Trajectory Control of Flexible Manipulators Using Forward and Inverse Models with Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Physical Model and Experimental Setup
2.2. Neural Network Training
2.2.1. Gradient Descent Approach
2.2.2. Newton’s Method
2.2.3. Levenberg–Marquardt Method
2.2.4. Neural Network Architecture
2.3. Derivation of Inverse Kinematics
2.4. Verification of Control
- Time-delay effects introduced by mechanical flexibility significantly impact tracking accuracy.
- Steady-state offsets arise from uncompensated structural and control limitations, especially when using minimal control schemes.
2.5. Neural Network Experiment Setup
3. Results and Discussion
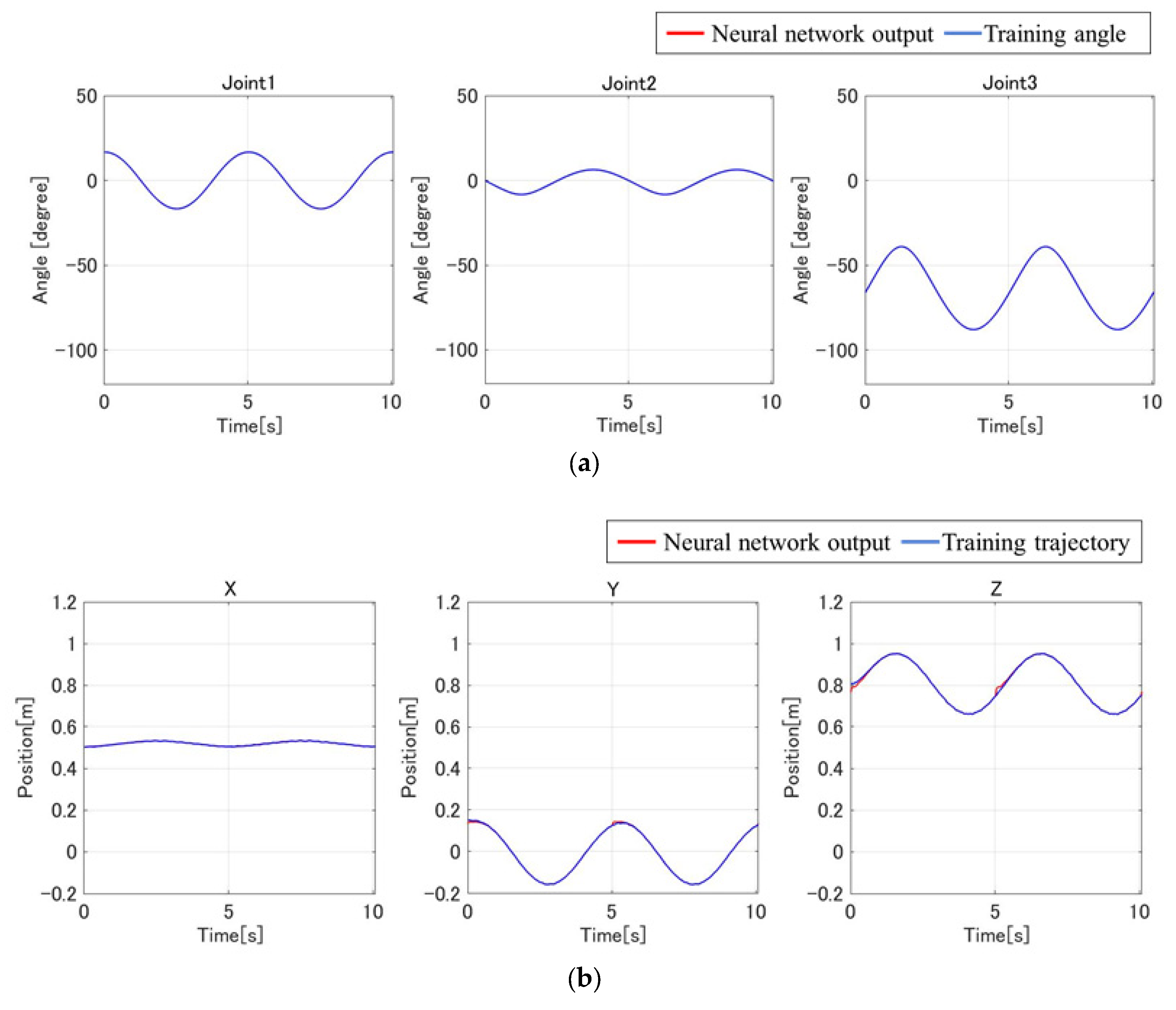
3.1. Training Performance of the Neural Network
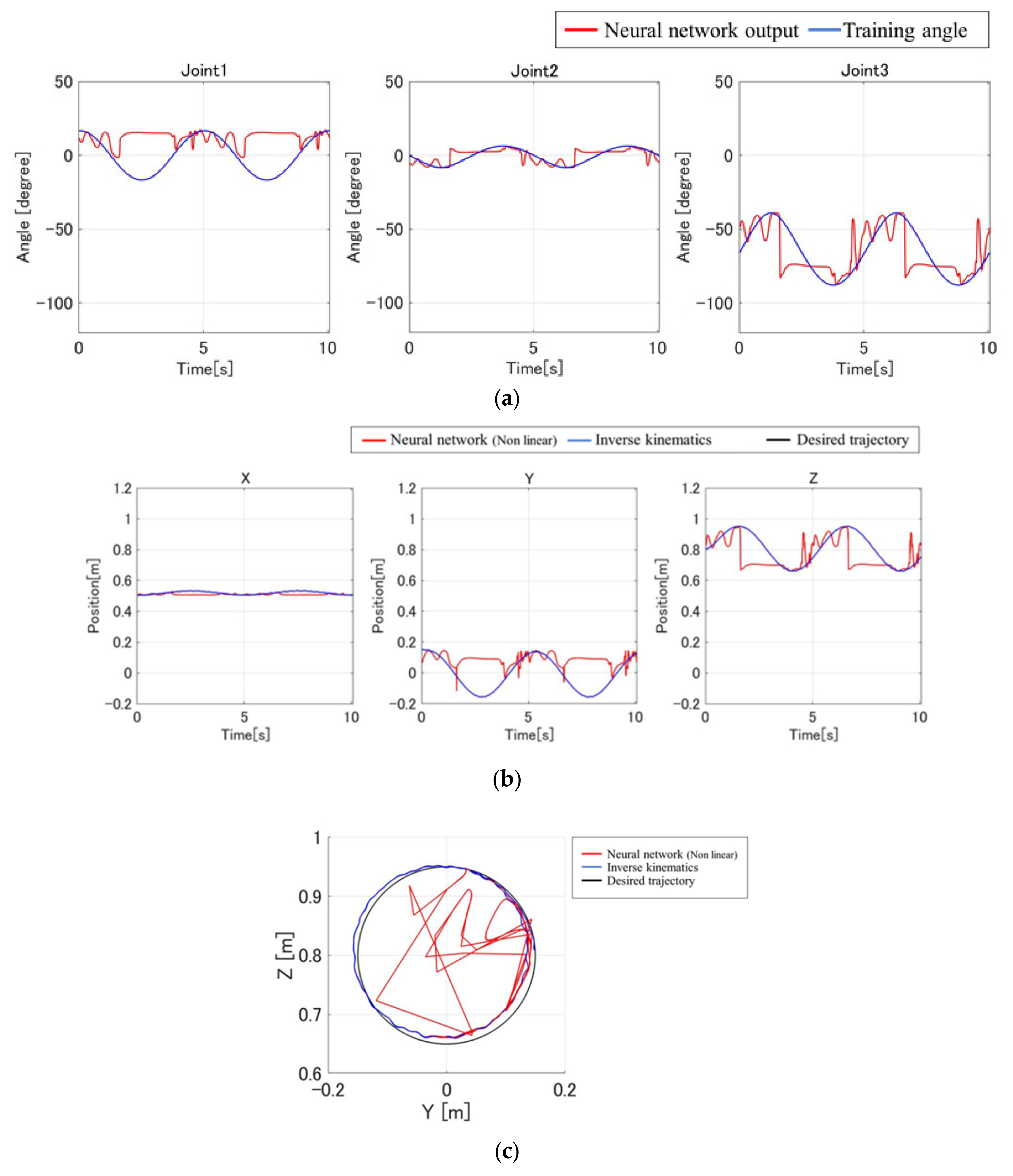
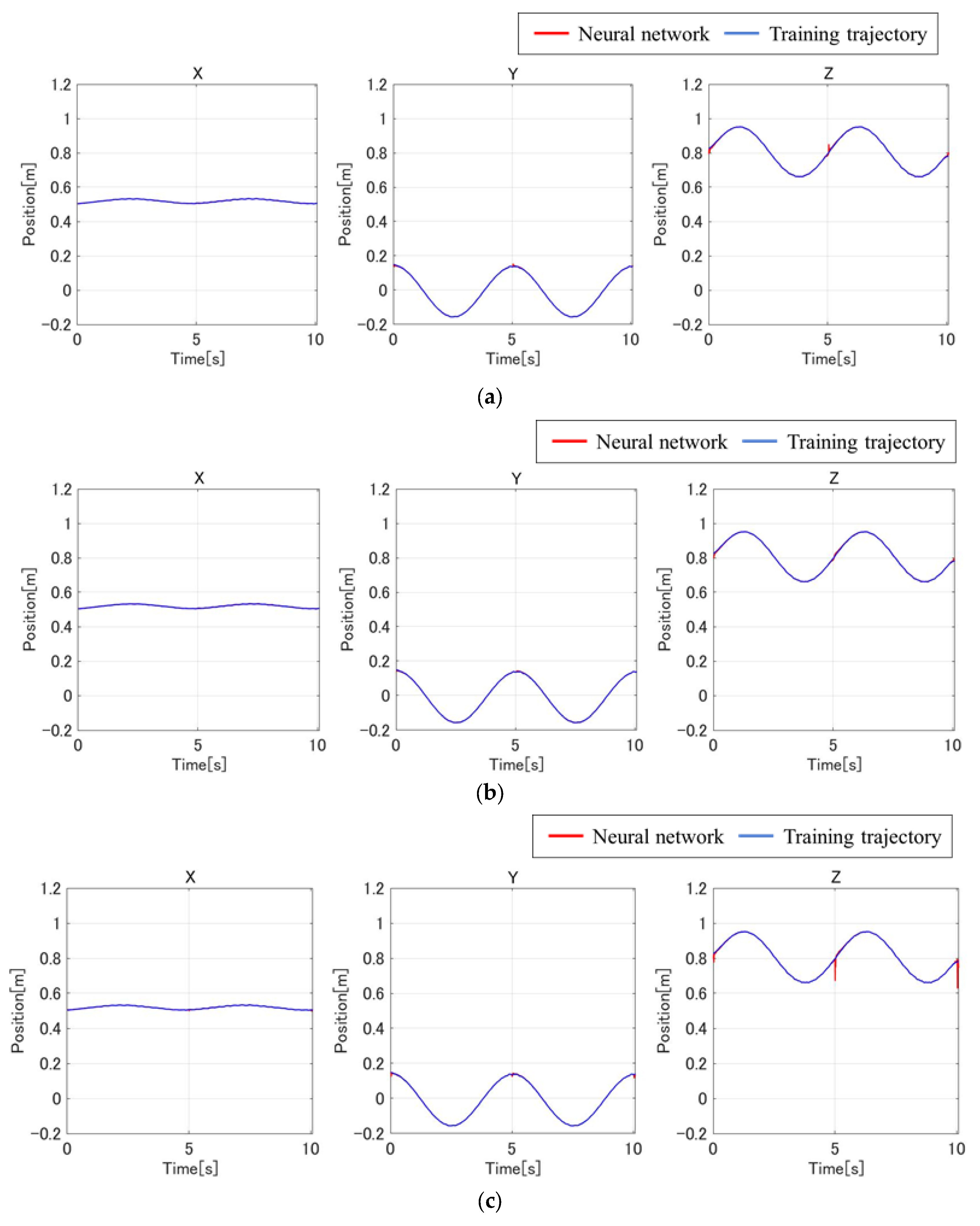
3.2. Results of Delay Compensation Through Adjusted Training Data
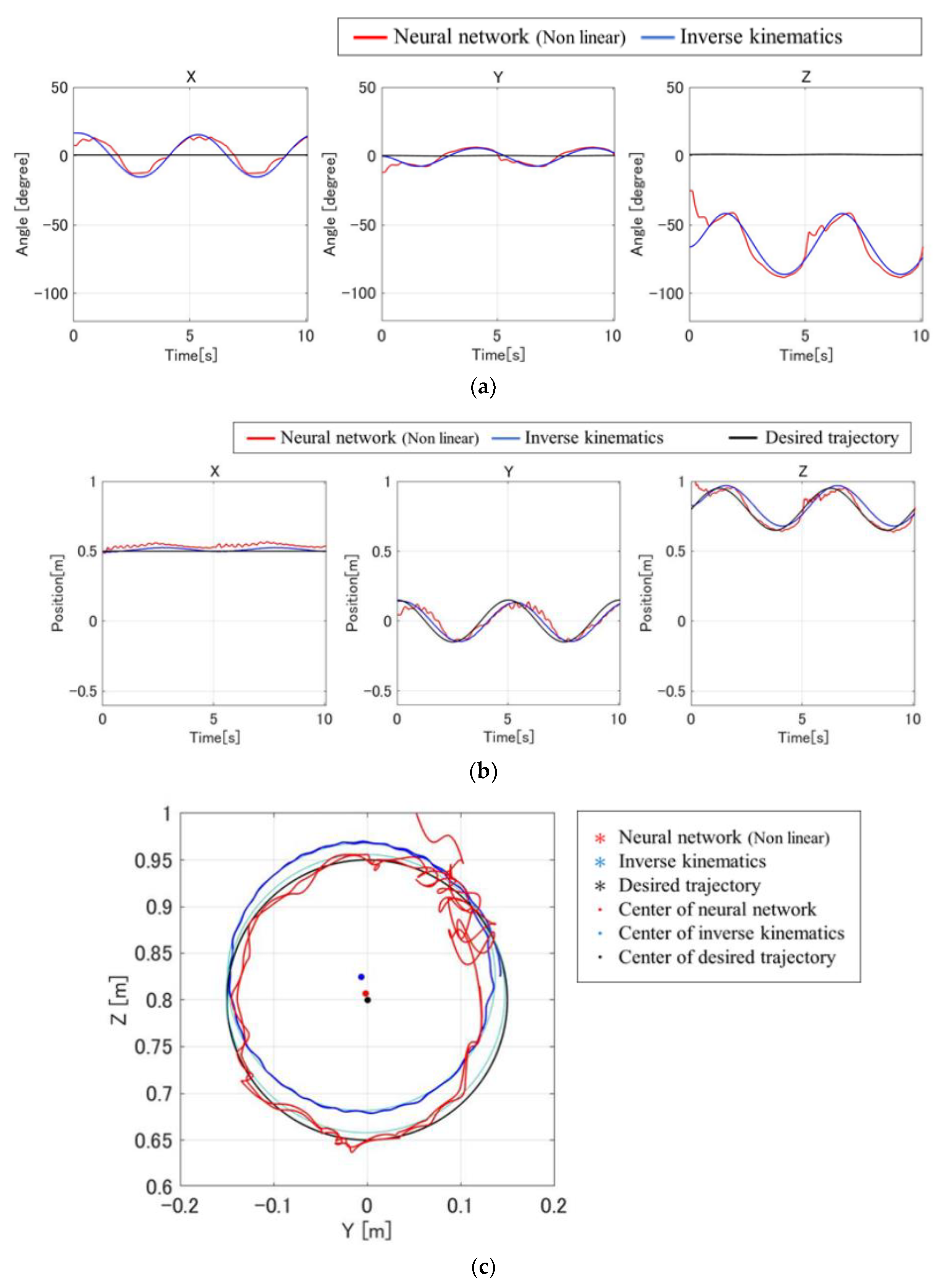
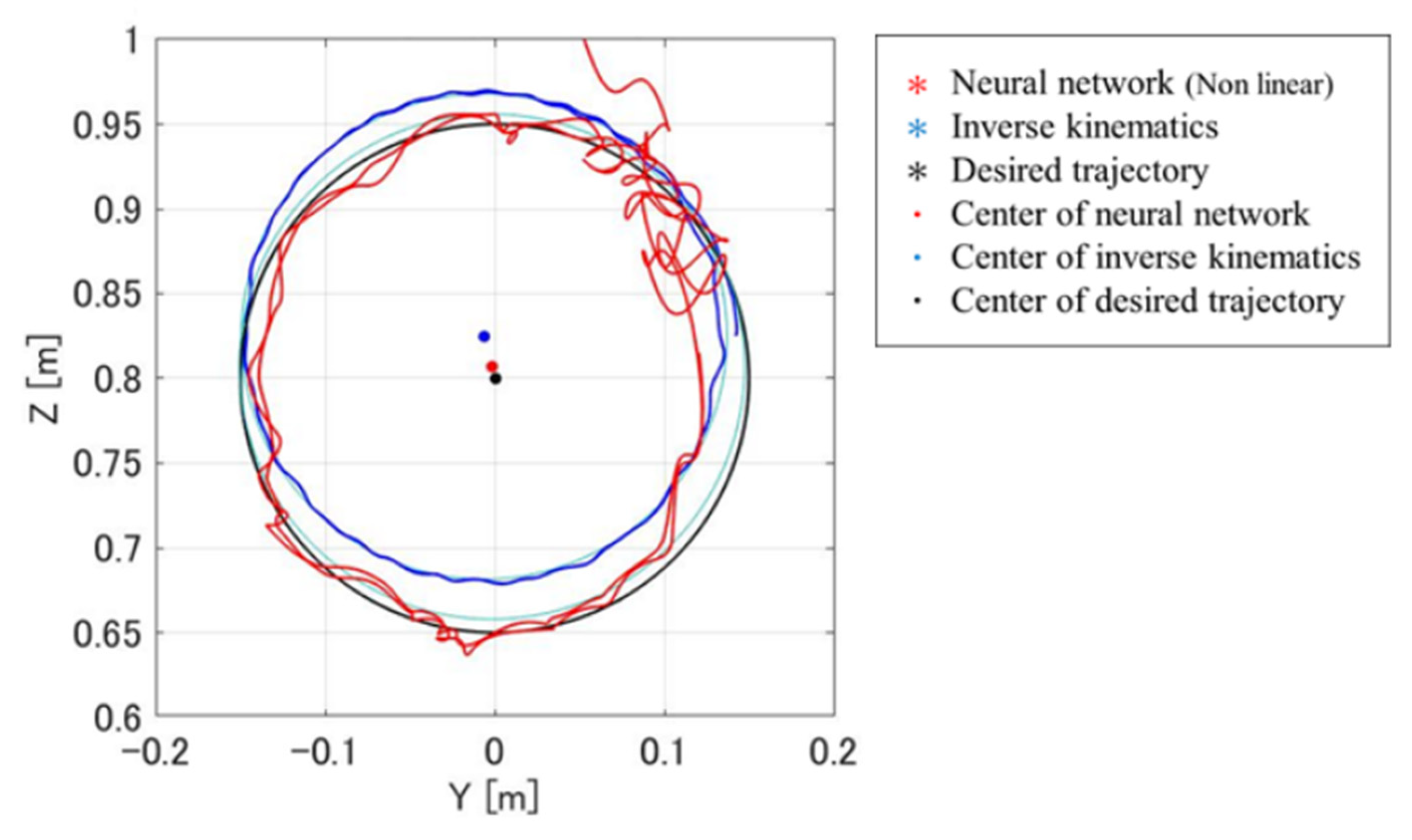
