Abstract
Background: Hospital-acquired infections with extensively drug-resistant (XDR) Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) have become a worrisome concern because of unfavorable outcomes and limited antimicrobial treatment options. Studies with new antimicrobial substances against XDR-PA show very promising results in different infection types, but the data for central nervous system (CNS) infections are scarce. Case presentation: Here, we report the case of a young patient with healthcare-associated meningitis caused by XDR-PA following severe craniocerebral injury. An off-label use of high-dose ceftolozane/tazobactam (C/T) monotherapy was administered for 10 days in parallel with source-controlling measures. Clinical and microbial recovery could be accomplished promptly. Conclusion: In patients with hospital-acquired CNS infections due to XDR-PA, C/T might be a new, safe and effective alternative with fewer adverse effects compared to older polymyxin- or aminoglycoside-based regimens.
1. Introduction
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) has become a major healthcare burden in recent years due to severe healthcare-associated infections and poor outcomes [1]. The treatment of PA is challenging due to its resistance to several antibiotics, including β-lactams. Resistance mechanisms include the production of AmpC β-lactamases, efflux pumps, the acquisition of extended-spectrum β-lactamases and carbapenemases. This led to a ‘comeback’ of older antibacterial substances such as polymyxins (colistin), aminoglycosides and fosfomycin in multidrug-resistant (MDR)-PA infections. Unfavorable side effects and unsatisfactory clinical success rates are major drawbacks of these antibiotics [2,3,4].
Ceftolozane/tazobactam (C/T) is a new fifth-generation cephalosporin that has been approved in adults for the treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections, complicated urinary tract infections, hospital-associated pneumonia and ventilator-acquired pneumonia [5,6,7]. Even though the clinical success rate in the off-label use of C/T in MDR- and extensively drug-resistant (XDR)-PA infections is as high as 76% [8], clinical efficacy data for PA-induced central nervous system (CNS) infections are rare. C/T for the treatment of meningitis has been described in the literature only in case reports.
