Abstract
Unscientific land use and cropping techniques have led high soil erosion and degradation of soil quality in the mid-hills of Nepal. To understand the effects of land use systems for selected soil chemical properties in mid-hills, composite soil samples at 0 cm to 20 cm depth were collected from five different land-use systems: Grassland, forest land, upland, lowland, and vegetable farms from Dhading district of Nepal in 2017. Soil samples were analyzed for soil fertility parameters: Soil pH, organic matter (OM), total nitrogen (N), available phosphorus (P), available potassium (K) and its effect due to different land use systems were compared. Results showed that soil pH was neutral in vegetable farms (6.61), whereas the rest of the land-use systems had acidic soils. Soil OM (3.55%) and N (0.18%) content was significantly higher in forest, but the lowest soil OM (1.26%) and N (0.06%) contents were recorded from upland and lowland farms, respectively. Available P was the highest in the vegetable farm (41.07 mg kg−1) and was the lowest in grazing land (2.89 mg kg−1). The upland farm had significantly higher P levels (39.89 mg kg−1) than the lowland farm (9.02 mg kg−1). Available K was the highest in the vegetable farm (130.2 mg kg−1) and lowest in grazing land (36.8 mg kg−1). These results indicated that the land under traditional mixed cereal-based farming had poor soil health compared with adjacent vegetable, grazing, and forest lands among the study area. The variations in soil fertility parameters suggest the immediate need for improvement in soil health of traditional farmlands.
1. Introduction
The Nepalese economy relies heavily upon the agriculture sector, a source of livelihoods for 65.6% of the country’s active population and contributes 29.23% to the total gross domestic product [1]. Healthy and vigorous plants are produced by healthy soils which help to increase crop production and can address the food requirements for human consumption [2]. However, Nepal is considered as one of the food insecure countries with very low (around 16%) arable land area [3]. About 86% of the total area of Nepal is occupied by hilly and mountain regions where cultivation is difficult, mainly due to topography [4].
Land usage in Nepal has been changing rapidly over the past decades. From 1961/1962 to 2001/2002, in a span of 40 years, the agricultural land use has increased by 53.6%, however in recent decades, it is starting to decrease. The total agricultural and arable lands have decreased by 0.3% and 3.1% respectively from 2001/2002 to 2011/2012 [5,6]. Additionally, high rates of soil erosion [7], subsistence and traditional farming practices [8], unscientific management of land [9], increased land fragmentation, deforestation [10,11], conversion of agriculture land to settlements, and unclear land tenure rights [12] are some of the major problems that limit agricultural development in Nepal.
Proper land use planning is important for increasing agricultural production, environmental conservation, and for the protection of biodiversity [13]. The land use decisions and governmental efforts for implementing land use are poor in Nepal. Although a land use policy was formulated in 2012 in Nepal, the practical application of this policy is difficult because of its flexibility and many loopholes within it [12].
The poor soil management practice in cultivated lands has led to a higher rate of soil erosion, decreased crop production and productivity, and declined soil quality [14]. It is estimated that 60% soils of Nepal have low organic matter (OM), 23% have low phosphorus (P), 18% have low potassium (K), and 67% of the soils are acidic [15]. It has been estimated that 310 kg ha−1 of plant nutrient is lost annually because of the cereal-based farming system, whereas only 67 kg ha−1 of fertilizer is added to the soil through various fertilizer sources [16].
The Government of Nepal run Prime Minister Agriculture Modernization Project (PMAMP) is set to establish variously specialized agriculture production areas throughout Nepal, which will have a major impact on land use system changes in a large area [17]. The specialized production areas will be utilized in intensive monoculture throughout the year. After the completion of PMAMP in 2025, it is aiming to convert 471,000 ha of traditionally used farmlands into an intensive cropping land through the establishment of pockets, blocks, zones, and super zones [18].
