A Sole Case of Concurrent Arterial and Venous Thromboses with Massive Pulmonary Embolism and Carriage of Four Genetic Polymorphisms: Factor V Leiden, PAI-1 4G/5G, MTHFR C677T, and ACE I/D—A Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction and Clinical Significance
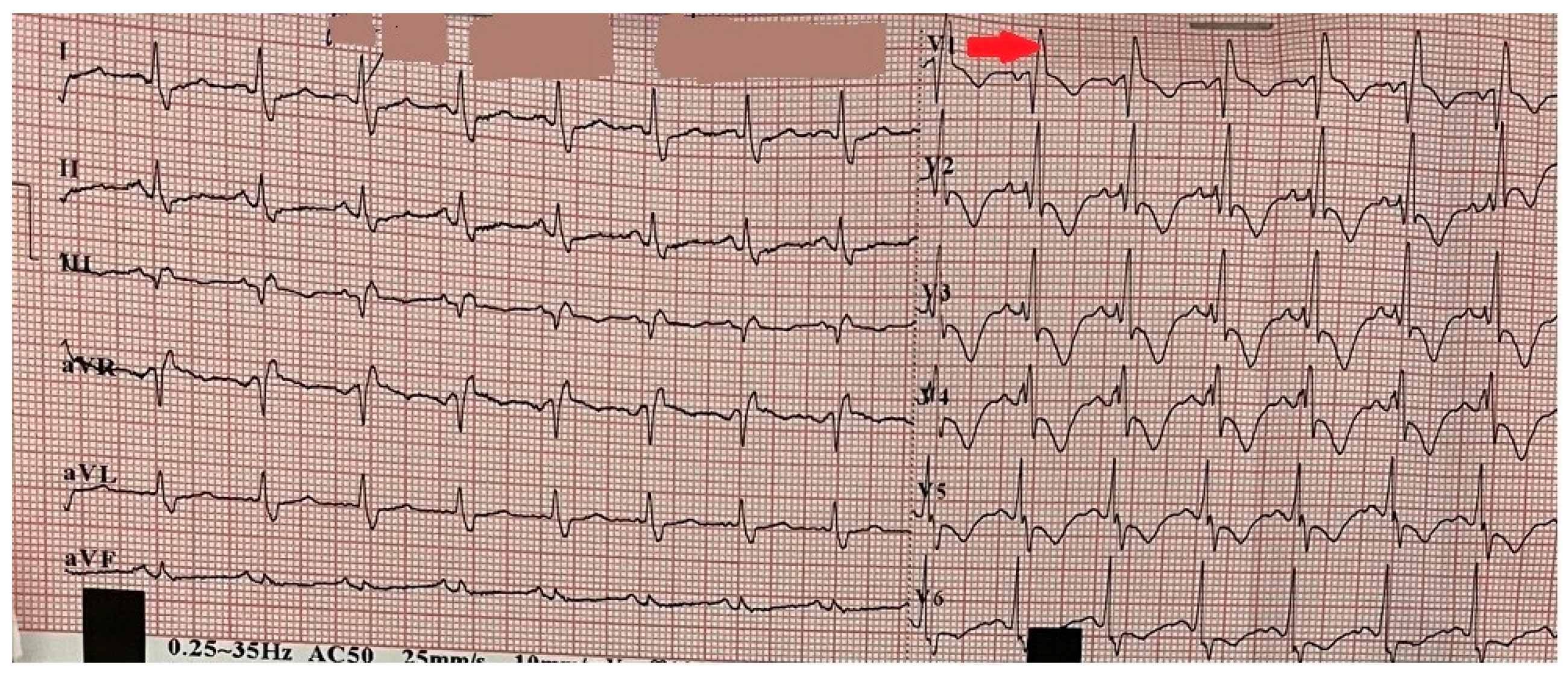
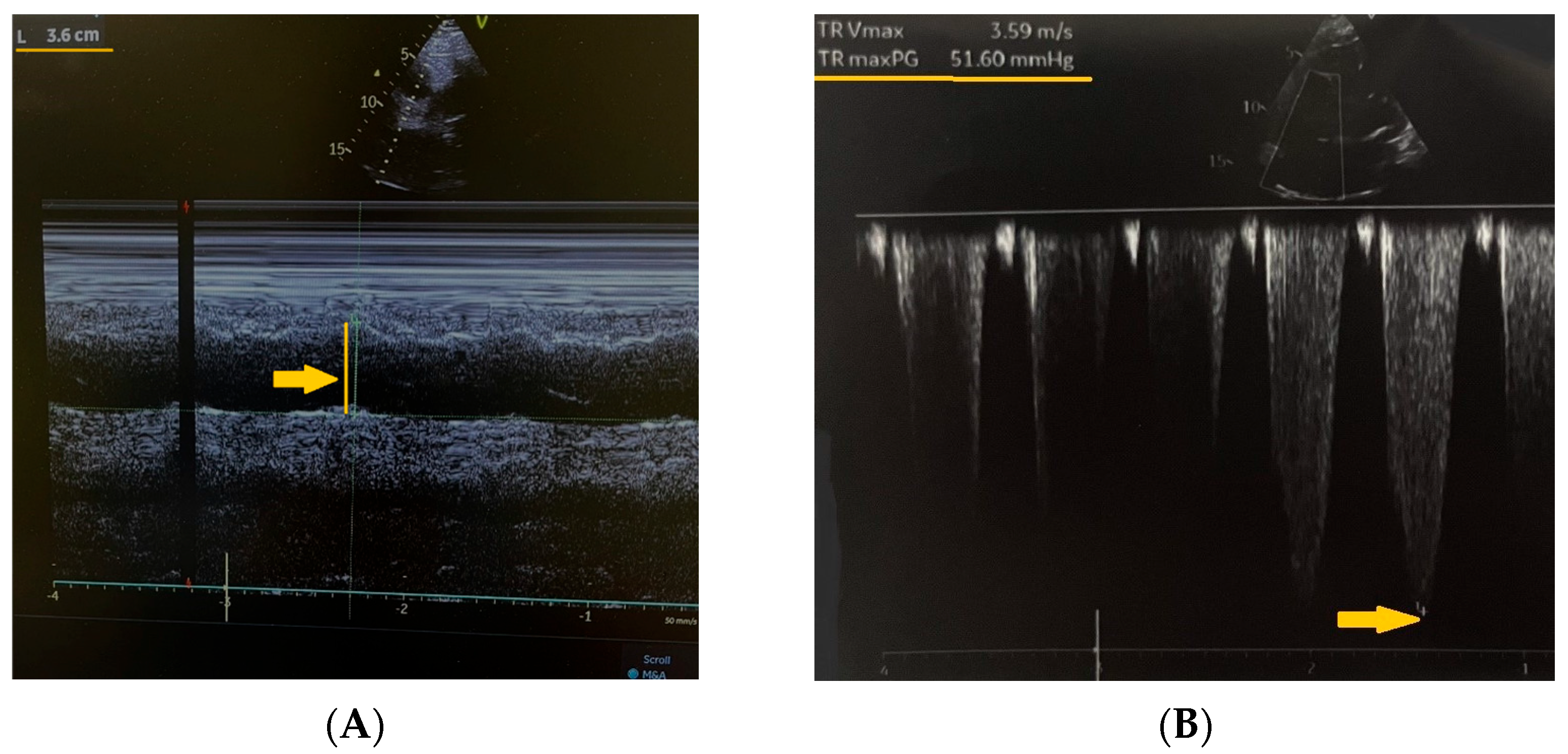
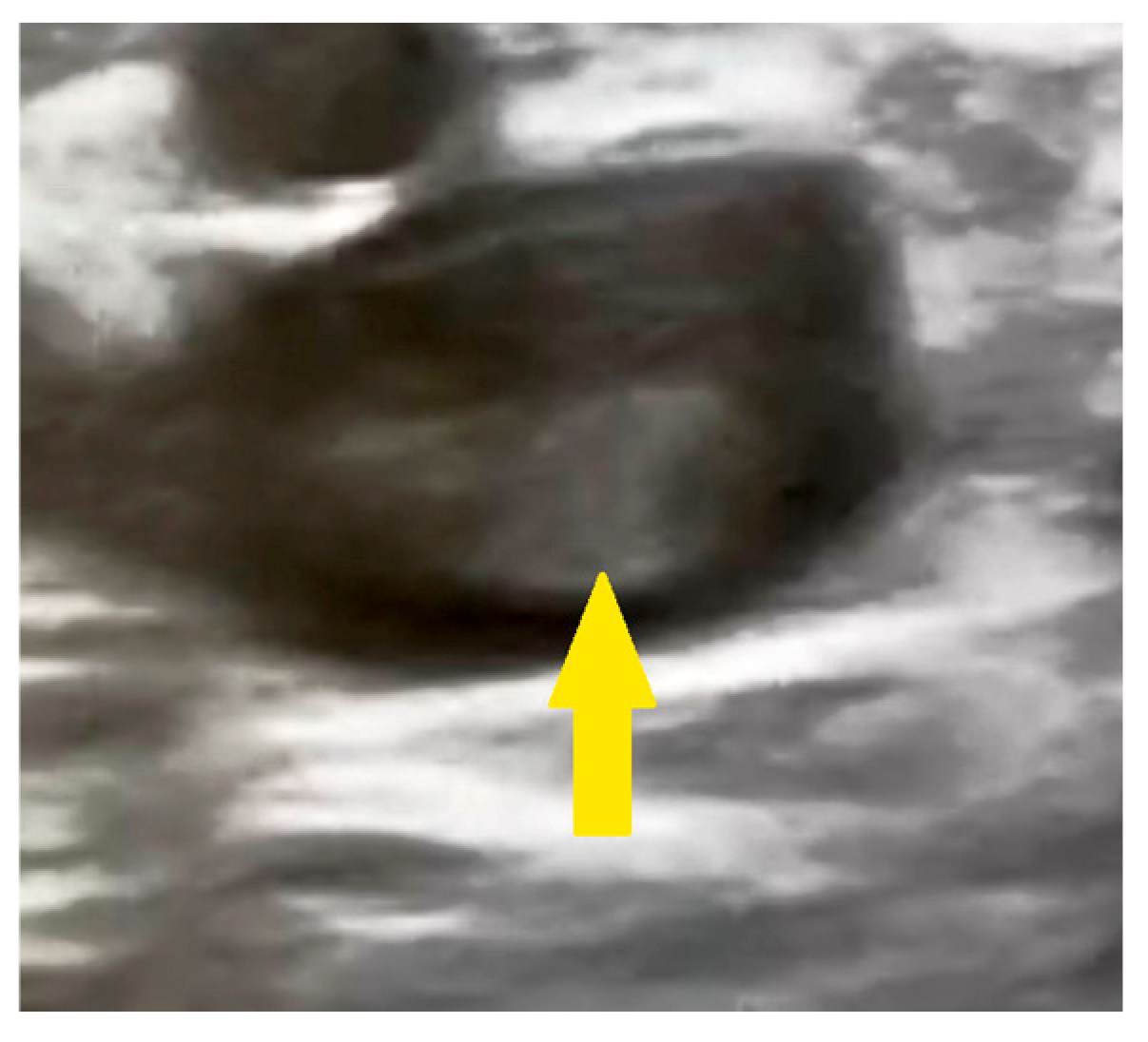
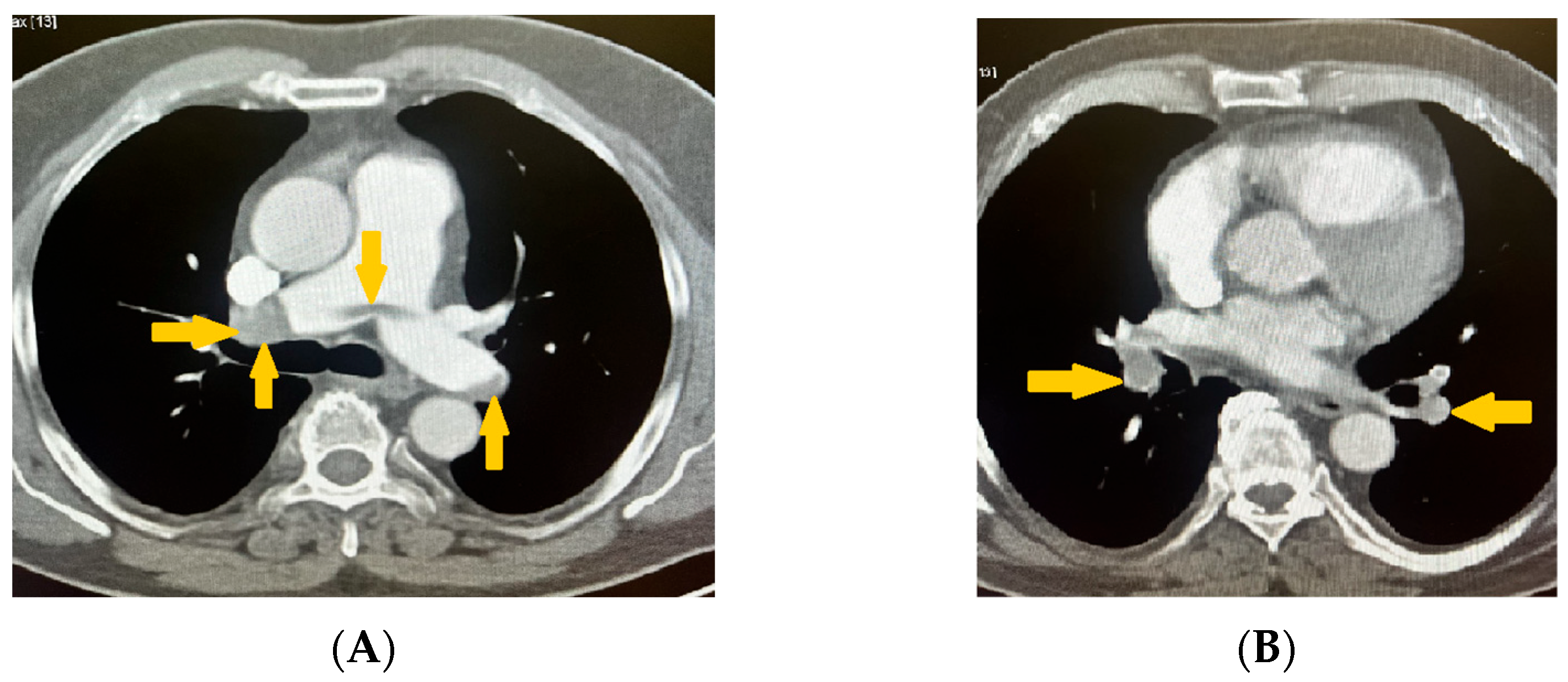
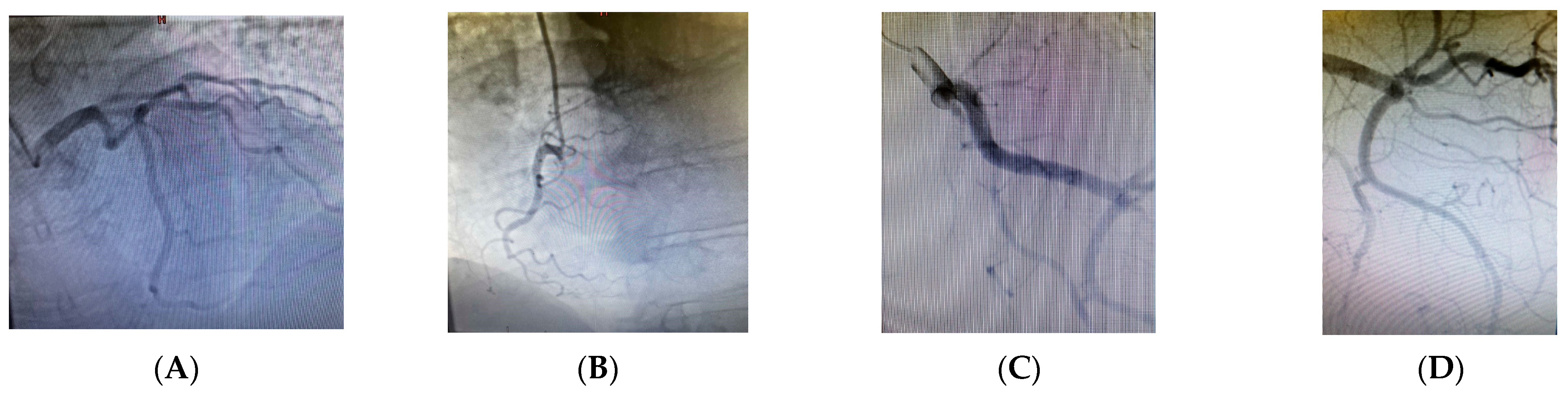
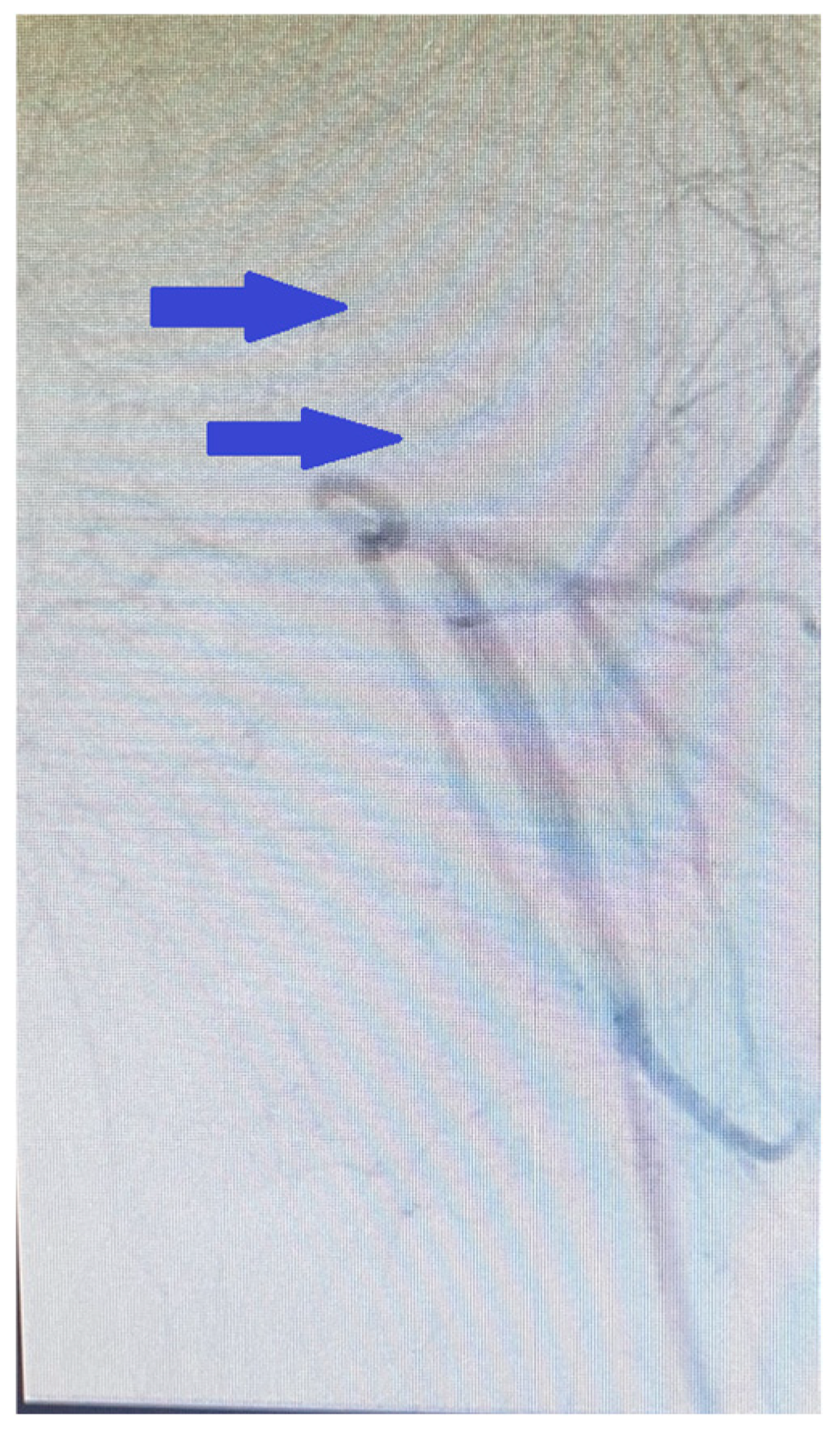
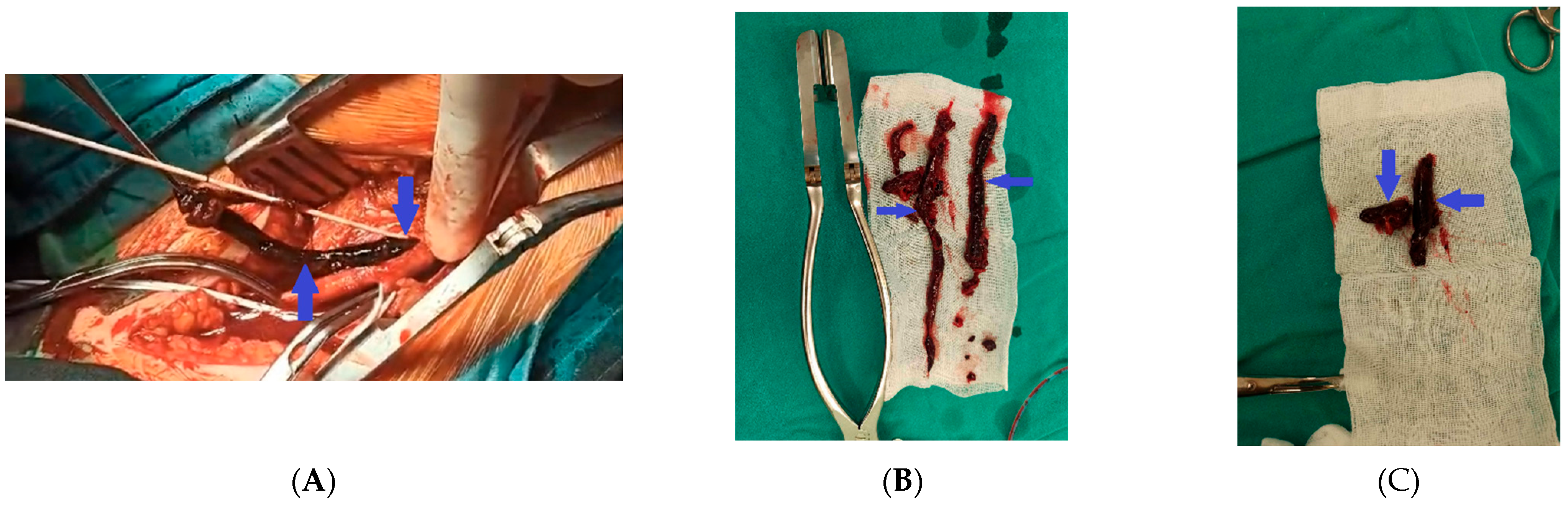
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PE | pulmonary embolism |
| DVT | deep vein thrombosis |
| DOACs | direct oral anticoagulants |
| VTE | venous thromboembolism |
| FVL | Factor V Leiden |
| MTHFR | methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase |
| PAI-1 | plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 |
| I/D | insertion/deletion |
| ACE | angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| ECG | electrocardiogram |
| CT | computed tomography |
| aPTT | activated partial thromboplastin time |
| HIT | heparin-induced thrombocytopenia |
| TEA | thromboendarterectomy |
| tPA | tissue plasminogen activator |
| F | factor |
| APS | antiphospholipid syndrome |
| aPL | antiphospholipid antibody |
| LAC | lupus anticoagulant |
| aCL | anticardiolipin antibodies |
| anti-β2GPI | anti-β2 glycoprotein I antibodies |
| ACR | American College of Rheumatology |
| EULAR | European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology |
| APC | activated protein C |
| uPA | urokinase plasminogen activator |
| 4G/5G | guanosine polymorphism |
| C | cytosine |
| T | thymine |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| VCAM-1 | vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor- kappaB |
| mRNA | messenger ribonucleic acid |
References
- Park, B.; Johnston-Cox, H. Simultaneous arterial and venous thromboembolism. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81 (Suppl. S8), 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmalek, R.; Mechal, H.; Zahidi, H.; Mounaouir, K.; Arous, S.; Benouna, M.E.G.; Drighil, A.; Habbal, R. Combined venous and arterial thrombosis revealing underlying myeloproliferative disorder in a young patient: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 15, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munaim, J.; Thwe, E.; Ibrahim, S.; Easley, L.; Loli, A. Simultaneous arterial and venous system thrombus in patient with suspected malignancy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83 (Suppl. S13), 4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmon, C.T. Basic mechanisms and pathogenesis of venous thrombosis. Blood Rev. 2009, 23, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Hansson, G.K. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature 2011, 473, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, J.B.; Brotman, D.J.; Necochea, A.J.; Emadi, A.; Samal, L.; Wilson, L.M.; Crim, M.T.; Bass, E.B. Predictive value of Factor V Leiden and prothrombin G20210A in adults with venous thromboembolism and in family members of those with a mutation: A systematic review. JAMA 2009, 301, 2472–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lijfering, W.M.; Middeldorp, S.; Veeger, N.J.G.M.; Hamulyák, K.; Prins, M.H.; Büller, H.R.; van der Meer, J. Risk of recurrent venous thrombosis in homozygous carriers and double heterozygous carriers of factor V Leiden and prothrombin G20210A. Circulation 2010, 121, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertina, R.M.; Koeleman, B.P.; Koster, T.