Here, we report the clinical case of a 16-year-old polytraumatized girl admitted to the emergency department with severe craniocerebral injury and abdominal blunt trauma. The disease course was complicated by hospital-acquired meningitis with XDR-PA, which was successfully treated with C/T monotherapy for 10 days.
2. Case Presentation
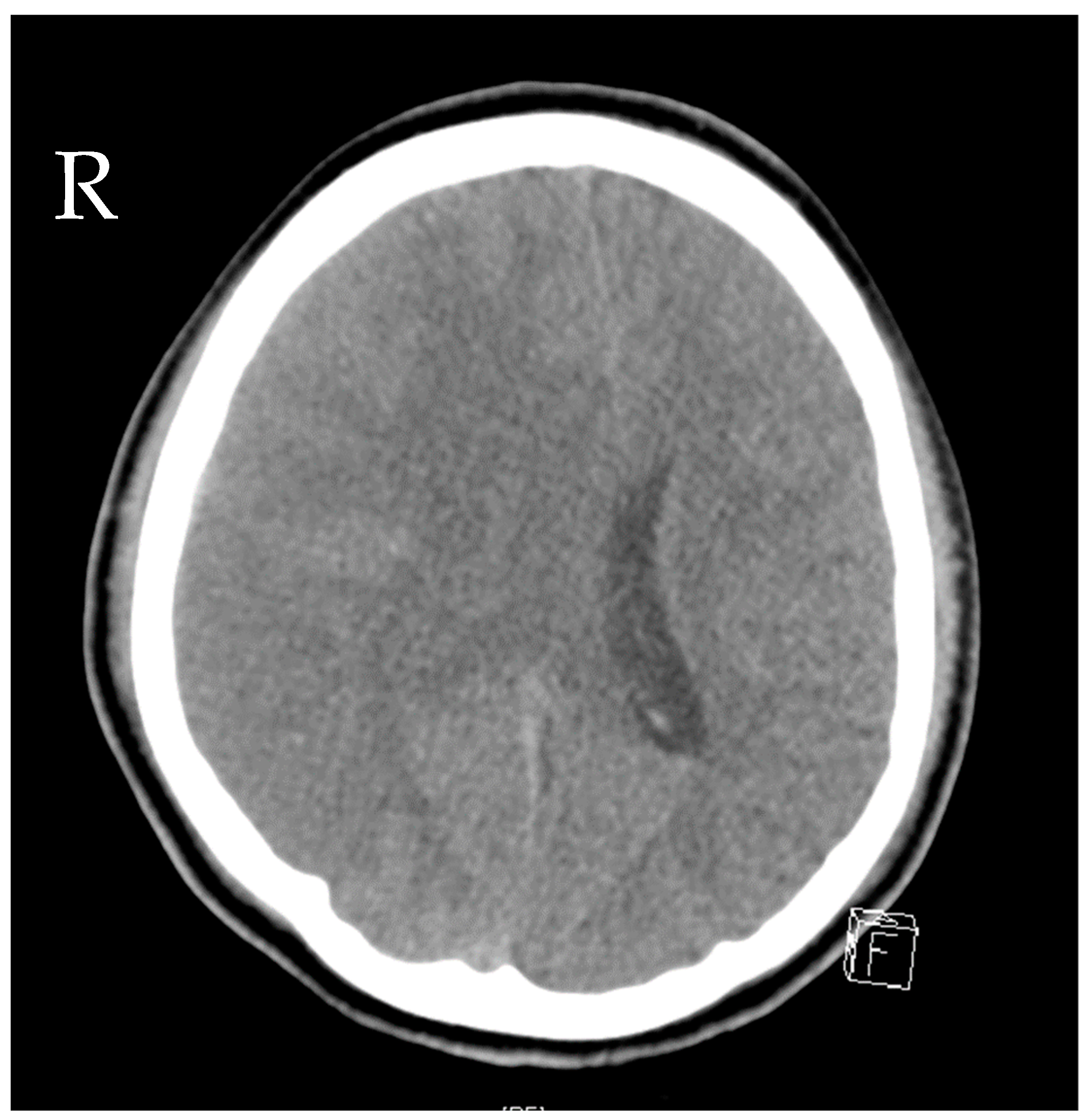
A 16-year-old girl was admitted to the emergency department after a car crash. By the time of admission, she was intubated, haemodynamically unstable and showed anisocoria. Haemodynamic instability was due to pneumothoraxes on both sides. Pleural drainage tubes were inserted immediately, and the circulation improved. A computed tomography scan showed polytrauma with severe craniocerebral injury and traumatic dissection of the right internal carotid artery. Moreover, there were severe bilateral pulmonary contusions, the laceration of the spleen and liver, a ruptured bladder with massive venous bleeding and an unstable pelvic fracture. Damage control surgery was performed subsequently with splenectomy, the opening of the bladder and the packing and temporary closure of the abdomen. The fractured pelvis was stabilized with an external fixator, and an intraventricular catheter was inserted to monitor the intracranial pressure (ICP). Only a few hours after the initial procedure, the patient presented with increasing ICP and dilated pupils on both sides. Another computed tomography scan revealed malignant, right hemispheric stroke due to the traumatic dissection with progressive cerebral oedema and signs of herniation (Figure 1). Decompressive craniectomy was conducted immediately to control the ICP. Postoperatively, the patient suffered multiple epileptic seizures and exhibited increasing blood sodium levels due to central diabetes insipidus.
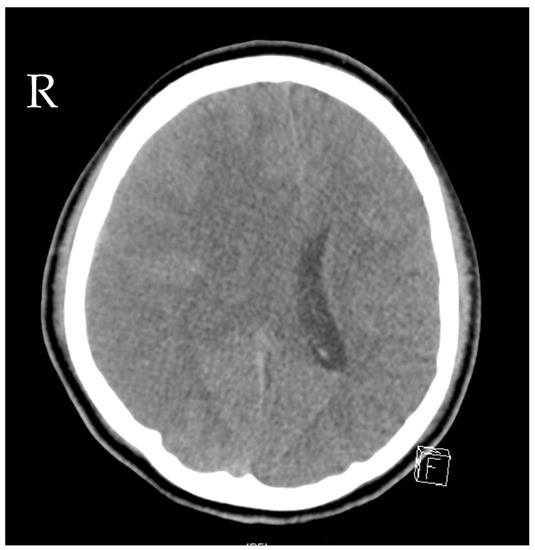
Figure 1.
Computed tomography of the head showing cerebral oedema and signs of herniation.
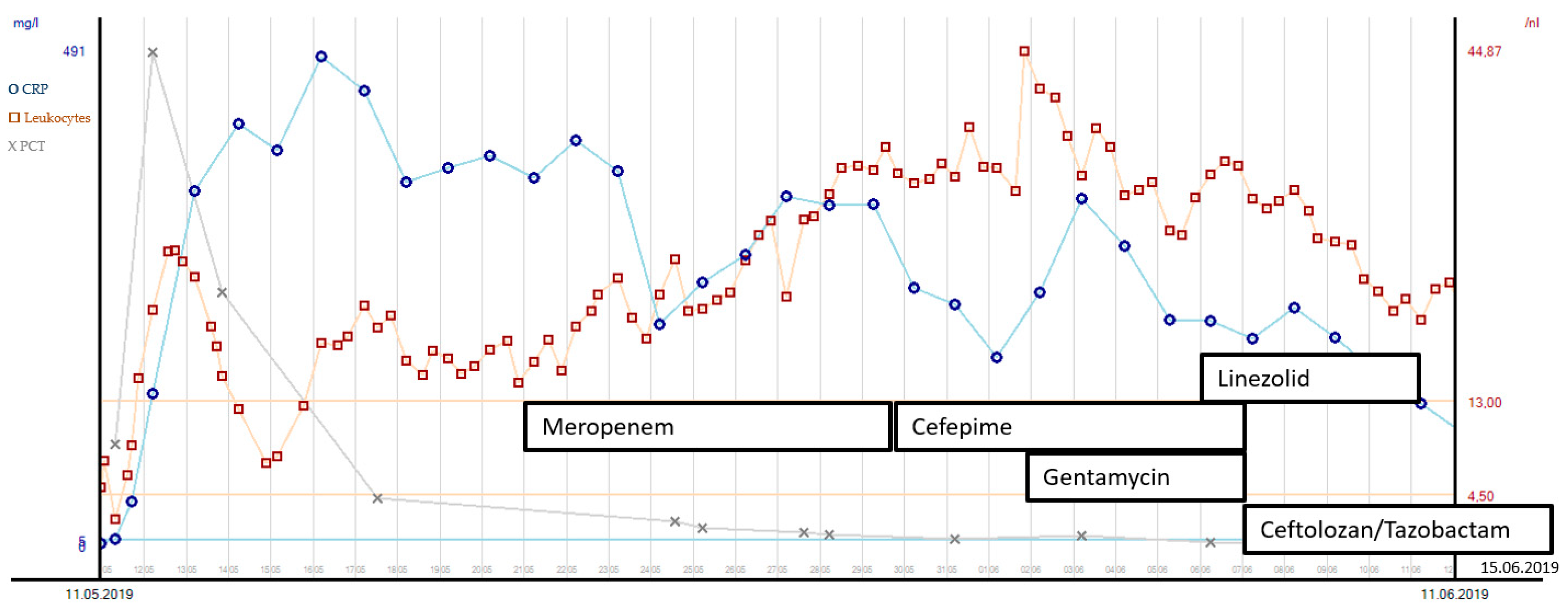
