Investigation of the Impact of Coal Fires on Soil: A Case Study of the Wugong Coal Fire Area, Xinjiang, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Sample Collection and Treatment
2.3. Sample Analysis
2.3.1. Soil Chemical Properties
2.3.2. Heavy Metal
2.4. Methods for Evaluating Soil Heavy Metal Pollution
2.4.1. Single Factor Pollution Index Method
2.4.2. Nemero’s Pollution Index Method
| Index | Classification | Specification | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single factor pollution index (Pi ) | Pi < 1 | Non-pollution (I) | [34,35] |
| 1 ≤ Pi < 2 | Mild pollution (II) | ||
| 2 ≤ Pi < 3 | Moderate pollution (III) | ||
| 3 ≤ Pi < 4 | High pollution (IV) | ||
| 4 ≤ Pi < 5 | Heavy pollution (V) | ||
| Geo-accumulation index (IGeo) | Igeo < 0 | Non-pollution (I) | [10] |
| 0 ≤ Igeo < 1 | Light to moderate pollution (II) | ||
| 1 ≤ Igeo < 2 | Moderate pollution (III) | ||
| 2 ≤ Igeo < 3 | Moderate to heavy pollution (IV) | ||
| 3 ≤ Igeo < 4 | Heavy pollution (V) | ||
| 4 ≤ Igeo < 5 | Heavy to strong pollution (VI) | ||
| Igeo ≥ 5 | Extreme pollution (VII) | ||
| Nemero’s pollution index (Pn) | Pn < 0.7 | Non-pollution (I) | [33] |
| 0.7 ≤ Pn < 1 | Mild pollution (II) | ||
| 1 ≤ Pn < 2 | Moderate Pollution (III) | ||
| 2 ≤ Pn < 3 | High pollution (IV) | ||
| Pn ≥ 3 | Heavy pollution (V) | ||
| Pollution load index (PLI) | PLI < 1 | Non-pollution (I) | [36,37] |
| 1 < PLI ≤ 2 | Mild pollution (II) | ||
| 2 < PLI ≤ 3 | Moderate pollution (III) | ||
| PLI > 3 | Heavy pollution (IV) | ||
| Ecological risk factor (Eri) and risk index (RI) | Eri < 40, RI < 150 | Low risk (I) | [34,38,39] |
| 40 ≤ Eri < 80, 150 ≤ RI < 300 | Moderate risk (II) | ||
| 80 ≤ Eri < 160, 300 ≤ RI < 600 | Considerable risk (III) | ||
| 160 ≤ Eri < 320, RI ≥ 600 | High risk (IV) | ||
| Eri ≥ 320 | Significantly high risk (V) |
2.4.3. Geo-Accumulation Index Method
2.4.4. Pollution Load Index
2.4.5. Analysis of Potential Ecological Risks
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of Soil Chemical Properties
3.2. Characteristics of Heavy Metal Pollution
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Soil Chemical Properties and Heavy Metals
3.4. Risk Assessment
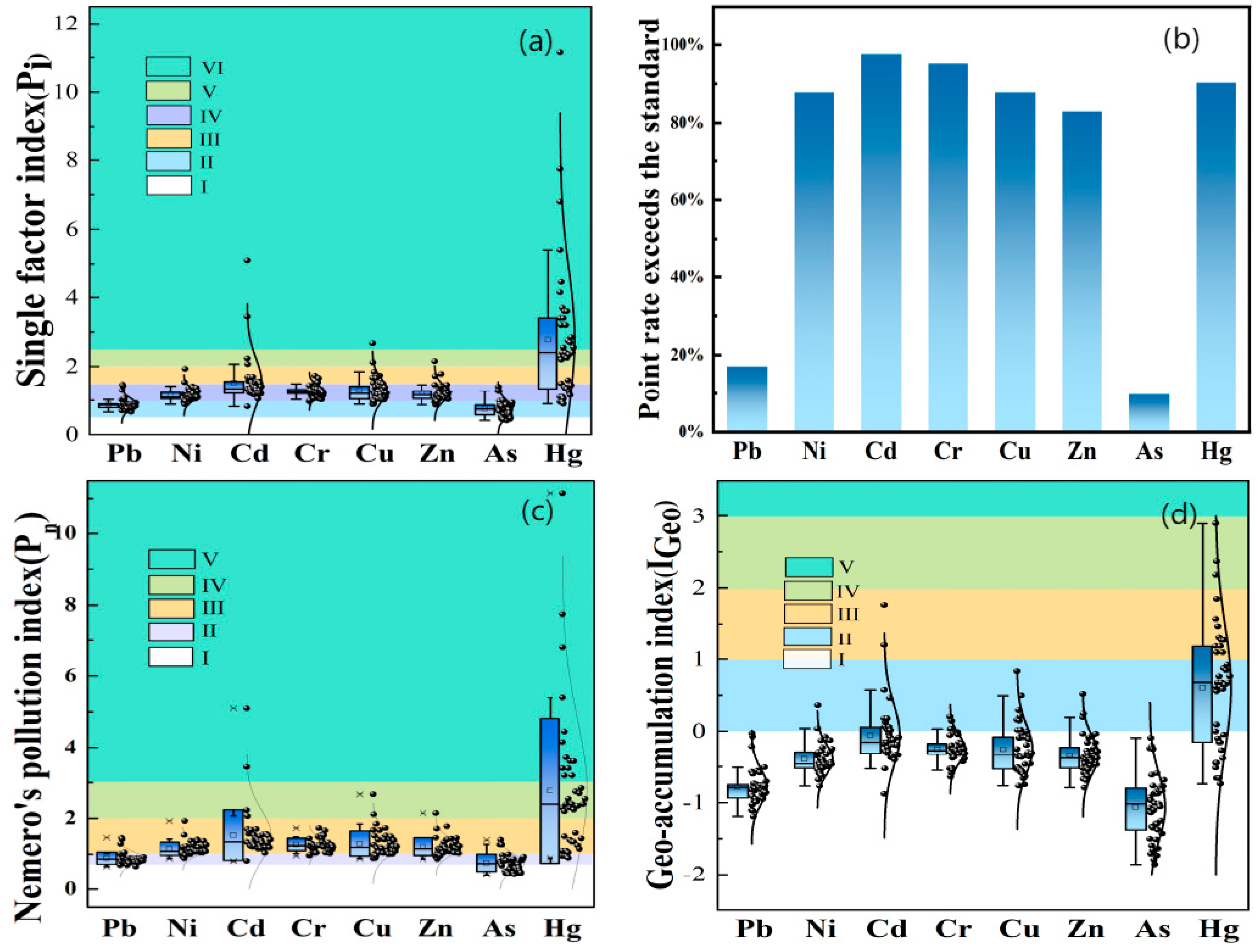
3.4.1. Soil Heavy Metal Pollution Assessment
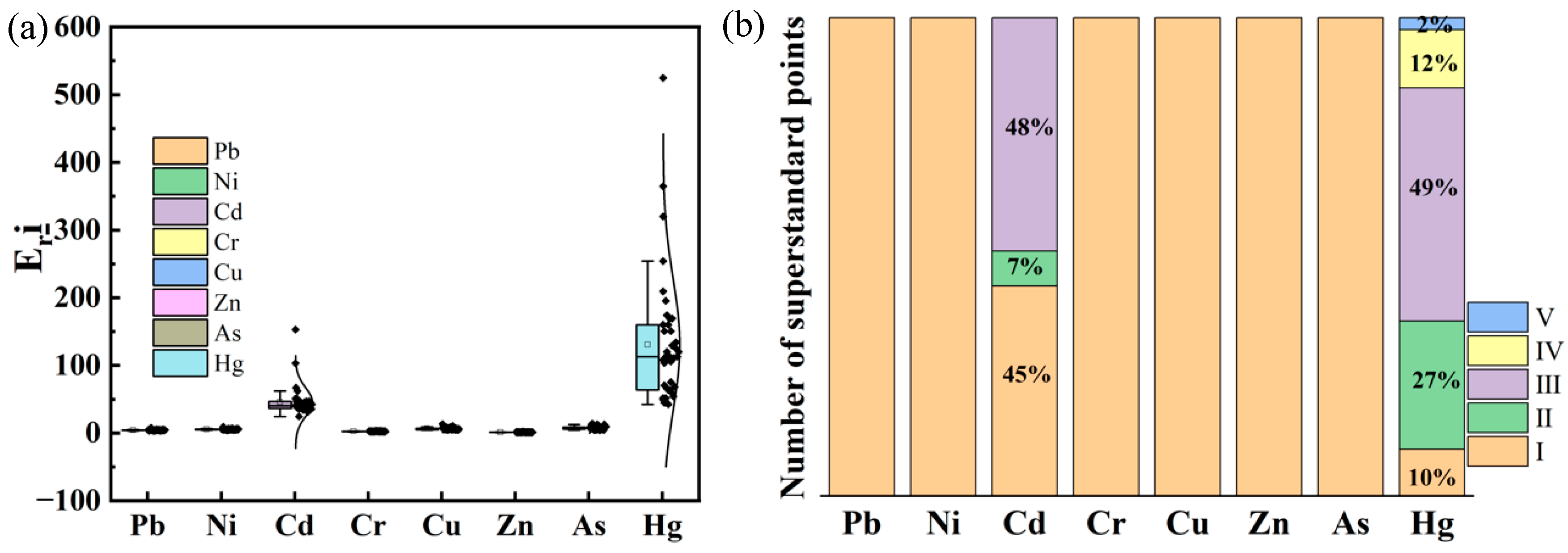
3.4.2. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, Z.; Kuenzer, C. Coal fires in China over the last decade: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 133, 72–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, S.; Tian, F.; Wang, S. Combustion mechanism and control approaches of underground coal fires: A review. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Dong, J.; Zhao, L. Investigation of the potential risk of coal fire to local environment: A case study of Daquanhu coal fire, Xinjiang region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Z.; Inyang, H.I.; Daniels, J.L.; Otto, F.; Struthers, S. Environmental issues from coal mining and their solutions. Min. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wen, H.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X. A method for evaluating the spontaneous combustion of coal by monitoring various gases. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 126, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Cao, F.; Dai, S.; Shan, B.; Qi, C.; Xu, Z.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Chen, J. Atmospheric Mercury Isotope Shifts in Response to Mercury Emissions from Underground Coal Fires. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 8638–8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, S.R.; Yue, T.; Zhang, X.Q.; Yu, M.D.; Li, X.F. Environmental effect analysis of coalfield fire in Xinjiang and its preventive. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1010, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Wattimena, R.K.; Armaghani, D.J.; Asteris, P.G.; Jiskani, I.M.; Mohamad, E.T. Intelligent based decision-making strategy to predict fire intensity in subsurface engineering environments. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 171, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerizghi, T.; Guo, Q.; Tian, L.; Wei, R.; Zhao, C. An integrated approach to quantify ecological and human health risks of soil heavy metal contamination around coal mining area. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Sen Gupta, B.; Patidar, S.; Hernández-Martínez, J.L.; Martín-Romero, F.; Meza-Figueroa, D.; Martínez-Villegas, N. A comprehensive study of source apportionment, spatial distribution, and health risks assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in the surface soils of a semi-arid mining region in Matehuala, Mexico. Environ. Res. 2024, 260, 119619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Huang, S.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Su, J.; Lin, K.; Chen, X.; He, T.; Li, Y.; Sha, C.; et al. Source-oriented health risk assessment and priority control factor analysis of heavy metals in urban soil of Shanghai. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wei, Y.; Lei, M.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z. Process, influencing factors, and simulation of the lateral transport of heavy metals in surface runoff in a mining area driven by rainfall: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Singh, N.; Rai, S.N.; Kumar, A.