Study on the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Hydrogen-Blended Natural Gas Leakage and Flare-Up in the Typical Semi-Open Space
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Models Construction
2.1. Mathematical Model
2.1.1. Diffusion and Ventilation Model
2.1.2. Combustion and Explosion Model
2.2. Independence of Geometry and Mesh
2.2.1. Typical Semi-Open Space Scenario
2.2.2. Typical Street-Front Restaurant Scenario
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. H-BNG Leak in a Semi-Open Space
3.1.1. Scenario
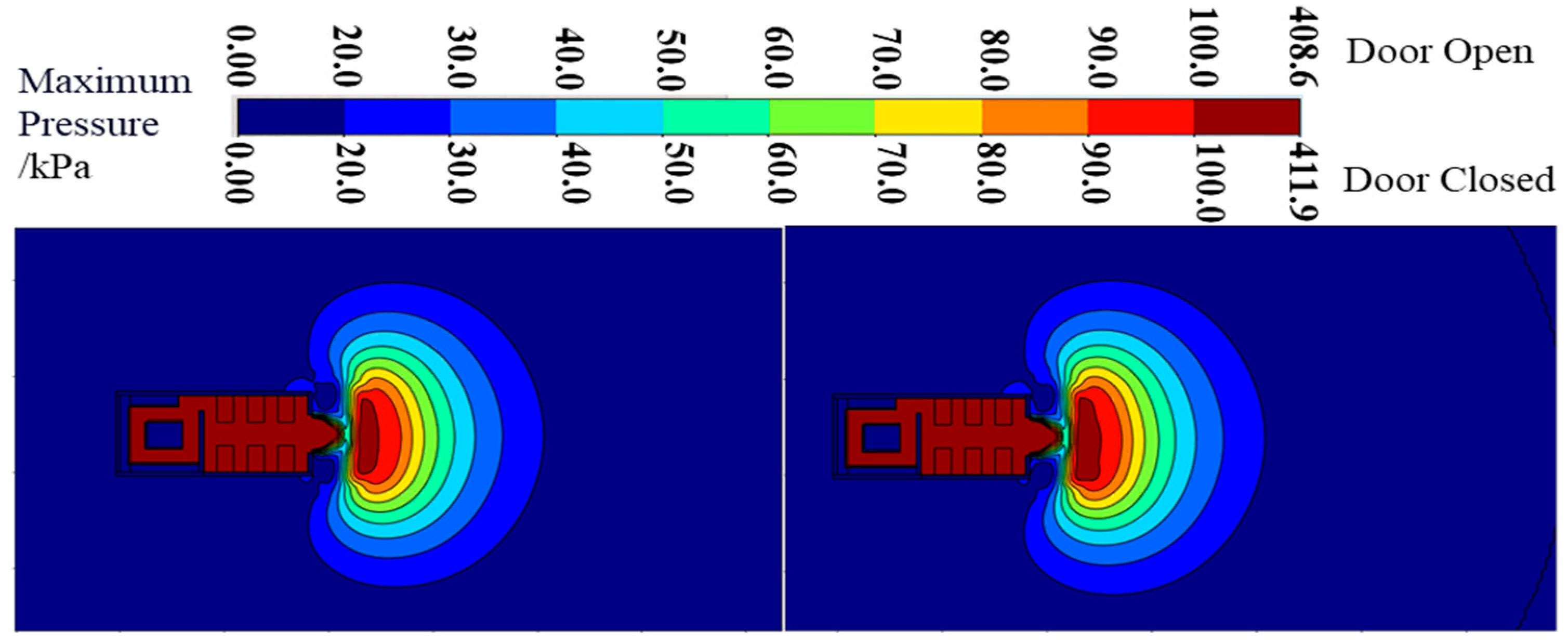
3.1.2. Pressure Field Distribution
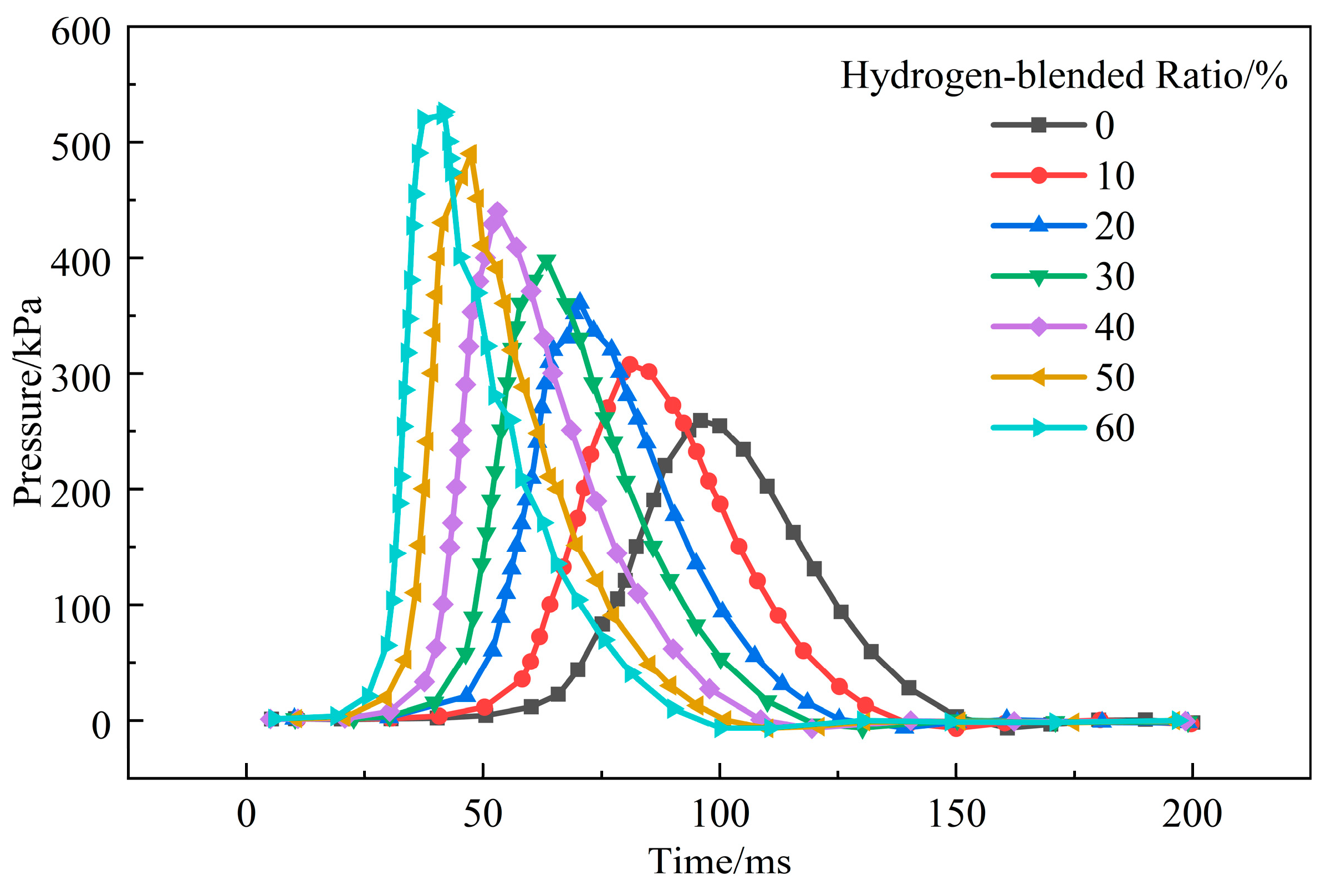
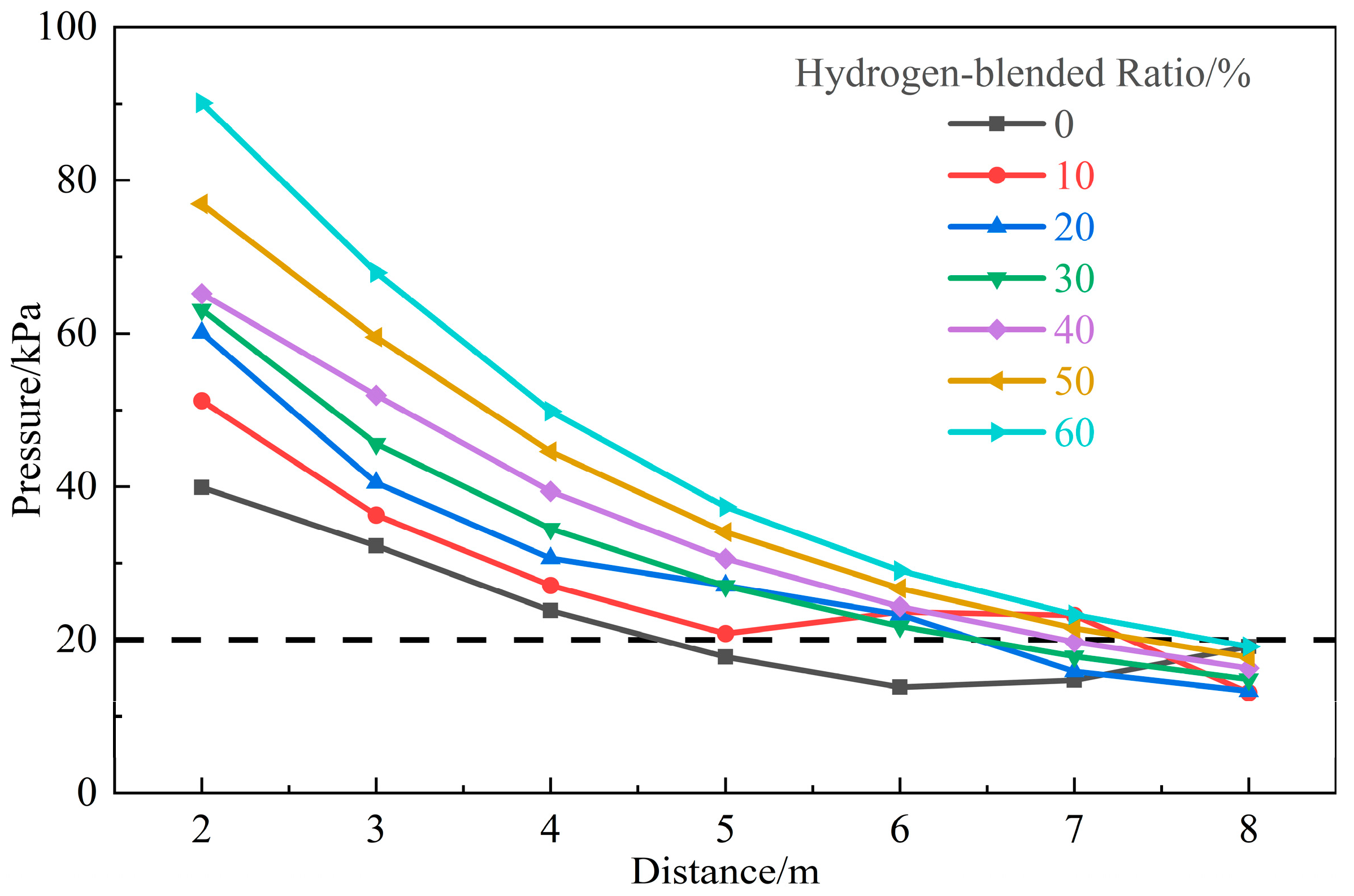
3.1.3. Influence of Hydrogen-Blended Ratio
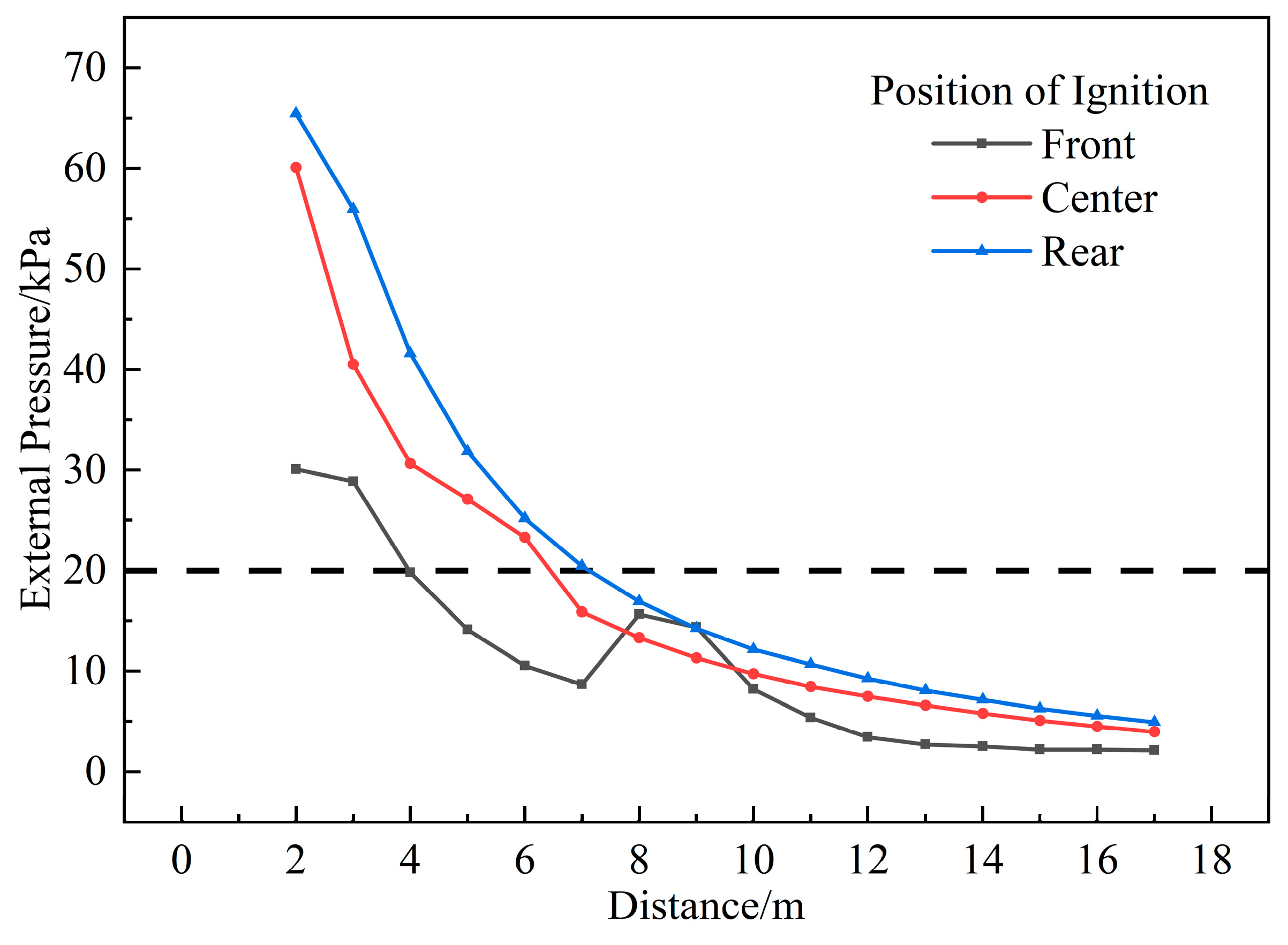
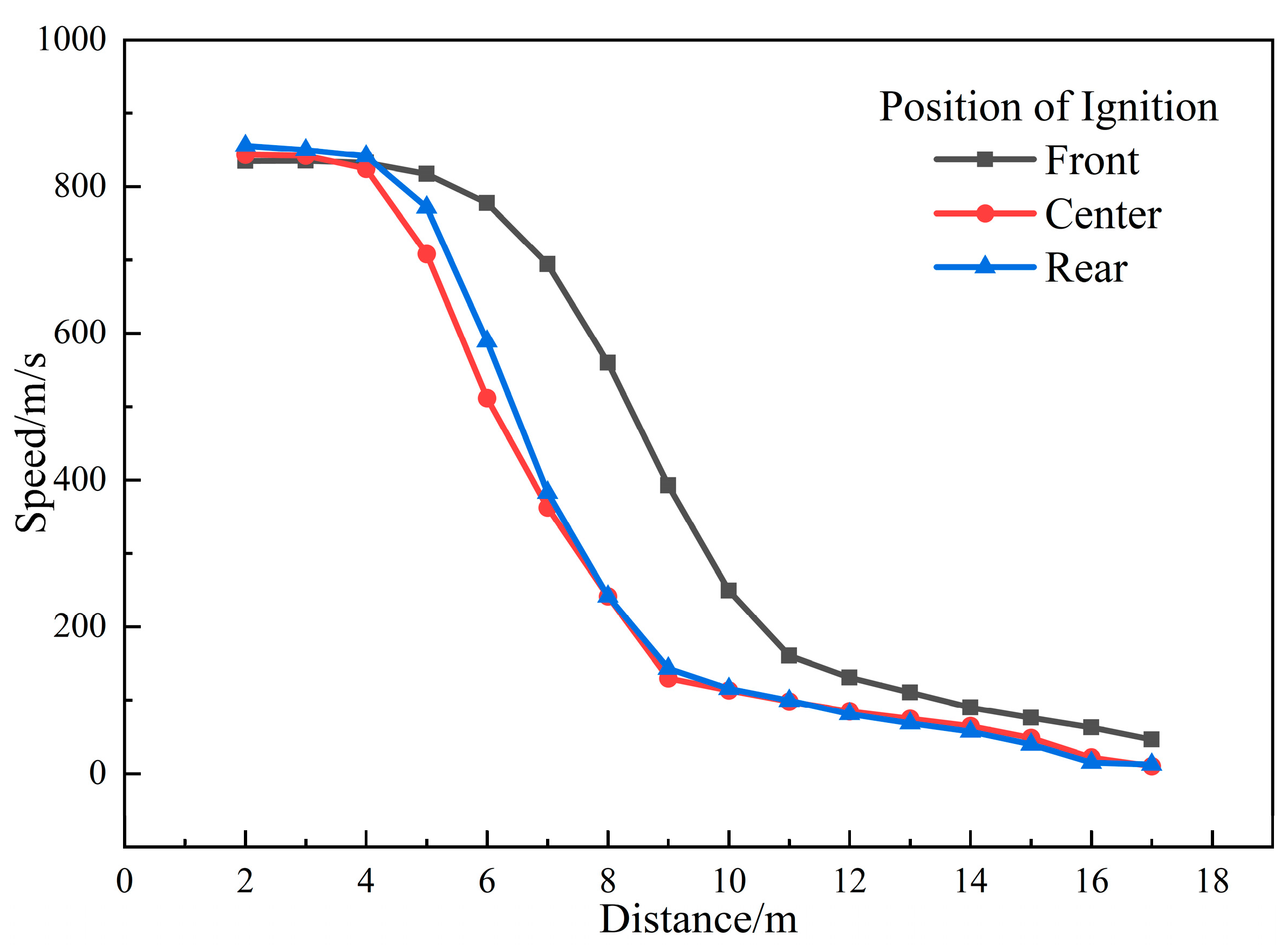
3.1.4. Influence of Ignition Position
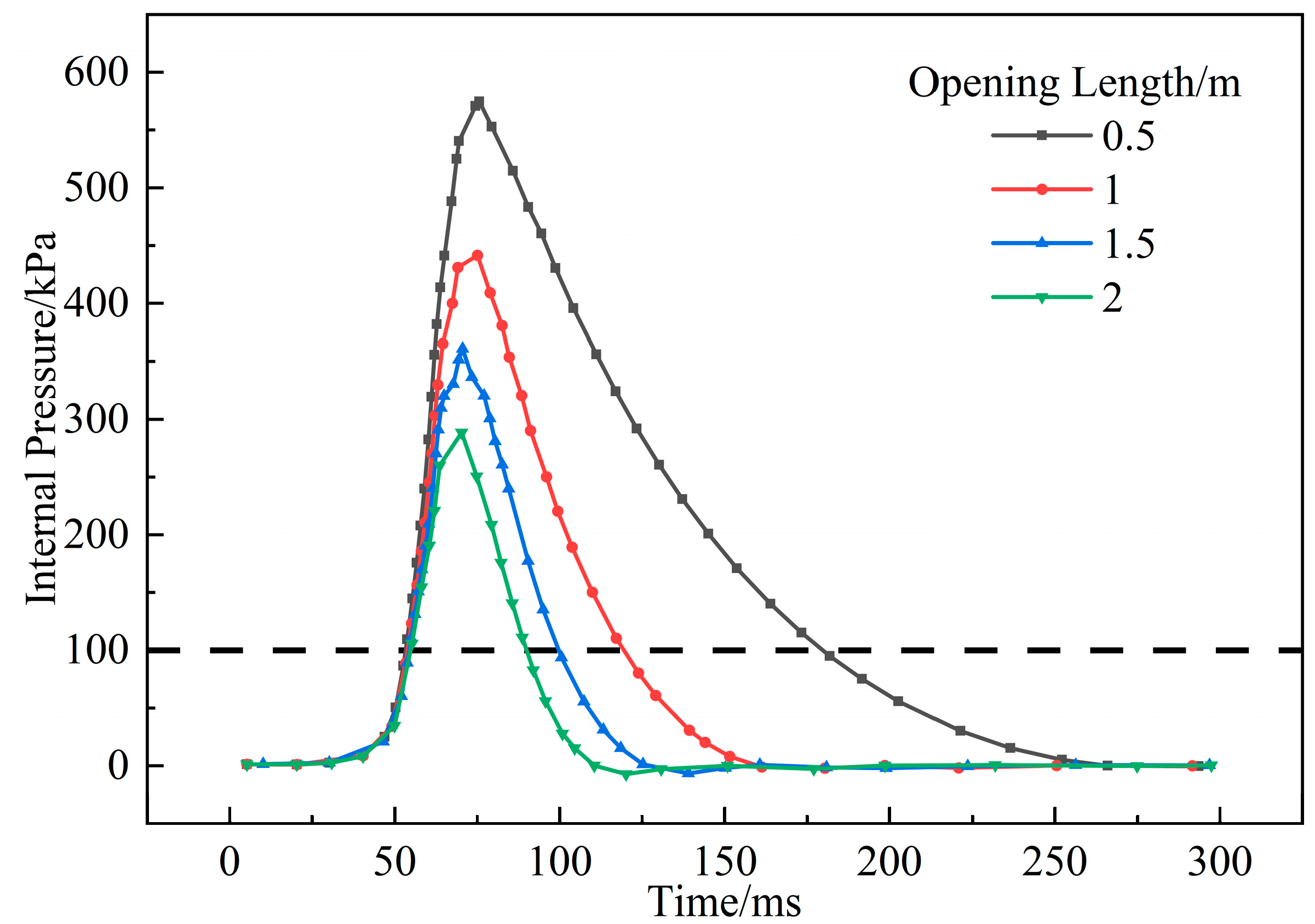
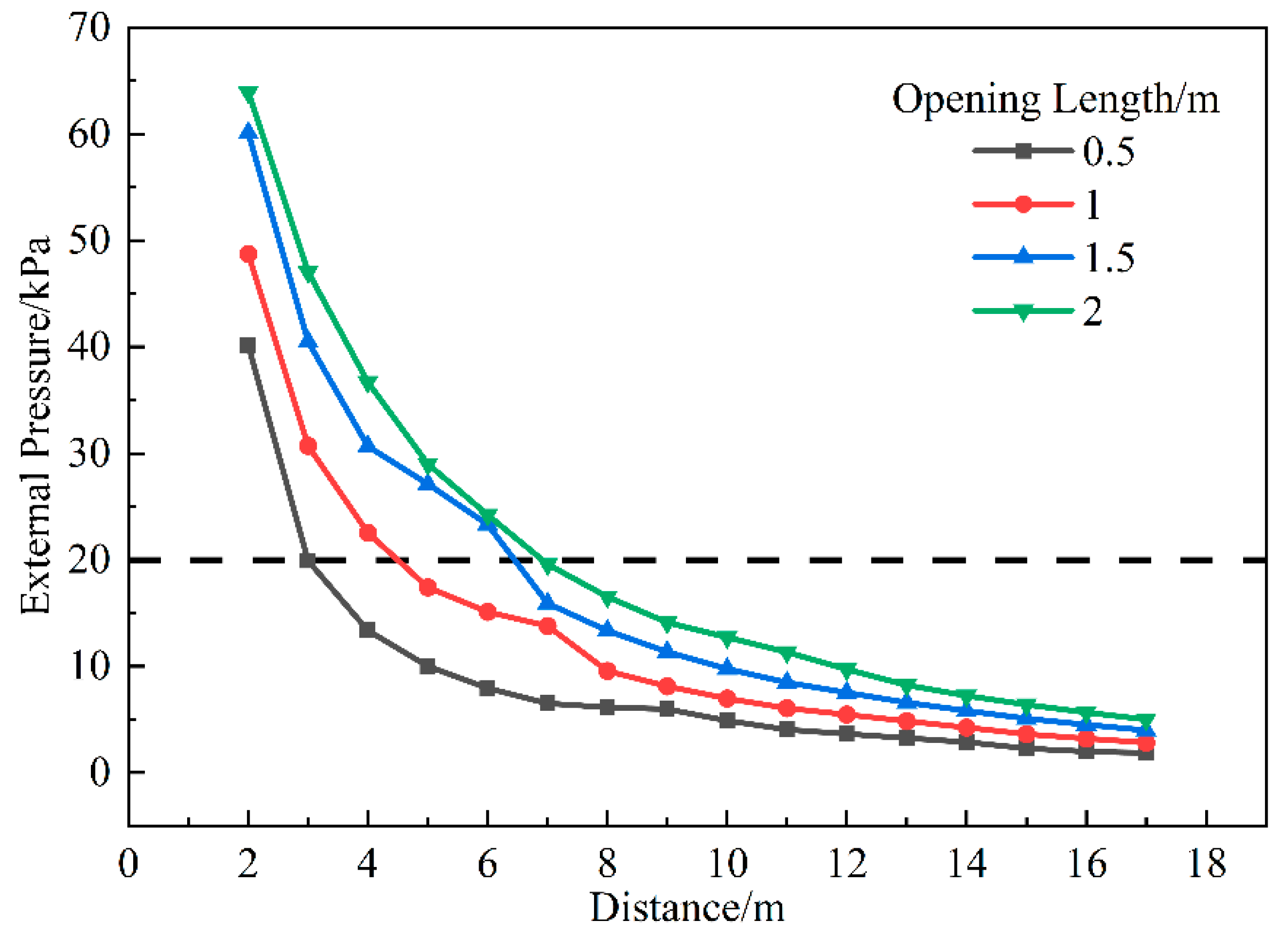
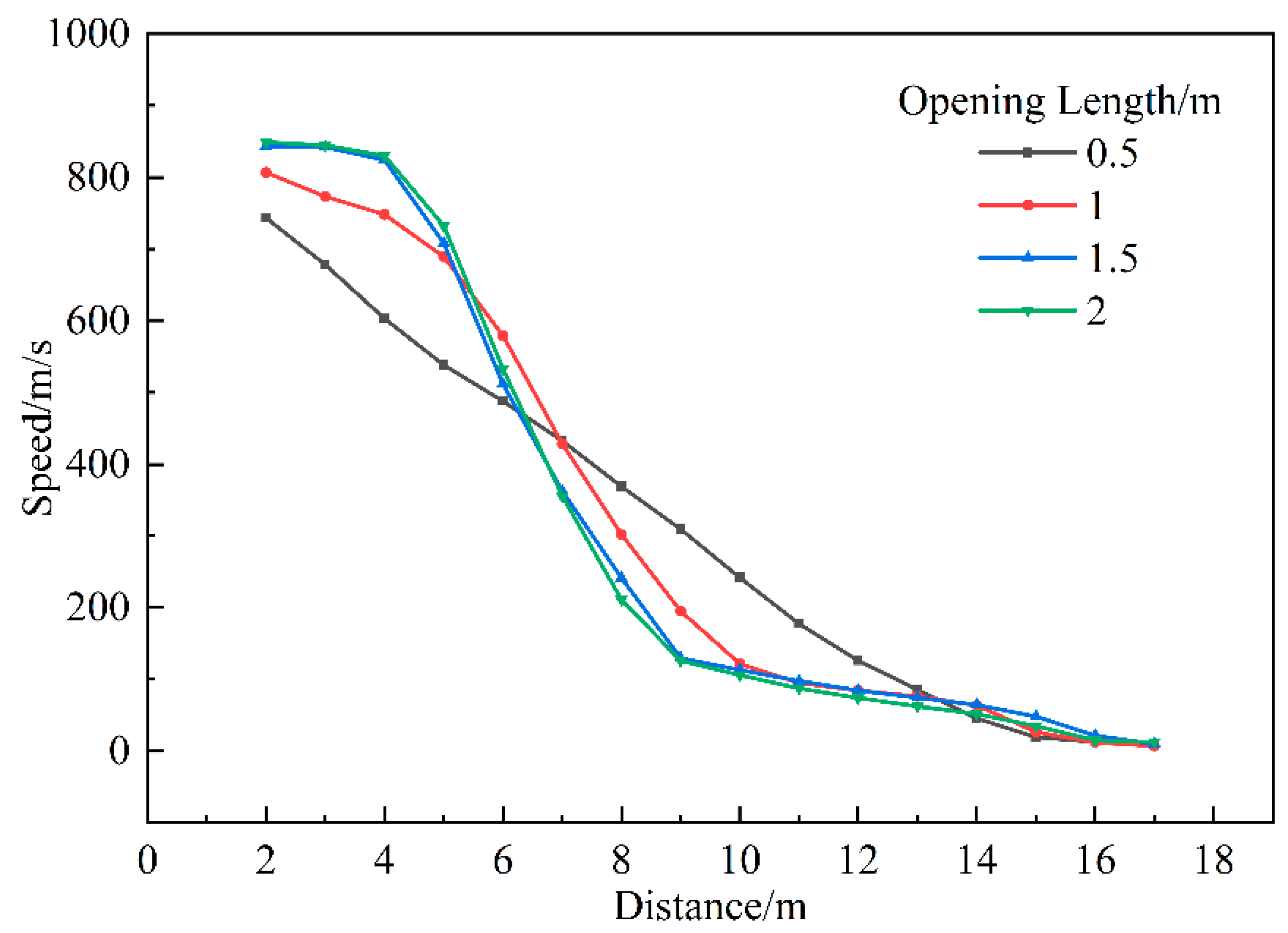
3.1.5. Influence of Opening Size
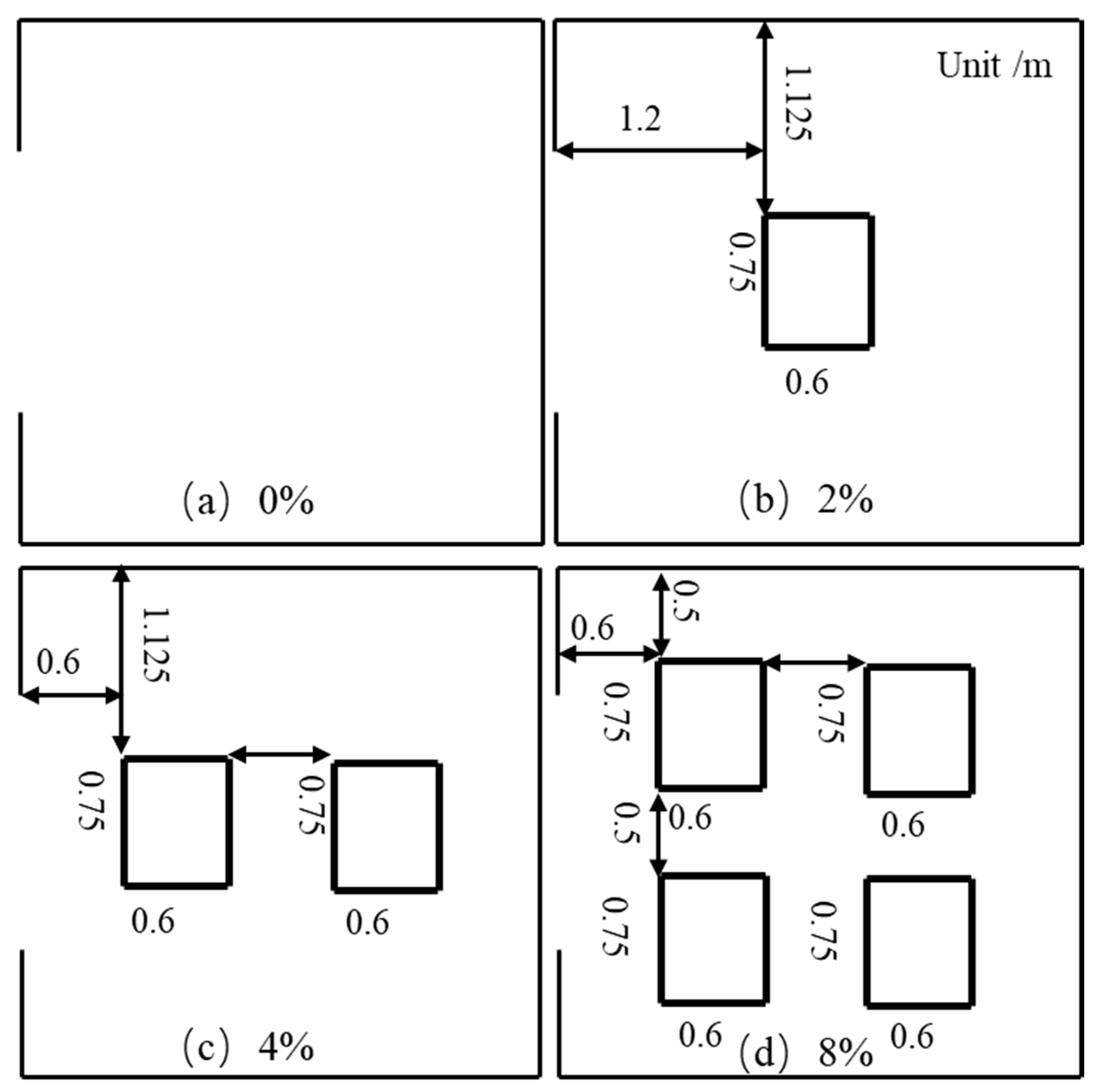
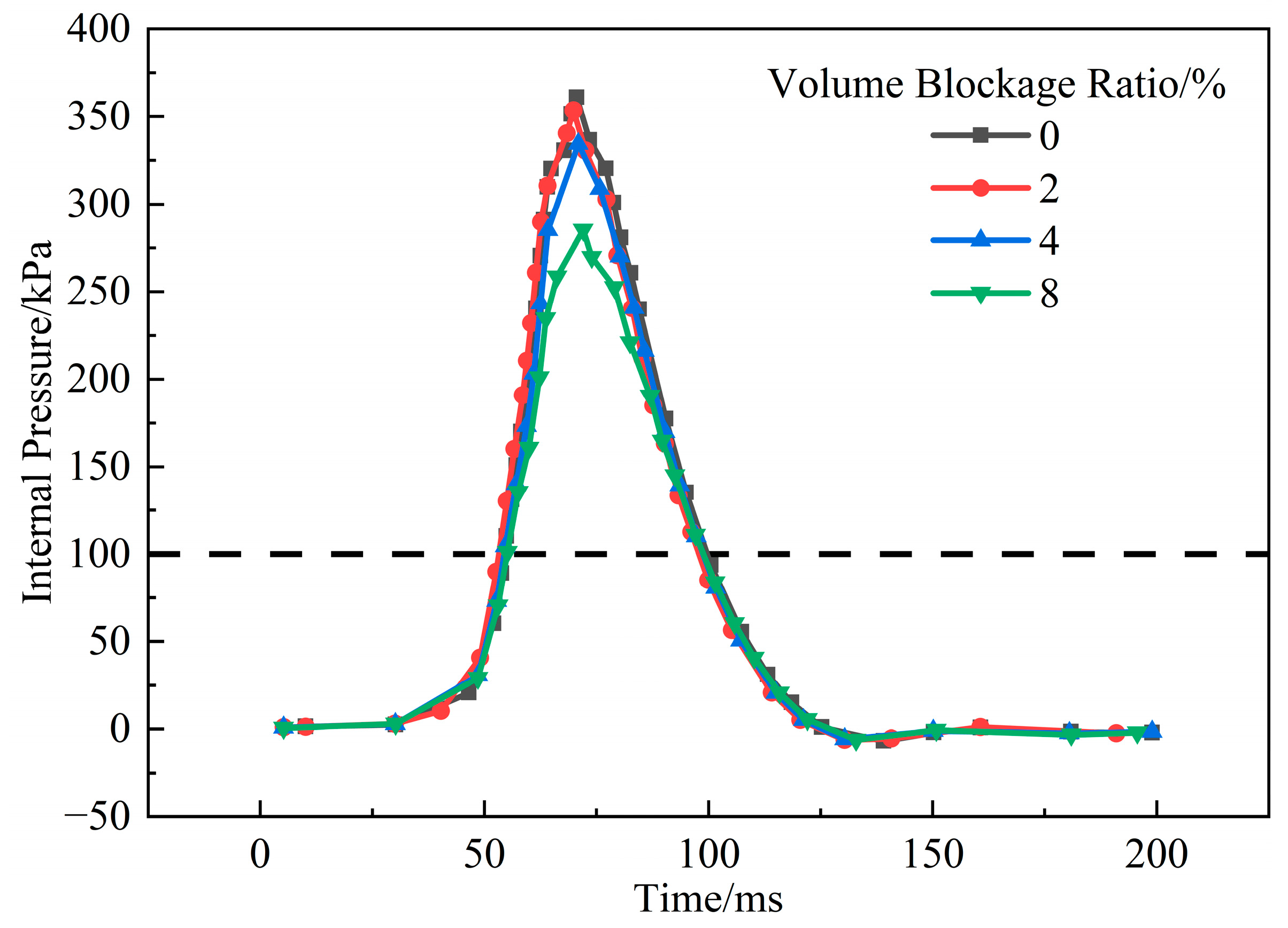
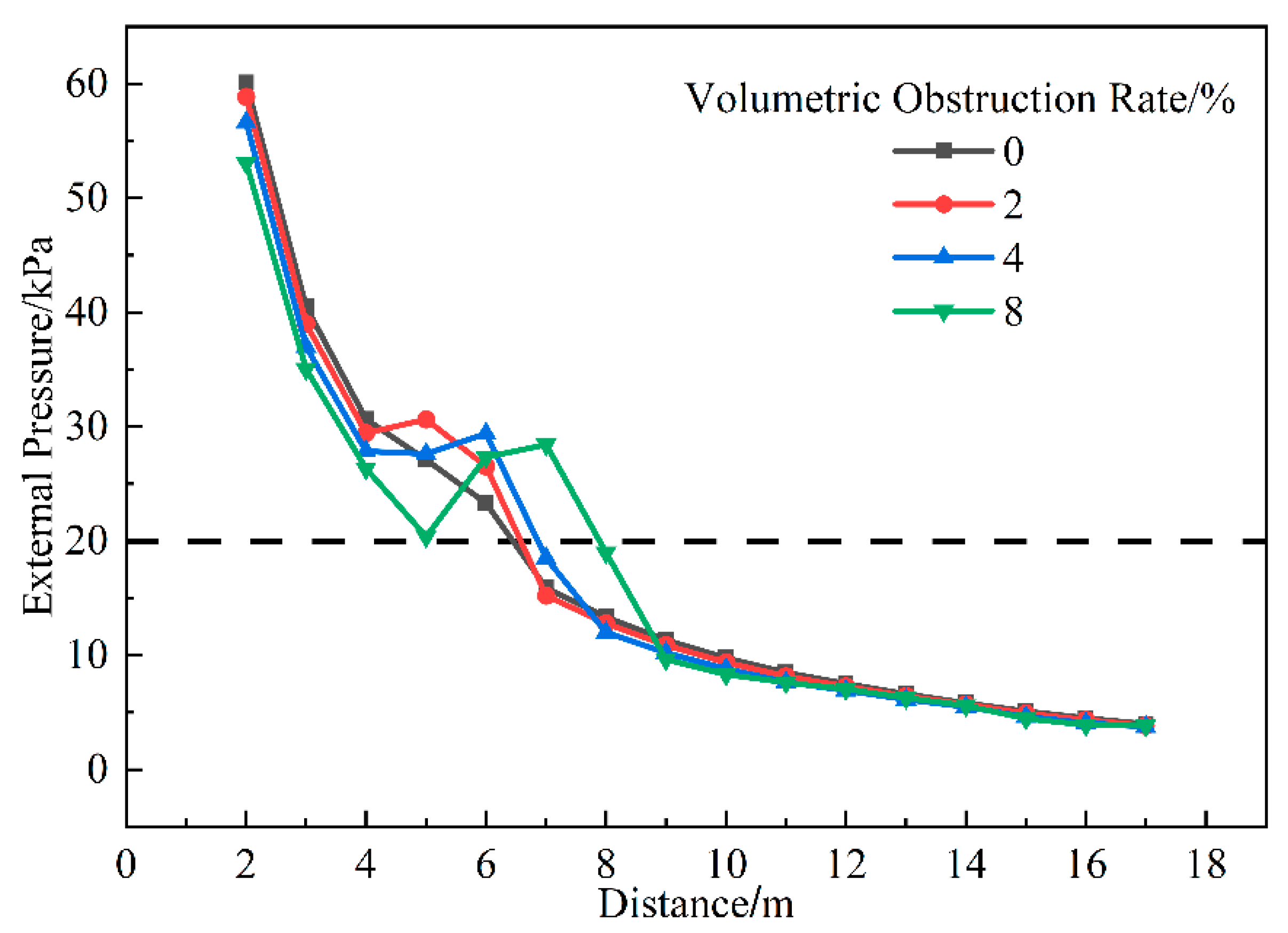
3.1.6. Influence of Volume Blockage Ratio
3.2. H-BNG Leak in a Typical Street- Front Restaurant
3.2.1. Scenario
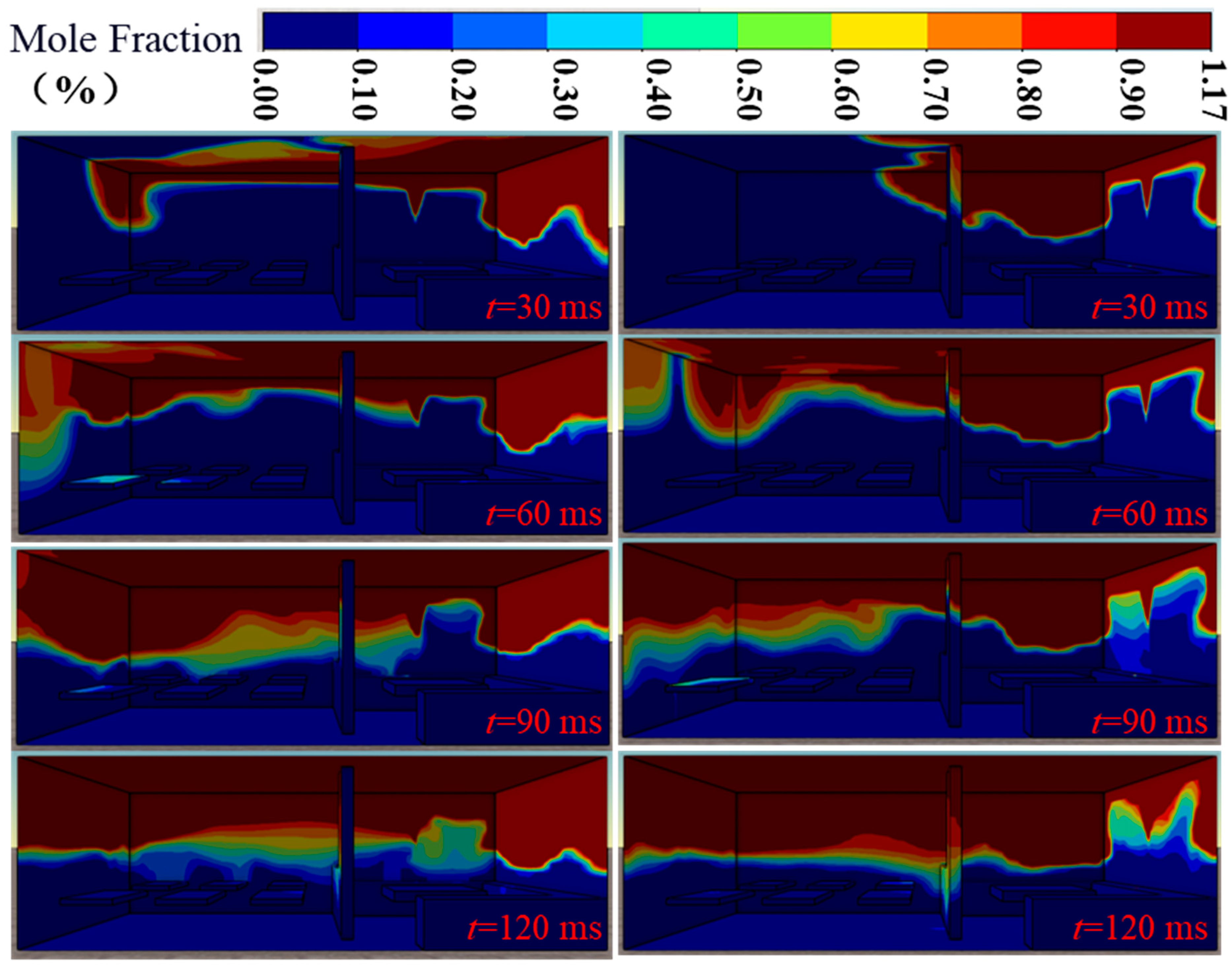
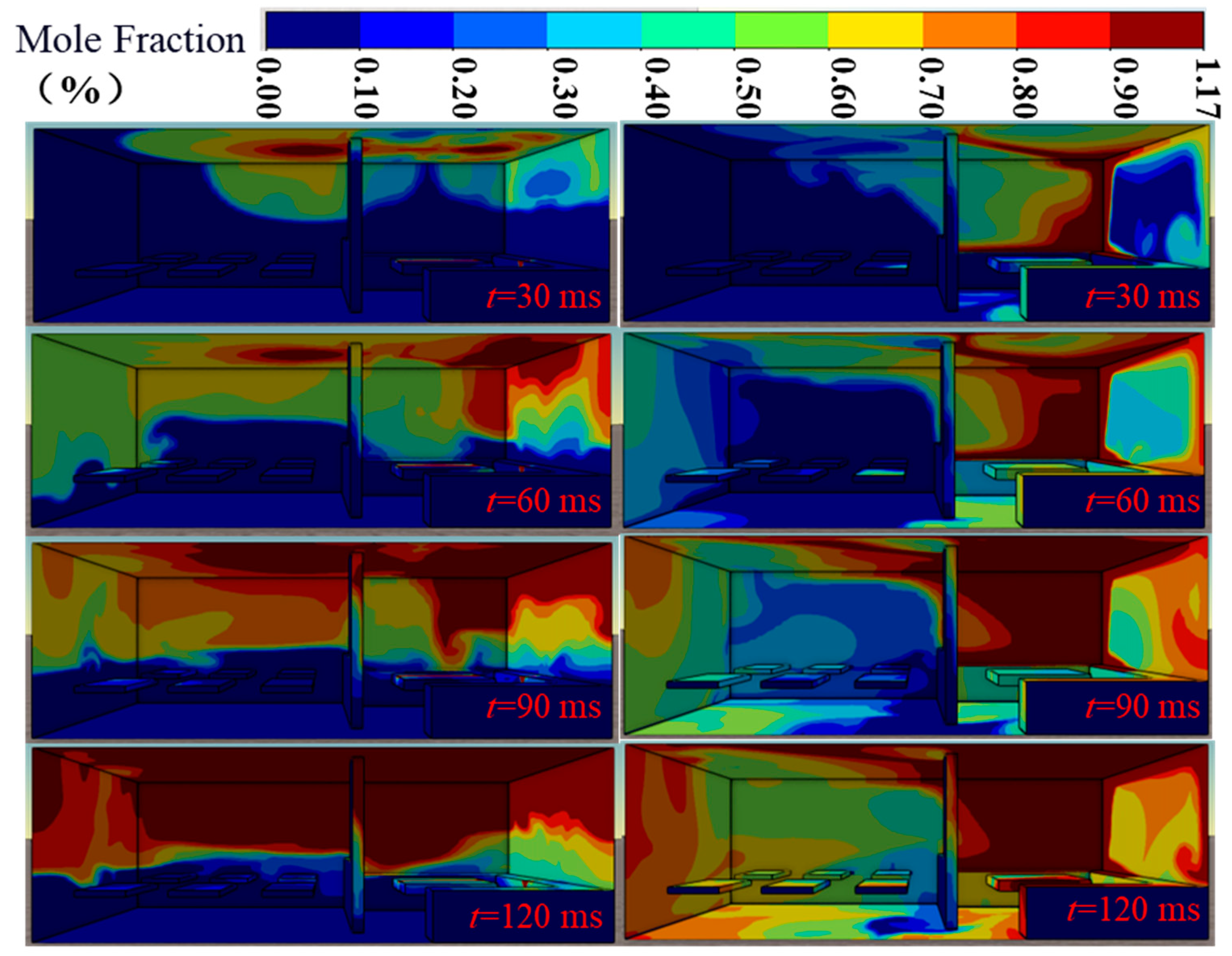
