Figure 2.
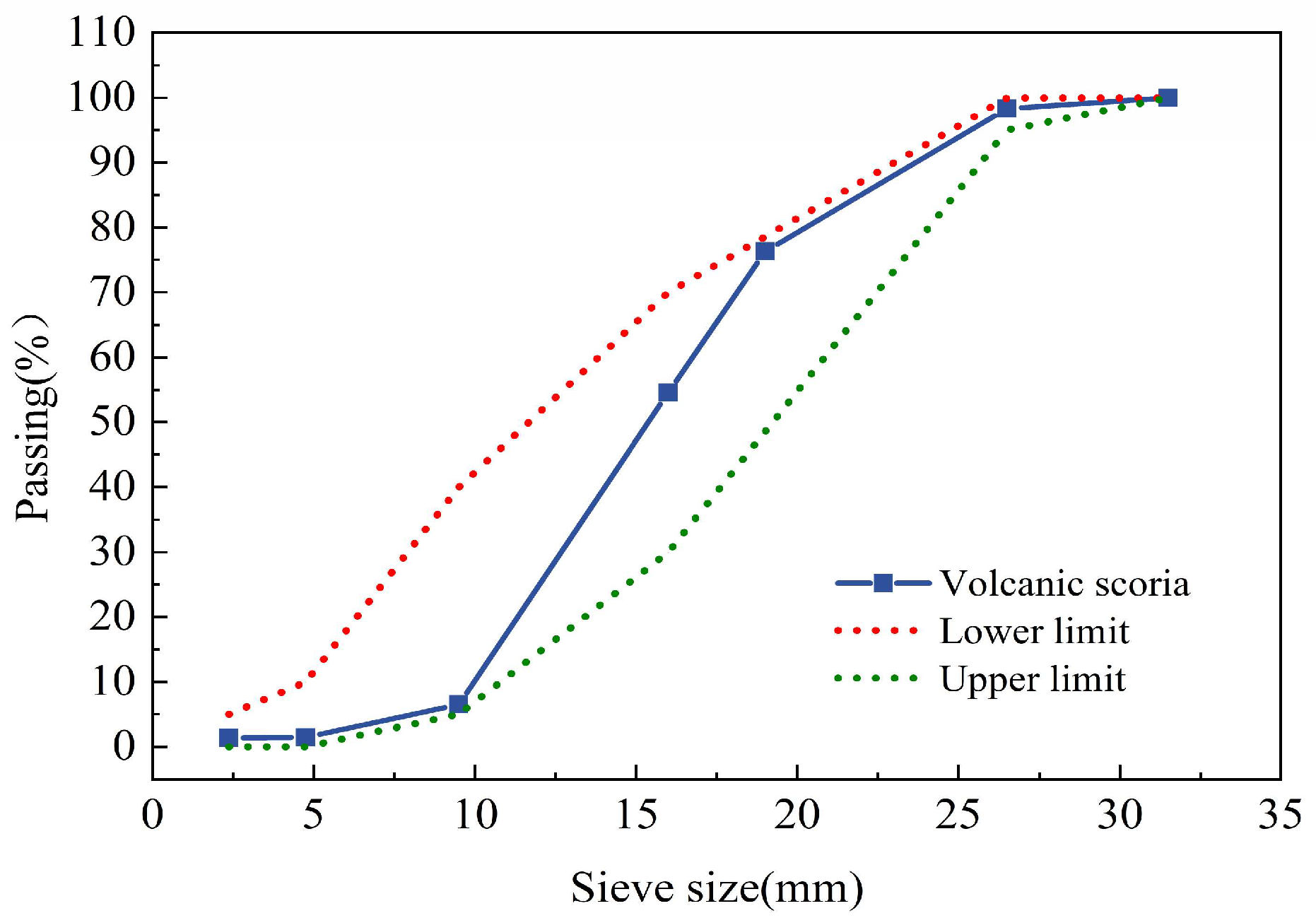
Grading curves of volcanic scoria aggregate.
Figure 2.
Grading curves of volcanic scoria aggregate.
Figure 3.
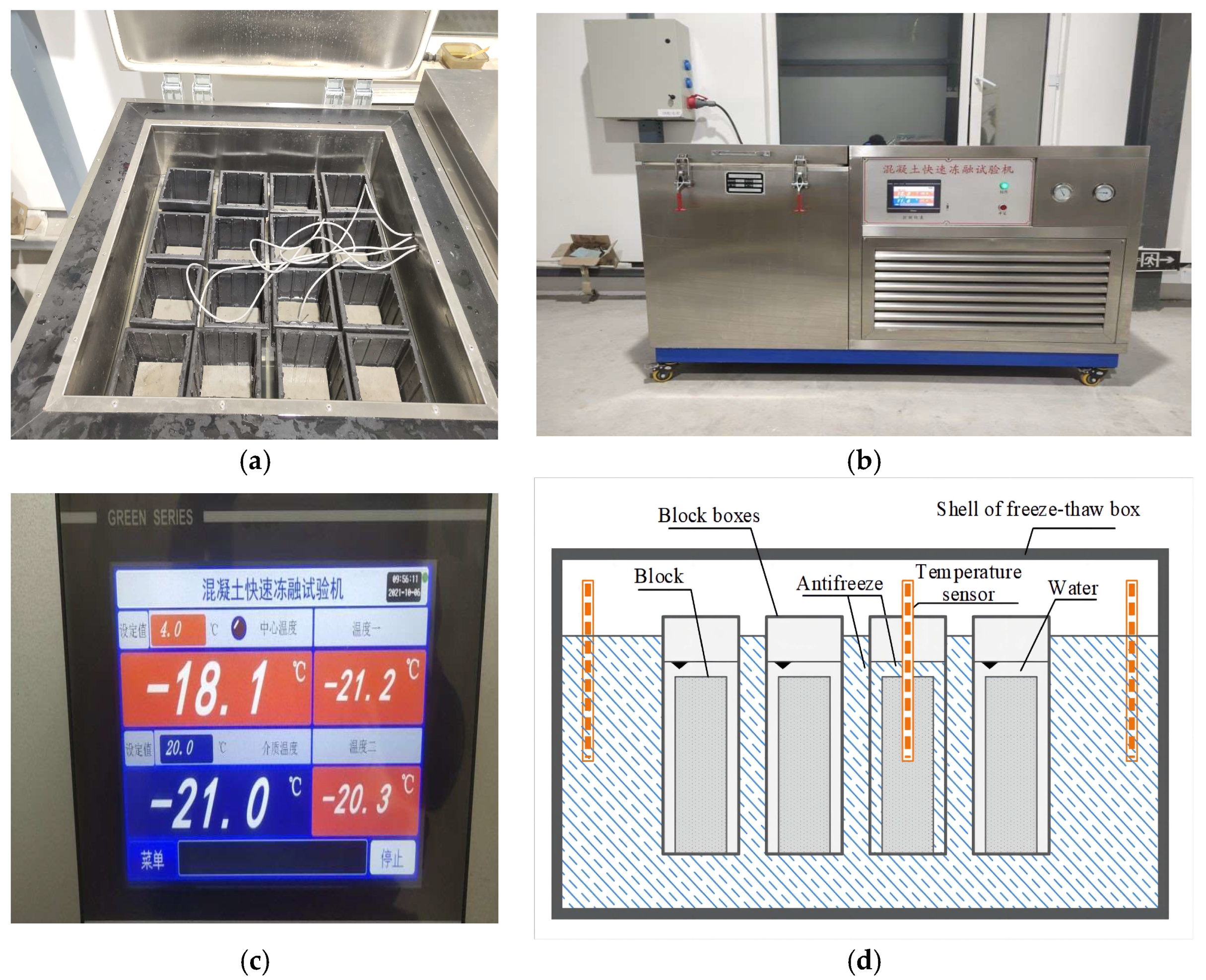
The instrument of the freeze-thaw test. (a) The interior of the freeze-thaw machine. (b) The exterior of freeze-thaw machine (c) Real-time temperature monitoring. (The legend shows the information on the outside display of the freeze-thaw machine to monitor the real-time temperature of the test block and the freeze-thaw cycle process. −18.1 °C represents the sensor center temperature; −21 °C indicates the temperature of the freezing fluid.) (d) Schematic diagram of the freeze-thaw machine.
Figure 3.
The instrument of the freeze-thaw test. (a) The interior of the freeze-thaw machine. (b) The exterior of freeze-thaw machine (c) Real-time temperature monitoring. (The legend shows the information on the outside display of the freeze-thaw machine to monitor the real-time temperature of the test block and the freeze-thaw cycle process. −18.1 °C represents the sensor center temperature; −21 °C indicates the temperature of the freezing fluid.) (d) Schematic diagram of the freeze-thaw machine.
Figure 4.
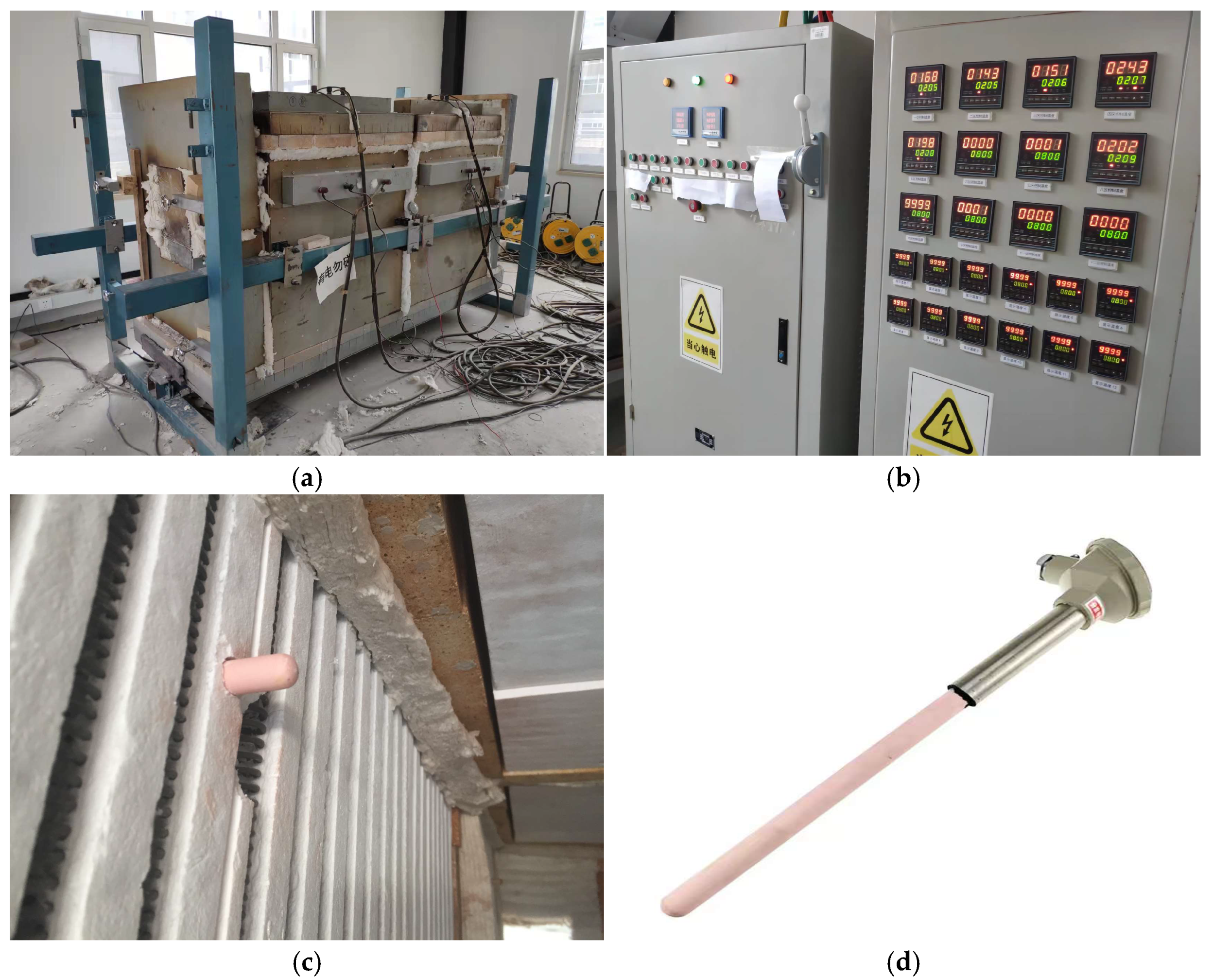
The instrument of the elevated temperature test. (a) Combined resistance furnace diagram. (b) Intelligent precision temperature controllers. (c) The thermocouples installed inside the furnace. (d) K-Type Thermocouple Sensors.
