Influence of Coupling Forces and Body Posture on the Rotational Hand–Arm Impedance in yh Direction
Abstract
1. Introduction
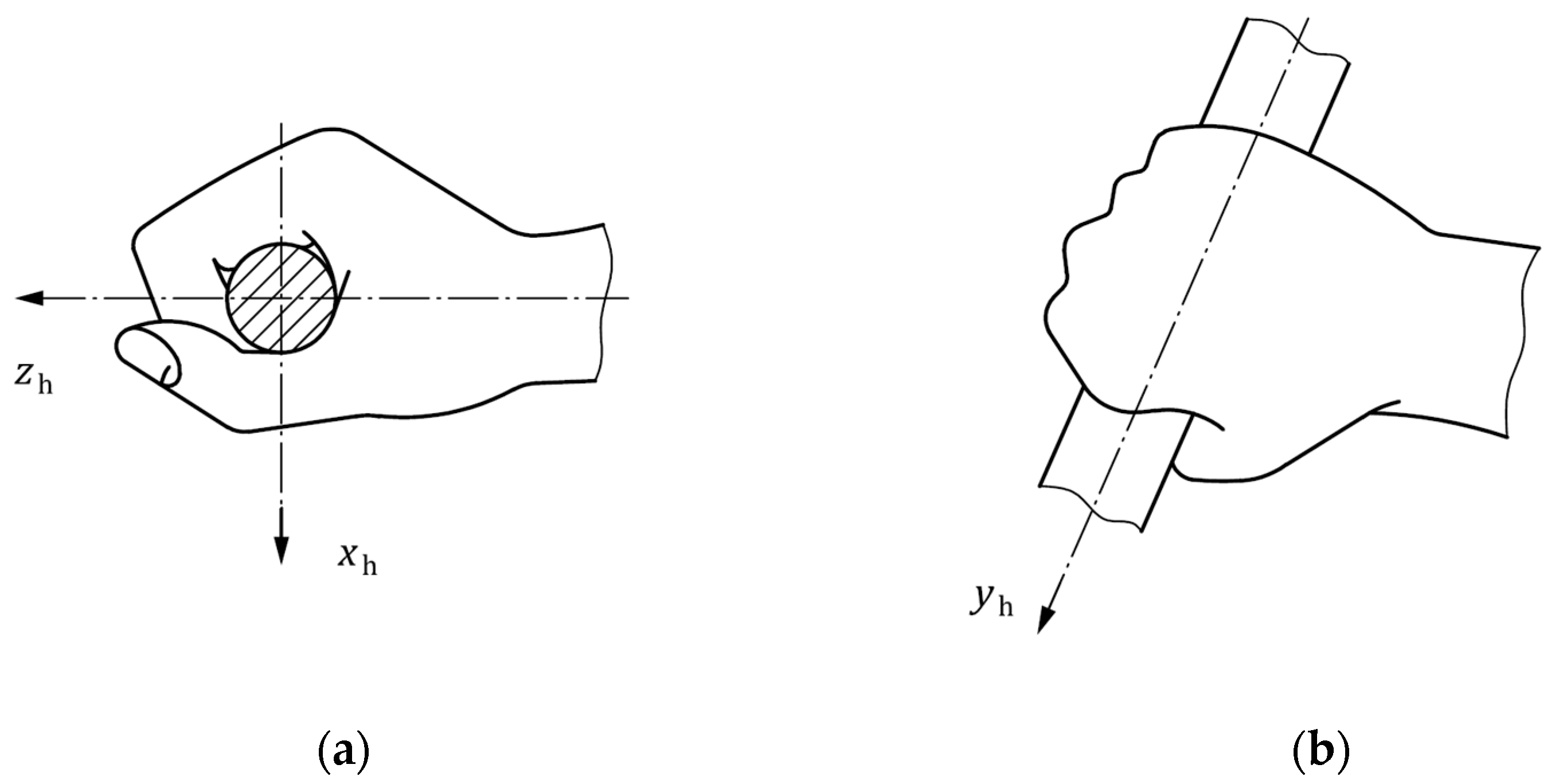
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Subjects
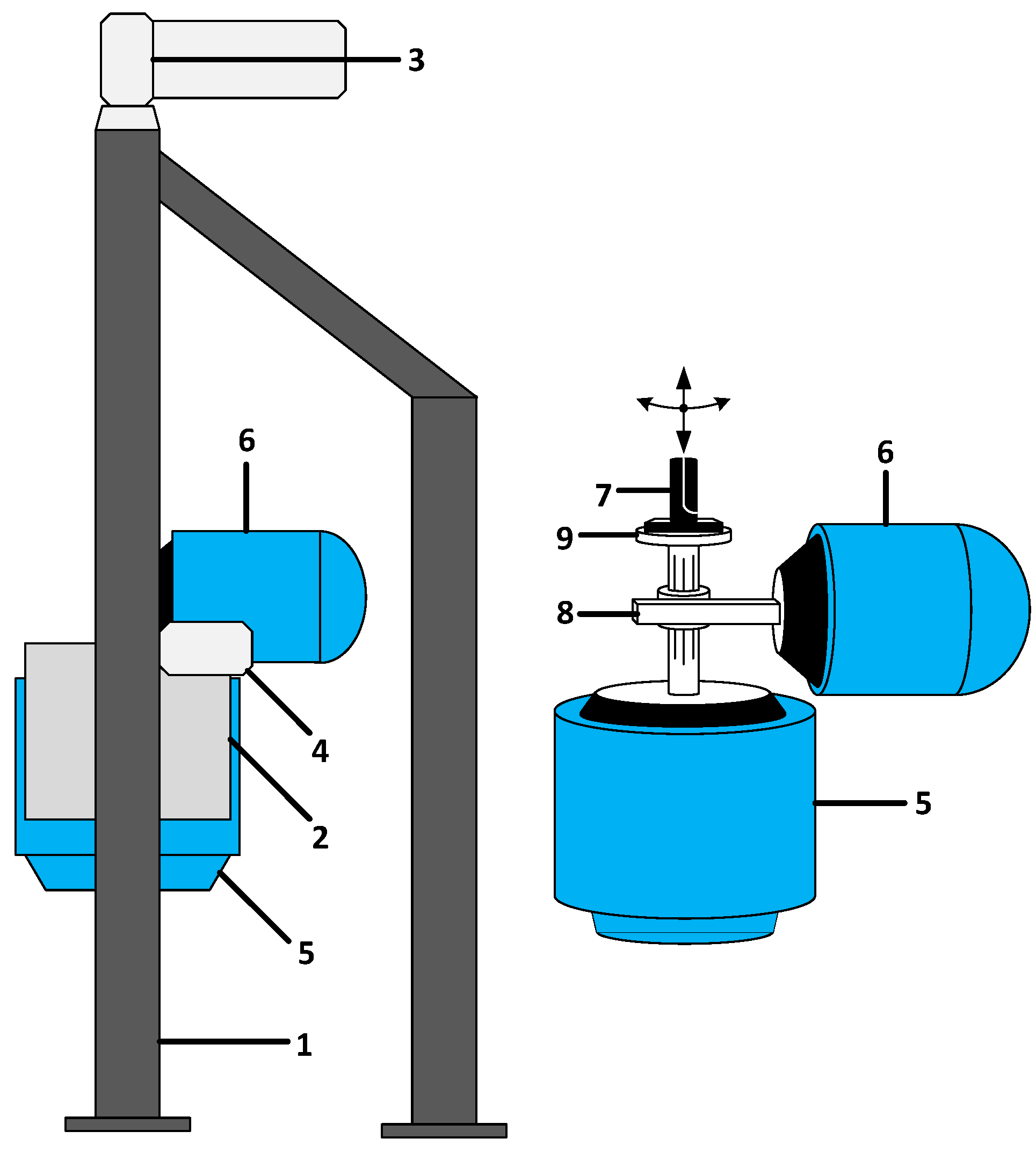
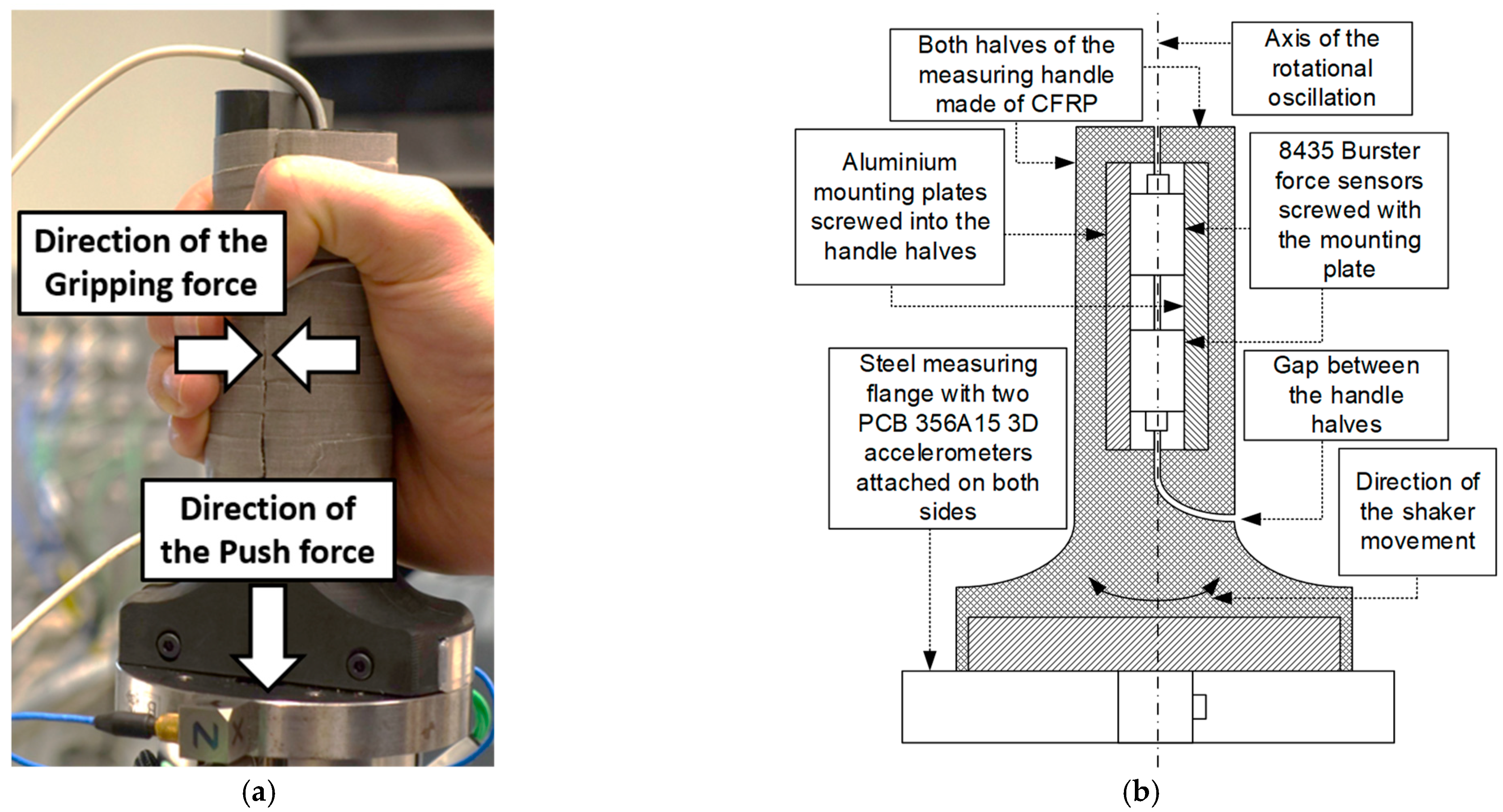
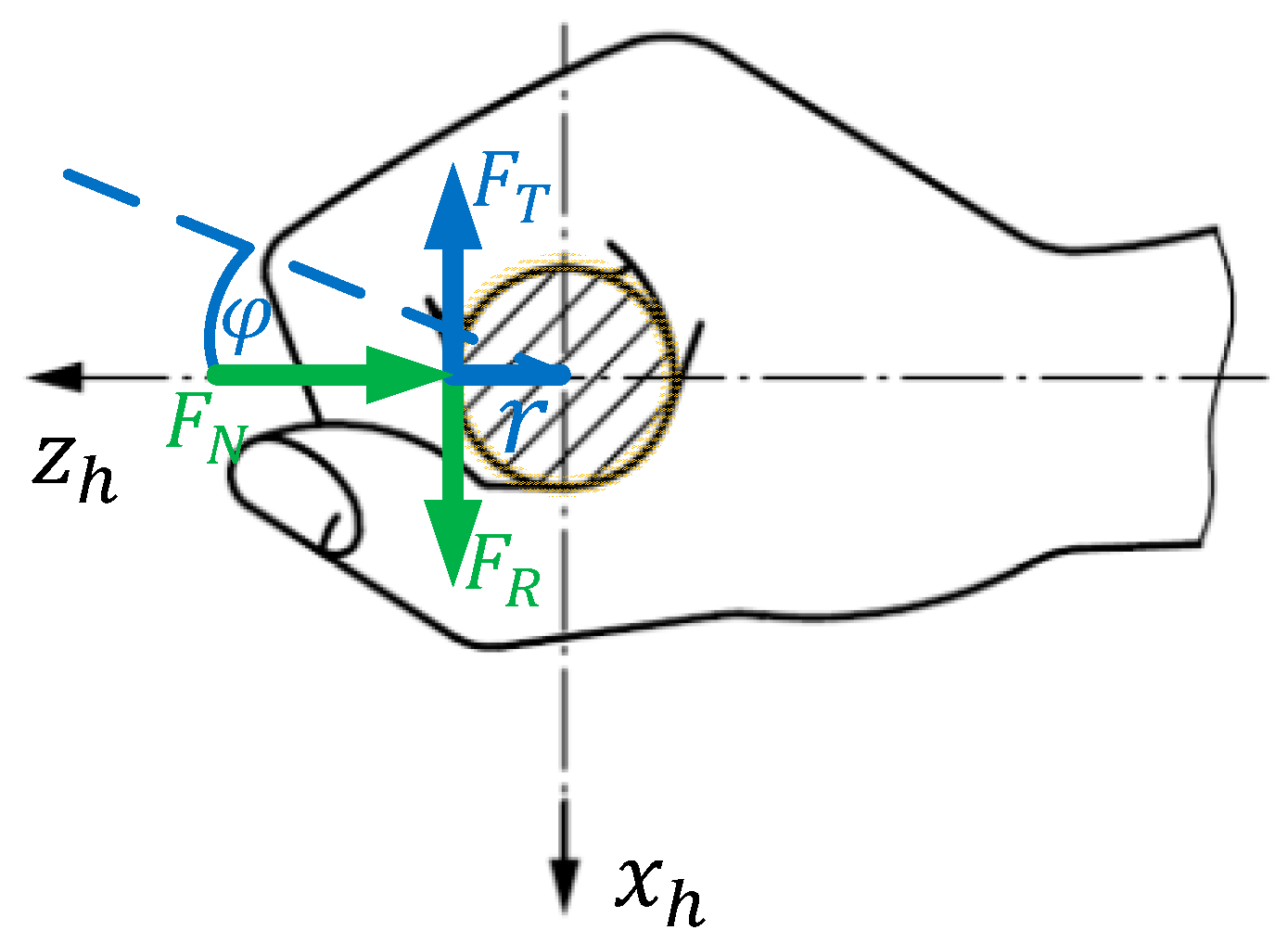
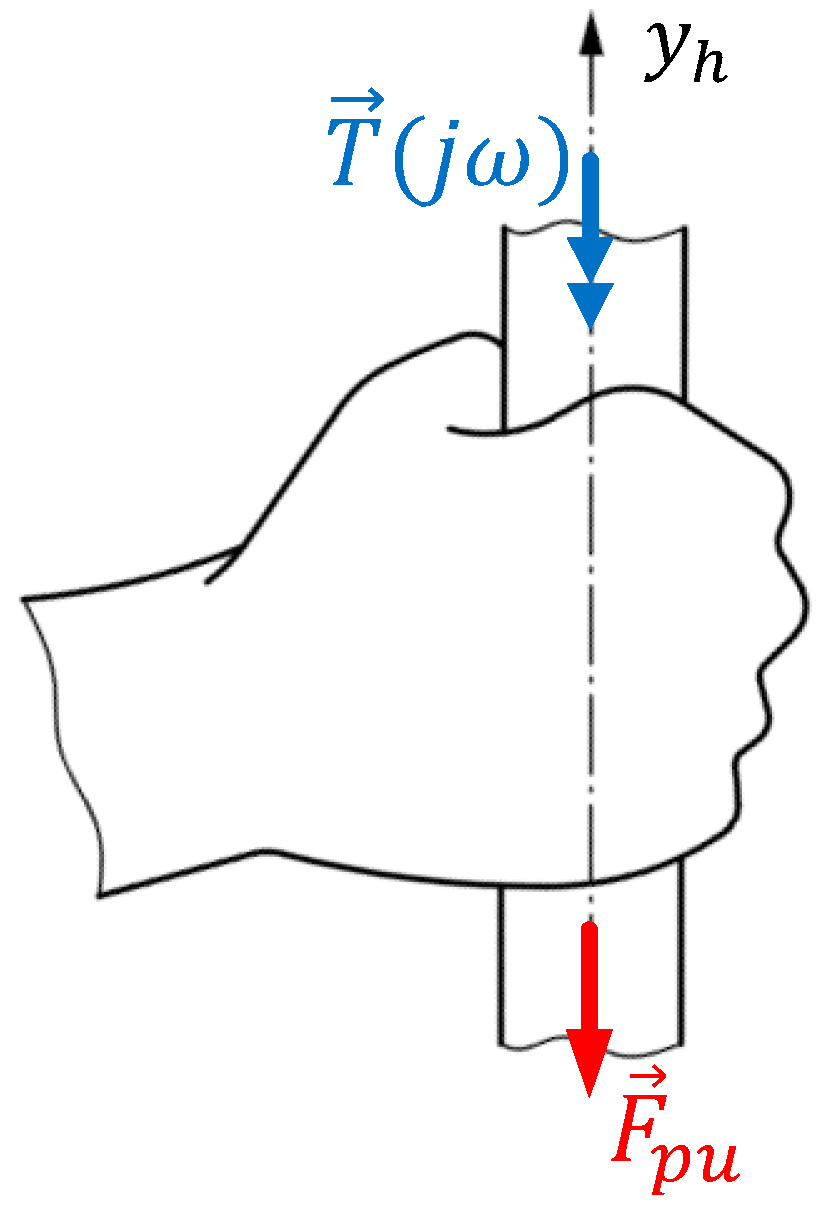
2.2. Test Apperatus
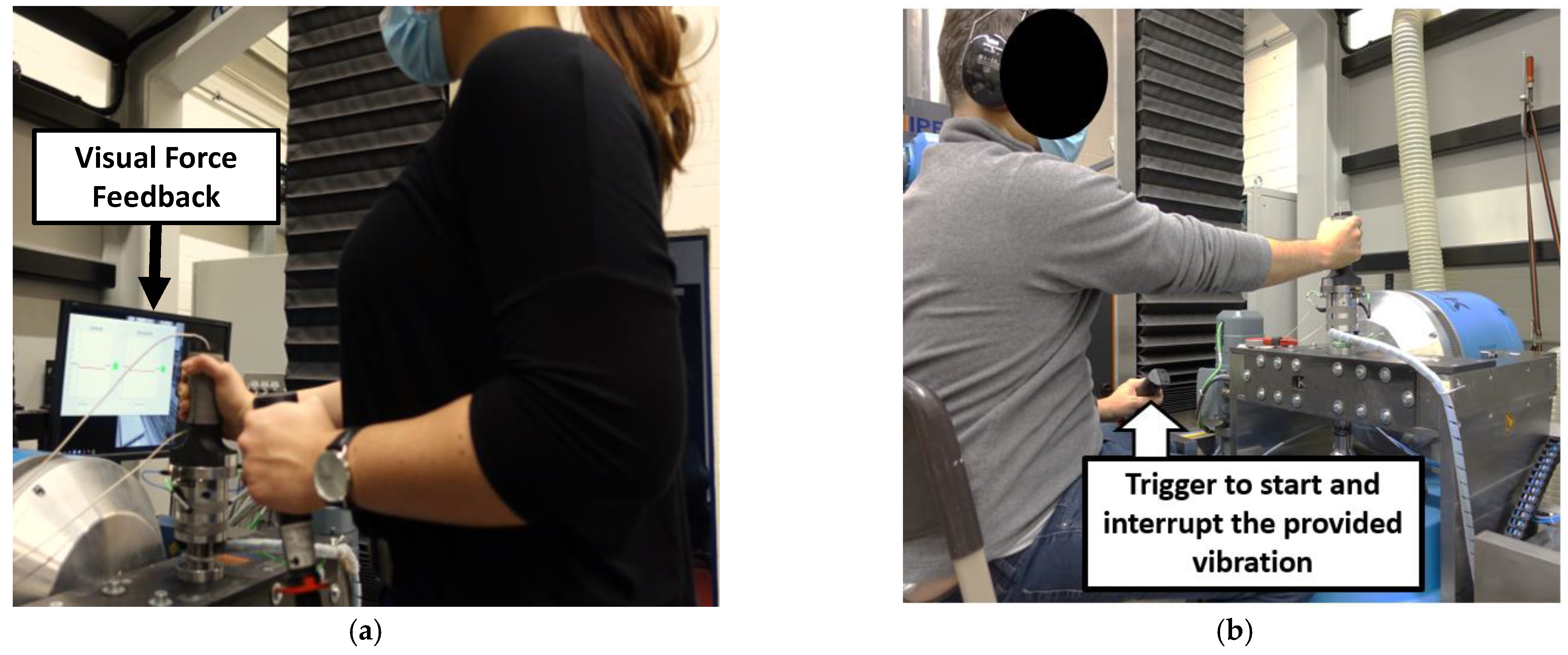
2.3. Test Procedure
2.4. Data Evaluation
3. Results
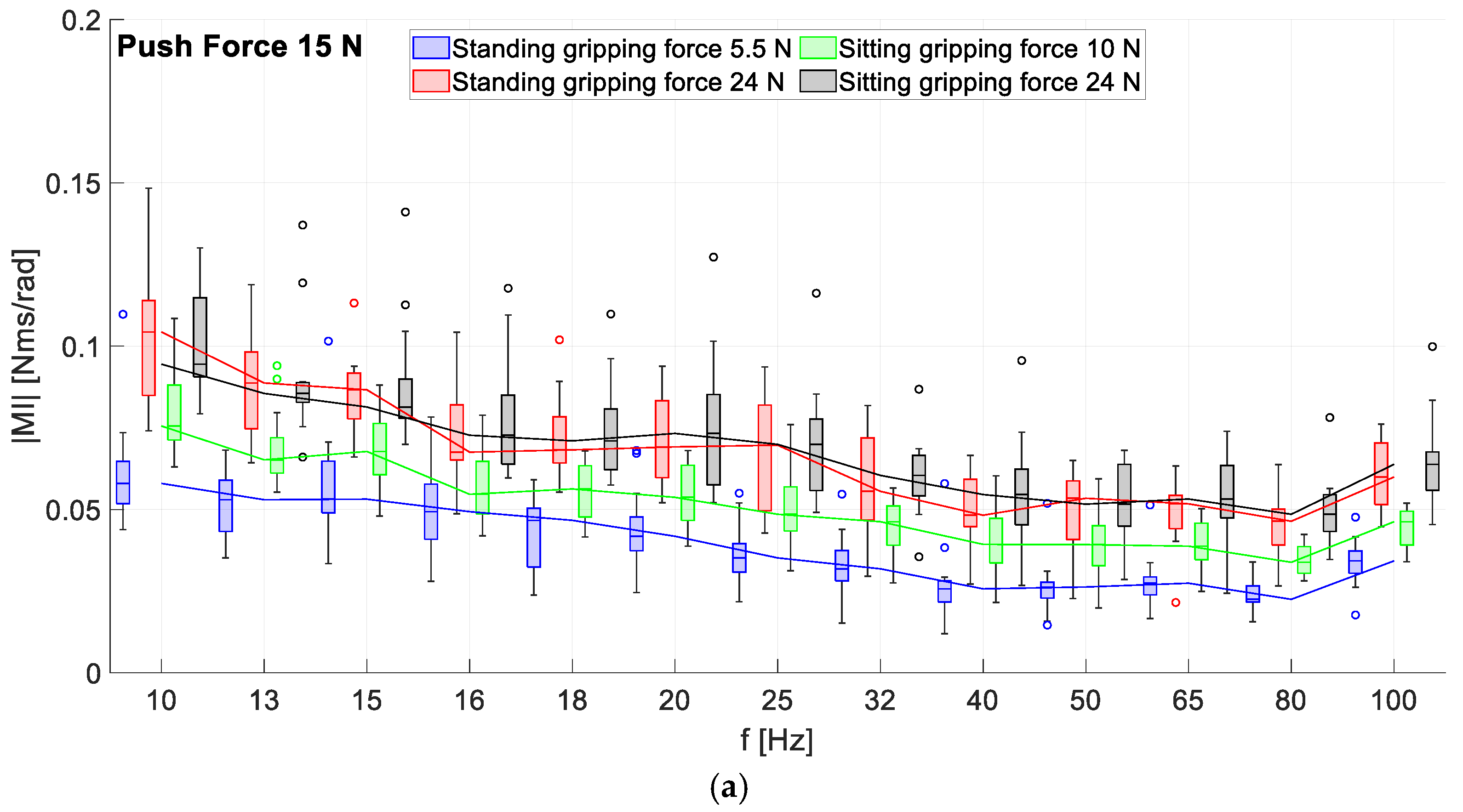
3.1. Influence of the Gripping Force on the RMI
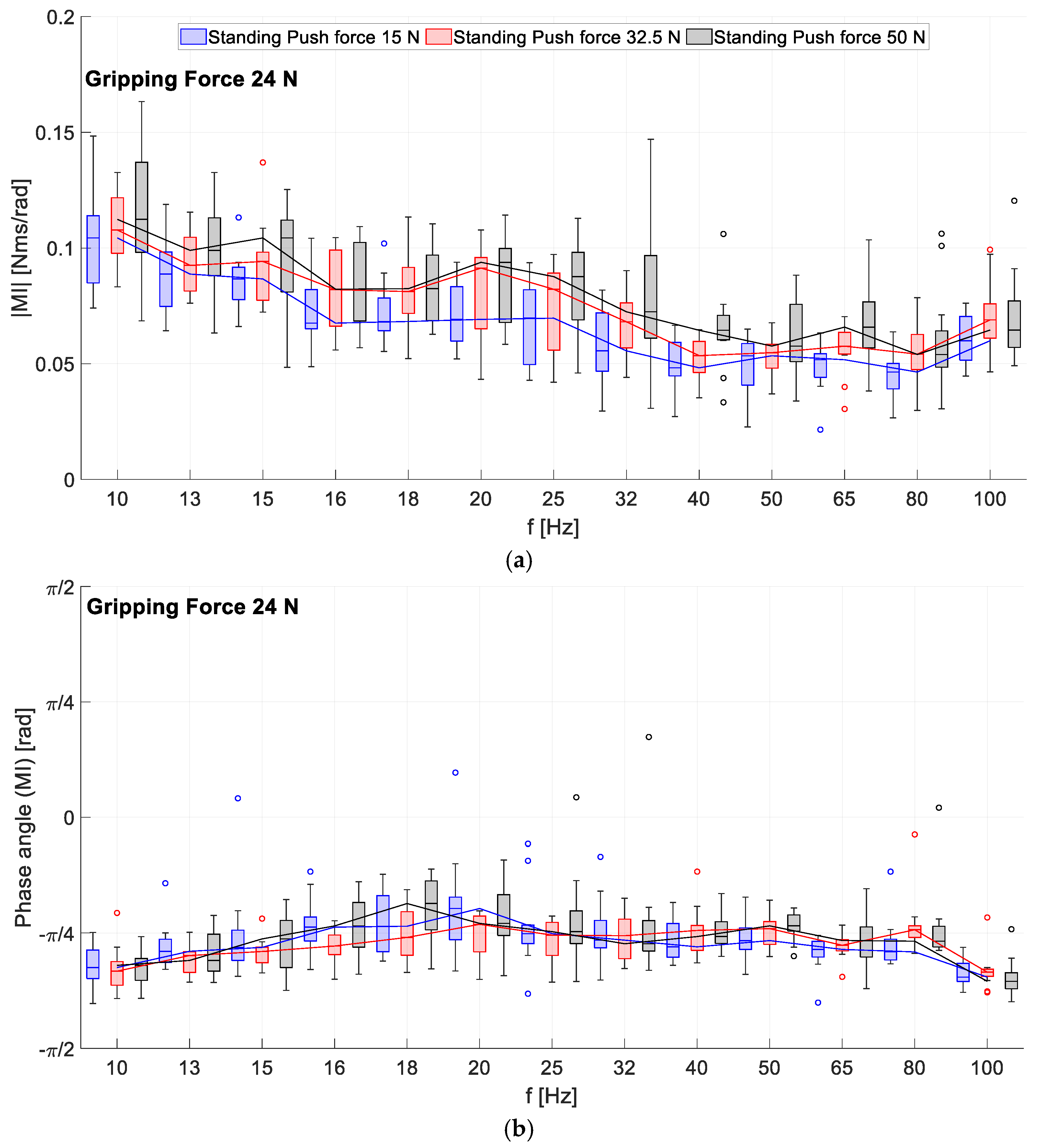
3.2. Influence of Push Force on the RMI
3.3. Influence of the Body Posture on the RMI
4. Discussion
4.1. What Is the Course of the RMI of the HAS for Rotational Vibration Excitation around the -axis?
4.2. How Is the RMI in Direction Influenced by Gripping Forces?
4.3. How Is the RMI in Direction Influenced by Push Forces?
4.4. How Is the RMI in Direction Influenced by Body Posture?
4.5. Relevance of the Results to Industrial Applications
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krajnak, K. Health effects associated with occupational exposure to hand-arm or whole body vibration. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2018, 21, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bovenzi, M. Hand-arm vibration syndrome and dose-response relation for vibration induced white finger among quarry drillers and stonecarvers. Italian