Black Esophagus and Recurrence of Duodenal Ulcers: Two Signs of the Same Pathogenic Pathway? A Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Detailed Case Description
2.1. Chief Complaints
2.2. History of Present Illness
2.3. History of Past Illness
2.4. Medical Therapy at Admission
2.5. Physical Examination
2.6. Laboratory Examinations
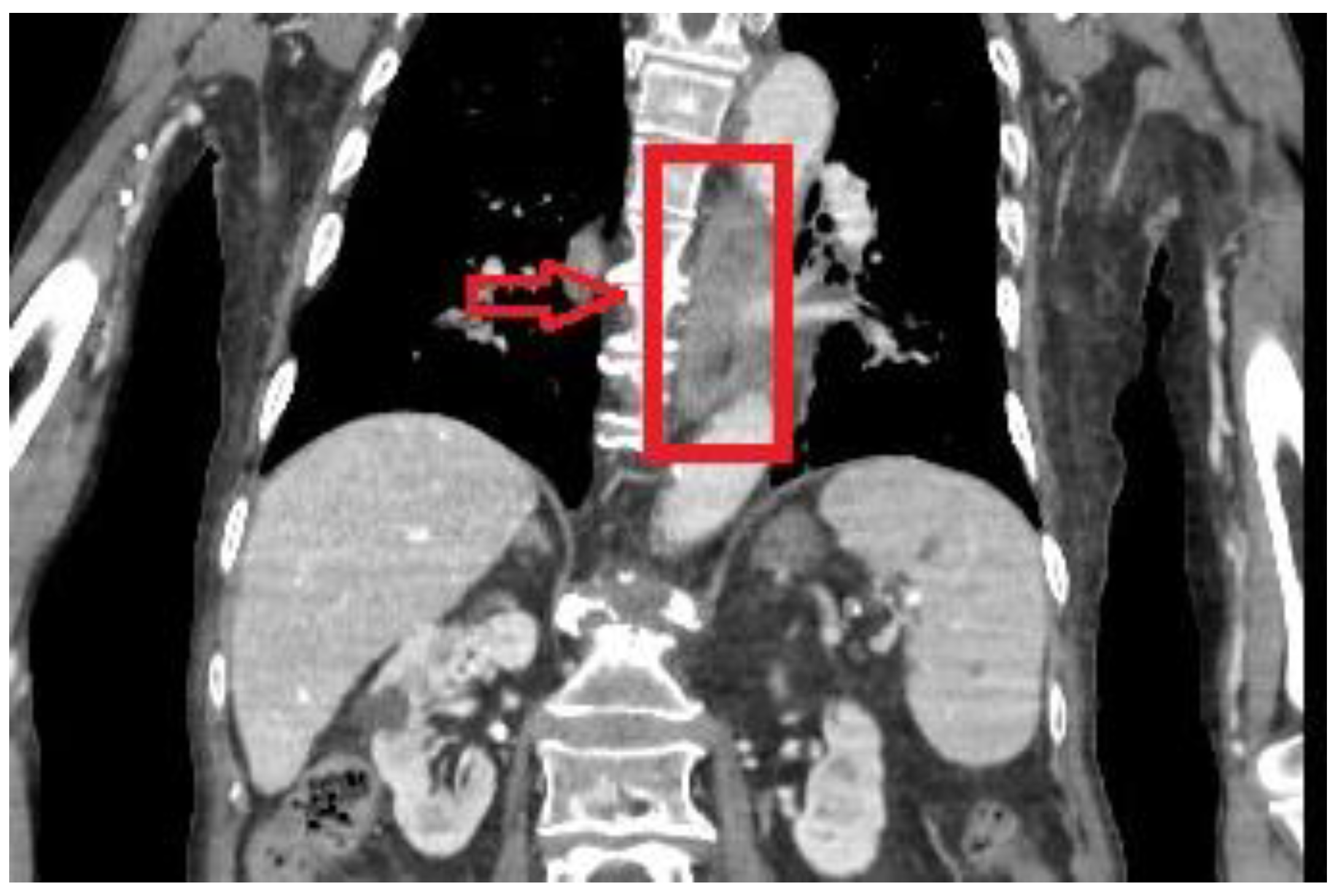
2.7. Imaging Examination
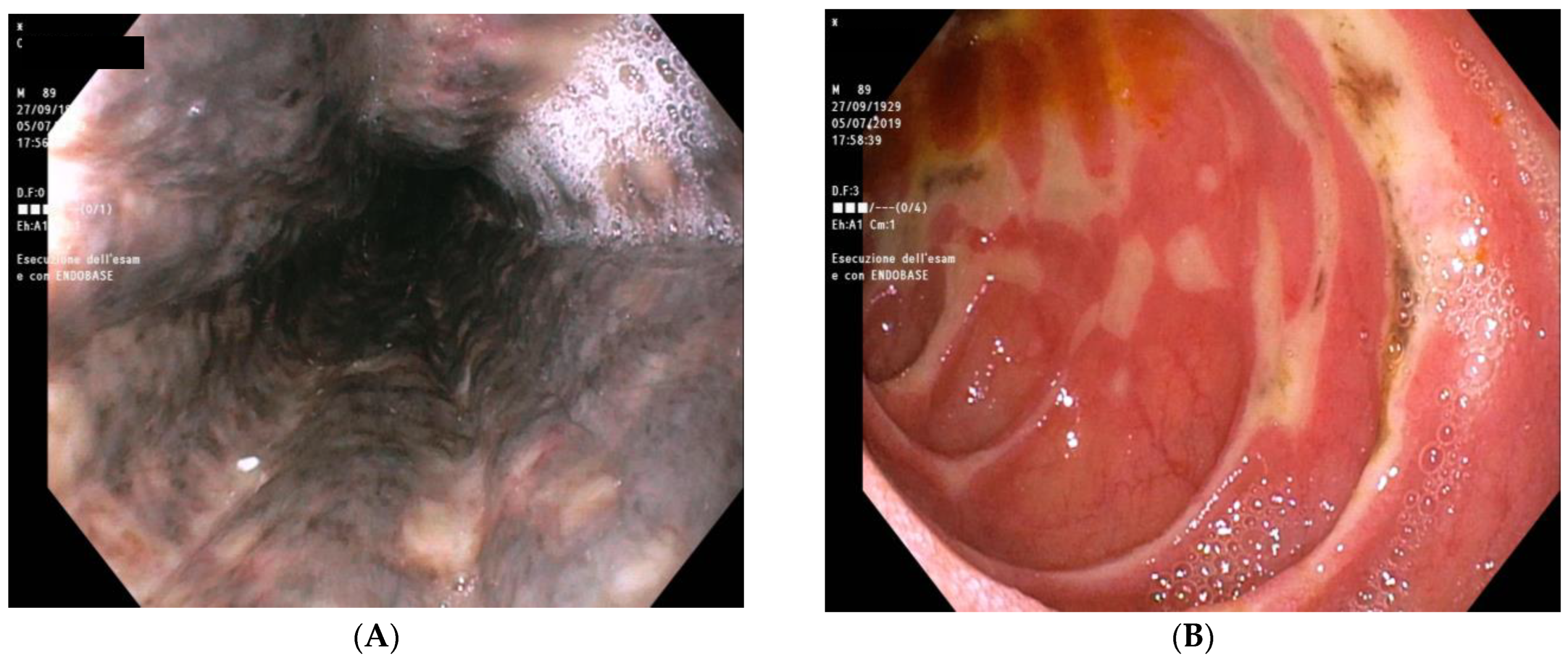
2.8. Further Diagnostic Work-Up
2.9. Final Diagnosis
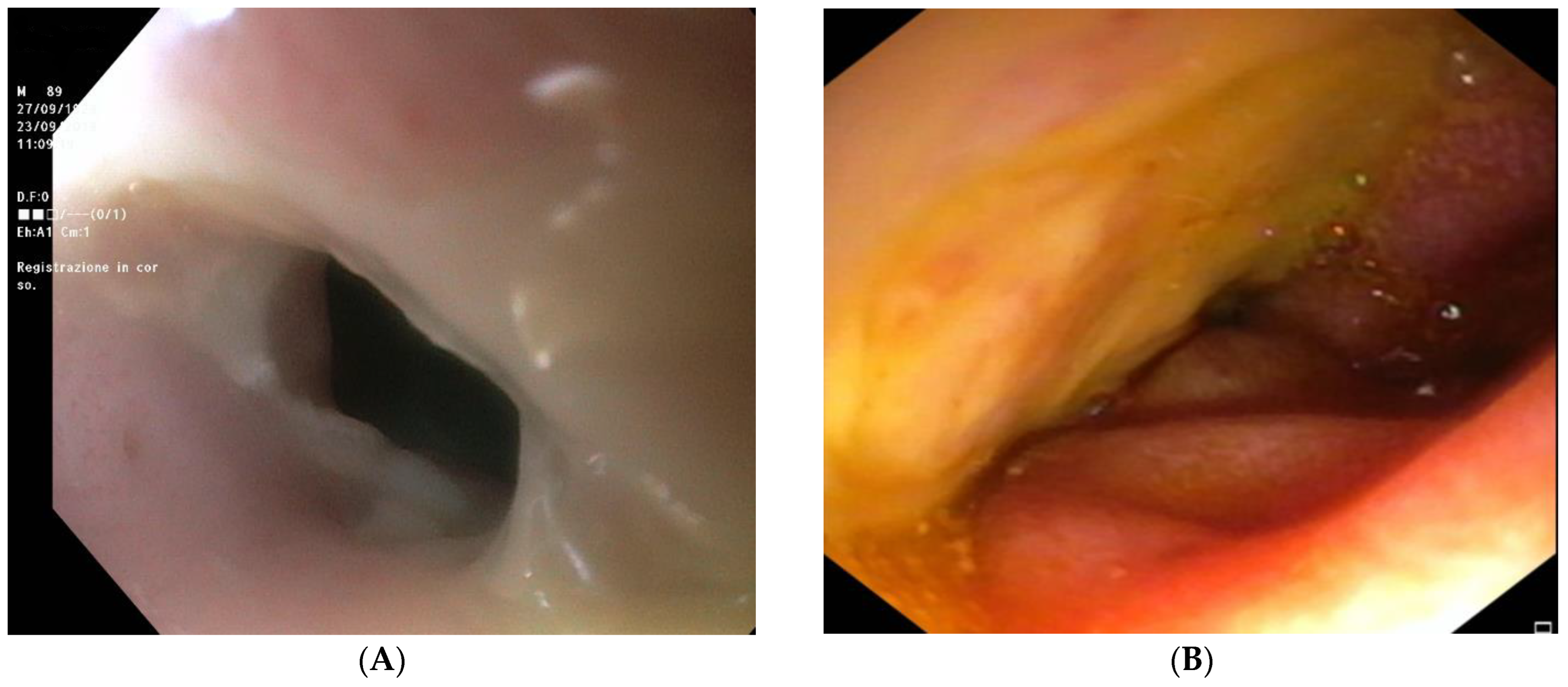
2.10. Treatment
2.11. Outcome and Follow-Up
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldenberg, S.P.; Wain, S.L.; Marignani, P. Acute necrotizing esophagitis. Gastroenterology 1990, 98, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy, B.E.; Toor, A.; Bensen, S.P.; Rothstein, R.I.; Maheshwari, Y. Acute esophageal necrosis: Report of two cases and a review of the literature. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1999, 49, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, F.; Fernandes, V.; Cremers, M.I.; Oliveira, A.P.; Lobato, C.; Alves, A.L.; Pinho, C.; de Freitas, J. Acute necrotizing esophagitis: A large retrospective case series. Endoscopy 2004, 36, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurvits, G.E.; Shapsis, A.; Lau, N.; Gualtieri, N.; Robilotti, J.G. Acute esophageal necrosis: A rare syndrome. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 42, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- eSilva Rodrigues, B.D.; dos Santos, R.; da Luz, M.M.P.; Chaves e Silva, F.; Reis, I.G.N. Acute esophageal necrosis. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 9, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurvits, G.E.; Cherian, K.; Shami, M.N.; Korabathina, R.; El-Nader, E.M.A.; Rayapudi, K.; Gandolfo, F.J.; Alshumrany, M.; Patel, H.; Chowdhury, D.N.; et al. Black Esophagus: New Insights and Multicenter International Experience in 2014. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichart, M.; Busch, O.R.C.; Bruno, M.J.; Van Lanschot, J.J.B. Black esophagus: A view in the dark. Dis. Esophagus 2008, 13, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurvits, G.E. Black esophagus: Acute esophageal necrosis syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 3219–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, H.; Yamada, M.; Endo, Y.; Inoue, K.; Yoshiba, M. Acute necrotizing esophagitis: Role of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 41, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelrud, D.; Noyer, C.M.; Brandt, L.J.; Brenner, S.M. LB-TAJ, 2000 undefined. Clinical features and outcomes of acute necrotizing esophagitis (black esophagus). Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, G.; Perego, D.; Corti, G.; Cambareri, A.R.; Buda, C.A.; Zoldan, C.; Baldini, V. Black esophagus: Should it be considered an unfavorable prognostic factor? Dis. Esophagus 2001, 14, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambyrajah, J.; Landray, M.J.; McGlynn, F.J.; Jones, H.J.; Wheeler, D.C.; Townend, J.N. Abnormalities of endothelial function in patients with predialysis renal failure. Heart 2000, 83, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghbayan, H.; Sarker, A.K.; Coomes, E.A. Black esophagus: Acute esophageal necrosis complicating diabetic ketoacidosis. CMAJ 2018, 190, E1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohra, I.; Attar, B.; Almoghrabi, A. Black Esophagus Due to Acute Necrosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqi, A.; Chaudhary, F.S.; Naqvi, H.A.; Saleh, N.; Farooqi, R.; Yousaf, M.N. Black esophagus: A syndrome of acute esophageal necrosis associated with active alcohol drinking. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2020, 7, e000466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padda, A.; Mandalia, A.; Sawalha, A.H. Clinical Images: Black Esophagus in Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odelowo, O.O.; Hassan, M.; Nidiry, J.J.; Marshalleck, J.J. Acute necrotizing esophagitis: A case report. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2002, 94, 735–737. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burtally, A.; Gregoire, P. Acute esophageal necrosis and low-flow state. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 21, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Soussan, E.; Savoye, G.; Hochain, P.; Hervé, S.; Antonietti, M.; Lemoine, F.; Ducrotté, P. Acute esophageal necrosis: A 1-year prospective study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2002, 56, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie-Christine, B.I.; Pascal, B.; Jean-Pierre, P. Acute necrotizing esophagitis: Another case. Gastroenterology 1991, 101, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.; Weissman, S.; Ahmad, S. The black esophagus and duodenum: A rare case report. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2020, 13, 264–267. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32821358 (accessed on 26 March 2021). [PubMed]
- Rejchrt, S.; Douda, T.; Kopáčová, M.; Široký, M.; Repák, R.; Nožička, J.; Špaček, J.; Bureš, J. Acute esophageal necrosis (Black Esophagus): Endoscopic and histopathologic appearance. Endoscopy 2004, 36, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitawaki, D.; Nishida, A.; Sakai, K.; Owaki, Y.; Nishino, K.; Noda, Y.; Imaeda, H. Gurvits syndrome: A case of acute esophageal necrosis associated with diabetic ketoacidosis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maubert, A.; Frey, S.; Rahili, A.; Filippi, J.; Benizri, E. Acute esophageal necrosis: Case report of an unknown entity. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2019, 61, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenveld, R.L. A black perforated esophagus treated with surgery: Report of a case. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2013, 5, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, D.A.; Francis, D.L.; Baron, T.H. Proximal black esophagus: A case report and review of the literature. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2009, 70, 180–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, N.; Neupane, R.; Bhatia, U.; Singla, A.; Rana, K. Isolated Proximal Black Esophagus in a COVID-19 Patient. Cureus 2023, 15, e36311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudell, A.B.M.; Mueller, P.S.; Viggiano, T.R. Black esophagus: Report of six cases and review of the literature, 1963–2003. Dis. Esophagus 2006, 19, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bong, H.S.S.; Soh, Y.S.A.; Shabbir, A.; So, J.B.Y. Gastrointestinal: Black esophagus. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangan, T.F.; Colley, A.T.; Wytock, D.H. Antibiotic-associated acute necrotizing esophagitis. Gastroenterology 1990, 99, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, T.S.; Helton, R.; Zaidi, Z. Total Parenteral Nutrition Successfully Treating Black Esophagus Secondary to Hypovolemic Shock. Case Rep. Gastrointest. Med. 2017, 2017, 4396870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, J.; Chavalitdhamrong, D.; Jensen, D.M.; Cortina, G.; Manuyakorn, A.; Jutabha, R. The Significance of Gastric and Duodenal Histological Ischemia Reported on Endoscopic Biopsy. A Case Series. Endoscopy 2011, 43, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Laboratory Test | Value | Normal Range |
