Influence of Terrain Slope on Sub-Surface Fire Behavior in Boreal Forests of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sampling and Processing of Humus
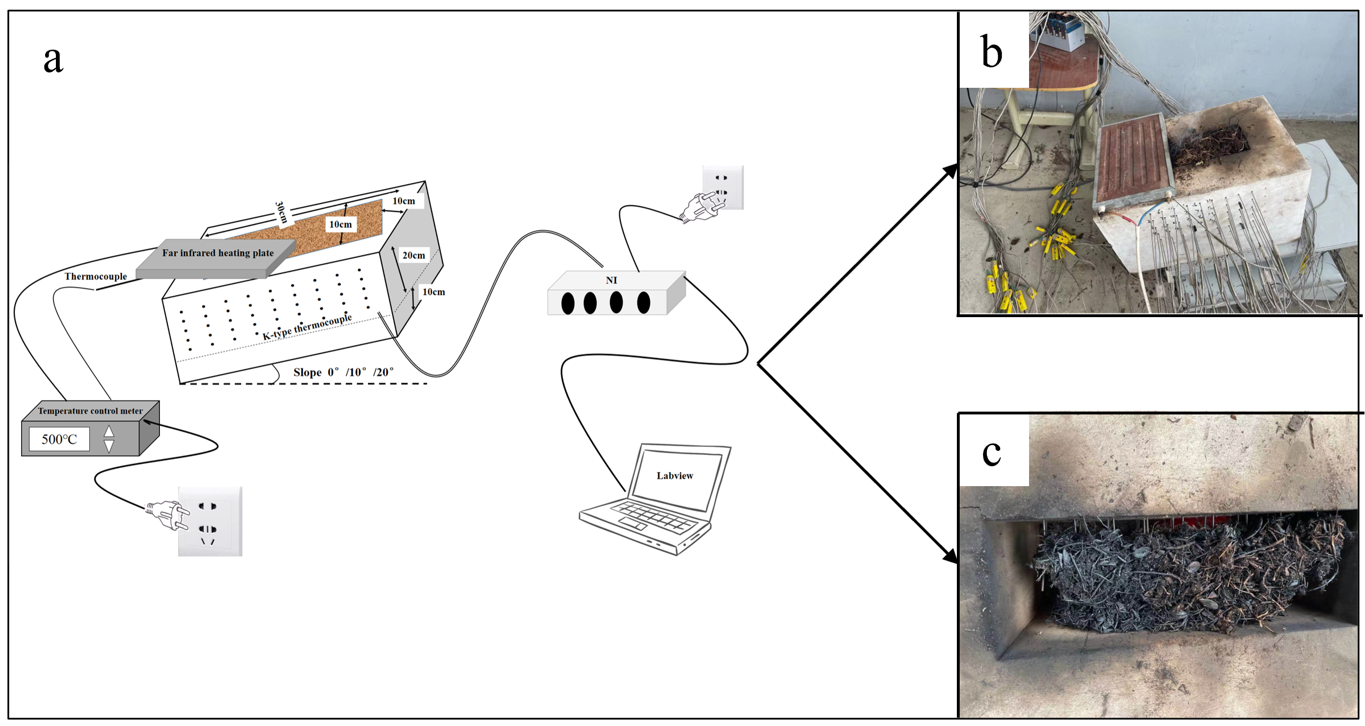
2.3. Simulating Smoldering Experiment
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
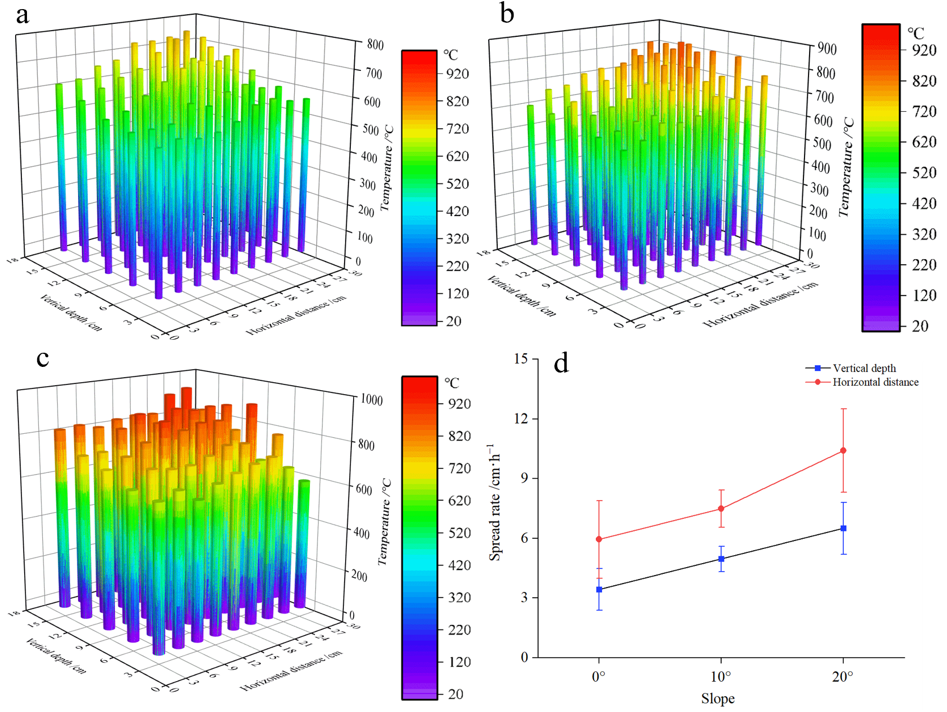
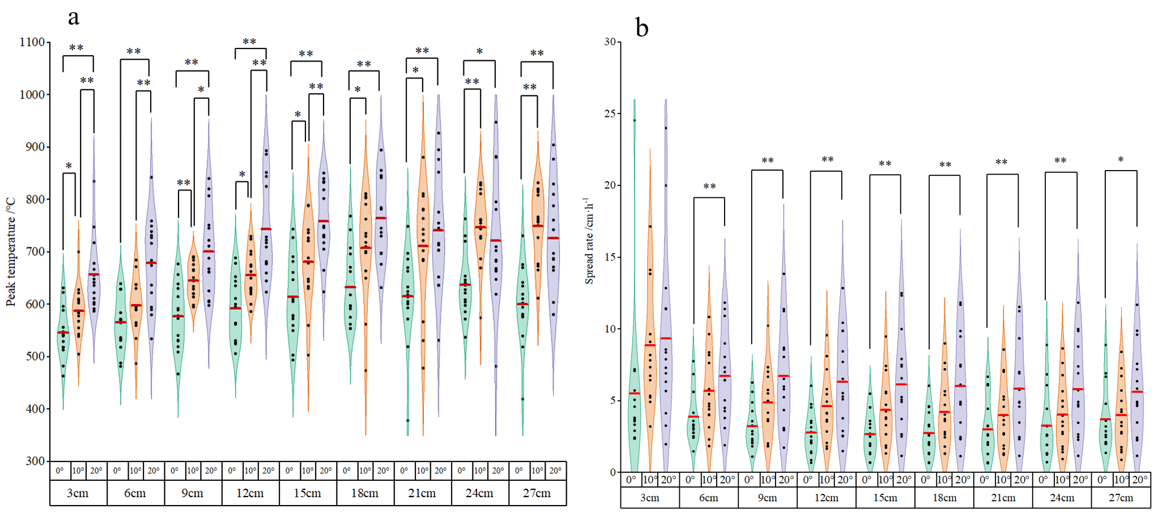
3.1. Characteristics of Sub-Surface Fire Smoldering under Different Slopes
3.2. Effect of Slope on Sub-Surface Fire Smoldering
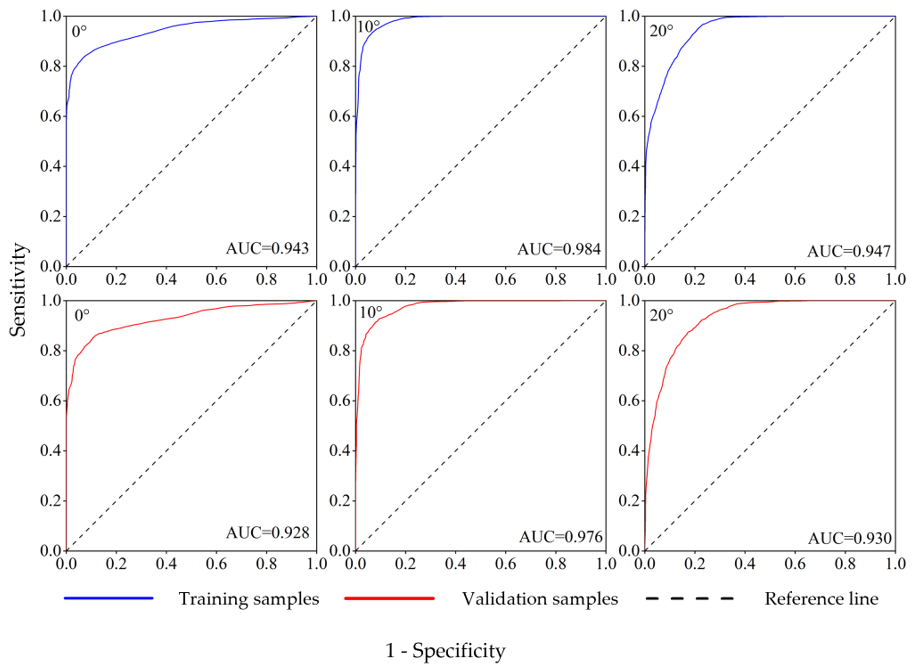
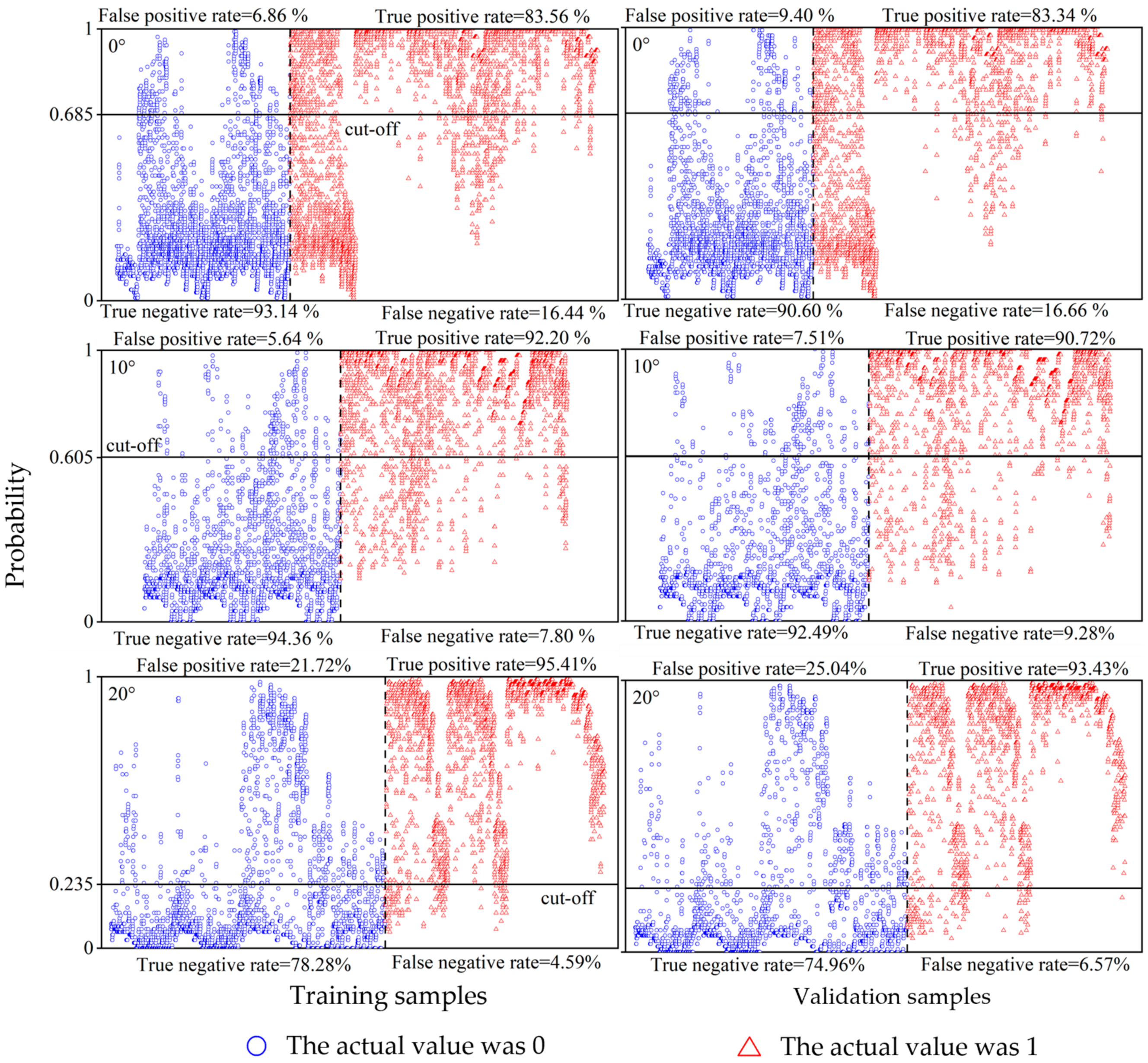
3.3. The Occurrence Probability Prediction of Sub-Surface Fire Smoldering at Different Slopes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dye, A.W.; Gao, P.; Kim, J.B.; Lei, T.; Riley, K.L.; Yocom, L. High-resolution wildfire simulations reveal complexity of climate change impacts on projected burn probability for Southern California. Fire Ecol. 2023, 19, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Restuccia, F.; Gramola, M.; Rein, G. Experimental study of the formation and collapse of an overhang in the lateral spread of smouldering peat fires. Combust. Flame 2016, 168, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickler, R.A.; Welch, D.P.; Bailey, A.D. Carbon emissions during wildland fire on a North American temperate peatland. Fire Ecol. 2017, 13, 34–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.C.; Kobziar, L.N. Smoldering combustion and ground fires: Ecological effects and multi-scale significance. Fire Ecol. 2013, 9, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turetsky, M.R.; Benscoter, B.; Page, S.; Rein, G.; van der Werf, G.R.; Watts, A. Global vulnerability of peatlands to fire and carbon loss. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauw, L.G.; van Logtestijn, R.S.P.; Broekman, R.; Aerts, R.; Cornelissen, J.H.C. Tree species identity in high-latitude forests determines fire spread through fuel ladders from branches to soil and vice versa. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 400, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evtyugina, M.; Calvo, A.I.; Nunes, T.; Alves, C.; Fernandes, A.P.; Tarelho, L.; Vicente, A.; Pio, C. VOC emissions of smouldering combustion from Mediterranean wildfires in central Portugal. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 64, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.K.