Fire Extinction Analysis and OH-PLIF Visualization of the Methane–Air Premixed Laminar Flame Interacting with the Downward Water Mist
Abstract
1. Introduction
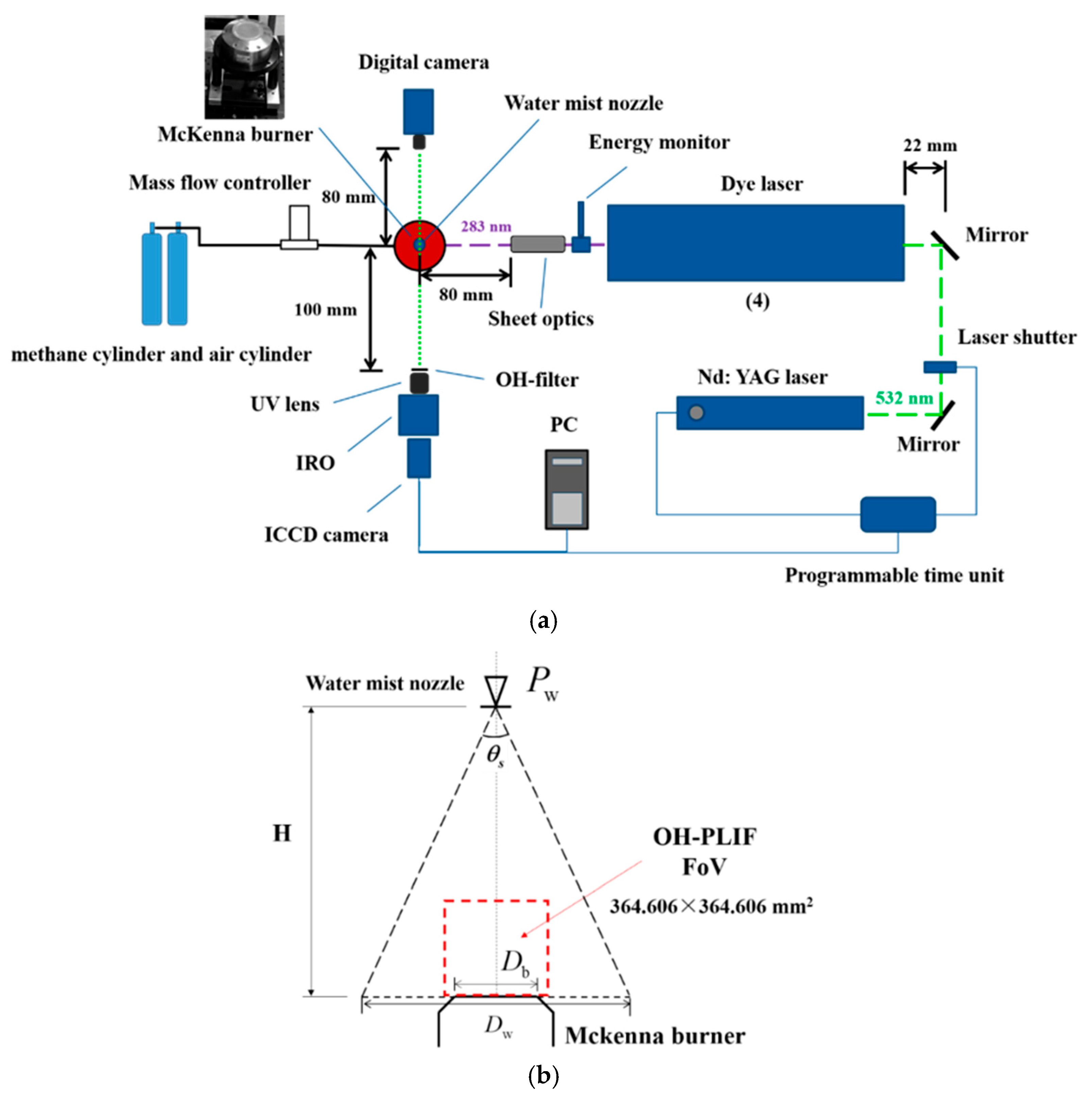
2. Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussions
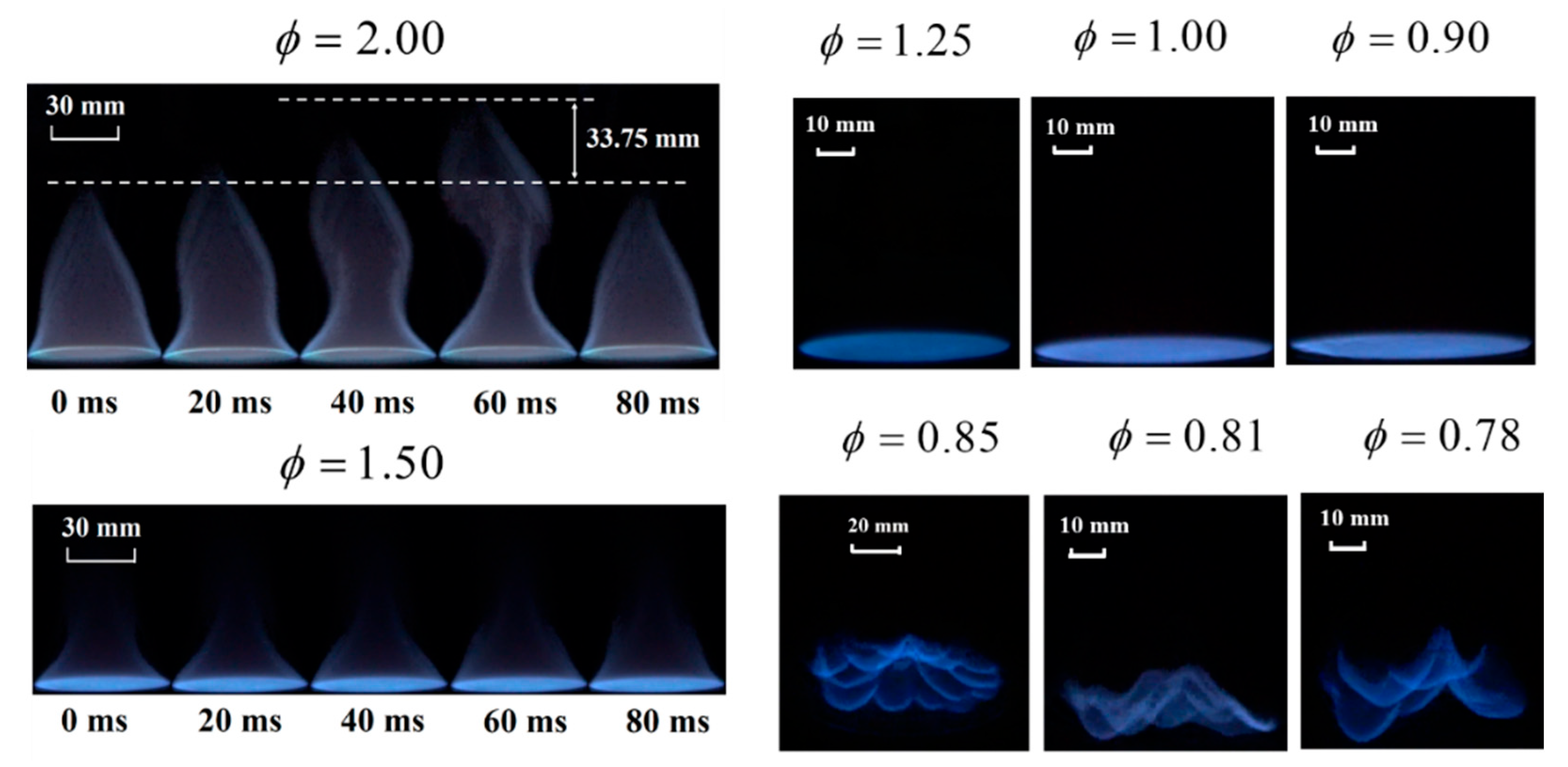
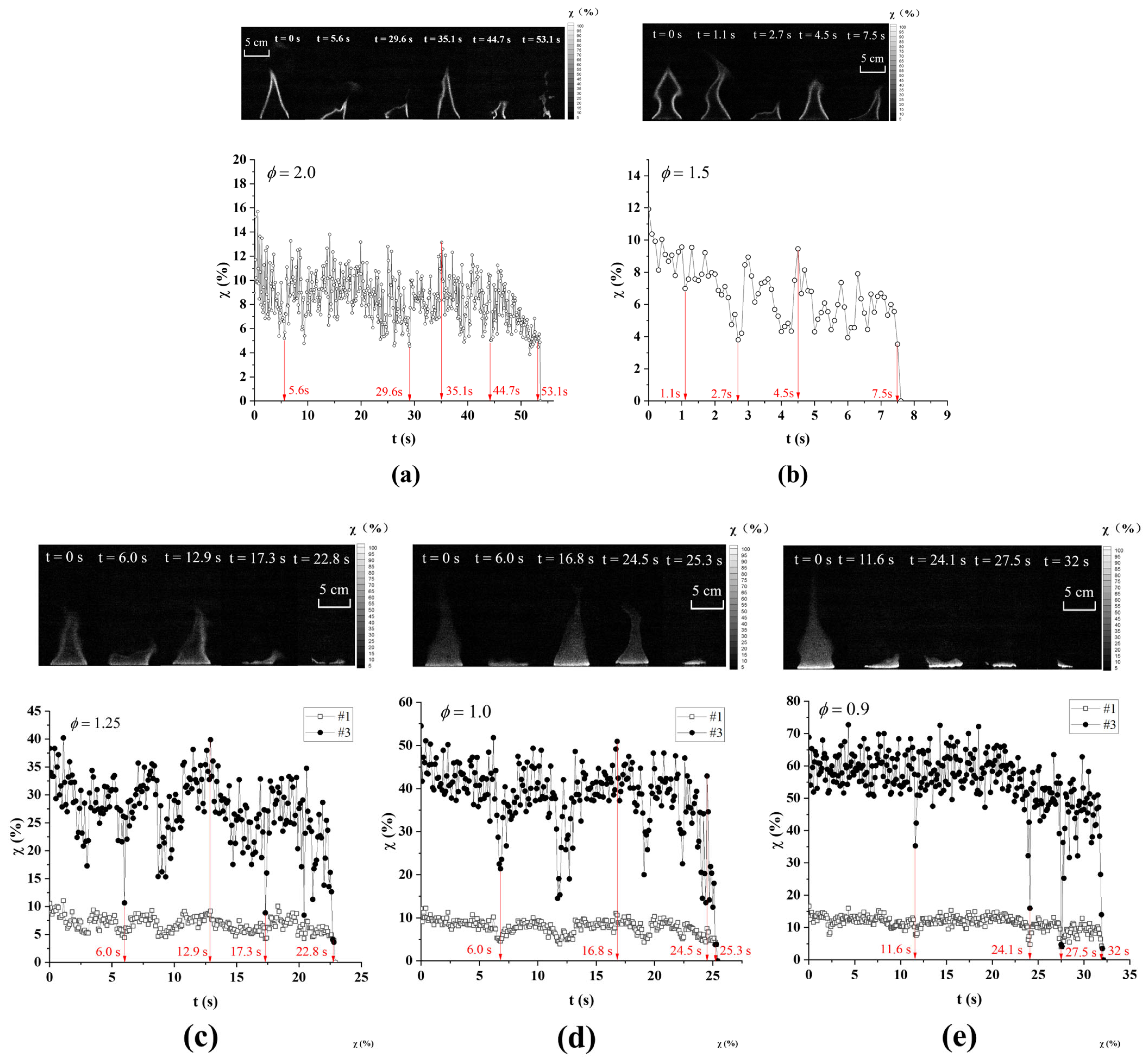
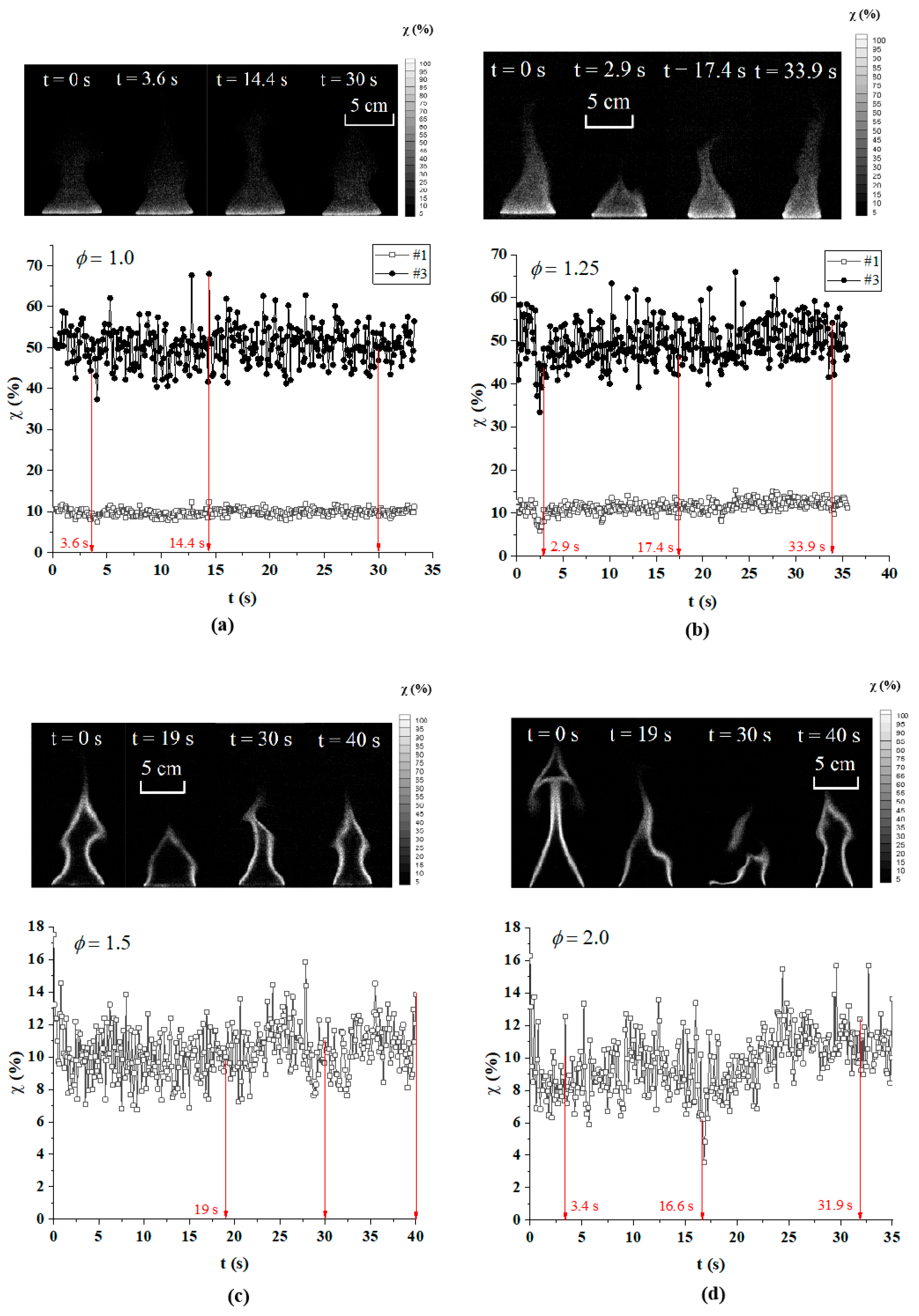
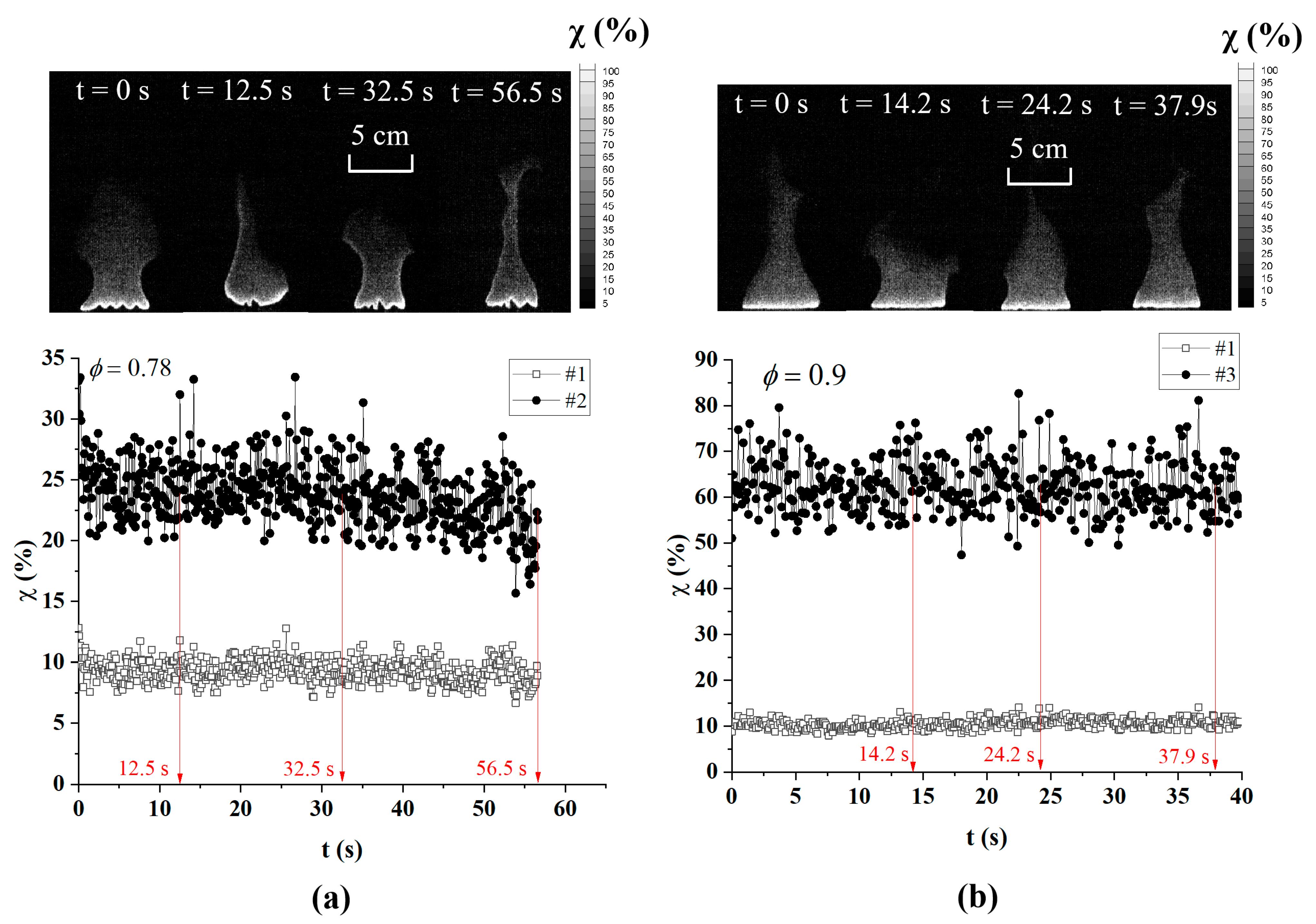
3.1. Combustion Characteristics Analysis
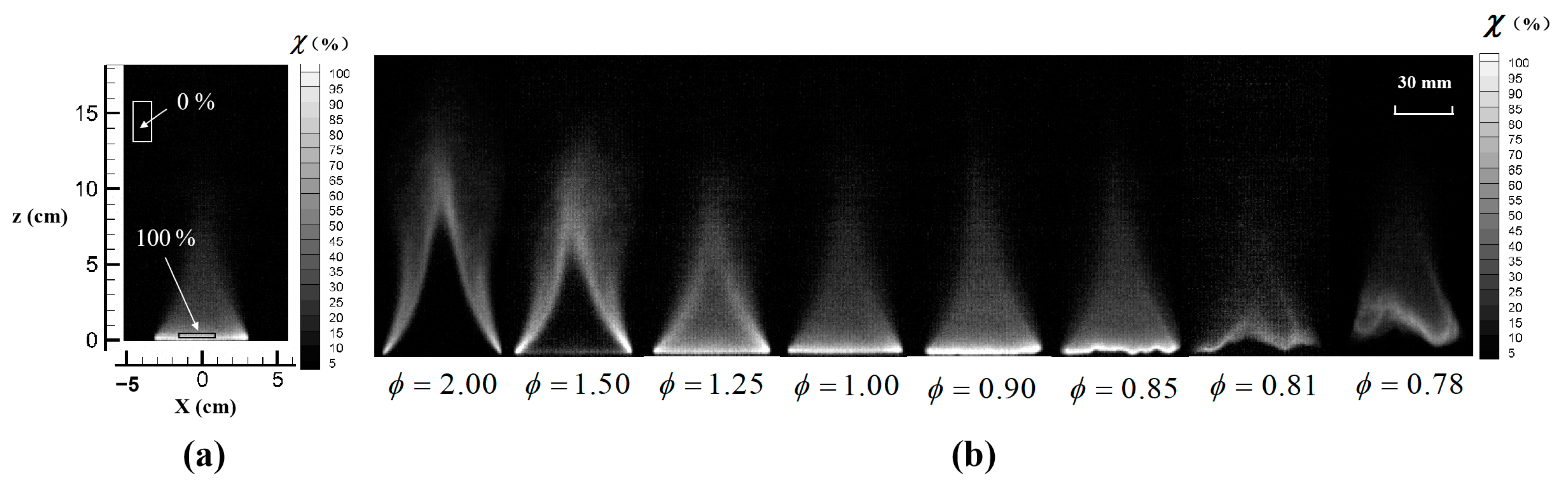
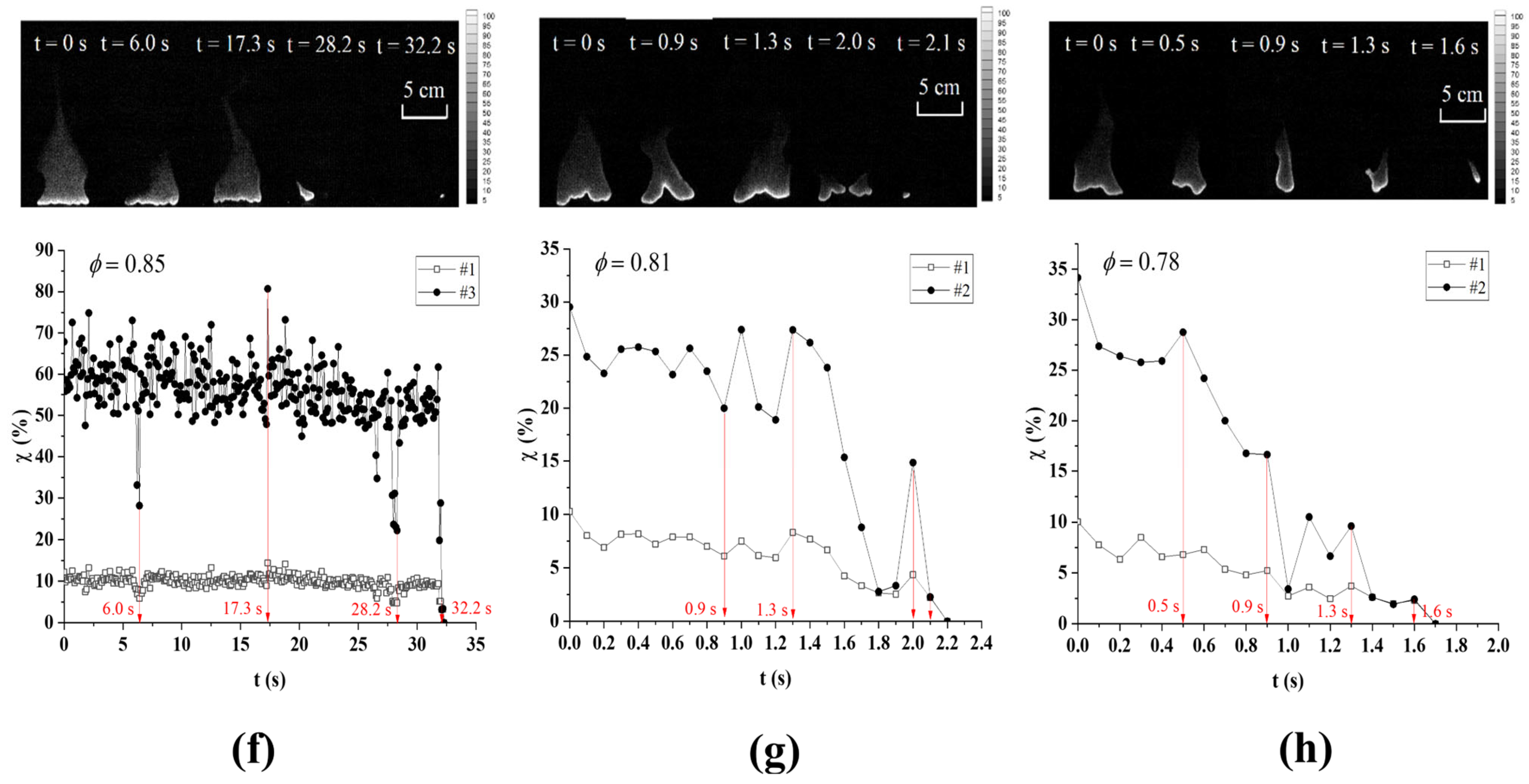
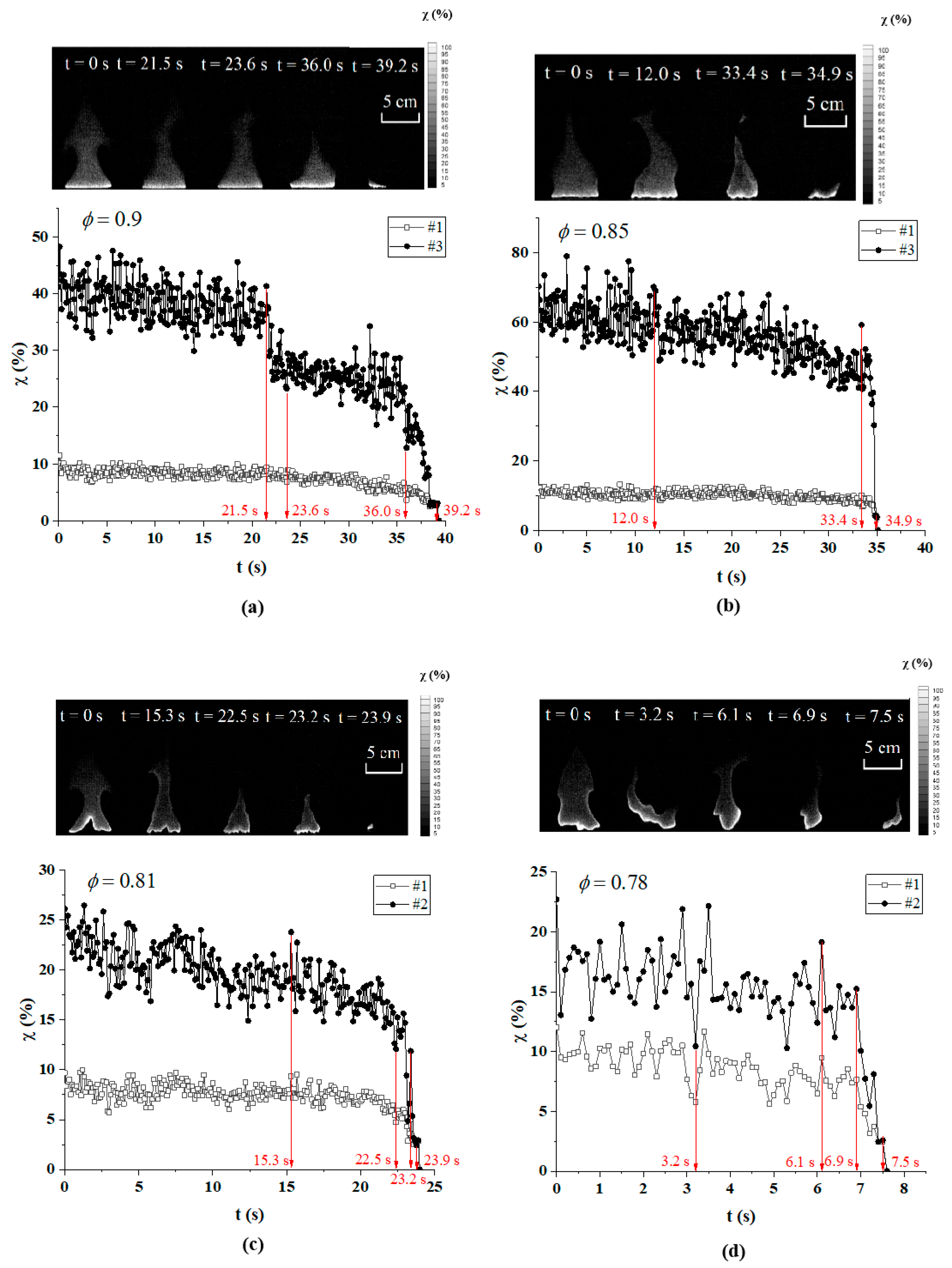
3.2. Flame Extinction Analysis Based on OH-PLIF Imaging
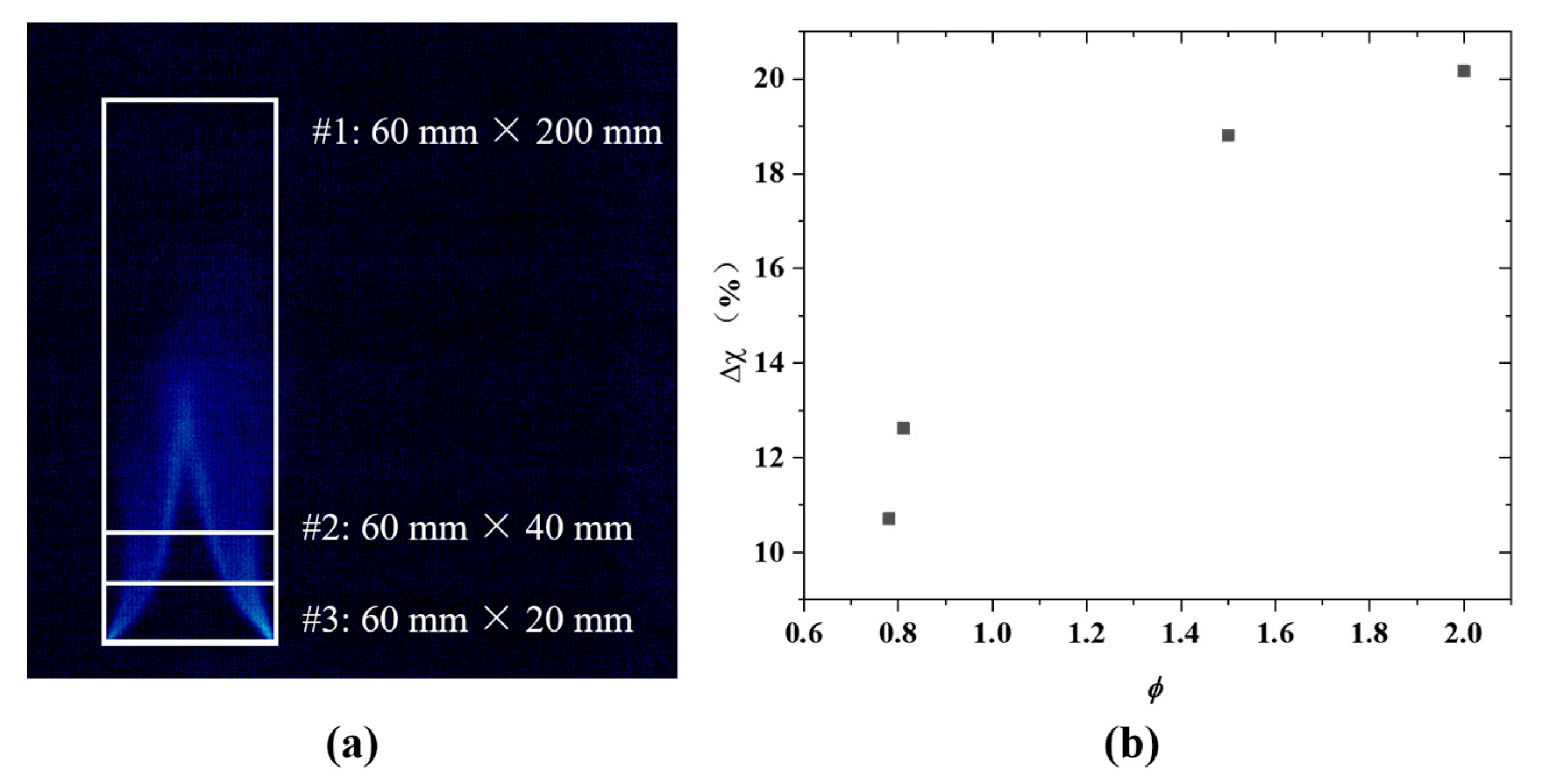
3.3. Critical Fire Extinguishing Characteristics Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Db | Diameter of obstacle (mm) |
| Dw | Spray max diameter at obstacle height (m) |
| Frf | Flame Froude number (-) |
| H | Height of the upper surface of the burner from the water mist nozzle (mm) |
| K | Water flow discharge coefficient of the nozzle |
| Pw | Water mist nozzle working pressure (MPa) |
| Air volumetric flow rate (L min−1) | |
| Methane volumetric flow rate (L min−1) | |
| Effective water mist flow rate (mL min−1) | |
| Reavg | Average Reynolds number (-) |
| v | The velocity of the methane–air mixture at the burner outlet (m/s) |
References