In the following 4 weeks, several re-laparotomies were performed to control the severe abdominal trauma and unclosed traumatic bladder injury. First, microbiology cultures from intra-abdominal swabs revealed broadly susceptible PA strains. Meropenem was administered due to its low sodium content and its probably lesser epileptogenic potential compared to imipenem. After the sixth abdominal procedure (at day 17), PA strains in abdominal swabs revealed multidrug resistance and were susceptible only to cefepime, fluoroquinolones and colistin. Therefore, cefepime was administered in combination with gentamicin for 7 days. Liver function was not compromised due to liver laceration. Another incision and stitching of the bladder were performed on day 21, after which XDR-PA strains were cultured in fresh abdominal swabs. These strains presented with resistance to cefepime and fluoroquinolones, so a new fifth-generation cephalosporin in combination with an old beta-lactamase inhibitor ceftolozane/tazobactam (C/T) was applied for a total of 10 days, since the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) for C/T was 1 µg/mL. The microorganisms found and the antibiotic susceptibility testing results are displayed in Table 1. See Figure 2 for the leucocyte count, procalcitonin (PCT) and c-reactive protein (CRP) course with corresponding antibiotic treatment over the first 30 days of the patient’s ICU stay. The patient’s kidney function showed an initial peak on day 2 after ICU admission with acute kidney insufficiency (creatinine values of 1.67 mg/dL, clearance 45 mL/min CKD-EPI) due to severe crush syndrome. The creatinine values normalized soon thereafter with normal values (clearance > 60 mL/min/1.73 m2) throughout the ICU stay. Due to severe craniocerebral injury and cerebral infarction, long-term dependency from mechanical ventilation was expected. This led to surgical tracheostomy on day 10 after ICU admission. During the weaning process, there was one setback with ventilator-associated pneumonia due to Serratia marcescens (see Table 1 for the susceptibility results). After the antibiotic treatment course with cefepime, pneumonia resumed, and weaning could be proceeded. Three weeks after tracheostomy, the patient could be successfully weaned from the ventilator.

Table 1.
Microorganisms found and antibiotic susceptibility testing results.
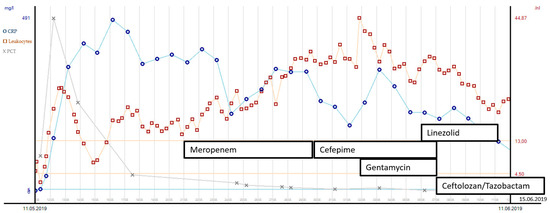
Figure 2.
Leucocyte count, PCT and CRP course with corresponding antibiotic treatment during the first 30 days after ICU admission.