3.3. Implementation Experiment and Physical Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sasaki, M.; Muguro, J.; Njeri, W.; Doss, A.S.A. Adaptive Notch Filter in a Two-Link Flexible Manipulator for the Compensation of Vibration and Gravity-Induced Distortion. Vibration 2023, 6, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H. Fundamentals of Industrial Vibration, 22nd ed.; Yokendou Co., Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki, H. Fundamentals of Robotics, 2nd ed.; Morikita Publishing Co., Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, M.; Maeno, D.; Muguro, J.; Takeda, M.; Njeri, W.; Matsushita, K. 3D vibration control of flexible manipulator using inverse system and strain feedback. In Vibration Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, M.; Asai, H.; Kawafuku, M.; Hori, Y. Self-Tuning Control of a Translational Flexible Arm Using Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Nashville, TN, USA, 8–11 October 2000; pp. 3259–3264. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, M.; Murasawa, H.; Ito, S. Control of a two-link flexible manipulator using neural networks. In Proceedings of the SPIE, ICMIT 2007 Mechatronics, MEMS, and Smart Materials, Gifu, Japan, 16–18 December 2007; Volume 6794 Part 1 of 2 Parts, pp. 679421Y-1–679421Y-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, M.; Asai, A.; Shimizu, T.; Ito, S. Self-Tuning Control of a Two-Link Flexible Manipulator using Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the ICCAS-SICE International Conference 2009 (CD-ROM), Fukuoka, Japan, 18–21 August 2009; Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5335303 (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Njeri, W.; Sasaki, M.; Matsushita, K. Gain tuning for high speed vibration control of a multilink flexible manipulator using artificial neural network. Trans. ASME J. Vib. Acoust. 2019, 141, 041011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Honda, N.; Njeri, W.; Matsushita, K. Gain tuning using neural network for Contact force control of flexible arm. J. Sustain. Res. Eng. 2020, 5, 