Figure 4.
The instrument of the elevated temperature test. (a) Combined resistance furnace diagram. (b) Intelligent precision temperature controllers. (c) The thermocouples installed inside the furnace. (d) K-Type Thermocouple Sensors.
Figure 5.
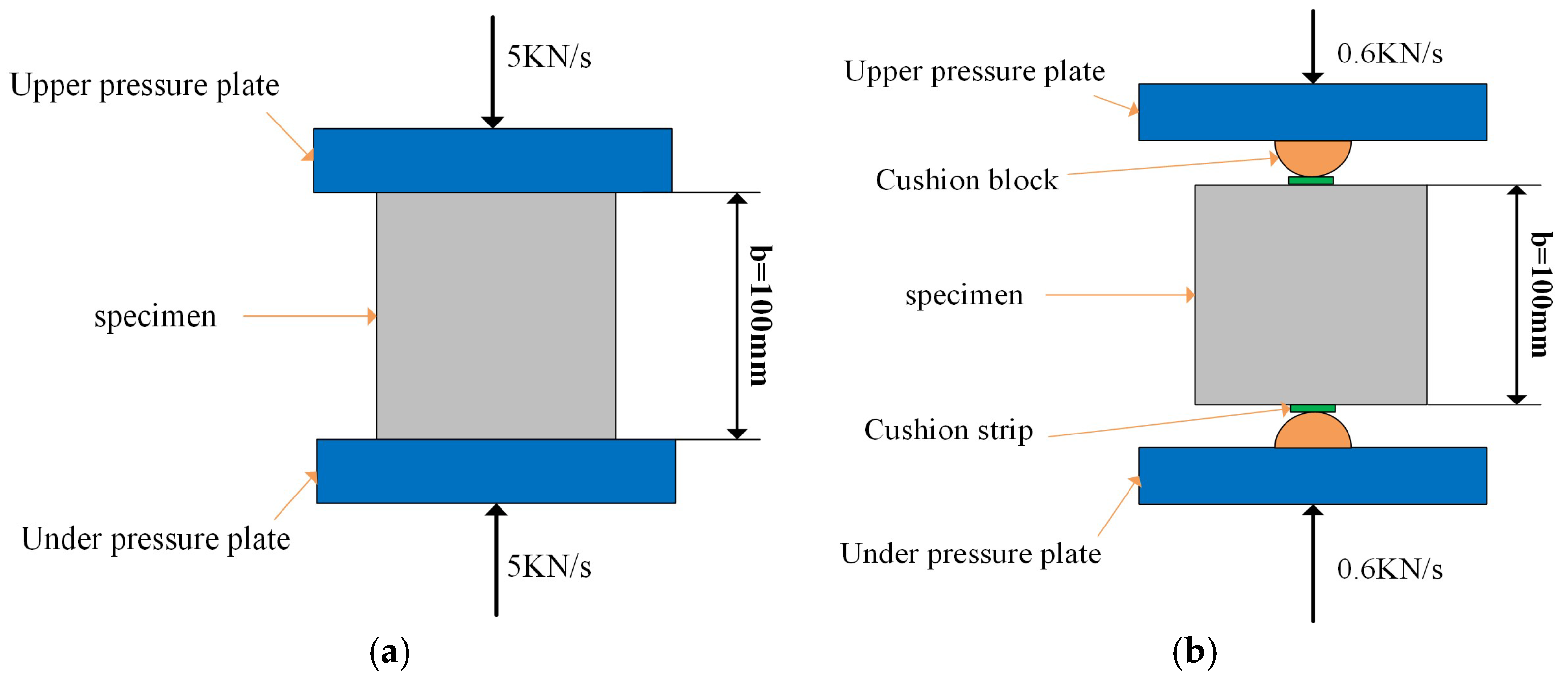
Schematic diagram of concrete strength tests. (a) Compressive strength. (b) Splitting tensile strength.
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of concrete strength tests. (a) Compressive strength. (b) Splitting tensile strength.
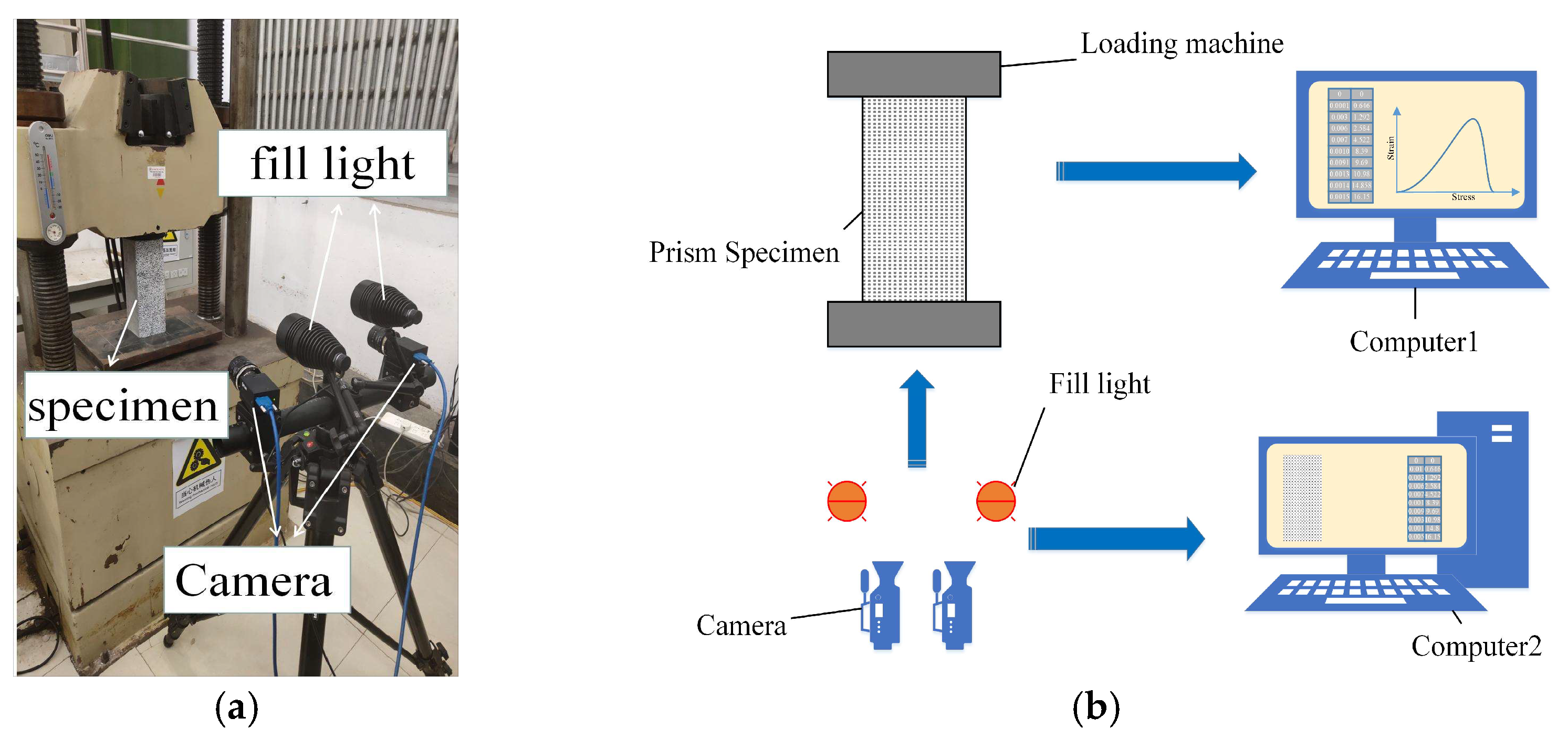
Figure 6.
Diagram of the DIC equipment. (a) Physical view of DIC equipment. (b) Diagram of the DIC equipment.
Figure 6.
Diagram of the DIC equipment. (a) Physical view of DIC equipment. (b) Diagram of the DIC equipment.
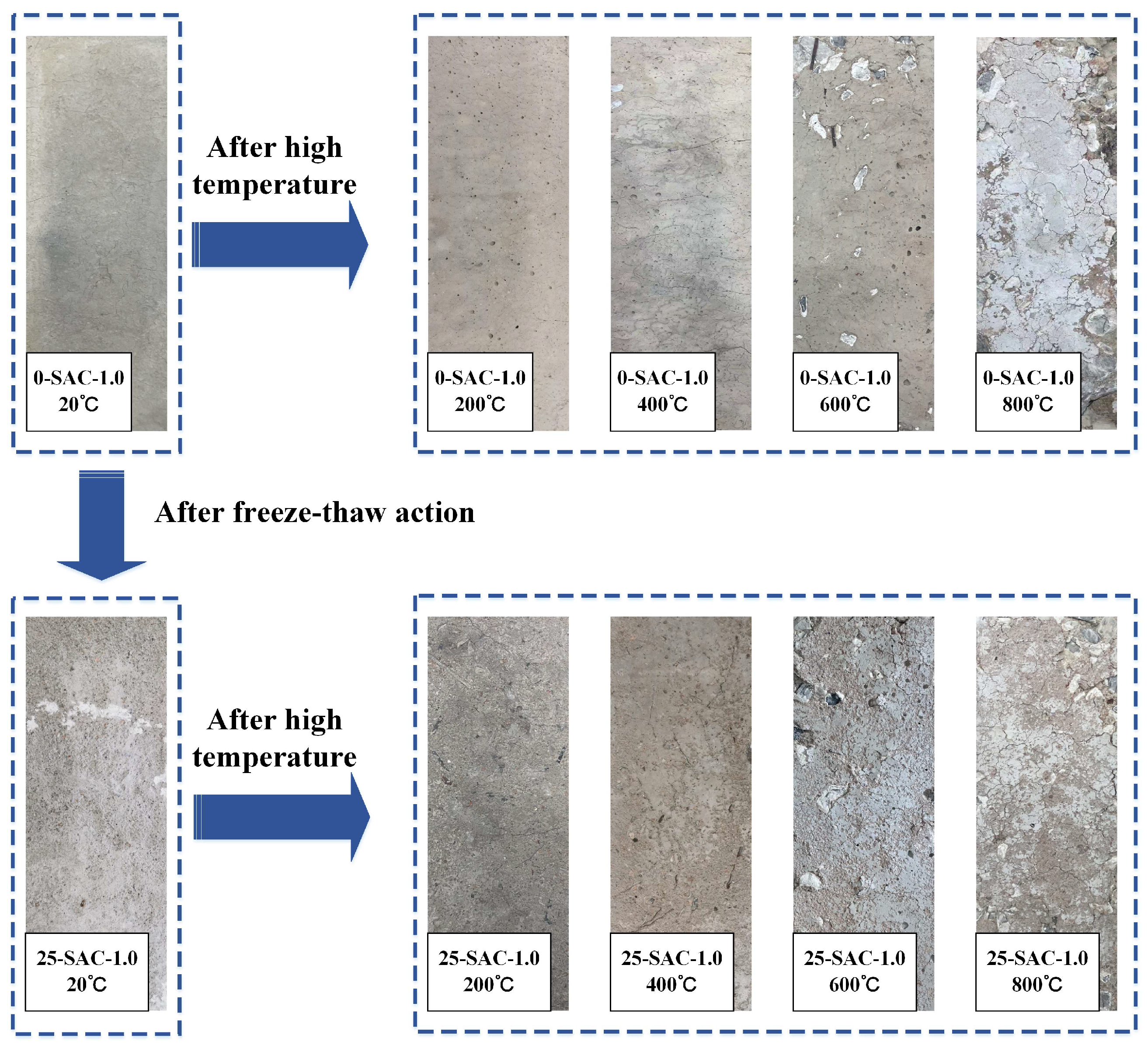
Figure 7.
