Microwave Chemical Looping Synergistic Gasification of Polypropylene Plastic and Water Hyacinth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials, Reagents and Equipments
2.1.1. Basic Experimental Materials
2.1.2. Major Experimental Reagents
2.1.3. Major Experimental Equipment
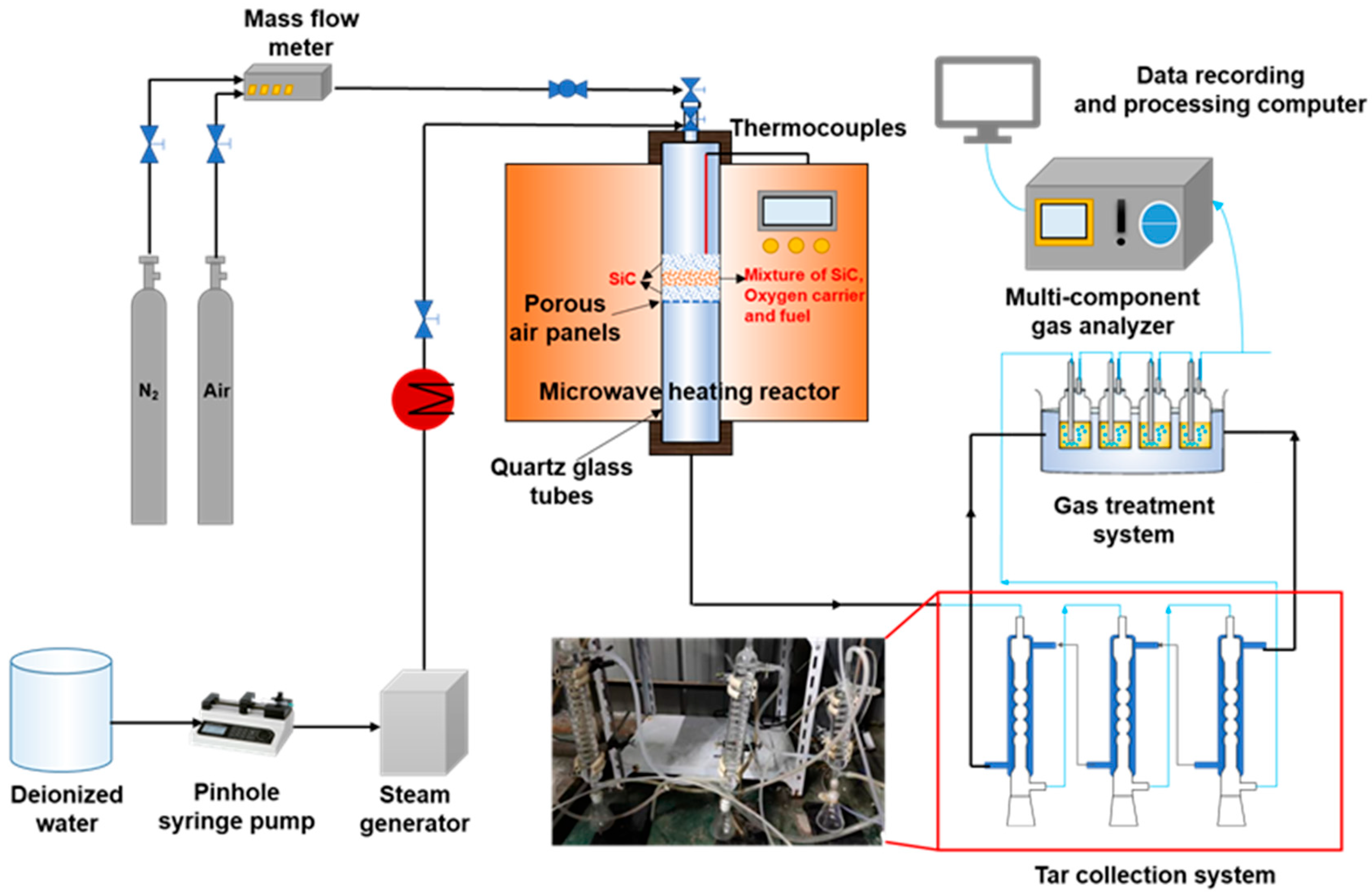
2.2. Experimental Device and Process
2.3. Experimental Conditions
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. Reactions Involving Tar
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Influence of Water Hyacinth Mixing on the Gasification Characteristics
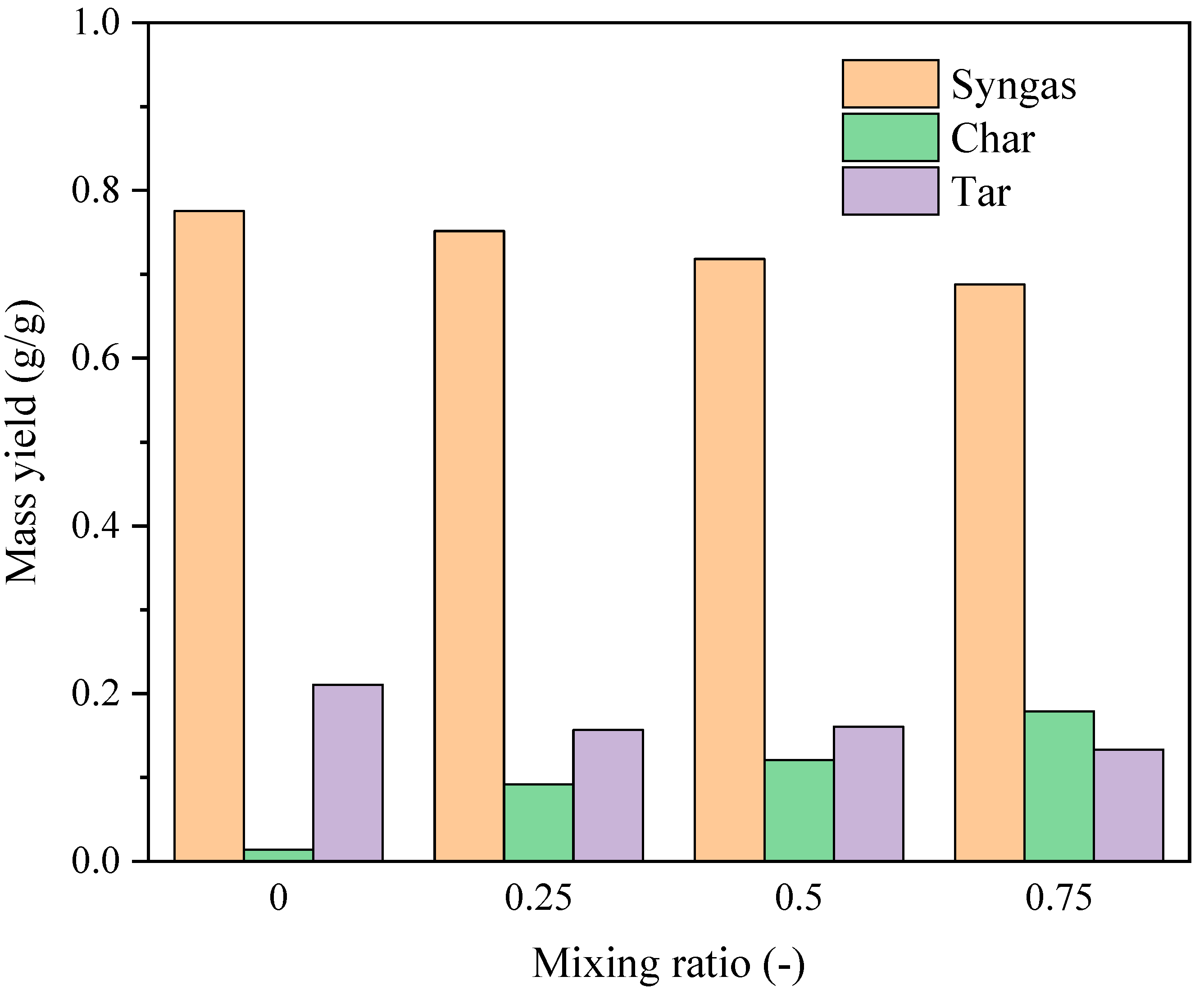
3.1.1. Evolution of Gas–Liquid–Solid Products
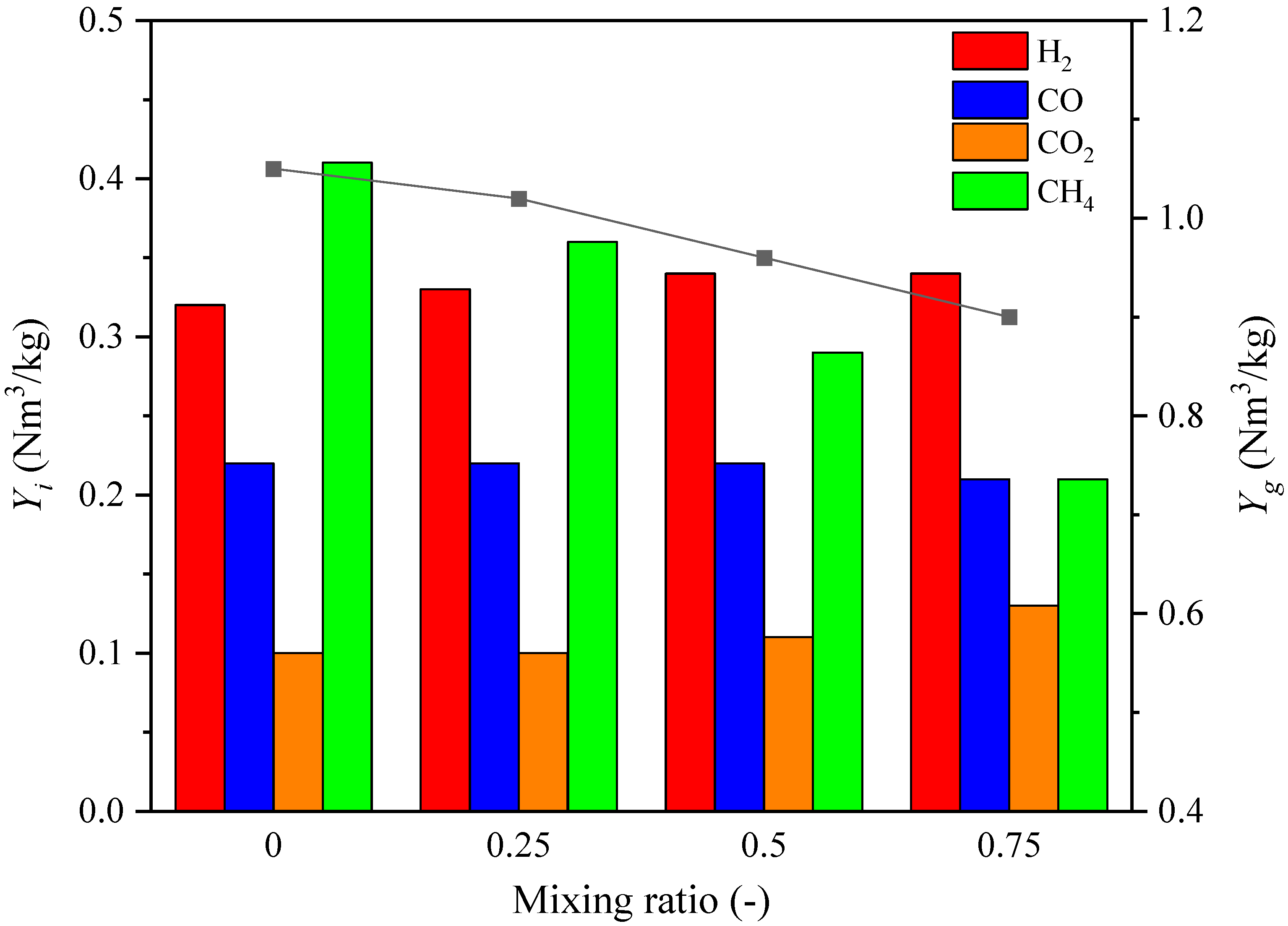
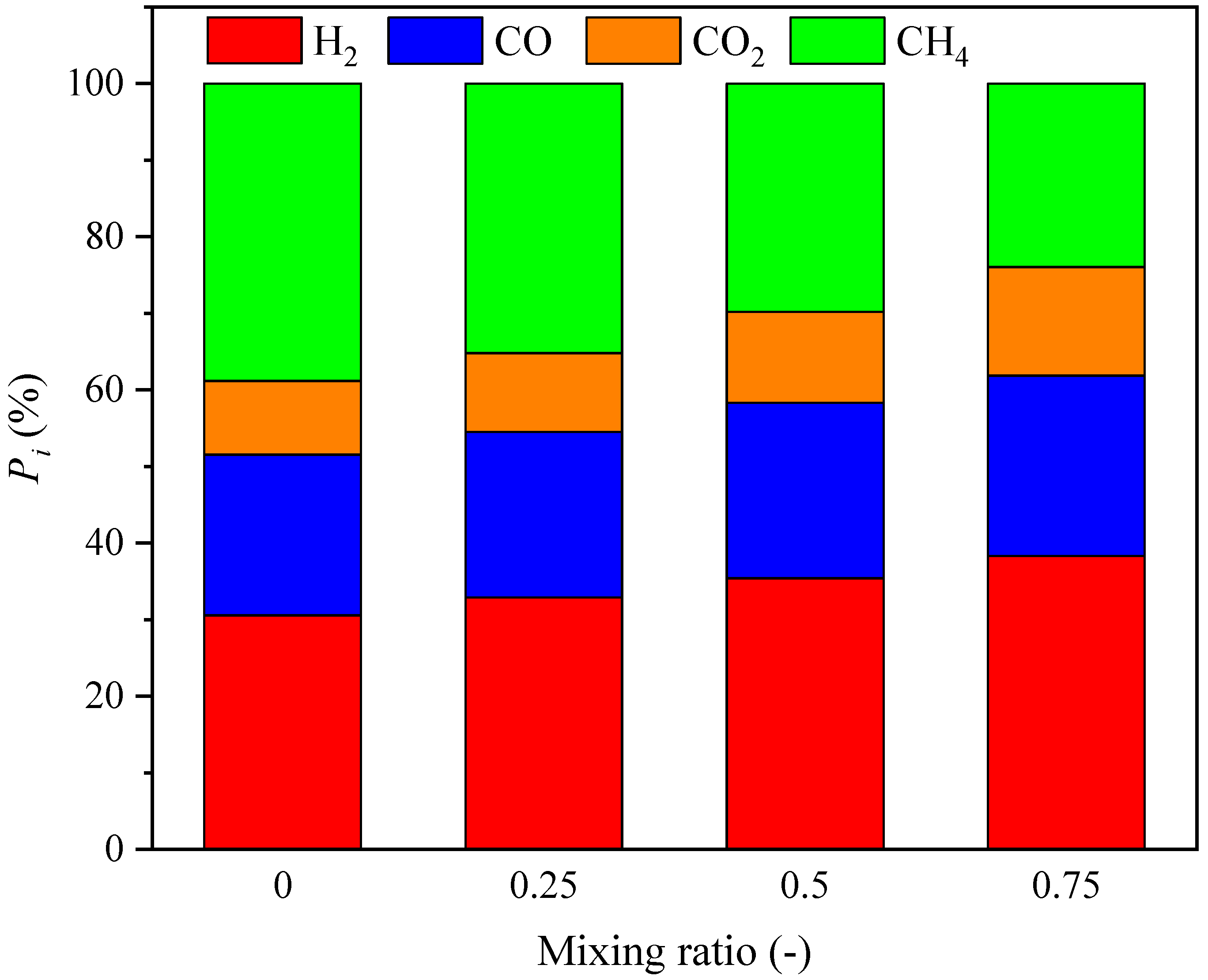
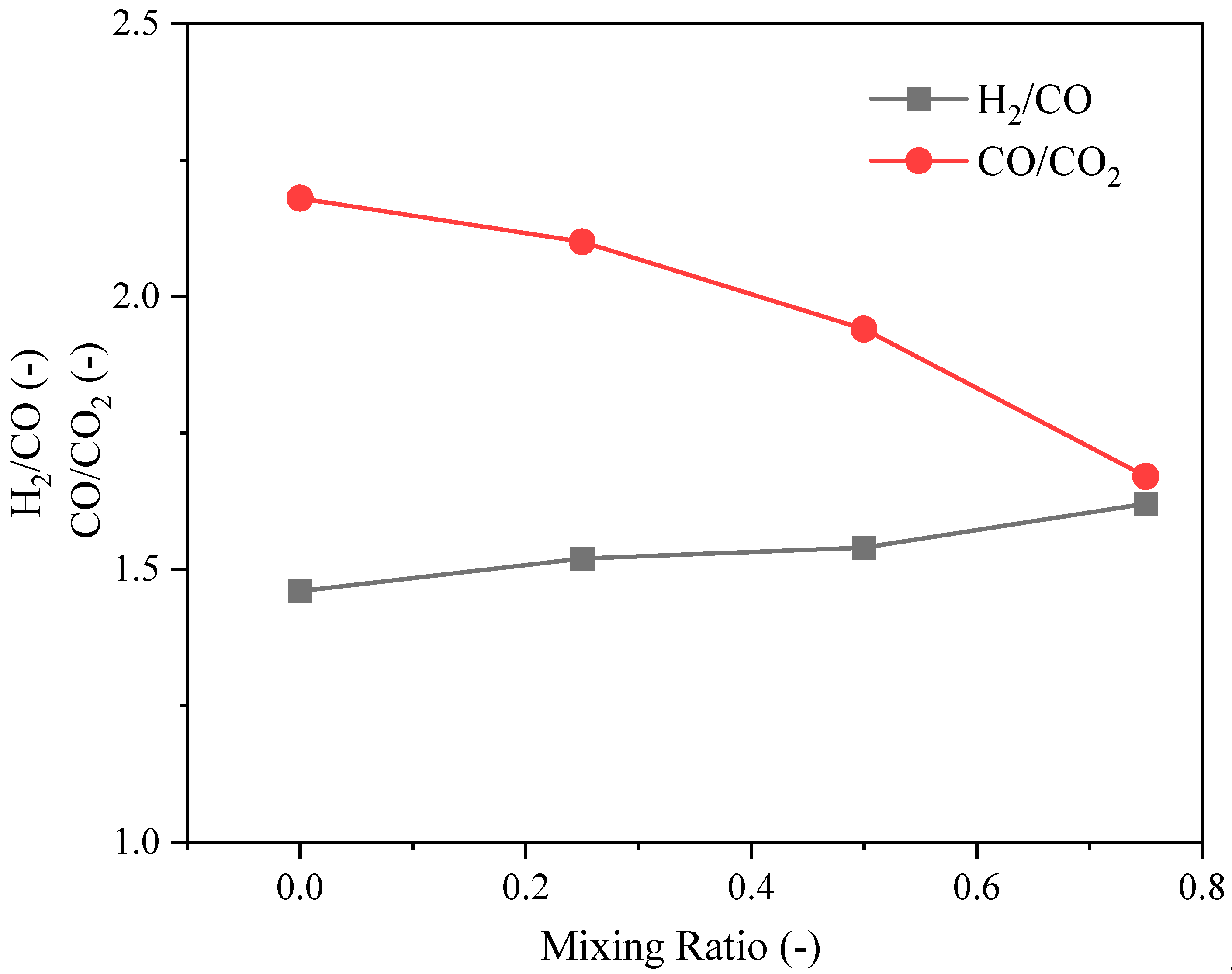
3.1.2. Syngas Composition Distributions
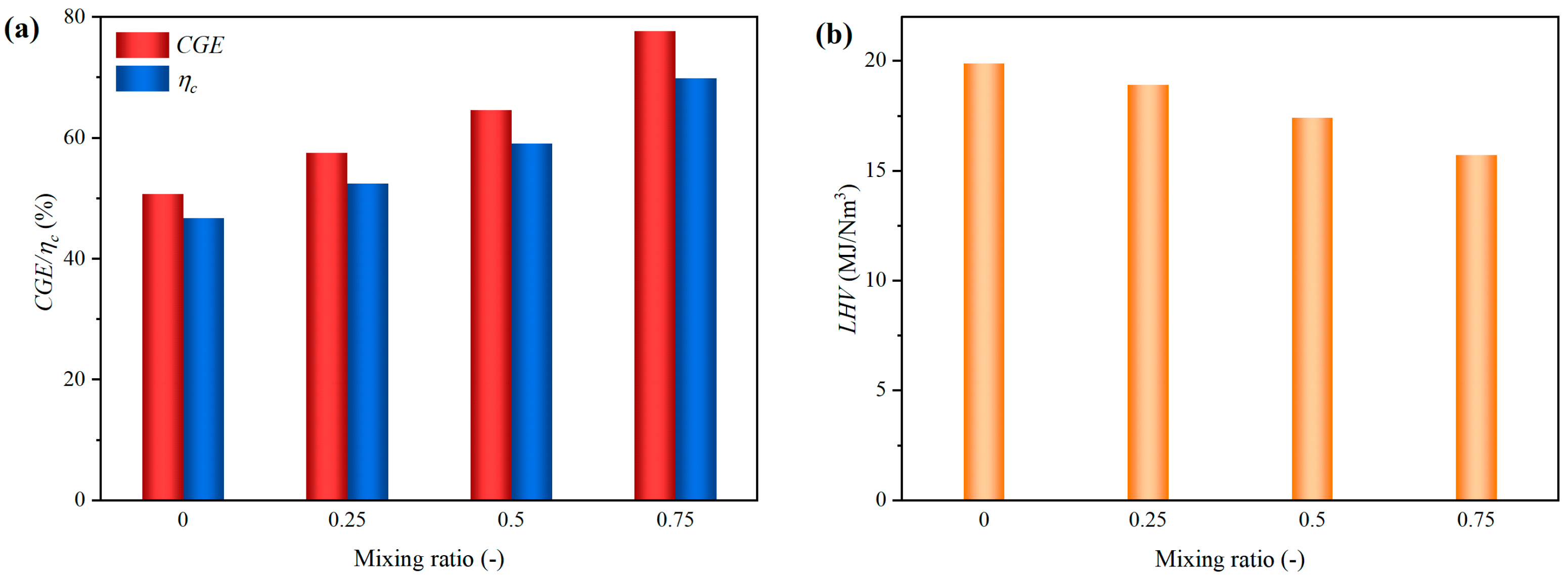
3.1.3. Gasification Characteristics
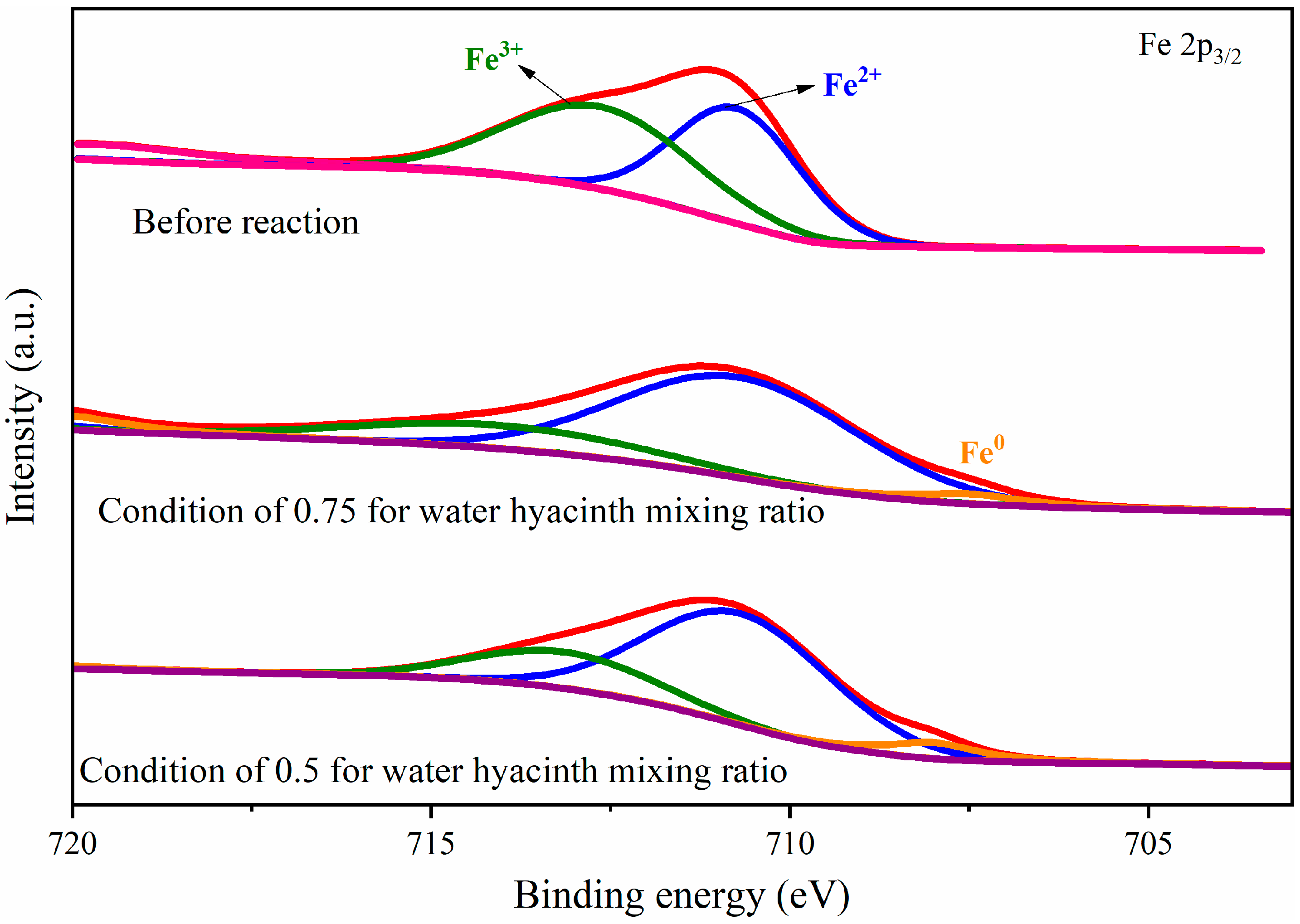
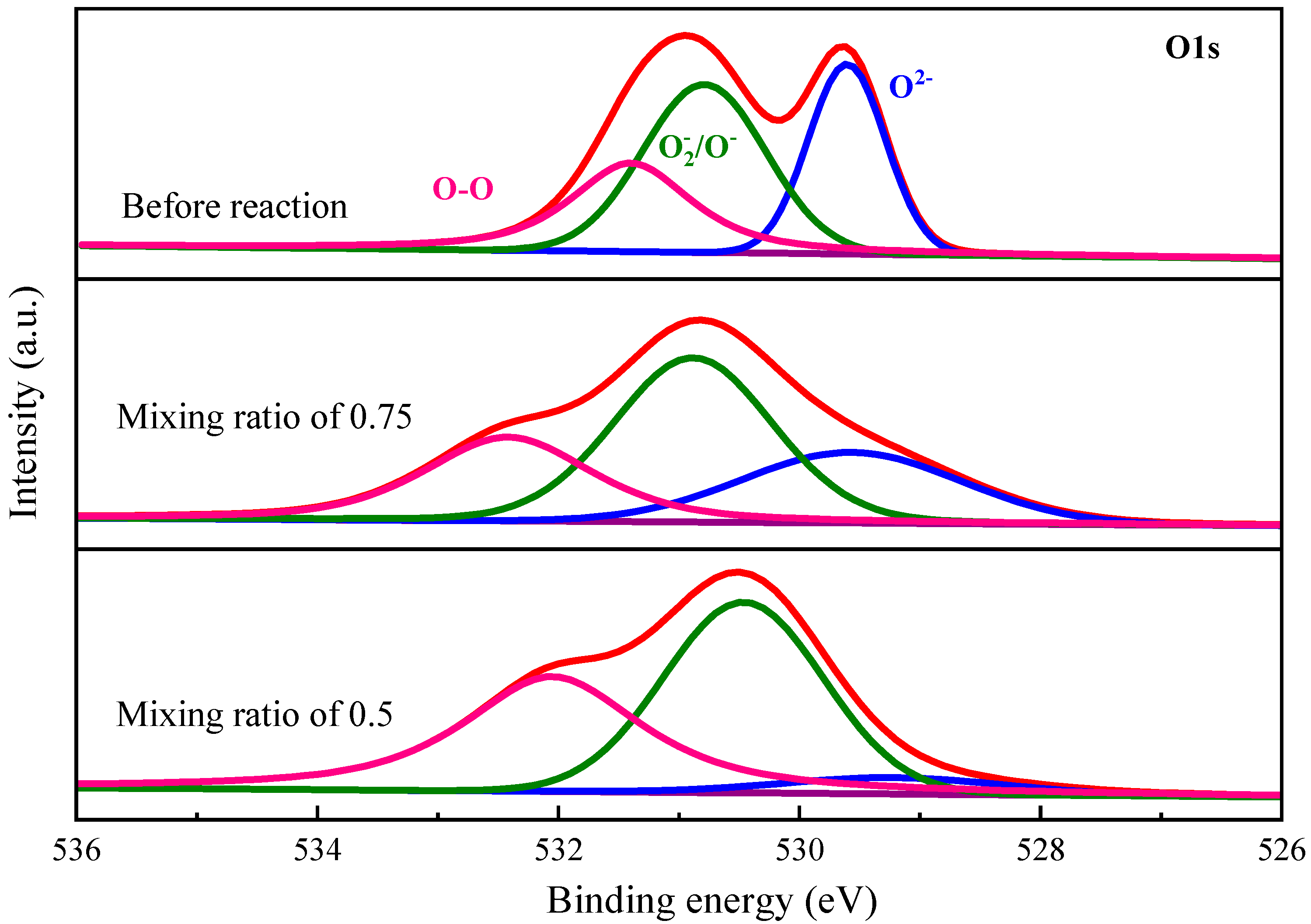
3.2. Element Valence States in Oxygen Carrier
3.3. Influence of Water Hyacinth Mixing on Tar Characteristics
3.3.1. Variation of Tar Yield Under Different Blending Ratios in Synergistic Gasification
3.3.2. Variation in the Contents of Tar Components Under Different Blending Ratios
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Abbreviation | |
| MAHs | Monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| NAHs | Naphthalene and bicyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| CLG | Chemical looping gasification |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| AR | Analytical reagent |
| SiC | Silicon carbide |
| GC-MS | Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| Variables | |
| Yi | Yield of each single gas component in the syngas, i = H2, CO, CO2, CH4 (Nm3/kg fuel) |