- Grant, G.; Brenton, J.; Drysdale, D. Fire suppresion by water mist. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2000, 26, 79–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Water Mist; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mawhinney, J.; Dlugogorski, B.; Kim, A. A Closer Look At The Fire Extinguishing Properties Of Water Mist. Fire Saf. J. 1994, 4, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Bu, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y. Numerical investigation on fire-extinguishing performance using pulsed water mist in open and confined spaces. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2019, 13, 100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.B.; Yong, J.J.; Yoon, M.O. Extinction limit of a pool fire with a water mist. Fire Saf. J. 1997, 28, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liao, G.; Qin, J.; Fan, W. Experimental Study on the Effectiveness of the Extinction of a Pool Fire with Water Mist. J. Fire Sci. 2002, 20, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Carpenter, D.; Kim, A.K. Characteristics of large cooking oil pool fires and their extinguishment by water mist. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2006, 19, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenft, A.; Collin, A.; Boulet, P.; Pianet, G.; Breton, A.; Muller, A. Experimental and numerical study of pool flame extinction using water mist. Fire Saf. J. 2014, 67, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Tao, C.; Zhang, H. Experimental study on fire smoke control using water mist curtain in channel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Bu, R.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Y. Full-scale experimental study on water mist flame extinction in a railway tunnel rescue station: Temperature distribution characteristics. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 146, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Kong, X.; Li, G. Cooling control of thermally-induced thermal runaway in 18,650 lithium ion battery with water mist. Energy Convers. Manage. 2019, 199, 111969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Tao, C.; Wang, X. Cooling control effect of water mist on thermal runaway propagation in lithium ion battery modules. Appl. Energy. 2020, 267, 115087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, P.; Cong, H.; Qin, W. Experimental investigation of methane/coal dust explosion under influence of obstacles and ultrafine water mist. J. Loss Prev. Process. Ind. 2017, 49, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Bi, M.; Huang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, W. Suppression mechanism of ultrafine water mist containing phosphorus compounds in methane/coal dust explosions. Energy 2022, 239, 121987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashwan, S.S.; Nemitallah, M.A.; Habib, M.A. Review on premixed combustion technology: Stability, emission control, applications, and numerical case study. Energy Fuels. 