It is necessary to understand the efficiency of land use systems in terms of nutrient cycling and soil conservation. Additionally, agricultural practices such as fertilization, tillage, irrigation, and crop residue left on the field alter soil chemical properties and nutrient dynamics throughout the soil profile [19,20]. Changes in land use can also disrupt carbon and nitrogen dynamics and organic matter content in soil [21]. Hence, this research aimed to assess the fertility status of different land use systems and their effect upon soil fertility parameters in Nilkantha Municipality and Siddalake Village Municipality in Dhading district of Nepal, where 100 ha of traditionally used farmland is set to convert into vegetable farm-land under PMAMP. It will help farmers and policymakers to direct their efforts in adopting improved soil management practices and better land use system planning to make Nepalese soils environmentally sound, while maintaining high production after land use change. Specifically, this research aims to study the differences in soil fertility parameters brought out by the land use systems.
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Area and Research Design
This research was conducted in Nilkantha municipality and Siddalake Village municipality of Dhading district of Nepal as shown in Figure 1. The altitude of research locations ranged from 575 m in lowlands to 760 m in forestland, with an expansion of geographic coordinates from 84°54.7′ E to 84°50.5′ E and 27°48.3′ N to 27°55.3′ N. The research was conducted in a randomized complete block design by selecting five different land-use systems: Grazing land, forest land, an upland farm, a vegetable farm and a lowland farm as treatments. Soil samples taken from each treatment plot were replicated five times. A field survey was used for the identification and selection of research locations based on the availability of land-use systems aimed at each study site. The majority of the study area was dominated by loam and silt loam soils and sandy loam in some cases.
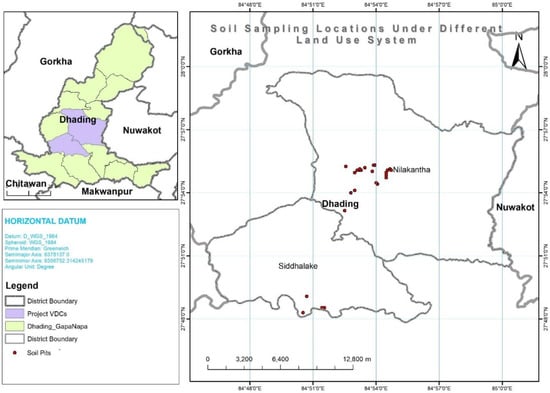
Figure 1.
Locations of soil sample collection in Dhading district of Nepal.
The grazing and forest lands represent a natural land use system without any human intervention. The lowland is characterized by bunds and the availability of irrigation facilities throughout the year, where rice (Oryza sativa L.) is grown during the summer and rainy seasons. The upland is rainfed, devoid of bunds where cereals like maize (Zea mays L.), millet (Pennisetum glaucum), and sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) are grown without any specific pattern. Vegetable farms receive a high rate of organic and inorganic fertilizers with well-developed irrigation facility where cucurbits, cole crops, and solanaceous crops are grown throughout the year.
2.2. Soil Sampling Techniques
Five composite soil samples, from 0 cm to 20 cm depths, were collected from each land use system by following the random sampling technique in between 15 May and 10 July 2017. Seven sub-samples were collected at each study site. A hand-held Garmin GPS device with 1 m precision was used to pinpoint the location of sampled points.
2.3. Soil Laboratory Analysis
The collected samples were sent to Regional Soil Testing Laboratory, Hetauda, Makawanpur district for chemical analysis. Air-dried samples were ground and sieved through a 2 mm sieve for pH, organic matter (OM), total nitrogen (N), available phosphorus (P), and available potassium (K) analysis. The collected soil samples were analyzed by following standard laboratory procedures of Regional Soil Testing Laboratory, Makawanpur, Nepal [22]. Data obtained from the laboratory were analyzed using Gen STAT and Microsoft Excel.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil pH
Results show that the lowest pH was found in forest land and the highest in vegetable farmland (Table 1). However, soil pH had the lowest coefficient of variation (CV) compared to other soil fertility parameters in different land uses, which represents the lowest degree of heterogeneity from collected soil samples. Soils of grazing land (5.17), forest land (4.74), the upland farm (5.56), and the lowland farm (5.4) were acidic in nature according to the rating chart adopted from Khatri-Chhetri [23]. The vegetable farm (6.61) had a pH in the neutral range. The land use system had a significant impact on the soil pH level at p < 0.001. However, the soil pH of grazing land, the upland farm, and the lowland farm was not significantly different.

