Abstract
Longitudinal ventilation and smoke extraction by shaft are common smoke control methods in road tunnel fires. Tunnels often adopt one of these methods in practical engineering. However, it may have a better effect to adopt the method of mixing the two smoke exhaust methods together, which has not been revealed in the previous literature. Hence, the coupled effects of longitudinal ventilation and natural ventilation with shafts on the smoke control in tunnel fires were studied in this work. Numerical simulation was carried out considering different longitudinal ventilation velocities (0–4 m/s) and 4 kinds of typical shaft arrangements (shaft lengths range of 3–12 m, shaft intervals range of 27–60 m). The smoke spread length and smoke exhaust efficiency were analyzed systematically. Results show that (1) with the increase in longitudinal ventilation velocity, the total smoke spread length firstly decreases (V < 1 m/s) and then keeps almost constant (1 m/s < V < 2 m/s), finally increasing significantly (V > 2 m/s). (2) The length of the dangerous area (over 60 °C) at human height is basically 0 for all cases (except for Scenario 4 of shaft arrangement) when the longitudinal ventilation velocity is less than 2 m/s. (3) The CO smoke flow rate through the shaft is relatively high when the longitudinal ventilation velocity is within the range of 1–2 m/s for 4 kinds of shaft arrangement scenarios. Factors such as smoke spread and smoke exhausted through the shaft are comprehensively considered to judge smoke exhaust performance. The following conclusions can be drawn: when the ventilation velocity ranges from 1–2 m/s, it has a positive impact on the smoke control in tunnel fires with natural ventilation with shafts. When the ventilation velocity exceeds 2 m/s, the total smoke spread length and the length of the danger area increase, and the smoke stratification becomes worse, which brings inconvenience to rescue work. The results can provide reference for the design of fire protection in tunnels.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, tunnel engineering has developed rapidly due to its great improvement in travel efficiency. At the same time, it also brings great fire risk, and tunnel fire accidents occur from time to time. Due to its long and narrow structure, it is easy for the smoke to accumulate in tunnel fires. Large numbers of statistics have shown that high temperature and toxic gases prohibit the evacuation of occupants [1,2,3]. There are mainly two sorts of ventilation modes, i.e., longitudinal ventilation and natural ventilation [4].
Longitudinal ventilation is the most common method for smoke control in tunnel fires, which has been studied by a great number of scholars in the past few decades. Wu et al. [5] studied the effects of fire heat release rate and tunnel geometry on the critical ventilation velocity by conducting numerical simulations, and an empiric formula for predicting critical velocity was obtained. Ingason et al. [6] studied the smoke back-layering length and critical velocity with small-scale experiments, and the relation between the critical velocity and fire heat release rate was discussed. Zhong et al. [7] studied the bifurcation behavior of smoke in bifurcated tunnels with longitudinal ventilation. Through analyzing the effect of longitudinal ventilation velocity on the smoke flow field, temperature distribution and height of the smoke layer, the generation mechanism of smoke bifurcation flow was revealed. Lee et al. [8] studied the effects of tunnel cross-section on critical velocity by conducting a set of reduced-scale experiments, and the results showed that the critical velocity increases with the aspect ratio of the tunnel section. Xu et al. [9] numerically studied the maximum smoke temperature and temperature distribution under different longitudinal ventilation velocities, and the results showed that with the increase in ventilation velocity, the temperature near the fire will drop, and the temperature along the tunnel will increase. Yao et al. [10] proposed the concept of turning velocity VT for the first time, and when , the smoke back-layering length will decrease with the decreasing pressure. When (critical velocity), the smoke back-layering length will increase with the decreasing pressure.
The longitudinal ventilation can provide a smoke-free space for both the passengers and fire fighters by preventing the smoke from spreading upstream. However, the strong longitudinal ventilation can destroy the stratification structure of the smoke layer and then hamper the processes of evacuation and rescue work. Newman [11] evaluated the fire-induced smoke stratification in a medium-scale coal lane. Results indicated that three regions of varying degrees of stratification can be identified in terms of specific Froude number values. Region I is the buoyancy-dominated temperature stratification where the gas temperature near the floor is essentially ambient (Fr < 0.9); Region II is dominated by strong interaction between imposed horizontal flow and buoyancy forces. Although not severely stratified or layered, it has vertical temperature gradients (0.9 ≤ Fr ≤ 10); Region III has insignificant vertical temperature gradients and consequently insignificant stratification (Fr > 10).
