Small-Scale Experimental Study on Smoke Blocking and Thermal Insulation Performance of Water Mist Sprinkler
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Water Mist Droplet Size Distribution Test Experiment
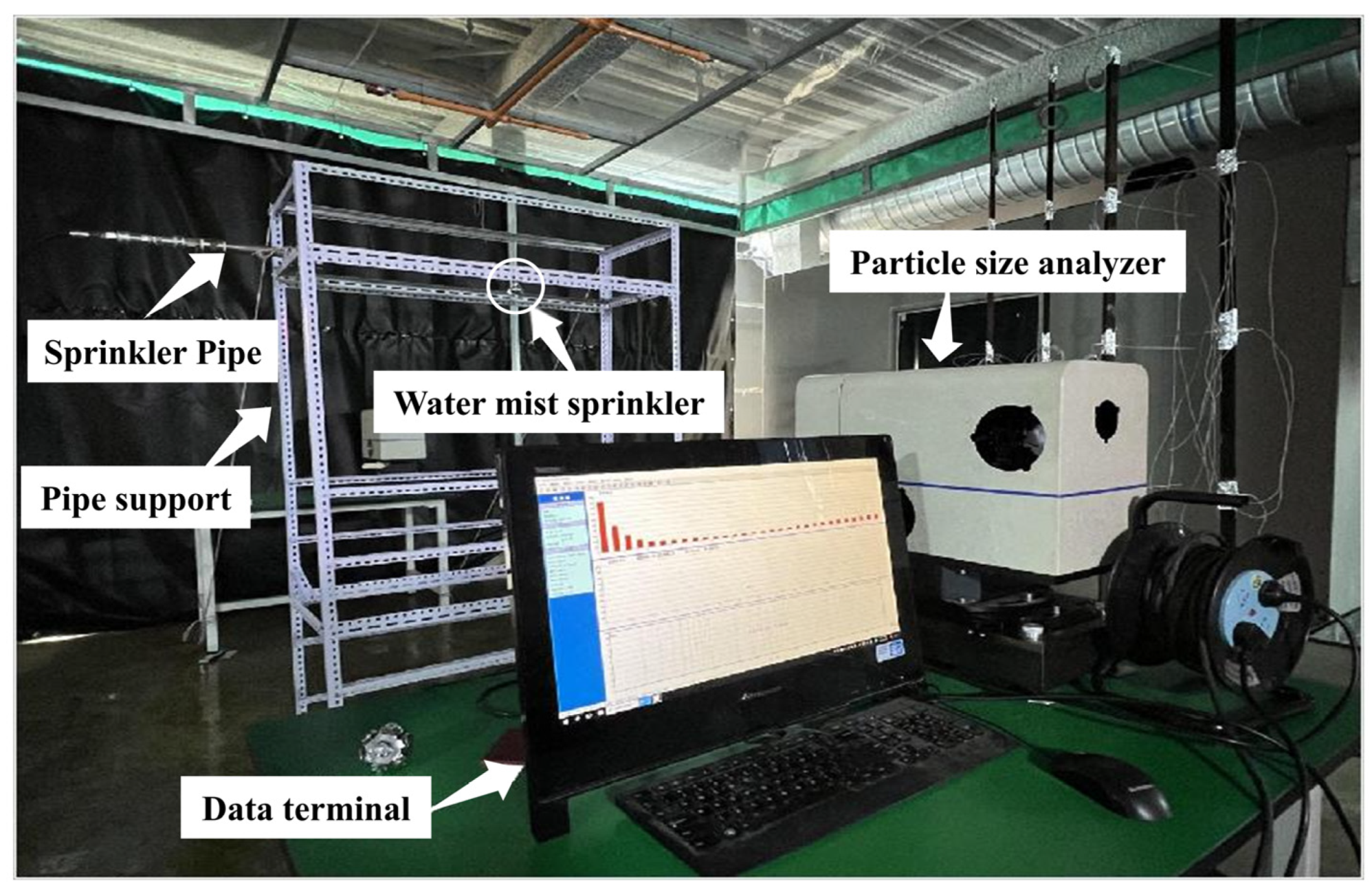
2.1.1. Mist Droplet Size Distribution Testing Workbench
2.1.2. Test Results and Analysis of Droplet Size Distribution for Water Mist Sprinkler
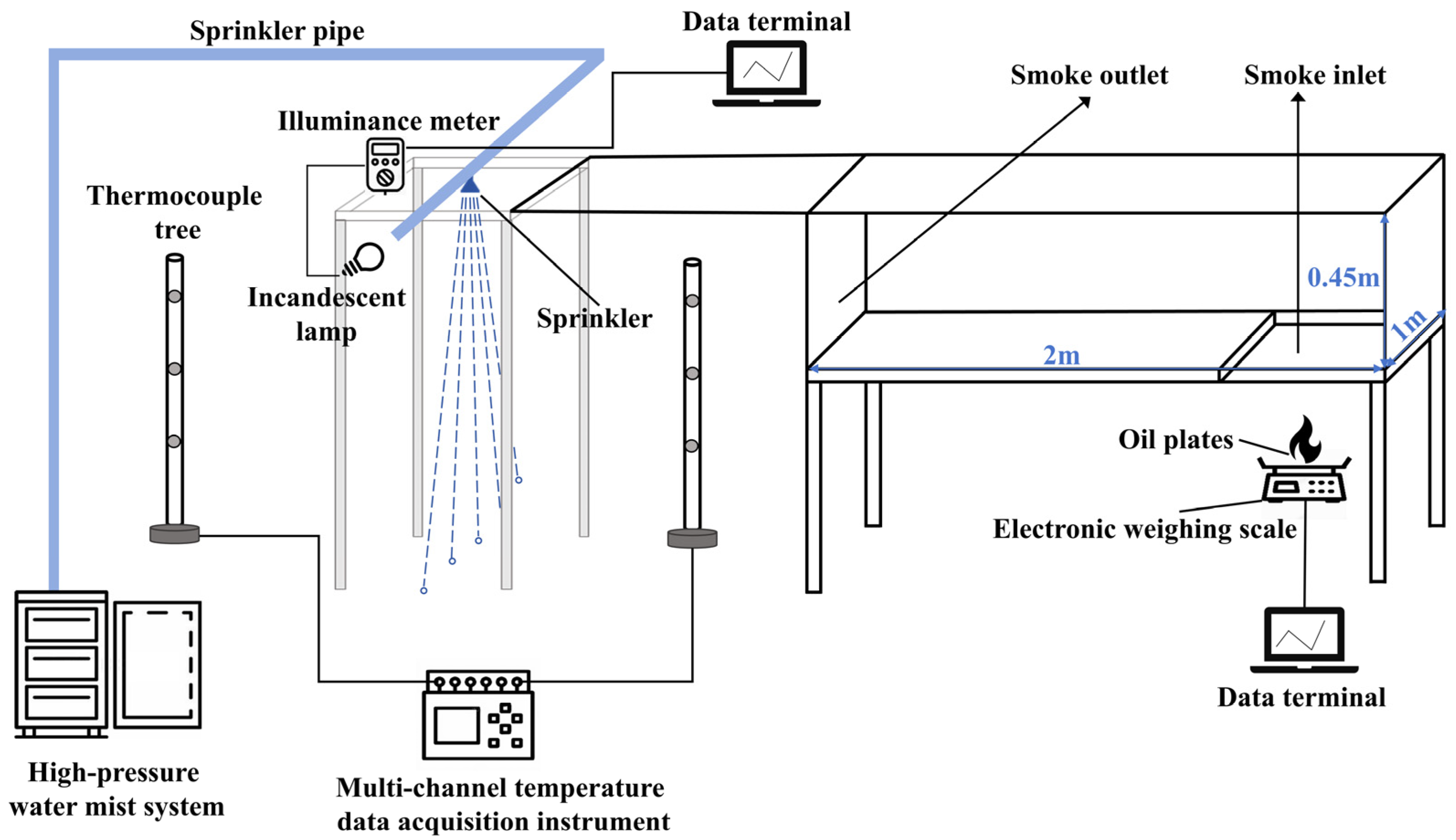
2.2. Smoke and Heat Barrier Test Apparatus and Parameter Measurement Point Layout
2.2.1. Smoke and Heat Barrier Test Bench Setup
2.2.2. Introduction to Experimental Measurement Equipment
- Temperature Measurement
- Measurement of Ignition Source Power
- Measurement of Smoke Opacity
2.3. Numerical Simulation of Small-Scale Smoke and Heat Barrier Experiments
2.3.1. Model Establishment
2.3.2. Grid Size Settings
2.3.3. Measurement Equipment Layout and Sprinkler Parameter Settings
3. Results
3.1. Comparison and Validation of Numerical Simulation Results with Experimental Results
3.1.1. Spray Pattern Characteristics of Water Mist Sprinklers