|---|---|---|
| White Blood Cells | 24 × 103/mmc | 4–10 × 103/mmc |
| Hemoglobin | 11.8 g/dL | 12.5–17 g/dL |
| Hematocrit | 35.5% | 40–50% |
| Platelets | 204 × 103/mmc | 150–400 × 103/mmc |
| Prothrombin activity | 62% | 70–130% |
| Fibrinogen | 647 mg/dL | 200–450 mg/dL |
| C-reactive Protein | 2.1 mg/dL | Up to 0.6 mg/dL |
| Creatinine | 1.61 mg/dL | 0.6–1.4 mg/dL |
| Fasting glucose | 334 mg/dL | 60–110 mg/dL |
| Albumin | 2.39 g/dL | 4.02–4.76 g/dL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balducci, D.; Quatraccioni, C.; Daretti, L.M.; Montori, M.; Bendia, E.; Maroni, L.; Benedetti, A. Black Esophagus and Recurrence of Duodenal Ulcers: Two Signs of the Same Pathogenic Pathway? A Case Report. Reports 2023, 6, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports6030037
Balducci D, Quatraccioni C, Daretti LM, Montori M, Bendia E, Maroni L, Benedetti A. Black Esophagus and Recurrence of Duodenal Ulcers: Two Signs of the Same Pathogenic Pathway? A Case Report. Reports. 2023; 6(3):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports6030037
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalducci, Daniele, Claudia Quatraccioni, Luigi Maria Daretti, Michele Montori, Emanuele Bendia, Luca Maroni, and Antonio Benedetti. 2023. "Black Esophagus and Recurrence of Duodenal Ulcers: Two Signs of the Same Pathogenic Pathway? A Case Report" Reports 6, no. 3: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports6030037
APA StyleBalducci, D., Quatraccioni, C., Daretti, L. M., Montori, M., Bendia, E., Maroni, L., & Benedetti, A. (2023). Black Esophagus and Recurrence of Duodenal Ulcers: Two Signs of the Same Pathogenic Pathway? A Case Report. Reports, 6(3), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports6030037