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; He, W.; Zhou, C.; Sun, C. Neural Network Control of a Two-Link Flexible Robotic Manipulator Using Assumed Mode Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhose, W.E. Command shaping for flexible systems: A review of the first 50 years. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2000, 1, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, J.; Yano, A.; Singhose, W. Comparison of robust input shapers. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 315, 797–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, K.; Singhose, W.; Dickerson, S. A controller enabling precise positioning and sway reduction in bridge and gantry cranes. Control Eng. Pract. 2005, 13, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, A. Trajectory Planning for Flexible Cartesian Robot Manipulators Using Artificial Neural Networks. Robotica 2011, 29, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Gao, H.; He, W.; Yu, Y. Fuzzy Neural Network Control of a Flexible Robotic Manipulator. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 5214–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wen, J.T. Neural-Learning Trajectory Tracking Control of Flexible-Joint Robot Manipulators with Unknown Dynamics. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Meng, L.; Fang, K.; Liu, F. Neural Network Adaptive Inverse Control of Flexible Joint Space Manipulator Considering the Influence of Gravity. Sensors 2024, 24, 6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhen, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J. Fixed-Time Adaptive Neural Network-Based Trajectory Tracking Control for Workspace Manipulators. Actuators 2024, 13, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
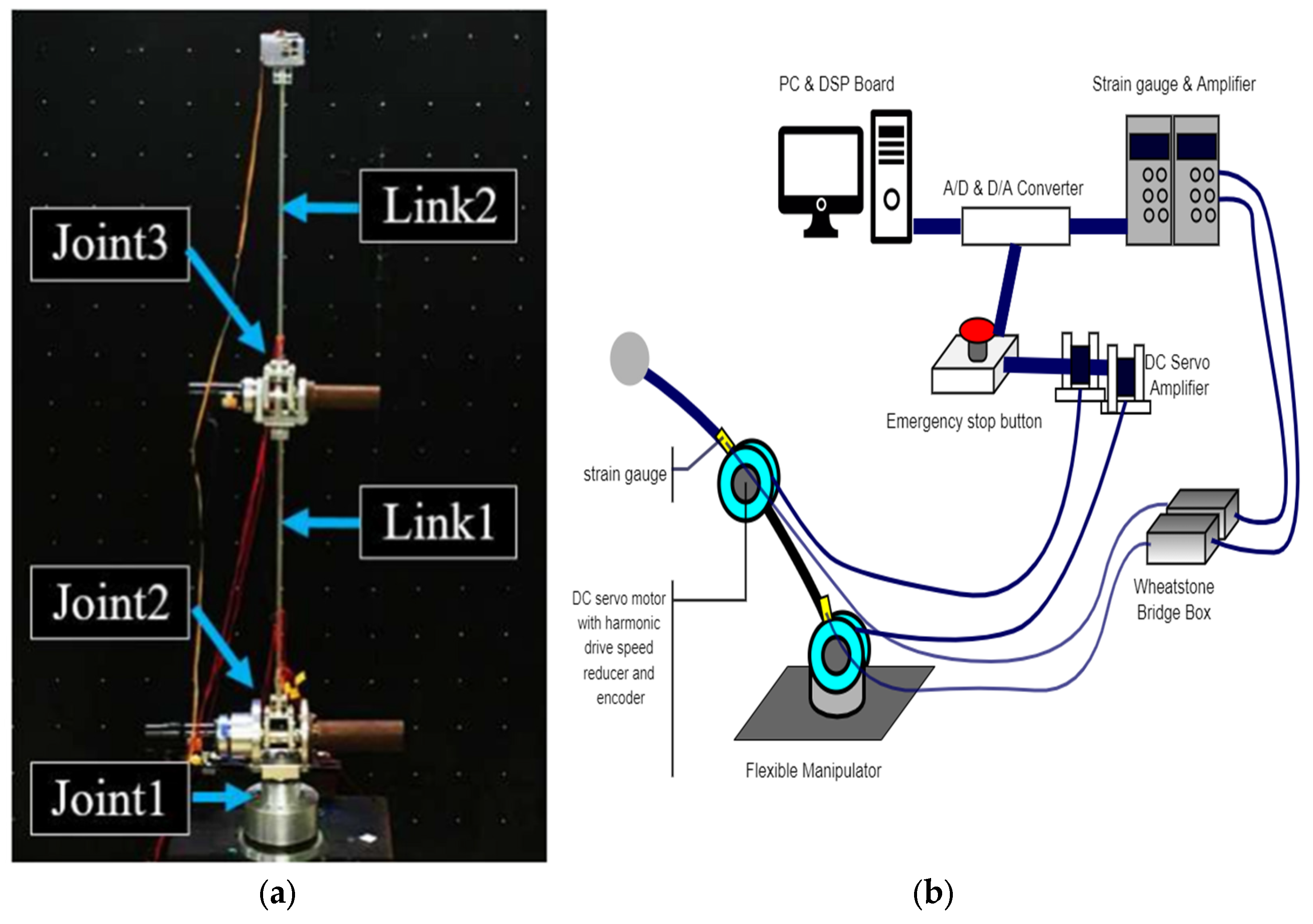
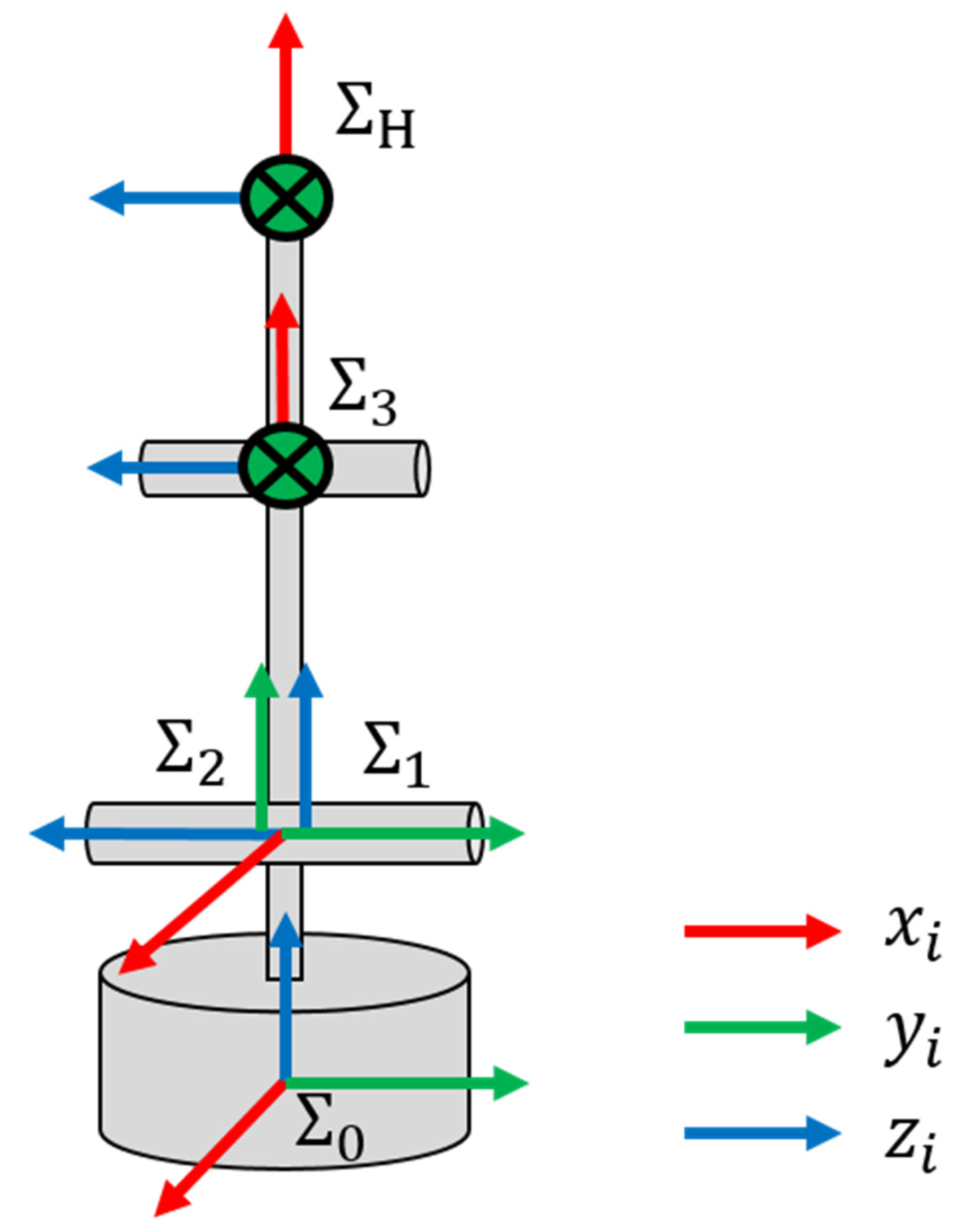
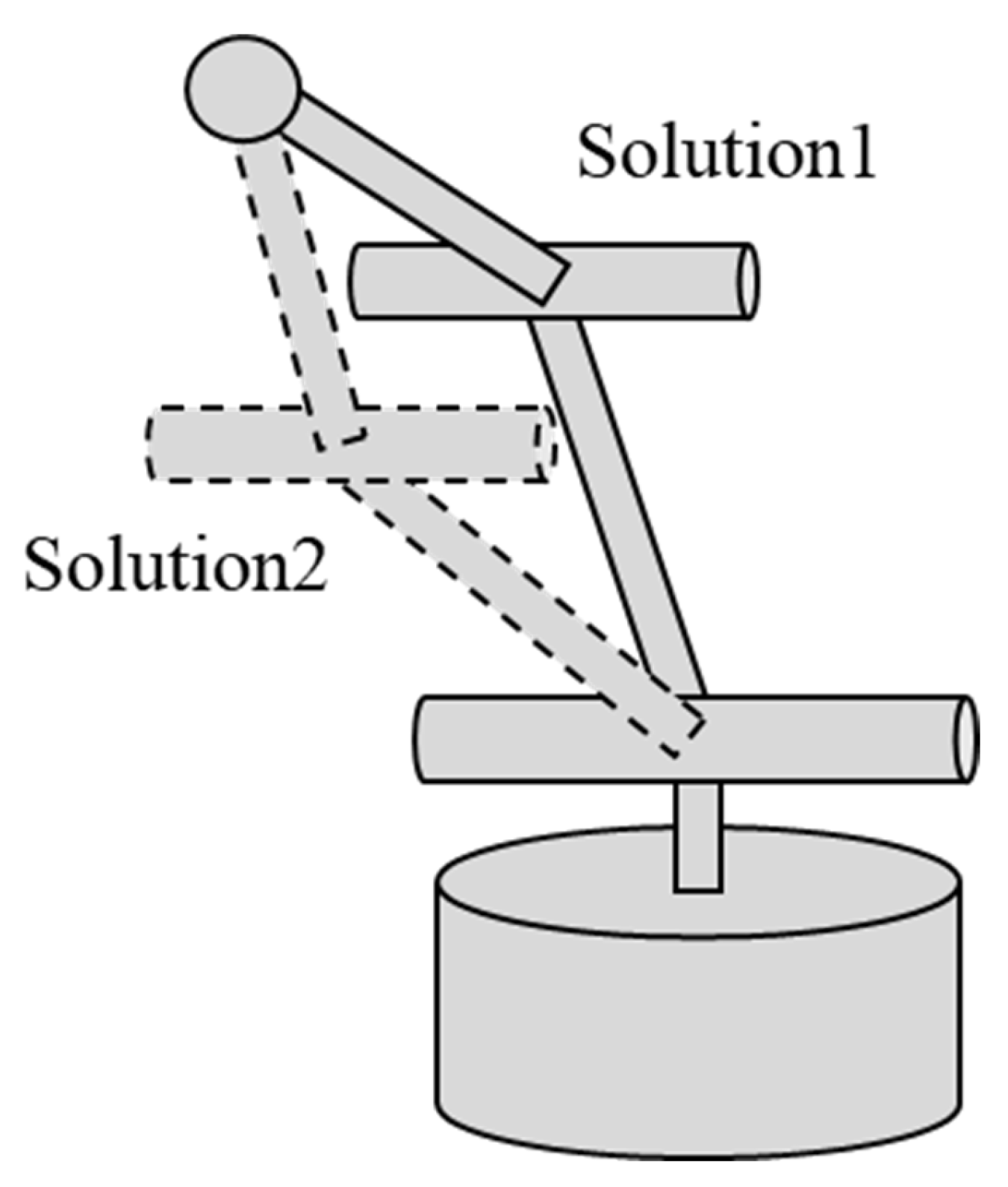

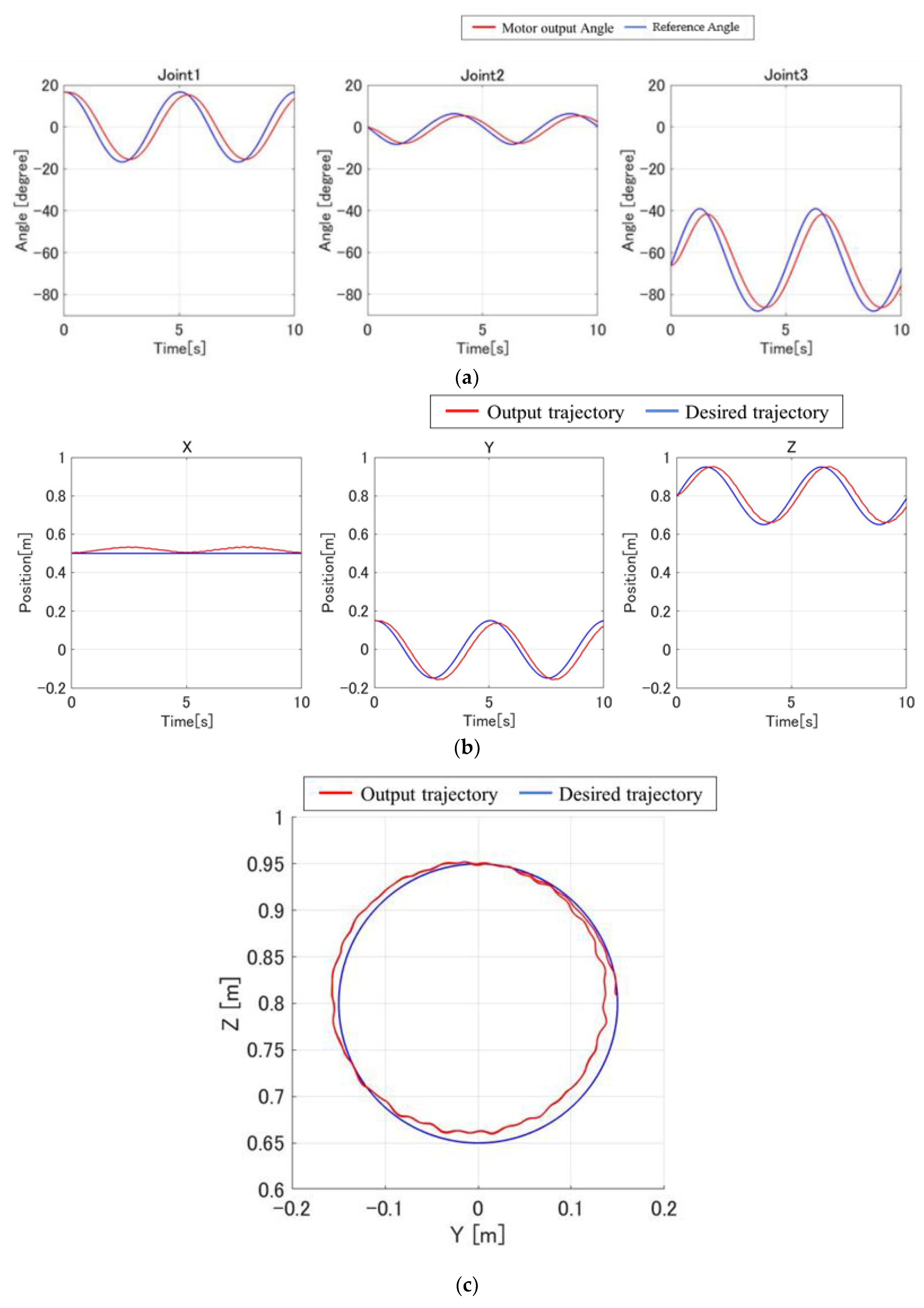


| Component | Specification |
|---|---|
| Servo Motor 1 (Joint 1) | Type: V850-012EL8; Voltage: 80 V; Current: 7.6 A; Power: 500 W; Speed: 2500 rpm; Torque: 1.96 N·m; Inertia: 0.60 × 10−3 kg·m2; Mass: 4.0 kg |