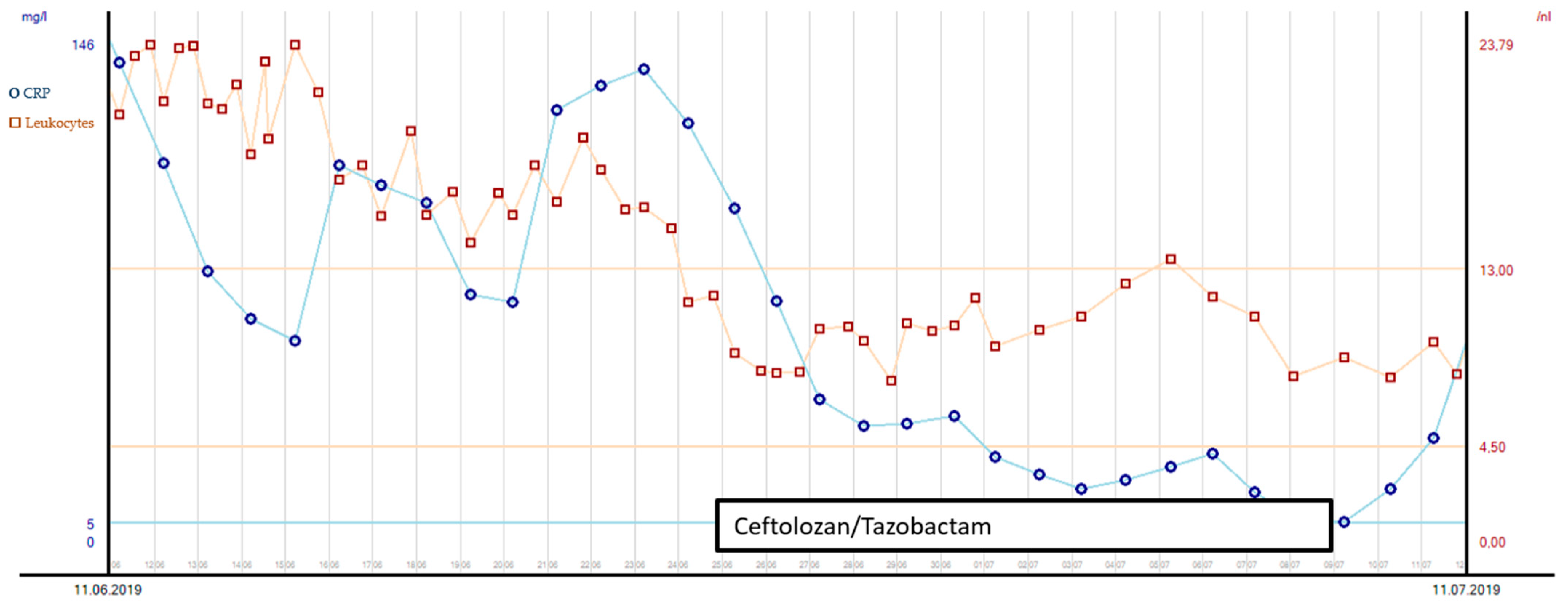
Elevated intracranial pressure due to the demarcation of infarction with secondary hydrocephalus was another challenge during the patient’s stay in intensive care. An external ventricular drain (EVD) was inserted after the hemicraniectomy on day 3. The removal of the EVD after 14 days led to a further increase in ICP and hydrocephalus, so a lumbar drain (LD) was inserted instead. On day 34 after the initial accident and day 5 after LD insertion, the quality of the liquor changed from colorless to yellow green. Additionally, her neurological status worsened, with reduced movements on the left side of her body. Although signs of inflammation in the blood had already peaked (see Figure 3), the liquor presented with an increased cell count. Carbapenem-resistant XDR-PA could be isolated from the liquor sample (as assessed by culture-based resistance testing). Although ciprofloxacin’s MIC was ≤0.25 µg/mL (sensitive, S), we did not consider it to be a suitable therapy for two reasons: the patient suffered from recurring epileptic seizures, and previous PA strains from intra-abdominal samples showed fluoroquinolone resistance. Gentamicin was not considered for use because we have already used it before, along with the risk of nephrotoxicity and a history of crush syndrome in this patient. Alternatively, C/T was used for antibacterial therapy and administered as a prolonged infusion over 3 h: 3 × 2 g + 1 g/24 h for 10 days, with an initial bolus of 3 g. See Figure 3 for the leucocyte count and the c-CRP course with the corresponding antibiotic treatment from days 31 and 60 of the patient’s ICU stay.
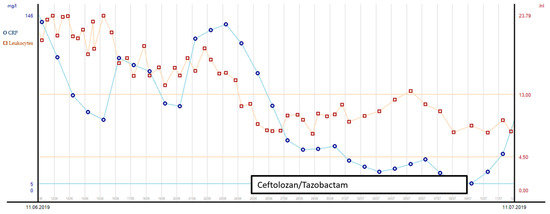
Figure 3.
Leucocyte count and CRP course with corresponding antibiotic treatment during days 31 and 60 after ICU admission.