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y. US wildfire potential: A historical view and future projection using high-resolution climate data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 16, 034060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuklina, V.; Sizov, O.; Rasputina, E.; Bilichenko, I.; Krasnoshtanova, N.; Bogdanov, V.; Petrov, A.N. Fires on ice: Emerging permafrost peatlands fire regimes in Russia’s subarctic taiga. Land 2022, 11, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, R.; Wright, I.A.; Reynolds, J.K. Loss of soil carbon in a world heritage peatland following a bushfire. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2023, 32, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.L.; Andersen, R.; Moore, P.A.; Davidson, S.J.; Granath, G.; Waddington, J.M. Wildfire and degradation accelerate northern peatland carbon release. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2023, 13, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xifré-Salvadó, M.À.; Prat-Guitart, N.; Francos, M.; Úbeda, X.; Castellnou, M. Smouldering combustion dynamics of a soil from a pinus halepensis mill. Forest. A case study of the rocallaura fires in northeastern Spain. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcotte, A.L.; Limpens, J.; Stoof, C.R.; Stoorvogel, J.J. Can ash from smoldering fires increase peatland soil pH? Int. J. Wildland Fire 2022, 31, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellasala, D.A.; Williams, J.E.; Williams, C.D.; Franklin, J.F. Beyond smoke and mirrors: A synthesis of fire policy and science. Conserv. Biol. 2004, 18, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadden, R.M.; Rein, G.; Belcher, C.M. Study of the competing chemical reactions in the initiation and spread of smouldering combustion in peat. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2013, 34, 2547–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Rein, G.; Liu, N. Numerical investigation of downward smoldering combustion in an organic soil column. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 84, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Rein, G. Upward-and-downward spread of smoldering peat fire. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2019, 37, 4025–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyman, P.; Metzen, D.; Noske, P.J.; Lane, P.N.J.; Sheridan, G.J. Quantifying the effects of topographic aspect on water content and temperature in fine surface fuel. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2015, 24, 1129–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdić, I.; Safner, T.; Rubinić, V.; Rutić, F.; Husnjak, S.; Filipović, V. Effect of slope position on soil properties and soil moisture regime of Stagnosol in the vineyard. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2022, 70, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, M.I.; Ferragut, L. On a wildland fire model with radiation. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2002, 54, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandini, F.; Silvani, X.; Dupuy, J.-L.; Susset, A. Fire spread across a sloping fuel bed: Flame dynamics and heat transfers. Combust. Flame 2018, 190, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossa, C.G.; Davim, D.A.; Viegas, D.X. Behaviour of slope and wind backing fires. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2015, 24, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouali, A.; Viegas, D.X.; Raposo, J.R. Analysis of the wind flow and fire spread dynamics over a sloped–ridgeline hill. Combust. Flame 2021, 234, 111724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.; Ribeiro, C.; Raposo, J.; Viegas, D.X.; André, J. Effect of canyons on a fire propagating laterally over slopes. Front. Mech. Eng. 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Xiang, D.; Kong, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Upslope fire spread and heat transfer mechanism over a pine needle fuel bed with different slopes and winds. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 229, 120605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, M.A.; Christensen, E.G.; Yang, J.; Rein, G. Review of the transition from smouldering to flaming combustion in wildfires. Front. Mech. Eng. 2019, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, J.; Hungerford, R.; Ryan, K. Factors affecting sustained smouldering in organic soils from pocosin and pond pine woodland wetlands. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2007, 16, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, J.J.; Curcio, G.M. Estimated smoldering probability: A new tool for predicting ground fire in the organic soils on the North Carolina Coastal Plain. Fire Manag. Today 2011, 4, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Schulte, M.L.; McLaughlin, D.L.; Wurster, F.C.; Varner, J.M.; Stewart, R.D.; Aust, W.M.; Jones, C.N.; Gile, B. Short-and long-term hydrologic controls on smouldering fire in wetland soils. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2019, 28, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lai, C.; Chen, X.; Yang, B.; Zhao, S.; Bai, X. Flood hazard risk assessment model based on random forest. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 1130–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolford, D.G.; Martell, D.L.; McFayden, C.B.; Evens, J.; Stacey, A.; Wotton, B.M.; Boychuk, D. The development and implementation of a human-caused wildland fire occurrence prediction system for the province of Ontario, Canada. Can. J. For. Res. 2021, 51, 303–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Li, Y.; Feng, Z.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H. Forest fire occurrence prediction in China based on machine learning methods. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Huang, Z. Analysis of forest fire dynamics, distribution and main drivers in the Atlantic Forest. Sustainability 2022, 14, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Ye, J. Seasonal differences in the spatial patterns of wildfire drivers and susceptibility in the southwest mountains of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuyen, T.T.; Jaafari, A.; Yen, H.P.H.; Nguyen-Thoi, T.; Phong, T.V.; Nguyen, H.D.; Le, H.V.; Phuong, T.T.M.; Nguyen, S.H.; Prakash, I.; et al. Mapping forest fire susceptibility using spatially explicit ensemble models based on the locally weighted learning algorithm. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 63, 101292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iban, M.C.; Sekertekin, A. Machine learning based wildfire susceptibility mapping using remotely sensed fire data and GIS: A case study of Adana and Mersin provinces, Turkey. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 69, 101647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trucchia, A.; Meschi, G.; Fiorucci, P.; Gollini, A.; Negro, D. Defining wildfire susceptibility maps in Italy for understanding seasonal wildfire regimes at the national level. Fire 2022, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radandima, G.U.E.R. I Identification of Land Fire Risk Areas with Random Forest Using Landsat Image Data 8 OLI. Int. J. Nat. Sci. Eng. 2022, 6, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Tan, S.; Yang, Z.; Wu, X. Forest Fire Smoke Detection Research Based on the Random Forest Algorithm and Sub-Pixel Mapping Method. Forests 2023, 14, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, V.E.; Cho, J.; Subramanian, M.; Naren, O.S. Forest fire and smoke detection using deep learning-based learning without forgetting. Fire Ecol. 2023, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, G.M.; Gray, A.; Rein, G.; Legg, C.J. Peat consumption and carbon loss due to smouldering wildfire in a temperate peatland. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 308, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X. How to build a firebreak to stop smouldering peat fire: Insights from a laboratory-scale study. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2021, 30, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, G.; Cleaver, N.; Ashton, C.; Pironi, P.; Torero, J.L. The severity of smouldering peat fires and damage to the forest soil. Catena 2008, 74, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, P.; Chen, H.; Liu, N.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, L. Lightning-induced smoldering ignition of peat: Simulation experiments by an electric arc with long continuing current. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2023, 39, 4185–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Trancoso, R.; Ma, Q.; Ciais, P.; Gouvêa, L.P.; Yue, C.; Assis, J.; Blanco, J.A. Carbon density in boreal forests responds non-linearly to temperature: An example from the Greater Khingan Mountains, northeast China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 338, 109519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Huang, X. Quenching of smoldering: Effect of wall cooling on extinction. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2021, 38, 5015–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancellieri, D.; Leroy-Cancellieri, V.; Leoni, E.; Simeoni, A.; Kuzin, A.Y.; Filkov, A.I.; Rein, G. Kinetic investigation on the smouldering combustion of boreal peat. Fuel 2012, 93, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Rein, G. Smouldering combustion of peat in wildfires: Inverse modelling of the drying and the thermal and oxidative decomposition kinetics. Combust. Flame 2014, 161, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z. A diffusion-flame analog of forward smolder waves:(I) 1-D steady structures. Combust. Flame 2018, 196, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat-Guitart, N.; Rein, G.; Hadden, R.M.; Belcher, C.M.; Yearsley, J.M. Effects of spatial heterogeneity in moisture content on the horizontal spread of peat fires. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 1422–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Cheung, Y.K.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, X. Can rain suppress smoldering peat fire? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlemiller, T.J. Modeling of smoldering combustion propagation. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1985, 11, 277–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.L.B.; Applegate, G.B.; Thomas, A.; Ryan, K.C.; Saharjo, B.H.; Cochrane, M.A. A field study of tropical peat fire behaviour and associated carbon emissions. Fire 2022, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.; Viegas, D.X.; Raposo, J.; Reis, L.; Sharples, J. Slope effect on junction fire with two non-symmetric fire fronts. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2023, 32, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimont, F.; Dupuy, J.-L.; Linn, R. Coupled slope and wind effects on fire spread with influences of fire size: A numerical study using FIRETEC. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2012, 21, 828–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Xie, X.; Zhang, L.; Yao, B.; Zhu, J.; Shan, Y. Effect of slope on spread of a linear flame front over a pine needle fuel bed: Experiments and modelling. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2014, 23, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Wang, G.; Su, Z.; Liang, H.; Wenhui, W.; Lin, F.; Liu, A. What drives forest fire in Fujian, China? Evidence from logistic regression and Random Forests. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2016, 25, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanović, S.; Marković, N.; Pamučar, D.; Gigovic, L.; Kostic, P.; Milanović, S.D. Forest Fire Probability Mapping in Eastern Serbia: Logistic Regression versus Random Forest Method. Forests 2020, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, R.; Azarnoush, M.R.; Kialashki, A.; Kazemzadeh, F. GIS-based forest fire susceptibility assessment by random forest, artificial neural network and logistic regression methods. J. Trop. For. Sci. 2021, 33, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigovic, L.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Drobnjak, S.; Bai, S. Testing a New Ensemble Model Based on SVM and Random Forest in Forest Fire Susceptibility Assessment and Its Mapping in Serbia’s Tara National Park. Forests 2019, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, M.; D’Este, M.; Ascoli, D.; Giannico, V.; Spano, G.; Ganga, A.; Colangelo, G.; Lafortezza, R.; Sanesi, G. Estimating the probability of wildfire occurrence in Mediterranean landscapes using Artificial Neural Networks. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2020, 85, 106474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Factors | Peak Temperature | Spread Rate in Vertical Direction | Spread Rate in Horizontal Direction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation Coefficient | Sig. | Correlation Coefficient | Sig. | Correlation Coefficient | Sig. | |
| Slope | 0.511 ** | <0.01 | 0.374 ** | <0.01 | 0.351 ** | <0.01 |