3.1.2. Smoke Spread Conditions
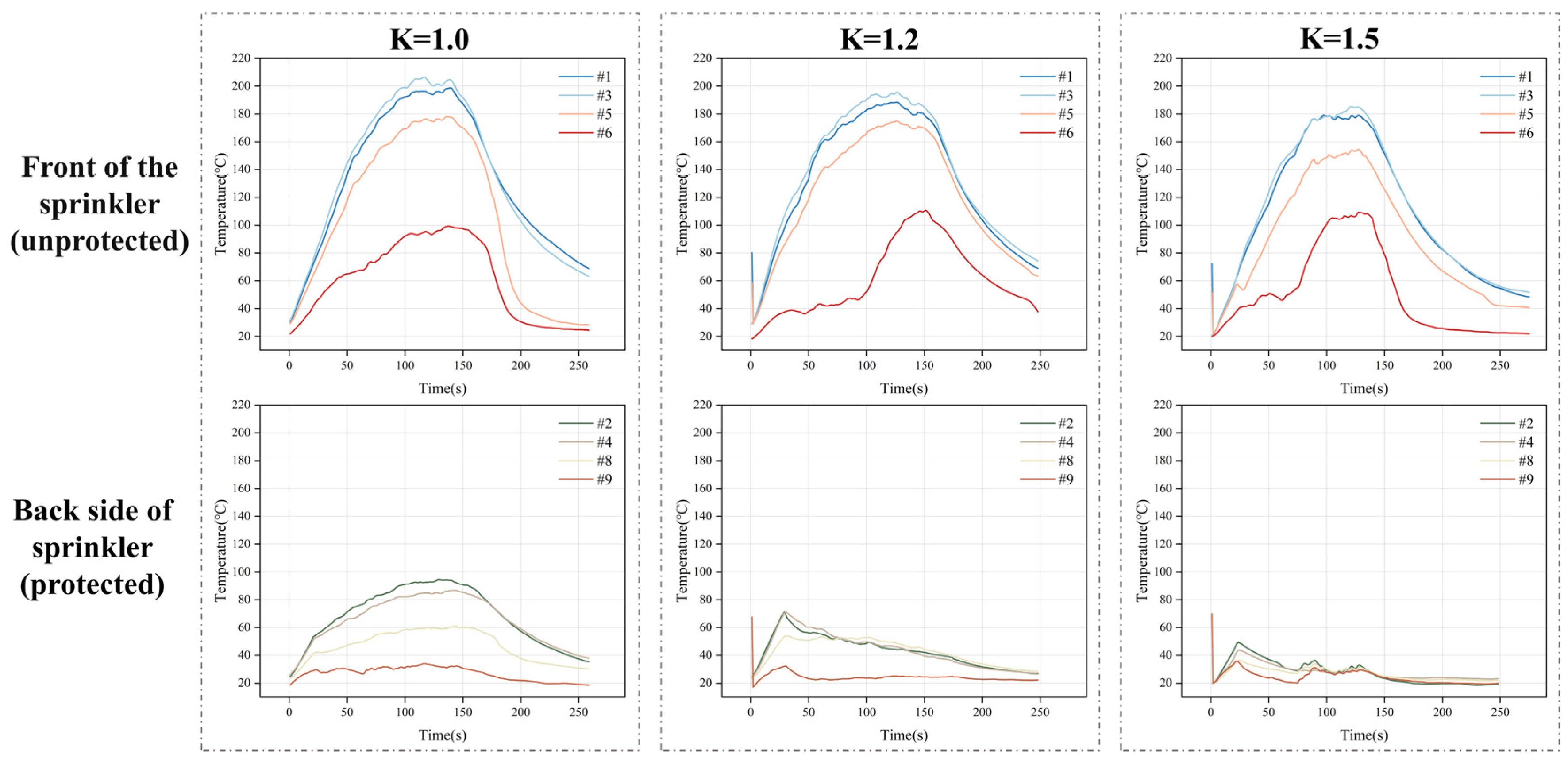
3.1.3. Temperature
3.1.4. Visible Distance
3.2. Optimal Sprinkler Flow Rate Parameter Selection
3.2.1. Comparison of Smoke Spread
3.2.2. Temperature Comparison
3.2.3. Visibility Comparison
4. Discussion and Conclusions
- Droplet size analysis indicates that droplet size does not exhibit a regular variation with increasing flow coefficient. Sprinklers with flow coefficients of 1.0, 1.2, and 1.5 demonstrate optimal atomization at 8 MPa, producing fine droplets (D32 ≤ 39.6 μm) and a concentrated distribution (fitting error ≤ 0.072), facilitating the formation of a uniform, dense water mist layer. This provides a foundation for subsequent studies on smoke barrier and thermal insulation performance.
- Comparison between small-scale experiments and FDS simulations confirmed high consistency in smoke propagation trends, temperature distribution, and visibility changes. This indicates that the established numerical model reliably reflects the smoke barrier and thermal insulation behavior of water mist.
