CNTCB-YOLOv7: An Effective Forest Fire Detection Model Based on ConvNeXtV2 and CBAM
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hyperparameter Settings and Dataset
2.1.1. Hyperparameter Settings
2.1.2. Dataset
2.1.3. Model Performance Evaluation Index
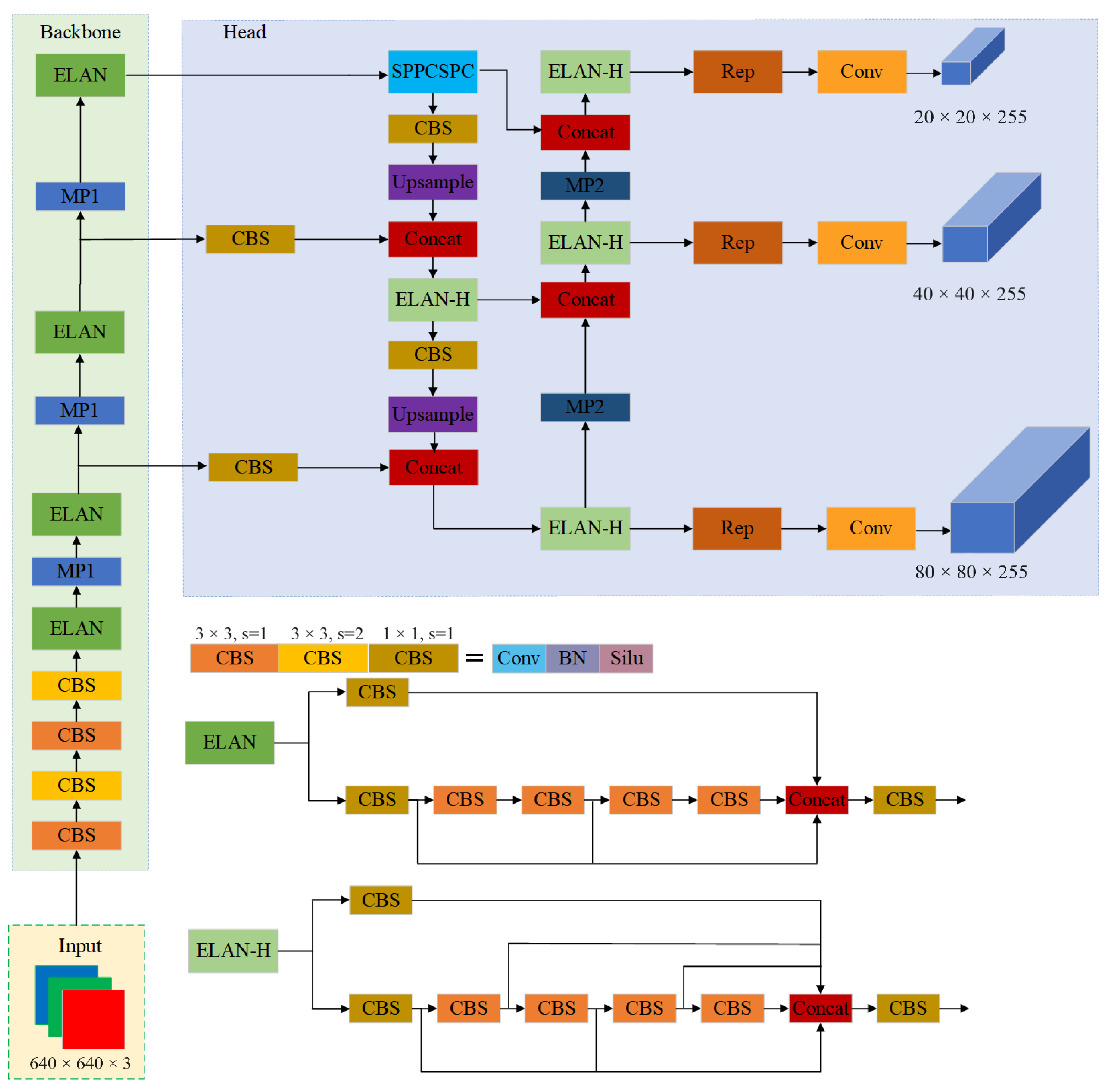
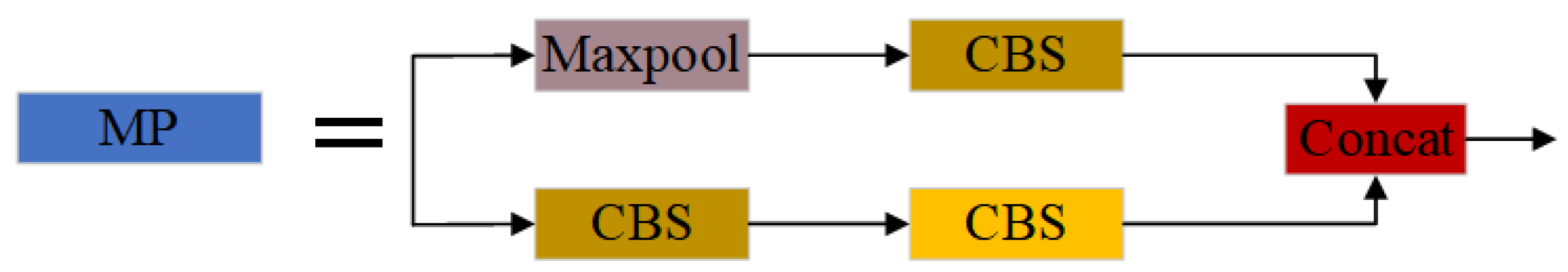
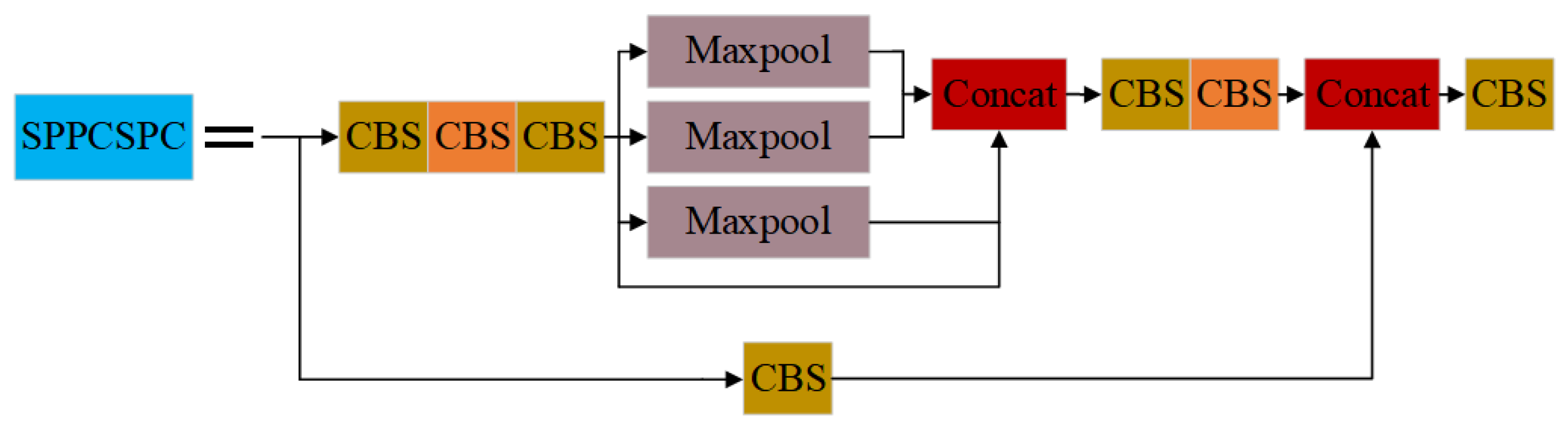
2.2. YOLOv7 Algorithm Structure
2.3. Improving the Network Used by the YOLO7 Algorithm
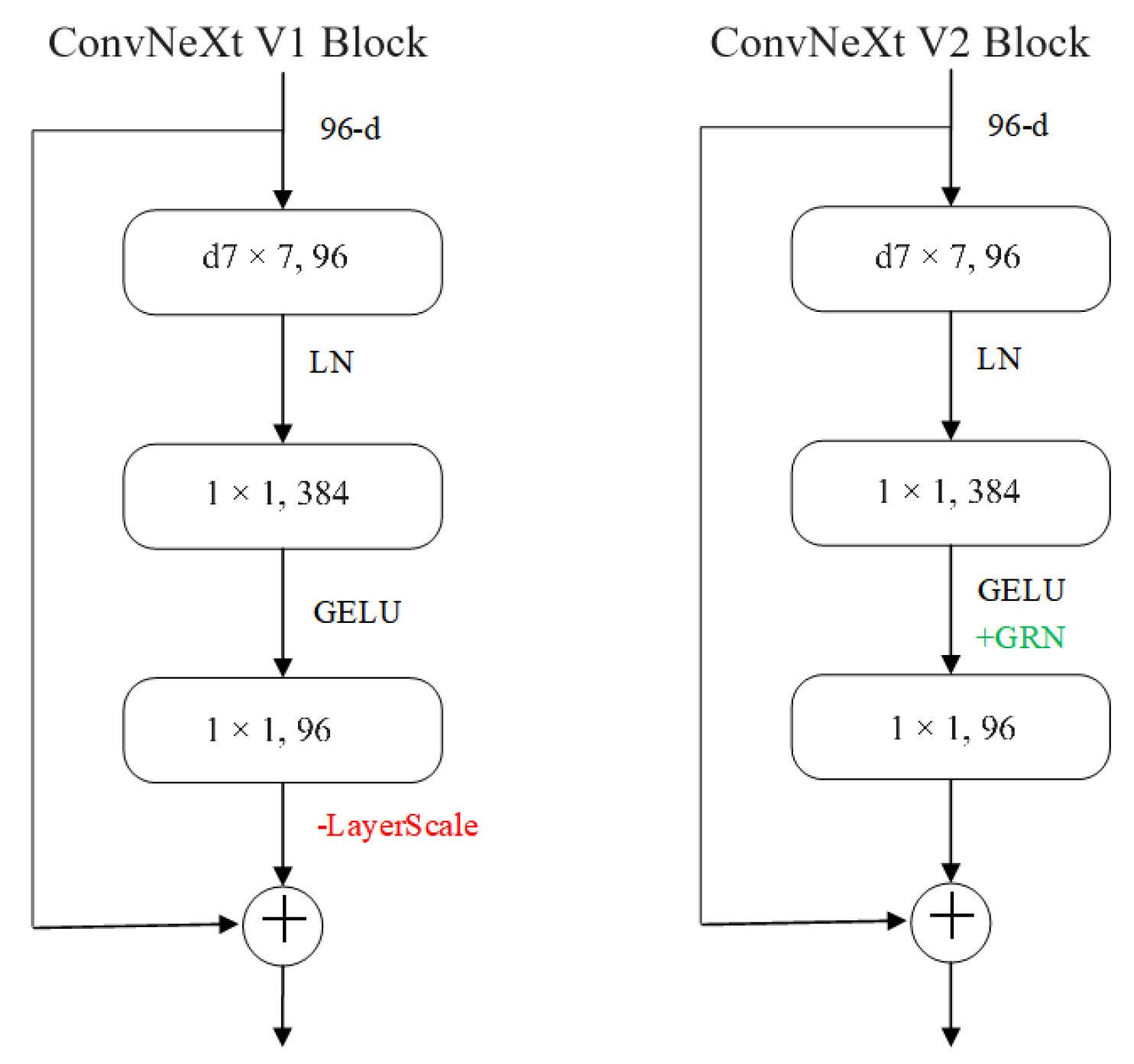
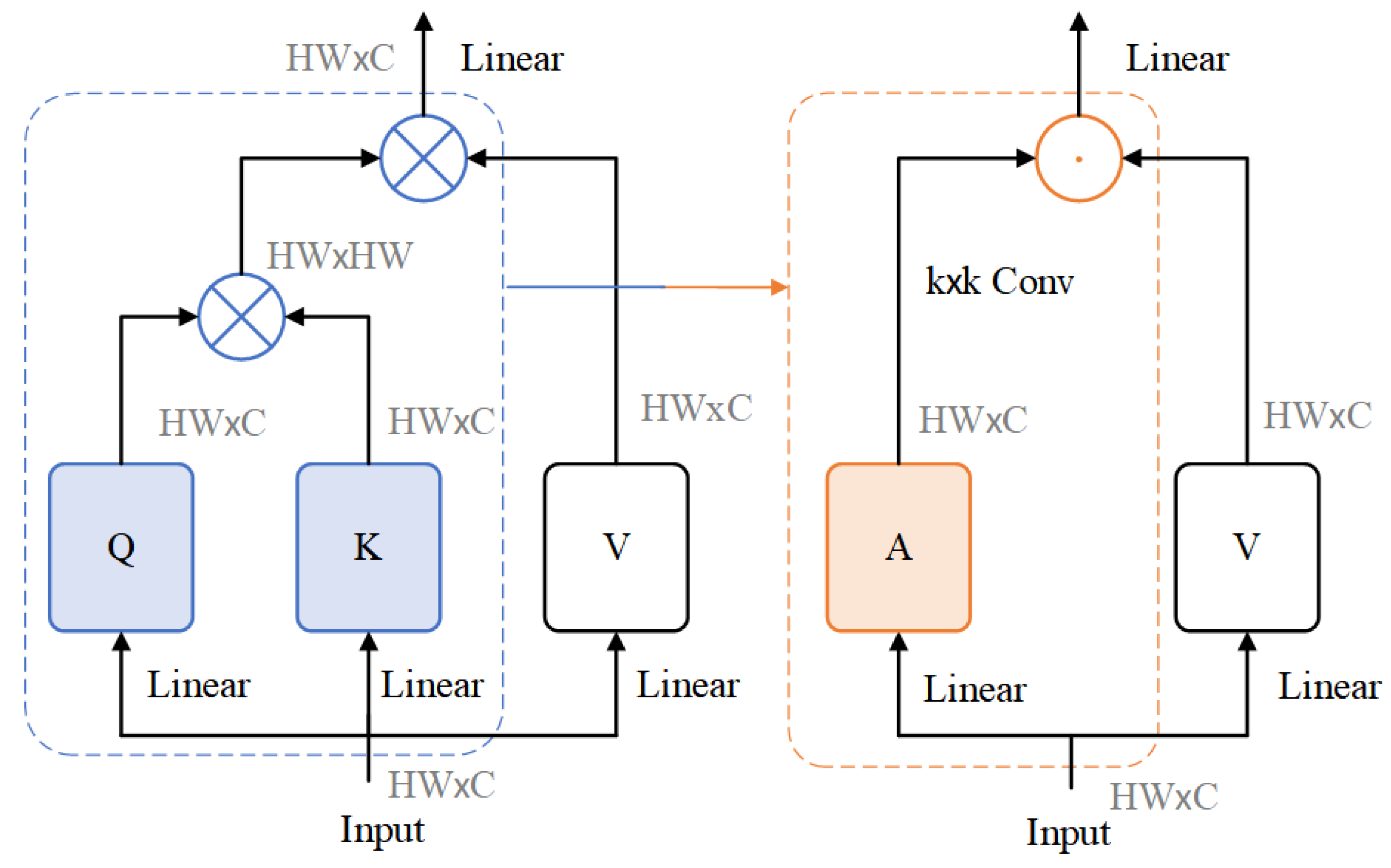
2.3.1. ConvNeXtV2
2.3.2. Conv2Former
2.4. Improved Strategy for YOLOv7
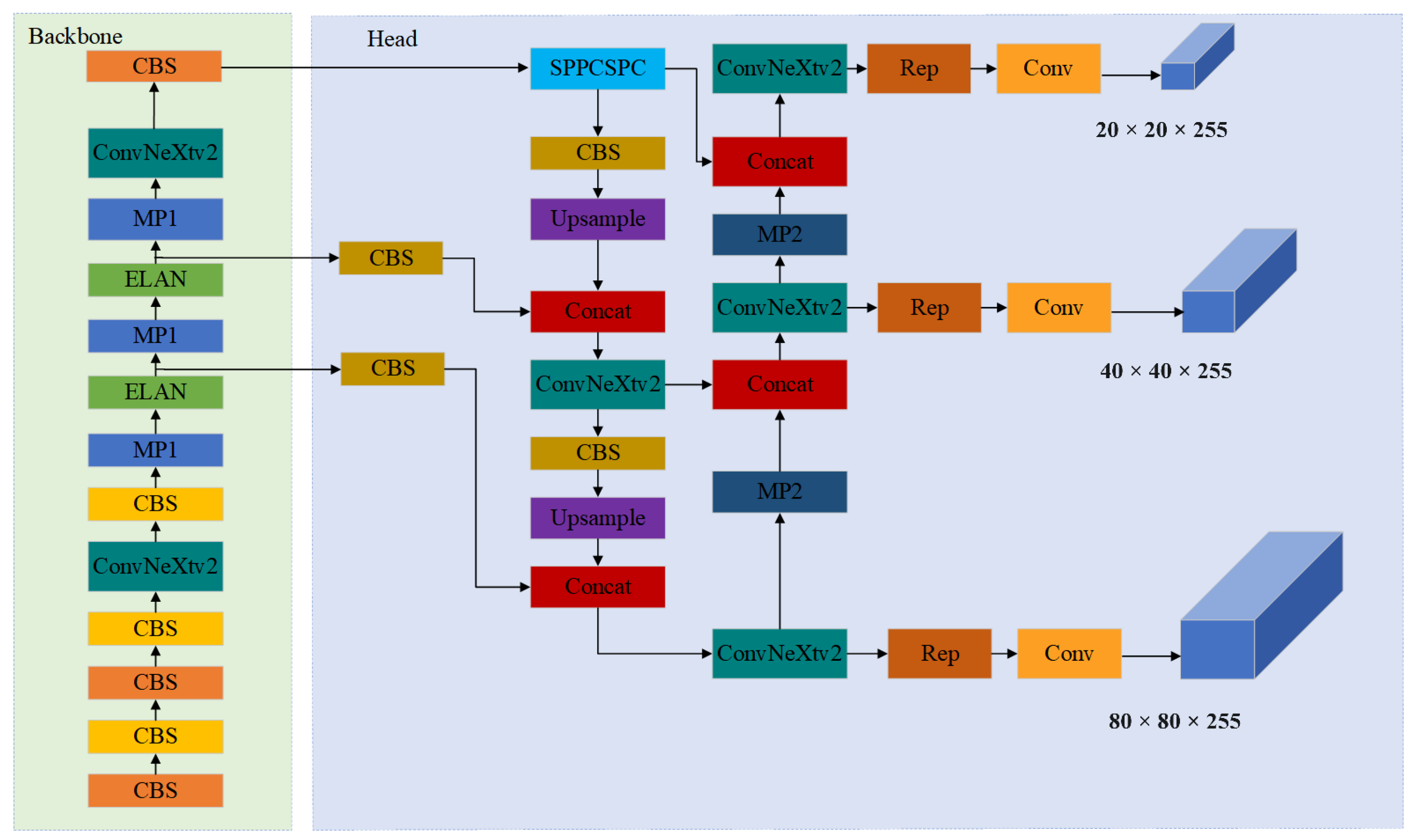
2.4.1. Backbone and Head Improvement
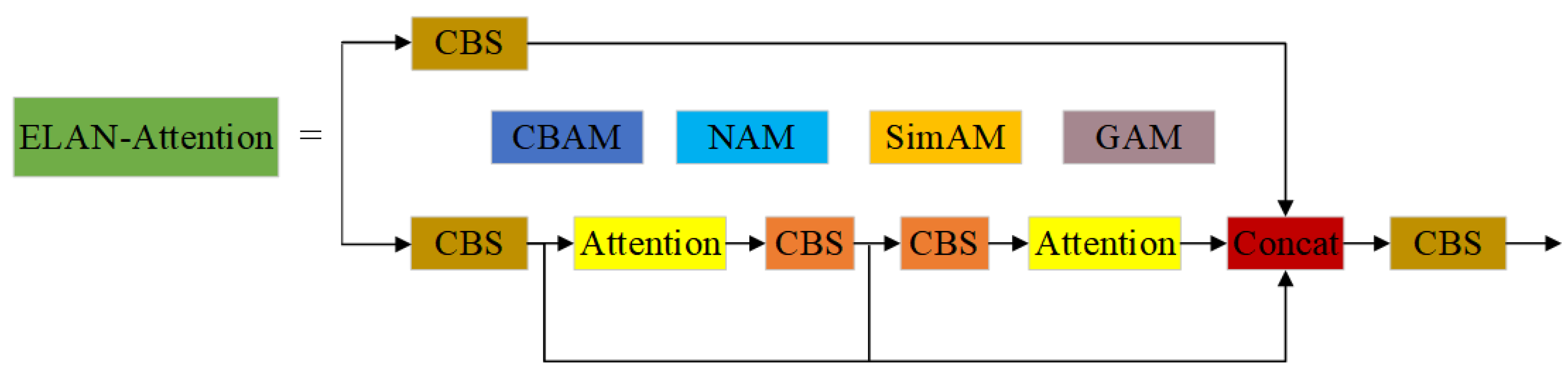
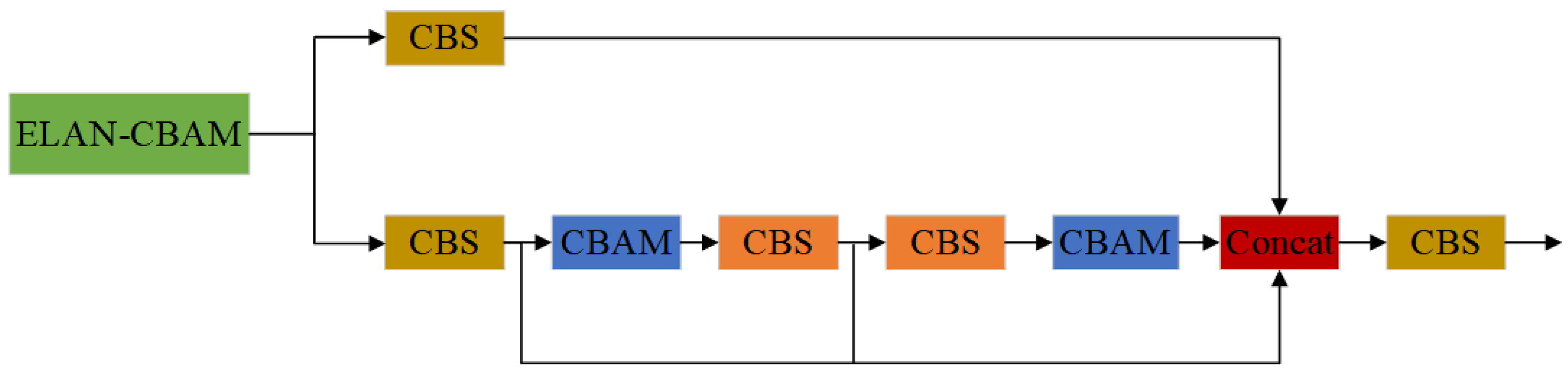
2.4.2. ELAN Structures That Introduce Attention Mechanisms
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Multiple Model Results
3.2. An Experimental Comparison of Attentional Mechanisms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tiemann, A.; Ring, I. Towards ecosystem service assessment: Developing biophysical indicators for forest ecosystem services. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, R.; Turner, M.G. Post-disturbance reorganization of forest ecosystems in a changing world. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2202190119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorge, S.; Mann, C.; Schleyer, C.; Loft, L.; Spacek, M.; Hernández-Morcillo, M.; Kluvankova, T. Understanding dynamics of forest ecosystem services governance: A socio-ecological-technical-analytical framework. Ecosyst. Serv. 2022, 55, 101427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, A.; Audretsch, D. Regional entrepreneurial ecosystems: Learning from forest ecosystems. Small Bus. Econ. 2023, 60, 1051–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdary, V.; Gupta, M.K. Automatic forest fire detection and monitoring techniques: A survey. In Intelligent Communication, Control and Devices: Proceedings of ICICCD 2017; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 1111–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, F.; Gharajeh, M.S. Intelligent and vision-based fire detection systems: A survey. Image Vis. Comput. 2019, 91, 103803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhall, A.; Dhasade, A.; Nalwade, A.; Mohan Raj, V.K.; Kulkarni, V. A survey on systematic approaches in managing forest fires. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 121, 102266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Lin, J.; Bai, D.; Xu, R.; Lin, H. Omni-Dimensional Dynamic Convolution Meets Bottleneck Transformer: A Novel Improved High Accuracy Forest Fire Smoke Detection Model. Forests 2023, 4, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, T.; Banj Shafiei, A.; Erfanian, M.; Hosseinzadeh, O.; Beygi Heidarlou, H. Using forest fire experts’ opinions and GIS/remote sensing techniques in locating forest fire lookout towers. Appl. Geomat. 