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Dirven, R.J.; de Ronde, H.; van der Velden, P.A.; Reitsma, P.H. Mutation in blood coagulation factor V associated with resistance to activated protein C. Nature 1994, 369, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poort, S.R.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Reitsma, P.H.; Bertina, R.M. A common genetic variation in the 3′-untranslated region of the prothrombin gene is associated with elevated plasma prothrombin levels and an increase in venous thrombosis. Blood 1996, 88, 3698–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramdass, S.K.; Loh, K.P.; Howard, L.M. Thrombosis in a bleeding disorder: Case of thromboembolism in factor VII deficiency. Clin. Case Rep. 2017, 5, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Marty, S.; Barro, C.; Chatelain, B.; Fimbel, B.; Tribout, B.; Reynaud, J.; Schved, J.F.; Giansily-Blaizot, M. The paradoxical association between inherited factor VII deficiency and venous thrombosis. Haemophilia 2008, 14, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacoviello, L.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; De Knijff, P.; D’Orazio, A.; Amore, C.; Arboretti, R.; Kluft, C.; Benedetta Donati, M. Polymorphisms in the coagulation factor VII gene and the risk of myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, E.A.; Sturm, A.C.; Misita, C.P.; Moll, S. Homocysteine and MTHFR Mutations: Relation to Thrombosis and Coronary Artery Disease. Circulation 2005, 111, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, M.T.; Danesin, C.; Saggiorato, G.; Tormene, D.; Simioni, P.; Spiezia, L.; Patrassi, G.M.; Girolami, A. The PAI-1 gene 4G/5G polymorphism and deep vein thrombosis in patients with inherited thrombophilia. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2003, 9, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-A.; Ko, Y.-L.; Hsu, T.-S.; Chang, C.J.; Teng, M.S.; Wu, S.; Hsu, L.A. Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme Gene Polymorphisms and the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism in an Ethnically Chinese Population Living in Taiwan. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2011, 27, 252–258. [Google Scholar]
- Makris, T.K.; Stavroulakis, G.A.; Dafni, U.G.; Gialeraki, A.E.; Krespi, P.G.; Hatzizacharias, A.N.; Tsoukala, C.G.; Vythoulkas, J.S.; Kyriakidis, M.K. ACE/DD genotype is associated with hemostasis balance disturbances reflecting hypercoagulability and endothelial dysfunction in patients with untreated hypertension. Am. Heart J. 2000, 140, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambien, F.; Poirier, O.; Lecerf, L.; Evans, A.; Cambou, J.P.; Arveiler, D.; Luc, G.; Bard, J.M.; Bara, L.; Ricard, S.; et al. Deletion polymorphism in the gene for angiotensin-converting enzyme is a potent risk factor for myocardial infarction. Nature 1992, 359, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhenc-Gelas, M.; Plu-Bureau, G.; Hugon-Rodin, J.; Picard, V.; Horellou, M.H. GFHT study group on Genetic Thrombophilia. Thrombotic risk according to SERPINC1 genotype in a large cohort of subjects with antithrombin inherited deficiency. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noiri, J.; Matsuzoe, H.; Nagaya, S.; Nishio, R.; Matsumoto, D.; Takaishi, H.; Morishita, E. A case of venous thromboembolism caused by protein C deficiency due to a novel gene mutation. J. Cardiol. Cases 2022, 26, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Liu, Z.; Chen, B. Protein C deficiency resulting from two mutations in PROC presenting with recurrent venous thromboembolism. J. Vasc. Surg. Cases Innov. Tech. 2017, 3, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Tun, A.M.; Gupta, K.; Tuma, F. Protein S Deficiency. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544344/ (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G.; Becattini, C.; Bueno, H.; Geersing, G.J.; Harjola, V.P.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Jennings, C.S.; Jiménez, D.; et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 543–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, G.; Vicaut, E.; Danays, T.; Agnelli, G.; Becattini, C.; Beyer-Westendorf, J.; Bluhmki, E.; Bouvaist, H.; Brenner, B.; Couturaud, F.; et al. PEITHO Investigators. Fibrinolysis for patients with intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R. Pentoxifylline—A biomedical profile. J. Med. 1979, 10, 307–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saraste, A.; Knuuti, J. ESC 2019 guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes: Recommendations for cardiovascular imaging. Herz 2020, 45, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gerhard-Herman, M.D.; Gornik, H.L.; Barrett, C.; Barshes, N.R.; Corriere, M.A.; Drachman, D.E.; Fleisher, L.A.; Fowkes, F.G.R.; Hamburg, M.N.; Kinlay, S.; et al. 2016 AHA/ACC Guideline on the Management of Patients With Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2017, 135, e726–e779, Erratum in Circulation 2017, 135, e791–e792. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Writing Committee Members; Creager, M.A.; Hamburg, N.M.; Calligaro, K.D.; Casanegra, A.I.; Freeman, R.; Gordon, P.A.; Gornik, H.L.; Kim, E.S.; Leeper, N.J.; et al. 2021 ACC/AHA/SVM/ACP Advanced Training Statement on Vascular Medicine (Revision of the 2004 ACC/ACP/SCAI/SVMB/SVS Clinical Competence Statement on Vascular Medicine and Catheter-Based Peripheral Vascular Interventions): A Report of the ACC Competency Management Committee. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 998–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsico, F.; Ruggiero, D.; Parente, A.; Pirozzi, E.; Musella, F.; Iudice, F.L.; Savarese, G.; Losco, T.; Giugliano, G.; Rengo, G.; et al. Prevalence and severity of asymptomatic coronary and carotid artery disease in patients with lower limbs arterial disease. Atherosclerosis 2013, 228, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokusai-VTE Investigators; Büller, H.R.; Décousus, H.; Grosso, M.A.; Mercuri, M.; Middeldorp, S.; Prins, M.H.; Raskob, G.E.; Schellong, S.M.; Schwocho, L.; et al. Edoxaban versus warfarin for the treatment of symptomatic venous thromboembolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1406–1415, Erratum in N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 390. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, H.; Yagi, S.; Torii, Y.; Amano, R.; Oomichi, Y.; Sangawa, T.; Fukuda, D.; Kadota, M.; Ise, T.; Ueno, R.; et al. Edoxaban improves acute venous thromboembolism while preserving protein C and protein S levels. J. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallelli, G.; Di Mizio, G.; Palleria, C.; Siniscalchi, A.; Rubino, P.; Muraca, L.; Cione, E.; Salerno, M.; De Sarro, G.; Gallelli, L. Data Recorded in Real Life Support the Safety of Nattokinase in Patients with Vascular Diseases. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Serra, R.; Ielapi, N.; Bitonti, A.; Candido, S.; Fregola, S.; Gallo, A.; Loria, A.; Muraca, L.; Raimondo, L.; Velcean, L.; et al. Efficacy of a Low-Dose Diosmin Therapy on Improving Symptoms and Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Venous Disease: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Miyakis, S.; Lockshin, M.D.; Atsumi, T.; Branch, D.W.; Brey, R.L.; Cervera, R.H.W.M.; Derksen, R.H.; de Groot, P.G.; Koike, T.; Meroni, P.L.; et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbhaiya, M.; Zuily, S.; Naden, R.; Hendry, A.; Manneville, F.; Amigo, M.C.; Amoura, Z.; Andrade, D.; Andreoli, L.; Artim-Esen, B.; et al. 2023 ACR/EULAR Antiphospholipid Syndrome Classification Criteria. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linnemann, B.; Hart, C. Laboratory Diagnostics in Thrombophilia. Hamostaseologie 2019, 39, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arachchillage, D.J.; Mackillop, L.; Chandratheva, A.; Motawani, J.; MacCallum, P.; Laffan, M. Thrombophilia testing: A British Society for Haematology guideline. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 198, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, C.S.W.; Hii, I.; Rahman, A. Simultaneous multiple organ emboli in a patient with solid organ malignancy: A case report. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2019, 3, ytz048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Šimon, S.; Roman, S. Case report of simultaneous phlegmasia cerulea dolens and acute limb ischemia. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2024, 125, 110596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kun, J.; Hunter, J. Massive arterial and venous thrombosis from smouldering multiple myeloma: Further evidence for monoclonal gammopathy of thrombotic significance. BMJ Case Rep. 2024, 17, e260061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiew, Y.R.; Kong, Y. Encephalopathy as the Only Manifestation in Simultaneous Arterial Infarct and Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis in Recent COVID-19 Infection. Am. J. Case Rep. 2022, 23, e938571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lane, D.A.; Grant, P.J. Role of hemostatic gene polymorphisms in venous and arterial thrombotic disease. Blood 2000, 95, 1517–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzimiri, N.; Meyer, B. World distribution of factor V Leiden. Lancet 1996, 347, 481–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorelli, E.; Kaufman, R.J.; Dahlbäck, B. Cleavage of factor V at Arg 506 by activated protein C and the expression of anticoagulant activity of factor V. Blood 1999, 93, 2552–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manten, B.; Westendorp, R.G.; Koster, T.; Reitsma, P.H.; Rosendaal, F.R. Risk factor profiles in patients with different clinical manifestations of venous thromboembolism: A focus on the factor V Leiden mutation. Thromb. Haemost. 1996, 76, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandegar, M.H.; Saidi, B.; Roshanali, F. Extensive arterial thrombosis in a patient with factor V Leiden mutation. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 11, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsvaht, T.; Hermlin, T.; Kern, H.; Kahre, T.; Starkopf, J. Aortic arch thrombosis in a neonate with heterozygous carrier status of factor V Leiden mutation. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2006, 1, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.; Brown, J.R.; Edmondson, R.A.; Tillyer, M.L. Catastrophic arterial thromboembolism associated with factor V Leiden. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2000, 19, 551–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Binder, B.R.; Christ, G.; Gruber, F.; Grubic, N.; Hufnagl, P.; Krebs, M.; Mihaly, J.; Prager, G.W. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1, Physiological and pathophysiological roles. Physiology 2002, 17, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baglin, T. Inherited and acquired risk factors for venous thromboembolism. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 33, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Jin, Y.; Li, X.; Peng, X.; Peng, N.; Song, J.; Xu, M. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) 4G/5G promoter polymorphisms and risk of venous thromboembolism—A meta-analysis and systematic review. Vasa 2020, 49, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, N.; Shu, C.; He, Y.; Zhou, Y. Association between the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 4G/5G polymorphism and risk of venous thromboembolism: A meta-analysis. Thromb. Res. 2014, 134, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, P.-G.; Nilsson, L.; Ardnor, S.N.; Eriksson, P.; Johansson, L.; Stegmayr, B.; Hamsten, A.; Holmberg, D.; Asplund, K. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 4G/5G Polymorphism and Risk of Stroke: Replicated Findings in Two Nested Case–Control Studies Based on Independent Cohorts. Stroke 2005, 36, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaglione, M.; Cappucci, G.; Colaizzo, D.; Giuliani, N.; Vecchione, G.; Grandone, E.; Pennelli, O.; Di Minno, G. The PAI-1 Gene Locus 4G/5G Polymorphism Is Associated With a Family History of Coronary Artery Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosst, P.; Blom, H.J.; Milos, R.; Goyette, P.; Sheppard, C.A.; Matthews, R.G.,; Boers, G.J.H.; Den Heijer, M.; Kluijtmans, L.A.J.; Van Den Heuve, L.P.; et al. A candidate genetic risk factor for vascular disease: A common mutation in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Nat. Genet. 1995, 10, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblatt, D.S. Inherited Disorders of Folate and Cobalamin. In Homocysteine Metabolism: From Basic Science to Clinical Medicine. Developments in Cardiovascular Medicine; Graham, I., Refsum, H., Rosenberg, I.H., Ueland, P.M., Shuman, J.M., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; Volume 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.; Rivera, I.; Ravasco, P.; Jakobs, C.; Blom, H.J.; Camilo, M.E.; De Almeida, I.T. 5,10—Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase 677C→T and 1298A→C mutations are genetic determinants of elevated homocysteine. QJM Int. J. Med. 2003, 96, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harker, L.A.; Harlan, J.M.; Ross, R. Effect of sulfinpyrazone on homocysteine-induced endothelial injury and arteriosclerosis in baboons. Circ. Res. 1983, 53, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harker, L.A.; Ross, R.; Slichter, S.J.; Scott, C.R. Homocystine-induced arteriosclerosis. The role of endothelial cell injury and platelet response in its genesis. J. Clin. Investig. 1976, 58, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthias, D.; Becker, C.H.; Riezler, R.; Kindling, P.H. Homocysteine induced arteriosclerosis-like alterations of the aorta in normotensive and hypertensive rats following application of high doses of methionine. Atherosclerosis 1996, 122, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraci, F.M. Hyperhomocysteinemia: A million ways to lose control. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamler, J.S.; Osborne, J.A.; Jaraki, O.; Rabbani, L.E.; Mullins, M.; Singel, D.; Loscalzo, J. Adverse vascular effects of homocysteine are modulated by endothelium-derived relaxing factor and related oxides of nitrogen. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, M.F.; McDowell, I.F.; Ramsey, M.W.; Brownlee, M.; Bones, C.; Newcombe, R.G.; Lewis, M.J. Hyperhomocysteinemia after an oral methionine load acutely impairs endothelial function in healthy adults. Circulation 1998, 98, 1848–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Welch, G.N.; Loscalzo, J. Homocysteine and atherothrombosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungvari, Z.; Csiszar, A.; Edwards, J.G.; Kaminski, P.M.; Wolin, M.S.; Kaley, G.; Koller, A. Increased superoxide production in coronary arteries in hyperhomocysteinemia: Role of tumor necrosis factor—alpha, NAD(P)H oxidase, and inducible nitric oxide synthase. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, N.; Heydrick, S.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Bierl, C.; Cap,, A.; Loscalzo, J. Cellular redox state and endothelial dysfunction in mildly hyperhomocysteinemic cystathionine beta-synthase-deficient mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiler, H.; Isermann, B.H. Thrombomodulin. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 1, 1515–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentz, S.R.; Sobey, C.G.; Piegors, D.J.; Bhopatkar, M.Y.; Faraci, F.M.; Malinow, M.R.; Heistad, D.D. Vascular dysfunction in monkeys with diet-induced hyperhomocyst(e)inemia. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayal, S.; Bottiglieri, T.; Arning, E.; Maeda, N.; Malinow, M.R.; Sigmund, D.S.; Heistad, D.D.; Faraci, F.M.; Lentz, S.R. Endothelial dysfunction and elevation of S-adenosylhomocysteine in cystathionine beta-synthase-deficient mice. Circ. Res. 2001, 88, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.A.; Lalla, E.; Lu, Y.; Gleason, M.R.; Wolf, B.M.; Tanji, N.; Ferran, L.J.; Kohl, B.; Rao, V.; Kisiel, W.; et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia enhances vascular inflammation and accelerates atherosclerosis in a murine model. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werstuck, G.H.; Lentz, S.R.; Dayal, S.; Hossain, G.S.; Sood, S.K.; Shi, Y.Y.; Zhou, J.; Maeda, N.; Krisans, S.K.; Malinow, M.R.; et al. Homocysteine-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress causes dysregulation of the cholesterol and triglyceride biosynthetic pathways. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.H.; Jeong, M.H.; Sim, D.S.; Hong, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, Y.; Kang, J.C. Pulmonary thromboembolism due to severe hyperhomocysteinemia associated with a methyltetrahydrofolate reductase mutation. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2013, 28, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmadonova, N.A.; Shilova, A.N.; Kozyreva, V.S.; Subbotovskaya, A.I.; Klevanets, J.E.; Karpenko, A.A. Association of folate metabolism gene polymorphisms and pulmonary embolism: A case-control study of West-Siberian population. Thromb. Res. 2015, 135, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basol, N.; Karakus, N.; Savas, A.Y.; Kaya, I.; Karakus, K.; Yigit, S. The importance of MTHFR C677T/A1298C combined polymorphisms in pulmonary embolism in Turkish population. Medicina 2016, 52, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandanpour, N.; Willis, G.; Meyer, F.J.; Armon, M.P.; Loke, Y.K.; Wright, A.J.; Finglas, P.M.; Jennings, B.A. Peripheral arterial disease and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T mutations: A case-control study and meta-analysis. J. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 49, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Silva, D.; Malone, M.V.; Seetharaman, K. MTHFR A1298C and C677T Polymorphisms Are Associated with Increased Risk of Venous Thromboembolism: A Retrospective Chart Review Study. Acta Haematol. 2017, 138, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Heijer, M.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Blom, H.J.; Gerrits, W.B.; Bos, G.M. Hyperhomocysteinemia and venous thrombosis: A meta-analysis. Thromb. Haemost. 