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, M.P.; Sahoo, A.; Shekhar, S.; Vamanu, E.; Mishra, V. Heavy Metal Contamination in the Aquatic Ecosystem: Toxicity and Its Remediation Using Eco-Friendly Approaches. Toxics 2023, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Huo, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, G.; An, Y. A hybrid framework for delineating the migration route of soil heavy metal pollution by heavy metal similarity calculation and machine learning method. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, D.; Ma, J.; Jin, B.; Peng, J.; He, X. Assessing the influence of immobilization remediation of heavy metal contaminated farmland on the physical properties of soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.X.; Xie, Z.H.; Huang, H.Y.; Zang, S.Y.; Lian, B. Heavy Metal Pollution Characteristics in the Kaili Coal Mining Region, Guizhou Province, China. J. Residuals Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, S123–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuralykyzy, B.; Wang, P.; Deng, X.; An, S.; Huang, Y. Heavy Metal Contents and Assessment of Soil Contamination in Different Land-Use Types in the Qaidam Basin. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhu, L.; Zhuo, J.; Hu, S. Analysis of the Environmental Impact of Coalfield Fires. Coal Saf. 2024, 55, 132–142. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Song, J.; Tan, M.L.; Kung, H.-T.; Johnson, V.C. Pollutant source, ecological and human health risks assessment of heavy metals in soils from coal mining areas in Xinjiang, China. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Lu, H.; Lin, H. Comprehensive study on the spatial distribution of heavy metals and their environmental risks in high-sulfur coal gangue dumps in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 136, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.L.; Hu, Z.Q.; Peng, W.H.; Ye, W.L.; Zhang, C.L.; Huang, X.R.; Chen, S.; Gui, H.R. Pollution Assessment and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in the Surrounding Soil of Typical Mining Areas in Tongling, Anhui Province. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 5494–5505. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhu, S. Mercury emission from coal seam fire at Wuda, Inner Mongolia, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 83, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Nie, J.; Pu, Y. Characteristics of the distribution of typical heavy metals in the soils of underground coal fire. J. China Coal Soc. 2016, 41, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.; Tiyip, T.; Wuttke, M.W.; Kurban, B. Characteristics of the heavy metal distribution in the soils of underground coal fire and the evaluation of its impact on environment. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2014, 43, 695–700. [Google Scholar]