2016, 30, 9981–10014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasslberger, J.; Ozel-Erol, G.; Chakraborty, N.; Klein, M.; Cant, S. Physical effects of water droplets interacting with turbulent premixed flames: A Direct Numerical Simulation analysis. Combust. Flame. 2021, 229, 111404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.; Wang, D.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, Y. Inhibition effect and mechanism of ultra-fine water mist on CH4/air detonation: Quantitative research based on CFD technology. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 148, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downie, B.; Polymeropoulos, C.; Gogos, G. Interaction of a water mist with a buoyant methane diffusion flame. Fire Saf. J. 1995, 24, 359–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.; Li, C.; Kailasanath, K. Optimizing water-mist injection characteristics for suppression of coflow diffusion flames. Symp. Combust. 1998, 27, 2847–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentati, A.M.; Chelliah, H.K. Dynamics of Water Droplets in a Counterflow Field and their Effect on Flame Extinction. Combust. Flame. 1998, 115, 158–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentati, A.M.; Chelliah, H.K. Physical, thermal, and chemical effects of fine-water droplets in extinguishing counterflow diffusion flames. Combust. Inst. 1998, 27, 2839–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, R.; Naito, H.; Yoshida, A. Extinguishment of counterflow diffusion flame stabilized in turbulent airflow by polydisperse water mist. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2019, 37, 4239–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndubizu, C.C.; Ananth, R.; Tatem, P.A.; Motevalli, V. On water mist flame extinction mechanisms in a gaseous diffusion flame. Fire Saf. J. 1998, 31, 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Zhao, Z. Preliminary study on extinguishing shielded fire with water mist. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 141, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, J.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Zhao, Z.; Ni, X.; Wang, X. Laser-based measurement and numerical simulation of methane-air jet flame extinction with water mist. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 148, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuss, S.P.; Chen, E.F.; Yang, W.; Kee, R.J.; Williams, B.A. Inhibition of premixed methane air flames by water mist. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2002, 29, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.O. The Quenching of Laminar Methane-Air Flames by Water Mists. Combust. Flame. 2002, 130, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelliah, H.K.; Lazzarini, A.K.; Wanigarathne, P.C.; Linteris, G.T. Inhibition of premixed and non-premixed flames with fine droplets of water and solutions. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2002, 29, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, A.; Udagawa, T.; Momomoto, Y.; Naito, H.; Saso, Y. Experimental study of suppressing effect of fine water droplets on propane/air premixed flames stabilized in the stagnation flowfield. Fire Saf. J. 2013, 58, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, A.; Okawa, T.; Ebina, W.; Naito, H. Experimental and numerical investigation of flame speed retardation by water mist. Combust. Flame. 2015, 162, 1772–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Chong, C.T.; Tanno, K.; McGrath, D.; Zheng, Y.; Hochgreb, S. Measurement of the effect of water droplets on strained laminar flames using two-phase PIV. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2021, 38, 3183–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Kee, R.J. The effect of monodispersed water mists on the structure, burning velocity, and extinction behavior of freely propagating, stoichiometric, premixed, methane-air flames. Combust. Flame. 2002, 130, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, A.U.; Abbud-Madrid, A.; Delplanque, J.-P.; Kee, R.J. The effect of mono-dispersed water mist on the suppression of laminar premixed hydrogen-, methane-, and propane-air flames. Combust. Flame. 2006, 144, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaVision GmbH. Laser Imaging for Combustion Species, FlameMaster Tunable LIF; LaVision GmbH: Göttingen, Germany, 2023; Available online: https://www.lavision.de/en/applications/combustion/flamemaster-tunable-lif/index.php (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Edmondson, H.; Heap, M.P.; Pritchard, R. Ambient atmosphere effects in flat-flame measurements of burning velocity. Combust. Flame. 