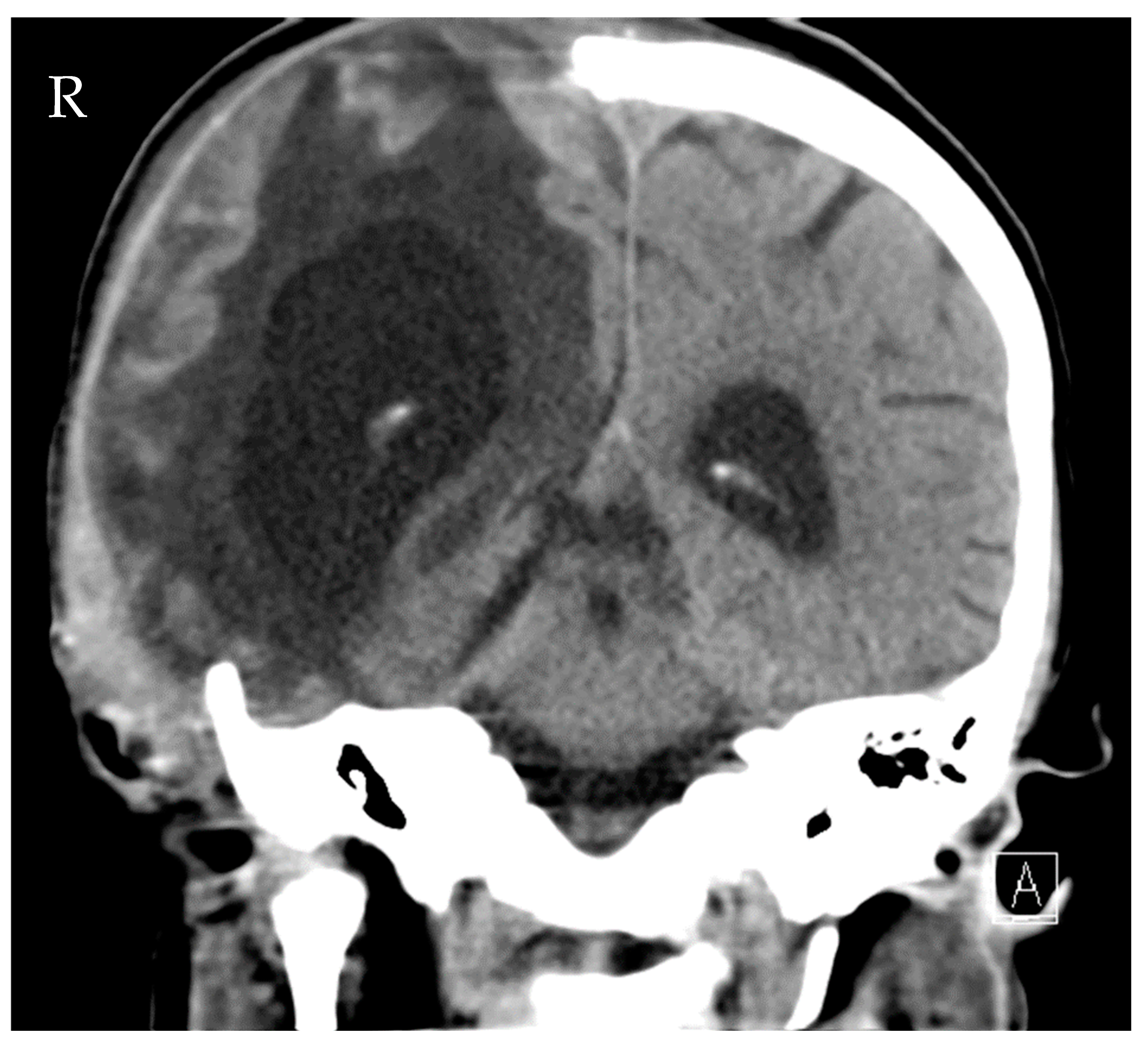
Source control was also conducted: the initial LD was removed, and a new EVD was inserted due to ongoing high ICP (combination of hydrocephalus e vacuo and malresorptivus). See Figure 4 for the corresponding computed tomography. Therapy success was measured through microbiology cure: The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) culture became negative after 7 days of C/T treatment, and the CSF cell count decreased. The neurological status improved rapidly as a sign of clinical therapy success, and the CRP and leucocytes decreased rapidly, as shown in Figure 3. Another 10 days later, the definitive treatment of hydrocephalus could be obtained with a ventriculoatrial catheter. By the time of hospital discharge, the patient was awake and able to move all four extremities.
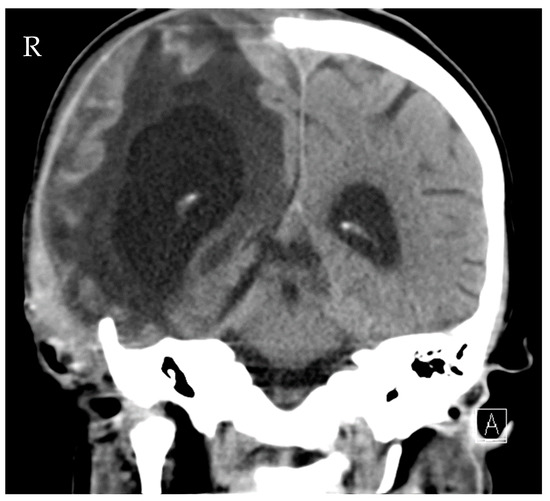
Figure 4.
Computed tomography of the head showing distinctive hydrocephalus with pronounced enlargement of the ventricular system (malresorptivus and e-vacuo components).
3. Discussion
Our report presents a new and interesting application for C/T because very few data exist for its use in CNS infections caused by XDR-PA. Furthermore, there is almost no information about its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties in an intensive care unit (ICU) setting.