Apparent condition of SAC-1.0 specimens after freeze-thaw and then high temperature.
Figure 7.
Apparent condition of SAC-1.0 specimens after freeze-thaw and then high temperature.
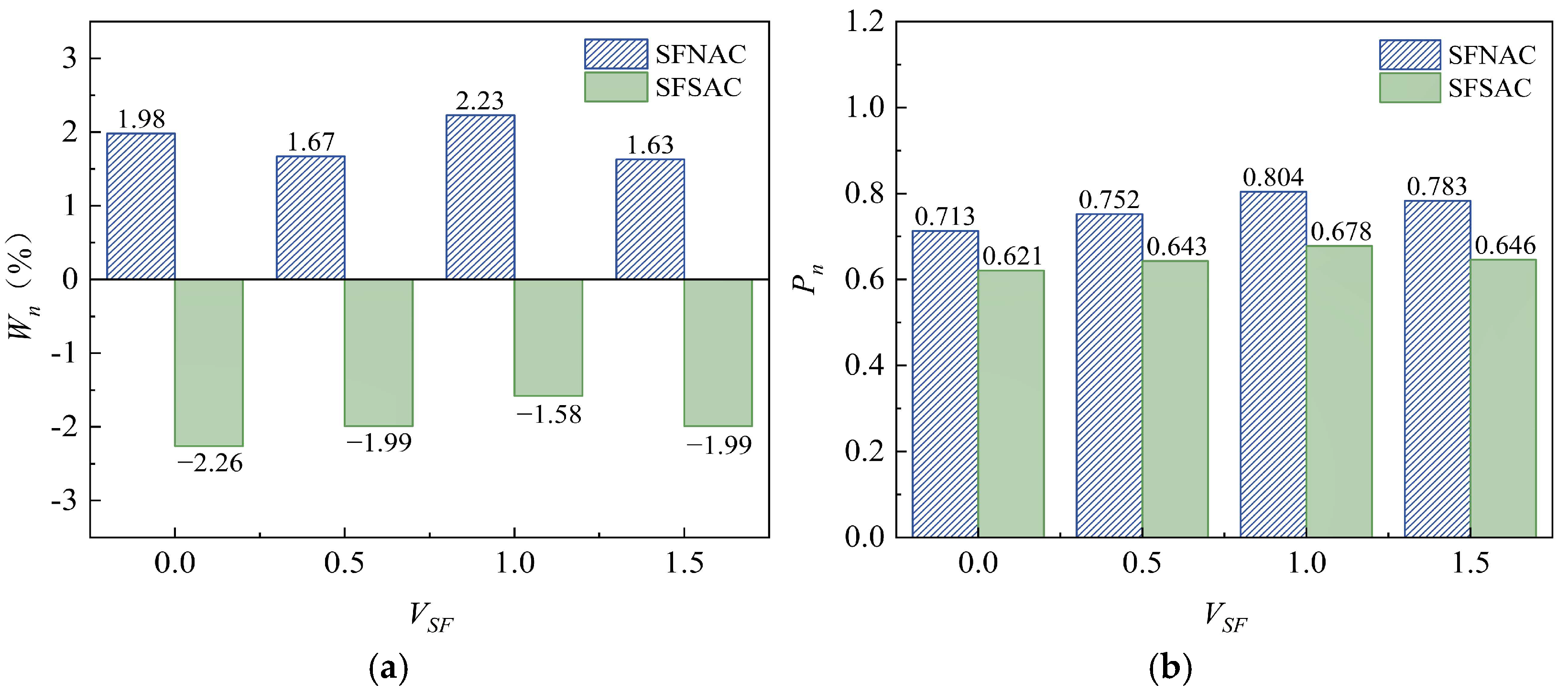
Figure 8.
(a) Comparison of mass loss rates of SFSAC and SFNAC with different steel fiber contents after 25 freeze-thaw cycles. (b) Comparison of relative dynamic elastic modulus of SFSAC and SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles.
Figure 8.
(a) Comparison of mass loss rates of SFSAC and SFNAC with different steel fiber contents after 25 freeze-thaw cycles. (b) Comparison of relative dynamic elastic modulus of SFSAC and SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles.
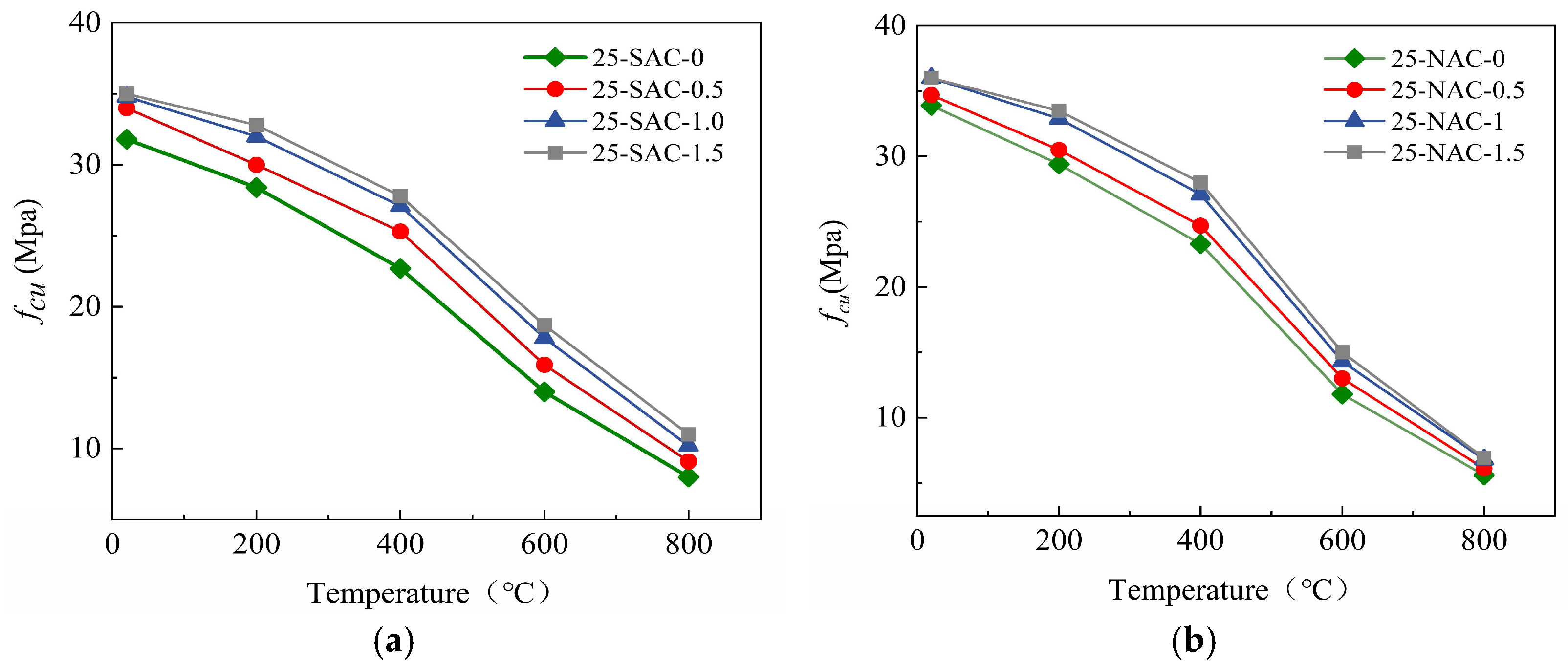
Figure 9.
Cube compressive strength of SFSAC and SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (a) Cube compressive strength of SFSAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (b) Cube compressive strength of SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature.
Figure 9.
Cube compressive strength of SFSAC and SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (a) Cube compressive strength of SFSAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (b) Cube compressive strength of SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature.
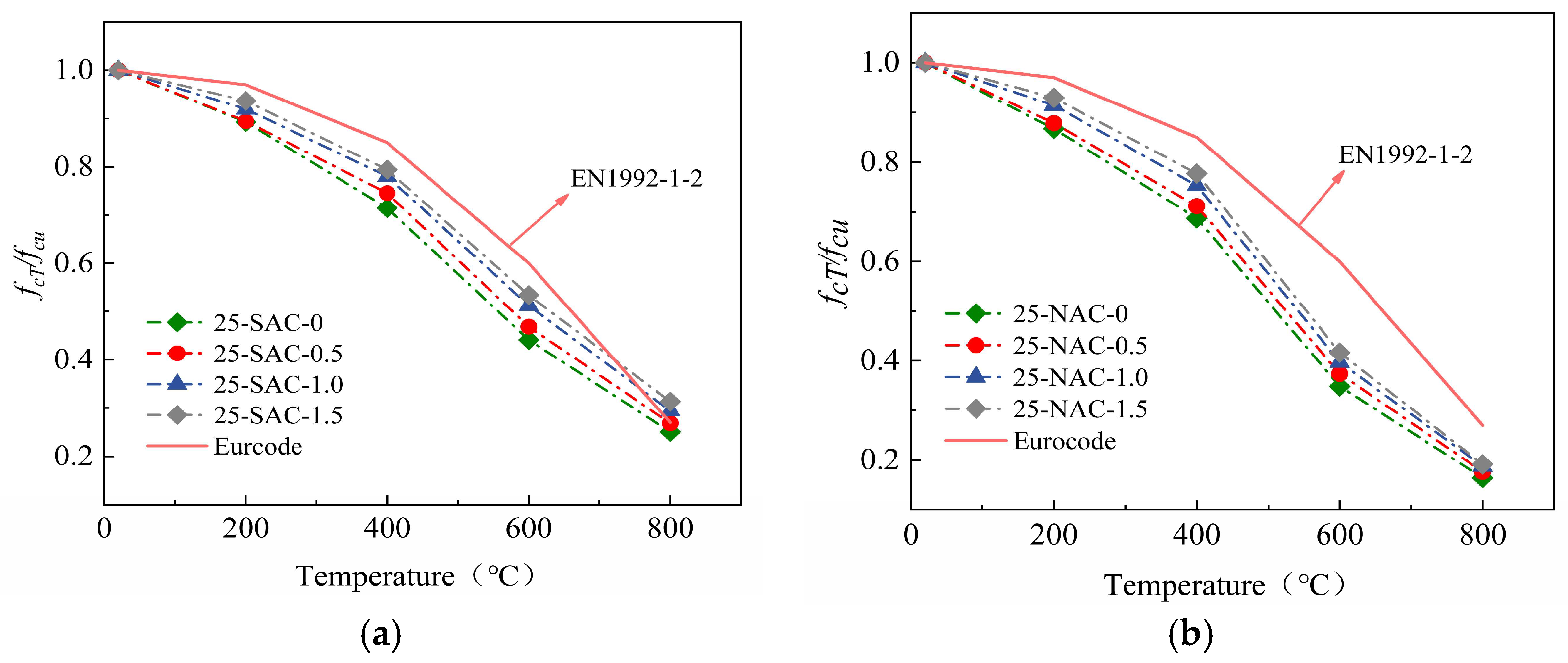
Figure 10.