As an effective alternative, natural ventilation by use of short vertical shafts (roof openings) in road tunnels has been applied in the last decade. Wang et al. [12] studied the effects of shaft dimension on the smoke propagation in tunnel fires by conducting a series of full-scale experiments. The effects of the shafts dimension on back-layering length were analyzed and a prediction model of smoke back-layering length was established. Yao et al. [13] numerically studied the overall smoke control of natural ventilation with vertical shafts. The shafts’ length and interval were considered in detail, and the results showed that the total exhaust area of shafts that is required to exhaust all the smoke is about 100 m2, and the first shaft pair plays a critical role in exhausting the smoke. Fan et al. [14] studied the influence of shaft dimension and amount on natural ventilation performance during tunnel fires by conducting numerical simulations, and the results showed that the total mass flow rate of smoke exhausted by shafts increases with the shaft amount under a given total area of shafts. Yuan et al. [15] studied the effects of fire size, shaft distance, shaft geometry, train blockage on ceiling temperature distributions and smoke exhaust from shafts by conducting a set of small-scale experiments, and the empirical equations for predicting ceiling temperature distributions and smoke exhaust were derived. Wang et al. [16] studied the suitable smoke extraction strategy considering three types of locations of the fire source, and the results showed that the temperature at the junction of the main tunnel and shaft is higher without the ventilation system. The fitting formulas of supply velocities for three HRRs are expressed. Zhong et al. [17] studied the influence of longitudinal wind on the smoke flow characteristics in natural ventilation with a vertical shaft by using FDS, and the results showed that plug-holing occurs at small longitudinal velocity and causes the reduction of the exhaust effect. Tong et al. [18] studied the smoke flow in natural ventilation road tunnel fires with shafts by conducting 3 full-scale experiments, and the results showed that large amounts of smoke and heat are released through shafts near the fire source, and the maximum smoke temperature beneath the ceiling is lower than 110 °C at the safe height farther than 3 m away from fires. Guo et al. [19] numerically studied the smoke back-layering length in a naturally ventilated tunnel by considering different HRRs and shaft intervals, and the results indicated that the smoke back-layering length is independent of the HRRs. Yao et al. [20] studied the effects of shaft inclination angle and shaft height on the capacity of smoke exhaust by FDS. It was found that the low and slightly tilted shaft can improve the capacity of smoke exhaust.
Studies on the performance of longitudinal ventilation and natural ventilation with multiple shafts were always carried out, respectively. However, the coupled effects of longitudinal ventilation and natural ventilation with shafts on the overall smoke control performance in tunnels have not been studied systematically. In fact, this hybrid ventilation and smoke control mode is also a potential smoke control method in tunnel fires. Therefore, this paper studies the overall smoke control of longitudinal ventilation coupled with natural ventilation systems with shafts in road tunnel fires by numerical modelling. The variables considered in the current study include the shaft length (size), interval (spacing distance) between two shafts and ventilation velocity.
2. Numerical Modeling
Due to the rapid development of computational techniques, Fire Dynamics Simulator (FDS) software developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST, USA) [21] has been widely used to study the smoke thermal characteristics in different building fires and is regarded as an effective tool for simulating fire smoke behavior [22]. The accuracy of FDS in predicting smoke diffusion characteristics in tunnel fires has been confirmed by many experimental results. For example, Gannouni et al. [23] compared the critical velocity for stopping smoke spread upstream between the FDS numerical results and experimental measurements and found that the simulations are in acceptable agreement with the experiments. Weng et al. [24] compared the dimensionless back-layering length between the FDS simulations and the model-scale experiments, and the comparison showed an acceptable agreement. Liu et al. [25] compared the longitudinal temperature distribution between FDS simulation and the full-scale experiment and found that the simulation results agree acceptably well with the experimental results.
2.1. Fire Scenarios
A full-scale road tunnel with dimensions of 450 m (length) × 10 m (width) × 5 m (height) was built in FDS, as shown in Figure 1. The material of the tunnel construction was assumed as concrete, and its density, conductivity and specific heat were 2280 kg/m3, 1.8 W/(m × K) and 1.04 kJ/(kg × K). “N-OCTANE” was used as the fire source, and the soot yield and CO yield were designed to be 0.1 and 0.05. The fire source was located 225 m away from the right portal of the tunnel at the centerline. A previous study has indicated that the smoke spread characteristic is closely independent of the heat release rate in tunnel fires with shafts [13]. The heat release rate was chosen to be 30 MW, which simulates more serious fire accidents, such as bus fires or truck fires. Furthermore, the 5 MW and 10 MW fires were simulated for comparison. The longitudinal ventilation was provided through the “Supply” surface on the left portal of the tunnel, where the velocity changed from 0–4.0 m/s with an interval of 0.4 m/s. The top boundaries of all the shafts were considered as “Open”. Following up the previous study [13], 4 kinds of typical shaft arrangements were considered, which are a 3 m long shaft with an interval of 27 m (Scenario 1), a 6 m long shaft with an interval of 42 m (Scenario 2), a 9 m long shaft with an interval of 27 m (Scenario 3) and a 12 m long shaft with an interval of 60 m (Scenario 4). Some other kinds of shaft arrangements were also simulated for a verification of conclusion. Tong et al. [26] surveyed the urban shallowly buried road tunnels and concluded that most of the height between the bottom and top of the vertical shaft used is approximately 4 m. Since the width of the shafts much depends on the road conditions, such as the width of green belt, the green belt width of the main road should not be less than 2.5 m according to the Chinese ‘Code for Planting Planning and Design on Urban Road’ [27]. After an investigation on the related design specifications and the widely used shaft sizes in full-scale road tunnels, the shaft height and width were fixed at 4 m and 3 m, respectively. Here, shafts were numbered as shaft 1, shaft -1, shaft 2, shaft -2, etc. Shaft 1 represents the first shaft in the downstream of the fire source, and shaft -1 represents the first shaft in the upstream of the fire source. A total of 63 fire cases were simulated, as summarized in Table 1.