- Comprehensive comparison of smoke and heat suppression performance across flow coefficients K = 1.0, 1.2, and 1.5 reveals that K = 1.5 sprinklers deliver optimal performance in suppressing smoke spread (minimum spread range) and reducing temperature (maximum protected-side temperature at 50 °C, representing a 20~45 °C reduction compared to K = 1.0 and K = 1.2 sprinklers). Although visibility was slightly lower than the K = 1.2 condition due to the influence of droplet size and particle count on visibility, the overall performance was optimal. Therefore, K = 1.5 was selected as the optimal flow rate parameter.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Ren, F.; Shi, C. Numerical Study on Coupled Smoke Control Using Longitudinal Ventilation and Naturally Ventilated Shafts during Fires in a Road Tunnel. Fire 2023, 6, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrill, J.B.; Montgomery, R.R.; Reinhardt, C.F. Toxic Gases from Fires. Science 1978, 200, 1343–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Gao, Z.H.; Fan, C.G.; Sun, J.H. Large Eddy Simulation of Stack Effect on Natural Smoke Exhausting Effect in Urban Road Tunnel Fires. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 66, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Qu, B.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Q. Theoretical and Numerical Study on Critical Velocity and Driving Force for Preventing Smoke Backlayering in a Connection Roadway Fire of Coal Mines. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 127, 104566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Zhao, Z. Preliminary Study on Extinguishing Shielded Fire with Water Mist. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 141, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Liang, W.; Vadim, Y.; Aleksei, N. The Review of the Water Mist Fire Extinguishing Technology. Bull. Sci. Pract. 2019, 5, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NFPA 750; Standard on Water Mist Fire Protection Systems. National Fire Protection Association: Quincy, MA, USA, 2019.
