Understanding the Relevance of Aging-Related Tau Astrogliopathy (ARTAG)
Abstract
1. Introduction: What Is ARTAG?
- Identify the morphologic and distribution types of ARTAG based on parenchymal localization of TSA and GFA: i.e., subpial, subependymal, perivascular, white matter, and gray matter.
- Identify involvement of gross anatomical regions such as the medial temporal lobe, further lobes of the brain, subcortical structures, and the brainstem.
- Document the severity of ARTAG pathology; in particular, whether this is seen in occasional or in numerous astrocytes and whether clusters or widespread distribution is noted.
- Finally, particularly for scientific discovery studies, detailed anatomical mapping is recommended.
2. ARTAG and Primary Tauopathies
3. ARTAG and Various Disorders Including Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
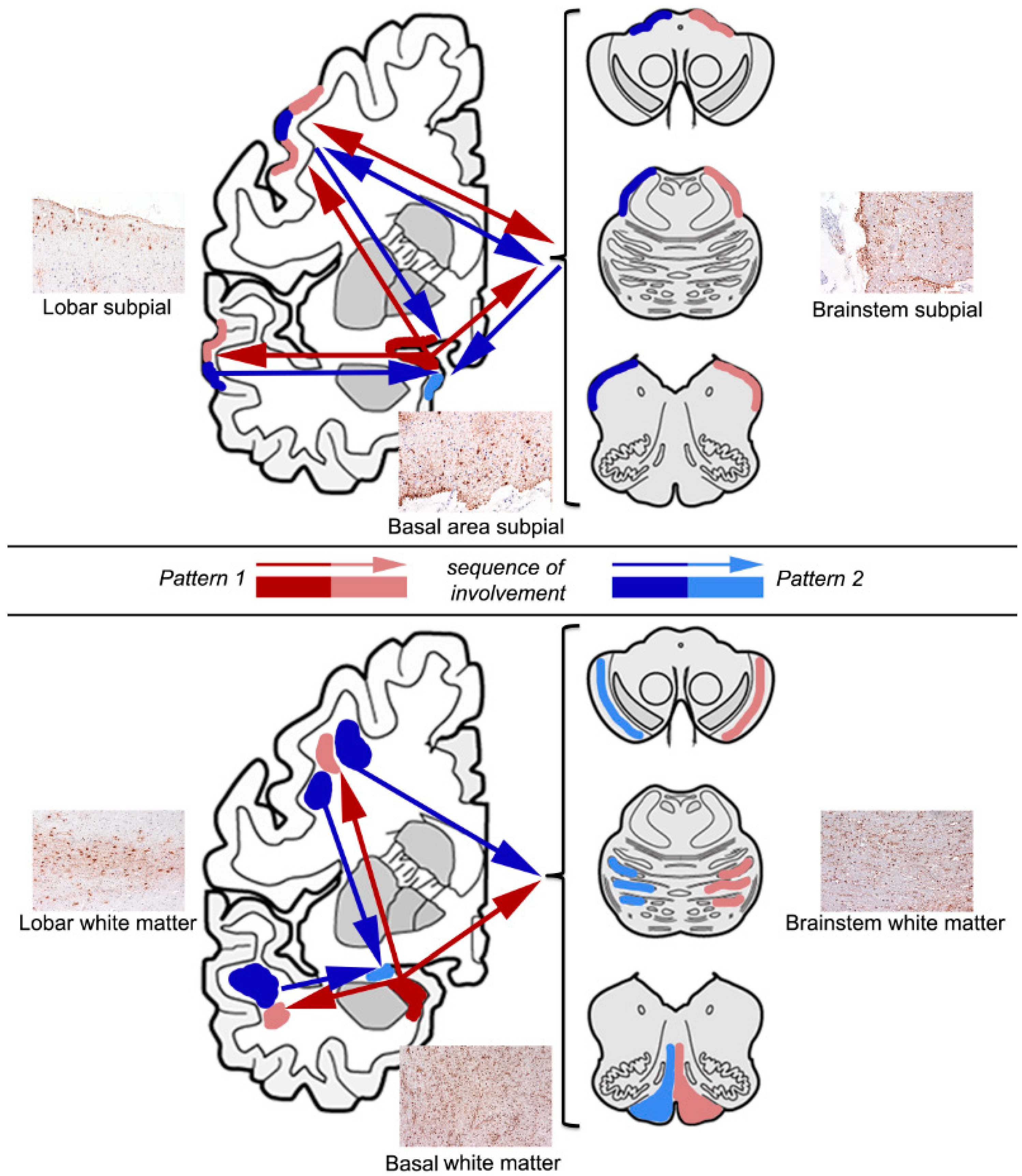
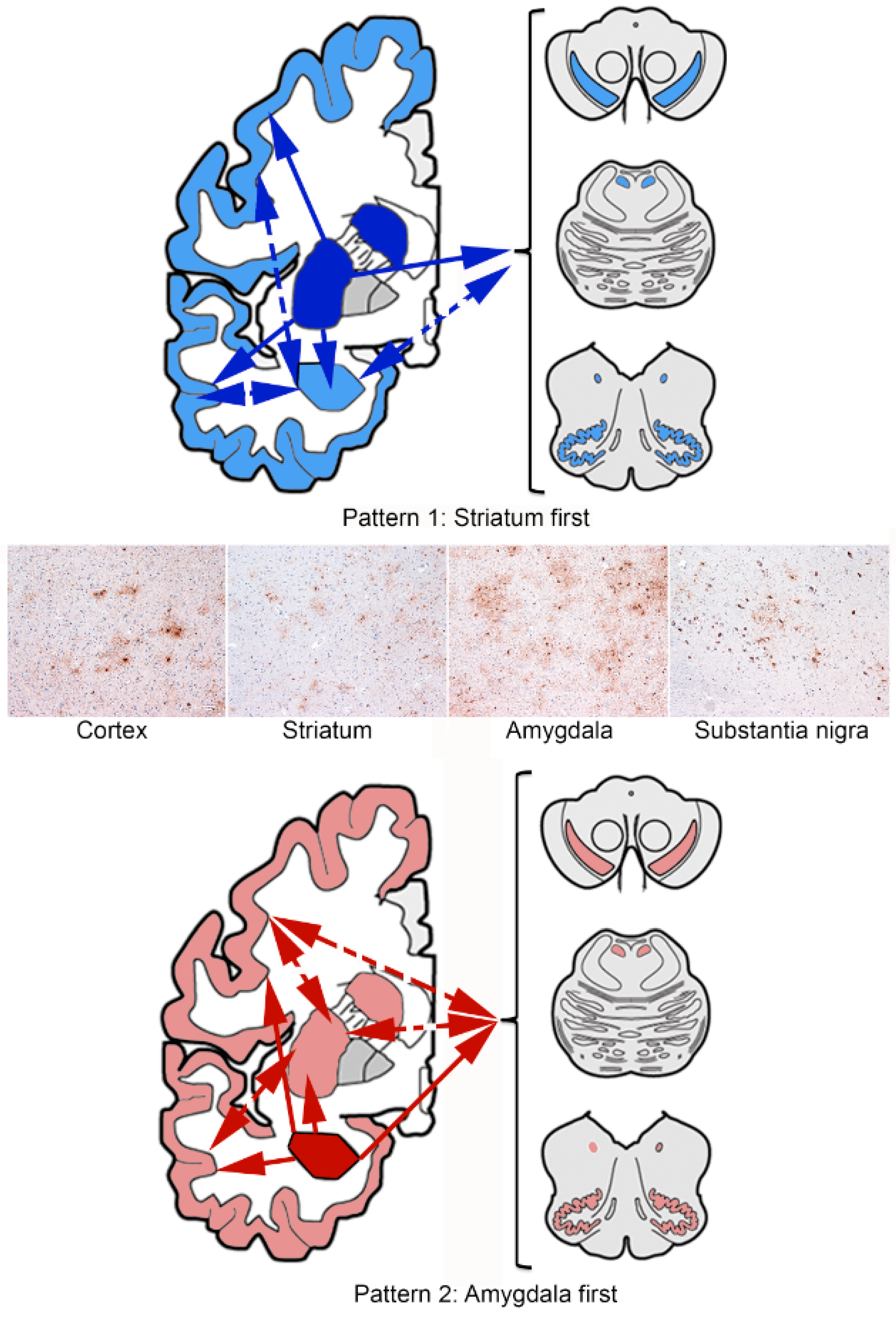
4. Sequential Distribution of ARTAG
4.1. Subpial ARTAG (Thorn-Shaped Astrocytes Morphology)
4.2. White Matter ARTAG (Thorn-Shaped Astrocytes Morphology)
4.3. Gray Matter ARTAG (Granular/Fuzzy Astrocytes Morphology)
5. Considerations on Pathogenesis
6. What Is the Clinical Relevance of ARTAG?
7. Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kovacs, G.G.; Ferrer, I.; Grinberg, L.T.; Alafuzoff, I.; Attems, J.; Budka, H.; Cairns, N.J.; Crary, J.F.; Duyckaerts, C.; Ghetti, B.; et al. Aging-related tau astrogliopathy (ARTAG): Harmonized evaluation strategy. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K. Glial fibrillary tangles and argyrophilic threads: Classification and disease specificity. Neuropathology 1996, 16, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Akiyama, H.; Arai, T.; Nishimura, T. Glial tau pathology in neurodegenerative diseases: Their nature and comparison with neuronal tangles. Neurobiol. Aging 1998, 19, S85–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Akiyama, H.; Kondo, H.; Haga, C.; Tanno, E.; Tokuda, T.; Ikeda, S. Thorn-shaped astrocytes: Possibly secondarily induced tau-positive glial fibrillary tangles. Acta Neuropathol. 1995, 90, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, C.; Ghebremedhin, E.; Del Tredici, K.; Rub, U.; Braak, H. High prevalence of thorn-shaped astrocytes in the aged human medial temporal lobe. Neurobiol. Aging 2004, 25, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, C.; Dehghani, F.; Hubbard, G.B.; Thal, D.R.; Struckhoff, G.; Braak, E.; Braak, H. Filamentous tau pathology in nerve cells, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes of aged baboons. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2000, 59, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, C.; Hubbard, G.B.; Rub, U.; Braak, E.; Braak, H. Age-related progression of tau pathology in brains of baboons. Neurobiol. Aging 2000, 21, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, S.E.; Raghanti, M.A.; Hof, P.R.; Kramer, L.; Ikonomovic, M.D.; Lacor, P.N.; Erwin, J.M.; Sherwood, C.C.; Mufson, E.J. Alzheimer’s disease pathology in the neocortex and hippocampus of the western lowland gorilla (Gorilla gorilla gorilla). J. Comp. Neurol. 