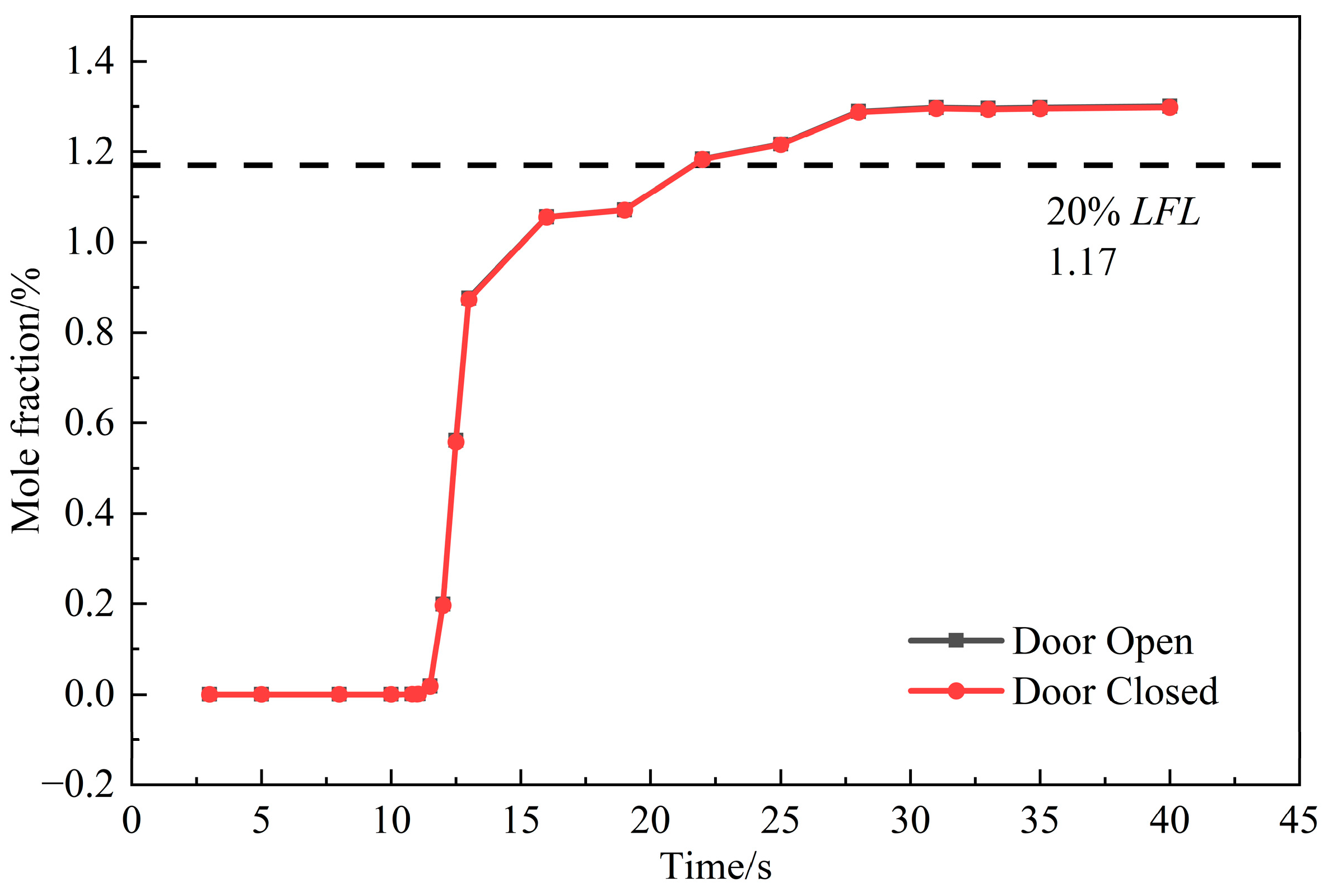
3.2.2. Diffusion Analysis
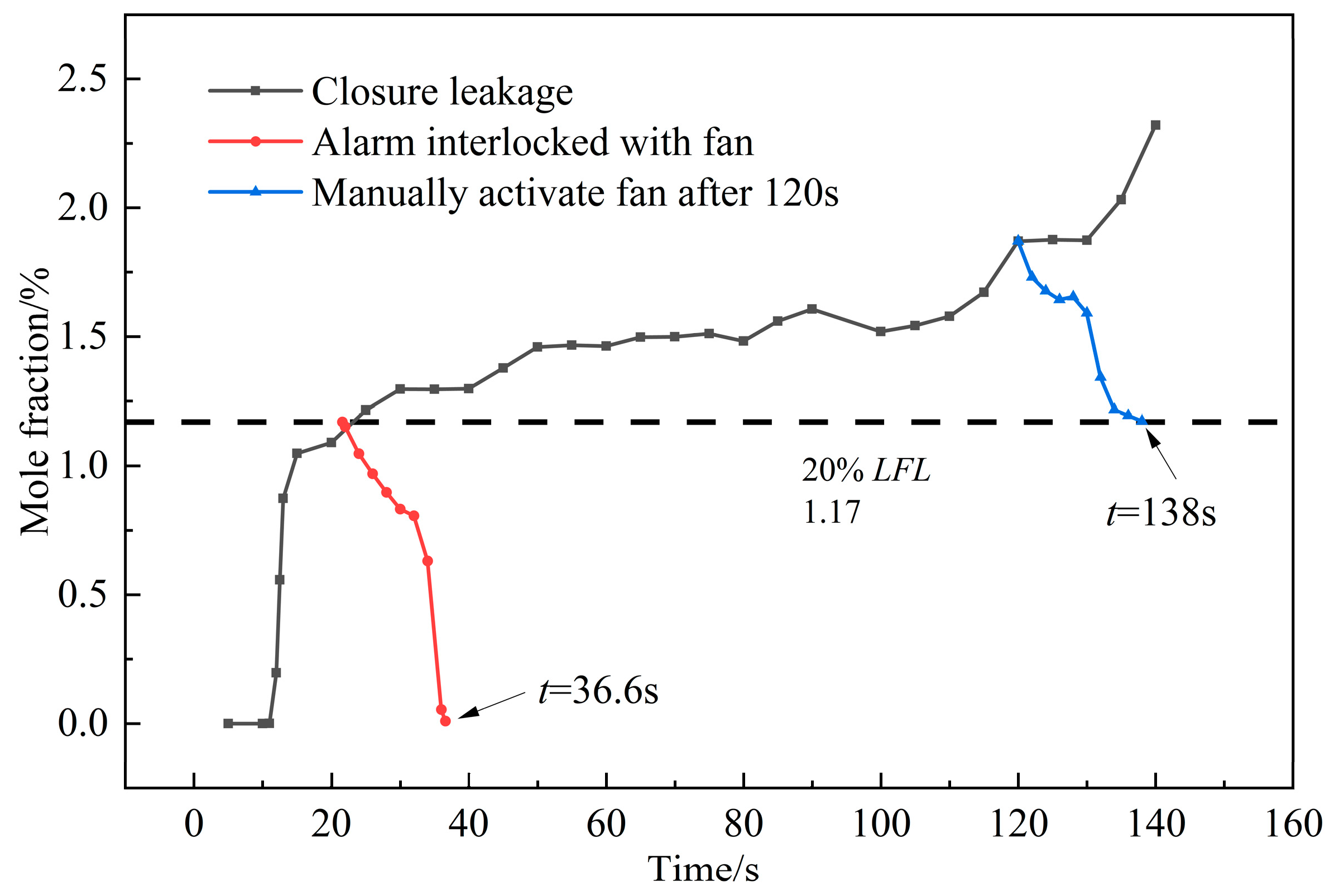
3.2.3. Ventilation Analysis
3.2.4. Explosion Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Volume porosity | Density | ||
| Area porosity in the j th direction | t | Time | |
| Mean velocity (j th component, vector) | Mass rate | ||
| Volume | Absolute pressure | ||
| Flow resistance due to sub-grid obstructions | Flow resistance due to walls | ||
| Ideal atmospheric density | Gravitational acceleration | ||
| Stress tensor | Specific enthalpy | ||
| Effective viscosity | Constant, 0.7 | ||
| Heat flow rate | k | Turbulent kinetic energy | |
| Constant, 1.0 | Dissipation of turbulent kinetic energy | ||
| Constant, 1.3 | Constant, 1.92 | ||
| Monin–Obukhov length scale | Specific heat capacity at constant pressure | ||
| Friction velocity | Von Karman constant (typically, = 0.41) | ||
| Sensible heat flux from the surface | Reference, characteristic velocity | ||
| z | Distance above the ground | Aerodynamical roughness length | |
| Canopy height | Prandtl–Schmidt number | ||
| Reaction rate for fuel | Mass fraction | ||
| Laminar burning velocity | Pressure exponent for the laminar burning velocity, | ||
| Quasi-laminar burning velocity | Progress variable | ||
| Turbulent burning velocity | Root mean square of velocity | ||