| Vertical depth | 0.444 ** | <0.01 | 0.497 ** | <0.01 | −0.153 ** | <0.01 |
| Horizontal distance | 0.339 ** | <0.01 | −0.239 ** | <0.01 | 0.649 ** | <0.01 |
| Parameter | Independent Variable | Standard Error | Sig. | p-Value | Equation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak temperature | Constant | 10.554 | <0.01 | <0.01 | y = 445.87 + 6.17x1 + 10.31x2 + 4.31x3 |
| Slope | 0.394 | <0.01 | |||
| Vertical depth | 0.759 | <0.01 | |||
| Horizontal distance | 0.416 | <0.01 | |||
| Spread rate in the vertical direction | Constant | 0.412 | 0.01 | <0.01 | y = 1.423 + 0.154x1 + 0.394x2 − 0.104x3 |
| Slope | 0.015 | <0.01 | |||
| Vertical depth | 0.030 | <0.01 | |||
| Horizontal distance | 0.016 | <0.01 | |||
| Spread rate in Horizontal distance | Constant | 0.558 | <0.01 | <0.01 | y = 0.882 + 0.223x1 − 0.187x2 + 0.434x3 |
| Slope | 0.021 | <0.01 | |||
| Vertical depth | 0.040 | <0.01 | |||
| Horizontal distance | 0.022 | <0.01 |
| Independent Variable | 0° | 10° | 20° |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal distance | 32.91% | 38.46% | 53.80% |
| Vertical depth | 32.12% | 19.91% | 14.02% |
| Combustion time | 68.38% | 51.98% | 50.64% |
| Slope | Smoldering/No Smoldering | Correct Forecast | Sample Size | Total Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0° | No smoldering | 3336 | 3682 | 85.95% |
| Smoldering | 5461 | 6553 | ||
| 10° | No smoldering | 2806 | 3034 | 91.54% |
| Smoldering | 3187 | 3513 | ||
| 20° | No smoldering | 2093 | 2792 | 83.17% |
| Smoldering | 2089 | 2236 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shan, Y.; Gao, B.; Yin, S.; Shao, D.; Cao, L.; Yu, B.; Cui, C.; Wang, M. Influence of Terrain Slope on Sub-Surface Fire Behavior in Boreal Forests of China. Fire 2024, 7, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7020055
Shan Y, Gao B, Yin S, Shao D, Cao L, Yu B, Cui C, Wang M. Influence of Terrain Slope on Sub-Surface Fire Behavior in Boreal Forests of China. Fire. 2024; 7(2):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7020055
Chicago/Turabian StyleShan, Yanlong, Bo Gao, Sainan Yin, Diankun Shao, Lili Cao, Bo Yu, Chenxi Cui, and Mingyu Wang. 2024. "Influence of Terrain Slope on Sub-Surface Fire Behavior in Boreal Forests of China" Fire 7, no. 2: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7020055
APA StyleShan, Y., Gao, B., Yin, S., Shao, D., Cao, L., Yu, B., Cui, C., & Wang, M. (2024). Influence of Terrain Slope on Sub-Surface Fire Behavior in Boreal Forests of China. Fire, 7(2), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7020055