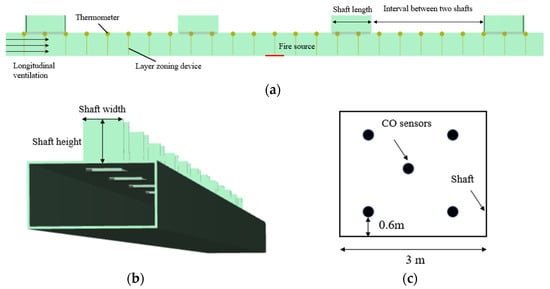
Figure 1.
The schematic drawings of the tunnel constructed in FDS. (a) Front view of the tunnel (only sections nearby fire are shown), (b) Side view of the tunnel, (c) Arrangement of CO sensors in the shaft.

Table 1.
A summary of all cases.
Ninety thermometers were positioned 0.1 m beneath the tunnel ceiling along the longitudinal centerline with an interval of 5 m. The mass flow devices were located at the top opening of the shaft to measure the exhaust rate through the shaft. Fifteen CO sensors were located evenly at the top opening of the shaft with the area of 3 × 9 m2 (20 for 3 × 12 m2 and 5 for 3 × 3 m2). Ninety layer-zoning devices were set at the centerline with an interval of 5 m to measure the smoke layer height. The specific arrangements of the measuring points are shown in Figure 1c. The top of the shafts and the right tunnel portal were set to be ‘‘OPEN’’ surface, which was connected with the external open environment. The ambient temperature was set to be 20 °C and the simulation time is 600 s.
2.2. Meshes
In FDS simulation, the grid size is a vital parameter. The smaller the grid size is, the more accurate the result is, but the smaller grid size will produce a longer computation time. Previous studies [28] have shown that when the ratio of the fire characteristic diameter to grid size D*/δx ranges from 4 to 16, the calculated results are more accurate [29].
For the heat release rate of 30 MW in this study, the characteristic diameter of the fire source is 3.74 m, and the grid size range proposed is 0.2–0.5 m. Five grid sizes from 0.2 m to 0.5 m were selected for comparison. In the case of grid independence analysis, there is no longitudinal ventilation, and the shaft length and interval are 9 m and 27 m, respectively. Figure 2 shows the vertical temperature distribution at 40 m away from the fire source for different grid sizes. The simulation time was 600 s. It is found that the temperature tends to be uniform with the decrease of grid size, and there is no significant improvement when the grid size decreases to 0.3 m. For the development of fire plume in the tunnel, computation accuracy in the vertical direction is more important than the horizontal direction. In order to save the computing time, the grid size in the vertical direction and the transverse direction was set to be 0.2 m, while in the longitudinal direction it was set to be 0.3 m.
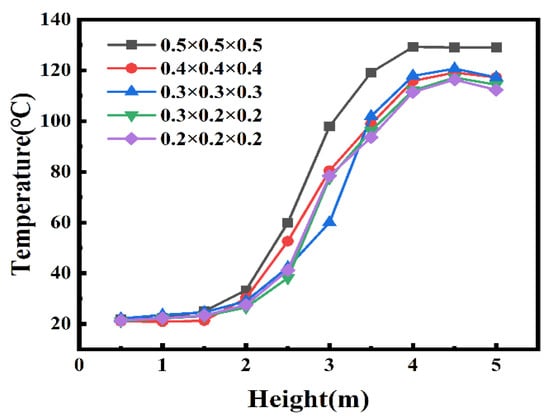
Figure 2.
Vertical temperature distribution for different grid sizes.
2.3. Verification of FDS Modelling
Simulation results were compared with the experimental data from the small-scale tests reported by Zhao et al. [30] in order to verify the numerical simulation. The model tunnel is 20 m long, 2 m wide and 1 m high. The fire source was located 2.5 m away from the entrance of the tunnel with a peak heat release rate of about 54.9 kW. Three shafts were set up along the tunnel, which were located 6.5 m, 11.5 m and 16.5 m from the portal of the tunnel. The shafts’ height is 1 m, and the shafts’ width is 0.4 m. Twenty thermocouples were placed 0.1 m beneath the ceiling along the tunnel with the interval of 1 m. The longitudinal ventilation velocity was 1.0 m/s. An identical tunnel was constructed using FDS for a comparison. Figure 3 presents the longitudinal temperature distribution beneath the tunnel ceiling between FDS simulations and small-scale tests. It is found that the longitudinal temperature distribution from simulations is basically consistent with that from experiments.
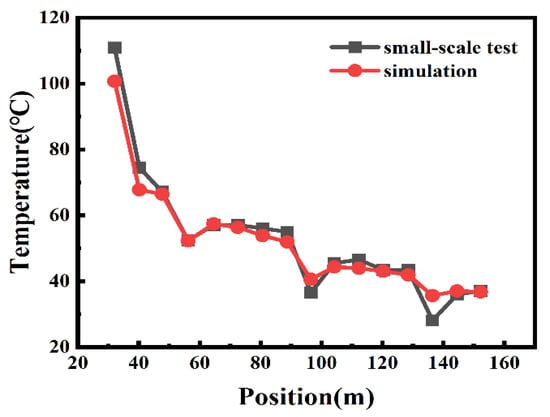
Figure 3.
