Exploring the Diversity and Antibiogram of the Soil around a Tertiary Care Hospital and a University Precinct in Southern India: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
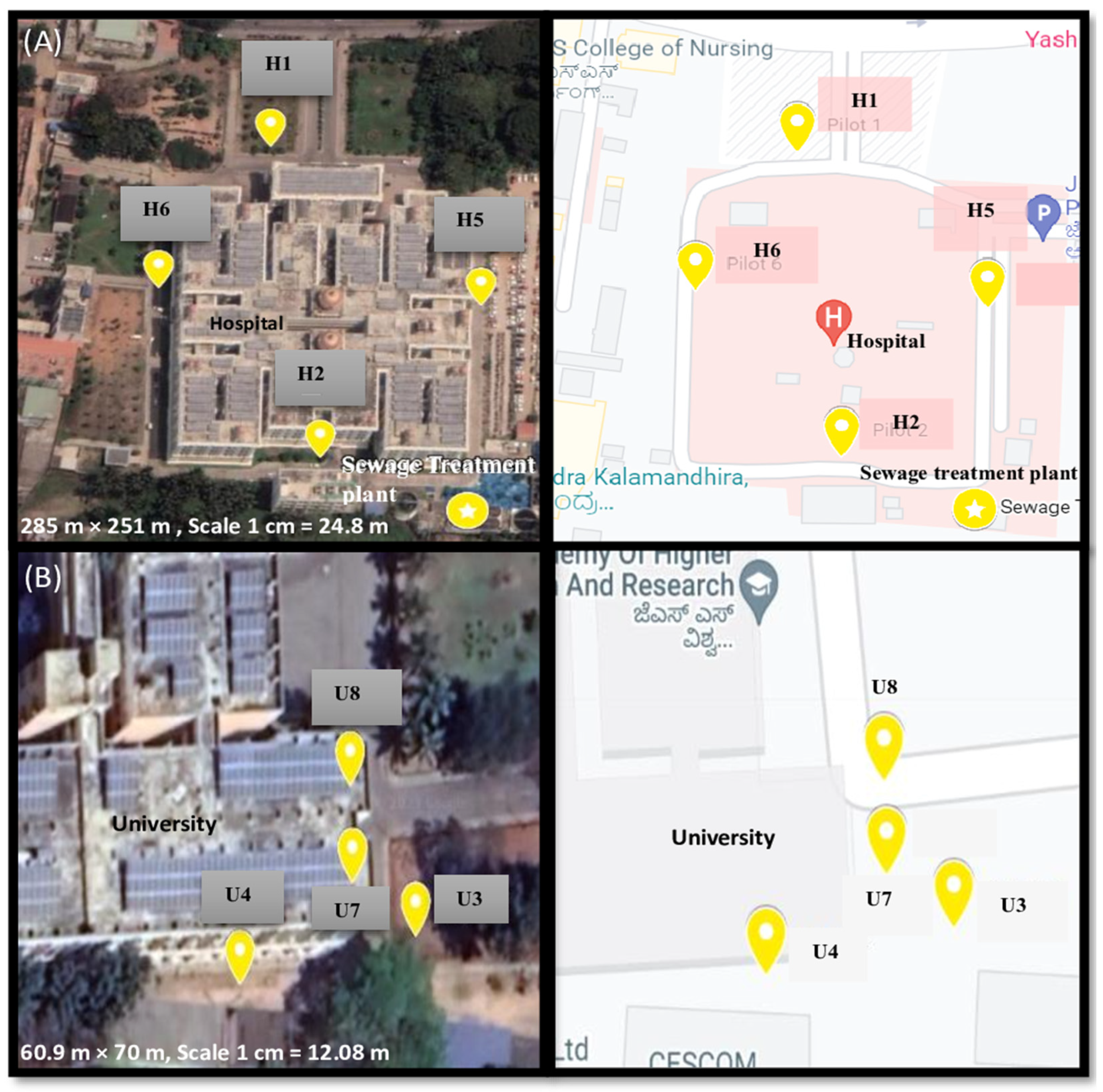
2.1. Sample Settings and Collection
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Identification and Antibiogram of Soil Isolates
3. Results
3.1. Genomic DNA Extraction and Sequencing
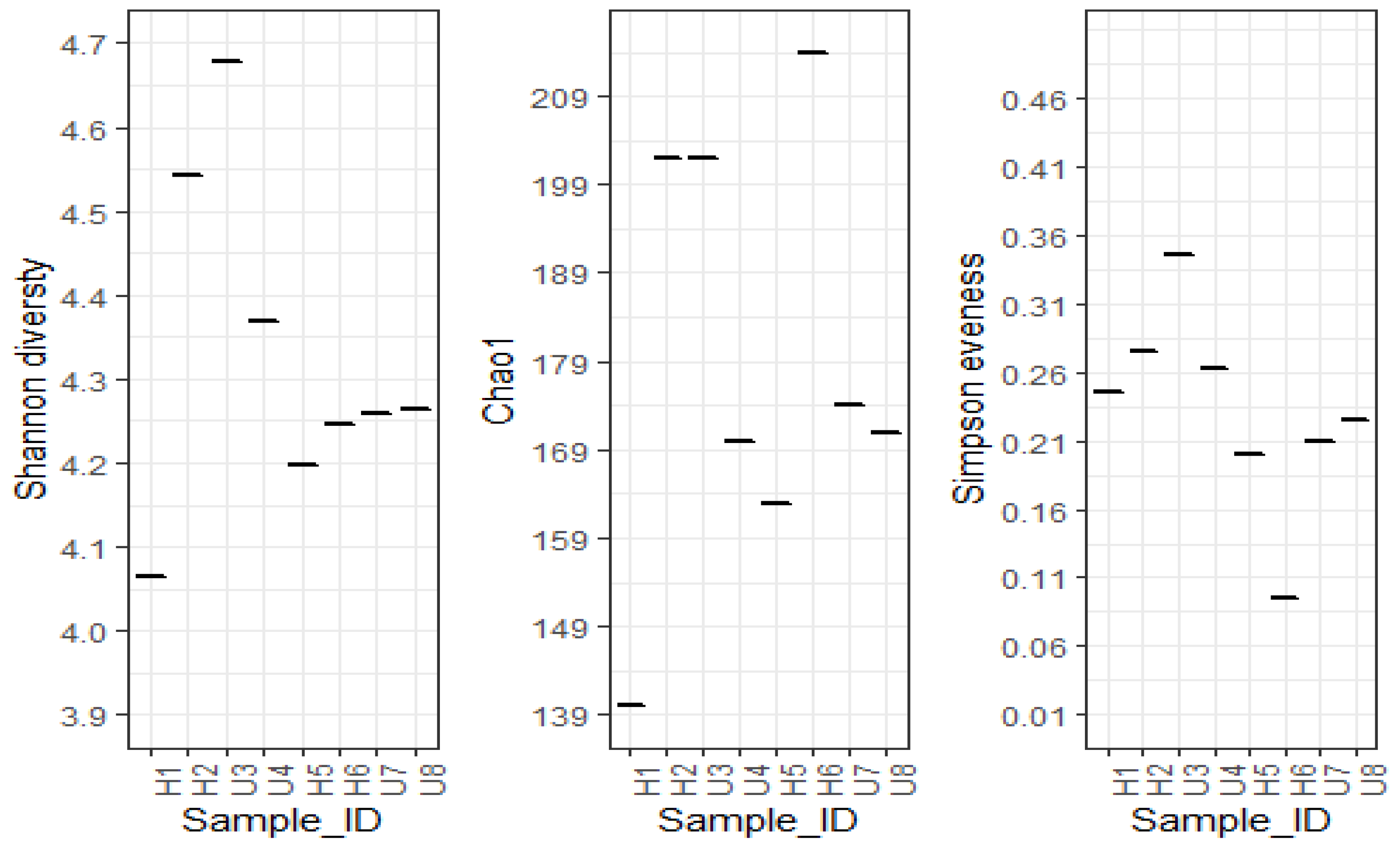
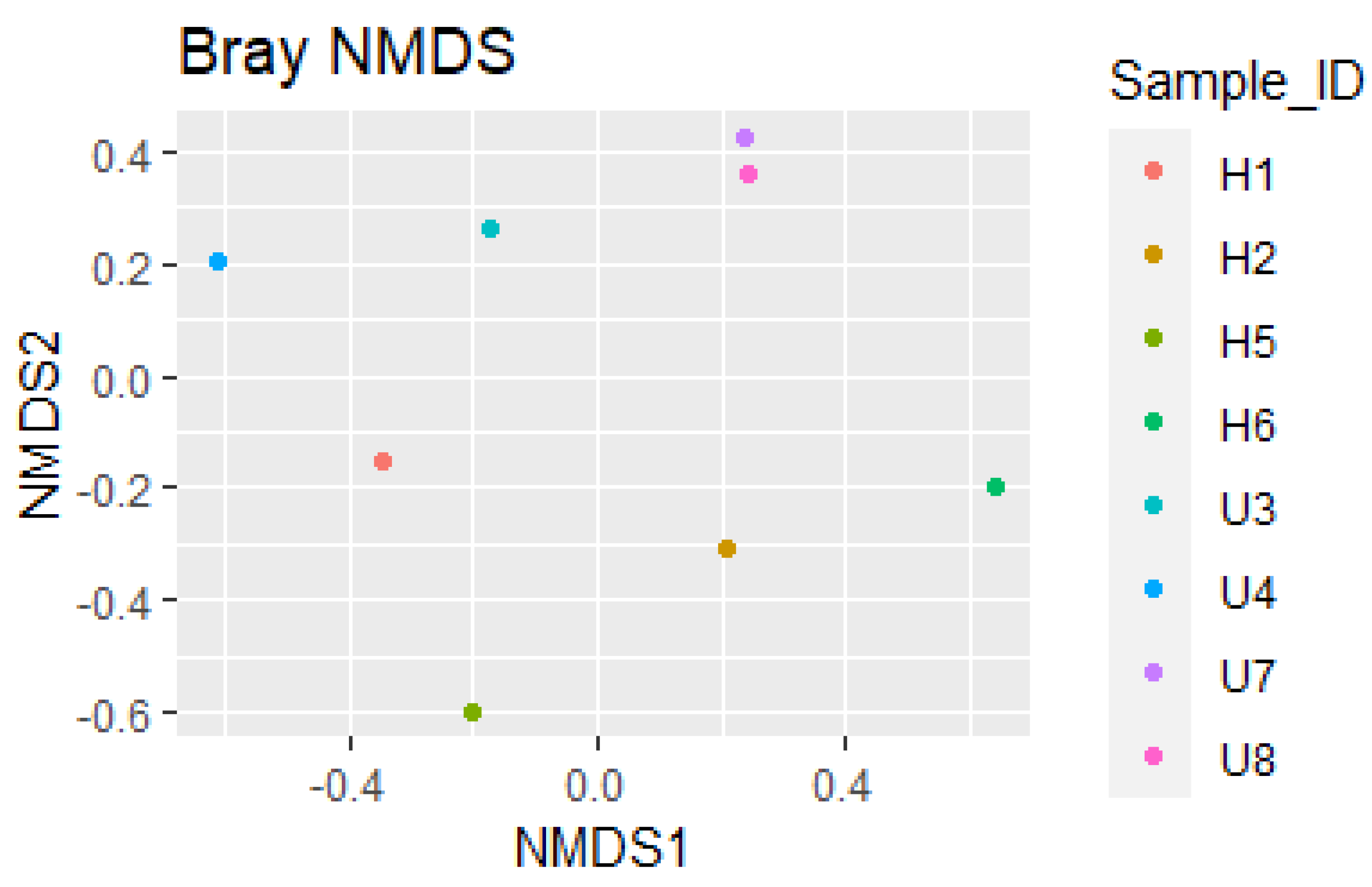
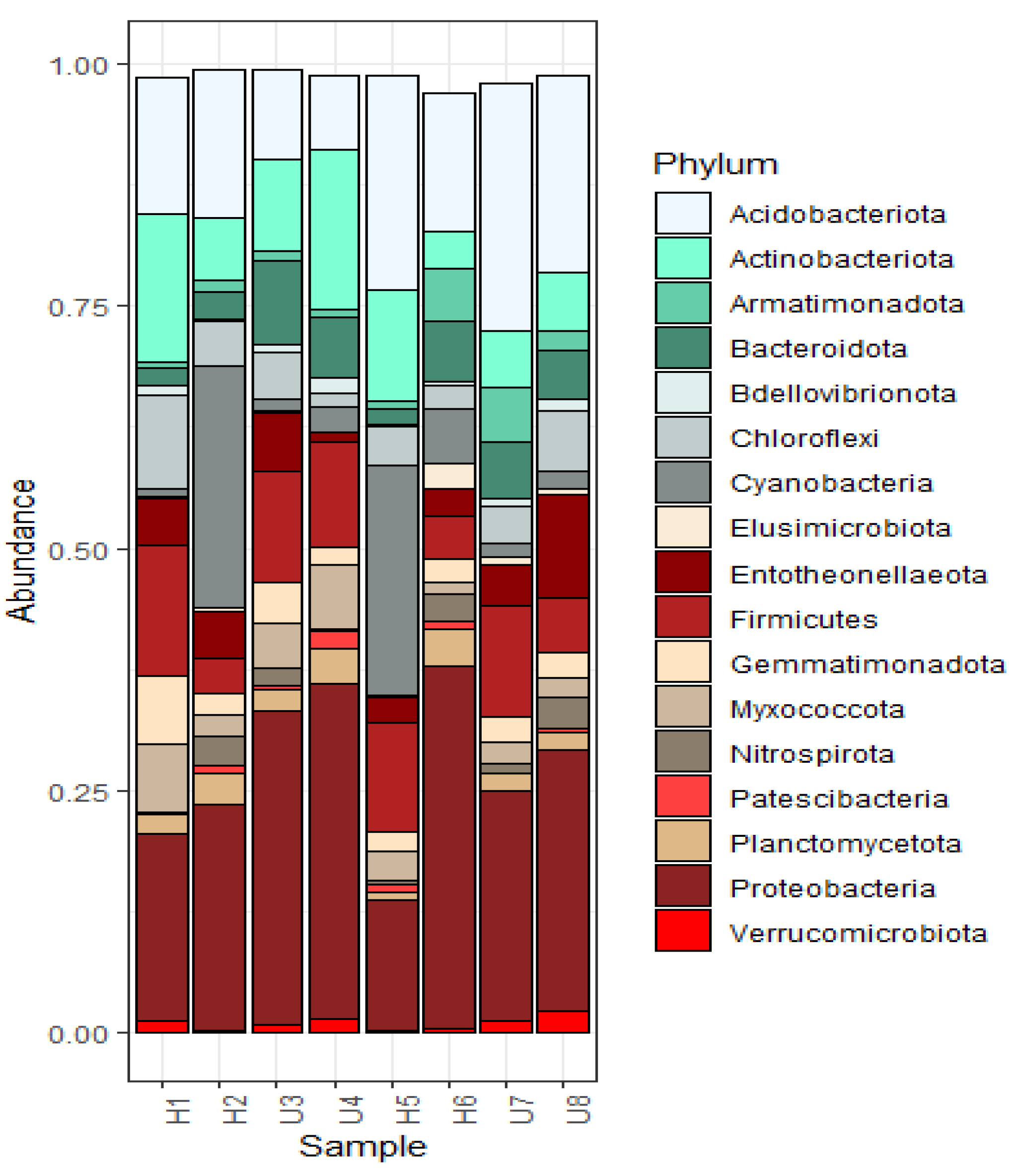
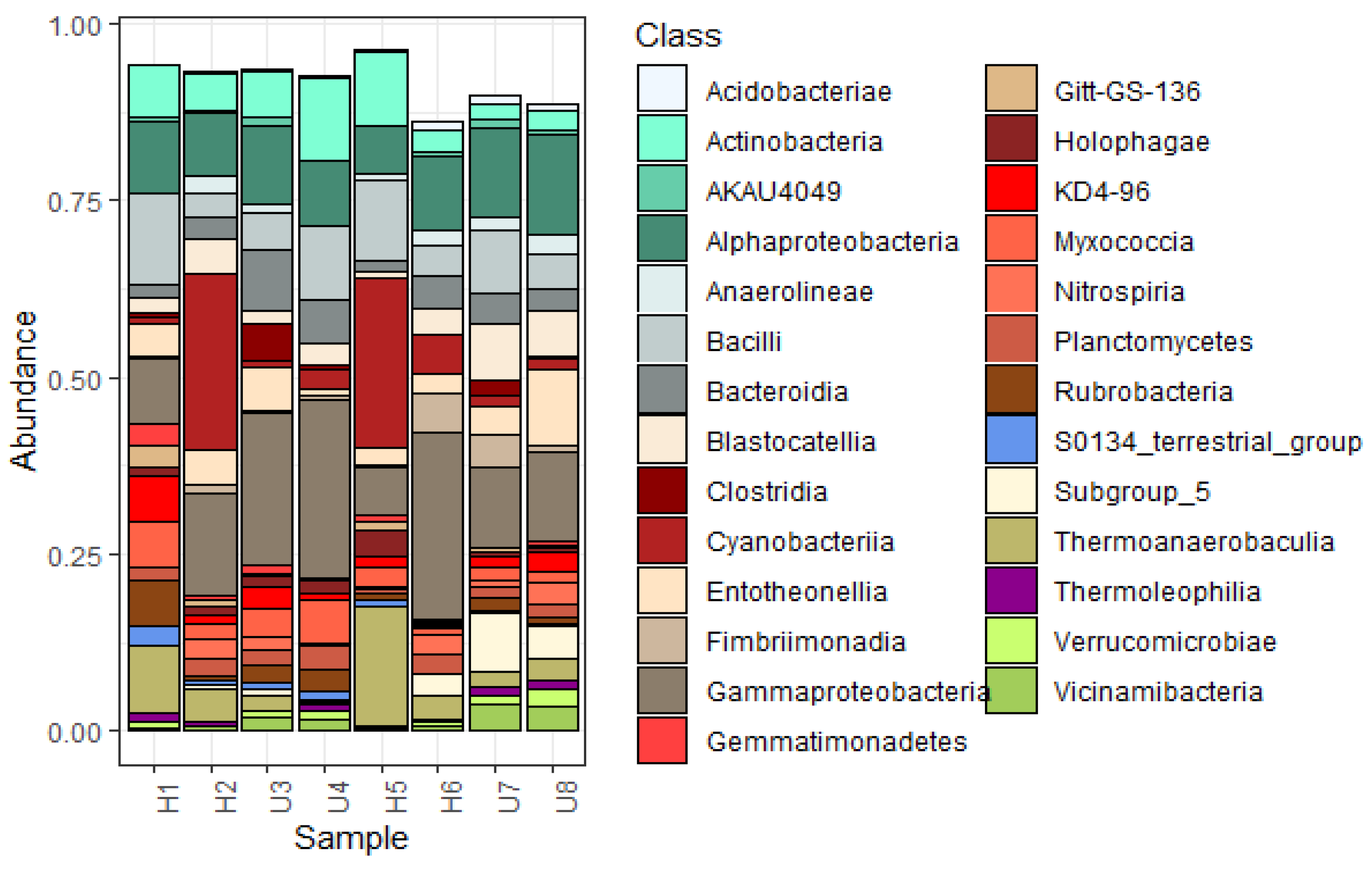
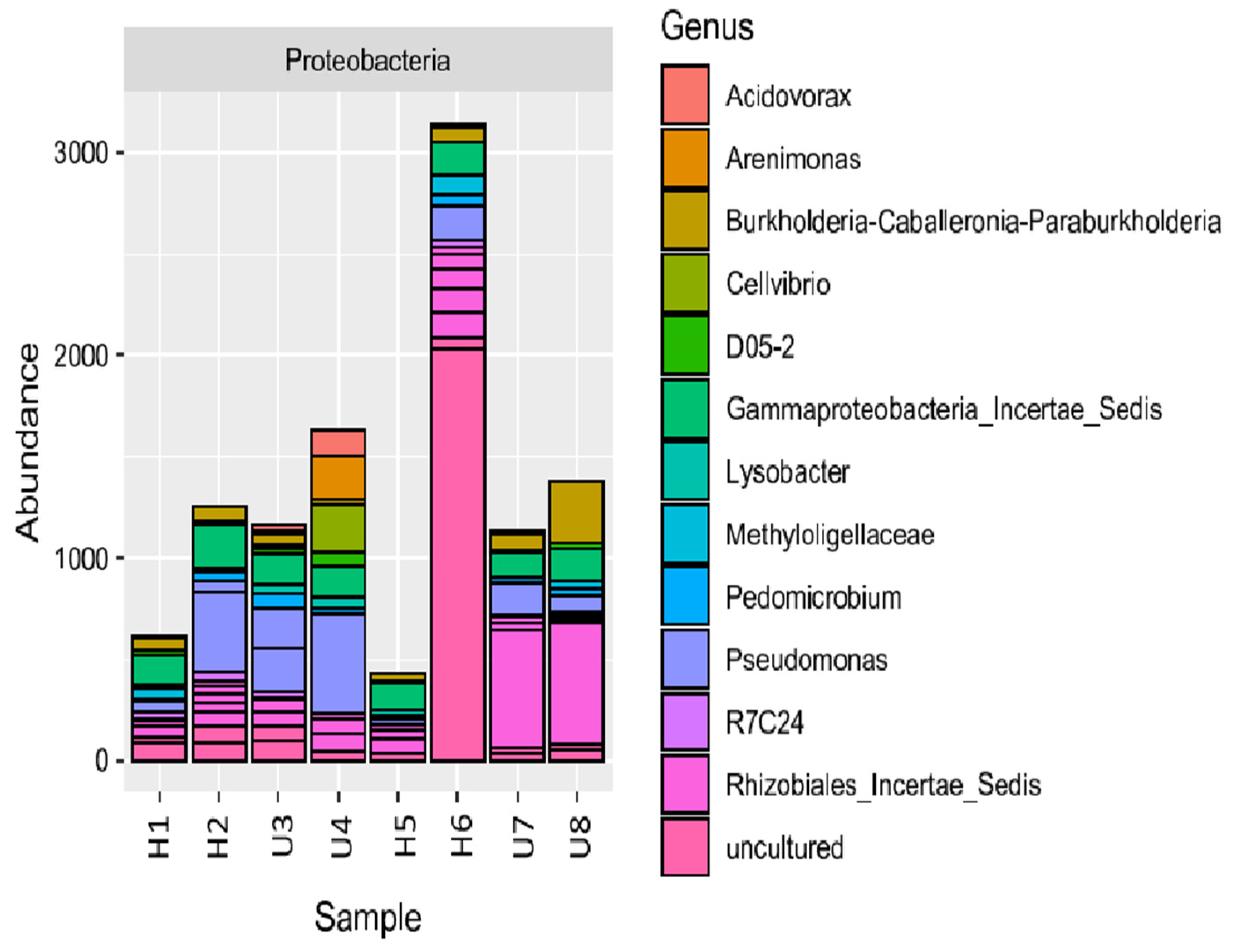
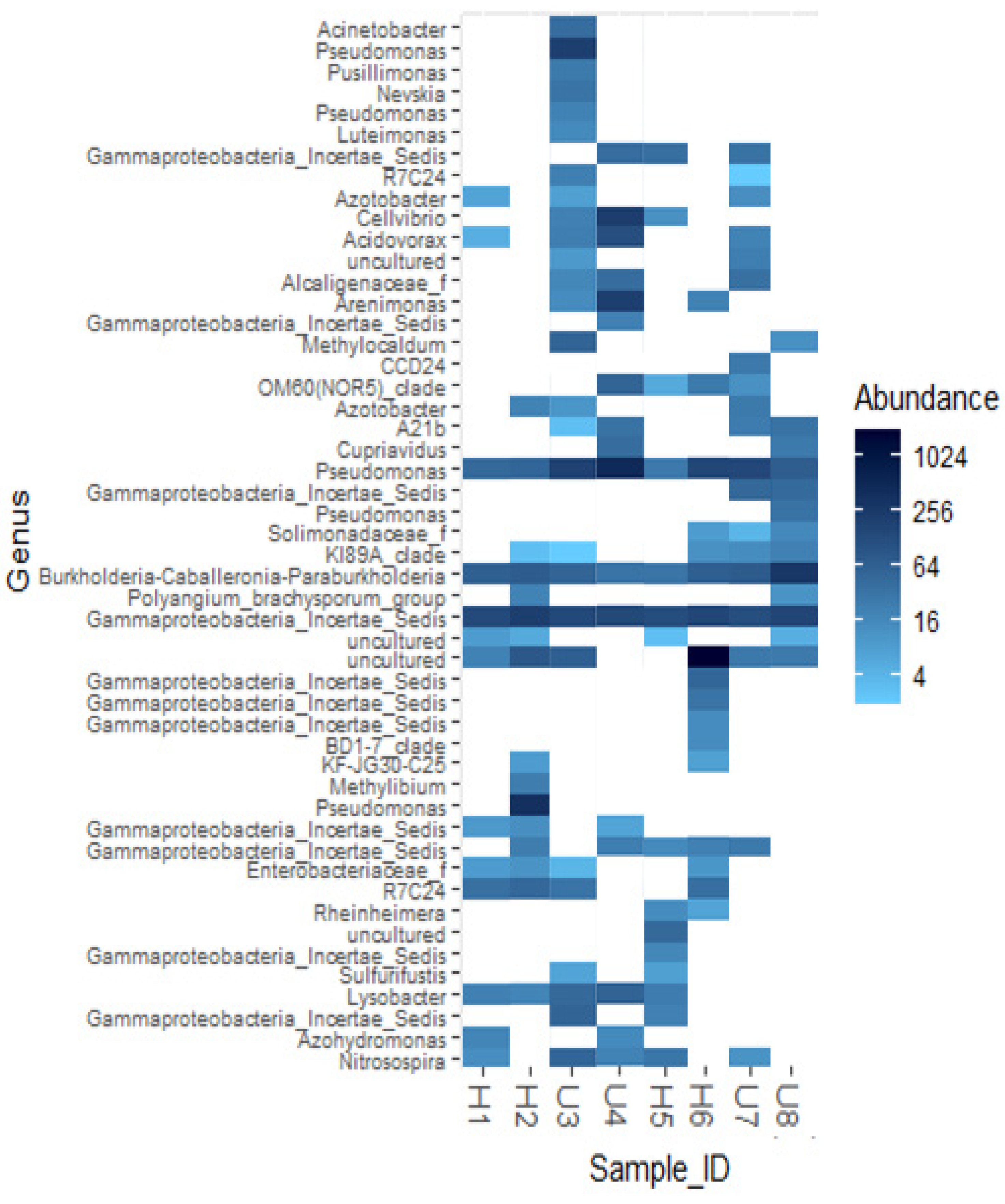
3.2. Analysis of Microbial Diversity and Community Composition
3.3. Identification and Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing of Soil Isolates
4. Discussion
4.1. Bacterial Diversity and Community Composition around a South Indian Hospital and University
4.2. Antibiotic Resistance Profile in Clinically Relevant Soil Bacteria
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sample ID | Organism Identified | LE5 | AT30 | CAZ30 | CL10 | COT25 | CPM30 | GEN10 | IMP10 | MRP10 | AK30 | MI30 | PIT100/10 | TGC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2.1 | A. baumannii | S | * | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | |
| M3.4 | A. baumannii | S | * | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | |
| M4.4 | A. baumannii | S | * | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | |
| M7.3 | A. baumannii | S | * | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | ||
| M2.2 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | S | I | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | * |
| M3.1 | P. aeruginosa | S | S | S | S | R | I | S | S | S | S | S | S | * |
| M3.2 | Pseudomonas spp. | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | * | |
| M4.2 | Pseudomonas spp. | S | R | S | S | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | * | |
| M4.3 | Pseudomonas spp. | S | R | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | * | |
| M5.1 | Pseudomonas spp. | S | I | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | * | |
| M7.2 | P. fluorescens | S | I | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | * |
| Sample ID | Organism Identified | CL10 | COT25 | CPM30 | GEN10 | IMP10 | MRP10 | AK30 | MI30 | PIT100/10 | C30 | CTR30 | AMC30 | CIP5 | AMP10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1.1 | K. pneumoniae | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | I | S | S | R | S | R |
| M3.5 | K. pneumoniae | S | S | S | S | S | S | I | I | S | S | S | R | I | R |
| M4.1 | Escherichia coli | S | S | S | S | S | S | I | S | S | S | S | S | S | I |
| M3.3 | Serratia marcescens | * | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | I | R |
| M6.2 | Enterobacter cloacae ssp. cloacae | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | R |
| Sample ID | Organism Identified | LE | AT | CAZ | CL | COT | CPM | GEN | IMP | MRP | AK | MI | PIT | TGC | CIP | TIC | SCF | DOR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2.1 | A. baumannii | S | * | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| M3.4 | A. baumannii | S | * | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| M4.4 | A. baumannii | S | * | S | S | * | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| M7.3 | A. baumannii | S | * | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| M2.2 | P. aeruginosa | S | I | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | * | ||||