Meningitis is a possible complication in patients with an EVD. The diagnosis of healthcare-associated meningitis following head injury and/or neurosurgery is difficult due to the lack of common symptoms in ICU patients [9]. The most likely pathogens linked to CSF infections are coagulase-negative staphylococci, Staphylococcus aureus, Cutibacterium acnes and Gram-negative bacilli (including PA) [10]. Our patient suffered from complicated intra-abdominal and urinary tract infections with PA due to the difficulty of controlling the focus. Apparently, the emergence of MDR-PA was provoked by recurrent peritonitis with the need for multiple courses of antibacterial treatment [11]. Bacterial translocation occurred, most likely from the abdominal cavity. As this MDR-PA was carbapenem-resistant (meropenem ≥ 16 µg/mL (resistant, R)), anti-infective treatment options were limited: piperacillin/tazobactam ≥ 128 µg/mL (R), cefepime ≥ 64 µg/mL (R), ciprofloxacin = 0.25 µg/mL (S), gentamicin = 2 µg/mL (S), colistin = 0.5 µg/mL (S) and amikacin = 4 µg/mL (S).
Ciprofloxacin has acceptable cerebral penetration, but its use is associated with an increased risk of cerebral seizures. A combination of colistin and gentamicin also seemed to be unfavorable because it can lead to serious nephrotoxicity in critically ill patients [12]. Since this patient showed crush syndrome at the beginning of ICU treatment and was only 16 years old, we did not want to take that risk. Moreover, colistin has poor cerebral penetration and may cause harm to neural cells [2]. The data regarding the CSF penetration of C/T in humans are scarce.
In vitro studies show a better time-kill analysis of MDR-PA when C/T is combined with colistin or fosfomycin compared to C/T alone [13]. The clinical cure rates for C/T monotherapy can be up to 70% in MDR- and XDR-PA infections [8,14]. Based on expert opinions, the early use of antimicrobial combination therapies is recommended in cases of suspected PA infection. As soon as susceptibility testing becomes available, an initial combination therapy should be followed by prompt de-escalation to anti-infective monotherapy [1]. Based on the antibiotic susceptibility pattern of the PA strain isolated from CSF and the disadvantageous pharmacokinetic profile of colistin in this clinical setting, we decided to use C/T monotherapy as a rescue therapy.
C/T for the treatment of meningitis is an off-label use, and, to the best of our knowledge, its use has been described only in several case reports. Most reports used C/T in combination with another PA effective drug, with different results. However, only one study group reported a case with C/T monotherapy that was not successful. McCreary [15] presented a case report of a patient with meningitis caused by MDR-PA, which was successfully treated with a combination therapy of C/T plus ciprofloxacin IV plus metronidazole IV plus tobramycin intraventricularly (IVT). Here, therapeutic concentrations of C/T could be achieved in both CSF and plasma using 3 g IV every 8 h. Meschiari et al. [16] reported a case of a patient with XDR-PA meningitis. This patient was treated effectively using C/T plus meropenem IV and amikacin IV. Winans [17] et al. published a case of MDR-PA meningitis after multiple neurosurgical interventions, which eventually was treated with C/T plus cefepime IV plus gentamicin IV plus gentamicin IVT. Samples of both serum and CSF were analyzed using continuous C/T infusion. The CSF concentration of C/T showed 84% of that in serum, reflecting sufficient therapeutic concentrations in CSF. Frattari et al. [18] delivered the only reported case of otogenous meningitis caused by XDR-PA in which a combination of C/T and fosfomycin was successfully used for definitive treatment; and Dinh et al. [19] reported a case of XDR-PA meningitis treated with C/T monotherapy, which resulted in clinical failure.
According to the recommendations for pneumonia, a high-dose regimen (2 g + 1 g every 8 h, with good kidney function) was applied to achieve high intra-cerebral drug concentrations for a total of 10 days in our patient. C/T was administered using a loading dose (3 g) followed by a prolonged infusion regimen over 3 h [20]. Although most recent data suggest that a continuous infusion regimen might be superior to a prolonged infusion strategy [21] in ICU patients with severe infections, this needs to be based on therapeutic drug monitoring. Even though therapeutic drug monitoring for C/T was not established in our daily clinical routine at that time, we were able to measure concentrations of C/T in the CSF (liquor) 2 days after the end of C/T treatment, which was shown to be 0.5 µg/mL. This is low, as the MIC for C/T was 1 µg/mL. Because of the positive clinical and microbiological development of the patient, we suggest that CSF levels must have been above the MIC during therapy. Considering the moment of concentration measurement in the liquor, by which time the intravenous (IV) application of C/T had finished 48 h prior, we hypothesize that the level of C/T in the CSF might have been higher during ongoing antibiotic therapy with C/T. Accordingly, C/T was able to effectively pass through the blood–brain barrier (BBB) in the presented patient with meningitis, which was already shown in other case reports. What this means is that the patient’s status improved shortly after the initiation of C/T treatment, and the number of cells in the CSF decreased to baseline on day 7. A very recently published study from Roberts et al. [22] showed inadequate CSF exposure after C/T (4.5 g/3 times daily) in 10 patients with an EVD. Interestingly, patients with signs of infection had 10× higher free areas under the curve (AUC) compared to patients without signs of infection. There are several points to address before comparing these important findings to our reported case. First, our patient suffered from meningitis. Animal models showed up to 15% increased penetration rates of the BBB in cases of meningitis [23] due to augmented paracellular passage. Second, Roberts et al. studied gram-negative pathogens with MIC for C/T ≥ 0.25 mg/L. In contrast, the causative agent in our case showed a higher MIC C/T of 1 µg/mL. Third, in the reported patient, the C/T in the CSF was measured 2 days after the end of a 10-day treatment course with C/T. Roberts et al. used first-dose data to measure the C/T in CSF. Fourth, all case reports successfully treating MDR-PA meningitis always used C/T with another PA effective antibiotic drug [15,16,17,18]. Further investigations are needed to distinguish between new cephalosporins/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations as a monotherapy versus combination therapies in patients with CNS infections caused by MDR-/XDR PA strains and to identify the optimal treatment duration.