Comparison of longitudinal temperature distribution beneath the tunnel ceiling between FDS simulation and small-scale test.
3. Results
3.1. Smoke Movement Behavior
3.1.1. Smoke Spread Length
Figure 4 shows the diffusion of smoke particles in the tunnel for the 30 MW fire in Scenario 3 (9 m long shaft with an interval of 27 m) under the ventilation velocities of 0 m/s, 2.0 m/s and 3.2 m/s. It is found that the smoke spread length on both sides of the fire source is symmetrical without longitudinal ventilation. However, in case of wind, under the inertial force of longitudinal ventilation, the smoke was inclined to the downstream of the fire source, and the smoke was mainly exhausted from the shaft at the downstream of the fire source. Meanwhile, due to the effect of longitudinal ventilation, the smoke layer near the fire source was disordered, and the height of the smoke layer reduced, which affects the safe evacuation of personnel.
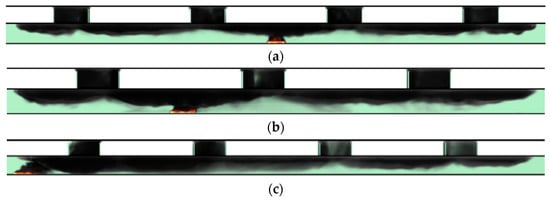
Figure 4.
Dispersion of smoke particles in the tunnel for heat release rate of 30 MW with ventilation velocity of 0 m/s, 2.0 m/s and 3.2 m/s. (a) 0 m/s, (b) 2.0 m/s, (c) 3.2 m/s.
Figure 5 shows the smoke back-layering length and total smoke spread length in Scenario 3 (9 m long shaft with an interval of 27 m) under different longitudinal ventilation velocities. It is found that the back-layering length of the fire source decreases with the increasing ventilation velocity. With the increase in ventilation velocity beyond 2 m/s, although the smoke spread length in the upstream of the fire source continues to decrease, the increasing inertial force makes the smoke spread length in the downstream increase significantly. With the increase in longitudinal ventilation velocity, the total smoke spread length firstly decreases and then keeps almost constant in the ventilation velocity range of 1–2 m/s, after which it starts to increase significantly, which indicates that it may have a better smoke exhaust effect when the longitudinal ventilation ranges from 1 m/s to 2 m/s.
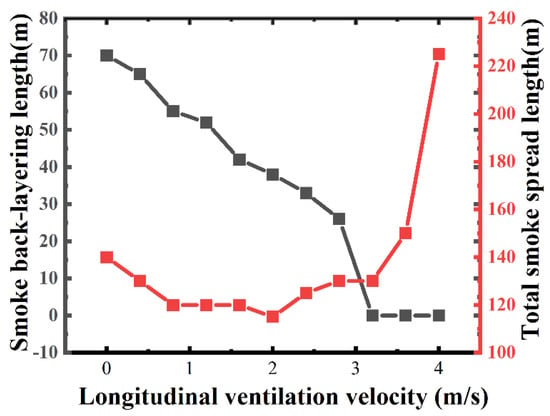
Figure 5.
Variation of smoke back−layering length and total smoke spread length under different longitudinal ventilation velocities.
Figure 6 shows the smoke back-layering length and total smoke spread length varied with longitudinal ventilation velocity under four kinds of shaft arrangement scenarios (L is the shaft length, and I is the shafts interval). It is found that with the increase in longitudinal ventilation velocity, the smoke back-layering length decreases gradually. It also can be seen that the smoke back-layering length and total smoke spread length in Scenario 3 are the shortest. This is because, except for the 3 m long shaft, the total exhaust area of shafts that is required to exhaust all the smoke is about 100 m2 according to the previous study [13]. While the number of shafts that is required to exhaust the smoke in the upstream of the fire source out of the tunnel is 3, 2, 2 and 2 for Scenarios 1–4, respectively, the distance between shafts in Scenario 3 is the shortest compared with the other scenarios. As a result, the high temperature under the shafts further enhances the stack effect of shafts, consequently exhausting more smoke and leaving a short smoke spread length.
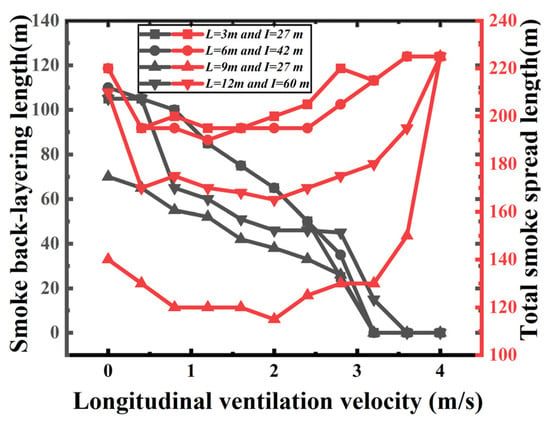
Figure 6.