Table 1.
Effect of land use system on soil fertility parameters in Dhading district of Nepal.
The primary reason for higher acidic soils in forest land could be due to parent materials high in elements such as silica, intense leaching of basic cations during monsoon season, and the atmospheric nature of aluminum in these soils [17,24,25]. Our results are consistent with the report published by Islam and Weil [26] who found that forest and reforested soils contributed significantly lower pH values than cultivated and grassland soils in Bangladesh. The lower soil pH in forest land also might be due to its higher slope [27], higher OM content [28], and less evaporation from the surface in the study area.
The acidic soils of cultivated lands might be due to continuous cultivation and addition of nitrogenous fertilizers. In cultivated lands, ammonium-based fertilizers largely cause soil acidification [29]. Due to the use of high level of urea and ammonium phosphates for agriculture in Nepal, the cultivated soils are made acidic in nature [30]. Judicious use of nitrogenous fertilizer sources and adoption of liming in may be the reasons for higher soil pH in vegetable land.
3.2. Organic Matter (OM)
Results of the study indicate that the highest (3.55%) amount of soil OM was found in forest land and the lowest (1.26%) in the upland farm (Table 1). The upland and lowland farms had a low amount of soil OM (1.61%) while grazing land and vegetable land had a medium amount of soil OM (2.61% and 2.49%, respectively). Furthermore, the effect of land use systems on soil OM content was significant at p < 0.001. These results were consistent with the findings of Bista [31] and Chauhan et al. [32] who reported a higher amount of soil OM in forest land compared to farmlands in Nuwakot and Chitwan districts of Nepal, respectively. Another study by Pandey et al. [17] reported that due to the intensive cropping system in some parts of Nepal, it has removed essential plant nutrients from the soil, thereby exerting pressure on soil fertility.
Tillage practice results in higher decomposition and mineralization of OM. The more a soil is tilled, the more the OM is broken down [33]. Tillage improves the aeration of the soil and causes a flush of microbial action speeding up the decomposition of OM and also often increases erosion [34]. Hence, the forest and grazing lands had higher soil OM due to high OM accumulation and no-tillage disturbance compared to lowland and upland farms, where conventional tillage was commonly practiced. The higher % of OM in the vegetable land might be attributed to supply of organic manures and adoption of soil management practices in the farm such as balanced fertilization, increased biomass production, the supply of organic manures, and refraining from burning which increases the soil OM [35].
3.3. Total Nitrogen (N)
Results show that a great variation in total nitrogen (N) level in different land use systems. The highest soil N (0.18%) was observed from forest land and the lowest (0.06%) was observed in the lowland farm (Table 1). There was no significant difference in N levels of upland and lowland farms. These results are in line with the findings of Duguma et al. [36] who found higher N level in woodlot and pasture land compared to cereal land. In a similar study conducted by Yimer et al. [37] found the organic carbon and N content to be significantly lower in cropland compared to grazing and forest lands. The lower N contents in upland and lowland might be due to low soil OM content and may be due to tillage, since soil tilling increases the susceptibility to erosion [34].
There was a strong positive correlation (r = 0.92, p < 0.01) between OM and N levels (Table 2), indicating that the higher nitrogen in forest, grazing and vegetable land was due to high organic matter content in respective lands. Brady and Weil [29] reported that the distribution of soil N paralleled that of soil OM due to the fact that N along with other nutrients, are present in organic combination and are slowly released by the process of mineralization. This was also supported by Matsumo and Ae [38] who reported that about 90% of total N in soil derives from organic sources. A meta-analysis by Shi et al. [39] reported that soil carbon and N can slightly decrease after forestation on pasture land and moderately increase after forestation on cereal land, but changes in soil carbon and N stocks through forestation depends on prior land use, climate and the tree species planted [40].

Table 2.
Correlation coefficient of different soil fertility parameters in Dhading district of Nepal.