- Coppalle, A.; Nedelka, D.; Bauer, B. Fire Protection: Water Curtains. Fire Saf. J. 1993, 20, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berour, N.; Lacroix, D.; Boulet, P.; Jeandel, G. Radiative and Conductive Heat Transfer in a Nongrey Semitransparent Medium. Application to Fire Protection Curtains. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2004, 86, 9–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, A.; Lechene, S.; Boulet, P.; Parent, G. Water Mist and Radiation Interactions: Application to a Water Curtain Used as a Radiative Shield. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A 2010, 57, 537–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembele, S.; Wen, J.X. Analysis of the Screening of Hydrogen Flares and Flames Thermal Radiation with Water Sprays. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 6146–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchlin, J.M. Mitigation of Industrial Hazards by Water Spray Curtains. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2017, 50, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.P.; Ho, S.P.; Chen, C.S.; Chien, S.W. Performance of a Spray System in a Full-Scale Tunnel Fire Test. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 67, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, E.; Boulet, P.; Fromy, P.; Desanghere, S.; Carlotti, P.; Vantelon, J.P.; Garo, J.P. Experimental and Numerical Study of the Interaction between Water Mist and Fire in an Intermediate Test Tunnel. Fire Technol. 2013, 50, 565–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Tao, C.; Zhang, H. Experimental Study on Fire Smoke Control Using Water Mist Curtain in Channel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembele, S.; Wen, J.X.; Sacadura, J.-F. Experimental Study of Water Sprays for the Attenuation of Fire Thermal Radiation. J. Heat Transf. 2000, 123, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Fang, Z.; Tang, Z.; Beji, T.; Merci, B. Experimental Study of the Effectiveness of a Water System in Blocking Fire-Induced Smoke and Heat in Reduced-Scale Tunnel Tests. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 56, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, R.; Izushi, Y.; Kurioka, H.; Kuwana, H.; Tsuruda, T.; Suzuki, T.; Ogawa, Y. Water Screen Fire Disaster Prevention System. Res. Prod. 2005, 57, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Tang, Z.; Fang, Z.; Yuan, J.; Wang, J. Experimental Study of the Effectiveness of a Water Mist Segment System in Blocking Fire-Induced Smoke and Heat in Mid-Scale Tunnel Tests. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 88, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehaddi, R.; Collin, A.; Boulet, P.; Acem, Z.; Telassamou, J.; Becker, S.; Demeurie, F.; Morel, J.