Relative compressive strength of SFSAC and SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (a) Relative compressive strength of SFSAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (b) Relative compressive strength of SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature.
Figure 10.
Relative compressive strength of SFSAC and SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (a) Relative compressive strength of SFSAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (b) Relative compressive strength of SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature.
Figure 11.
(a) Cube compressive strength of NAC-1.0 and SAC-1.0 before and after freeze-thaw cycle. (b) Fitting and test results of the cubes’ compressive strength of SFSAC after freeze-thaw cycles and then elevated-temperature exposure.
Figure 11.
(a) Cube compressive strength of NAC-1.0 and SAC-1.0 before and after freeze-thaw cycle. (b) Fitting and test results of the cubes’ compressive strength of SFSAC after freeze-thaw cycles and then elevated-temperature exposure.
Figure 12.
Cube splitting tensile strength of SFSAC and SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (a) Cube splitting tensile strength of SFSAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (b) Cube splitting tensile strength of SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature.
Figure 12.
Cube splitting tensile strength of SFSAC and SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (a) Cube splitting tensile strength of SFSAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (b) Cube splitting tensile strength of SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature.
Figure 13.
Relative cube splitting tensile strength of SFSAC and SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (a) Relative cube splitting tensile strength of SFSAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (b) Relative cube splitting tensile strength of SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature.
Figure 13.
Relative cube splitting tensile strength of SFSAC and SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (a) Relative cube splitting tensile strength of SFSAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature. (b) Relative cube splitting tensile strength of SFNAC after 25 freeze-thaw cycles and then high temperature.
Figure 14.
(a) Cube splitting tensile strength of SAC-1.0 and NAC-1.0 before and after freeze-thaw cycle. (b) Fitting and test results of SFSAC splitting tensile strength after freeze-thaw cycles and then elevated-temperature exposure.
Figure 14.
(a) Cube splitting tensile strength of SAC-1.0 and NAC-1.0 before and after freeze-thaw cycle. (b) Fitting and test results of SFSAC splitting tensile strength after freeze-thaw cycles and then elevated-temperature exposure.
Figure 15.
(a) Elastic modulus of SFSAC and SFNAC after freeze-thaw cycle and then elevated-temperature exposure. (b) Elastic modulus of SAC-1.0 and NAC-1.0 before and then after freeze-thaw cycle.
Figure 15.
(a) Elastic modulus of SFSAC and SFNAC after freeze-thaw cycle and then elevated-temperature exposure. (b) Elastic modulus of SAC-1.0 and NAC-1.0 before and then after freeze-thaw cycle.
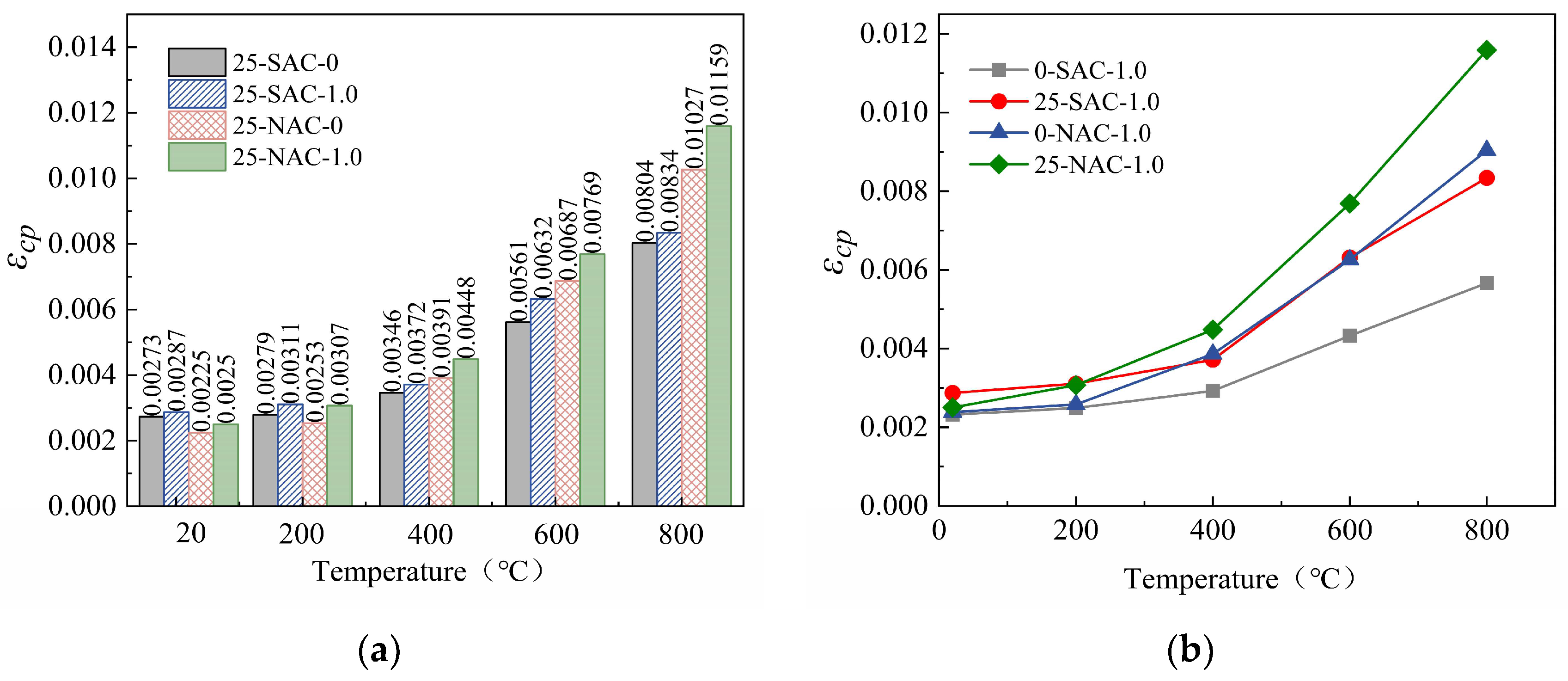
Figure 16.
(a) Peak strain of SFSAC and SFNAC after freeze-thaw cycle and then elevated-temperature exposure. (b) Peak strain of SAC-1.0 and NAC-1.0 before and after freeze-thaw cycle.
Figure 16.
(a) Peak strain of SFSAC and SFNAC after freeze-thaw cycle and then elevated-temperature exposure. (b) Peak strain of SAC-1.0 and NAC-1.0 before and after freeze-thaw cycle.
Figure 17.
The stress–strain curves of SFSAC with steel fiber contents of 0% and 1% after elevated-temperature exposure. (a) 0-SAC-0. (b) 0-SAC-1.0.
Figure 17.
The stress–strain curves of SFSAC with steel fiber contents of 0% and 1% after elevated-temperature exposure. (a) 0-SAC-0. (b) 0-SAC-1.0.
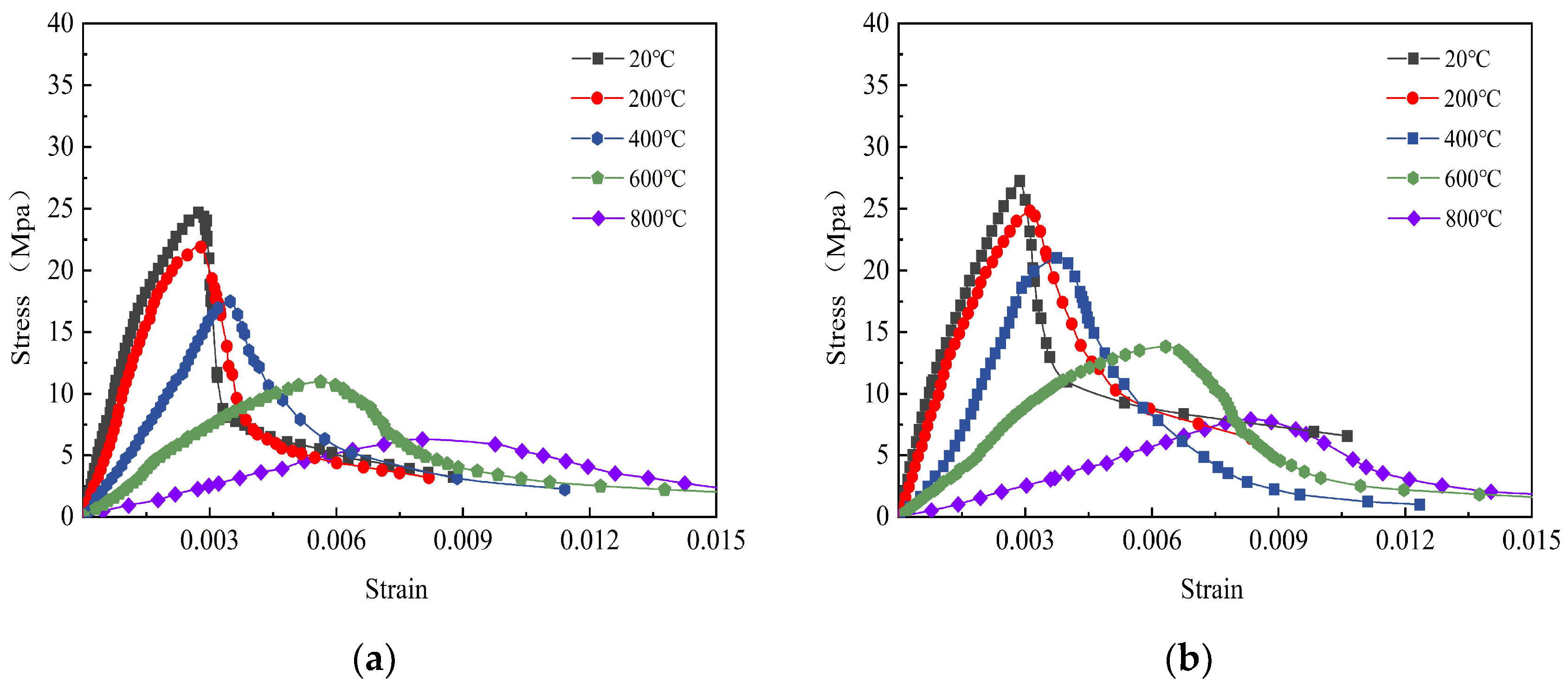
Figure 18.
Stress–strain curve of SFSAC with steel fiber contents of 0% and 1% after freeze-thaw cycle and then high temperature. (a) 25-SAC-0. (b) 25-SAC-1.0.
Figure 18.
Stress–strain curve of SFSAC with steel fiber contents of 0% and 1% after freeze-thaw cycle and then high temperature. (a) 25-SAC-0. (b) 25-SAC-1.0.
Figure 19.
Stress–strain curve of SFNAC with steel fiber contents of 0% and 1% after elevated-temperature exposure. (a) 0-NAC-0. (b) 0-NAC-1.0.
Figure 19.
Stress–strain curve of SFNAC with steel fiber contents of 0% and 1% after elevated-temperature exposure. (a) 0-NAC-0. (b) 0-NAC-1.0.