3.4. Available Phosphorus (P)
The effect of land use systems on available phosphorus (P) is shown in Table 1. Available P had the highest coefficient of variation (CV) compared to other soil fertility parameters in different land use which represents the highest degree of heterogeneity from collected soil samples. The highest (41.07 mg kg−1) amount of P was found in the vegetable farm and the lowest (2.89 mg kg−1) in grazing land. Available P in forest land (4.15 mg kg−1) and the upland farm (39.89 mg kg−1) were on par with that of grazing land and the vegetable farm respectively. Available P in the lowland farm (9.02 mg kg−1) was significantly higher than in forest and grazing lands. These results were similar to the findings of Bista [31] who reported a significantly lower P level in the forest compared to farmland in Nuwakot and Chitwan districts of Nepal.
Availability of P in cultivated soil strongly depends on soil pH [41]. Hence, very low P in grazing and forest lands might be due to low pH. The pH in grazing land (5.17) and forest land (4.74) were lower than 5.5, a favorable condition in which P is fixed in the soil as aluminum phosphate (AlPO4) and becomes unavailable [42]. The lower P content might be also due to no external sources of P were applied to these natural lands. The very high P in the vegetable farm and cereal land may be due to greater pH and the residual effect of external chemical fertilizers, since only 20% to 50% of the P applied is absorbed by crops during the growing season and unused P is retained in the soils, ultimately increasing the soil available P concentration [43]. The lower amount of P in lowland compared to upland and vegetable farms may be due to the small amount of OM reducing the organic P source significantly [44,45].
3.5. Available Potassium (K)
Available potassium (K) was significantly affected by the land use systems at p < 0.001 (Table 1). Available K level in the vegetable land (130.2 mg kg−1) was found to be significantly higher than all other land use systems. The forest land (77.5 mg kg−1) had higher K level than the upland farm (57 mg kg−1). However, there was no significant difference in the K level between grazing land (36.8 mg kg−1) and the lowland farm (43.2 mg kg−1), both showing the relatively low level of K compared to other land use systems. Bista [31] also reported significantly higher K level in forest land than a traditional cereal-based lowland farm of Chitwan district, Nepal. However, those results are in contrast to the findings of Chauhan [32] who reported no difference in K levels of natural and artificial land use systems.
The low level of K in the lowland farm might be due to higher leaching loss and more K harvest from soils. Under irrigated conditions, K is subjected to considerable leaching loss [28]. In the lowland farm, cereal crops are harvested along with the whole plant (for the purpose of haymaking) and little residue is left on the soil surface. Burning of crop stubbles after crop harvest and higher soil pH might be the reasons for high available K in the vegetable farm. Heavy soils that contain more clay tend to have large reserves of K which are available to the crop and produce higher soil K indices on analysis [46].
The availability of K increases with increasing pH as calcium (Ca) displace K from the clay lattice and make it more available in solution for plants [22,46]. The higher available K in forest land compared to grazing land may be due to its extensive and deep-rooted trees. Trees act as a nutrient pump and extract nutrients from the deep subsoil horizons and recycle it into surface layer through leaf fall [25].
4. Conclusions
Land use change influences a number of biological and physiological processes. Poor land use decisions can lead to land degradation and poor soil health. In Nepal, where land use change is occurring rapidly, erosion, deforestation, poor soil nutrient management, indiscriminate chemical fertilizer use in cultivated lands, and unscientific land use have affected a large population dependent upon agriculture. This study compared the fertility parameters of soil in different natural and artificial land use systems.
Results of the study show evidence of poor soil health in land under traditionally mixed cereal-based farming (upland and lowland) compared to vegetable farmland, grazing land and forest lands in the Dhading district of Nepal. The variations in soil fertility parameters suggest the immediate need for improvement in soil health of traditional farmlands. Moreover, it is suggested sustainable soil nutrient management practices with increased organic matter addition, practices of crop rotation, biomass incorporation, increasing crop diversity, maintaining soil cover in cultivated lands are needed to amend soil problems in traditional farmlands and maintain soil health in vegetable farmlands.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.K. and B.R.K.; Methodology, S.K.; Software, S.K.; Validation, S.K., B.R.K. and D.P.; Formal Analysis, S.K. and D.P.; Investigation, S.K.; Resources, S.K.; Data Curation, S.K. and D.P.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, S.K.; Writing-Review & Editing, S.K. and D.P.; Visualization, S.K. and D.P.; Supervision, B.R.K.; Project Administration, S.K.; Funding Acquisition, S.K.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Gopal Shrestha and Salikram Chaudhary from District Agriculture Development Office (Dhading) for soil sample collections, R. P. Chauhan from FAO-Nepal (District Technical Coordinator- Siraha) for moral support during the research period, and Bikesh Twanabasu for technical support for study map during the preparation of the manuscript. We would also like to thank anonymous reviewers and an academic editor for their valuable comments and suggestions which helped us on improving this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- AICC. Agriculture Information and Communication/Ministry of Agriculture, Land Management and Cooperatives. Hariharbhawan, Lalitpur, Nepal. Available online: http://www.aicc.gov.np/home/ (accessed on 27 May 2017).