| Kinematic viscosity | Turbulent integral scale |
References
- Messaoudani, Z.L.; Rigas, F.; Binti Hamid, M.D.; Che Hassan, C.R. Hazards, safety and knowledge gaps on hydrogen transmission via natural gas grid: A critical review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 17511–17525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhong, W. Numerical study on the influence of venting interlayer structure on the explosion venting effects. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 156, 107714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurca Adrian, M.; Florin, A.P.; Mihai, C.P. Ignition risk assessment to the non-electrical equipment from hydrogen production, storage, transport and use facilities. In MATEC Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2024; Volume 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, W.; Dai, X.; Guo, Y.; Pang, L. Effect of hydrogen ratio on leakage and explosion characteristics of hydrogen-blended natural gas in utility tunnels. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 64, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowesmith, B.J.; Hankinson, G.; Spataru, C.; Stobbart, M. Gas build-up in a domestic property following releases of methane/hydrogen mixtures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 5932–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangon, A.; Carcassi, M.N. Hydrogen–methane mixtures: Dispersion and stratification studies. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 6160–6168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, B.; Zhao, Y. Numerical investigation on the leakage and diffusion characteristics of hydrogen-blended natural gas in a domestic kitchen. Renew. Energy 2022, 189, 899–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, X.; Du, H.; Teng, L.; Shao, Y.; Bian, J. Numerical simulation of leakage and diffusion distribution of natural gas and hydrogen mixtures in a closed container. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 35928–35939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitu, M.; Razus, D.; Schroeder, V. Laminar Burning Velocities of Hydrogen-Blended Methane–Air and Natural Gas–Air Mixtures, Calculated from the Early Stage of p(t) Records in a Spherical Vessel. Energies 2021, 14, 7556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Shi, Y. Effects of hydrogen on combustion characteristics of methane in air. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 11291–11298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, A.; Rusin, A.; Majkut, M.; Stolecka, K. Analysis of compression and transport of the methane/hydrogen mixture in existing natural gas pipelines. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2018, 166, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middha, P.; Engel, D.; Hansen, O.R. Can the addition of hydrogen to natural gas reduce the explosion risk? Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 2628–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sarli, V.; Di Benedetto, A.; Long, E.J.; Hargrave, G.K. Time-Resolved Particle Image Velocimetry of dynamic interactions between hydrogen-enriched methane/air premixed flames and toroidal vortex structures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 16201–16213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Luan, P.; Zheng, K.; Yang, X.; Han, S.; Duan, Y. Experimental study on explosion characteristics of syngas with different ignition positions and hydrogen fraction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 15553–15564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, F. Experiments on vented deflagration of stoichiometric hydrogen–methane–air mixtures: Effect of hydrogen fraction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 25615–25622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shen, X.; Wen, J.X.; Xiu, G. The behavior of methane/hydrogen/air premixed flame in a closed channel with inhibition. Fuel 2020, 265, 116810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wei, Z.; Lv, Z.; Guo, W.; Liu, X. The behaviors of supersonic combustion wave through a perforated plate in a stoichiometric mixtures of H2/CH4/O2 and H2/O2. Fuel 2022, 317, 123092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Pang, L.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J. Effects of hydrogen addition on the confined and vented explosion behavior of methane in air. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2014, 27, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Yang, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y. Study on leakage and explosion consequence for hydrogen blended natural gas in urban distribution networks. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 27096–27115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolecka, K. Hazards of hydrogen transport in the existing natural gas pipeline network. J. Power Technol. 2018, 98, 329. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, H.; Huang, X.; Peng, S. Numerical simulation on methane-hydrogen explosion in gas compartment in utility tunnel. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 140, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-K.; Bang, H.-J.; Jo, Y.-D. Consequence Analysis of Hydrogen Blended Natural Gas(HCNG) using 3D CFD Simulation. J. Korean Inst. Gas 2013, 17, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sarli, V.; Di Benedetto, A. Effects of non-equidiffusion on unsteady propagation of hydrogen-enriched methane/air premixed flames. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 7510–7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellek, M.S. Flameless combustion investigation of CH4/H2 in the laboratory-scaled furnace. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 35208–35222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Z.; Tang, C.; Miao, H.; Wang, X. Numerical study of the effect of hydrogen addition on methane–air mixtures combustion. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 1084–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gexcon, A.S. FLACS v22.1 User’s Manual; Gexcon AS: Bergen, Norway, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S. Study on Explosion Characteristics of Hydrogen with Concentration Gradient in Cube Chamber; Hefei University of Technology: Hefei, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
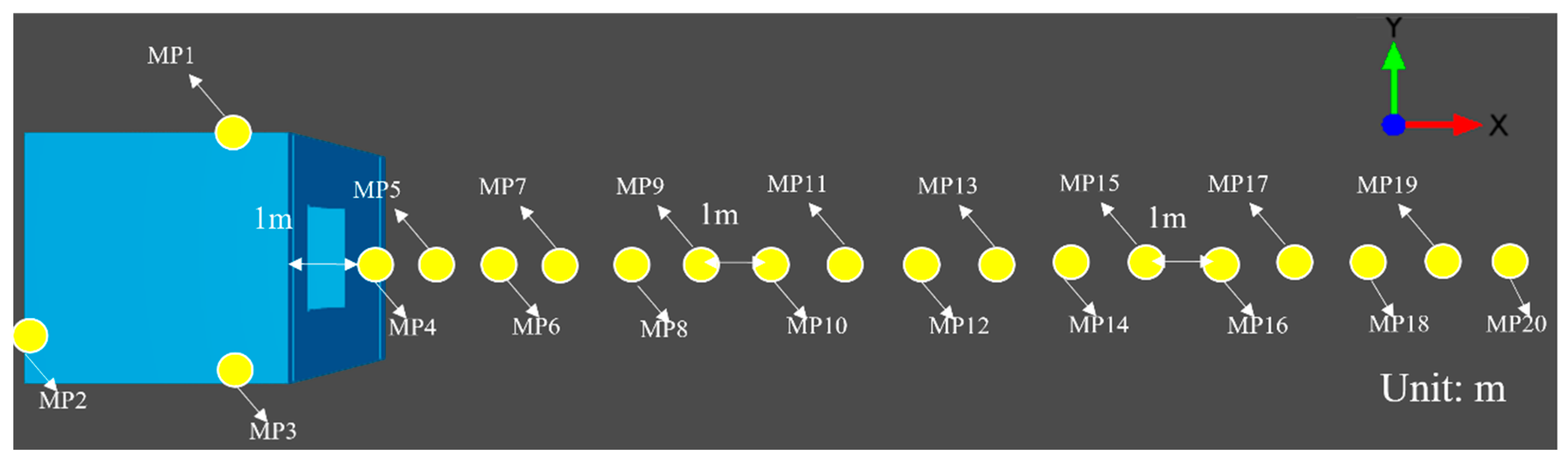
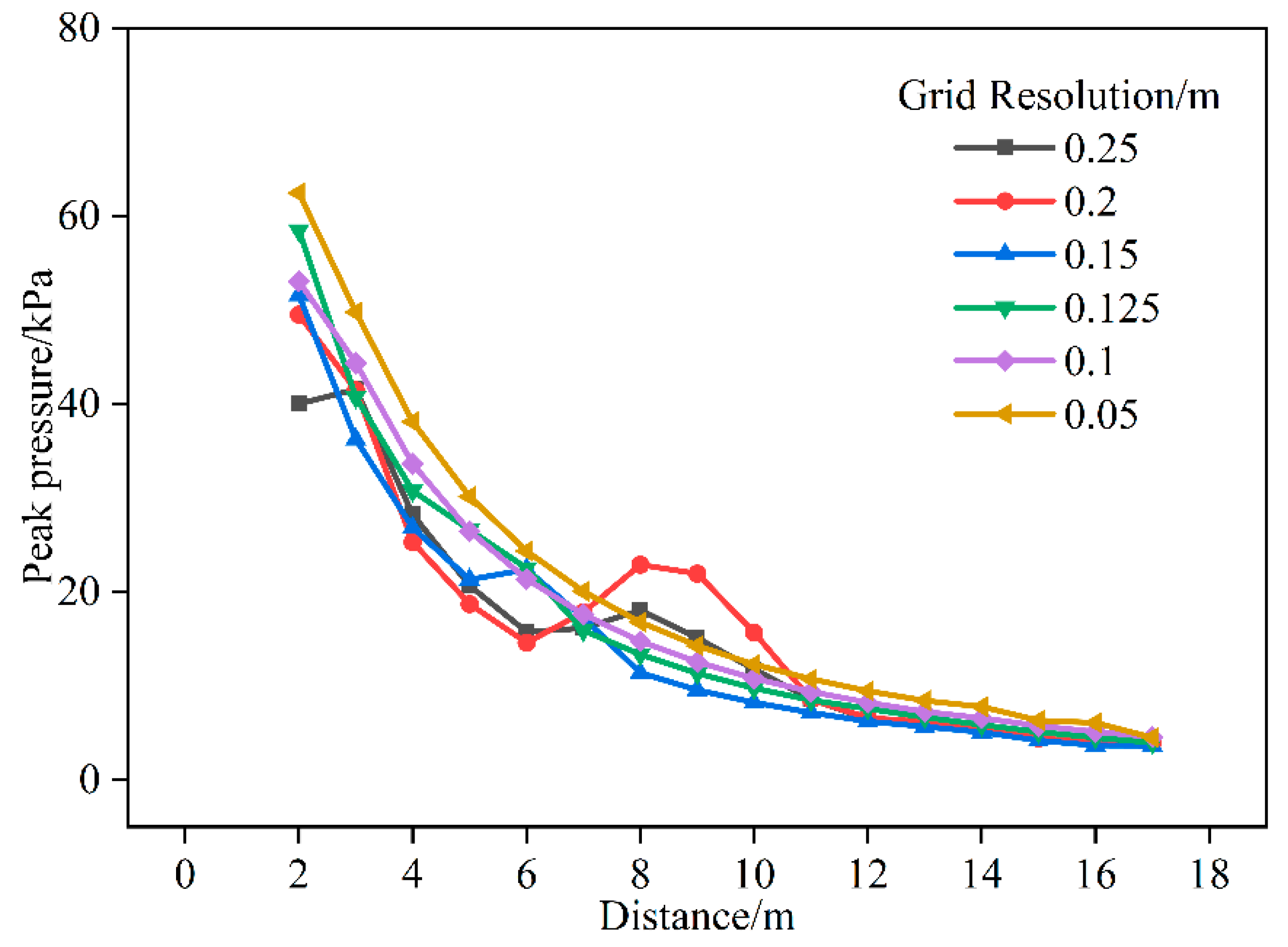

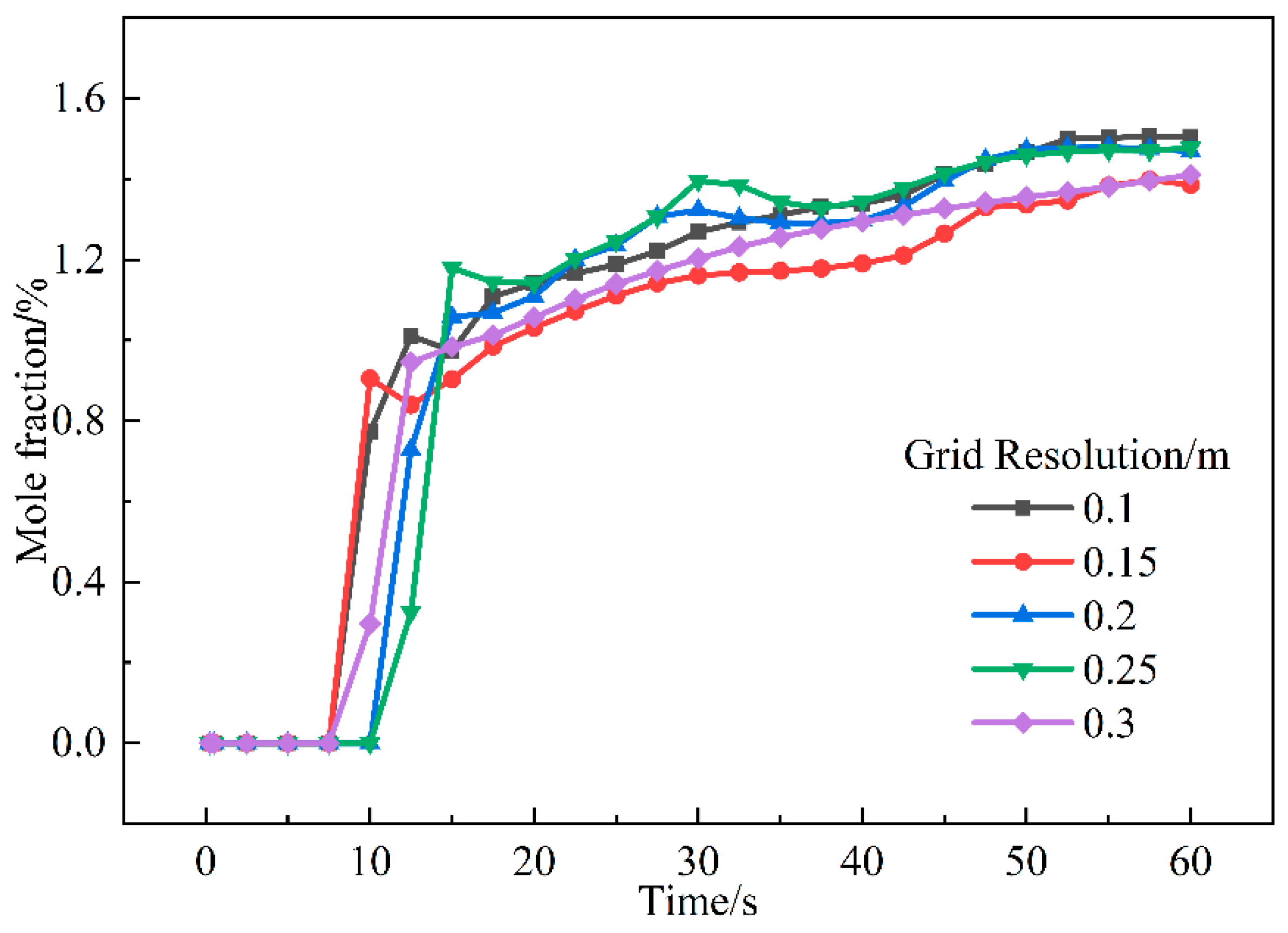
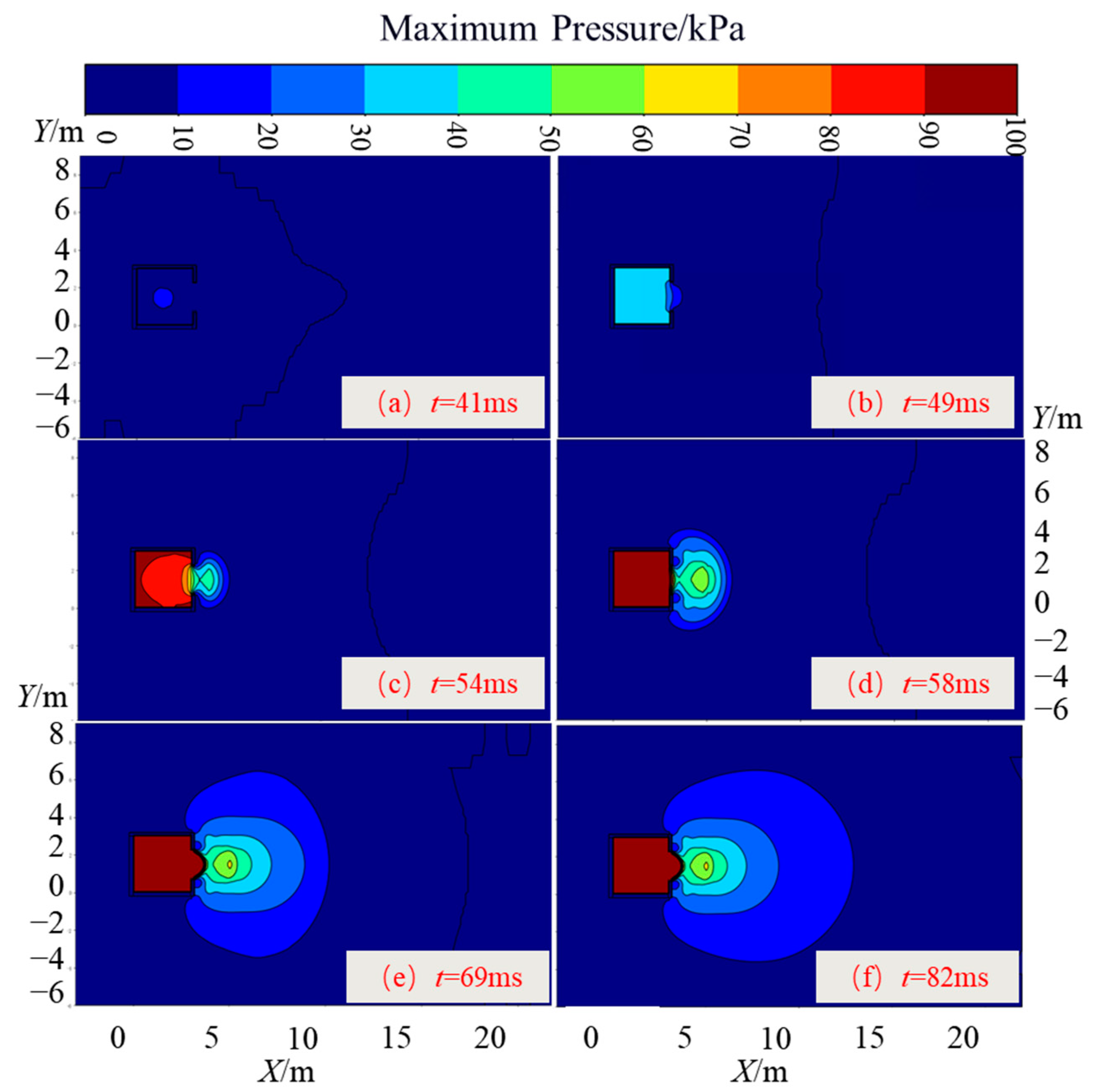









| Object Name | Upper Surface (m) | Lower Surface (m) | Object Name | Upper Surface (m) | Lower Surface (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dining Table | 0.8 | 0.7 | Stove | 0.8 | 0 |
| Serving Counter | 1.2 | 0 | Workstation | 0.8 | 0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Hu, S.; Zhang, S.; Duo, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, T. Study on the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Hydrogen-Blended Natural Gas Leakage and Flare-Up in the Typical Semi-Open Space. Fire 2025, 8, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8040146
Wang X, Hu S, Zhang S, Duo Y, Xu J, Zhao T. Study on the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Hydrogen-Blended Natural Gas Leakage and Flare-Up in the Typical Semi-Open Space. Fire. 2025; 8(4):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8040146
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xu, Saitao Hu, Shengzhu Zhang, Yingquan Duo, Jinhuai Xu, and Tong Zhao. 2025. "Study on the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Hydrogen-Blended Natural Gas Leakage and Flare-Up in the Typical Semi-Open Space" Fire 8, no. 4: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8040146
APA StyleWang, X., Hu, S., Zhang, S., Duo, Y., Xu, J., & Zhao, T. (2025). Study on the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Hydrogen-Blended Natural Gas Leakage and Flare-Up in the Typical Semi-Open Space. Fire, 8(4), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8040146