The primary lesson learned from this case report is that, in cases with limited antimicrobial treatment options and severe CNS infections due to XDR-PA, C/T monotherapy might be a safe and effective treatment option if the MIC for the C/T of the causative agent is low.
Author Contributions
S.D. is the corresponding author and was a major contributor in the writing of the manuscript, T.B. substantively revised the manuscript, S.Z. interpreted and analyzed the microbiological samples, A.R. interpreted and analyzed the drug analysis, D.C.R. substantively revised the manuscript, A.H. helped in interpreting the data. M.A.W. conceived and designed the idea of the case report and T.M. reviewed and interpreted the computed tomography results. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The present research was not funded institutionally or by anyone else.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived since ceftolozane/tazobactam is FDA approved and was used as an off-label indication for an individual medical treatment.
Informed Consent Statement
Consent from the legal guardian was obtained.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request due to restrictions of privacy or ethical. The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Markus Weigand is on the advisory boards of MSD (Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA), Gilead (Foster City, CA, USA), Pfizer (New York City, NY, USA) and Shionogi (Osaka, Japan). Thorsten Brenner received research funding from the German Research Foundation (DFG, Bonn, Germany), the Heidelberg Foundation of Surgery and the Dietmar Hopp Foundation (Walldorf, Germany). Thorsten Brenner received honoraria for lectures and advisory boards from: Biotest AG (Dreieich, Germany), Baxter Deutschland GmbH (Unterschleißheim, Germany), Schöchl medical education GmbH (Mattsee, Austria), Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH (Ingelheim am Rhein, Germany), CSL Behring GmbH (Marburg, Germany), Astellas Pharma GmbH (München, Germany), B. Braun Melsungen AG (Melsungen, Germany) and MSD Sharp & Dohme GmbH MSD (Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA). Alexandra Heininger received speaker honorary from MSD Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA) and Pfizer (New York City, NY, USA).Theresa Mokry received speaker honorary by Bracco (Milano, Italy) and Bayer (Leverkusen, Germany). Simon Dubler, Stefan Zimmermann, Anka Röhr and Daniel Richter declare that they have no competing interests.
Abbreviations
| PA | pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| MDR | in multidrug-resistant |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| XDR | extensively drug-resistant |
| ICP | intracranial pressure |
| C/T | ceftolozane/tazobactam |
| MIC | minimal inhibitory concentration |
| ICU | intensive care unit |
| EVD | extra ventricular drainage |
| LD | lumbar drainage |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| IV | intravenous |
| IVT | intraventricular |
| AUC | area under the curve |
References
- Bassetti, M.; Vena, A.; Croxatto, A.; Righi, E.; Guery, B. How to manage Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Drugs Context 2018, 7, 212527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velkov, T.; Dai, C.; Ciccotosto, G.D.; Cappai, R.; Hoyer, D.; Li, J. Polymyxins for CNS infections: Pharmacology and neurotoxicity. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 181, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogue, J.M.; Kaye, K.S.; Veve, M.P.; Patel, T.S.; Gerlach, A.T.; Davis, S.L.; Puzniak, L.A.; File, T.M.; Olson, S.; Dhar, S.; et al. Ceftolozane/Tazobactam vs Polymyxin or Aminoglycoside-based Regimens for the Treatment of Drug-resistant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 71, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nau, R.; Sorgel, F.; Eiffert, H. Penetration of drugs through the blood-cerebrospinal fluid/blood-brain barrier for treatment of central nervous system infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 858–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenlehner, F.M.; Umeh, O.; Steenbergen, J.; Yuan, G.; Darouiche, R.O. Ceftolozane-tazobactam compared with levofloxacin in the treatment of complicated urinary-tract infections, including pyelonephritis: A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial (ASPECT-cUTI). Lancet 2015, 385, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomkin, J.; Hershberger, E.; Miller, B.; Popejoy, M.; Friedland, I.; Steenbergen, J.; Yoon, M.; Collins, S.; Yuan, G.; Barie, P.S.; et al. Ceftolozane/Tazobactam Plus Metronidazole for Complicated Intra-abdominal Infections in an Era of Multidrug Resistance: Results From a Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Trial (ASPECT-cIAI). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollef, M.H.; Novacek, M.; Kivistik, U.; Rea-Neto, A.; Shime, N.