-Y. Use of a Water Mist for Smoke Confinement and Radiation Shielding in Case of Fire during Tunnel Construction. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2020, 148, 106156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Shi, C.; Gong, Z.; Tan, X. Numerical Study on Water Curtain System for Fire Evacuation in a Long and Narrow Tunnel under Construction. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 83, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cachinho Cordeiro, I.M.; Liu, H.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Chen, T.B.Y.; Li, A.; Wang, C.; Cao, R.; Yeoh, G.H. On the Large Eddy Simulation Modelling of Water Suppression Systems Droplet Impact and Coverage Area. Fire 2022, 5, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, D.; Kong, X.; Jiang, X.; Lu, K. Water Spray Effects on Fire Smoke Temperature Distribution beneath a Symmetrical V-Shaped Tunnel Ceiling. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 51, 103568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, H.M.I.; Moinuddin, K.A.M.; Thorpe, G.R. Experimental and Numerical Study of High-Pressure Water-Mist Nozzle Sprays. Fire Saf. J. 2016, 81, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelliah, H.K. Flame Inhibition/Suppression by Water Mist: Droplet Size/Surface Area, Flame Structure, and Flow Residence Time Effects. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2007, 31, 2711–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Jin, J.Y.; Han, P.; Yang, X.; Du, X.; Hu, Q. Direct and Indirect Measurement of Liquid Film Thickness by Common Optical Methods. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2025, 96, 081501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Gao, T.; Said, Z.; Sharma, S. Prediction Model of Volume Average Diameter and Analysis of Atomization Characteristics in Electrostatic Atomization Minimum Quantity Lubrication. Friction 2023, 11, 2107–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, C.; Song, W.; Zhang, S. Establishment of Fog Droplet Distribution Model and Study on Canopy Deposition Uniformity. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 077113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moinuddin, K.; Mahmud, H.M.I.; Joseph, P.; Gamble, G.; Suendermann, B.; Wilkinson, C.; Bossard, J. Experimental and Numerical Studies on the Efficacy of Water Mist to Suppress Hydrocarbon Fires in Enclosures. Fire 2024, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgotra, A.; Rangarajan, G.; Tauseef, S.M. CFD-Based Study and Analysis on the Effectiveness of Water Mist in Interacting Pool Fire Suppression. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 152, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, N.M. Assessing the Feasibility of Reducing the Grid Resolution in FDS Field Modelling; School of Engineering, University of Canterbury: Christchurch, New Zealand, 2002; ISSN 1173-5996. [Google Scholar]