| M3.1 | P. aeruginosa | S | S | S | S | * | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | * | ||||
| M3.2 | Pseudomonas spp. | S | S | S | S | * | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | * | ||||
| M4.2 | Pseudomonas spp. | TERMINATED | ||||||||||||||||
| M4.3 | Pseudomonas spp. | S | R | S | S | * | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | * | ||||
| M5.1 | Pseudomonas spp. | S | I | S | S | * | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | * | ||||
| M7.2 | P. fluorescens | S | I | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | * | ||||
| Sample ID | Organism Identified | CL | COT | CPM | GEN | IMP | MRP | AK | PIT | TGC | CTR | AMC | CIP | AMP | SCF | CXM | CXM/AXT | ERT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1.1 | K. pneumoniae | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | * | S | S | S | S |
| M3.5 | K. pneumoniae | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | * | S | S | S | S |
| M4.1 | Escherichia coli | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| M3.3 | Serratia marcescens | * | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | * | S | * | S | * | * | S |
| M6.2 | Enterobacter cloacae ssp. cloacae | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | * | S | * | S | * | * | S |
References
- Jansson, J.K.; Hofmockel, K.S. The soil microbiome—From metagenomics to metaphenomics. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 43, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powlson, D.S.; Hirsch, P.R.; Brookes, P.C. The role of soil microorganisms in soil organic matter conservation in the tropics. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2001, 61, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynaud, X.; Nunan, N. Spatial ecology of bacteria at the microscale in soil. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.K.; Millard, P.; Whiteley, A.S.; Murrell, J.C. Unravelling rhizosphere–microbial interactions: Opportunities and limitations. Trends Microbiol. 2004, 12, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, T.M.; Simonet, P.; Jansson, J.K.; Hirsch, P.R.; Tiedje, J.M.; Van Elsas, J.D.; Bailey, M.J.; Nalin, R.; Philippot, L. TerraGenome: A consortium for the sequencing of a soil metagenome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesenfeld, C.S.; Goodman, R.M.; Handelsman, J. Uncultured soil bacteria are a reservoir of new antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, J.J.; Moe, L.A.; Converse, B.J.; Smart, K.D.; Berklein, F.C.; McManus, P.S.; Handelsman, J. Metagenomic analysis of apple orchard soil reveals antibiotic resistance genes encoding predicted bifunctional proteins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4396–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Costa, V.M.; McGrann, K.M.; Hughes, D.W.; Wright, G.D. Sampling the antibiotic resistome. Science 2006, 311, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, J.-M.; Demanèche, S.; Delmont, T.O.; Mathieu, A.; Vogel, T.M.; Simonet, P. Metagenomic exploration of antibiotic resistance in soil. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Nisar, M.A.; Alvi, R.F.; Aslam, M.A.; Qamar, M.U. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Office of Infectious Disease Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013. Apr, 2013. 2015. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013 (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Schmieder, R.; Edwards, R. Insights into antibiotic resistance through metagenomic approaches. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.L. Effect of antibiotics on bacterial populations: A multi-hierachical selection process. F1000Research 2017, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Lin, H.; Yang, Y. Microplastics are a hotspot for antibiotic resistance genes: Progress and perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Yang, X.; Tang, Z.; Fu, J.; Chen, F.; Zhao, Y.; Ruan, L.; Yang, Y. Downward transport of naturally-aged light microplastics in natural loamy sand and the implication to the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, E.; Kaur, P. Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms in Bacteria: Relationships Between Resistance Determinants of Antibiotic Producers, Environmental Bacteria, and Clinical Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.E. The end of an era? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.R.; Griffith, M.P.; Sundermann, A.J.; Shutt, K.A.; Saul, M.I.; Mustapha, M.M.; Marsh, J.W.; Cooper, V.S.; Harrison, L.H.; Van Tyne, D. Systematic detection of horizontal gene transfer across genera among multidrug-resistant bacteria in a single hospital. eLife 2020, 9, e53886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virolle, C.; Goldlust, K.; Djermoun, S.; Bigot, S.; Lesterlin, C. Plasmid transfer by conjugation in Gram-negative bacteria: From the cellular to the community level. Genes 2020, 11, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panicker, V.; Nayak, P.; Krishna, R.; Sreenivaasan, N.; Thomas, J.; Sreedevan, V.; Anjaneyan, G.; Jagadeesan, S.; Lekshmi, S. Gram stain. J. Ski. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2023, 5, 60–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiner, K. Catalase test protocol. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2010, 1–6. Available online: https://asm.org/getattachment/72a871fc-ba92-4128-a194-6f1bab5c3ab7/Catalase (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Shields, P.; Cathcart, L. Oxidase test protocol. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2010, 1–9. Available online: https://asm.org/getattachment/00ce8639-8e76-4acb-8591-0f7b22a347c6/oxidase-test-protocol-3229.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- MacWilliams, M.P. Indole test protocol. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2012. Available online: https://asm.org/getattachment/200d3f34-c75e-4072-a7e6-df912c792f62/indole-test-protocol-3202.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- MacWilliams, M.P. Citrate test protocol. Am. Soc. Microbiol. Lab. Protocols. 2009, 3203. Available online: https://www.asmscience.org/content/education/protocol/protocol (accessed on 17 January 2020).
- Lehman, D. Triple sugar iron agar protocols. Microbe Libr. 2005. Available online: https://asm.org/ASM/media/Protocol-Images/Triple-Sugar-Iron-Agar-Protocols.pdf?ext=.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Hudzicki, J. Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion susceptibility test protocol. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2009, 15, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Kunhikannan, S.; Thomas, C.J.; Franks, A.E.; Mahadevaiah, S.; Kumar, S.; Petrovski, S. Environmental hotspots for antibiotic resistance genes. Microbiologyopen 2021, 10, e1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armalytė, J.; Skerniškytė, J.; Bakienė, E.; Krasauskas, R.; Šiugždinienė, R.; Kareivienė, V.; Kerzienė, S.; Klimienė, I.; Sužiedėlienė, E.; Ružauskas, M. Microbial diversity and antimicrobial resistance profile in microbiota from soils of conventional and organic farming systems. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mandal, S.; Mathipi, V.; Muthukumaran, R.B.; Gurusubramanian, G.; Lalnunmawii, E.; Kumar, N.S. Amplicon sequencing and imputed metagenomic analysis of waste soil and sediment microbiome reveals unique bacterial communities and their functional attributes. Env. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanentzap, A.J.; Fitch, A.; Orland, C.; Emilson, E.J.; Yakimovich, K.M.; Osterholz, H.; Dittmar, T. Chemical and microbial diversity covary in fresh water to influence ecosystem functioning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24689–24695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pippo, F.; Crognale, S.; Levantesi, C.; Vitanza, L.; Sighicelli, M.; Pietrelli, L.; Di Vito, S.; Amalfitano, S.; Rossetti, S. Plastisphere in lake waters: Microbial diversity, biofilm structure, and potential implications for freshwater ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 310, 119876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-L.; Chen, K.-H.; Chen, W.-P.; Chen, Z.-F.; Kuo, H.-Y.; Hung, H.-F.; Tang, C.Y.; Liou, M.-L. Bacterial diversity among four healthcare-associated institutes in Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, R.; Shimoda, T.; Watanabe, R.; Kuroki, Y.; Okubo, T.; Nakamura, S.; Matsuo, J.; Yoshimura, S.; Yamaguchi, H. Diversity changes of microbial communities into hospital surface environments. J. Infect. Chemother. 2017, 23, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowan, D.; Lebre, P.; Amon, C.; Becker, R.; Boga, H.; Boulangé, A.; Chiyaka, T.; Coetzee, T.; de Jager, P.; Dikinya, O. Biogeographical survey of soil microbiomes across sub-Saharan Africa: Structure, drivers, and predicted climate-driven changes. Microbiome 2022, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köberl, M.; Wagner, P.; Müller, H.; Matzer, R.; Unterfrauner, H.; Cernava, T.; Berg, G. Unraveling the complexity of soil microbiomes in a large-scale study subjected to different agricultural management in Styria. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.H.M.P. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Yao, M.; Lv, L.; Ling, Z.; Li, L. The human microbiota in health and disease. Engineering 2017, 3, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.-R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.-W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Wang, Y.; Tang, W.; Lei, Y. Bacterial community diversity in municipal waste landfill sites. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 7745–7756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzatti, G.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Gibiino, G.; Binda, C.; Gasbarrini, A. Proteobacteria: A Common Factor in Human Diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9351507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhya, I.; Hansen, R.; El-Omar, E.M.; Hold, G.L. IBD—What role do Proteobacteria play? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faith, J.J.; Guruge, J.L.; Charbonneau, M.; Subramanian, S.; Seedorf, H.; Goodman, A.L.; Clemente, J.C.; Knight, R.; Heath, A.C.; Leibel, R.L. The long-term stability of the human gut microbiota. Science 2013, 341, 1237439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas, G.; Sommer, M.O.; Oluwasegun, R.D.; Church, G.M. Bacteria subsisting on antibiotics. Science 2008, 320, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Ramaiah, N. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profiling of bacterial communities composition in Arabian Sea. J. Environ. Biol. 2011, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, J.J.; Konwar, K.M.; Hallam, S.J. Microbial ecology of expanding oxygen minimum zones. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Samaddar, S.; Chatterjee, P.; Roy Choudhury, A.; Choi, J.; Choi, J.; Sa, T. Structural and Functional Shift in Soil Bacterial Community in Response to Long-Term Compost Amendment in Paddy Field. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.; Khandeparker, R.; Bandekar, M.; Meena, R.M.; Ramaiah, N. Quantitative analyses of denitrifying bacterial diversity from a seasonally hypoxic monsoon governed tropical coastal region. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2018, 156, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, C.L. Waterborne transmission of infectious agents. Man. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 222–248. [Google Scholar]
- Wade, T.; Sams, E.; Brenner, K.; Haugland, R.; Chern, E.; Beach, M.; Wymer, L.; Rankin, C.; Love, D.; Li, Q. Environmental health: A global access science source [electronic resource]. Env. Health 2010, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, S.; Basu, A.; Ahmad, I.; Sayyed, R.; El-Enshasy, H.A.; Dailin, D.J.; Suriani, N.L. Recent understanding of soil acidobacteria and their ecological significance: A critical review. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 580024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebmeyer, S.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D. A framework for identifying the recent origins of mobile antibiotic resistance genes. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Rodriguez-Martinez, J.-M.; Mammeri, H.; Liard, A.; Nordmann, P. Origin of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinant QnrA. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 3523–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, R.A.; Szabo, D. Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in Acinetobacter species and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, S49–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, L.B. Federal funding for the study of antimicrobial resistance in nosocomial pathogens: No ESKAPE. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1079–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahendra, M.; Jayaraj, B.S.; Lokesh, K.S.; Chaya, S.K.; Veerapaneni, V.V.; Limaye, S.; Dhar, R.; Swarnakar, R.; Ambalkar, S.; Mahesh, P.A. Antibiotic Prescription, Organisms and its Resistance Pattern in Patients Admitted to Respiratory ICU with Respiratory Infection in Mysuru. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 22, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osbiston, K.; Oxbrough, A.; Fernández-Martínez, L.T. Antibiotic resistance levels in soils from urban and rural land uses in Great Britain. Access Microbiol. 2021, 3, 000181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esiobu, N.; Armenta, L.; Ike, J. Antibiotic resistance in soil and water environments. Int. J. Environ. Heal. Res. 2002, 12, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakolwa, M.A.; Woodd, S.L.; Aiken, A.M.; Manzi, F.; Gon, G.; Graham, W.J.; Kabanywanyi, A.M. Overuse of antibiotics in maternity and neonatal wards, a descriptive report from public hospitals in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Chusri, S.; Sangthong, R.; McNeil, E.; Hu, J.; Du, W.; Li, D.; Fan, X.; Zhou, H.; Chongsuvivatwong, V.; et al. Clinical pattern of antibiotic overuse and misuse in primary healthcare hospitals in the southwest of China. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulis, G.; Daniels, B.; Kwan, A.; Gandra, S.; Daftary, A.; Das, J.; Pai, M. Antibiotic overuse in the primary health care setting: A secondary data analysis of standardised patient studies from India, China and Kenya. BMJ Glob. Health 2020, 5, e003393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the offense with a strong defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsberg, K.J.; Reyes, A.; Wang, B.; Selleck, E.M.; Sommer, M.O.; Dantas, G. The shared antibiotic resistome of soil bacteria and human pathogens. Science 2012, 337, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, A.M.A.; Uddin, K.N. Analysis of the Occurrence of Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria in the Hospital’s Effluent and its Receiving Environment. Microbiol. Insights 2022, 15, 11786361221078211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, L.; Sandvang, D.; Hansen, L.H.; Bagger-Skjøt, L.; Westh, H.; Jørgensen, C.; Hansen, D.S.; Pedersen, B.M.; Monnet, D.L.; Frimodt-Møller, N. Characterisation, dissemination and persistence of gentamicin resistant Escherichia coli from a Danish university hospital to the waste water environment. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, T.; Pereira, W.d.C.; Silva, D.; Seki, L.; Carvalho, A.D.A.; Asensi, M.D. Detection of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in effluents and sludge of a hospital sewage treatment plant. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, P.; Delangle, M.-H.; Merrien, D.; Barillé, S.; Reynaud, A.; Minozzi, C.; Richet, H. Fluoroquinolone use and fluoroquinolone resistance: Is there an association? Clin. Infect. Dis. 1994, 19, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeau, J.; Yaschuk, Y. Canadian ciprofloxacin susceptibility study: Comparative study from 15 medical centers. Canadian Ciprofloxacin Study Group. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 1729–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dancer, S.J. Controlling hospital-acquired infection: Focus on the role of the environment and new technologies for decontamination. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 665–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalpana, P.; Trivedi, P.; Bhavsar, P.; Patel, K.; Yasobant, S.; Saxena, D. Evidence of Antimicrobial Resistance from Maternity Units and Labor Rooms: A Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH) Study from Gujarat, India. Healthcare 2022, 10, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellatly, S.L.; Hancock, R.E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: New insights into pathogenesis and host defenses. Pathog. Dis. 2013, 67, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekic, S.; Hrenovic, J.; Durn, G.; Venter, C. Survival of extensively-and pandrug-resistant isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii in soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 147, 103396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.; Flach, C.-F. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Antibiotic Drugs Used for Disc Diffusion | |
|---|---|
| Pseudomonas & Acinetobacter Species | Enterobacteriaceae |