| N2 flow rate at the inlet under room temperature (m3/s) | |
| Xi | Volume fraction of each single gas component measured online by the gas analyzer, i = H2, CO, CO2, CH4 (%) |
| m0 | Total mass of fuel introduced to the reactor (kg) |
| Yg | Total gas yield (Nm3/kg fuel) |
| Pi | Relative portion of each single gas component in the gas product (%) |
| Lower heating value (MJ/Nm3) | |
| Carbon conversion rate (%) | |
| CGE | Cold gas efficiency (%) |
| fc | Mass fraction of carbon in the added fuel (%) |
| Low calorific value of the introduced fuel (MJ/kg) | |
| H2/CO ratio in the gas product | |
| CO/CO2 ratio in the gas product |
References
- Stephen, J.L.; Periyasamy, B. Innovative developments in biofuels production from organic waste materials: A review. Fuel 2018, 214, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglinski, B.; Kujawski, W.; Kielkowska, U. Pyrolysis of Waste Biomass: Technical and Process Achievements, and Future Development—A Review. Energies 2023, 16, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetland, J.; Yowargana, P.; Leduc, S.; Kraxner, F. Carbon-negative emissions: Systemic impacts of biomass conversion: A case study on CO2 capture and storage options. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2016, 49, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Monteiro, E.; Brito, P.; Vilarinho, C. Biomass resources in Portugal: Current status and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 1221–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condori, O.; García-Labiano, F.; de Diego, L.F.; Izquierdo, M.T.; Abad, A.; Adánez, J. Biomass chemical looping gasification for syngas production using ilmenite as oxygen carrier in a 1.5 kWth unit. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samprón, I.; de Diego, L.F.; García-Labiano, F.; Izquierdo, M.T.; Abad, A.; Adánez, J. Biomass Chemical Looping Gasification of pine wood using a synthetic Fe2O3/Al2O3 oxygen carrier in a continuous unit. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.H.; Chi, Z.Y.; Li, M. Advancements in biomass gasification research utilizing iron-based oxygen carriers in chemical looing: A review. Mater. Rep. Energy 2024, 4, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.J.; Shen, L.H.; Feng, F.; Jiang, S.X. Experiments on biomass gasification using chemical looping with nickel-based oxygen carrier in a 25 kWth reactor. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 85, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampron, I.; Purnomo, V.; Mattiósson, T.; Leion, H.; de Diego, L.F.; García-Labiano, F. Catalytic Activity of Oxygen Carriers on the Removal of Tar Byproducts for Biomass Chemical Looping Gasification Application. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 16629–16638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.Q.; He, F.; Zhao, Z.L.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, A.Q.; Zhao, K.; Li, H.B. Performance of Fe-Ni bimetallic oxygen carriers for chemical looping gasification of biomass in a 10 kWth interconnected circulating fluidized bed reactor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 16021–16032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.R.; He, H.; Li, H.P.; Jia, J.B.; Huang, G.X.; Xing, B.L.; Zhang, C.X.; Cao, Y.J. Characteristics and kinetics of coal char steam gasification under microwave heating. Fuel 2019, 256, 115899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tao, J.Y.; Yan, B.B.; Jiao, L.G.; Chen, G.Y.; Hu, J.L. Review of microwave-based treatments of biomass gasification tar. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 150, 111510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.Q.; Cui, P.Z.; Liu, Z.Q.; Xu, Z.F.; Yao, D.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Yang, S. Conceptual design and comprehensive analysis for novel municipal sludge gasification-based hydrogen production via plasma gasifier. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 245, 114635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, M.L.; Li, S.; Wu, W.F.; Li, L.; Miao, Y.J.; Ge, Y. Graphite-assisted microwave carbon dioxide gasification of wet stalks. Renew. Energy 2023, 219, 119445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, C.; Abdelsayed, V.; Smith, M.; Shekhawat, D. Comparative evaluation of microwave and conventional gasification of different coal types: Experimental reaction studies. Fuel 2022, 321, 124055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.T.; Deng, W.Y.; Su, Y.X.; Wang, L.H.; Chen, G. Production of hydrogen-rich syngas through microwave-assisted gasification of sewage sludge in steam-CO2 atmosphere. Fuel 2024, 357, 129855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, T.; Kawakami, K.; Nishioka, M.; Ogura, M. Direct decomposition of NO on metal-loaded zeolites with coexistence of oxygen and water vapor under unsteady-state conditions by NO concentration and microwave rapid heating. Catal. Today 2017, 281, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S.A.; Roslan, R.; Inayat, M.; Naz, M.Y. Effect of blending ratio and catalyst loading on co-gasification of wood chips and coconut waste. J. Energy Inst. 2018, 91, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Gao, L.; Chen, Z.H.; Ma, C.F.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Ma, S.; Laghari, M.