproduction and avoidance behaviour of Folsomia candida and Eisenia andrei. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 2113–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, S.; D’Souza, D. Effect of pesticides on the reproductive output of Eisenia fetida. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 79, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, F.V.; Moreira, J.C. Effects of glyphosate and 2,4-D on earthworms (Eisenia fetida) in laboratory tests. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Torres, T.; Giuffre, L.; Romaniuk, R.; Rios, R.P.; Pagano, E.A. Exposure Assessment to Glyphosate of Two Species of Annelids. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 93, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owagboriaye, F.; Dedeke, G.; Bamidele, J.; Aladesida, A.; Isibor, P.; Feyisola, R.; Adeleke, M. Biochemical response and vermiremediation assessment of three earthworm species (Alma millsoni, Eudrilus eugeniae and Libyodrilus violaceus) in soil contaminated with a glyphosate-based herbicide. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owagboriaye, F.; Mesnage, R.; Dedeke, G.; Adegboyega, T.; Aladesida, A.; Adeleke, M.; Owa, S.; Antoniou, M.N. Impacts of a glyphosate-based herbicide on the gut microbiome of three earthworm species (Alma millsoni, Eudrilus eugeniae and Libyodrilus violaceus): A pilot study. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contardo-Jara, V.; Klingelmann, E.; Wiegand, C. Bioaccumulation of glyphosate and its formulation Roundup Ultra in Lumbriculus variegatus and its effects on biotransformation and antioxidant enzymes. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piola, L.; Fuchs, J.; Oneto, M.L.; Basack, S.; Kesten, E.; Casabé, N. Comparative toxicity of two glyphosate-based formulations to Eisenia andrei under laboratory conditions. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, F.; Gruber, E.; Hein, T.; Bondar-Kunze, E.; Ivanković, M.; Mentler, A.; Brühl, C.A.; Spangl, B.; Zaller, J.G. Non-target effects of a glyphosate-based herbicide on Common toad larvae (Bufo bufo, Amphibia) and associated algae are altered by temperature. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, F.; Jedinger, M.; Gruber, E.; Zaller, J.G. Temperature-dependence of glyphosate-based herbicide’s effects on egg and tadpole growth of Common Toads. Front. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hoesel, W.; Tiefenbacher, A.; König, N.; Dorn, V.M.; Hagenguth, J.F.; Prah, U.; Widhalm, T.; Wiklicky, V.; Koller, R.; Bonkowski, M.; et al. Single and Combined Effects of Pesticide Seed Dressings and Herbicides on Earthworms, Soil Microorganisms, and Litter Decomposition. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, J.C.; de Santo, F.B.; Guerra, N.; Ricardo Filho, A.M.; Pech, T.M. Do recommended doses of glyphosate-based herbicides affect soil invertebrates? Field and laboratory screening tests to risk assessment. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casabé, N.; Piola, L.; Fuchs, J.; Oneto, M.L.; Pamparato, L.; Basack, S.; Giménez, R.; Massaro, R.; Papa, J.C.; Kesten, E. Ecotoxicological assessment of the effects of glyphosate and chlorpyrifos in an Argentine soya field. J. Soils Sediments 2007, 8, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouché, M.B. Strategies lombriciennes. Ecol. Bull. 1977, 25, 122–132. [Google Scholar]
- Székács, A.; Darvas, B. Forty years with glyphosate. In Herbicides—Properties, Synthesis and Control of Weeds; Hasaneen, M., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 247–284. [Google Scholar]