1998, 80, 874–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aday, A.W.; Duran, E.K.; Van Denburgh, M.; Kim, E.; Christen, W.G.; Manson, J.E.; Ridker, P.M.; Pradhan, A.D. Homocysteine Is Associated With Future Venous Thromboembolism in 2 Prospective Cohorts of Women. Arter. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, P.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Lu, Z. Association between MTHFR C677T polymorphism and venous thromboembolism risk in the Chinese population: A meta-analysis of 24 case-controlled studies. Angiology 2015, 66, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirstoveanu, C.; Calin, N.; Heriseanu, C.; Filip, C.; Vasile, C.M.; Margarint, I.; Marcu, V.; Dimitriu, M.; Ples, L.; Tarnoveanu, S.; et al. Consistent Correlation between MTHFR and Vascular Thrombosis in Neonates-Case Series and Clinical Considerations. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Au-Yeung, K.K.; Woo, C.W.; Sung, F.L.; Yip, J.C.; Siow, Y.L.; O, K. Hyperhomocysteinemia activates nuclear factor-kappaB in endothelial cells via oxidative stress. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigat, B.; Hubert, C.; Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Cambien, F.; Corvol, P.; Soubrier, F. An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene accounting for half the variance of serum enzyme levels. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 1343–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiret, L.; Rigat, B.; Visvikis, S.; Breda, C.; Corvol, P.; Cambien, F.; Soubrier, F. Evidence, from combined segregation and linkage analysis, that a variant of the angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) gene controls plasma ACE levels. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1992, 51, 197–205. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, S.; Elliott, H.L.; Morton, J.J.; Connell, J.M. Enhanced pressor response to angiotensin I in normotensive men with the deletion genotype (DD) for angiotensin-converting enzyme. Hypertension 1995, 25, 1266–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, P.K.; Griendling, K.K. Angiotensin II cell signaling: Physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C82–C97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambien, F.; Costerousse, O.; Tiret, L.; Poirier, O.; Lecerf, L.; Gonzales, M.F.; Evans, A.; Arveiler, D.; Cambou, J.P.; Luc, G. Plasma level and gene polymorphism of angiotensin-converting enzyme in relation to myocardial infarction. Circulation 1994, 90, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, E.; Corneli, P.S.; Anderson, J.L.; Marshall, H.W.; Lalouel, J.M.; Ward, R.H. Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphism is associated with myocardial infarction but not with development of coronary stenosis. Circulation 1995, 91, 2120–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.J.; Vaughan, D.E. The Renin-Angiotensin and fibrinolytic systems co-conspirators in the pathogenesis of ischemic cardiovascular disease. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 1996, 6, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Gaboury, C.L.; Conlin, P.R.; Seely, E.W.; Williams, G.H.; Vaughan, D.E. Stimulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor in vivo by infusion of angiotensin II. Evidence of a potential interaction between the renin-angiotensin system and fibrinolytic function. Circulation 1993, 87, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, R.T.; Kol, A.; Andreotti, F.; Kluft, C.; Maseri, A.; Sperti, G. Angiotensin II increases plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 and tissue-type plasminogen activator messenger RNA in cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Circulation 1994, 90, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, D.E.; Lazos, S.A.; Tong, K. Angiotensin II regulates the expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cultured endothelial cells. A potential link between the renin-angiotensin system and thrombosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feener, E.P.; Northrup, J.M.; Aiello, L.P.; King, G.L. Angiotensin II induces plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and -2 expression in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-K.