- Sazawa, K.; Sugano, T.; Kuramitz, H. High-heat Effects on the Physical and Chemical Properties of Soil Organic Matter and Its Water-soluble Components in Japan’s Forests: A Comprehensive Approach Using Multiple Analytical Methods. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, J.; Zeng, J.; Lou, K. Diversity of prokaryotes associated with soils around coal-fire gas vents in MaNasi county of Xinjiang, China. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2013, 103, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Bian, Z.; Lei, S. Impact on soil physical qualities by the subsidence of coal mining: A case study in Western China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Q.; Xie, K.; Sun, P.; Kim, Y. Characterization of phosphorus in the sedimentary environments of inundated agricultural soils around the Huainan Coal Mines, Anhui, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Bai, Z.; Zhou, W.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, G. Changes in soil properties in the soil profile after mining and reclamation in an opencast coal mine on the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; He, F.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yuan, M.Y.; Lai, P.M.; Guo, J.K. Pollution Characteristics, Source Analysis, and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil and Crops in a Typical molybdenum Mining Area of Qinling Mountains. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 5526–5537. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Ni, Q. Determination of Copper, Zinc, Lead, Nickel, and Manganese in Soils by Microwave Digestion-Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Guangzhou Chem. Ind. 2006, 34, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Gyamfi, E.; Appiah-Adjei, E.K.; Adjei, K.A. Potential Heavy Metal Pollution of Soil and Water Resources from Artisanal Mining in Kokoteasua, Ghana. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.-Y.; Dong, Q.-Y.; Song, C.; Yang, Z.-J. Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals in the Eastern Mountainous Area of the Nanyang Basin. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 5500–5509. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qian, X.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H. Chemical speciation and human health risk of trace metals in urban street dusts from a metropolitan city, Nanjing, SE China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 456–457, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; da Silva, J.B.; dos Santos, I.F.; de Oliveira, O.M.C.; Cerda, V.; Queiroz, A.F.S. Use of pollution indices and ecological risk in the assessment of contamination from chemical elements in soils and sediments—Practical aspects. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 35, e00169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, J.B.; Mazurek, R.; Gąsiorek, M.; Zaleski, T. Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination–A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2395–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, P.; Kumari, R. Toxic metals distribution, seasonal variations and environmental risk assessment in surficial sediment and mangrove plants (A. marina), Gulf of Kachchh (India). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Ni, S.; Tu, X.; Zhang, C. Calculation of Heavy Metal Toxicity Coefficients in the Potential Ecological Hazard Index Method. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 2, 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Li, K.; Li, M.; Yang, K.; Liu, F.; Cheng, X. Geochemical Background and Baseline Values of Chemical Elements in Urban Soils of China. Earth Sci. Front. 2014, 21, 265–306. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, S.; Gao, L.; Zhao, J. Distribution and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Xinzhuangzi Reclamation Soil from the Huainan Coal Mining Area, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2015, 21, 900–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Wen, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, C.; Ouyang, H.; Hu, N.; Li, X.; Qiu, X. The coupling of sulfide and Fe-Mn mineral promotes the migration of lead and zinc in the redox cycle of high pH floodplain soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Ding, K.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Baker, A.J.M.; Yang, W.; et al. Factors influencing heavy metal availability and risk assessment of soils at typical metal mines in Eastern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sui, W.; Wang, K.; Tang, G.; Li, X. Changes in Particle Size Composition under Seepage Conditions of Reclaimed Soil in Xinjiang, China. Processes 2018, 6, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.-R.; Wang, M.-L.; Yang, J.-J.; Ding, Z.-L.; Cao, Y.-E. Effect of coal mining activities on soil properties and erodibility. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 33, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Feng, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Fu, B. Evaluation index system of comprehensive benefits of ecological restoration in key ecologically vulnerable regions. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 7356–7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Lu, N.; Luo, Y. Analysis of soil fertility and toxic metal characteristics in open-pit mining areas in northern Shaanxi. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Yao, B.-L.; Li, N.; Cai, G.-X.; Han, Q.