- Seike, M.; Kawabata, N.; Hasegawa, M. Experiments of Evacuation Speed in Smoke-Filled Tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 53, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, B. Numerical Investigation of Water Curtain for Smoke Blocking and Heat Insulation in Urban Underground Road. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2022, 35, 101468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
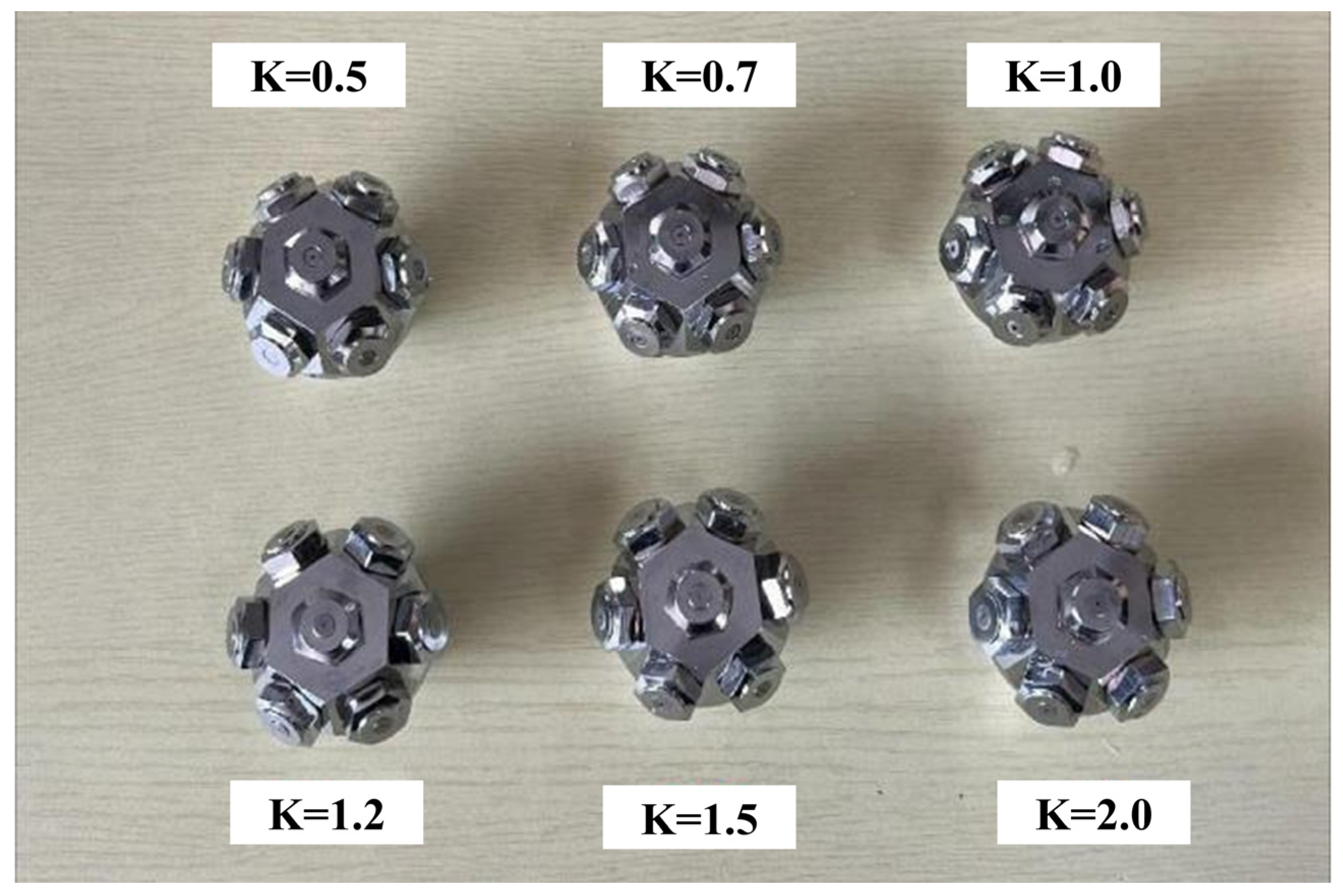













| Flow Coefficient | Particle Size (μm) | Fitting Error | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D10 | D32 | D50 | D90 | ||
| 0.5 | 30.631 | 45.319 | 50.417 | 69.302 | 0.096 |
| 0.7 | 25.265 | 38.958 | 44.987 | 65.064 | 0.153 |
| 1.0 | 32.623 | 39.600 | 41.303 | 48.141 | 0.055 |
| 1.2 | 26.942 | 34.464 | 26.942 | 26.942 | 0.072 |
| 1.5 | 28.985 | 37.366 | 39.275 | 47.821 | 0.054 |
| 2.0 | 32.359 | 41.131 | 43.489 | 52.672 | 0.072 |
| Grid | Grid Area | Unit Grid Size | Number of Grids | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | |||
| Mesh1 | −1.0~0.1 | −0.5~1.5 | 0~2 | 0.4 | 70,000 |
| Mesh2 | 0.1~2.5 | −0.5~1.5 | 0~2 | 0.2 | 1100 |
| Work Pressure (Mpa) | Flow Coefficient (K) | Droplet Size (μm) | Atomization Cone Angle (°) | Initial Velocity of the Droplet (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 1.0 | 39.600 | 100 | 30 |
| 1.2 | 34.464 | 113 | ||
| 1.5 | 37.366 | 136 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Men, J.; Liang, Q.; Xu, H.; Liu, Z.; Lv, J.; Wang, X. Small-Scale Experimental Study on Smoke Blocking and Thermal Insulation Performance of Water Mist Sprinkler. Fire 2025, 8, 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8100401
Men J, Liang Q, Xu H, Liu Z, Lv J, Wang X. Small-Scale Experimental Study on Smoke Blocking and Thermal Insulation Performance of Water Mist Sprinkler. Fire. 2025; 8(10):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8100401
Chicago/Turabian StyleMen, Jianan, Qiang Liang, Hui Xu, Zhenyu Liu, Jielong Lv, and Xiaopo Wang. 2025. "Small-Scale Experimental Study on Smoke Blocking and Thermal Insulation Performance of Water Mist Sprinkler" Fire 8, no. 10: 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8100401
APA StyleMen, J., Liang, Q., Xu, H., Liu, Z., Lv, J., & Wang, X. (2025). Small-Scale Experimental Study on Smoke Blocking and Thermal Insulation Performance of Water Mist Sprinkler. Fire, 8(10), 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8100401