Evolution of the smoke back−layering length and total smoke spread length under different longitudinal ventilation velocities for four kinds of shaft arrangement scenarios.
Furthermore, compared with the condition only using the shaft smoke exhaust mode, the average values of total smoke spread length under the coupling smoke exhaust mode decreases 10.5%, 11.4%, 15.7% and 39.5% for Scenarios 1–4, respectively, when the longitudinal ventilation ranges from 1 m/s to 2 m/s.
Figure 7 shows the total smoke spread length under different longitudinal ventilation velocities in Scenario 3 (9 m long shaft with an interval of 27 m), with the heat release rate of 5 MW and 10 MW. It can be seen that the total smoke spread length in both cases is basically the same, which indicates that the total smoke spread length is independent of the heat release rate. This is because when the heat release rate is larger, more smoke flow is produced, and the smoke temperature beneath the ceiling is also higher, indicating stronger thermal buoyancy and more smoke being exhausted by shafts. Meanwhile, when the heat release rate is smaller, less smoke is produced, and the thermal buoyancy of the smoke becomes smaller, leading to less smoke being exhausted by shafts. The result consists with Yao et al.’s study [13] and Ura et al.’s study [31].
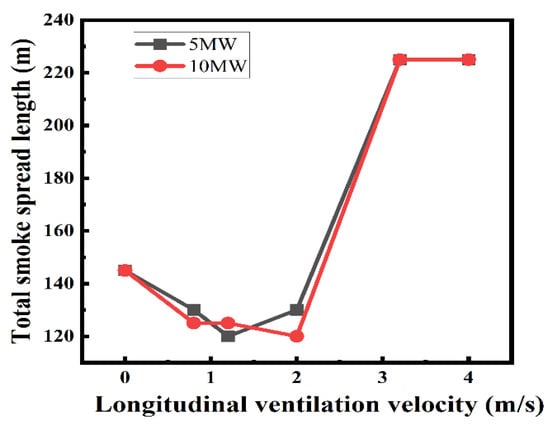
Figure 7.
Variation of the total smoke spread length with longitudinal ventilation velocity for heat release rate of 5 MW and 10 MW.
3.1.2. Smoke Temperature at Human Height
The smoke temperature at human height (1.8 m applied here) is also an important factor affecting escape and rescue work in tunnel fires, and the critical temperature is about 60 °C [32]. Taking Scenario 4 (12 m long shaft with an interval of 60 m) with ventilation velocity of 0 m/s and 2.8 m/s as an example, Figure 8 shows the temperature field of vertical cross-section along the longitudinal tunnel for the heat release rate of 30 MW. It is found that the temperature at human height is around 40 °C under natural ventilation conditions with good smoke stratification. However, the temperature distribution is asymmetric with the longitudinal ventilation velocity of 2.8 m/s, where the temperature upstream of the fire source is close to the ambient temperature, and the temperature downstream of the fire source is relatively high.
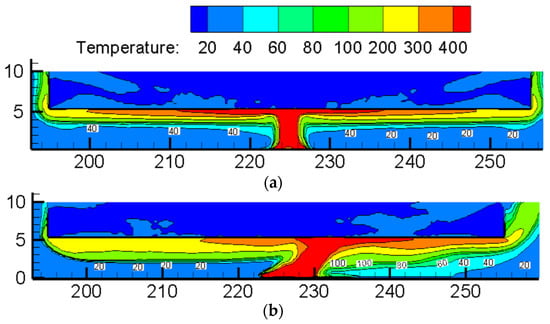
Figure 8.
Temperature field of vertical cross-section along the longitudinal tunnel for heat release rate of 30 MW (Unit: °C). (a) 0 m/s, (b) 2.8 m/s.
Using the same method, the length of the dangerous area (over 60 °C) at human height under all cases is shown in Figure 9. It is found that the temperature at human height is basically less than 60 °C for all cases with a ventilation velocity less than 1 m/s. With the increase in ventilation velocity from 1 m/s–2 m/s, the length of the danger area increases gradually in Scenario 4, but it is still less than 5 m altogether. When the longitudinal ventilation velocity ranges from 2 m/s to 3 m/s, the length of the danger area increases sharply, even reaching 20 m in Scenarios 1 and 4.
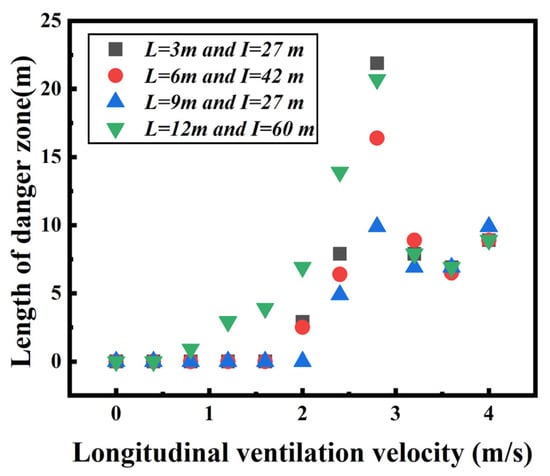
Figure 9.