-S. Effects of soil film residue on seedling emergence rate and salinity of cotton under brackish water irrigation. Water Sav. Irrig. 2021, 3, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, F.; Bian, P.; Liu, Y. Spatial distribution and human health risk assessment of soil heavy metals based on sequential Gaussian simulation and positive matrix factorization model: A case study in irrigation area of the Yellow River. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 225, 112752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Wang, X.-Y.; Ma, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Z. Buffer analysis of heavy metal ecological risk in the Hongshaquan mining area of East Junggar Basin. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 51, 227–233. [Google Scholar]
- Alfaro, M.R.; Montero, A.; Ugarte, O.M.; do Nascimento, C.W.A.; de Aguiar Accioly, A.M.; Biondi, C.M.; da Silva, Y.J.A.B. Background concentrations and reference values for heavy metals in soils of Cuba. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 187, 4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Villegas, N.; Hernández, A.; Meza-Figueroa, D.; Sen Gupta, B. Distribution of Arsenic and Risk Assessment of Activities on Soccer Pitches Irrigated with Arsenic-Contaminated Water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjoka, F.; Duering, R.-A.; Siemens, J. Background concentrations and spatial distribution of heavy metals in Albania’s soils. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Gupta, B.S.; Patidar, S.; Martínez-Villegas, N. Evaluation of Potential Ecological Risk Index of Toxic Metals Contamination in the Soils. Chem. Proc. 2022, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ogundele, D.; Adio, A.; Oludele, O. Heavy metal concentrations in plants and soil along heavy traffic roads in North Central Nigeria. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 5, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Wu, J.; Ye, Z.; Zhao, W.; Ding, L.; Fu, W.J. Risk assessment, spatial patterns and source apportionment of soil heavy metals in a typical Chinese hickory plantation region of southeastern China. Geoderma 2020, 360, 114011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, F.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C. Phytoremediation potential of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) intercropped with Sedum plumbizincicola in metal-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 27244–27253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlova, M. The influence of heavy metals on soil biological and chemical properties. Soil Water Res. 2010, 5, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.; Jiao, W.-B.; Qiu, H.-Y.; Chen, B.; Huang, X.