1970, 14, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, R.; Janisch, G. Measurements of burning velocity in a flat flame front. Combust. Flame. 1972, 19, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosschaart, K.J.; de Goey, L.P.H. The laminar burning velocity of flames propagating in mixtures of hydrocarbons and air measured with the heat flux method. Combust. Flame. 2004, 136, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavision GmbH. Tunable LIF, Product-Manual for DaVis 10.0; Lavision GmbH: Gottingen, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- GRI-Mech, Version 3.0. 2002. Available online: http://combustion.berkeley.edu/gri-mech/new21/version21/text21.html (accessed on 18 September 2025).

| Case No. | H (mm) | Results * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.25 | 0.78/0.81/0.85/0.9/1.0/1.25/1.5/2.0 | 650 | × |
| B | 0.25 | 1.0/1.25/1.5/2.0 | 500 | × |
| 0.78/0.81/0.85/0.9 | √ | |||
| C | 0.30 | 0.78/0.81/0.85/0.9/1.0/1.25/1.5/2.0 | 500 | √ |
| 2 | 24.40 | 0.78 | 1.2484 | 0.1556 | 1.6627 | 701 |
| 2 | 23.40 | 0.81 | 1.2467 | 0.1497 | 1.6606 | 674 |
| 2 | 22.40 | 0.85 | 1.2449 | 0.1438 | 1.6584 | 648 |
| 2 | 21.16 | 0.90 | 1.2423 | 0.1365 | 1.6553 | 615 |
| 2 | 19.04 | 1.00 | 1.2374 | 0.1240 | 1.6493 | 558 |
| 2 | 15.23 | 1.25 | 1.2253 | 0.1016 | 1.6348 | 457 |
| 2 | 12.70 | 1.50 | 1.2137 | 0.0866 | 1.6210 | 389 |