2022, 15, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucuk, O.; Topaloglu, O.; Altunel, A.O.; Cetin, M. Visibility analysis of fire lookout towers in the Boyabat State Forest Enterprise in Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, P.; Liang, H.; Zheng, C.; Yin, J.; Tian, Y.; Cui, W. Semantic segmentation and analysis on sensitive parameters of forest fire smoke using smoke-unet and landsat-8 imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Jang, E.; Im, J.; Kwon, C. A deep learning model using geostationary satellite data for forest fire detection with reduced detection latency. GISci. Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 2019–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdary, V.; Deogharia, D.; Sowrabh, S.; Dubey, S. Forest fire detection system using barrier coverage in wireless sensor networks. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 64, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, Y. Real-time forest smoke detection using hand-designed features and deep learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 167, 105029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, F. A Semi-Supervised Method for Real-Time Forest Fire Detection Algorithm Based on Adaptively Spatial Feature Fusion. Forests 2023, 2, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Sun, M.; Song, D.; Huang, L.; Yang, J.; Joo, Y.H. Real-time detection of wind power abnormal data based on semi-supervised learning Robust Random Cut Forest. Energy 2022, 257, 124761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydi, S.T.; Saeidi, V.; Kalantar, B.; Ueda, N.; Halin, A.A. Fire-Net: A deep learning framework for active forest fire detection. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 8044390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vipin, V. Image processing based forest fire detection. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2012, 2, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Zhou, H.; Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Bai, D.; Xu, R.; Lin, H. Multi-Scale Forest Fire Recognition Model Based on Improved YOLOv5s. Forests 2023, 2, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yar, H.; Khan, Z.A.; Ullah, F.U.M.; Ullah, W.; Baik, S.W. A modified YOLOv5 architecture for efficient fire detection in smart cities. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 231, 120465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Smadi, Y.; Alauthman, M.; Al-Qerem, A.; Aldweesh, A.; Quaddoura, R.; Aburub, F.; Mansour, K.; Alhmiedat, T. Early Wildfire Smoke Detection Using Different YOLO Models. Machines 2023, 11, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Li, J. UAV forest fire detection based on lightweight YOLOv5 model. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilli, B.; Suguna, M. Early Thermal Forest Fire Detection using UAV and Saliency map. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I), Uttar Pradesh, India, 14–16 December 2022; pp. 1523–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, C.; Xu, H.; Chen, A.; Li, L.; Zhou, G. MMFNet: Forest Fire Smoke Detection Using Multiscale Convergence Coordinated Pyramid Network with Mixed Attention and Fast-robust NMS. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 18168–18180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Zheng, A.; Wu, Z.; Tong, C. Real-time fire smoke detection method combining a self-attention mechanism and radial multi-scale feature connection. Sensors 2023, 23, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, D.Y.; Avalhais, L.P.; Rodrigues, J.F.; Traina, A.J. Bowfire: Detection of fire in still images by integrating pixel color and texture analysis. In Proceedings of the 2015 28th SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images, Salvador, Brazil, 26–29 August 2015; pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Mu, J.; Jiao, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhu, Y. Automatic Identification of Landslides Based on Deep Learning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everingham, M.; Eslami, S.A.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes challenge: A retrospective. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 111, 98–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M. Evaluation: From precision, recall and F-measure to ROC, informedness, markedness and correlation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2010.16061. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, P.; Ferrari, V. End-to-end training of object class detectors for mean average precision. In Proceedings of the 13th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 November 2016; pp. 198–213. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Q.; Lin, H.; Wang, F. FCDM: An Improved Forest Fire Classification and Detection Model Based on YOLOv5. Forests 2022, 13, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.S.A.; Ansari, M.S.; Aslam, A.; Kanwal, N.; Asghar, M.; Lee, B. A survey of modern deep learning based object detection models. Digit. Signal Process. 2022, 126, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A convnet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11976–11986. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Debnath, S.; Hu, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Kweon, I.S.; Xie, S. ConvNeXt V2: Co-designing and Scaling ConvNets with Masked Autoencoders. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.00808. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Lu, C.Z.; Cheng, M.M.; Feng, J. Conv2Former: A Simple Transformer-Style ConvNet for Visual Recognition. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.11943. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Teng, Y.; Hoffmann, N. NAM: Normalization-based attention module. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.12419. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Hoffmann, N. Global attention mechanism: Retain information to enhance channel-spatial interactions. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.05561. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, R.Y.; Li, L.; Xie, X. Simam: A simple, parameter-free attention module for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 11863–11874. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, X.; Jin, S.; An, F.; Zhang, H.; Fan, J.; Eichhorn, M.P.; Jin, C.; Chen, B.; Jiang, L.; Yun, T. Shortwave radiation calculation for forest plots using airborne LiDAR data and computer graphics. Plant Phenom. 2022, 2022, 9856739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; An, F.; Zhang, H.; Yun, T. Simulation on Different Patterns of Mobile Laser Scanning with Extended Application on Solar Beam Illumination for Forest Plot. Forests 2022, 13, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Model | P, % | R, % | AP, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv7 | 83.79 | 81.12 | 87.22 |
| Conv2Former-YOLOv7 | 83.17 | 80.43 | 87.22 |
| ConvNeXtV2-YOLOv7 | 85.81 | 81.71 | 87.83 |
| Model | P, % | R, % | AP, % | Parameter, M |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv7 | 83.79 | 81.12 | 87.22 | 37.2 |
| ConNeXtV2-YOLOv7 | 85.81 | 81.71 | 87.83 | 34.48 |
| ConNeXtV2-YOLOv7 + NAM | 86.03 | 77.9 | 88.07 | 33.71 |
| ConNeXtV2-YOLOv7 + SimAM | 83.75 | 81.46 | 87.67 | 33.71 |
| ConNeXtV2-YOLOv7 + GAM | 84.82 | 79.92 | 87.05 | 50.1 |
| ConNeXtV2-YOLOv7 + CBAM | 86.18 | 81.85 | 88.36 | 33.73 |
| Model | P, % | R, % | AP, % | Parameter, M |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv7 | 83.79 | 81.12 | 87.22 | 37.2 |
| CNTCB-YOLOv7 | 86.18 | 81.85 | 88.36 | 33.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, F. CNTCB-YOLOv7: An Effective Forest Fire Detection Model Based on ConvNeXtV2 and CBAM. Fire 2024, 7, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7020054
Xu Y, Li J, Zhang L, Liu H, Zhang F. CNTCB-YOLOv7: An Effective Forest Fire Detection Model Based on ConvNeXtV2 and CBAM. Fire. 2024; 7(2):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7020054
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yiqing, Jiaming Li, Long Zhang, Hongying Liu, and Fuquan Zhang. 2024. "CNTCB-YOLOv7: An Effective Forest Fire Detection Model Based on ConvNeXtV2 and CBAM" Fire 7, no. 2: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7020054
APA StyleXu, Y., Li, J., Zhang, L., Liu, H., & Zhang, F. (2024). CNTCB-YOLOv7: An Effective Forest Fire Detection Model Based on ConvNeXtV2 and CBAM. Fire, 7(2), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7020054