| Levofloxacin (5 µg) | Colistin (10 µg) |
| Aztreonam (30 µg) | Cotrimoxazole (25 µg) |
| Ceftazidime (30 µg) | Cefepime (30 µg) |
| Colistin (10 µg) | Gentamycin (10 µg) |
| Cotrimoxazole (25 µg) | Imipenem (10 µg) |
| Cefepime (30 µg) | Meropenem (10 µg) |
| Gentamycin (10 µg) | Amikacin (30 µg) |
| Imipenem (10 µg) | Minocycline (30 µg) |
| Meropenem (10 µg) | Piperacillin/tazobactum (100/10 µg) |
| Amikacin (30 µg) | Chloramphenicol (30 µg) |
| Minocycline (30 µg) | Ceftriaxone (30 µg) |
| Piperacillin/tazobactum (100/10 µg) | Amoxyclav (30 µg) |
| Tigecycline (15 µg) | Ciprofloxacin (5 µg) |
| Ampicillin (10 µg) | |
| p Value | H1 | H2 | U3 | U4 | H5 | H6 | U7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2 | 0.873 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| U3 | 0.999 | 0.991 | - | - | - | - | - |
| U4 | 0.982 | 0.999 | 0.999 | - | - | - | - |
| H5 | 0.958 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | - | - | - |
| H6 | 0.027 * | 0.576 | 0.127 | 0.299 | 0.393 | - | - |
| U7 | 0.965 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.368 | - |
| U8 | 0.983 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 0.293 | 1.000 |
| Soil Sample Site | Sample ID | LF/NLF | Gram Staining | Oxidase | Indole | Citrate | Triple Sugar Iron |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | M1.1 | LF | GNB | - | - | + | A/A with gas no H2S |
| H2 | M2.1 | NLF | GNcB | - | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| H2 | M2.2 | NLF | GNB slender | + | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| U3 | M3.1 | NLF | GNB | + | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| U3 | M3.2 | NLF | GNB | + | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| U3 | M3.3 | LF | GNB | - | - | + | K/A no H2S |
| U3 | M3.4 | NLF | GNcB | - | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| U3 | M3.5 | LF | GNB | - | - | + | A/A with gas no H2S |
| U4 | M4.1 | LF | GNB | - | + | - | A/A with gas no H2S |
| U4 | M4.2 | NLF | GNB | + | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| U4 | M4.3 | NLF | GNB | + | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| U4 | M4.4 | NLF | GNcB | - | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| H5 | M5.1 | NLF | GNB | + | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| H5 | M5.2 | NLF | GNB short | + | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| H6 | M6.1 | NLF | GNB | + | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| H6 | M6.2 | LF | GNB | - | - | + | A/A with gas no H2S |
| U7 | M7.1 | NLF | GNB | + | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| U7 | M7.2 | NLF | GNB | + | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| U7 | M7.3 | NLF | GNcB | - | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| U8 | M8.1 | NLF | GNB short | + | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| U8 | M8.2 | NLF | GNB | + | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| U8 | M8.3 | NLF | GNB | + | - | + | K/no change no H2S |
| Sampling Site | Sample ID | Organism Identified |
|---|---|---|
| H1 | M1.1 | Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| H2 | M2.1 | Acinetobacter baumannii |
| H2 | M2.2 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| U3 | M3.1 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| U3 | M3.2 | Pseudomonas species |
| U3 | M3.3 | Serratia marcescens |
| U3 | M3.4 | Acinetobacter baumannii |
| U3 | M3.5 | Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| U4 | M4.1 | Escherichia coli |
| U4 | M4.2 | Pseudomonas species |