- FAO. Healthy Soils Are the Basis for Healthy Food Production. Available online: http://www.fao.org/soils-2015/news/news-detail/en/c/277682/ (accessed on 22 May 2018).
- MOAD. Agriculture Development Strategy; Ministry of Agricultural Development: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2013.
- NPC. National Planning Commissions: “Nepal status paper—United Nations conference on sustainable development 2012 (Rio+ 20) synopsis”. In Proceedings of the United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 20–22 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- CBS. National Sample Census of Agriculture Nepal (2001/02); Central Bureau of Statistics: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2003.
- CBS. Compendium of Environment Statistics; Central Bureau of Statistics: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2016.
- Uddin, K.M.; Murthy, S.R.; Wahid, S.M.; Matin, M.A. Estimation of soil erosion dynamics in the Koshi basin using gis and remote sensing to assess priority areas for conservation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panday, D. Adapting climate change in agriculture: The sustainable way in Nepalese context. Hydro Nepal J. Water Energy Environ. 2012, 11, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijal, S.P. Soil fertility decline in Nepal: Problem and strategy. Nepal J. Sci. Technol. 2001, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, A.K.; Kafle, N. Land degradation issues in Nepal and its management through agroforestry. J. Agric. Environ. 2009, 10, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshar, B.D. An overview of agricultural degradation in Nepal and its impact on economy and environment. Glob. J. Econ. Soc. Dev. 2013, 3, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Paudel, B.; Pandit, J.; Reed, B. Fragmentation and Conversion of Agriculture Land in Nepal and Land Use Policy 2012. 2013. Available online: https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/58880/1/MPRA_paper_58880.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2018).
- Kennedy, C.M.; Hawthorne, P.L.; Miteva, D.A.; Baumgarten, L.; Sochi, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Evans, J.S.; Polasky, S.; Hamel, P.; Vieira, E.M.; et al. Optimizing land use decision-making to sustain Brazilian agricultural profits, biodiversity and ecosystem services. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 204, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D.; Burgess, M. Soil Erosion Threatens Food Production. Agriculture 2013, 3, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.N. National Workshop on Sustainable Soil Management Program; Soil Management Directorate: Lalitpur, Nepal, 2007.
- MOAD. Statistical Information on Nepalese Agriculture; Ministry of Agricultural Development, Monitoring, Evaluation and Statistics Division: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2017.
- Pandey, S.; Bhatta, N.P.; Paudel, P.; Pariyar, R.; Maskey, K.H.; Khadka, J.; Thapa, T.B.; Rijal, B.; Panday, D. Improving fertilizer recommendations for Nepalese farmers with the help of soil-testing mobile van. J. Crop Improv. 2018, 32, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PMAMP. Project Prepared for Assisting the Implementation of Agriculture Development Strategy; Ministry of Agriculture Development and Cooperatives: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2016.