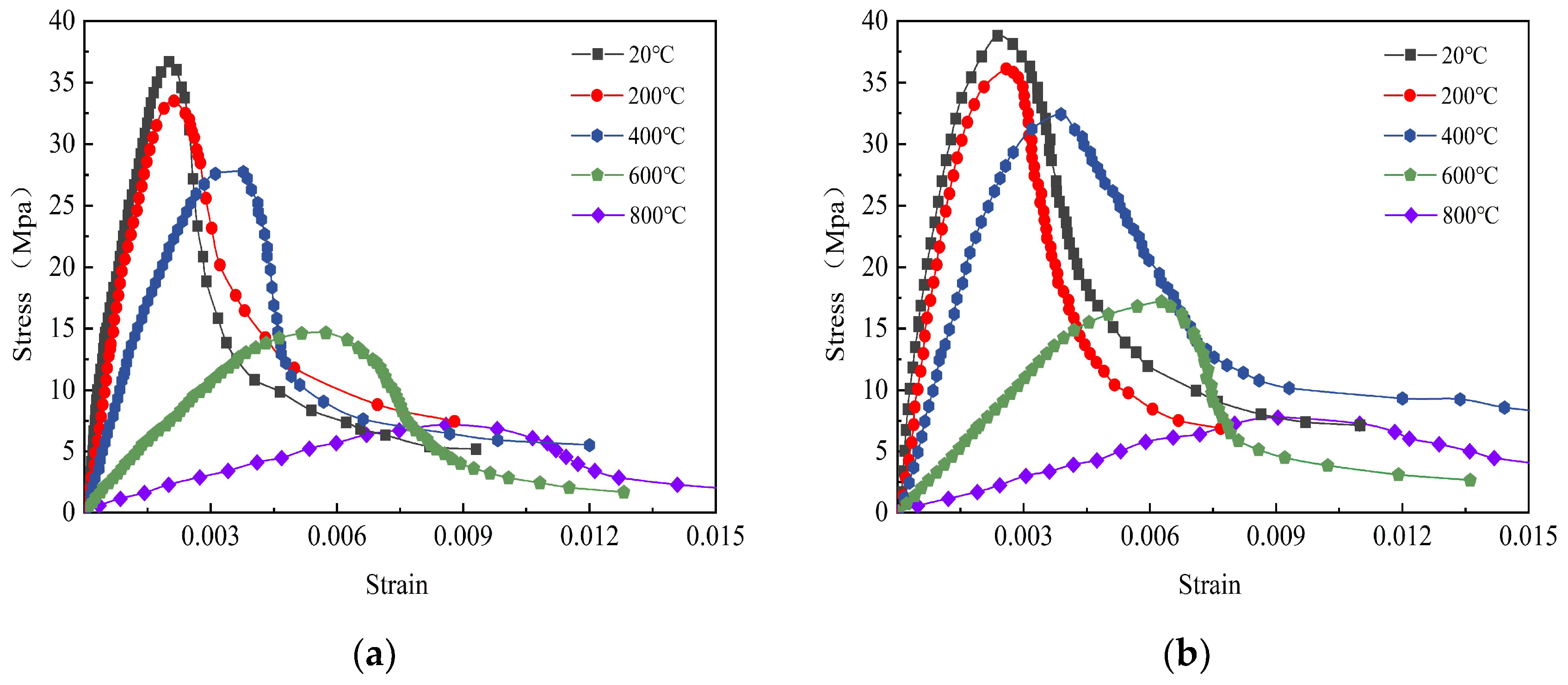
Figure 20.
Stress–strain curve of SFNAC with steel fiber contents of 0% and 1% after freeze-thaw cycle and then high temperature. (a) 25-NAC-0. (b) 25-NAC-1.0.
Figure 20.
Stress–strain curve of SFNAC with steel fiber contents of 0% and 1% after freeze-thaw cycle and then high temperature. (a) 25-NAC-0. (b) 25-NAC-1.0.
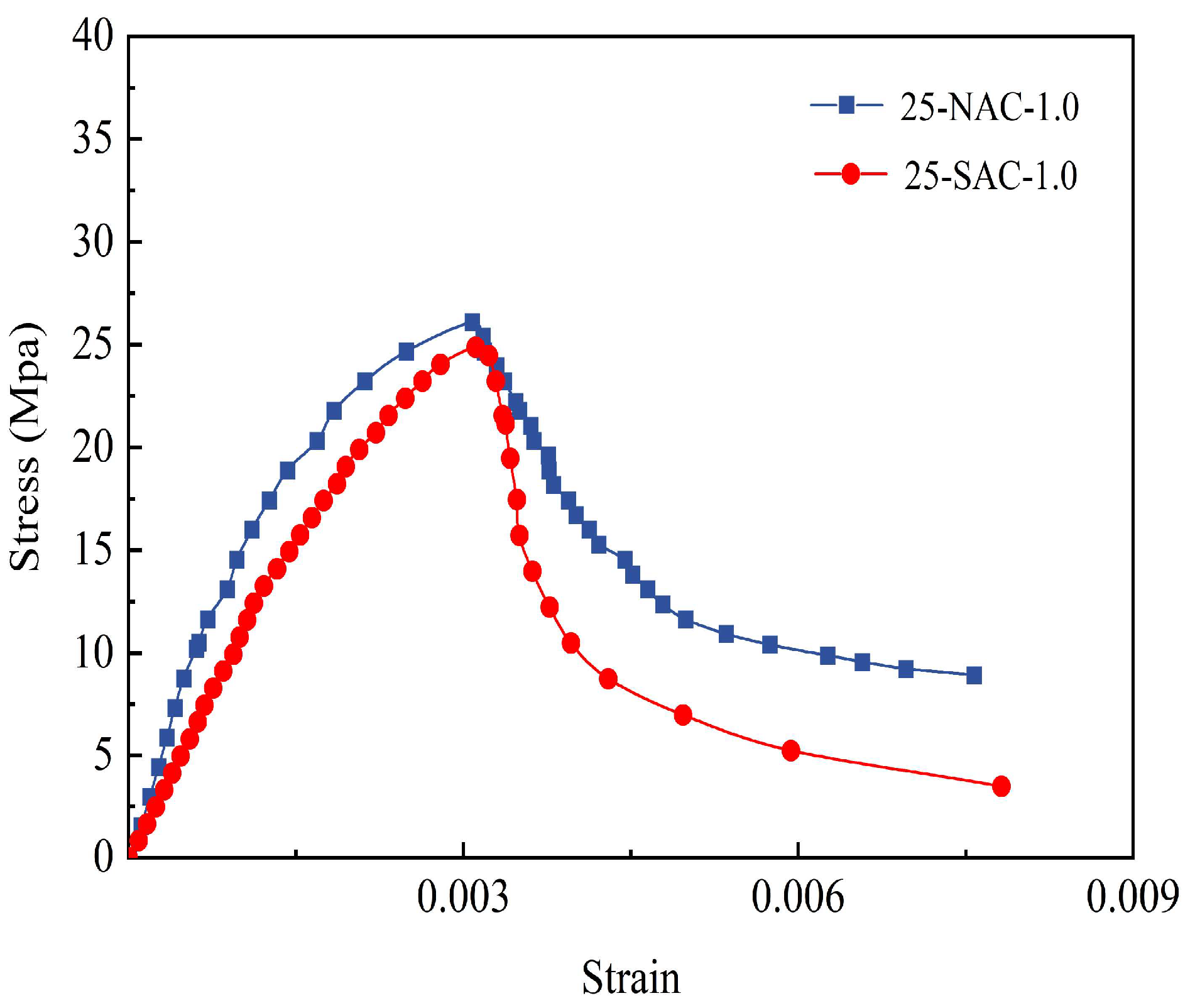
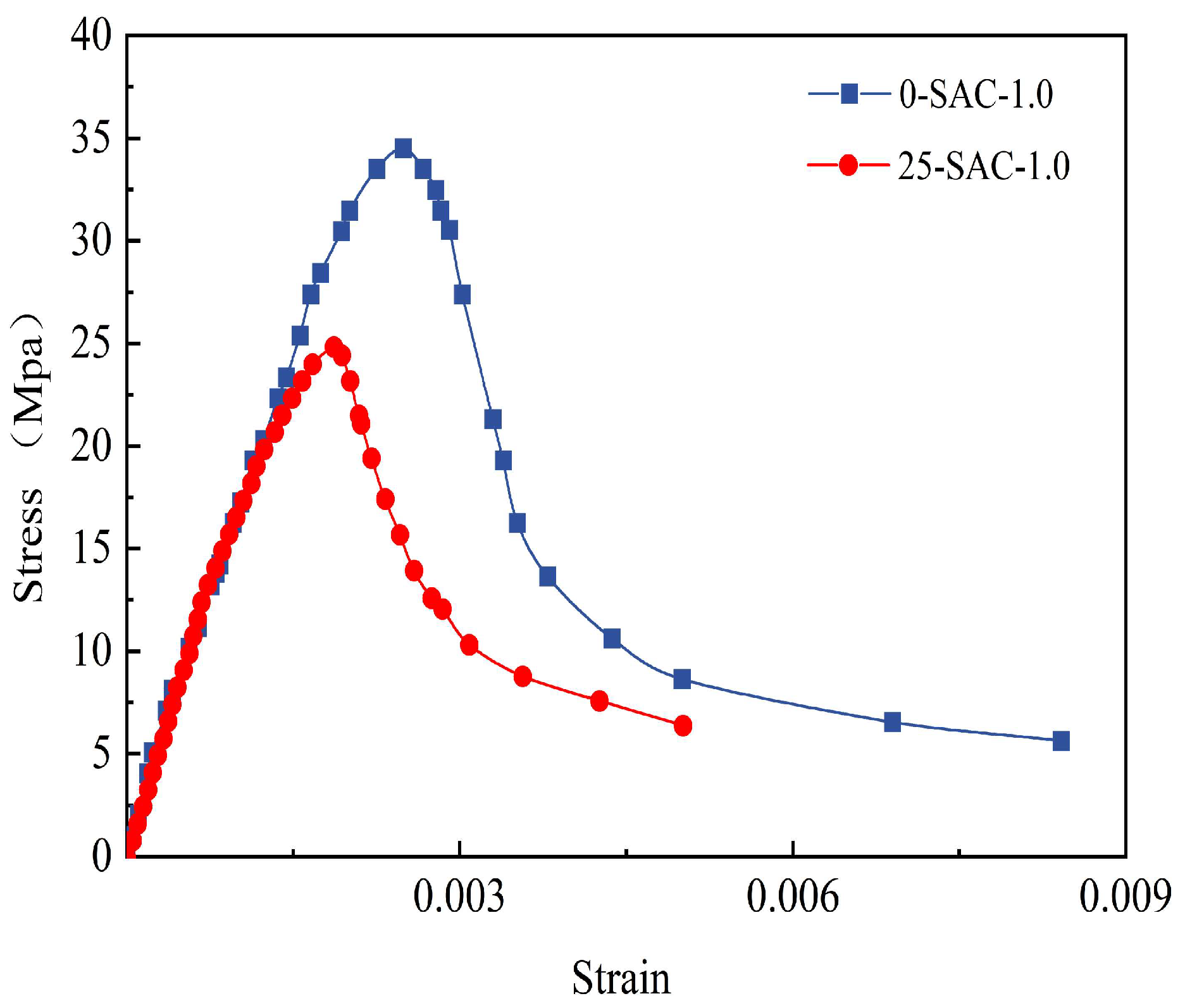
Figure 21.
Comparison of stress–strain curves of 25-NAC-1.0-200 °C and 25-SAC-1.0-200 °C.
Figure 21.