Evolution of the length of the danger area under different longitudinal ventilation velocities.
3.2. Smoke Exhaust Performance
3.2.1. Mass Flow Rate of Smoke Exhaust through Shaft
The mass flow rate of CO through shafts is one of the most important parameters to determine their capacity of smoke exhaust, which can be expressed as:
Here, is mass flow rate of smoke, and is CO mass fraction. The average value during the stable period is used for analysis.
Figure 10 shows the mass flow rate of smoke against the longitudinal ventilation velocity for four kinds of shaft arrangement scenarios. It is found that the mass flow rate of smoke increases gradually with the increasing ventilation velocity for each shaft arrangement scenario. This is attributed to the fact that more ambient air is exhausted through those shafts under the effect of longitudinal ventilation: the larger the longitudinal ventilation, the larger the mass flow rate of smoke.
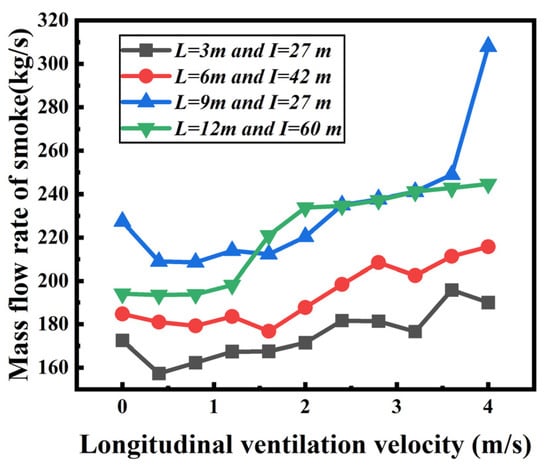
Figure 10.
Variation of mass flow rate of smoke under different longitudinal ventilation velocities.
Figure 11 shows the average CO mass fraction at the openings of shafts against longitudinal ventilation velocity for four kinds of shaft arrangement scenarios. It is found that the CO mass fraction decreases gradually with the increasing ventilation velocity due to the stronger air entrainment, and the CO mass fraction in Scenario 1 is larger than the other scenarios. This is because the shaft length in Scenario 1 is shorter compared with the other scenarios: the plug-holing is less likely to occur, the smoke can fill the shaft, and it can be exhausted more effectively.
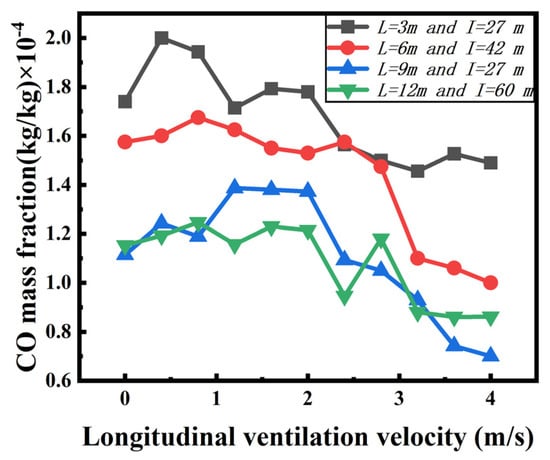
Figure 11.
Variation of CO mass fraction under different longitudinal ventilation velocities.
Figure 12 shows the CO smoke flow rate against longitudinal ventilation velocity for four kinds of shaft arrangement scenarios, which is the sum of CO smoke flow rate at the openings of all shafts. It is found that the CO smoke flow rate first increases with increasing ventilation velocity before 1 m/s, then keeps almost unchanged. However, when the ventilation velocity is more than 3 m/s, the CO smoke flow rate drops sharply. Additionally, the CO smoke flow rate in Scenario 1 is larger than the other scenarios. This is because the plug-holing is less likely to occur with the shorter shaft length, and the smoke can be exhausted more effectively, relatively.
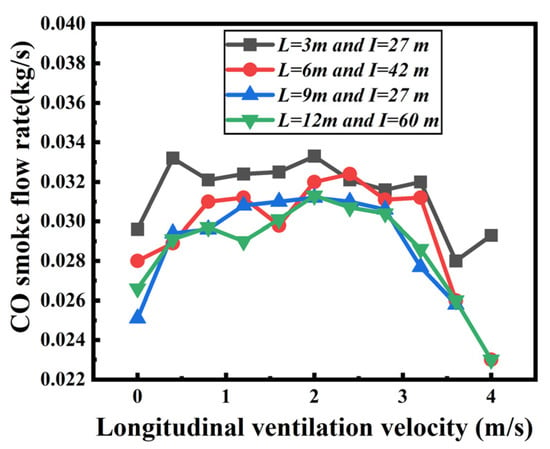
Figure 12.
CO smoke flow rate under different longitudinal ventilation velocities.