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, S.; Gwon, H.-C.; Ryu, J.C.; Huh, J.E.; Choo, J.A.; Choi, Y.; Rhee, C.H.; Lee, W.R. Polymorphism of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Gene Is Associated With Circulating Levels of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biolog. 1997, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilley, A.; Austin, H.; Hooper, W.C.; Lally, C.; Ribeiro, J.A.; Wenger, N.K.; Rawlins, P.; Evatt, B. Relation of three genetic traits to venous thrombosis in an African-American population. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1998, 147, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philipp, C.S.; Dilley, A.; Saidi, P.; Evatt, B.; Austin, H.; Zawadsky, J.; Harwood, D.; Ellingsen, D.; Barnhart, E.; Phillips, D.J.; et al. Deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin-converting enzyme gene as a thrombophilic risk factor after hip arthroplasty. Thromb. Haemost. 1998, 80, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, J.G.; Carreira, J.F.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Sánchez, L.M.; Díaz, R.A.; Martinez, M.A.; Garcia, E.C. Risk of venous thromboembolism associated with the insertion/deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin-converting enzyme gene. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2000, 11, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, A.; Brown, K.; Langdown, J.; Luddington, R.; Baglin, T. Effect of the angiotensin-converting enzyme gene deletion polymorphism on the risk of venous thromboembolism. Br. J. Haematol. 2000, 111, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, F.-C.; Hsu, L.-A. Meta-Analysis of Association Between Insertion/Deletion Polymorphism of the Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Gene and Venous Thromboembolism. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2011, 17, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ivanova, N. A Sole Case of Concurrent Arterial and Venous Thromboses with Massive Pulmonary Embolism and Carriage of Four Genetic Polymorphisms: Factor V Leiden, PAI-1 4G/5G, MTHFR C677T, and ACE I/D—A Case Report. Reports 2025, 8, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8030167
Ivanova N. A Sole Case of Concurrent Arterial and Venous Thromboses with Massive Pulmonary Embolism and Carriage of Four Genetic Polymorphisms: Factor V Leiden, PAI-1 4G/5G, MTHFR C677T, and ACE I/D—A Case Report. Reports. 2025; 8(3):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8030167
Chicago/Turabian StyleIvanova, Nevena. 2025. "A Sole Case of Concurrent Arterial and Venous Thromboses with Massive Pulmonary Embolism and Carriage of Four Genetic Polymorphisms: Factor V Leiden, PAI-1 4G/5G, MTHFR C677T, and ACE I/D—A Case Report" Reports 8, no. 3: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8030167
APA StyleIvanova, N. (2025). A Sole Case of Concurrent Arterial and Venous Thromboses with Massive Pulmonary Embolism and Carriage of Four Genetic Polymorphisms: Factor V Leiden, PAI-1 4G/5G, MTHFR C677T, and ACE I/D—A Case Report. Reports, 8(3), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports8030167