Comparison of stress–strain curves of 25-NAC-1.0-200 °C and 25-SAC-1.0-200 °C.
Figure 22.
Comparison of stress–strain curves of 0-SAC-1.0-200 °C and 25-SAC-1.0-200 °C.
Figure 22.
Comparison of stress–strain curves of 0-SAC-1.0-200 °C and 25-SAC-1.0-200 °C.
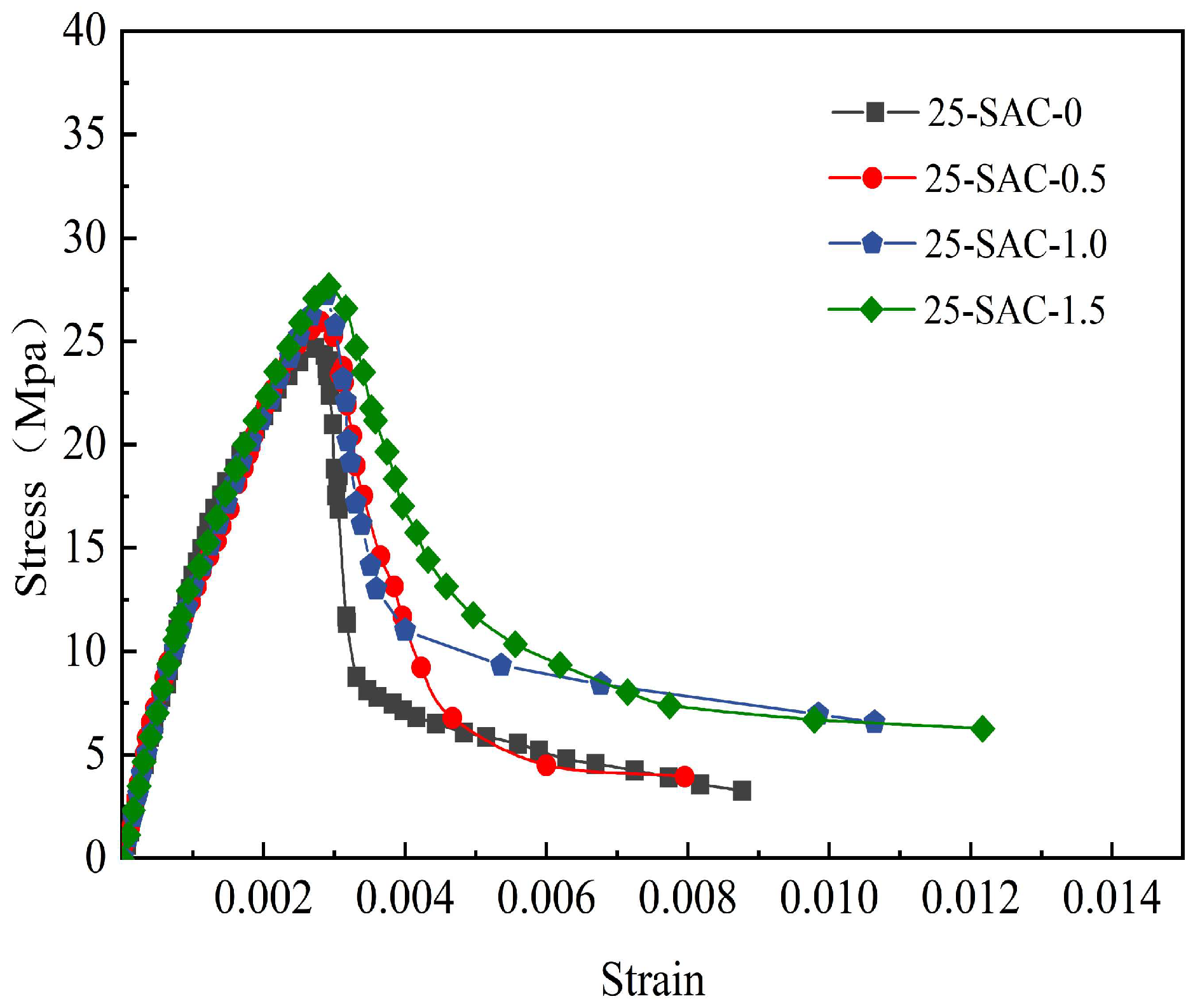
Figure 23.
Stress–strain curves of SFSAC with various steel fiber contents after 25 freeze-thaw cycles.
Figure 23.
Stress–strain curves of SFSAC with various steel fiber contents after 25 freeze-thaw cycles.
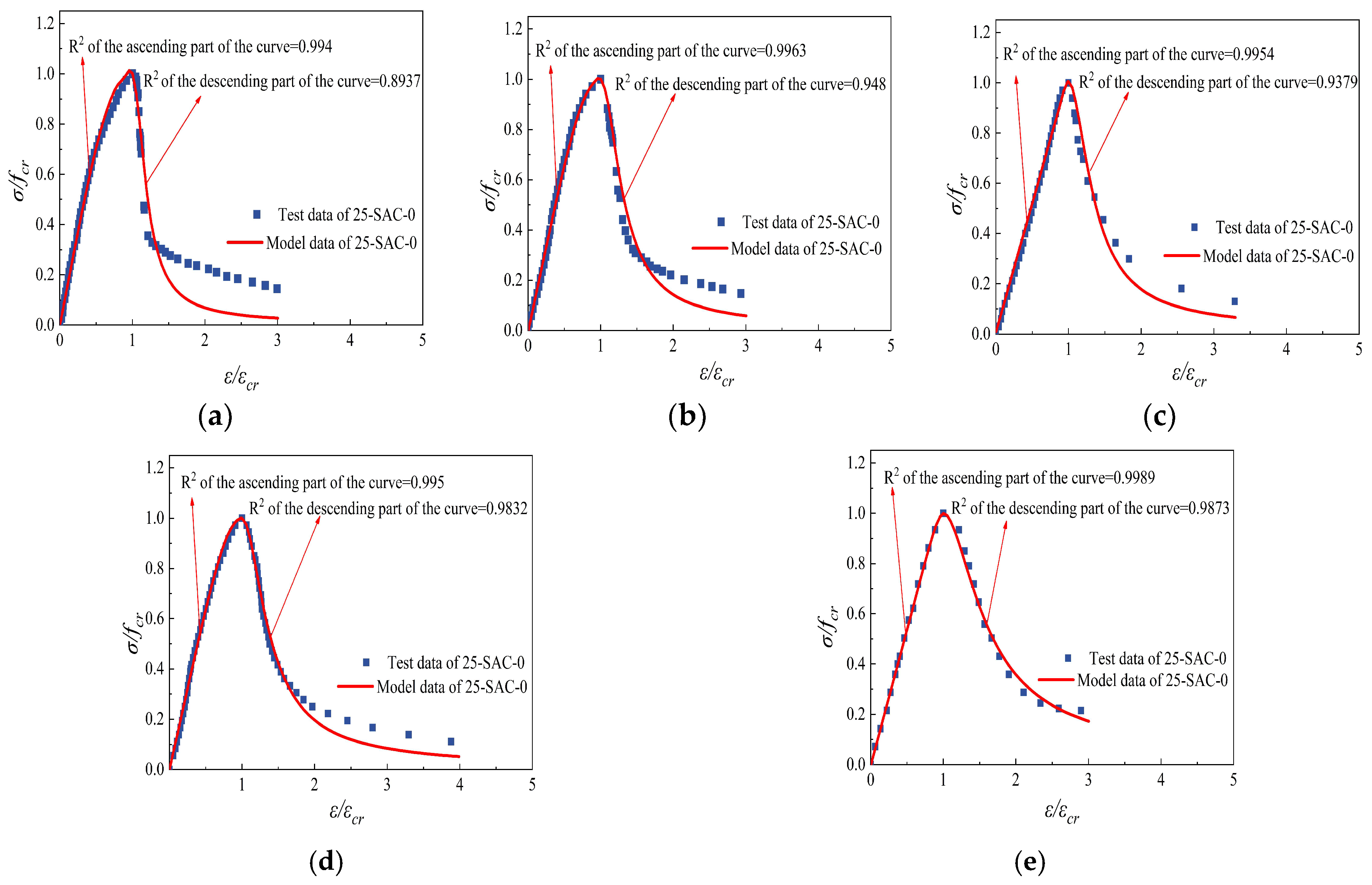
Figure 24.
Comparison of constitutive curves tested and fitted of 25-SAC-0 after freeze-thaw cycle and then high temperature. (a) 25-SAC-0-20 °C (b) 25-SAC-0-200 °C (c) 25-SAC-0-400 °C (d) 25-SAC-0-600 °C (e) 25-SAC-0-800 °C.
Figure 24.
Comparison of constitutive curves tested and fitted of 25-SAC-0 after freeze-thaw cycle and then high temperature. (a) 25-SAC-0-20 °C (b) 25-SAC-0-200 °C (c) 25-SAC-0-400 °C (d) 25-SAC-0-600 °C (e) 25-SAC-0-800 °C.
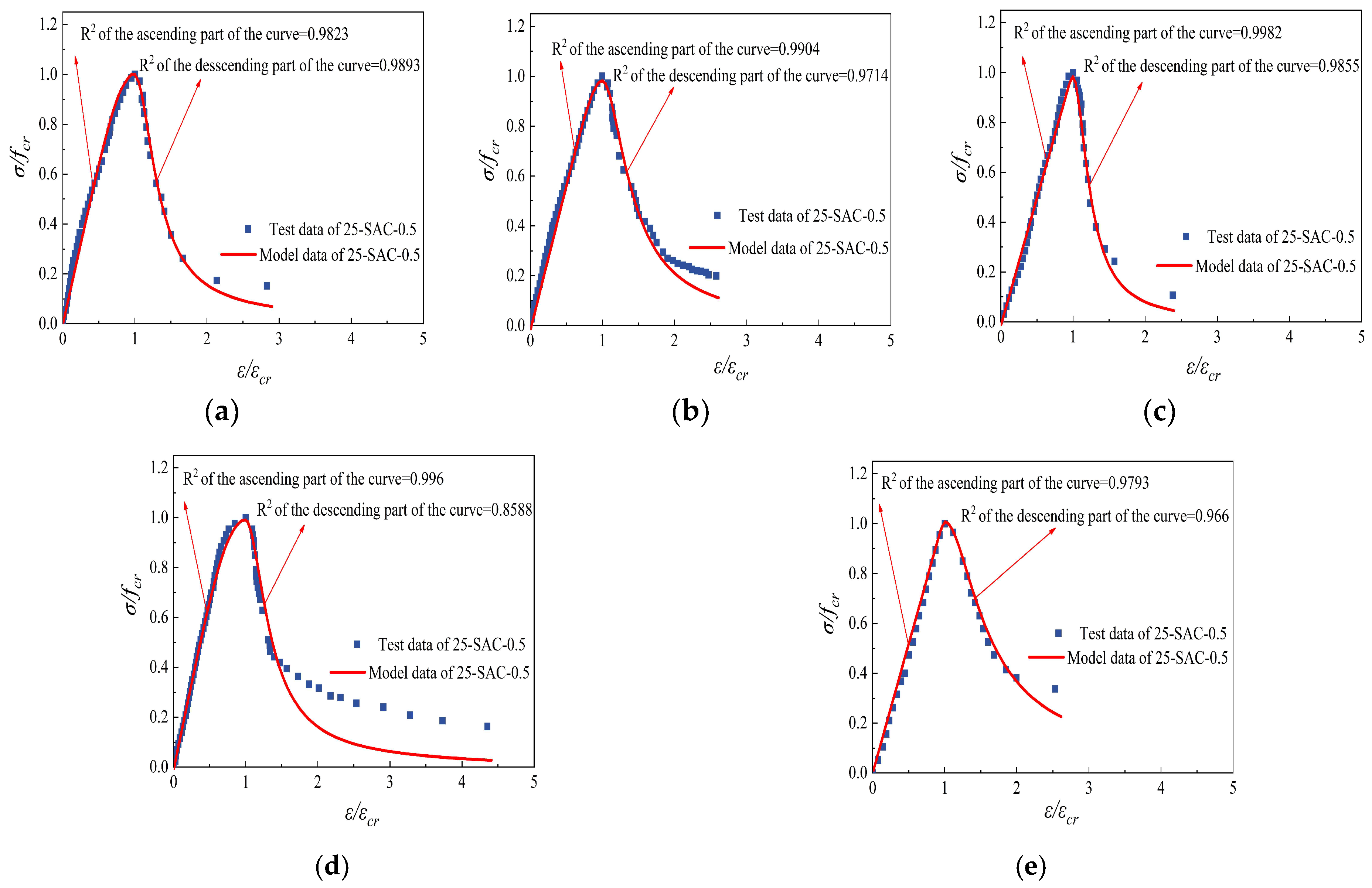
Figure 25.