| U4 | M4.3 | Pseudomonas species |
| U4 | M4.4 | Acinetobacter baumannii |
| H5 | M5.1 | Pseudomonas species |
| H5 | M5.2 | Aeromonas salmonicida |
| H6 | M6.1 | Unidentified by VITEK |
| H6 | M6.2 | Enterobacter cloacae ssp. cloacae |
| U7 | M7.1 | Unidentified by VITEK |
| U7 | M7.2 | Pseudomonas fluorescens |
| U7 | M7.3 | Acinetobacter baumannii |
| U8 | M8.1 | Aeromonas salmonicida |
| U8 | M8.2 | Unidentified by VITEK |
| Organism Identified | LE | AT | CAZ | CL | COT | CPM | GEN | IPM | MRP | AK | MI | PIT | TGC | CIP | TIC | SCF | DOR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas species, n = 6 | S | 6 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 | ||||
| I | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| R | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | |||||
| Acinetobacter baumannii, n = 4 | S | 4 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| I | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| R | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Organism Identified | CL | COT | CPM | GEN | IMP | MRP | AK | PIT | TGC | CTR | AMC | CIP | AMP | SCF | CXM | CXM/AXT | ERT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Klebsiella pneumoniae n = 2 | S | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| I | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| R | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Escherichia coli n = 1 | S | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| I | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| R | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Serratia marsescens n = 1 | S | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| I | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| R | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| Enterobacter cloacae ssp. cloacae n = 1 | S | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| I | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| R | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kunhikannan, S.; Stanton, C.R.; Rose, J.; Thomas, C.J.; Franks, A.E.; Neelambike, S.M.; Kumar, S.; Petrovski, S.; Shindler, A.E. Exploring the Diversity and Antibiogram of the Soil around a Tertiary Care Hospital and a University Precinct in Southern India: A Pilot Study. Soil Syst. 2023, 7, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7020045
Kunhikannan S, Stanton CR, Rose J, Thomas CJ, Franks AE, Neelambike SM, Kumar S, Petrovski S, Shindler AE. Exploring the Diversity and Antibiogram of the Soil around a Tertiary Care Hospital and a University Precinct in Southern India: A Pilot Study. Soil Systems. 2023; 7(2):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7020045
Chicago/Turabian StyleKunhikannan, Shalini, Cassandra R. Stanton, Jayson Rose, Colleen J. Thomas, Ashley E. Franks, Sumana M. Neelambike, Sumana Kumar, Steve Petrovski, and Anya E. Shindler. 2023. "Exploring the Diversity and Antibiogram of the Soil around a Tertiary Care Hospital and a University Precinct in Southern India: A Pilot Study" Soil Systems 7, no. 2: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7020045
APA StyleKunhikannan, S., Stanton, C. R., Rose, J., Thomas, C. J., Franks, A. E., Neelambike, S. M., Kumar, S., Petrovski, S., & Shindler, A. E. (2023). Exploring the Diversity and Antibiogram of the Soil around a Tertiary Care Hospital and a University Precinct in Southern India: A Pilot Study. Soil Systems, 7(2), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7020045