2013, 521, 4318–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, I. Astrogliopathy in Tauopathies. Neuroglia 2018, 1, 126–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, M.; Craxton, M.; Jakes, R.; Arendt, T.; Goedert, M. Tau gene (MAPT) sequence variation among primates. Gene 2004, 341, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.G.; Molnar, K.; Laszlo, L.; Strobel, T.; Botond, G.; Honigschnabl, S.; Reiner-Concin, A.; Palkovits, M.; Fischer, P.; Budka, H. A peculiar constellation of tau pathology defines a subset of dementia in the elderly. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 122, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.G.; Xie, S.X.; Lee, E.B.; Robinson, J.L.; Caswell, C.; Irwin, D.J.; Toledo, J.B.; Johnson, V.E.; Smith, D.H.; Alafuzoff, I.; et al. Multisite Assessment of Aging-Related Tau Astrogliopathy (ARTAG). J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 76, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, M.; Namba, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Oda, M. Glial fibrillary tangles with straight tubules in the brains of patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurosci. Lett. 1992, 143, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, G.G.; Robinson, J.L.; Xie, S.X.; Lee, E.B.; Grossman, M.; Wolk, D.A.; Irwin, D.J.; Weintraub, D.; Kim, C.F.; Schuck, T.; et al. Evaluating the Patterns of Aging-Related Tau Astrogliopathy Unravels Novel Insights into Brain Aging and Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 76, 270–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.G. Invited review: Neuropathology of tauopathies: Principles and practice. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2015, 41, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botez, G.; Probst, A.; Ipsen, S.; Tolnay, M. Astrocytes expressing hyperphosphorylated tau protein without glial fibrillary tangles in argyrophilic grain disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1999, 98, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolnay, M.; Clavaguera, F. Argyrophilic grain disease: A late-onset dementia with distinctive features among tauopathies. Neuropathology 2004, 24, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crary, J.F.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Schneider, J.A.; Abisambra, J.F.; Abner, E.L.; Alafuzoff, I.; Arnold, S.E.; Attems, J.; Beach, T.G.; Bigio, E.H.; et al. Primary age-related tauopathy (PART): A common pathology associated with human aging. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghetti, B.; Oblak, A.L.; Boeve, B.F.; Johnson, K.A.; Dickerson, B.C.; Goedert, M. Invited review: Frontotemporal dementia caused by microtubule-associated protein tau gene (MAPT) mutations: A chameleon for neuropathology and neuroimaging. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2015, 41, 24–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.G.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J. Protein astrogliopathies in human neurodegenerative diseases and aging. Brain Pathol. 2017, 27, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.; Kalev, O.; Mehrabian, S.; Traykov, L.; Raycheva, M.; Kanakis, D.; Drineas, P.; Lutz, M.I.; Strobel, T.; Penz, T.; et al. Familial early-onset dementia with complex neuropathologic phenotype and genomic background. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 42, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guennec, K.; Quenez, O.; Nicolas, G.; Wallon, D.; Rousseau, S.; Richard, A.C.; Alexander, J.; Paschou, P.; Charbonnier, C.; Bellenguez, C.; et al. 17q21.31 duplication causes prominent tau-related dementia with increased MAPT expression. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, C.; Yokota, O.; Nagao, S.; Ishizu, H.; Oshima, E.; Hasegawa, M.; Okahisa, Y.; Terada, S.; Yamada, N. The Relationship Between Development of Neuronal and Astrocytic Tau Pathologies in Subcortical Nuclei and Progression of Argyrophilic Grain Disease. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 488–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, I.; Lopez-Gonzalez, I.; Carmona, M.; Arregui, L.; Dalfo, E.; Torrejon-Escribano, B.; Diehl, R.; Kovacs, G.G. Glial and neuronal tau pathology in tauopathies: Characterization of disease-specific phenotypes and tau pathology progression. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 73, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Gonzalez, I.; Carmona, M.; Blanco, R.; Luna-Munoz, J.; Martinez-Mandonado, A.; Mena, R.; Ferrer, I. Characterization of thorn-shaped astrocytes in white matter of temporal lobe in Alzheimer’s disease brains. Brain Pathol. 2013, 23, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, A.C.; Cairns, N.J.; Dickson, D.W.; Folkerth, R.D.; Keene, C.D.; Litvan, I.; Perl, D.P.; Stein, T.D.; Vonsattel, J.P.; Stewart, W.; et al. The first NINDS/NIBIB consensus meeting to define neuropathological criteria for the diagnosis of chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, A.C.; Daneshvar, D.H. The neuropathology of traumatic brain injury. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 127, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.K.; Goldfinger, M.H.; Questari, H.E.; Pearce, R.K.; Gentleman, S.M. ARTAG in the basal forebrain: Widening the constellation of astrocytic tau pathology. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, A.C.; Stein, T.D.; Kiernan, P.T.; Alvarez, V.E. The neuropathology of chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Brain Pathol. 2015, 25, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, A.C.; Stern, R.A.; Nowinski, C.J.; Stein, T.D.; Alvarez, V.E.; Daneshvar, D.H.; Lee, H.S.; Wojtowicz, S.M.; Hall, G.; Baugh, C.M.; et al. The spectrum of disease in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Brain 2013, 136, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.G.; Xie, S.X.; Robinson, J.L.; Lee, E.B.; Smith, D.H.; Schuck, T.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Sequential stages and distribution patterns of aging-related tau astrogliopathy (ARTAG) in the human brain. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.G.; Rahimi, J.; Strobel, T.; Lutz, M.I.; Regelsberger, G.; Streichenberger, N.; Perret-Liaudet, A.; Hoftberger, R.; Liberski, P.P.; Budka, H.; et al. Tau pathology in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease revisited. Brain Pathol. 2017, 27, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brettschneider, J.; Del Tredici, K.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Spreading of pathology in neurodegenerative diseases: A focus on human studies. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, H.; Kovacs, G.G.; Vonsattel, J.P.; Davey, K.; Mok, K.Y.; Hardy, J.; Morris, H.R.; Warner, T.T.; Holton, J.L.; Revesz, T. Astrogliopathy predominates the earliest stage of corticobasal degeneration pathology. Brain 2016, 139, 3237–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chvátal, A.; Verkhratsky, A. An Early History of Neuroglial Research: Personalities. Neuroglia 2018, 1, 245–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, K.; Yagishita, S.; Nakamura, A.; Uchihara, T. Perivascular orientation of astrocytic plaques and tuft-shaped astrocytes. Brain Res. 2011, 1404, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, I.; Legati, A.; Garcia-Monco, J.C.; Gomez-Beldarrain, M.; Carmona, M.; Blanco, R.; Seeley, W.W.; Coppola, G. Familial behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia associated with astrocyte-predominant tauopathy. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 74, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.G.; Yousef, A.; Kaindl, S.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Connexin-43 and Aquaporin-4 are markers of ARTAG-related astroglial response. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.S.; Clarke, L.E.; Wang, G.X.; Stafford, B.K.; Sher, A.; Chakraborty, C.; Joung, J.; Foo, L.C.; Thompson, A.; Chen, C.; et al. Astrocytes mediate synapse elimination through MEGF10 and MERTK pathways. Nature 2013, 504, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.H.; Kim, K.Y.; Bushong, E.A.; Mills, E.A.; Boassa, D.; Shih, T.; Kinebuchi, M.; Phan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Bihlmeyer, N.A.; et al. Transcellular degradation of axonal mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9633–9638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Yang, G.Y. Aquaporin-4: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Cerebral Edema. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhan, S.; Guo, J.L.; Changolkar, L.; Stieber, A.; McBride, J.D.; Silva, L.V.; He, Z.; Zhang, B.; Gathagan, R.J.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Pathological Tau Strains from Human Brains Recapitulate the Diversity of Tauopathies in Nontransgenic Mouse Brain. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 11406–11423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, I.; Garcia, M.A.; Gonzalez, I.L.; Lucena, D.D.; Villalonga, A.R.; Tech, M.C.; Llorens, F.; Garcia-Esparcia, P.; Martinez-Maldonado, A.; Mendez, M.F.; et al. Aging-related tau astrogliopathy (ARTAG): Not only tau phosphorylation in astrocytes. Brain Pathol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, M.; Ishihara, T.; Zhang, B.; Hong, M.; Andreadis, A.; Trojanowski, J.; Lee, V.M. Transgenic mouse model of tauopathies with glial pathology and nervous system degeneration. Neuron 2002, 35, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, M.S.; Lal, D.; Zhang, B.; Dabir, D.V.; Swanson, E.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Transgenic mouse model of tau pathology in astrocytes leading to nervous system degeneration. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 3539–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, D.G.; Woulfe, J.; Kertesz, A. Argyrophilic thorny astrocyte clusters in association with Alzheimer’s disease pathology in possible primary progressive aphasia. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigio, E.H.; Mishra, M.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; White, C.L., 3rd; Johnson, N.; Rademaker, A.; Weitner, B.B.; Deng, H.X.; Dubner, S.D.; Weintraub, S.; et al. TDP-43 pathology in primary progressive aphasia and frontotemporal dementia with pathologic Alzheimer disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesulam, M.; Wicklund, A.; Johnson, N.; Rogalski, E.; Leger, G.C.; Rademaker, A.; Weintraub, S.; Bigio, E.H. Alzheimer and frontotemporal pathology in subsets of primary progressive aphasia. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.G.; Milenkovic, I.; Wohrer, A.; Hoftberger, R.; Gelpi, E.; Haberler, C.; Honigschnabl, S.; Reiner-Concin, A.; Heinzl, H.; Jungwirth, S.; et al. Non-Alzheimer neurodegenerative pathologies and their combinations are more frequent than commonly believed in the elderly brain: A community-based autopsy series. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lace, G.; Ince, P.G.; Brayne, C.; Savva, G.M.; Matthews, F.E.; de Silva, R.; Simpson, J.E.; Wharton, S.B. Mesial temporal astrocyte tau pathology in the MRC-CFAS ageing brain cohort. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2012, 34, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milenkovic, I.; Petrov, T.; Kovacs, G.G. Patterns of hippocampal tau pathology differentiate neurodegenerative dementias. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2014, 38, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.L.; Corrada, M.M.; Kovacs, G.G.; Dominique, M.; Caswell, C.; Xie, S.X.; Lee, V.M.; Kawas, C.H.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Non-Alzheimer’s contributions to dementia and cognitive resilience in the 90+ Study. Acta Neuropathol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Oberheim Bush, N.A.; Nedergaard, M.; Butt, A. The Special Case of Human Astrocytes. Neuroglia 2018, 1, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herculano-Houzel, S.; Dos Santos, S.E. You Do Not Mess with the Glia. Neuroglia 2018, 1, 193–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, I. Diversity of astroglial responses across human neurodegenerative disorders and brain aging. Brain Pathol. 2017, 27, 645–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Zorec, R.; Parpura, V. Stratification of astrocytes in healthy and diseased brain. Brain Pathol. 2017, 27, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovacs, G.G. Understanding the Relevance of Aging-Related Tau Astrogliopathy (ARTAG). Neuroglia 2018, 1, 339-350. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia1020023
Kovacs GG. Understanding the Relevance of Aging-Related Tau Astrogliopathy (ARTAG). Neuroglia. 2018; 1(2):339-350. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia1020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovacs, Gabor G. 2018. "Understanding the Relevance of Aging-Related Tau Astrogliopathy (ARTAG)" Neuroglia 1, no. 2: 339-350. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia1020023
APA StyleKovacs, G. G. (2018). Understanding the Relevance of Aging-Related Tau Astrogliopathy (ARTAG). Neuroglia, 1(2), 339-350. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia1020023