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Timsit, J.F.; Wunderink, R.G.; Bruno, C.J.; Huntington, J.A.; et al. Ceftolozane-tazobactam versus meropenem for treatment of nosocomial pneumonia (ASPECT-NP): A randomised, controlled, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraolo, A.E.; Mazzitelli, M.; Trecarichi, E.M.; Buonomo, A.R.; Torti, C.; Gentile, I. Ceftolozane/tazobactam for difficult-to-treat Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: A systematic review of its efficacy and safety for off-label indications. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, S.; Bedford, L.; Ruramayi, R.; Aliyu, S.H.; Sule, J.; Maslin, D.; Enoch, D.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa meningitis/ventriculitis in a UK tertiary referral hospital. QJM Int. J. Med. 2016, 109, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunkel, A.R.; Hasbun, R.; Bhimraj, A.; Byers, K.; Kaplan, S.L.; Scheld, W.M.; van de Beek, D.; Bleck, T.P.; Garton, H.J.L.; Zunt, J.R. 2017 Infectious Diseases Society of America’s Clinical Practice Guidelines for Healthcare-Associated Ventriculitis and Meningitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, e34–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montravers, P.; Dufour, G.; Guglielminotti, J.; Desmard, M.; Muller, C.; Houissa, H.; Allou, N.; Marmuse, J.P.; Augustin, P. Dynamic changes of microbial flora and therapeutic consequences in persistent peritonitis. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocco, M.; Montini, L.; Alessandri, E.; Venditti, M.; Laderchi, A.; De Pascale, G.; Raponi, G.; Vitale, M.; Pietropaoli, P.; Antonelli, M. Risk factors for acute kidney injury in critically ill patients receiving high intravenous doses of colistin methanesulfonate and/or other nephrotoxic antibiotics: A retrospective cohort study. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monogue, M.L.; Nicolau, D.P. Antibacterial activity of ceftolozane/tazobactam alone and in combination with other antimicrobial agents against MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidar, G.; Philips, N.J.; Shields, R.K.; Snyder, D.; Cheng, S.; Potoski, B.A.; Doi, Y.; Hao, B.; Press, E.G.; Cooper, V.S.; et al. Ceftolozane-Tazobactam for the Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections: Clinical Effectiveness and Evolution of Resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCreary, E.K.; Byers, K.E.; Fernandes, C.; Kline, E.G.; Nicolau, D.P.; Shields, R.K. Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Ceftolozane and Tazobactam during Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Meningitis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meschiari, M.; Franconi, I.; Bacca, E.; Bianco, V.; Orlando, G.; Cuomo, G.; Bedini, A.; Mussini, C. Ceftazidime/avibactam and ceftolozane/tazobactam for the treatment of extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa post-neurosurgical infections: Three cases and a review of the literature. Infection 2021, 49, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winans, S.A.; Guerrero-Wooley, R.L.; Park, S.H.; Hino, G., Jr.; Forland, S.C. Continuous infusion of ceftolozane-tazobactam resulted in high cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of ceftolozane in a patient with multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa meningitis. Infection 2021, 49, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frattari, A.; Savini, V.; Polilli, E.; Cibelli, D.; Talamazzi, S.; Bosco, D.; Consorte, A.; Fazii, P.; Parruti, G. Ceftolozane-tazobactam and Fosfomycin for rescue treatment of otogenous meningitis caused by XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Case report and review of the literature. IDCases 2018, 14, e00451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, A.; Wyplosz, B.; Kerneis, S.; Lebeaux, D.; Bouchand, F.; Duran, C.; Beraud, G.; Lazaro, P.; Davido, B.; Henard, S.; et al. Use of ceftolozane/tazobactam as salvage therapy for infections due to extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 782–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardakas, K.Z.; Voulgaris, G.L.; Maliaros, A.; Samonis, G.; Falagas, M.E. Prolonged versus short-term intravenous infusion of antipseudomonal beta-lactams for patients with sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilmis, B.; Petitjean, G.; Lesprit, P.; Lafaurie, M.; El Helali, N.; Le Monnier, A.; on behalf the ATB PK/PD study group. Continuous infusion of ceftolozane/tazobactam is associated with a higher probability of target attainment in patients infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sime, F.B.; Lassig-Smith, M.; Starr, T.; Stuart, J.; Pandey, S.; Parker, S.L.; Wallis, S.C.; Lipman, J.; Roberts, J.A. Cerebrospinal fluid penetration of ceftolozane/tazobactam in critically ill patients with an indwelling external ventricular drain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 65, e01698-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quagliarello, V.J.; Long, W.J.; Scheld, W.M. Morphologic alterations of the blood-brain barrier with experimental meningitis in the rat. Temporal sequence and role of encapsulation. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 77, 1084–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).