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, B.P.; et al. Syngas production by catalytic in-situ steam co-gasification of wet sewage sludge and pine sawdust. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 111, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, J.; Pathak, T.S.; Srivastava, R.; Singh, A.C. Catalytic co-pyrolysis of paper biomass and plastic mixtures (HDPE (high density polyethylene), PP (polypropylene) and PET (polyethylene terephthalate)) and product analysis. Energy 2016, 103, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.H.; Wang, Z.W.; Chen, G.F.; Zhang, M.J.; Sun, T.L.; Wang, Q.; Du, Z.M.; Chen, Y.; Wu, M.G.; Li, Z.F.; et al. Co-pyrolysis characteristics of forestry and agricultural residues and waste plastics: Thermal decomposition and products distribution. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 177, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, L.M.; Wee, M.X.J.; Chew, J.J.; Khaerudini, D.S.; Darsono, N.; Aqsha, A.; Saptoro, A.; Sunarso, J. Catalytic co-pyrolysis of oil palm trunk and polypropylene with Ni-Mo/TiO2 and Ni/Al2O3: Oil composition and mechanism. Environ. Res. 2023, 224, 115550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maari, M.A.; Ahmad, M.A.; Din, A.T.M.; Hassan, H.; Alsobaai, A.M. Co-pyrolysis of oil palm empty fruit bunch and oil palm frond with low-density polyethylene and polypropylene for bio-oil production. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.W.; Burra, K.G.; Lei, T.Z.; Gupta, A.K. Co-pyrolysis of waste plastic and solid biomass for synergistic production of biofuels and chemicals—A review. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2021, 84, 100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.H.; Hu, K.M.; Li, R.D.; Sun, Y.; Kai, X.P. Cogasification of typical plastics and rice straw with carbon dioxide. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2015, 34, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Yue, X.M.; Yin, Z.Y.; Pan, T.T.; Dong, M.J.; Sun, T.Y. Study of the co-pyrolysis behavior of sewage-sludge/rice-straw and the kinetics. Proc. Int. Conf. Min. Sci. Technol. 2009, 1, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torquato, L.M.; Braz, C.E.M.; Ribeiro, C.A.; Capela, J.M.V.; Crespi, M.S. Kinetic study of the co-firing of bagasse-sludge blends. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 121, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahijani, P.; Zainal, Z.A.; Mohamed, A.R.; Mohammadi, M. Co-gasification of tire and biomass for enhancement of tire-char reactivity in CO2 gasification process. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 138, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.M.; Zhang, Y.N.; Cao, W.T.; Zhao, W.K.; Li, B.X. Microwave-assisted chemical looping gasification of plastics for H2-rich gas production. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.X.; Chen, D.L.; Zhong, Z.P.; Wang, X.J. Experimental investigation of the effect of microwave power on the chemical looping gasification of aquatic plant water hyacinth. J. Energy Inst. 2024, 114, 101537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burra, K.G.; Gupta, A.K. Synergistic effects in steam gasification of combined biomass and plastic waste mixtures. Appl. Energy 2018, 211, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S.; Okolie, J.A.; Patel, R.; Pattnaik, F.; Fang, Z.; Dalai, A.K.; Kozinski, J.A.; Naik, S. Catalytic hydrothermal co-gasification of canola meal and low-density polyethylene using mixed metal oxides