| 2 | 9.52 | 2.00 | 1.1922 | 0.0679 | 1.5951 | 305 |
| Pw (MPa) | H (mm) | (mL min−1) | Results * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.78~2.0 | 650 | 8.44 | × |
| 0.25 | 1.0~2.0 | 500 | 8.83 | × |
| 0.78~0.9 | √ | |||
| 0.3 | 0.78~2.0 | 500 | 9.55 | √ |
| 0.5 | 650 | 11.40 | √ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Pan, C.; Li, G.; Wu, Z. Fire Extinction Analysis and OH-PLIF Visualization of the Methane–Air Premixed Laminar Flame Interacting with the Downward Water Mist. Fire 2025, 8, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8100375
Liu Y, Zhou Y, Zhong Y, Pan C, Li G, Wu Z. Fire Extinction Analysis and OH-PLIF Visualization of the Methane–Air Premixed Laminar Flame Interacting with the Downward Water Mist. Fire. 2025; 8(10):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8100375
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yangpeng, Yufei Zhou, Yingxia Zhong, Chuanyu Pan, Guochun Li, and Zepeng Wu. 2025. "Fire Extinction Analysis and OH-PLIF Visualization of the Methane–Air Premixed Laminar Flame Interacting with the Downward Water Mist" Fire 8, no. 10: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8100375
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhou, Y., Zhong, Y., Pan, C., Li, G., & Wu, Z. (2025). Fire Extinction Analysis and OH-PLIF Visualization of the Methane–Air Premixed Laminar Flame Interacting with the Downward Water Mist. Fire, 8(10), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8100375