| Servo Motor 2 (Joint 2) | Type: T511-012EL8; Voltage: 75 V; Current: 2 A; Power: 100 W; Speed: 3000 rpm; Torque: 0.34 N·m; Inertia: 0.037 × 10−3 kg·m2; Mass: 0.95 kg |
| Servo Motor 3 (Joint 3) | Type: V404-012EL8; Voltage: 72 V; Current: 1 A; Power: 40 W; Speed: 3000 rpm; Torque: 0.13 N·m; Inertia: 0.0084 × 10−3 kg·m2; Mass: 0.4 kg |
| Encoder | Resolution: 1000 P/R; Reduction Ratio: 1/100 |
| Harmonic Drive—Joint 1 | Type: CSF-40-100-2A-R-SP; Ratio: 1/100; Spring Constant: 23 N·m/rad; Inertia: 4.50 × 10−4 kg·m2 |
| Harmonic Drive—Joint 2 | Type: CSF-17-100-2A-R-SP; Ratio: 1/100; Spring Constant: 1.6 × 10−4 N·m/rad; Inertia: 0.079 × 10−4 kg·m2 |
| Harmonic Drive—Joint 3 | Type: CSF-14-100-2A-R-SP; Ratio: 1/100; Spring Constant: 0.71 × 10−4 N·m/rad; Inertia: 0.033 × 10−4 kg·m2 |
| Link 1 | Material: Stainless Steel; Length: 0.44 m; Radius: 0.0005 m |
| Link 2 | Material: Aluminum; Length: 0.44 m; Radius: 0.004 m |
| Strain Gauge | Type: KGF-2-120-C1-23L1M2R |