- Bordoloi, R.; Das, B.; Yam, G.; Pandey, P.K.; Tripathi, O.P. Modeling of Water Holding Capacity Using Readily Available Soil Characteristics. Agric. Res. 2019, 8, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaller, J.G.; Wechselberger, K.F.; Gorfer, M.; Hann, P.; Frank, T.; Wanek, W.; Drapela, T. Subsurface earthworm casts can be important soil microsites specifically influencing the growth of grassland plants. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungers, G.; Portet-Koltalo, F.; Cosme, J.; Séralini, G.-E. Petroleum in Pesticides: A Need to Change Regulatory Toxicology. Toxics 2022, 10, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Séralini, G.-E.; Jungers, G. Toxic compounds in herbicides without glyphosate. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 146, 111770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | Soil 1 | Soil 2 | Assessment Soil 1 | Assessment Soil 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOM content [%] | 3.0 | 4.1 | humous | humous |
| Phosphorus [mg kg−1] | 73 | 113 | sufficient | high |
| Potassium [mg kg−1] | 140 | 234 | sufficient | high |
| pH [CaCl2] | 7.7 | 7.7 | alkaline | alkaline |
| GBH | AI | Recommended Dosage (L ha−1) | AI Content (g L−1) | GBH (mL pot−1) | AI (g pot−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TQ | am | 5.0 | 360 | 0.0375 | 0.0135 |
| PF | po | 3.75 | 588 | 0.0281 | 0.0165 |
| LB | is | 5.0 | 360 | 0.0375 | 0.0135 |
| Parameter | GBH | AI | SOM | GBH × SOM | AI × SOM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cumulative toothpick index (pot−1) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 | 0.695 | 0.014 |
| Cumulative cast number (pot−1) | 0.003 | 0.777 | 0.808 | 0.571 | 0.928 |
| Cumulative cast weight (g pot−1) | 0.005 | 0.538 | 0.945 | 0.853 | 0.640 |
| Soil moisture (%) | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.228 | 0.624 | <0.001 |
| Soil temperature (°C) | 0.075 | 0.246 | 0.530 | n.a. | n.a. |
| Soil’s electrical conductivity (dS m−1) | 0.032 | 0.682 | 0.001 | 0.309 | 0.005 |
| Parameter | TQ | LB | PF | am | Is | po | SOM | TQ × SOM | LB × SOM | PF × SOM | am × SOM | is × SOM | po × SOM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cumul. toothpicks | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.423 | 0.844 | <0.001 | 1.000 | 0.689 | 0.742 | 0.047 | 0.672 | 0.258 | <0.001 |
| Cumul. cast no. | <0.001 | 0.170 | 0.012 | 0.205 | 0.262 | 0.348 | 0.808 | 0.139 | 0.780 | 0.674 | 0.627 | 0.676 | 0.444 |
| Cumul. cast weight | <0.001 | 0.024 | 0.313 | 0.128 | 0.982 | 0.985 | 0.945 | 0.970 | 0.388 | 0.174 | 0.746 | 0.638 | 0.191 |
| Parameter | Low SOM | High SOM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO | GBH | AI | CO | GBH | AI | |
| Soil moisture (%) | 17.2 ± 0.8 | 20.1 ± 0.4 | 21.1± 0.5 | 16.2 ± 0.5 | 20.8 ± 0.6 | 15.8 ± 0.4 |
| Soil temperature (°C) | 20.8 ± 0.3 | 20.8 ± 0.1 | 20.8 ± 0.1 | 20.8 ± 0.3 | 20.8 ± 0.1 | 20.8 ± 0.1 |
| Soil’s electrical conductivity (dS m−1) | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.0 | 1.5 ± 0.0 | 1.2 ± 0.0 | 1.3 ± 0.0 | 1.1 ± 0.0 |
| Parameter | GBH | AI | SOM | GBH × SOM | AI × SOM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cumulative toothpick index (pot−1) | <0.001 | 0.074 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.325 |
| Cumulative cast number (pot−1) | 0.015 | 0.011 | 0.316 | 0.169 | 0.480 |
| Cumulative cast weight (g pot−1) | 0.291 | 0.068 | 0.490 | 0.864 | 0.228 |
| Earthworm number end (pot−1) | 0.925 | 0.849 | 0.747 | 0.643 | 0.455 |
| Weight change (g) | 0.762 | 0.410 | 0.414 | 0.849 | 0.736 |
| Reproduction index (ind. pot−1) | 0.993 | 0.993 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Infiltration time (s L−1) | 0.021 | 0.922 | 0.019 | 0.220 | 0.528 |
| Leachate amount (mL pot−1) | 0.006 | 0.834 | 0.005 | 0.069 | 0.515 |
