Surface Radiative Forcing as a Climate-Change Indicator in North India due to the Combined Effects of Dust and Biomass Burning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Datasets and Methodology
2.1. Datasets
2.1.1. Satellite Remote Sensing Data
2.1.2. Reanalysis Data
2.1.3. CAMS Data
2.2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
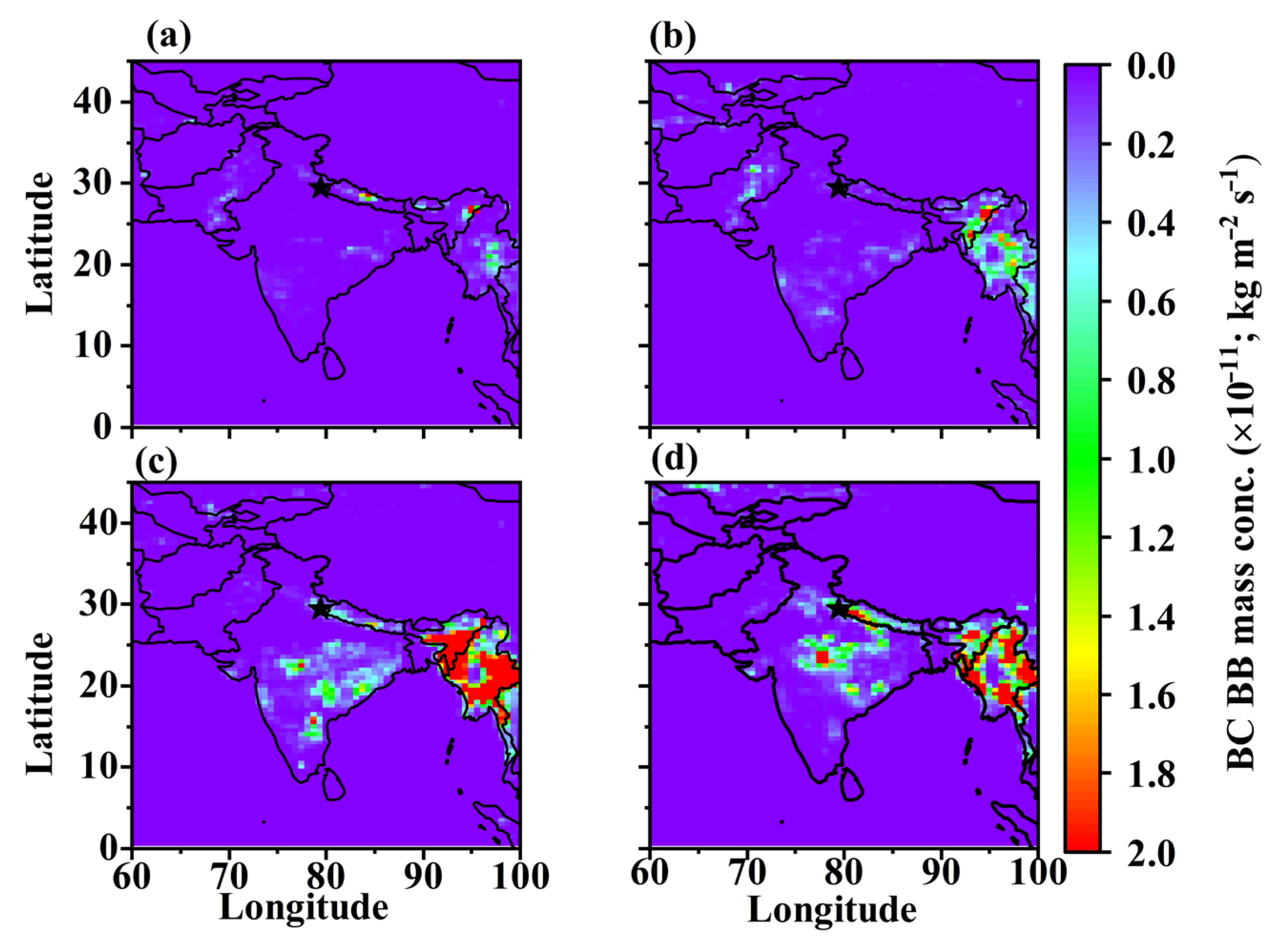
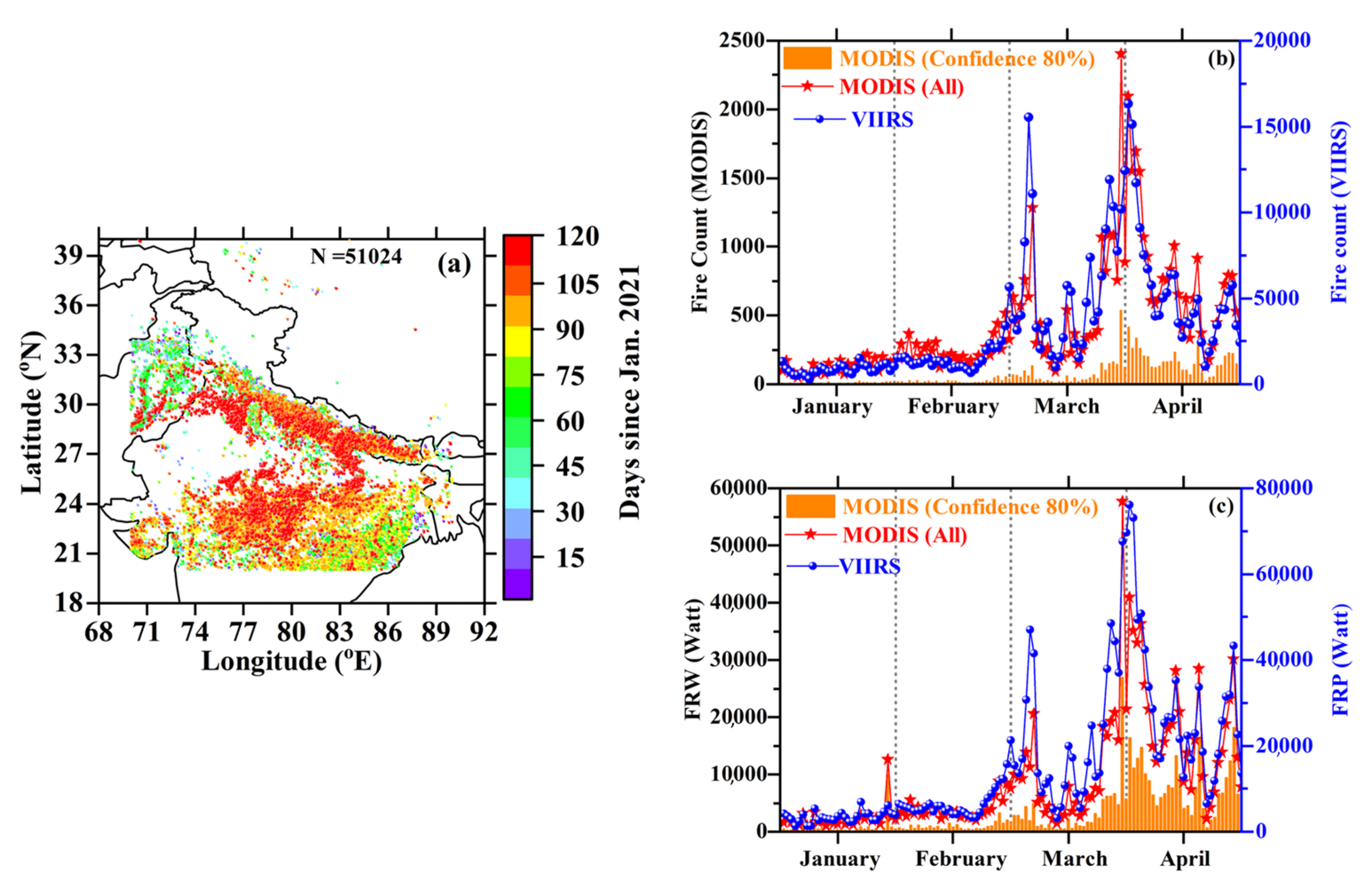
3.1. Fire Counts
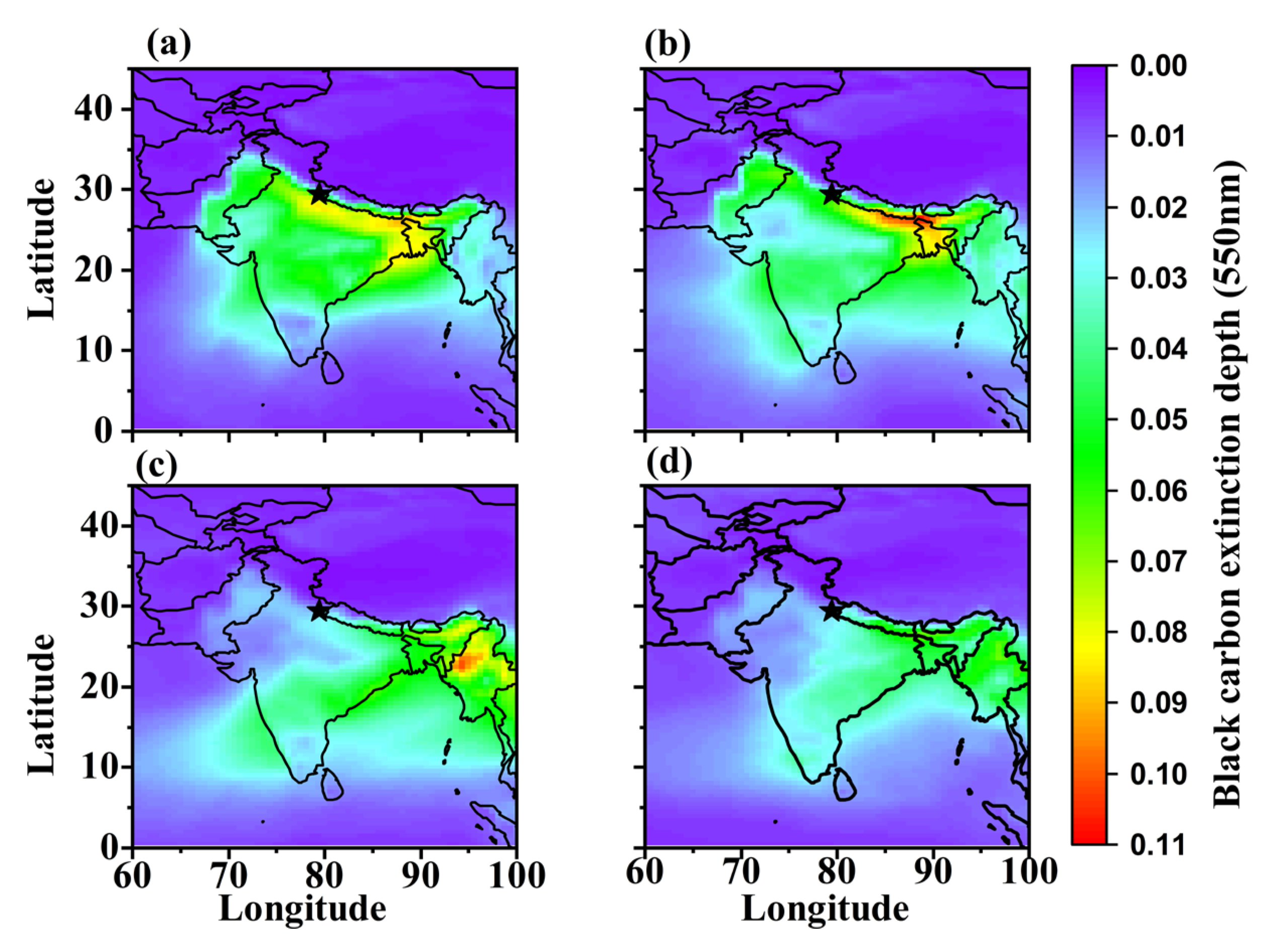
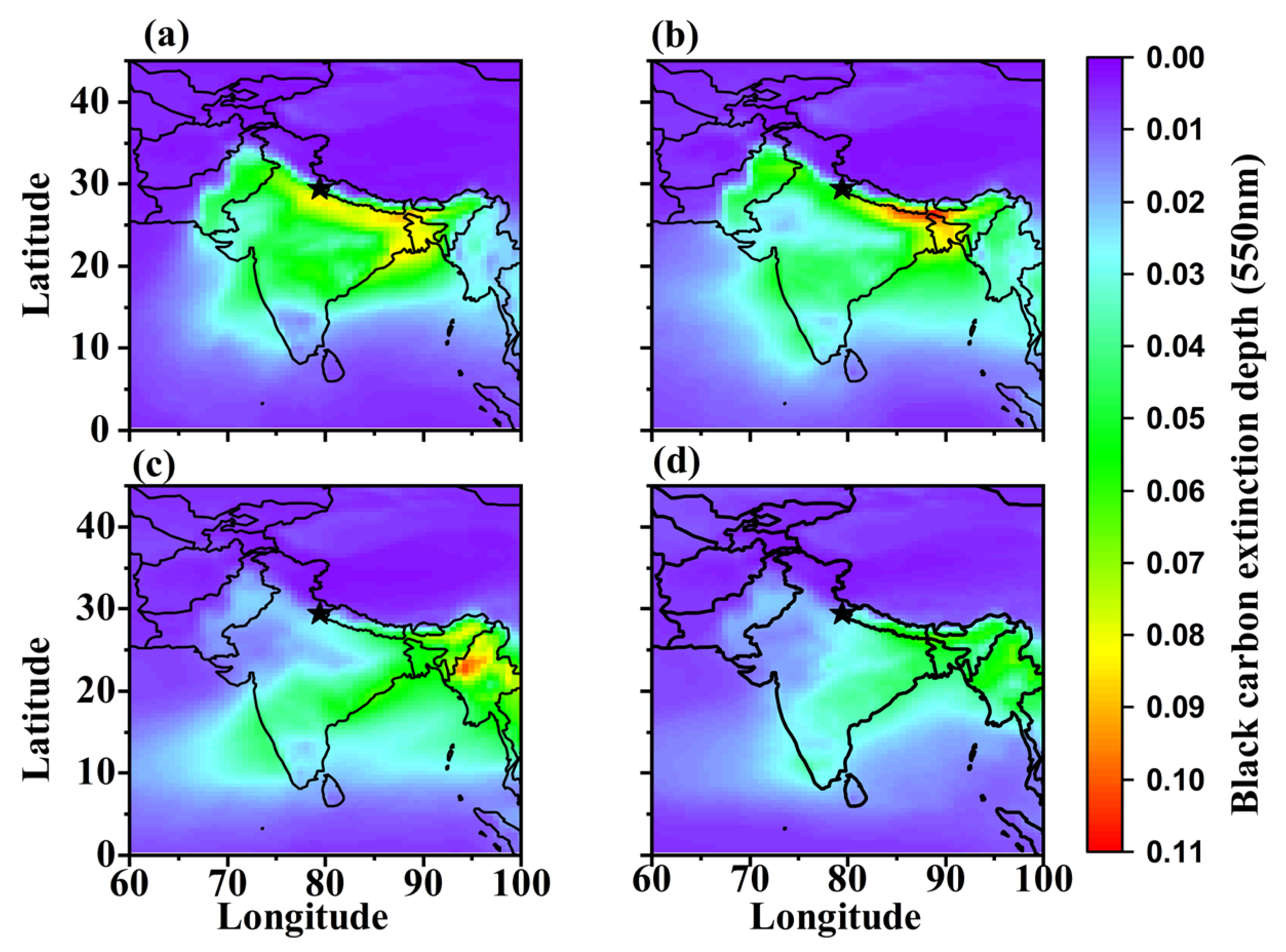
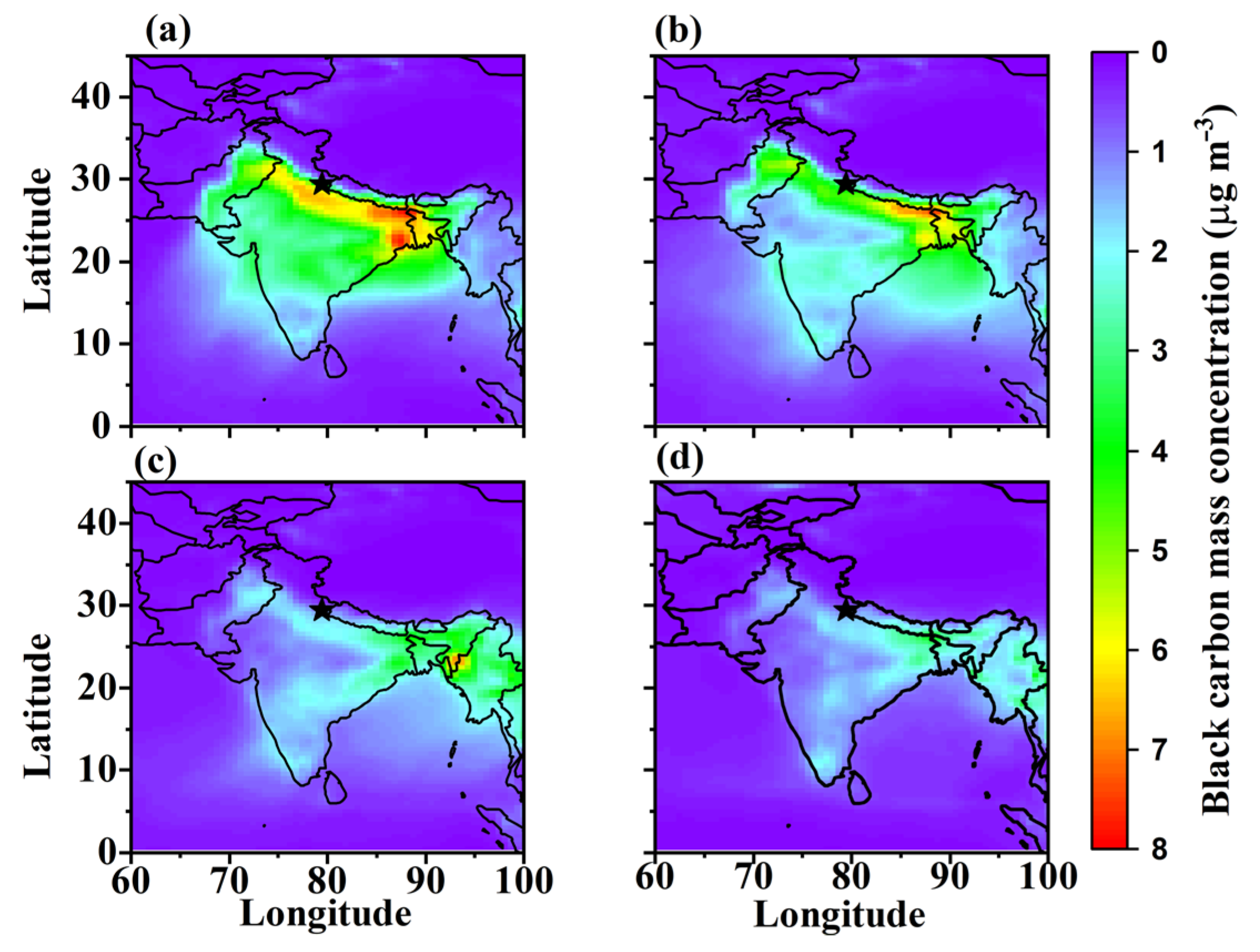
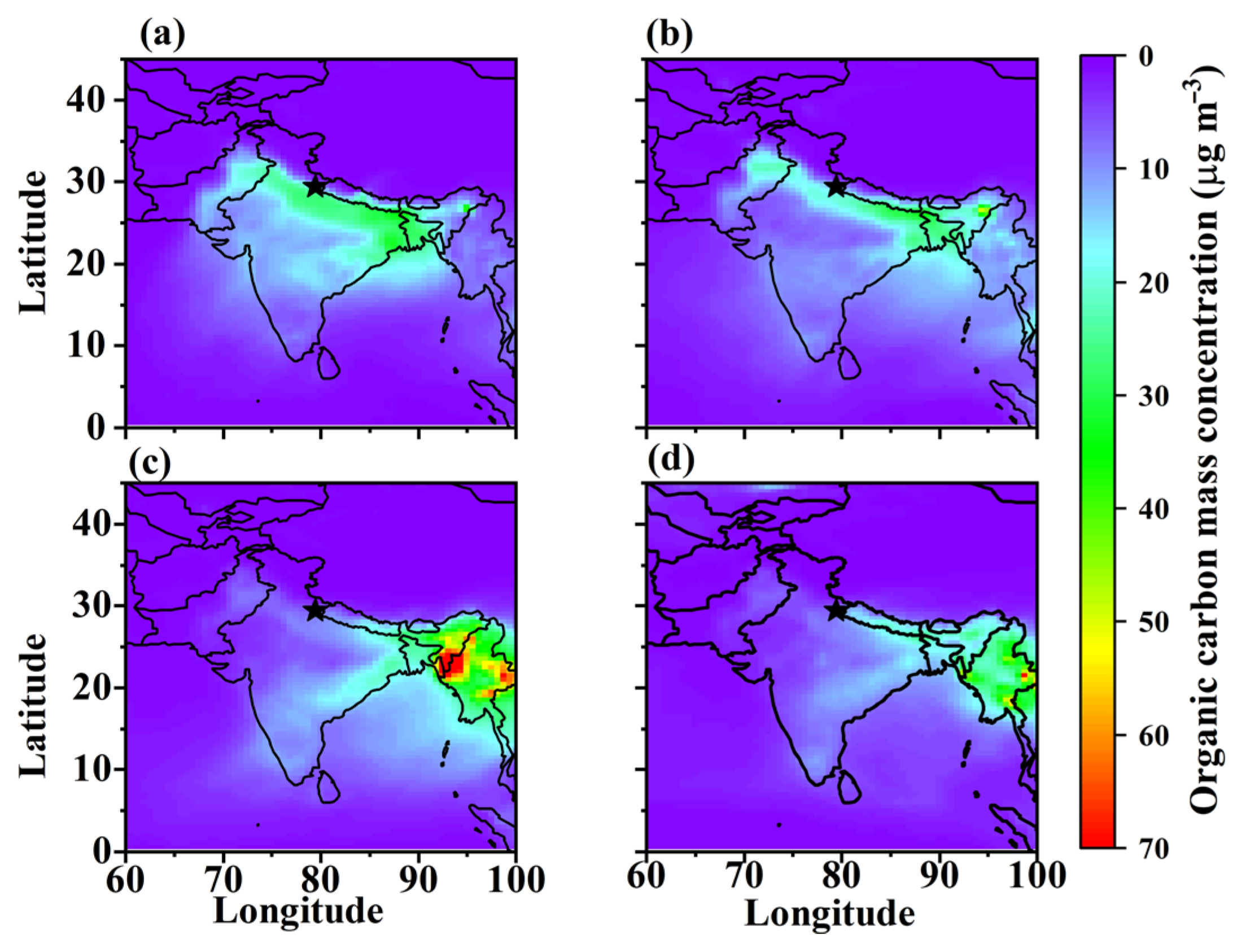
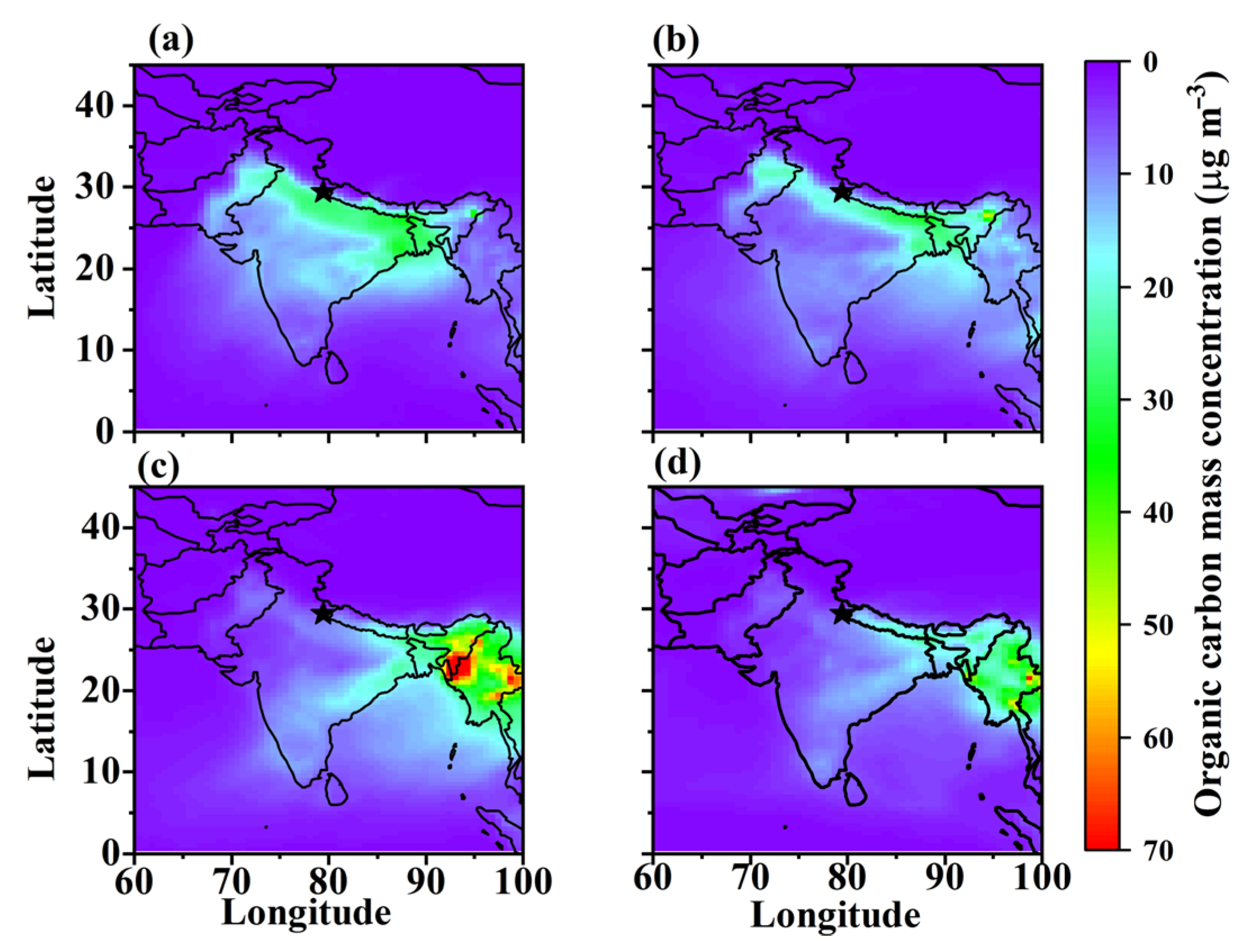
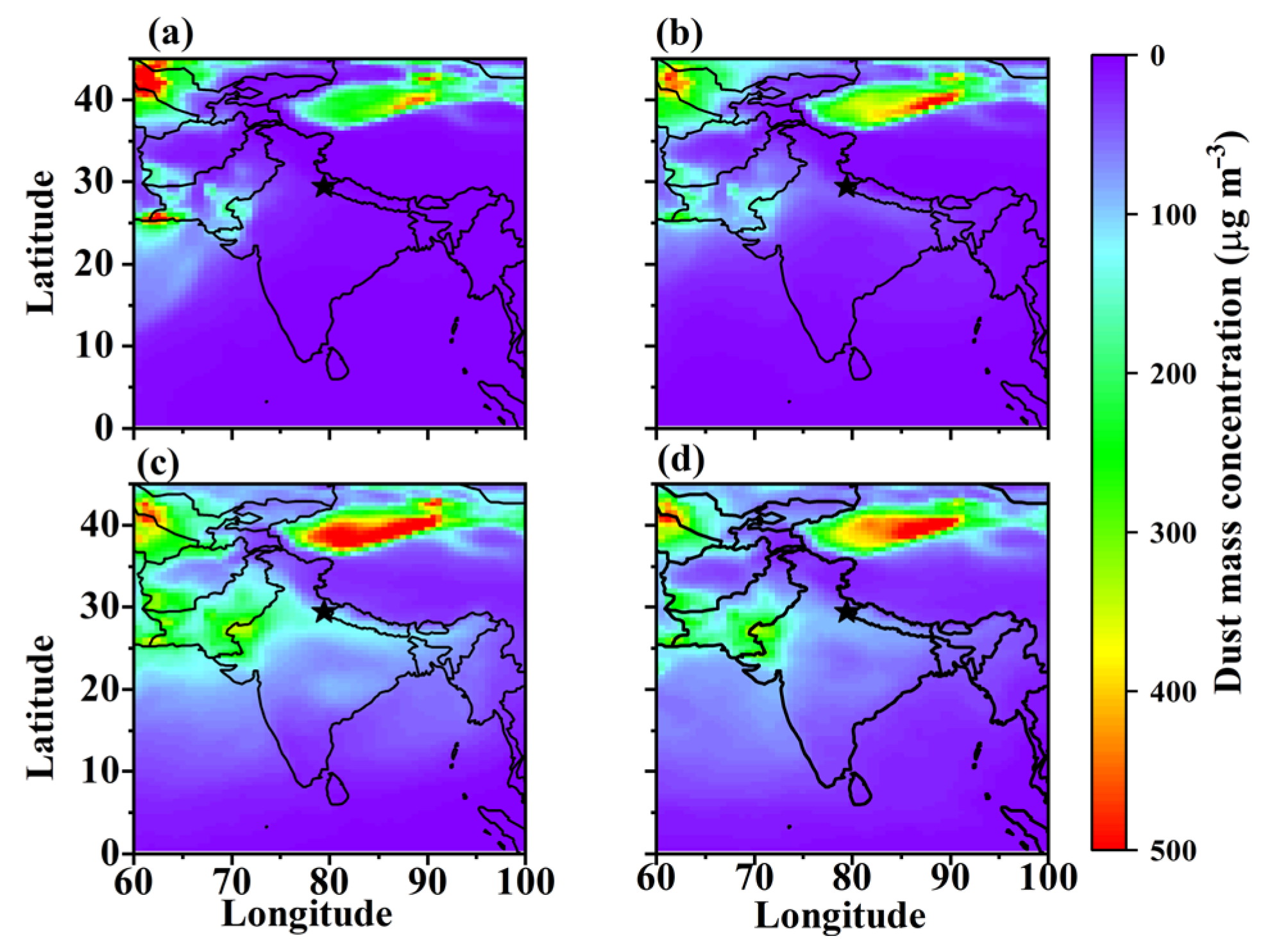
3.2. Spatial-Temporal Variation in Carbonaceous Aerosols and Dust
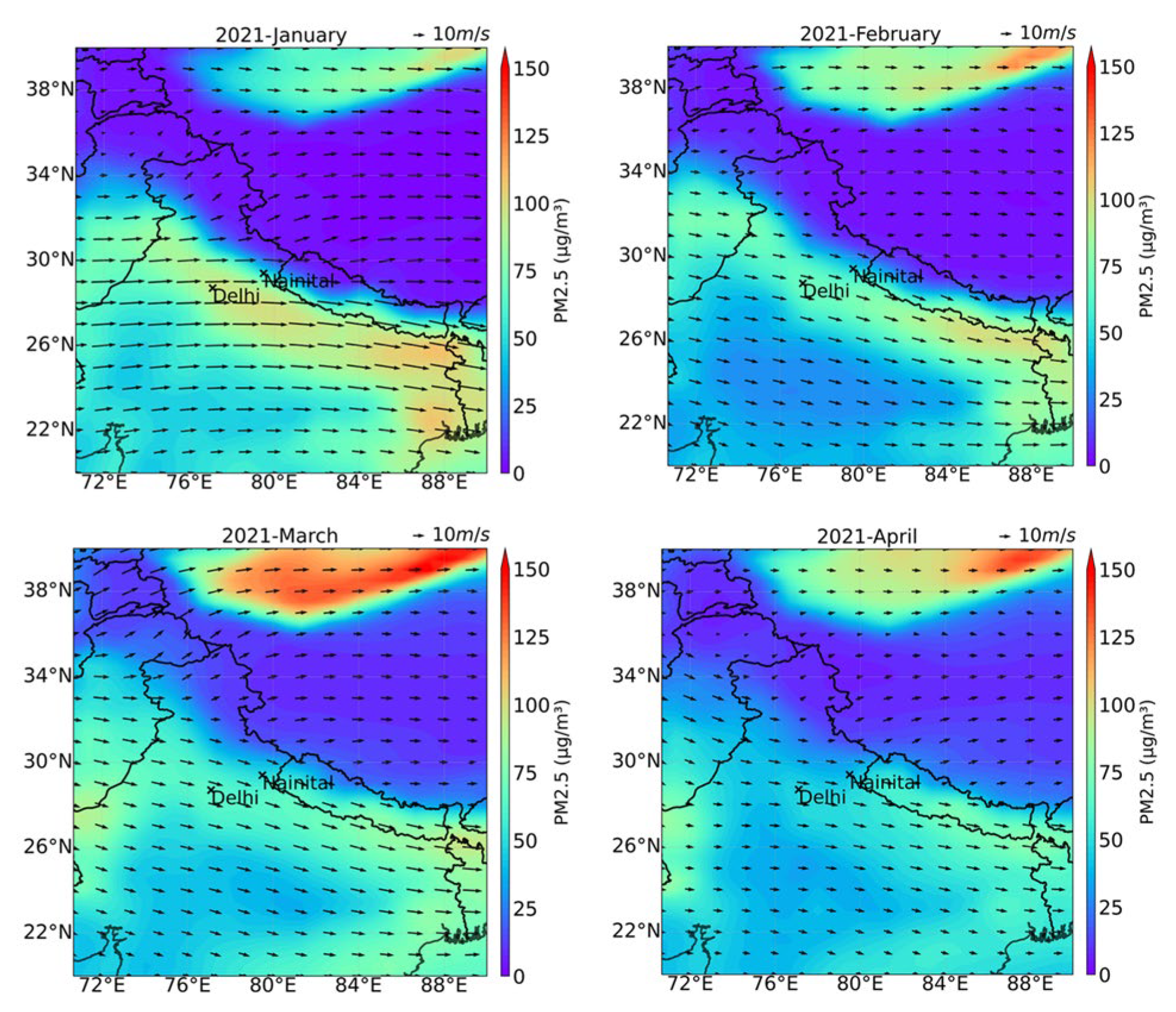
3.3. Surface Distribution of PM2.5
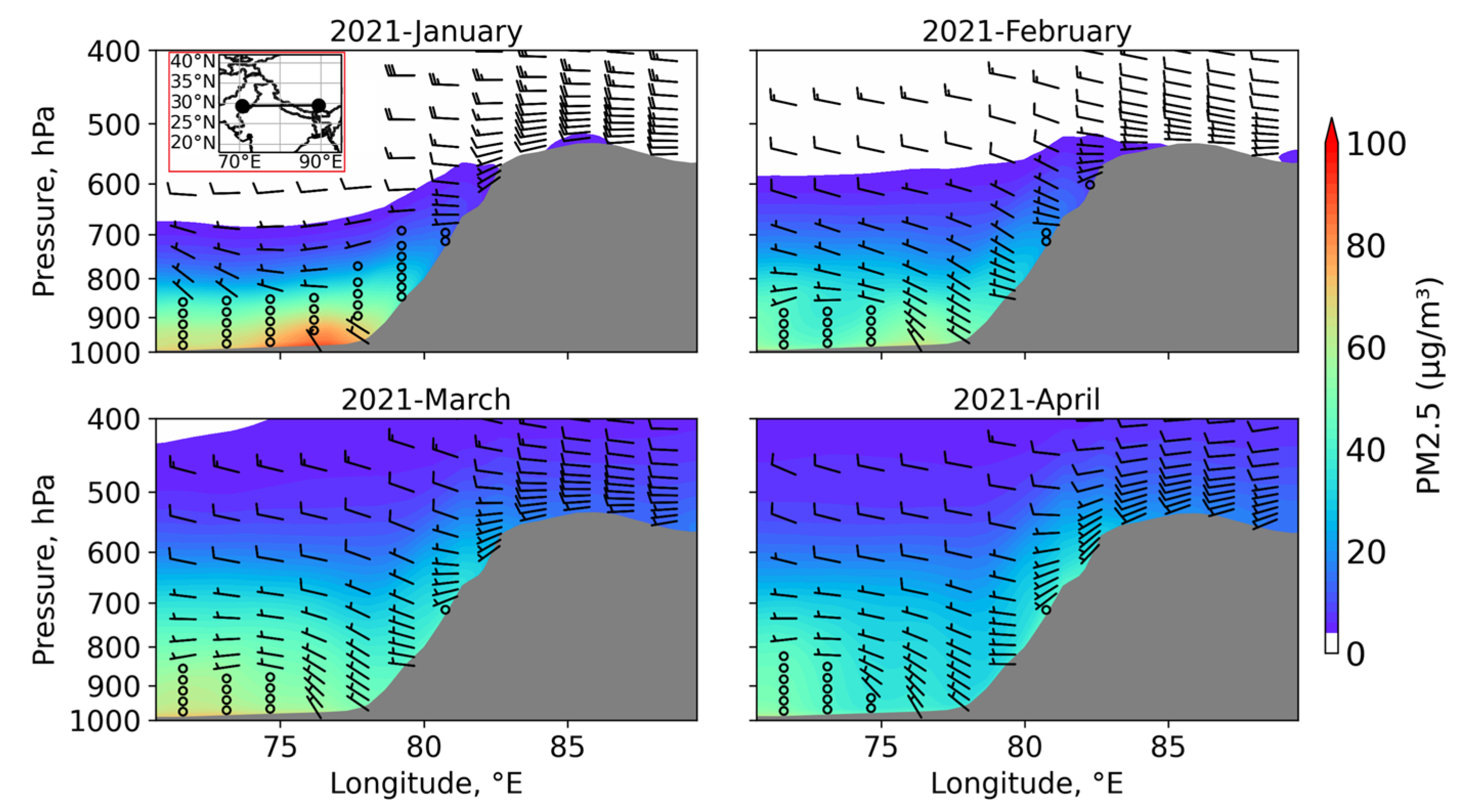
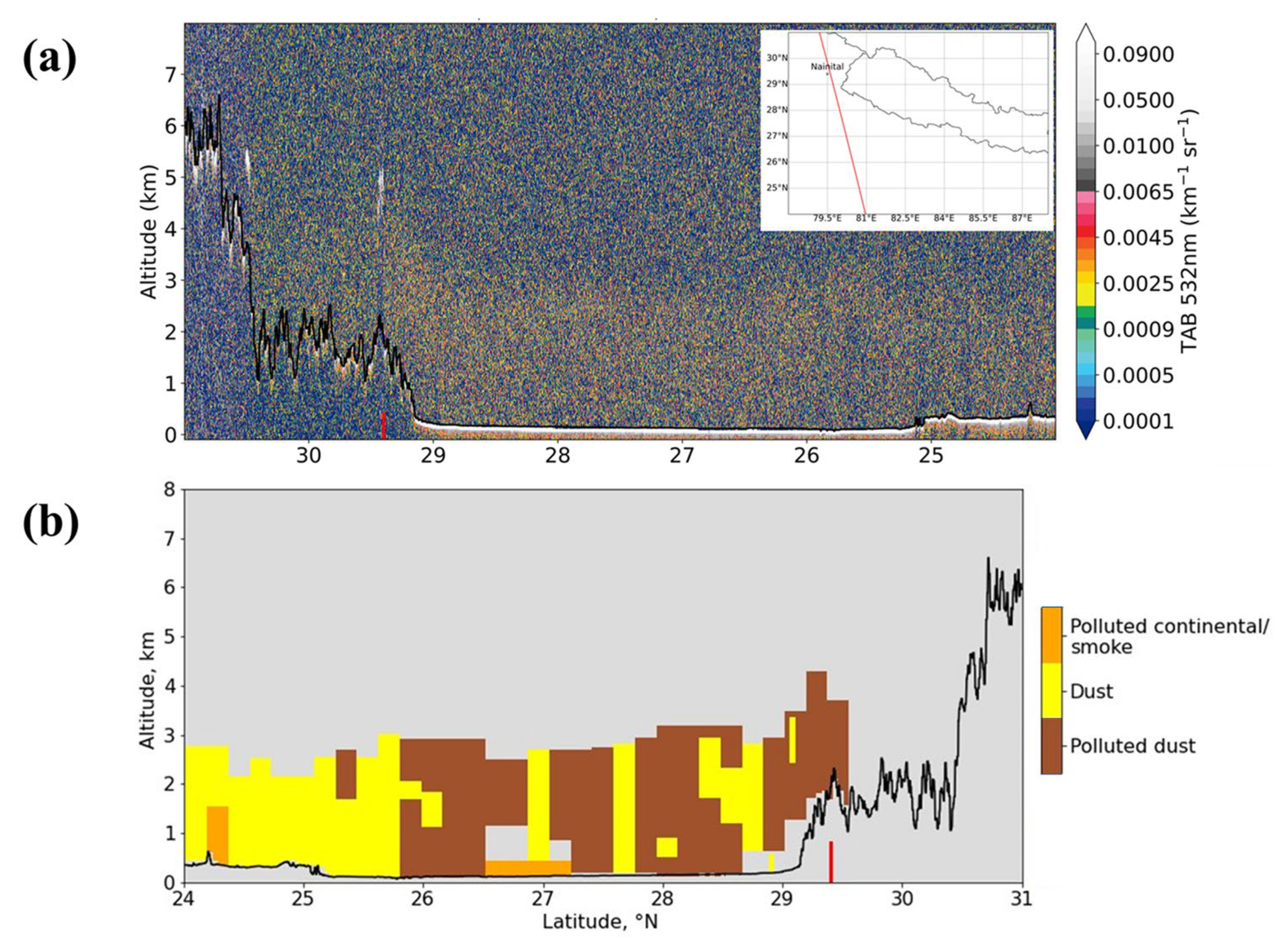
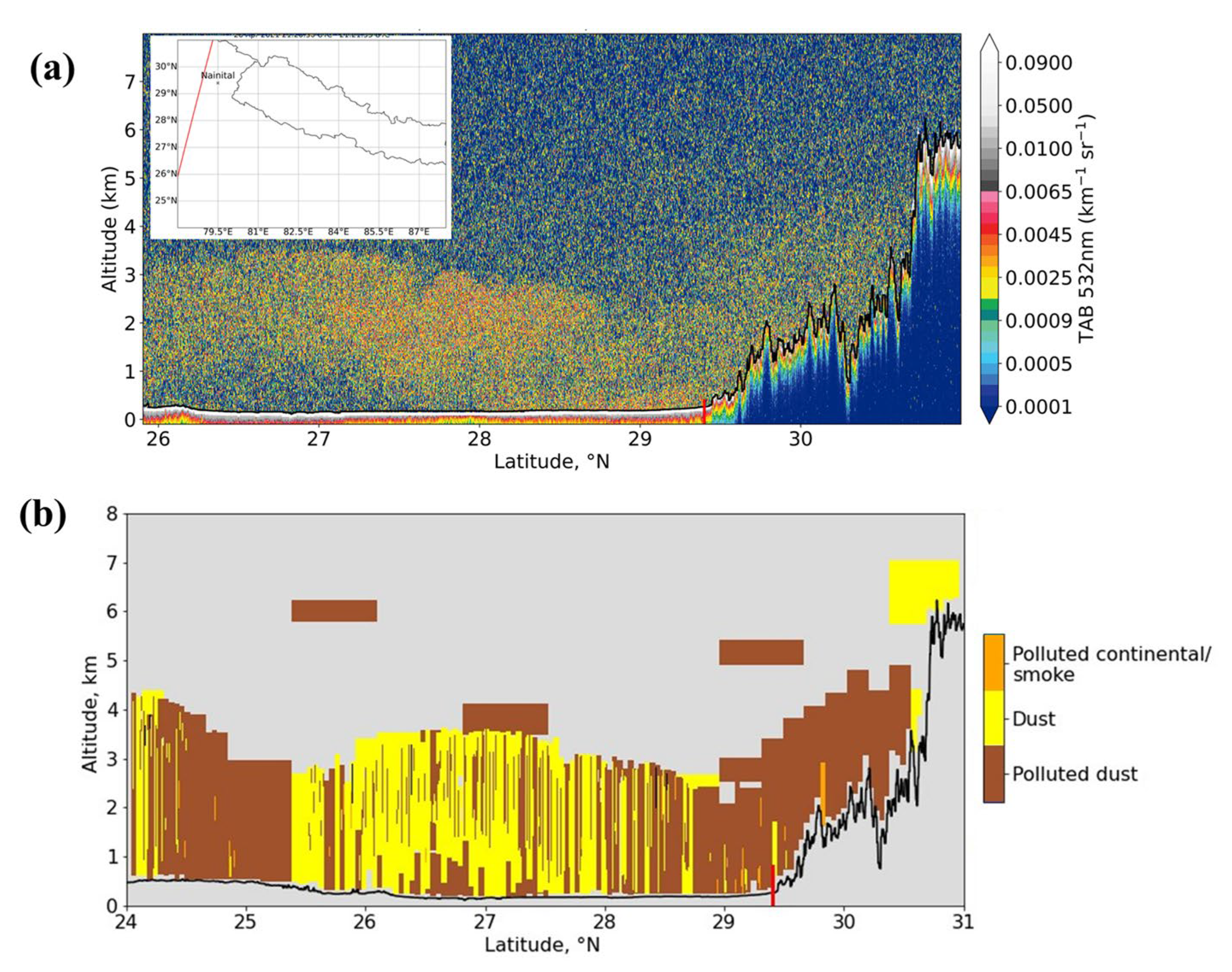
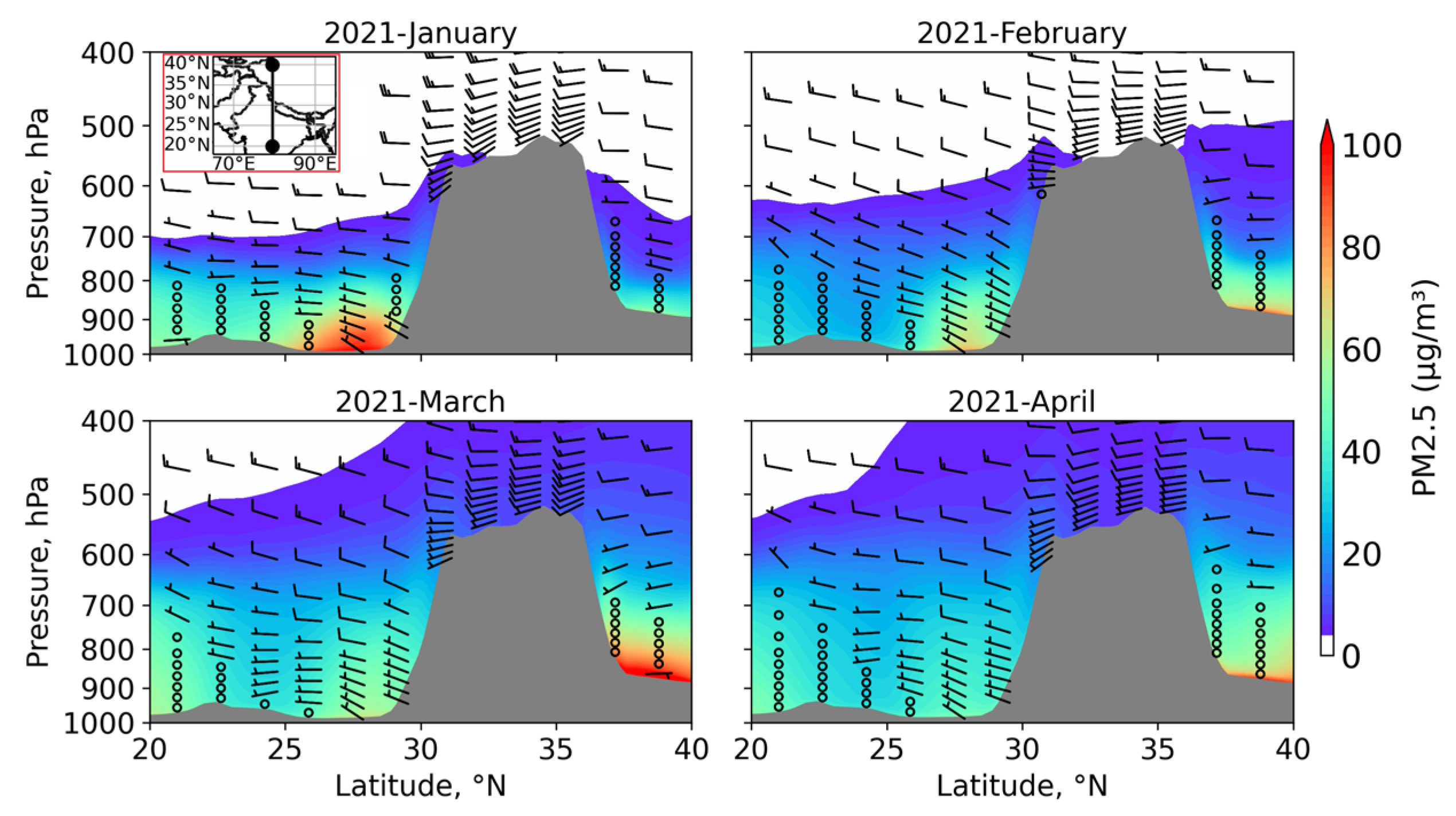
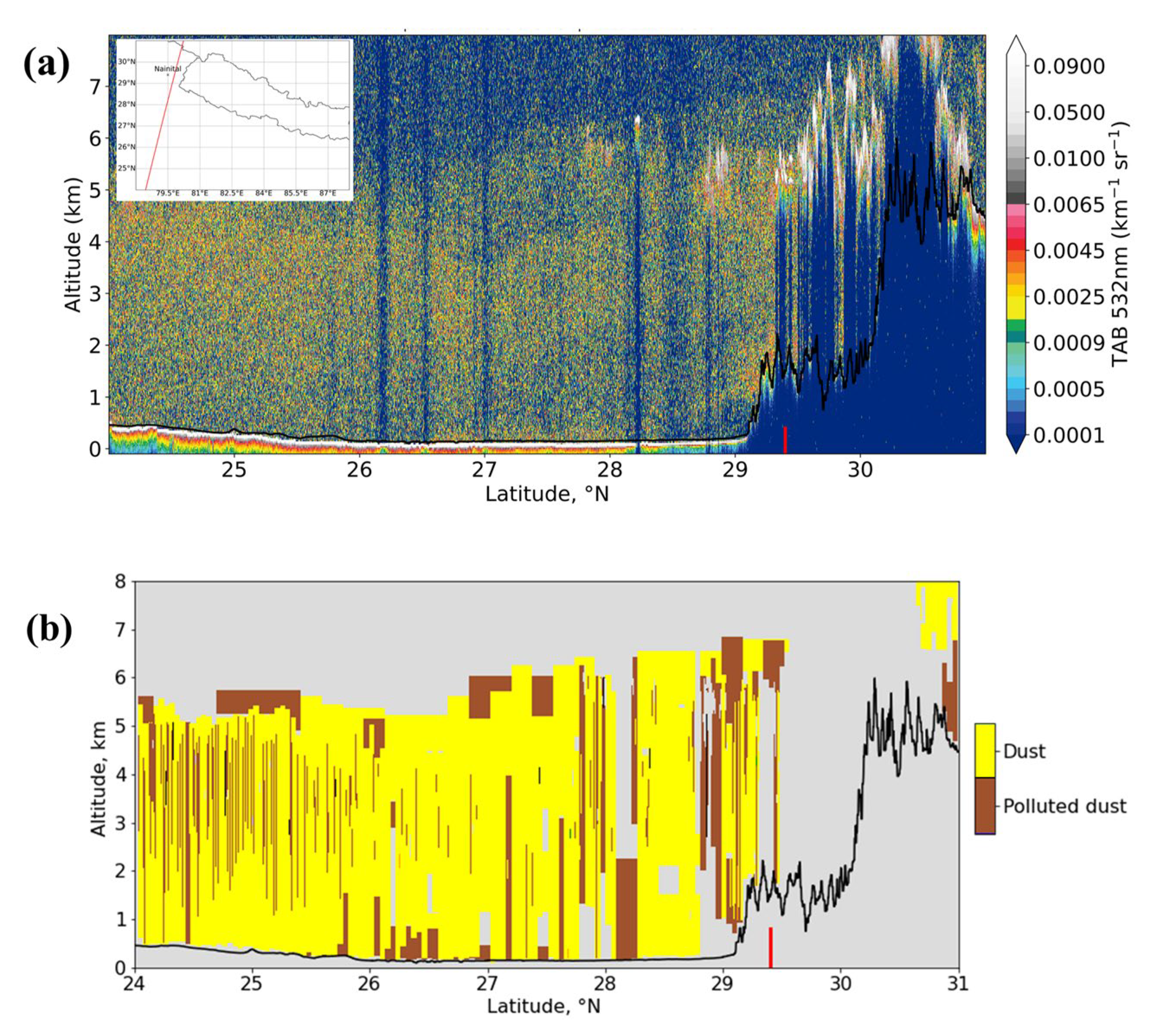
3.4. Vertical Distribution of PM2.5
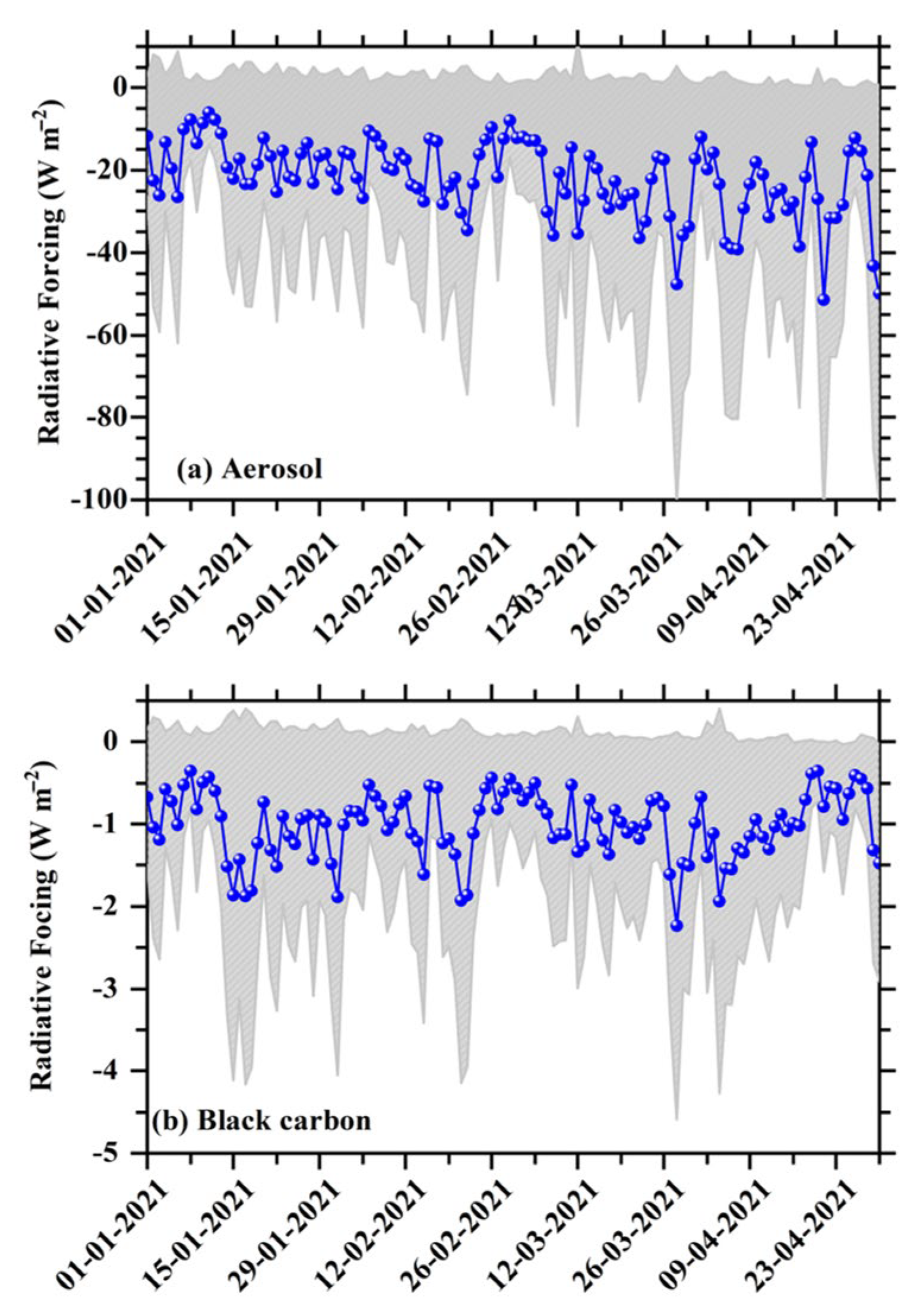
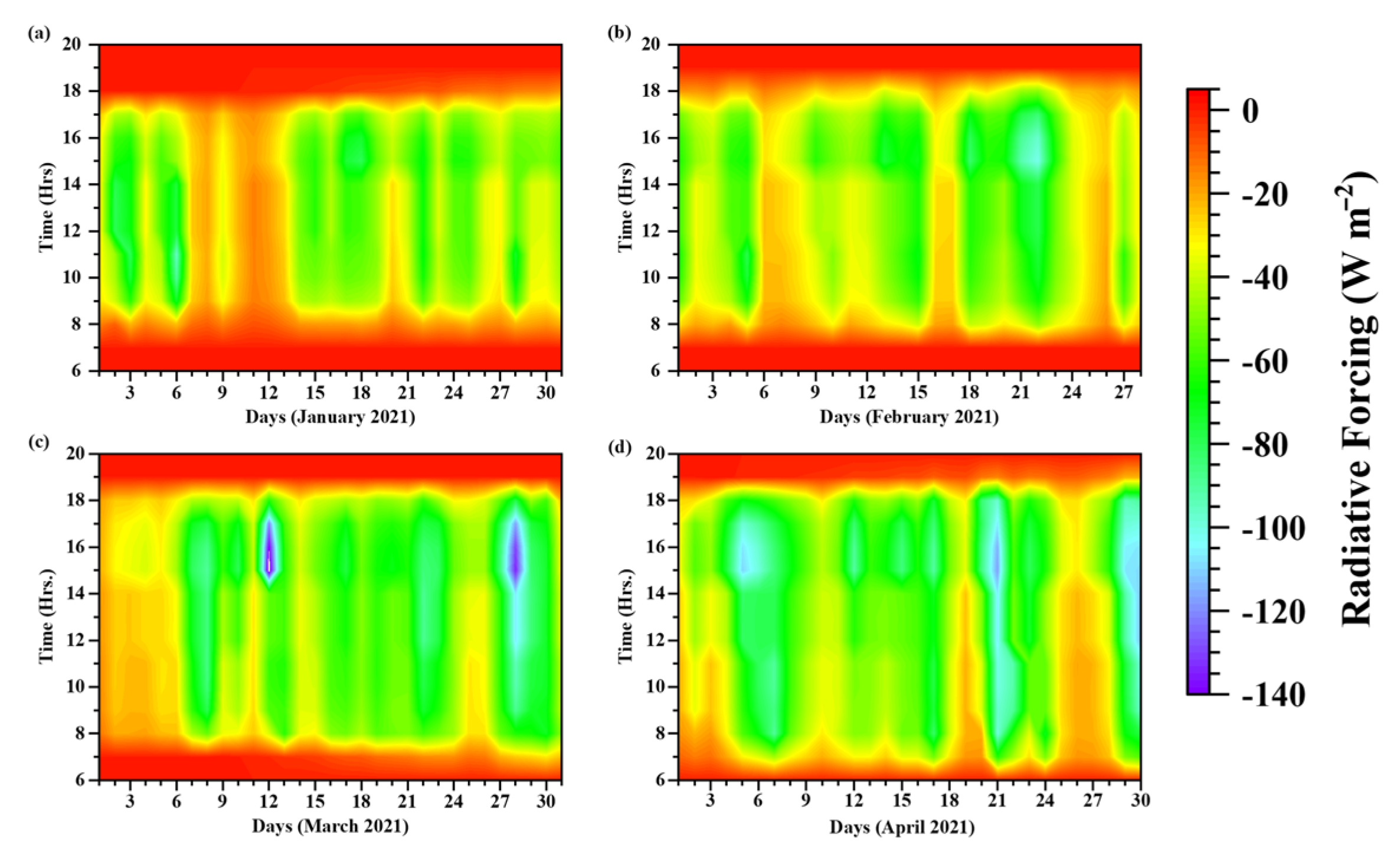
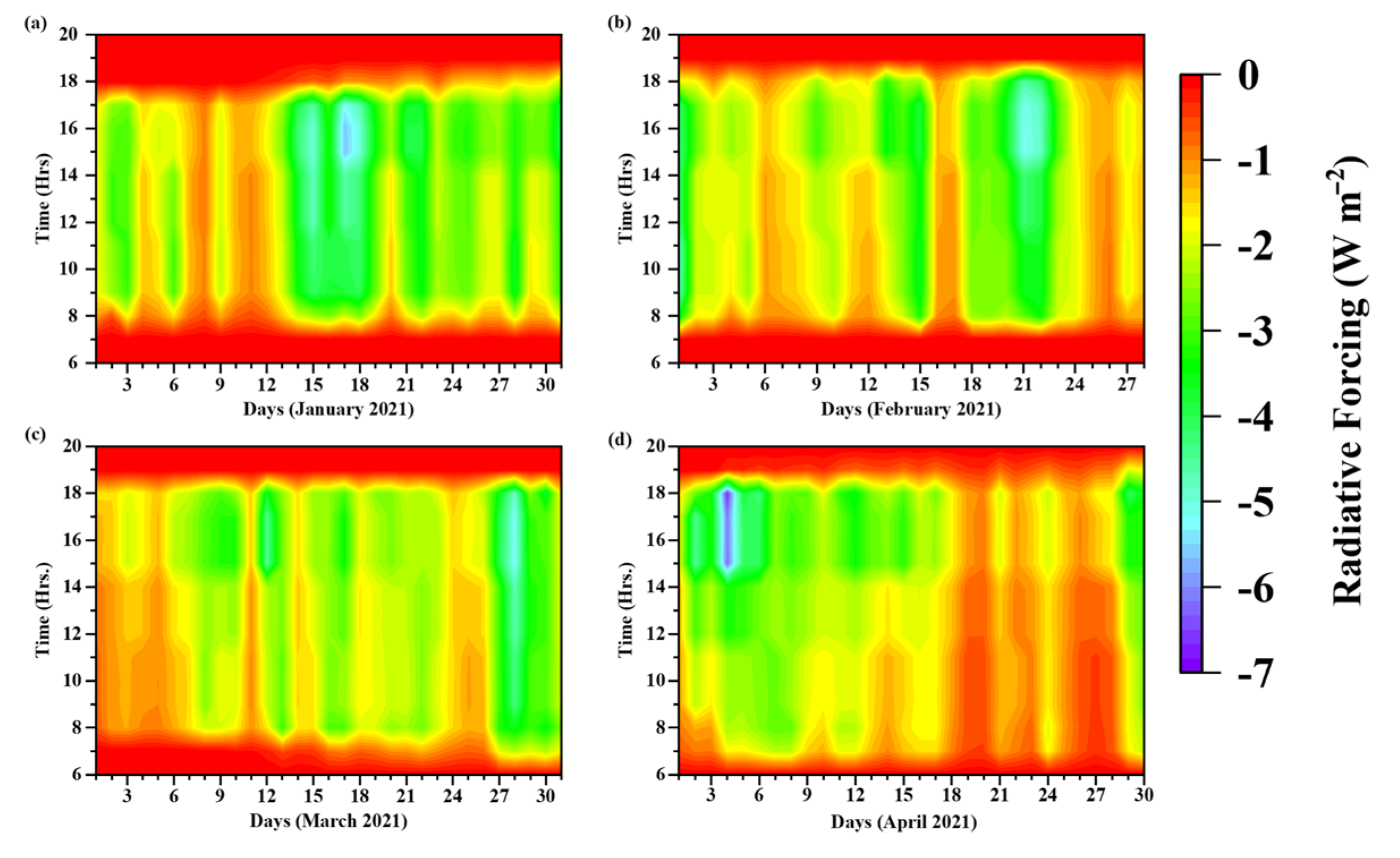
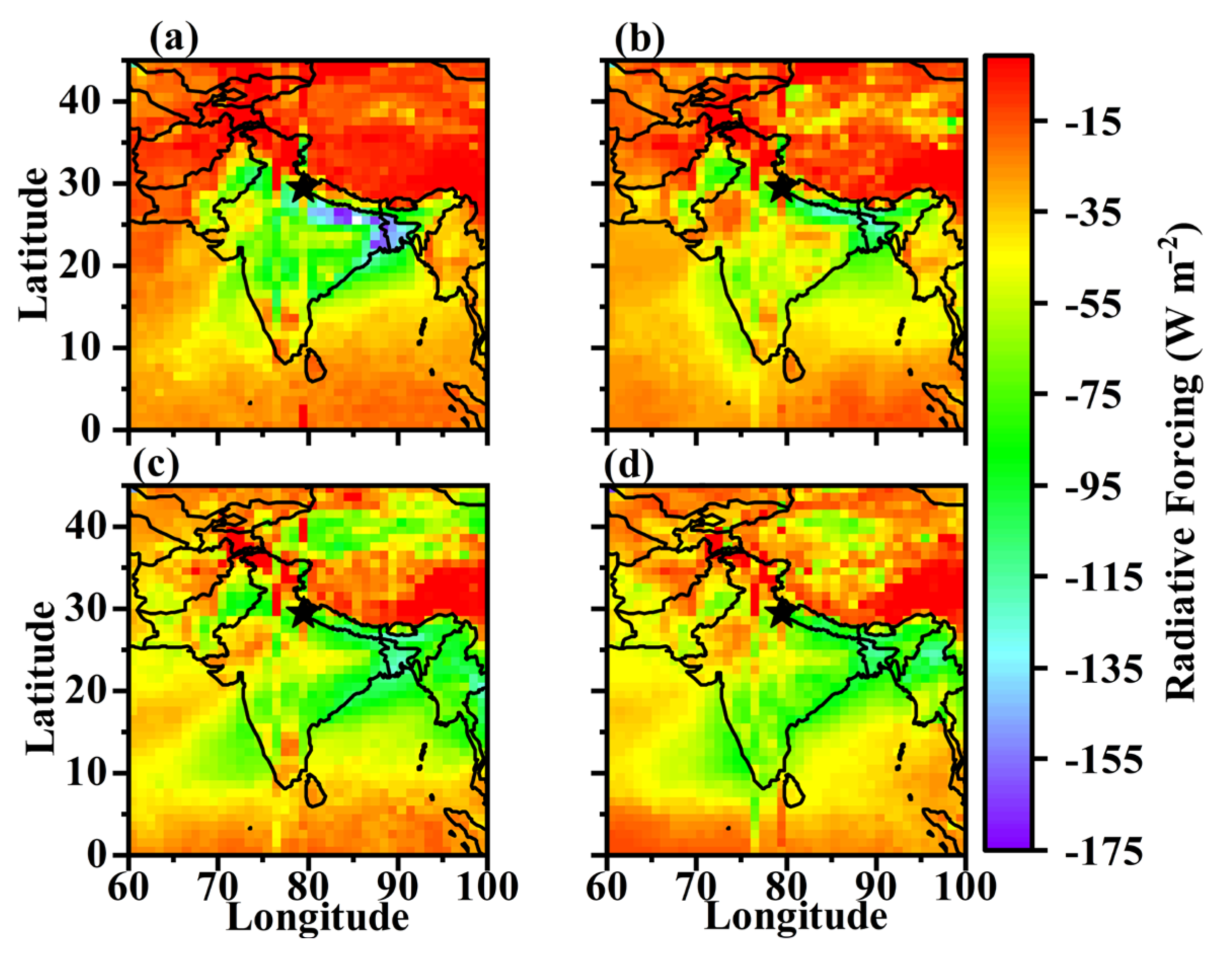
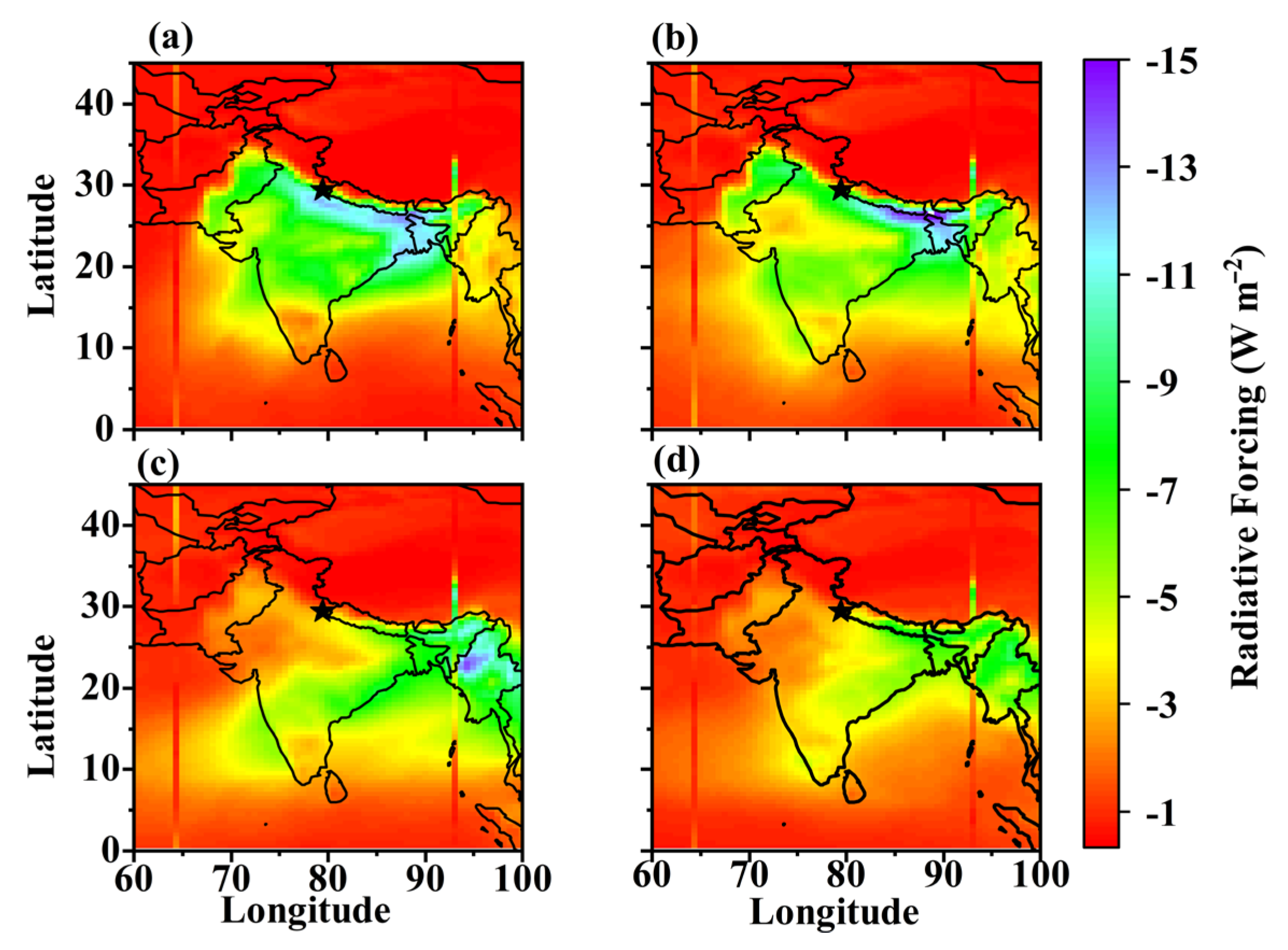
3.5. Surface Radiative Forcing
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Size Bin | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MERRA-2 dust | 0.2–2.0 | 2.0–3.6 | 3.6–6.0 | 6.0–12.0 | 12.0–20.0 |
| MERRA-2 sea salt | 0.06–0.2 | 0.2–1.0 | 1.0–3.0 | 3.0–10.0 | 10.0–20.0 |
References
- Bikkina, S.; Sarin, M. Brown carbon in the continental outflow to the North Indian Ocean. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 970–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jethva, H.; Chand, D.; Torres, O.; Gupta, P.; Lyapustin, A.; Patadia, F. Agricultural burning and air quality over northern india: A synergistic analysis using nasa’s a-train satellite data and ground measurements. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1756–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jethva, H.; Torres, O.; Field, R.D.; Lyapustin, A.; Gautam, R.; Kayetha, V. Connecting Crop Productivity, Residue Fires, and Air Quality over Northern India. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, S.K.; Wang, S.H.; Lin, N.H.; Chantara, S.; Lee, C.T.; Thepnuan, D. Black carbon over an urban atmosphere in northern peninsular Southeast Asia: Characteristics, source apportionment, and associated health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, P.; Sonwani, S.; Srivastava, A.; Jain, M.; Srivastava, A.; Bharti, A.; Rangra, D.; Mongia, N.; Tejan, S.; Bhardwaj, S. Impact of crop residue burning in Haryana on the air quality of Delhi, India. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Satish, R.V.; Rastogi, N. Characteristics and sources of fine organic aerosol over a big semi-arid urban city of western India using HR-ToF-AMS. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 208, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrevu, K.P.; Lasko, K.; Giglio, L.; Schroeder, W.; Biswas, S.; Justice, C. Trends in Vegetation fires in South and Southeast Asian Countries. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, T.T.; Van Der Werf, G.R. Spatial and temporal variability in the ratio of trace gases emitted from biomass burning. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 3611–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, C.; Niu, S.; Lv, J.; Jia, X.; Xu, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yan, S. Diverse Dispersion Effects and Parameterization of Relative Dispersion in Urban Fog in Eastern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2023, 128, e2022JD037514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Tian, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, B.; Zheng, W. Haze Grading Using the Convolutional Neural Networks. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, F.H.; Henderson, S.B.; Chen, Y.; Randerson, J.T.; Marlier, M.; DeFries, R.S.; Kinney, P.; Bowman, D.M.J.S.; Brauer, M. Estimated global mortality attributable to smoke from landscape fires. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garra, P.; Maschowski, C.; Liaud, C.; Dieterlen, A.; Trouvé, G.; Le Calvé, S.; Jaffrezo, J.L.; Leyssens, G.; Schönnenbeck, C.; Kohler, S.; et al. Fluorescence Microscopy Analysis of Particulate Matter from Biomass Burning: Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons as Main Contributors. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaivosoja, T.; Jalava, P.I.; Lamberg, H.; Virén, A.; Tapanainen, M.; Torvela, T.; Tapper, U.; Sippula, O.; Tissari, J.; Hillamo, R.; et al. Comparison of emissions and toxicological properties of fine particles from wood and oil boilers in small (20-25 kW) and medium (5-10 MW) scale. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; Deangelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumka, U.C.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Tiwari, S.; Safai, P.D.; Attri, S.D.; Soni, V.K.; Singh, N.; Mihalopoulos, N. Assessment of biomass burning and fossil fuel contribution to black carbon concentrations in Delhi during winter. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 194, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Carmichael, G. Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, C.; Habib, G.; Eiguren-Fernandez, A.; Miguel, A.H.; Friedlander, S.K. Residential biofuels in South Asia: Carbonaceous aerosol emissions and climate impacts. Science 2005, 307, 1454–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, S.K.; Lin, N.H.; Chantara, S.; Wang, S.H.; Khamkaew, C.; Prapamontol, T.; Janjai, S. Radiative response of biomass-burning aerosols over an urban atmosphere in northern peninsular Southeast Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 892–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Y.; Liu, X.; Yin, Z.; Li, X.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Effect of urbanization on aerosol optical depth over Beijing: Land use and surface temperature analysis. Urban Clim. 2023, 51, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Naja, M.; Satheesh, S.K.; Ojha, N.; Joshi, H.; Sarangi, T.; Pant, P.; Dumka, U.C.; Hegde, P.; Venkataramani, S. Influences of the springtime northern Indian biomass burning over the central Himalayas. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumka, U.C.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Francis, D.; Chaboureau, J.P.; Rashki, A.; Tiwari, S.; Singh, S.; Liakakou, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. The Role of the Intertropical Discontinuity Region and the Heat Low in Dust Emission and Transport Over the Thar Desert, India: A Premonsoon Case Study. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 13197–13219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Lalchandani, V.; Bhattu, D.; Dave, J.S.; Rai, P.; Thamban, N.M.; Mishra, S.; Gaddamidi, S.; Tripathi, N.; Vats, P.; et al. Real-time quantification and source apportionment of fine particulate matter including organics and elements in Delhi during summertime. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 261, 118598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, S. Identification of aerosol types over Indo-Gangetic Basin: Implications to optical properties and associated radiative forcing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12246–12260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair Jayachandran, V.; Nair Suresh Babu, S.; Vaishya, A.; Gogoi, M.M.; Nair, V.S.; Krishnakumari Satheesh, S.; Krishna Moorthy, K. Altitude profiles of cloud condensation nuclei characteristics across the Indo-Gangetic Plain prior to the onset of the Indian summer monsoon. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Panda, J.; Kant, S.; Mukherjee, A. Influence of smoke aerosols on low-level clouds over the Indian region during winter. Atmos. Res. 2022, 278, 106358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spracklen, D.V.; Carslaw, K.S.; Pöschl, U.; Rap, A.; Forster, P.M. Global cloud condensation nuclei influenced by carbonaceous combustion aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9067–9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumka, U.C.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Devara, P.C.S.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, S.; Tiwari, S.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Year-long variability of the fossil fuel and wood burning black carbon components at a rural site in southern Delhi outskirts. Atmos. Res. 2019, 216, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, G.; Kunchala, R.K.; Fadnavis, S.; Kaskaoutis, D.G. Long term variability of carbonaceous aerosols over Southeast Asia via reanalysis: Association with changes in vegetation cover and biomass burning. Atmos. Res. 2020, 245, 105064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.G.; Lelieveld, J. Atmospheric pollutant outflow from southern Asia: A review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 11017–11096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G. Sulfur dioxide and primary carbonaceous aerosol emissions in China and India, 1996–2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9839–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, N.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, M.; Girach, I.; Ansari, T.U.; Sharma, S.K.; Singh, N.; Pozzer, A.; Gunthe, S.S. On the widespread enhancement in fine particulate matter across the Indo-Gangetic Plain towards winter. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pani, S.K.; Chantara, S.; Khamkaew, C.; Lee, C.T.; Lin, N.H. Biomass burning in the northern peninsular Southeast Asia: Aerosol chemical profile and potential exposure. Atmos. Res. 2019, 224, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Sarangi, C.; Kanawade, V.P. Recent Increase in Winter Hazy Days over Central India and the Arabian Sea. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, D.; Singh, R.P.; Kharol, S.K.; Sharma, M.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.; Singh, D. Effects of crop residue burning on aerosol properties, plume characteristics, and long-range transport over northern India. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 5424–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, N.B.; Babu, S.S.; Nair, V.S. Recent Regime Shifts in Mineral Dust Trends over South Asia from Long-Term CALIPSO Observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4485–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.K.; Vinoj, V.; Landu, K.; Babu, S.S. Declining pre-monsoon dust loading over South Asia: Signature of a changing regional climate. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Descloitres, J.; Justice, C.O.; Kaufman, Y.J. An enhanced contextual fire detection algorithm for MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Schroeder, W.; Justice, C.O. The collection 6 MODIS active fire detection algorithm and fire products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningombam, S.S.; Dumka, U.C.; Srivastava, A.K.; Song, H.J. Optical and physical properties of aerosols during active fire events occurring in the Indo-Gangetic Plains: Implications for aerosol radiative forcing. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumka, U.C.; Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Patel, P.N. Can Forest Fires Be an Important Factor in the Reduction in Solar Power Production in India? Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.H.; Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Hu, Y.; Trepte, C.R.; Ferrare, R.A.; Lee, K.P.; Hostetler, C.A.; Kittaka, C.; Rogers, R.; et al. The CALIPSO Automated Aerosol Classification and Lidar Ratio Selection Algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1994–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Hunt, W.H.; McGill, M.J. Initial performance assessment of CALIOP. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L19803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Omar, A.H.; Tackett, J.L.; Vaughan, M.A.; Winker, D.M.; Trepte, C.R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Poole, L.R.; Pitts, M.C.; et al. The CALIPSO version 4 automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 6107–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchard, V.; Randles, C.A.; da Silva, A.M.; Darmenov, A.; Colarco, P.R.; Govindaraju, R.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; Beyersdorf, A.J.; Ziemba, L.D.; et al. The MERRA-2 Aerosol Reanalysis, 1980 Onward. Part II: Evaluation and Case Studies. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6851–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelaro, R.; McCarty, W.; Suárez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Randles, C.A.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Reichle, R.; et al. The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications, version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5419–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.; Pokhrel, R.P.; Pokharel, B.; Becker, S.; Giri, B.; Adhikari, L.; LaPlante, M.D. An episode of transboundary air pollution in the central Himalayas during agricultural residue burning season in North India. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navinya, C.D.; Vinoj, V.; Pandey, S.K. Evaluation of pm2.5 surface concentrations simulated by nasa’s merra version 2 aerosol reanalysis over india and its relation to the air quality index. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, C.A.; da Silva, A.M.; Buchard, V.; Colarco, P.R.; Darmenov, A.; Govindaraju, R.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; et al. The MERRA-2 aerosol reanalysis, 1980 onward. Part I: System description and data assimilation evaluation. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6823–6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.; Sapkota, R.P.; Pokharel, B.; Adhikari, L.; Pokhrel, R.P.; Khanal, S.; Giri, B. Particulate matter variability in Kathmandu based on in-situ measurements, remote sensing, and reanalysis data. Atmos. Res. 2021, 258, 105623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchard, V.; da Silva, A.M.; Randles, C.A.; Colarco, P.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; Hostetler, C.; Tackett, J.; Winker, D. Evaluation of the surface PM2.5 in Version 1 of the NASA MERRA Aerosol Reanalysis over the United States. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 125, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Lin, A.; Chen, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, Z.; He, P. Assessment of MERRA-2 Surface PM2.5 over the Yangtze River Basin: Ground-based verification, spatiotemporal distribution and meteorological dependence. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, P.; Hayasaka, T.; Holben, B.; Tripathi, S.N.; Misra, P.; Patra, P.K.; Hayashida, S.; Dumka, U.C. Aerosol Loading and Radiation Budget Perturbations in Densely Populated and Highly Polluted Indo-Gangetic Plain by COVID-19: Influences on Cloud Properties and Air Temperature. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.C.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Chen, L.W.A.; Wang, X.; Watson, J.G. Mass reconstruction methods for PM2.5: A review. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2015, 8, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hand, J.L.; Schichtel, B.A.; Malm, W.C.; Frank, N.H. Spatial and temporal trends in PM2.5 organic and elemental carbon across the United States. Adv. Meteorol. 2013, 2013, 367674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukhov, A.; Mostamandi, S.; Da Silva, A.; Flemming, J.; Alshehri, Y.; Shevchenko, I.; Stenchikov, G. Assessment of natural and anthropogenic aerosol air pollution in the Middle East using MERRA-2, CAMS data assimilation products, and high-resolution WRF-Chem model simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 9281–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukhov, A.; Mostamandi, S.; Krotkov, N.; Flemming, J.; da Silva, A.; Li, C.; Fioletov, V.; McLinden, C.; Anisimov, A.; Alshehri, Y.M.; et al. Study of SO2 Pollution in the Middle East Using MERRA-2, CAMS Data Assimilation Products, and High-Resolution WRF-Chem Simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inness, A.; Ades, M.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Barr, J.; Benedictow, A.; Blechschmidt, A.M.; Jose Dominguez, J.; Engelen, R.; Eskes, H.; Flemming, J.; et al. The CAMS reanalysis of atmospheric composition. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3515–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcrette, J.J.; Boucher, O.; Jones, L.; Salmond, D.; Bechtold, P.; Beljaars, A.; Benedetti, A.; Bonet, A.; Kaiser, J.W.; Razinger, M.; et al. Aerosol analysis and forecast in the european centre for medium-range weather forecasts integrated forecast system: Forward modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Mhawish, A.; Nichol, J.E.; Qiu, Z.; Nazeer, M.; Ali, M.A.; de Leeuw, G.; Levy, R.C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Air pollution scenario over Pakistan: Characterization and ranking of extremely polluted cities using long-term concentrations of aerosols and trace gases. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emde, C.; Buras-Schnell, R.; Kylling, A.; Mayer, B.; Gasteiger, J.; Hamann, U.; Kylling, J.; Richter, B.; Pause, C.; Dowling, T.; et al. The libRadtran software package for radiative transfer calculations (version 2.0.1). Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1647–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.; Kylling, A. Technical note: The libRadtran software package for radiative transfer calculations—Description and examples of use. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 1855–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Kazadzis, S.; Taylor, M.; Raptis, P.I.; Keramitsoglou, I.; Kiranoudis, C.; Bais, A.F. Assessment of surface solar irradiance derived from real-time modelling techniques and verification with ground-based measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumka, U.C.; Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Ningombam, S.S.; Masoom, A. Impact of Aerosol and Cloud on the Solar Energy Potential over the Central Gangetic Himalayan Region. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoom, A.; Kosmopoulos, P.; Bansal, A.; Kazadzis, S. Solar energy estimations in india using remote sensing technologies and validation with sun photometers in urban areas. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoom, A.; Kosmopoulos, P.; Kashyap, Y.; Kumar, S.; Bansal, A. Rooftop photovoltaic energy production management in india using earth-observation data and modeling techniques. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, M.A.; Mishra, A.K.; Sharma, S.; Mayer, I.A.; Ahmad, M. Source profiling of air pollution and its association with acute respiratory infections in the Himalayan-bound region of India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 68600–68614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhawish, A.; Sarangi, C.; Babu, P.; Kumar, M.; Bilal, M.; Qiu, Z. Remote Sensing of Environment Observational evidence of elevated smoke layers during crop residue burning season over Delhi: Potential implications on associated heterogeneous PM 2.5 enhancements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Yin, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Predict the effect of meteorological factors on haze using BP neural network. Urban Clim. 2023, 51, 101630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Liu, S.; Yang, B.; Zheng, W. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Haze in Beijing Based on the Multi-Convolution Model. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumka, U.C.; Tiwari, S.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Hopke, P.K.; Singh, J.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bisht, D.S.; Attri, S.D.; Tyagi, S.; Misra, A.; et al. Assessment of PM2.5 chemical compositions in Delhi: Primary vs secondary emissions and contribution to light extinction coefficient and visibility degradation. J. Atmos. Chem. 2017, 74, 423–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Dey, S.; Rawat, P.; Mukherjee, A.; Mao, J.; Jia, S.; Khillare, P.S.; Yadav, A.K.; Sarkar, S. Optical properties of aerosol brown carbon (BrC) in the eastern Indo-Gangetic Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Jia, S.; Sarkar, S. Black carbon aerosol in India: A comprehensive review of current status and future prospects. Atmos. Res. 2019, 218, 207–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikkina, P.; Bikkina, S.; Kawamura, K.; Sudheer, A.K.; Mahesh, G.; Kumar, S.K. Evidence for brown carbon absorption over the Bay of Bengal during the southwest monsoon season: A possible oceanic source. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 1743–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Choudhary, R.K.; Upadhyay, A.; Dash, S.K. Aerosol-modulated heat stress in the present and future climate of India. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 124022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, B.; Sarin, M.M. Brown carbon in atmospheric outflow from the Indo-Gangetic Plain: Mass absorption efficiency and temporal variability. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, B.; Sarin, M.M. PM2.5, EC and OC in atmospheric outflow from the Indo-Gangetic Plain: Temporal variability and aerosol organic carbon-to-organic mass conversion factor. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, N.; Haque, M.A.; Rahman, A.K.M.F.; Khalequzzaman, M.; Mashreky, S.R. Association of biomass fuel smoke exposure and hypertension among rural women of Bangladesh: A cross-sectional study. Indian J. Public Health 2019, 63, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaishya, A.; Singh, P.; Rastogi, S.; Babu, S.S. Aerosol black carbon quantification in the central Indo-Gangetic Plain: Seasonal heterogeneity and source apportionment. Atmos. Res. 2017, 185, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, B.; Rastogi, N.; Sarin, M.M.; Singh, A.; Singh, D. Mass absorption efficiency of light absorbing organic aerosols from source region of paddy-residue burning emissions in the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 125, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H. Library Software Awareness: A Survey of OPAC vs Card Catalogue in IIT Delhi, IIT Kanpur, and Kashmir University. DESIDOC J. Libr. Inf. Technol. 2014, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.A.; Romshoo, S.A.; Beig, G. Aerosol black carbon at an urban site-Srinagar, Northwestern Himalaya, India: Seasonality, sources, meteorology and radiative forcing. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinjamuri, K.S.; Mhawish, A.; Banerjee, T.; Sorek-Hamer, M.; Broday, D.M.; Mall, R.K.; Latif, M.T. Vertical distribution of smoke aerosols over upper Indo-Gangetic Plain. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, S.; Rupakheti, M.; Lawrence, M.G. Black carbon dominates the aerosol absorption over the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayan foothills. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanakidou, M.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N.; Barnes, I.; Dentener, F.J.; Facchini, M.C.; Van Dingenen, R.; Ervens, B.; Nenes, A.; Nielsen, C.J.; et al. Organic aerosol and global climate modelling: A review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 1053–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satish, R.; Rastogi, N.; Singh, A.; Singh, D. Change in characteristics of water-soluble and water-insoluble brown carbon aerosols during a large-scale biomass burning. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 33339–33350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamjad, P.M.; Satish, R.V.; Thamban, N.M.; Rastogi, N.; Tripathi, S.N. Absorbing Refractive Index and Direct Radiative Forcing of Atmospheric Brown Carbon over Gangetic Plain. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2018, 2, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Sarawade, P.; Adhikary, B. Carbonaceous aerosol from open burning and its impact on regional weather in South Asia. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, C.; Andersson, A.; Kirillova, E.N.; Budhavant, K.; Tiwari, S.; Praveen, P.S.; Russell, L.M.; Beres, N.D.; Ramanathan, V.; Gustafsson, Ö. Source-diagnostic dual-isotope composition and optical properties of water-soluble organic carbon and elemental carbon in the South Asian outflow intercepted over the Indian Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 11743–11759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, V.; Rajput, P.; Gupta, T. Absorption properties and forcing efficiency of light-absorbing water-soluble organic aerosols: Seasonal and spatial variability. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 115932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, V.; Singh, G.K.; Gupta, T.; Paul, D. Absorption and radiative characteristics of brown carbon aerosols during crop residue burning in the source region of Indo-Gangetic Plain. Atmos. Res. 2021, 249, 105285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, V.; Rajput, P.; Singh, D.K.; Singh, A.K.; Gupta, T. Light absorption characteristics of brown carbon during foggy and non-foggy episodes over the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillova, E.N.; Andersson, A.; Tiwari, S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bisht, D.S.; Gustafsson, Ö. Water-soluble organic carbon aerosols during a full New Delhi winter: Isotope-based source apportionment and optical properties. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 3476–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillova, E.N.; Marinoni, A.; Bonasoni, P.; Vuillermoz, E.; Facchini, M.C.; Fuzzi, S.; Decesari, S. Light absorption properties of brown carbon in the high Himalayas. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 9621–9639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Tripathi, S.N.; Lalchandani, V.; Rupakheti, M.; Bhowmik, H.S.; Shukla, A.K.; Murari, V.; Sahu, R.; Jain, V.; Tripathi, N.; et al. Air pollution in new delhi during late winter: An overview of a group of campaign studies focusing on composition and sources. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, A.; Bhattu, D.; Canonaco, F.; Lalchandani, V.; Shukla, A.; Thamban, N.M.; Mishra, S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bisht, D.S.; Tiwari, S.; et al. Chemical characterization of PM2.5 and source apportionment of organic aerosol in New Delhi, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Kumar, S.; Singh, A.K. Elevated black carbon concentrations and atmospheric pollution around singrauli coal-fired thermal power plants (India) using ground and satellite data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Mehrotra, B.J.; Singh, A.; Singh, V.; Bisht, D.S.; Tiwari, S.; Srivastava, M.K. Implications of different aerosol species to direct radiative forcing and atmospheric heating rate. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 241, 117820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.; Hsu, N.C.; Kafatos, M. Annales Geophysicae Aerosol and rainfall variability over the Indian monsoon region: Distributions, trends and coupling. Sci. Technol. 2009, 27, 3691–3703. [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarty, K.; Vincent, V.; Vellore, R.; Srivastava, A.K.; Rastogi, A.; Soni, V.K. Revisiting Andhi in northern India: A case study of severe dust-storm over the urban megacity of New Delhi. Urban Clim. 2021, 37, 100825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Srivastava, A.K.; Pathak, V.; Shukla, A.K. Quantifying the impact of biomass burning and dust storm activities on aerosol characteristics over the Indo-Gangetic Basin. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 270, 118893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, K.K.; Babu, S.S.; Satheesh, S.K.; Srinivasan, J.; Dutt, C.B.S. Dust absorption over the “Great Indian Desert” inferred using ground-based and satellite remote sensing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Kumar, M.; Singh, R.S.; Rai, B.N.; Mall, R.K.; Banerjee, T. Long-term observation of black carbon aerosols at an urban location over the central Indo-Gangetic Plain, South Asia. Atmosfera 2019, 32, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Xu, J.; Shen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, A.; Piao, S. Enhanced habitat loss of the Himalayan endemic flora driven by warming-forced upslope tree expansion. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 6, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Han, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, M.; Jian, B.; Huang, Z.; Yan, H. Climatology of dust-forced radiative heating over the Tibetan Plateau and its surroundings. J. Geophys. Res. 2020, 125, e2020JD032942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, W.C.; Schichtel, B.A.; Pitchford, M.L. Uncertainties in PM2.5 gravimetric and speciation measurements and what we can learn from them. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 61, 1131–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dumka, U.C.; Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Baxevanaki, E.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Huda, M.N.; Khan, M.F.; Bilal, M.; Ambade, B.; Khanal, S.; Munshi, P. Surface Radiative Forcing as a Climate-Change Indicator in North India due to the Combined Effects of Dust and Biomass Burning. Fire 2023, 6, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6090365
Dumka UC, Kosmopoulos PG, Baxevanaki E, Kaskaoutis DG, Huda MN, Khan MF, Bilal M, Ambade B, Khanal S, Munshi P. Surface Radiative Forcing as a Climate-Change Indicator in North India due to the Combined Effects of Dust and Biomass Burning. Fire. 2023; 6(9):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6090365
Chicago/Turabian StyleDumka, Umesh Chandra, Panagiotis G. Kosmopoulos, Effrosyni Baxevanaki, Dimitris G. Kaskaoutis, Muhammad Nurul Huda, Md Firoz Khan, Muhammad Bilal, Balram Ambade, Sujan Khanal, and Pavel Munshi. 2023. "Surface Radiative Forcing as a Climate-Change Indicator in North India due to the Combined Effects of Dust and Biomass Burning" Fire 6, no. 9: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6090365
APA StyleDumka, U. C., Kosmopoulos, P. G., Baxevanaki, E., Kaskaoutis, D. G., Huda, M. N., Khan, M. F., Bilal, M., Ambade, B., Khanal, S., & Munshi, P. (2023). Surface Radiative Forcing as a Climate-Change Indicator in North India due to the Combined Effects of Dust and Biomass Burning. Fire, 6(9), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire6090365