3.2.2. Smoke Exhaust Efficiency
The smoke exhaust efficiency is also one of the most important parameters to reflect the natural ventilation performance with shafts, which can be expressed by the ratio of the mass flow rate of CO exhausted by each shaft to the total mass flow rate of CO produced from the fire source [13]. Figure 13 shows the smoke exhaust efficiency of each shaft under different longitudinal ventilation velocities (0 m/s, 1.2 m/s, 2.4 m/s and 3.2 m/s) for 4 kinds of shaft arrangement scenarios. It is found that for the natural ventilation condition (V = 0 m/s), the smoke exhaust efficiency in each shaft is basically symmetrical on both sides of the fire source. The exhaust efficiency of the shaft decreases with the increase in the distance between the shaft and the fire source. Namely, the first shaft pair (shaft −1 and shaft 1) plays the most important role in exhausting smoke. Especially for the longer shafts, such as 9 m and 12 m, the exhaust efficiency reaches up to 0.6 and 0.9, respectively. With the increase in longitudinal ventilation velocity, the smoke back-layering length decreases, and, thereby, the available shafts in the upstream of the fire source used for exhaust decreases. As a result, the smoke exhaust efficiency in each shaft on both sides of the fire source is not symmetrical. For a moderate ventilation velocity (such as 1.2 m/s for the 9 m and 12 m long shaft), the smoke exhaust efficiency in the first shaft pair on both sides of the fire source increases significantly, exceeding 0.8 and 0.95, respectively. This means that a moderate ventilation velocity can effectively improve the smoke exhaust efficiency for those shafts near the fire source. However, when the ventilation velocity approaches the critical velocity, the smoke exhaust efficiency of the first shaft in the upstream of the fire source decreases to a low level, and the smoke exhaust efficiency of the first shaft in the downstream increases significantly, which is over 30%, 60%, 50% and 80% for four kinds of shaft arrangement scenarios, respectively.
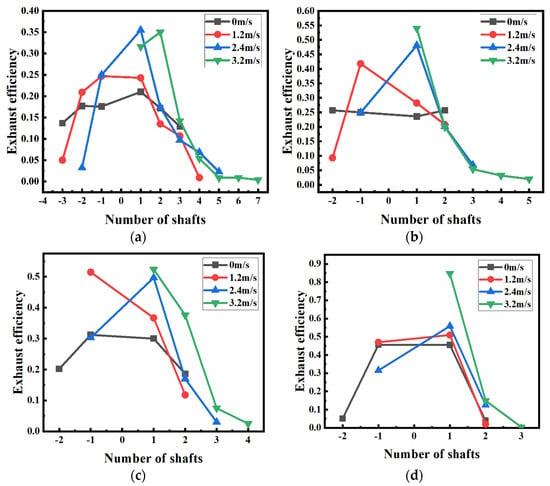
Figure 13.
Exhaust efficiency of each shaft for four kinds of shaft arrangement scenarios. (a) Scenario 1 (b) Scenario 2 (c) Scenario 3 (d) Scenario 4.
4. Conclusions
This paper numerically studied the coupled effects of longitudinal ventilation and natural ventilation with shafts on smoke control in tunnel fires. The smoke spread length and smoke exhaust effect were analyzed systematically. The main findings are as follows:
- (1)
- With the increase in longitudinal ventilation velocity, the total smoke spread length firstly decreases (V < 1 m/s) and then keeps almost constant (1 m/s < V < 2 m/s), fi-nally increasing significantly (V > 2 m/s).
- (2)
- The length of the dangerous area (over 60 °C) at human height is basically 0 for all cases (except for Scenario 4 of shaft arrangement) when the longitudinal ventilation velocity is less than 2 m/s.
- (3)
- The CO smoke flow rate through the shaft is relatively high when the longitudinal ventilation velocity is within the range of 1–2 m/s for 4 kinds of shaft arrangement scenarios.
From the above analysis, it is found that when the ventilation velocity ranges from 1–2 m/s, it has a positive impact on smoke control in tunnel fires. When the ventilation velocity exceeds 2 m/s, the total smoke spread length and the length of the danger area increase, and the smoke stratification becomes worse, which brings inconvenience to rescue work. Furthermore, arranging the shafts according to Scenario 3 (9 m long shaft with an interval of 27 m) is better than other situations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Y.; methodology, Y.Y.; software, Y.W.; validation, Y.Y. and Y.W.; formal analysis, L.C. and F.R.; investigation, Y.Y. and Y.W.; resources, Y.Y. and C.S.; data curation, Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Y. and Y.W.; writing—review and editing, Y.Y., Y.W., L.C., F.R. and C.S.; supervision, C.S.; project administration, F.R.; funding acquisition, Y.Y. and F.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [No. 52206186&52006204] and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities [No. 2022JCCXAQ05].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
We thank China University of Mining & Technology, Beijing and China Academy of Safety Science and Technology for the basic research conditions provided for this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ji, J.; Gao, Z.H.; Fan, C.G.; Sun, J.H. Large Eddy Simulation of stack effect on natural smoke exhausting effect in urban road tunnel fires. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 66, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.Z.; Qu, B.L.; Zhu, H.Q.; Wang, J.X.; Zhao, S.Z.; Wang, Q. Theoretical and numerical study on critical velocity and driving force for preventing smoke backlayering in a connection roadway fire of coal mines. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 127, 104566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.N.; Guo, X.H.; Ni, G.B.; Yu, L.; Li, C.H. A Discussion on the Control Standards for Smoke CO Concentration during Fires in High-altitude Railway Tunnels. Mod. Tunn. Technol. 2022, 59, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.H. Studies on Thermal Physics of Smoke Movement in Tunnel Fires. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Bakar, M. Control of smoke flow in tunnel fires using longitudinal ventilation systems—A study of the critical velocity. Fire Saf. J. 2000, 35, 363–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingason, H.; Li, Y.Z. Model scale tunnel fire tests with longitudinal ventilation. Fire Saf. J. 2010, 45, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Lv, J.J.; Li, Z.Z.; Liang, T.S. A study of bifurcation flow of fire smoke in tunnel with longitudinal ventilation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 67, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, R.L.; Hong, R. An Experimental Study of the Effect of the Aspect Ratio on the Critical Velocity in Longitudinal Ventilation Tunnel Fires. J. Fire Sci. 2005, 23, 119–138. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.S.; Li, D.J.; Xue, P.; Zhao, H.L. Study on Fire Temperature Field Distribution in Longitudinal Ventilation Tunnel. China Saf. Sci. J. 2010, 20, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.Q.; Han, Z.Q. Effects of ambient pressure on characteristics of smoke movement in tunnel fires. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 134, 104981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.S. Experimental evaluation of fire-induced stratification. Combust. Flame 1984, 57, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Yan, P.N.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, J.C. Thermal buoyant smoke back-layering length in a naturally ventilated tunnel with vertical shafts. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 93, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.Z.; Li, Y.Z.; Ingason, H.; Cheng, X. Numerical study on overall smoke control using naturally ventilated shafts during fires in a road tunnel. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 140, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.G.; Ji, J.; Wang, W.; Sun, J.H. Effects of vertical shaft arrangement on natural ventilation performance during tunnel fires. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 73, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Lei, B.; Kashef, A. Experimental and Theoretical Study for Tunnel Fires with Natural Ventilation. Fire Technol. 2013, 51, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.N.; Guo, X.H.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.T.; Tian, Y. Experimental and numerical studies on the smoke extraction strategies by longitudinal ventilation with shafts during tunnel fire. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 116, 1034030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Fan, C.G.; Ji, J.; Yang, J.P. Influence of longitudinal wind on natural ventilation with vertical shaft in a road tunnel fire. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 57, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Shi, M.H.; Gong, Y.F.; He, J.P. Full-scale experimental study on smoke flow in natural ventilation road tunnel fires with shafts. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2009, 24, 627–633. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.H.; Zhu, H.H.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Z.G. Theoretical and experimental studies on the fire-induced smoke flow in naturally ventilated tunnels with large cross-sectional vertical shafts. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 99, 103359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.Z.; Zhang, S.G.; Shi, L.; Cheng, X.D. Effects of shaft inclination angle on the capacity of smoke exhaust under tunnel fire. Indoor Built Environ. 2019, 28, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.B.; Li, Y.F.; Dong, B.Y.; Li, J.M.; Liang, Q. Numerical investigation on the maximum ceiling temperature and longitudinal decay in a sealing tunnel fire. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 72, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jae, S.R.; Hong, S.R.; Dong, H.K.; Woo, S.J.; Yong, J.J. Critical velocity and burning rate in pool fire during longitudinal ventilation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2007, 22, 262–271. [Google Scholar]
- Gannouni, S.; Maad, R. Numerical study of the effect of blockage on critical velocity and backlayering length in longitudinally ventilated tunnel fires. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2015, 48, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, M.C.; Lu, X.L.; Liu, F.; Shi, X.P.; Yu, L.X. Prediction of backlayering length and critical velocity in metro tunnel fires. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2015, 47, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Mao, J.; Xi, Y.H.; Hu, J.W. Effects of altitude on smoke movement velocity and longitudinal temperature distribution in tunnel fires. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 112, 103850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Zhai, J.; Wang, C.; Zhou, B.; Niu, X. Possibility of using roof openings for natural ventilation in a shallow urban road tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 54, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Development. CJJ75-97, Code for Planting Planning and Design on Urban Road; China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 1997.
- Fan, C.G.; Zhang, L.; Jiao, S.C.; Yang, Z.W.; Li, M.H.; Liu, X.P. Smoke spread characteristics inside a tunnel with natural ventilation under a strong environmental wind. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 82, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgrattan, K.B.; Hostikka, S.; Floyd, J.E. Fire Dynamics Simulator (Version 5): User’s Guide; NIST Special Publications: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2010; Volume 4, pp. 206–207. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.Z.; Li, Y.Z.; Ingason, H.; Liu, F. A theoretical and experimental study on the buoyancy-driven smoke flow in a tunnel with vertical shafts. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 141, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ura, F.; Kawabata, N.; Tanaka, F. Characteristics of smoke extraction by natural ventilation during a fire in a shallow urban road tunnel with roof openings. Fire Saf. J. 2014, 67, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehandler, J.; Eymann, L.; Regeffe, M. Limit-Based Fire Hazard Model for Evaluating Tunnel Life Safety. Fire Technol. 2015, 51, 585–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).