- Wright, A.L.; Dou, F.; Hons, F.M. Crop species and tillage effects on carbon sequestration in subsurface soil. Soil Sci. 2007, 172, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panday, D.; Maharjan, B. Yield response and ammonia volatilization in variably irrigated corn in western Nebraska. In Proceedings of Great Plains Soil Fertility Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 6–7 March 2018; Volume 17, pp. 162–168. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, R.; Wright, A.L.; Inglett, K.; Wang, Y.; Ogram, A.V.; Reddy, K.R. Land-Use Effects on Soil Nutrient Cycling and Microbial Community Dynamics in the Everglades Agricultural Area, Florida. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2009, 1, 2725–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panday, D.; Maharjan, B.; Chalise, D.; Shrestha, R.K.; Twanabasu, B. Digital Soil Mapping in the Bara District of Nepal using Kriging Tool in ArcGIS. PLoS ONE 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri-Chhetri, T.B. Introduction to Soils and Soil Fertility; Tribhuvan University Institute of Agricultural and Animal Science: Rampur, Chitwan, Nepal, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- McCauley, A.; Jones, C.; Jacobsen, J. Soil pH and organic matter. In Nutrient Management Module; Montana State University Extension: Bozeman, MT, USA, 2009; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, S.K. Textbook of Soil Science; Oxford and IBH Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, K.R.; Weil, R.R. Land use effects on soil quality in a tropical forest ecosystem of Bangladesh. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 79, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshaneh, G.T. Effect of slope position on Soil Physico-Chemical properties with different management practices in Small Holder Cultivated Farms of Abuhoy Gara Catchment, Gidan District, North Wollo. Am. J. Environ. Prot. 2015, 3, 174–179. [Google Scholar]
- Harter, R.D. Acid Soils of the Tropics; Echo Tehnical Note: North Fort Myers, FL, USA, 2007; Available online: http://courses.umass.edu/psoil370/Syllabus-files/Acid_Soils_of_the_Tropics.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2018).
- Brady, N.C.; Weil, R.R. The Nature and Properties of Soil, 12th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Diwakar, J.; Prasai, T.; Pant, S.R.; Jayana, B.L. Study on major pesticides and fertilizers used in Nepal. Sci. World 2008, 6, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bista, P. Effect of Different Land Use Systems and Management Practices in Soil Fertility Status of Nuwakot and Chitwan Valley; Unpublished Graduate Dissertation; Institute of Agriculture and Animal Sciences: Rampur, Nepal, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, R.P.; Pande, K.R.; Thakur, S. Soil properties affected by land use systems in Western Chitwan, Nepal. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 2, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanz, J. Saving Our Soil: Solutions for Sustaining Earth’s Vital Resource; Johnson Books: Chicago, IL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Funderburg, E. Organic Matter Serves Important Role in Soil Health; Noble Research Institute: Ardmore, OK, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bot, A.; Benites, J. The Importance of Soil Organic Matter: Key to Drought-Resistant Soil and Sustained Food Production. No. 80; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Duguma, L.A.; Hager, H.; Sieghardt, M. Effects of land use types on soil chemical properties in smallholder farmers of central highland Ethiopia. Ekológia (Bratislava) 2010, 29, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimer, F.; Ledin, S.; Abdelkadir, A. Changes in soil organic carbon and total nitrogen contents in three adjacent land use types in the Bale Mountains, south-eastern highlands of Ethiopia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 242, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Ae, N. Characteristics of extractable soil organic nitrogen determine using various chemical solutions and its significance for nitrogen uptake by crops. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2004, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Peng, C.; Wang, M.; Qiuan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xi, T. A global meta-analysis of changes in soil carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur, and stoichiometric shifts after forestation. Plant Soil 2016, 407, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Niu, S.; Luo, Y. Global patterns of the dynamics of soil carbon and nitrogen stocks following afforestation: A meta-analysis. New Phytol. 2012, 195, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, W.L. Chemical Equilibria in Soils; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Thomason, W. Understanding Phosphorus Behavior in Soils; Noble Research Institute: Ardmore, OK, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, A.E.; Barea, J.M.; McNeill, A.M.; Prigent-Combaret, C. Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant Soil 2009, 321, 305–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N.O.; Janke, R.R. Phosphorus sources and management in organic production systems. HortTechnology 2007, 17, 442–454. [Google Scholar]
- Pavinato, P.S.; Merlin, A.; Rosolem, C.A. Organic compounds from plant extracts and their effect on soil phosphorus availability. Pesqu. Agropecu. Bras. 2008, 43, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, P. Soil Texture and pH Effects on Potassium and Phosphorus Availability; The potash Development Association: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).