| Litter decomposition rate (k) | 0.649 | 0.538 | 0.379 | 0.641 | 0.294 |
| Litter stabilization factor (S) | 0.959 | 0.506 | 0.774 | 0.408 | 0.351 |
| Soil moisture (%) | <0.001 | 0.048 | 0.435 | 0.475 | <0.001 |
| Soil temperature (°C) | 0.020 | 0.142 | 0.392 | n.a. | n.a. |
| Soil’s electrical conductivity (dS m−1) | 0.002 | 0.036 | 0.143 | 0.160 | 0.065 |
| Parameter | TQ | LB | PF | am | is | po | SOM | TQ × SOM | LB × SOM | PF × SOM | am × SOM | is × SOM | po × SOM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cumul. toothpick index | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.023 | 0.062 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.191 | 0.197 | 0.292 | 0.848 |
| Cumul. cast numbers | <0.001 | 0.008 | 0.945 | 0.001 | 0.130 | 0.156 | 0.316 | 0.008 | 0.206 | 0.700 | 0.389 | 0.752 | 0.239 |
| Cumul. cast weight | 0.143 | 0.629 | 0.526 | 0.041 | 0.168 | 0.300 | 0.490 | 0.570 | 0.056 | 0.040 | 0.512 | 0.121 | 0.436 |
| Earthworm number end | 0.359 | 0.342 | 0.816 | 0.233 | 1.000 | 0.489 | 0.747 | 0.655 | 0.643 | 0.819 | 0.096 | 0.650 | 0.836 |
| Difference in weight | 0.536 | 0.661 | 0.580 | 0.253 | 0.906 | 0.463 | 0.414 | 0.494 | 0.953 | 0.273 | 0.349 | 0.327 | 0.426 |
| Earthworm reproduction | 0.993 | 0.994 | 0.993 | 0.993 | 0.994 | 0.993 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 1.000 |
| Infiltration time | 0.103 | 0.045 | 0.042 | 0.365 | 0.164 | 0.797 | 0.019 | 0.547 | 0.334 | 0.152 | 0.538 | 0.112 | 0.539 |
| Leachate amount | 0.002 | 0.022 | 0.055 | 0.173 | 0.389 | 0.965 | 0.005 | 0.176 | 0.101 | 0.073 | 0.246 | 0.410 | 0.658 |
| Decomposition rate (k) | 0.374 | 0.975 | 0.047 | 0.643 | 0.656 | 0.512 | 0.379 | 0.331 | 0.075 | 0.135 | 0.618 | 0.132 | 0.396 |
| Stabilization factor (S) | 0.651 | 0.649 | 0.896 | 0.668 | 0.687 | 0.097 | 0.774 | 0.882 | 0.778 | 0.108 | 0.616 | 0.624 | 0.189 |
| Parameter/Period | Low SOM | High SOM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| after Treatment | CO | GBH | AI | CO | GBH | AI |
| Soil moisture (%) | 20.3 ± 1.0 | 23.7 ± 0.5 | 23.7 ± 0.5 | 19.5 ± 1.0 | 22.0 ± 0.6 | 18.9 ± 0.6 |
| Soil temperature (°C) | 16.3 ± 0.4 | 17.1 ± 0.2 | 16.5 ± 0.2 | 16.3 ± 0.3 | 17.0 ± 0.2 | 17.0 ± 0.3 |
| Soil’s electrical conductivity (dS m−1) | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.0 | 1.3 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brandmaier, V.; Altmanninger, A.; Leisch, F.; Gruber, E.; Takács, E.; Mörtl, M.; Klátyik, S.; Székács, A.; Zaller, J.G. Glyphosate-Based Herbicide Formulations with Greater Impact on Earthworms and Water Infiltration than Pure Glyphosate. Soil Syst. 2023, 7, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7030066
Brandmaier V, Altmanninger A, Leisch F, Gruber E, Takács E, Mörtl M, Klátyik S, Székács A, Zaller JG. Glyphosate-Based Herbicide Formulations with Greater Impact on Earthworms and Water Infiltration than Pure Glyphosate. Soil Systems. 2023; 7(3):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7030066
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrandmaier, Verena, Anna Altmanninger, Friedrich Leisch, Edith Gruber, Eszter Takács, Mária Mörtl, Szandra Klátyik, András Székács, and Johann G. Zaller. 2023. "Glyphosate-Based Herbicide Formulations with Greater Impact on Earthworms and Water Infiltration than Pure Glyphosate" Soil Systems 7, no. 3: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7030066
APA StyleBrandmaier, V., Altmanninger, A., Leisch, F., Gruber, E., Takács, E., Mörtl, M., Klátyik, S., Székács, A., & Zaller, J. G. (2023). Glyphosate-Based Herbicide Formulations with Greater Impact on Earthworms and Water Infiltration than Pure Glyphosate. Soil Systems, 7(3), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7030066