-X.; Kang, B. Origin and spatial distribution of heavy metals and carcinogenic risk assessment in mining areas at You’xi County southeast China. Geoderma 2018, 310, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Site, A. Factors affecting sorption of organic compounds in natural sorbent/water systems and sorption coefficients for selected pollutants. A review. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. 2001, 30, 187–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Liu, J.-X.; Wang, X.-G.; Ju, L.-X.; He, X.; Zhou, J.-W.; Zhang, Y. Pollution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in soil of a typical pyrite concentrated mining area in Anhui Province. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 5275–5287. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qing, C. Contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil of agricultural land in Weining Plain, northwest China. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 31, 2216–2224. [Google Scholar]

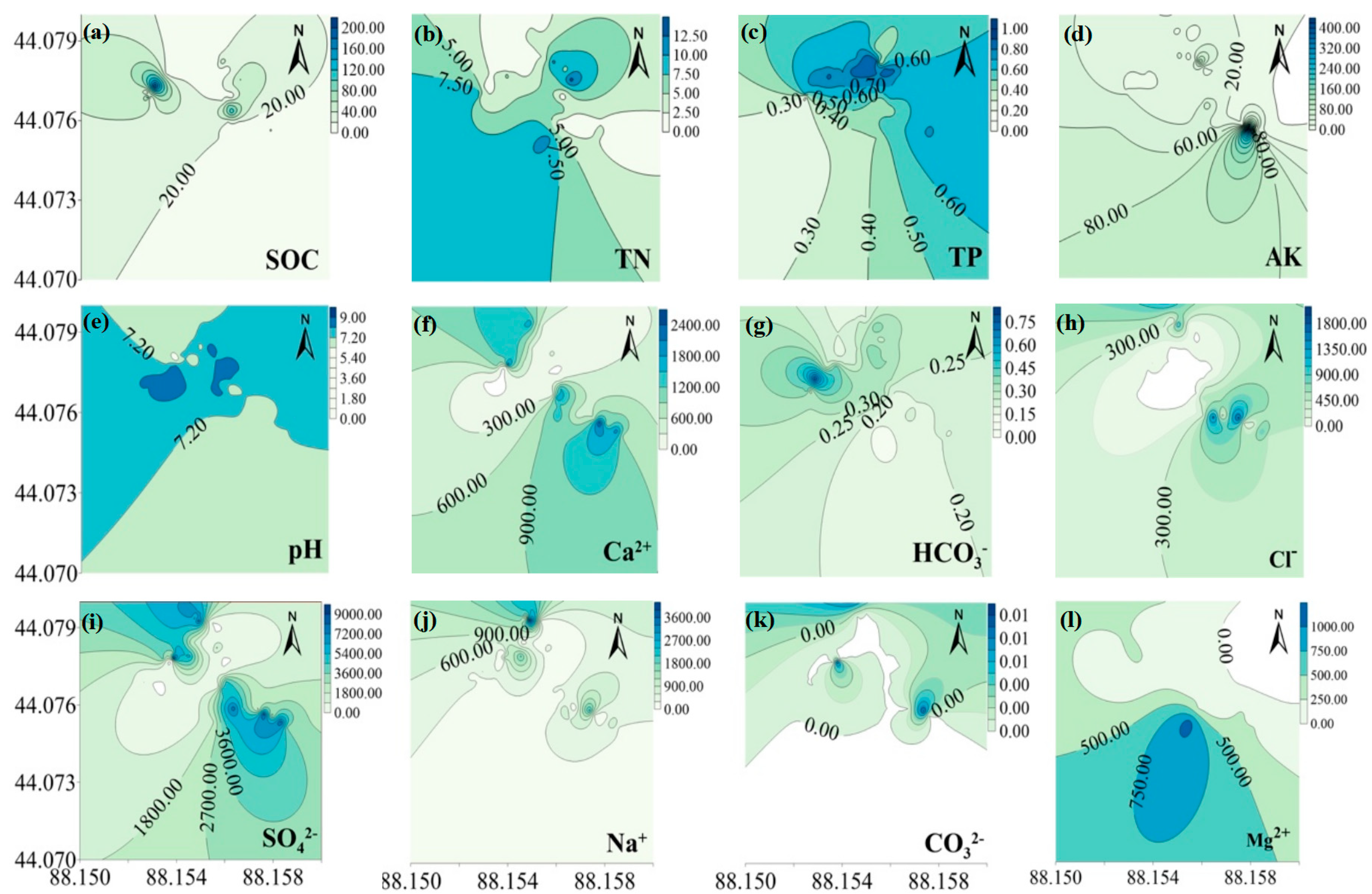
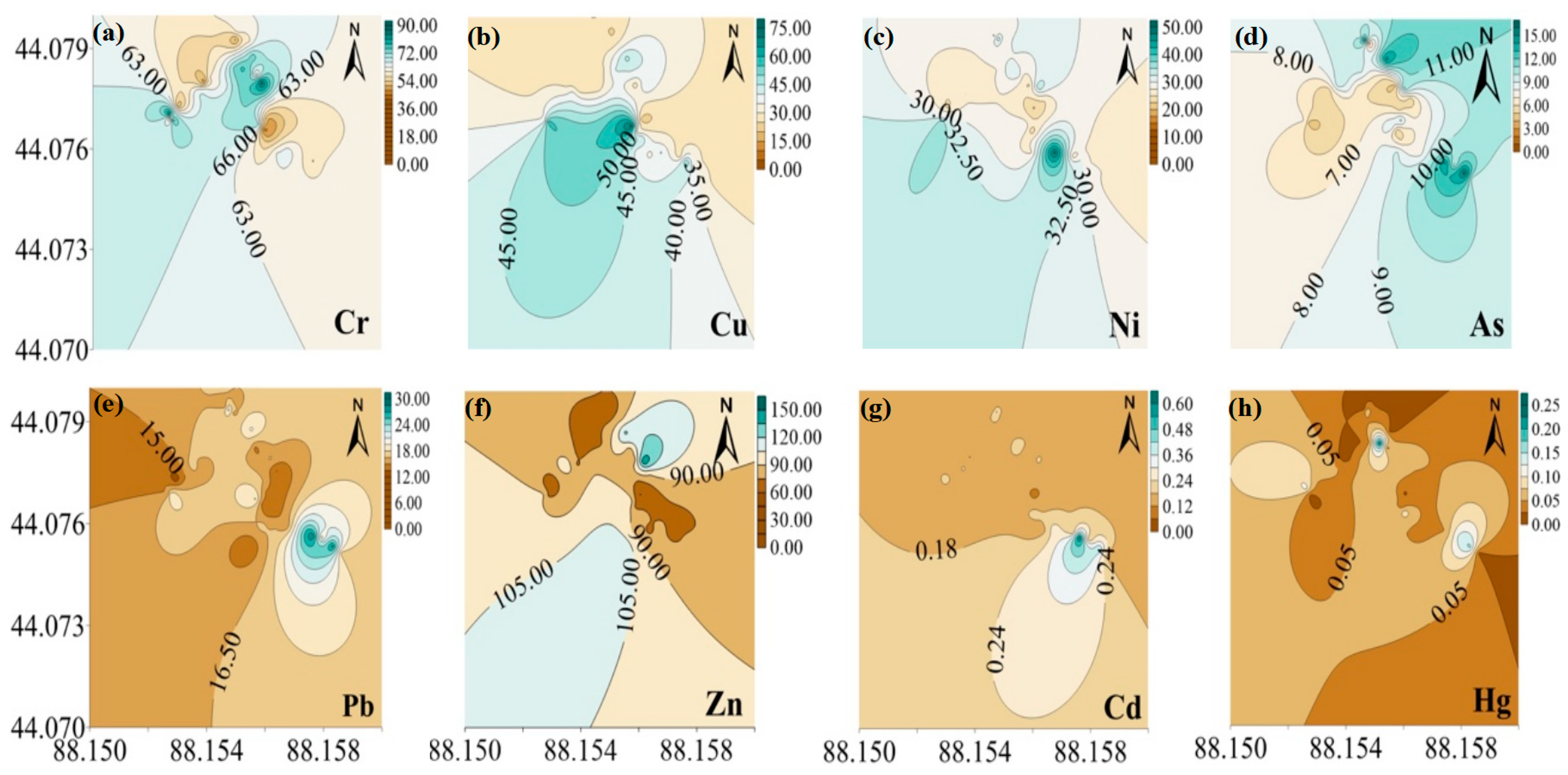


| Index | Minimum | Maximum | Median | Mean (Measured) | Standard Deviation (SD) | Coefficient of Variation (CV, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AK | 12.30 | 403.80 | 29.00 | 42.32 | 61.17 | 1.45 |
| Ca2+ | 29.90 | 2472.00 | 769.10 | 763.58 | 679.69 | 0.89 |
| Na+ | 22.90 | 3881.20 | 216.40 | 621.75 | 866.88 | 1.39 |
| Mg2+ | 6.00 | 1105.70 | 88.00 | 131.39 | 183.35 | 1.40 |
| CO32− | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.60 |
| HCO3− | 0.13 | 0.77 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.40 |
| Cl− | 0.00 | 1860.00 | 54.30 | 228.05 | 410.05 | 1.80 |
| SO42− | 67.80 | 8560.00 | 2380.00 | 3168.13 | 2873.19 | 0.91 |
| TP | 0.16 | 0.89 | 0.65 | 0.63 | 0.15 | 0.24 |
| TN | 0.15 | 13.41 | 2.65 | 3.88 | 3.23 | 0.83 |
| SOC | 1.60 | 199.99 | 10.53 | 24.10 | 37.42 | 1.55 |
| pH | 5.60 | 8.52 | 7.33 | 7.46 | 0.64 | 0.09 |
| Index | Pb | Ni | Cd | Cr | Cu | Zn | As | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 12.75 | 22.2 | 0.1 | 47.46 | 23.58 | 59.64 | 4.64 | 0.02 |
| Maximum | 28.52 | 48.64 | 0.61 | 85.47 | 71.4 | 147.79 | 15.77 | 0.22 |
| Median | 16.82 | 27.51 | 0.16 | 61.41 | 31.88 | 79.43 | 8.3 | 0.05 |
| Mean | 17.24 | 29.08 | 0.18 | 62.67 | 34.68 | 83.38 | 8.45 | 0.06 |
| Standard deviation (SD) | 3.31 | 4.7 | 0.08 | 8.55 | 9.4 | 17.1 | 2.74 | 0.04 |
| Coefficient of variation (CV, %) | 13.64 | 27.12 | 20.51 | 45.96 | 19.22 | 16.15 | 73.27 | 32.43 |
| Background value (Xinjiang) [51] | 19.4 | 26.6 | 0.12 | 49.3 | 26.7 | 68.8 | 11.2 | 0.017 |
| Toxic response factor | 5 | 5 | 30 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 10 | 40 |
| Metal | Pb | Ni | Cd | Hg | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indices | Pi | IGeo | Pn | Eri | Pi | IGeo | Pn | Eri | Pi | IGeo | Pn | Eri | Pi | IGeo | Pn | Eri |