Study Group on Physical Hazards in the Stone Industry. Occup. Environ. Med. 1994, 51, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, D.J.; Rillie, I.; Chileshe, N.; Lai, J.; Hosseini, M.R.; Thwala, W.D.D. A field survey of hand–arm vibration exposure in the UK utilities sector. Eng. Constr. Arch. Manag. 2020, 27, 2179–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, Z.; Shafiq, M.; Cocca, P.; Marciano, F.; Tayyab, A. Hand Arm Vibration, Grip Strength Assessment and the Prevalence of Health Disorders Among Stone Crushing Workers. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vihlborg, P.; Bryngelsson, I.-L.; Lindgren, B.; Gunnarsson, L.G.; Graff, P. Association between vibration exposure and hand-arm vibration symptoms in a Swedish mechanical industry. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2017, 62, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademacher, A.; Küffer, G.; Spengel, F. Vibration white finger-Syndrom bei acht Schleifern eines großen metallverarbeitenden Betriebes. Med. Klinik 1993, 10, 568–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verberk, M.M.; Sallé, H.J.; Kempers, O. Vibratory and tactile sense of the fingers after working with sanders. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 1985, 56, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenmann, A.; Uhl, M.; Gwosch, T.; Matthiesen, S. The influence of human interaction on the vibration of hand-held human-machine systems—The effect of body posture, feed force, and gripping forces on the vibration of hammer drills. Appl. Ergon. 