for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 42084–42098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.W.; Li, D.H.; Pei, T.; Wang, J.D.; Liu, C.; Lu, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, J.R.; Zheng, Z.F. Mechanism of synergistic effects and kinetic analysis in bamboo-LDPE waste ex-situ catalytic co-pyrolysis for enhanced aromatic hydrocarbon production via CeZrAl and HZSM-5 dual catalyst. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hognon, C.; Dupont, C.; Grateau, M.; Delrue, F. Comparison of steam gasification reactivity of algal and lignocellulosic biomass: Influence of inorganic elements. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 164, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, W.; Zhao, W.; Xiong, Q.; Li, B. Microwave-assisted chemical looping gasification of sugarcane bagasse biomass using Fe3O4 as oxygen carrier for H2/CO-rich syngas production. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 501, 157675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Material | C | H | O | N | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water hyacinth | 28.55 | 4.03 | 32.30 | 2.04 | 0.81 |
| PP plastic | 83.61 | 12.82 | 3.57 | 0 | - |
| Valence State of the Element | Unit | Before Reaction | Mixing Ratio of 0.75 | Mixing Ratio of 0.5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe2p3/2 | Fe3+ | at% | 51.77 | 21.22 | 22.87 |
| Fe2+ | at% | 48.23 | 73.86 | 69.67 | |
| Fe0 | at% | - | 4.92 | 7.46 | |
| Valence State of the Element | Unit | Pre-Reaction | Mixing Ratio of 0.75 | Mixing Ratio of 0.5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1s | O2− | at% | 29.70 | 15.65 | 5.86 |
| O2−/O− | at% | 41.76 | 45.66 | 49.07 | |
| O2 | at% | 28.53 | 38.69 | 45.07 | |
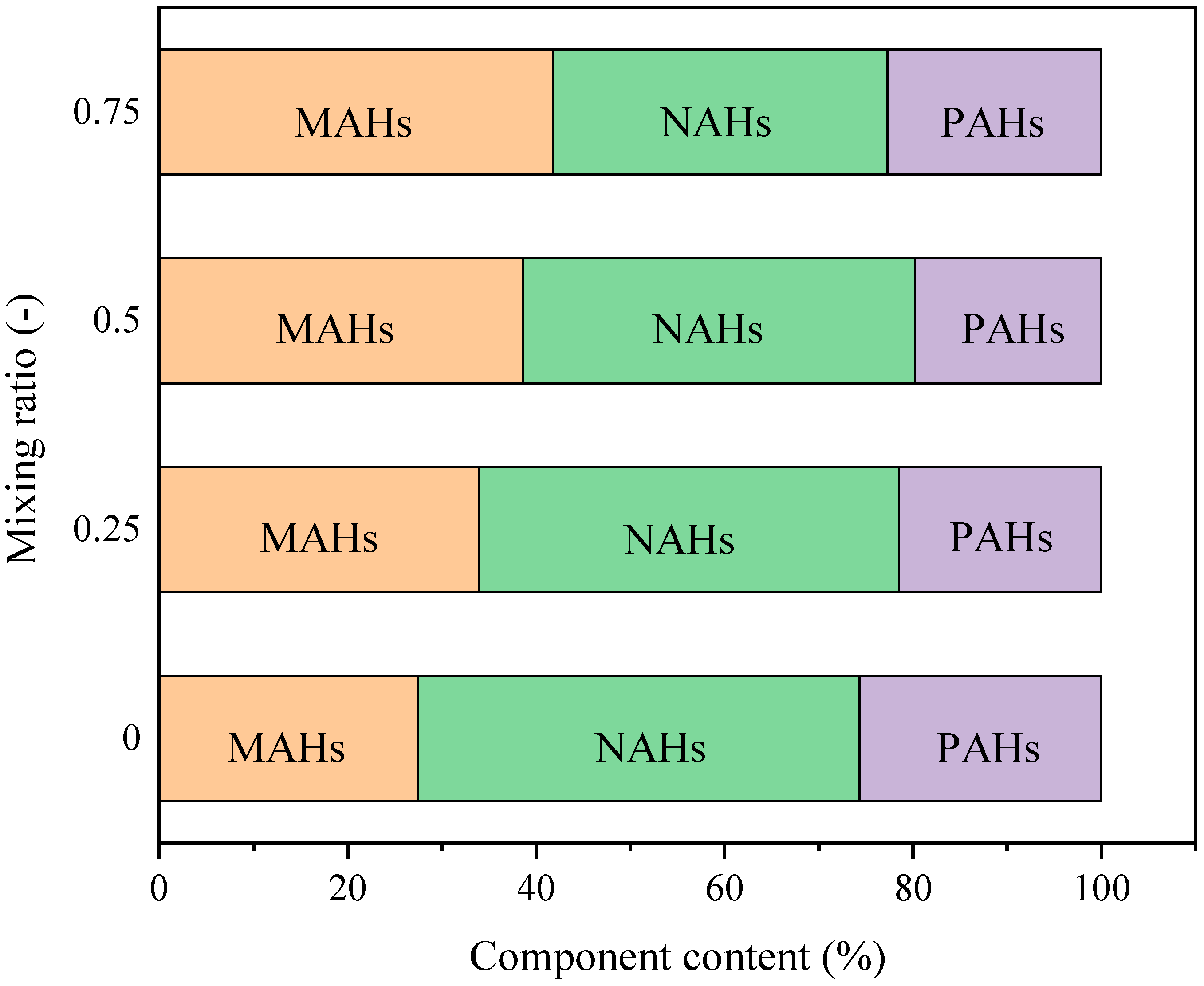