| Mean | 0.89 | −0.78 | 1.22 | 4.44 | 1.09 | −0.39 | 1.51 | 5.77 | 1.27 | −0.05 | 3.79 | 45.91 | 3.27 | 0.61 | 9.68 | 111.07 |
| Median | 0.87 | −0.79 | 1.21 | 4.33 | 1.03 | −0.46 | 1.49 | 5.46 | 1.25 | −0.15 | 3.73 | 40.50 | 2.82 | 0.68 | 9.49 | 96.00 |
| Minimum | 0.66 | −1.19 | 1.14 | 3.29 | 0.83 | −0.77 | 1.42 | 4.40 | 0.96 | −0.88 | 3.65 | 24.50 | 1.06 | −0.74 | 9.31 | 36.00 |
| Maximum | 1.47 | −0.03 | 1.47 | 7.35 | 1.83 | 0.36 | 1.83 | 9.65 | 1.73 | 1.77 | 5.10 | 153.00 | 13.12 | 2.89 | 13.12 | 446.00 |
| SD | 0.17 | 0.24 | 0.07 | 0.85 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.93 | 0.17 | 0.44 | 0.24 | 21.10 | 2.39 | 0.89 | 0.68 | 81.38 |
| Metal | Cr | Cu | Zn | As | ||||||||||||
| Indices | Pi | IGeo | Pn | Eri | Pi | IGeo | Pn | Eri | Pi | IGeo | Pn | Eri | Pi | IGeo | Pn | Eri |
| Mean | 1.53 | −0.25 | 1.52 | 2.54 | 1.30 | −0.25 | 2.11 | 6.49 | 1.21 | −0.33 | 1.75 | 1.21 | 0.75 | −1.06 | 1.14 | 7.54 |
| Median | 1.35 | −0.27 | 1.51 | 2.49 | 1.19 | −0.33 | 2.07 | 5.97 | 1.15 | −0.38 | 1.73 | 1.15 | 0.74 | −1.02 | 1.13 | 7.41 |
| Minimum | 0.82 | −0.64 | 1.40 | 1.93 | 0.88 | −0.76 | 1.99 | 4.41 | 0.87 | −0.79 | 1.64 | 0.87 | 0.41 | −1.86 | 1.04 | 4.14 |
| Maximum | 5.10 | 0.21 | 1.73 | 3.47 | 2.67 | 0.83 | 2.67 | 13.36 | 2.15 | 0.52 | 2.15 | 2.15 | 1.41 | −0.09 | 1.41 | 14.08 |
| SD | 0.70 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 1.76 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.45 | 0.09 | 2.45 |
| Mean | Median | Minimum | Maximum | Standard deviation (SD) | ||||||||||||
| PLI | 1.51 | 1.41 | 0.79 | 2.66 | 1.56 | |||||||||||
| RI | 184.97 | 163.31 | 79.54 | 649.06 | 109.07 | |||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, R.; Zeng, Q.; Ren, T.; Wu, S.; Li, H. Investigation of the Impact of Coal Fires on Soil: A Case Study of the Wugong Coal Fire Area, Xinjiang, China. Fire 2025, 8, 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8100385
Hao R, Zeng Q, Ren T, Wu S, Li H. Investigation of the Impact of Coal Fires on Soil: A Case Study of the Wugong Coal Fire Area, Xinjiang, China. Fire. 2025; 8(10):385. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8100385
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Ruirui, Qiang Zeng, Ting Ren, Suqing Wu, and Haijian Li. 2025. "Investigation of the Impact of Coal Fires on Soil: A Case Study of the Wugong Coal Fire Area, Xinjiang, China" Fire 8, no. 10: 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8100385
APA StyleHao, R., Zeng, Q., Ren, T., Wu, S., & Li, H. (2025). Investigation of the Impact of Coal Fires on Soil: A Case Study of the Wugong Coal Fire Area, Xinjiang, China. Fire, 8(10), 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8100385