2021, 95, 103430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.G.; Welcome, D.E.; McDowell, T.W.; Wu, J.Z. Modeling of the biodynamic responses distributed at the fingers and palm of the hand in three orthogonal directions. J. Sound Vib. 2013, 332, 1125–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.G.; Welcome, D.E.; McCormick, R.E. 3-D laboratory simulation of hand-transmitted vibration. In Proceedings of the 13th Japan Group Meeting on Human Responses to Vibration, Osaka, Japan, 3–5 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rakheja, S.; Wu, J.; Dong, R.; Schopper, A.; Boileau, P. A Comparison of biodynamic Models of the human Hand–Arm System for Applications to Hand-held Power Tools. J. Sound Vib. 2002, 249, 55–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronjäger, L.; Jahn, R.; Riederer, H. Entwicklung eines Versuchsstandes zur reproduzierbaren Messung der Vibration schlagender handgeführter Maschinen. In Development of a Test Bench for the Reproducible Measurement of the Vibration of Hand Held Percussive Machines; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Adewusi, S.; Rakheja, S.; Marcotte, P. Biomechanical models of the human hand-arm to simulate distributed biodynamic responses for different postures. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2012, 42, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.G.; Welcome, D.E.; Wu, J.Z.; McDowell, T.W. Development of hand-arm system models for vibrating tool analysis and test rig construction. Noise Control Eng. J. 2008, 56, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcotte, P.; Boutin, J.; Jasinski, J. Development of a hand-arm mechanical analogue for evaluating chipping hammer vibration emission values. J. Sound Vib. 2010, 329, 1968–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.H.; Radwin, R.G.; Richard, T.G. A single-degree-of-freedom dynamic model predicts the range of human responses to impulsive forces produced by power hand tools. J. Biomech. 2003, 36, 1845–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakheja, S.; Gurram, R.; Gouw, G.J. Development of linear and nonlinear hand-arm vibration models using optimization and linearization techniques. J. Biomech. 1993, 26, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempel, D.; Barr, A.; Antonucci, A. A New Test Bench System for Hammer Drills: Validation for Handle Vibration. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2017, 62, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempel, D.; Barr, A.; Antonucci, A. Evaluation of Handle Vibration for Hammer Drills Using A New Test Bench System. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Hand-Arm Vibration, Beijing, China, 13–16 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Radwin, R.G.; Armstrong, T.J. Assessment of hand vibration exposure on an assembly line. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1985, 46, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangold, S. Erfassung heterogener passiver Anwendereigenschaften und deren Abbildung in einem einstellbaren Hand-Arm Modell am Beispiel eines Impulsschraubers: Acquisition of user’s heterogeneous biodynamic response and possibilities to model those in an adjustable hand-arm model using the example of an impulse wrench. In Forschungsberichte des IPEK—Institut für Produktentwicklung; Albers, A., Matthiesen, S., Eds.; IPEK–Institut für Produktentwicklung am KIT: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Matysek, M.; Kern, T.A. Entwicklung Haptischer Geräte: Ein Einstieg für Ingenieure. In Haptic Device Development: An Introduction for Engineers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10068:2012(E); Mechanical Vibration and Shock—Mechanical Impedance of the Human Hand-Arm System at the Driving Point. ISO—International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- DIN EN ISO 5349-1:2001-12; Mechanische Schwingungen—Messung und Bewertung der Einwirkung von Schwingungen auf das Hand-Arm-System des Menschen Teil 1: Allgemeine Anforderungen: Mechanical vibration—Measurement and evaluation of human exposure—Part 1: General requirements, 5349–1. DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung e. V.: Berlin, Germany, 2001.
- Aldien, Y.; Marcotte, P.; Rakheja, S.; Boileau, P.-E. Mechanical Impedance and Absorbed Power of Hand-Arm under xh-Axis Vibration and Role of Hand Forces and Posture. Ind. Health 2005, 43, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.G.; Welcome, D.E.; Xu, X.S.; Warren, C.; McDowell, T.W.; Wu, J.Z.; Rakheja, S. Mechanical impedances distributed at the fingers and palm of the human hand in three orthogonal directions. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 1191–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.G.; Welcome, D.E.; McDowell, T.W.; Wu, J.Z. Measurement of biodynamic response of human hand-arm system. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 294, 807–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.G.; Welcome, D.E.; Wu, J.Z. Estimation of Biodynamic Forces Distributed on the Fingers and the Palm Exposed to Vibration. Ind. Health 2005, 43, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldien, Y.; Marcotte, P.; Rakheja, S.; Boileau, P.-E. Influence of hand-arm posture on biodynamic response of the human hand-arm exposed to zh-axis vibration. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2006, 36, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.S.; Welcome, D.E.; McDowell, T.W.; Wu, J.Z.; Wimer, B.; Warren, C.; Dong, R.G. The vibration transmissibility and driving-point biodynamic response of the hand exposed to vibration normal to the palm. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2011, 41, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burström, L. The influence of biodynamic factors on the mechanical impedance of the hand and arm. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 1997, 69, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, M.; Rakheja, S.; Marcotte, P.; Dewangan, K.N.; Adewusi, S. Measurement of coupling forces at the power tool handle-hand interface. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2015, 50, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenmann, A.; Matthiesen, S. The Rotational Mechanical Impedance of the Hand-Arm System—A Preliminary Study. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Hand-Arm-Vibration, Nancy, France, 6–9 June 2019; pp. 75–76. Available online: https://publikationen.bibliothek.kit.edu/1000095936 (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- Schröder, T.; Lindenmann, A.; Resch, A.; Matthiesen, S.; Gwosch, T. Influence of Coupling Forces on the Rotational Hand-Arm Impedance in xh direction. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN ISO 7250-1:2017; Basic Human Body Measurements for Technological Design—Part 1: Body Measurement Definitions and Landmarks. DIN—Deutsches Institut für Normung: Berlin, Germany, 2017.
- DIN CEN ISO 7250-2; Wesentliche Maße des Menschlichen Körpers Für Die technische Gestaltung—Teil 2: Anthropometrische Datenbanken Einzelner Nationaler: Basic Human Body Measurements for Technological Design. DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung e. V.: Berlin, Germany; ISO—International Organization for Standardization: Berlin, Germany, 2013.