Comparison of constitutive curves tested and fitted of 25-SAC-0.5 after freeze-thaw cycle and then high temperature. (a) 25-SAC-0.5-20 °C (b) 25-SAC-0.5-200 °C (c) 25-SAC-0.5-400 °C (d) 25-SAC-0.5-600 °C (e) 25-SAC-0.5-800 °C.
Figure 25.
Comparison of constitutive curves tested and fitted of 25-SAC-0.5 after freeze-thaw cycle and then high temperature. (a) 25-SAC-0.5-20 °C (b) 25-SAC-0.5-200 °C (c) 25-SAC-0.5-400 °C (d) 25-SAC-0.5-600 °C (e) 25-SAC-0.5-800 °C.
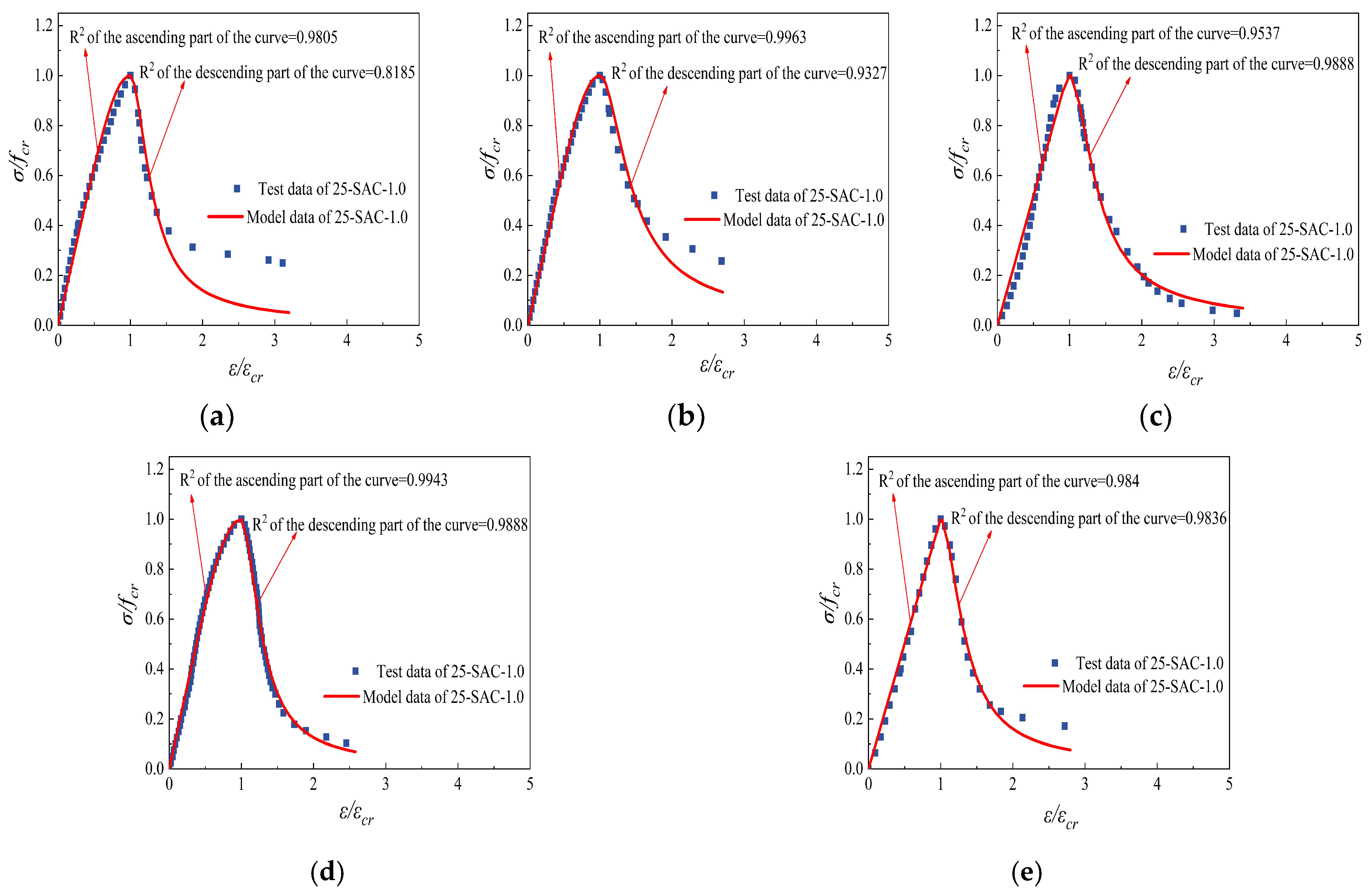
Figure 26.
Comparison of constitutive curves tested and fitted of 25-SAC-1.0 after freeze-thaw cycle and then high temperature. (a) 25-SAC-1.0-20 °C (b) 25-SAC-1.0-200 °C (c) 25-SAC-1.0-400 °C (d) 25-SAC-1.0-600 °C (e) 25-SAC-1.0-800 °C.
Figure 26.
Comparison of constitutive curves tested and fitted of 25-SAC-1.0 after freeze-thaw cycle and then high temperature. (a) 25-SAC-1.0-20 °C (b) 25-SAC-1.0-200 °C (c) 25-SAC-1.0-400 °C (d) 25-SAC-1.0-600 °C (e) 25-SAC-1.0-800 °C.
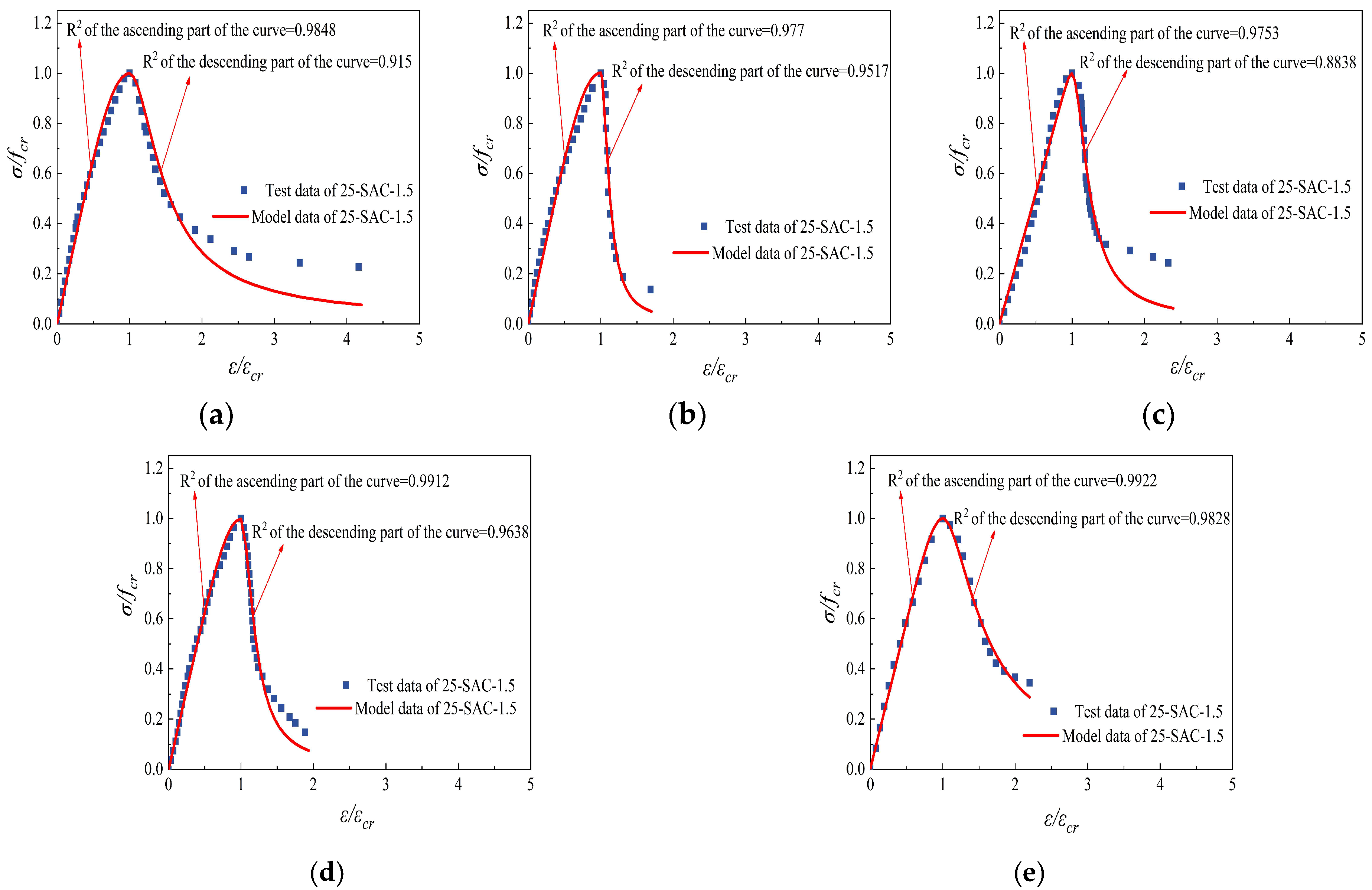
Figure 27.
Comparison of constitutive curves tested and fitted of 25-SAC-1.5 after freeze-thaw cycle and then high temperature. (a) 25-SAC-1.5-20 °C (b) 25-SAC-1.5-200 °C (c) 25-SAC-1.5-400 °C (d) 25-SAC-1.5-600 °C (e) 25-SAC-1.5-800 °C.
Figure 27.
Comparison of constitutive curves tested and fitted of 25-SAC-1.5 after freeze-thaw cycle and then high temperature. (a) 25-SAC-1.5-20 °C (b) 25-SAC-1.5-200 °C (c) 25-SAC-1.5-400 °C (d) 25-SAC-1.5-600 °C (e) 25-SAC-1.5-800 °C.
Table 1.
Materials for experimental.
Table 1.
Materials for experimental.
| Materials | Information |
|---|
| Cement | P.O42.5 ordinary Portland cement of Jilin Yatai Cement Co., Ltd., Changchun, China. |
| Sand | River sand; the fineness modulus: 2.7; the bulk density: 1260 kg/m3 |
| Stone | Ordinary gravel; size gradation: 16–35 mm; the bulk density: 1480 kg/m3 |
| Scoria | Size gradation: 5–25 mm; the bulk density: 750 kg/m3; 1 h water absorption: 35.6%; crushing index: 21% |
| Fly ash | I grade fly ash of Changchun FAW Group; the bulk density: 2560 kg/m3 |
| SF | Wave type; density: 7900 kg/m3; tensile strength: 1300 MPa; elastic modulus: 3.75 GPa; crack elongation: 3.2%; aspect ratio: 52 |
| Water | Ordinary tap water |
Table 2.