| Tar Components | 0 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.75 |
| PAHs | 25.68 | 21.52 | 19.82 | 22.73 |
| NAHs | 46.92 | 44.54 | 41.59 | 35.46 |
| MAHs | 27.40 | 33.94 | 38.59 | 41.81 |
| Feedstock | Condition | Oxygen Carrier | Gasification Effct | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP | 890 W, 900 °C, air | NiFe20Ox | Gas yield = 81.3 mmol/g PP, Tar yield = 23.3 wt.% | [29] |
| Sugarcane bagasse | 880 W, 800 °C, air | Fe3O4 | Syngas yield (wt.%) = 88.23% | [35] |
| Water hyacinth: PP = 0.75 | 900 °C, 1000 W, steam = 0.1 mL/min | Iron Ore | ηc = 69.9%, CGE = 77.64%, H2 yield = 0.34 Nm3/kg, tar yield = 0.133 g/g | This Study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, F.; Chen, D.; Mao, W.; Yu, Y.; Shao, D.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, X. Microwave Chemical Looping Synergistic Gasification of Polypropylene Plastic and Water Hyacinth. Fire 2025, 8, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8020076
An F, Chen D, Mao W, Yu Y, Shao D, Zhong Z, Wang X. Microwave Chemical Looping Synergistic Gasification of Polypropylene Plastic and Water Hyacinth. Fire. 2025; 8(2):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8020076
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Fengxia, Delu Chen, Wenli Mao, Ying Yu, Danyang Shao, Zhaoping Zhong, and Xiaojia Wang. 2025. "Microwave Chemical Looping Synergistic Gasification of Polypropylene Plastic and Water Hyacinth" Fire 8, no. 2: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8020076
APA StyleAn, F., Chen, D., Mao, W., Yu, Y., Shao, D., Zhong, Z., & Wang, X. (2025). Microwave Chemical Looping Synergistic Gasification of Polypropylene Plastic and Water Hyacinth. Fire, 8(2), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8020076