- Matthiesen, S.; Lindenmann, A.; Bruchmueller, T. Anforderungen an ein Messsystem zur Ermittlung der Rotationsimpedanz von Hand-Arm Systemen. Humanschwingungen 2018, 2018, 91–106. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenmann, A.; Schröder, T.; Germann, R.; Gwosch, T.; Matthiesen, S. Effect of high level grip-and push force and elevated arm posture on the zh-axis hand-arm impedance. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2022, 92, 103375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10819:2012-7; Mechanical Vibration and Shock—Hand-Arm Vibration—Measurement and Evaluation of the Vibration Transmissibility of Gloves at the Palm of the Hand. ISO—International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- DIN EN ISO 10819:2019-5; Mechanische Schwingungen und Stöße—Hand-Arm-Schwingungen—Messung und Bewertung der Schwingungsübertragung von Handschuhen in der Handfläche: Mechanical Vibration and Shock—Hand-Arm Vibration—Measurement and Evaluation of Glove Palm Vibration Transmission. DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung e. V.: Berlin, Germany, 2019.
- World Medical Association. Declaration of Helsinki. 2013. Available online: https://www.uni-goettingen.de/de/document/download/a91ef4324cf47306d6dbf334687e70dc.pdf/helsinki.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2022).
- Cohen, J. Quantitative methods in psychology: A power primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 155–159. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.1043.9095 (accessed on 12 October 2022). [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.G.; Rakheja, S.; Schopper, A.W.; Han, B.; Smutz, W.P. Hand-transmitted vibration and biodynamic response of the human hand-arm: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 29, 393–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 15230:2007(E); Mechanical Vibration and Shock—Coupling forces at the Man-Machine Interface for Hand-Transmitted Vibration. ISO—International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.






| Arm Length (cm)  | Forearm Length (cm) | Thumb Length (mm)  | Hand Length (mm)  | Palm Length (mm)  | Hand Width (mm)  | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 76 | 37 | 70 | 195 | 105 | 85 |
| 5th percentile | 68.5 | 31.4 | 65 | 173 | 93 | 76 |
| 95th percentile | 81.4 | 41 | 79 | 205 | 115 | 95 |
| Body Posture | Minimum | Lower Quartile | Median | Upper Quartile | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sitting | 153.0 N | 316.4 N | 411.7 N | 418.9 N | 556.6 N |
| Standing | 148.1 N | 189.0 N | 351.6 N | 409.2 N | 611.3 N |
| Level | Body Posture | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Full factorial | |||
| 1 | Standing | ||
| 2 | |||
| 3 | |||
| Full factorial | |||
| 1 | Sitting | ||
| 2 | |||
| 3 |
| Specified Coupling Forces | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| - | |||
| - | |||
| Push Force: | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body Posture: | Standing | Sitting | Standing | Sitting | ||||
| Gripping Force | ||||||||
| f (Hz) | p | R | p | R | p | R | p | R |
| 10 | <0.001 * | 0.769 | 0.002 * | 0.578 | <0.001 * | 0.704 | 0.081* | - |
| 13 | <0.001 * | 0.840 | 0.002 * | 0.578 | <0.001 * | 0.715 | 0.057* | 0.377 |
| 15 | <0.001 * | 0.699 | 0.002 * | 0.598 | <0.001 * | 0.704 | 0.014* | 0.478 |
| 16 | 0.001 * | 0.629 | 0.001 * | 0.629 | 0.002 * | 0.597 | 0.113 * | - |
| 18 | <0.001 * | 0.840 | 0.001 * | 0.629 | <0.001 * | 0.672 | 0.002 * | 0.578 |
| 20 | <0.001 * | 0.709 | 0.004 * | 0.548 | 0.001 * | 0.640 | 0.014* | 0.478 |
| 25 | <0.001 * | 0.769 | 0.002 * | 0.588 | 0.001 * | 0.619 | <0.001 * | 0.709 |
| 32 | <0.001 * | 0.689 | 0.001 * | 0.619 | <0.001 * | 0.651 | 0.005 * | 0.538 |
| 40 | <0.001 * | 0.719 | 0.005 * | 0.538 | <0.001 * | 0.661 | 0.006 * | 0.528 |
| 50 | <0.001 * | 0.699 | 0.006 * | 0.528 | <0.001 * | 0.725 | 0.005 * | 0.538 |
| 65 | <0.001 * | 0.689 | 0.002 * | 0.588 | <0.001 * | 0.715 | <0.001 * | 0.689 |
| 80 | <0.001 * | 0.800 | <0.001 * | 0.749 | <0.001 * | 0.736 | 0.005 * | 0.538 |
| 100 | <0.001 * | 0.830 | <0.001 * | 0.811 | <0.001 * | 0.779 | <0.001 * | 0.749 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schröder, T.; Lindenmann, A.; Matthiesen, S. Influence of Coupling Forces and Body Posture on the Rotational Hand–Arm Impedance in yh Direction. Vibration 2023, 6, 375-398. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration6020023
Schröder T, Lindenmann A, Matthiesen S. Influence of Coupling Forces and Body Posture on the Rotational Hand–Arm Impedance in yh Direction. Vibration. 2023; 6(2):375-398. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration6020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchröder, Tassilo, Andreas Lindenmann, and Sven Matthiesen. 2023. "Influence of Coupling Forces and Body Posture on the Rotational Hand–Arm Impedance in yh Direction" Vibration 6, no. 2: 375-398. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration6020023
APA StyleSchröder, T., Lindenmann, A., & Matthiesen, S. (2023). Influence of Coupling Forces and Body Posture on the Rotational Hand–Arm Impedance in yh Direction. Vibration, 6(2), 375-398. https://doi.org/10.3390/vibration6020023