| Epoch | 5000 |
| Minimum performance gradient | 10 × 10−15 |
| Maximum validation failure | 1000 |
| Maximum parameter μ | 10 × 1060 |
| Model Type | Dataset | Advance Time | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.28 s | 0.29 s | 0.30 s | ||
| Feed forward model | Training data | 2.8921 × 10−6 | 3.0479 × 10−6 | 2.348 × 10−6 |
| Test data | 9.9402 × 10−6 | 2.739 × 10−6 | 0.00010036 | |
| Validation data | 1.8928 × 10−6 | 5.4948 × 10−6 | 2.0567 × 10−6 | |
| Inverse model | Training data | 0.0014128 | 4.3452 × 10−5 | 8.1377 × 10−5 |
| Test data | 0.01554 | 0.0058988 | 0.0084634 | |
| Validation data | 0.005191 | 0.0005195 | 0.0063507 | |
| Method | Center (Y, Z) | Radius |
|---|---|---|
| Neural network | (−0.0016, 0.8069) | 0.1490 |
| Inverse kinematics | (−0.0062, 0.8247) | 0.1433 |
| Desired trajectory | (0.00055983, 0.8000) | 0.1500 |
| Method | (x, y) | r |
|---|---|---|
| NN | (−0.0016, 0.8069) | 0.1490 |
| IK | (−0.0062, 0.8247) | 0.1433 |
| desired | (0.00055983, 0.8000) | 0.1500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sasaki, M.; Takeda, M.; Muguro, J.; Njeri, W. Trajectory Control of Flexible Manipulators Using Forward and Inverse Models with Neural Networks. Vibration 2025, 8, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration8030048
Sasaki M, Takeda M, Muguro J, Njeri W. Trajectory Control of Flexible Manipulators Using Forward and Inverse Models with Neural Networks. Vibration. 2025; 8(3):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration8030048
Chicago/Turabian StyleSasaki, Minoru, Mizuki Takeda, Joseph Muguro, and Waweru Njeri. 2025. "Trajectory Control of Flexible Manipulators Using Forward and Inverse Models with Neural Networks" Vibration 8, no. 3: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration8030048
APA StyleSasaki, M., Takeda, M., Muguro, J., & Njeri, W. (2025). Trajectory Control of Flexible Manipulators Using Forward and Inverse Models with Neural Networks. Vibration, 8(3), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration8030048