Chemical composition of volcanic scoria.
Table 2.
Chemical composition of volcanic scoria.
| Chemical Composition | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | MnO | LOI |
|---|
| Content (%) | 67.85 | 14.50 | 3.55 | 2.24 | 0.85 | 2.59 | 2.56 | 0.51 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 5.04 |
Table 3.
Mineral composition of volcanic scoria.
Table 3.
Mineral composition of volcanic scoria.
| Mineral Composition | Plagioclase | Pyroxene | Amorphous Material |
|---|
| Content (%) | 30 | 20 | 50 |
Table 4.
Mix ratio of fiber reinforced scoria aggregate concrete.
Table 4.
Mix ratio of fiber reinforced scoria aggregate concrete.
| Groups | Cement | Water | Fly Ash | Sand | Gravel | Scoria | VSF |
|---|
| NAC-0 | 382 | 210 | 85 | 564 | 1127 | 0 | 0 |
| NAC-0.5 | 382 | 210 | 85 | 564 | 1127 | 0 | 0.5 |
| NAC-1.0 | 382 | 210 | 85 | 564 | 1127 | 0 | 1.0 |
| NAC-1.5 | 382 | 210 | 85 | 564 | 1127 | 0 | 1.5 |
| SAC-0 | 382 | 210 | 85 | 564 | 676 | 258 | 0 |
| SAC-0.5 | 382 | 210 | 85 | 564 | 676 | 258 | 0.5 |
| SAC-1.0 | 382 | 210 | 85 | 564 | 676 | 258 | 1.0 |
| SAC-1.5 | 382 | 210 | 85 | 564 | 676 | 258 | 1.5 |
Table 5.
Cube compressive strength of all test blocks (MPa).
Table 5.
Cube compressive strength of all test blocks (MPa).
| Number of Freezing and Thawing | Groups | Temperature (°C) |
|---|
| 20 °C | 200 °C | 400 °C | 600 °C | 800 °C |
|---|
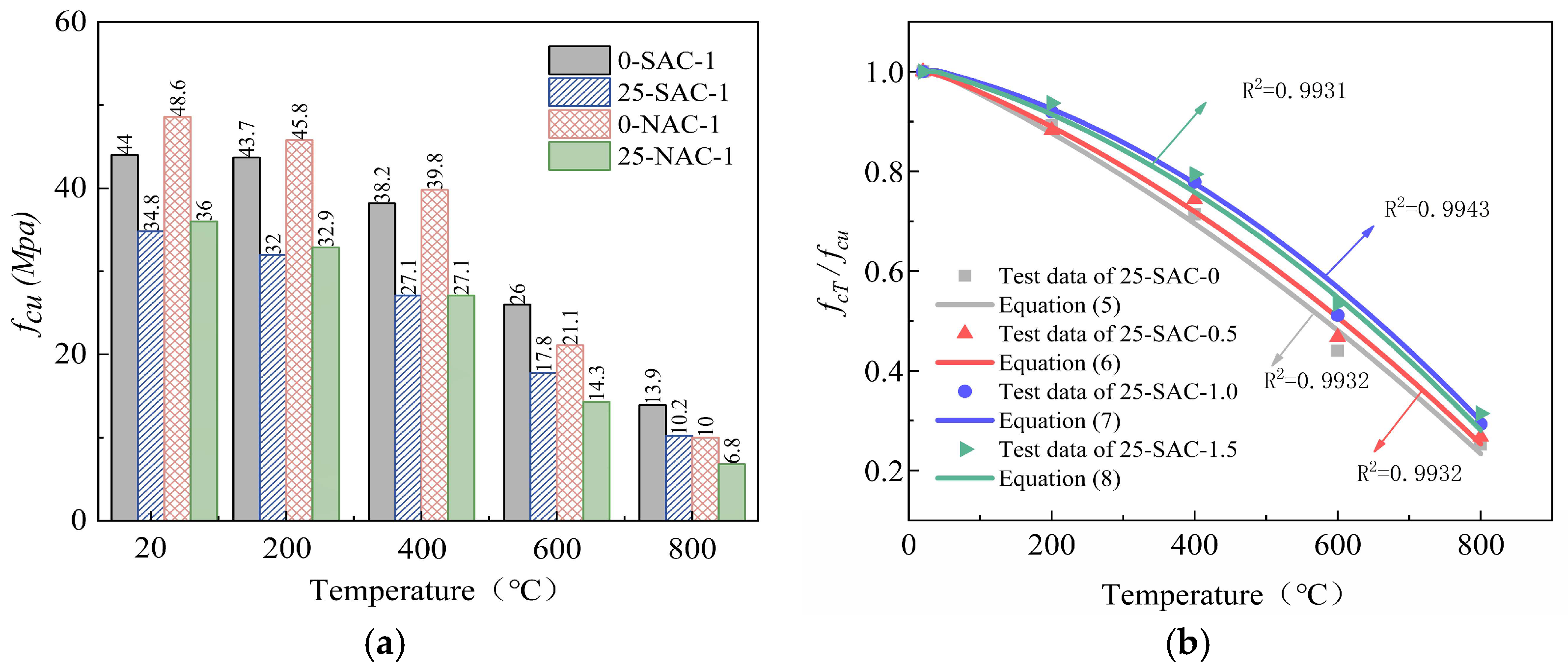
| 0 | SAC-0 | 41.4 | 40.9 | 33.4 | 20.7 | 11.8 |
| 0 | SAC-0.5 | 43.3 | 42.9 | 35.9 | 23.5 | 12.2 |
| 0 | SAC-1.0 | 44.0 | 43.7 | 38.2 | 26.0 | 13.9 |
| 0 | SAC-1.5 | 44.2 | 44.1 | 39.1 | 27.3 | 14.0 |
| 0 | NAC-0 | 46.0 | 42.8 | 34.6 | 17.9 | 9.0 |
| 0 | NAC-0.5 | 46.6 | 43.5 | 36.3 | 19.2 | 9.7 |
| 0 | NAC-1.0 | 48.6 | 45.8 | 39.8 | 21.1 | 10.0 |
| 0 | NAC-1.5 | 49.1 | 47.0 | 40.9 | 21.9 | 10.1 |
| 25 | SAC-0 | 31.8 | 28.4 | 22.7 | 14.0 | 8.0 |
| 25 | SAC-0.5 | 34.0 | 30.0 | 25.3 | 15.9 | 9.1 |
| 25 | SAC-1.0 | 34.8 | 32.0 | 27.1 | 17.8 | 10.2 |
| 25 | SAC-1.5 | 35.0 | 32.8 | 27.8 | 18.7 | 11.0 |
| 25 | NAC-0 | 33.9 | 29.4 | 23.3 | 11.8 | 5.6 |
| 25 | NAC-0.5 | 34.7 | 30.5 | 24.7 | 13.0 | 6.1 |
| 25 | NAC-1 | 36.0 | 32.9 | 27.1 | 14.3 | 6.8 |
| 25 | NAC-1.5 | 36.0 | 33.5 | 28.0 | 15.0 | 6.9 |
Table 6.
The fitting formulas for the cube compressive strengths of SFSAC.
Table 6.
The fitting formulas for the cube compressive strengths of SFSAC.
| Steel Fiber Content | Compressive Strength Fitting Formula | R2 |
|---|
| VSF = 0% | | (5) | 0.9932 |
| VSF = 0.5% | | (6) | 0.9932 |
| VSF = 1.0% | | (7) | 0.9943 |
| VSF = 1.5% | | (8) | 0.9931 |
Table 7.
Cube splitting tensile strength of all test blocks (MPa).
Table 7.
Cube splitting tensile strength of all test blocks (MPa).
| Number of Freezing and Thawing | Groups | Temperature (°C) |
|---|
| 20 °C | 200 °C | 400 °C | 600 °C | 800 °C |
|---|
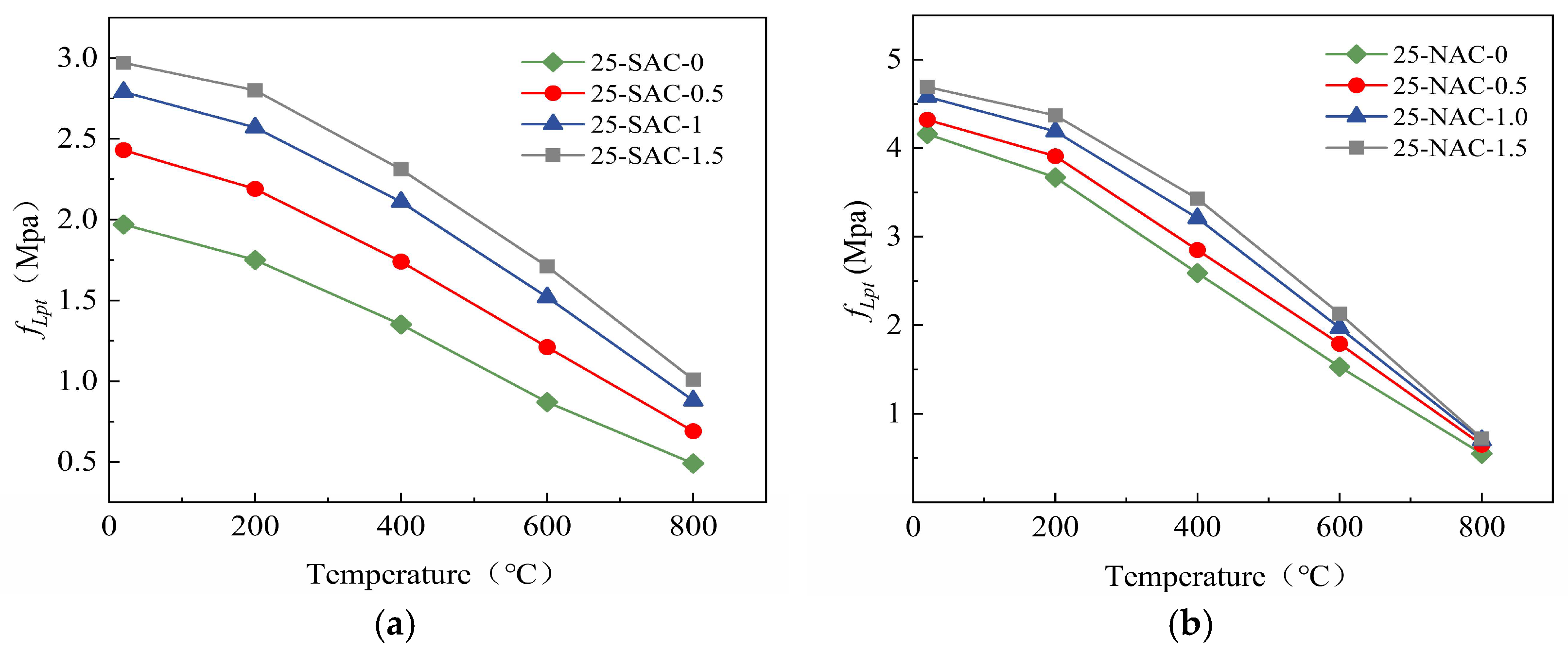
| 0 | SAC-0 | 3.13 | 2.80 | 2.41 | 1.57 | 0.92 |
| 0 | SAC-0.5 | 3.75 | 3.39 | 3.01 | 1.99 | 1.06 |
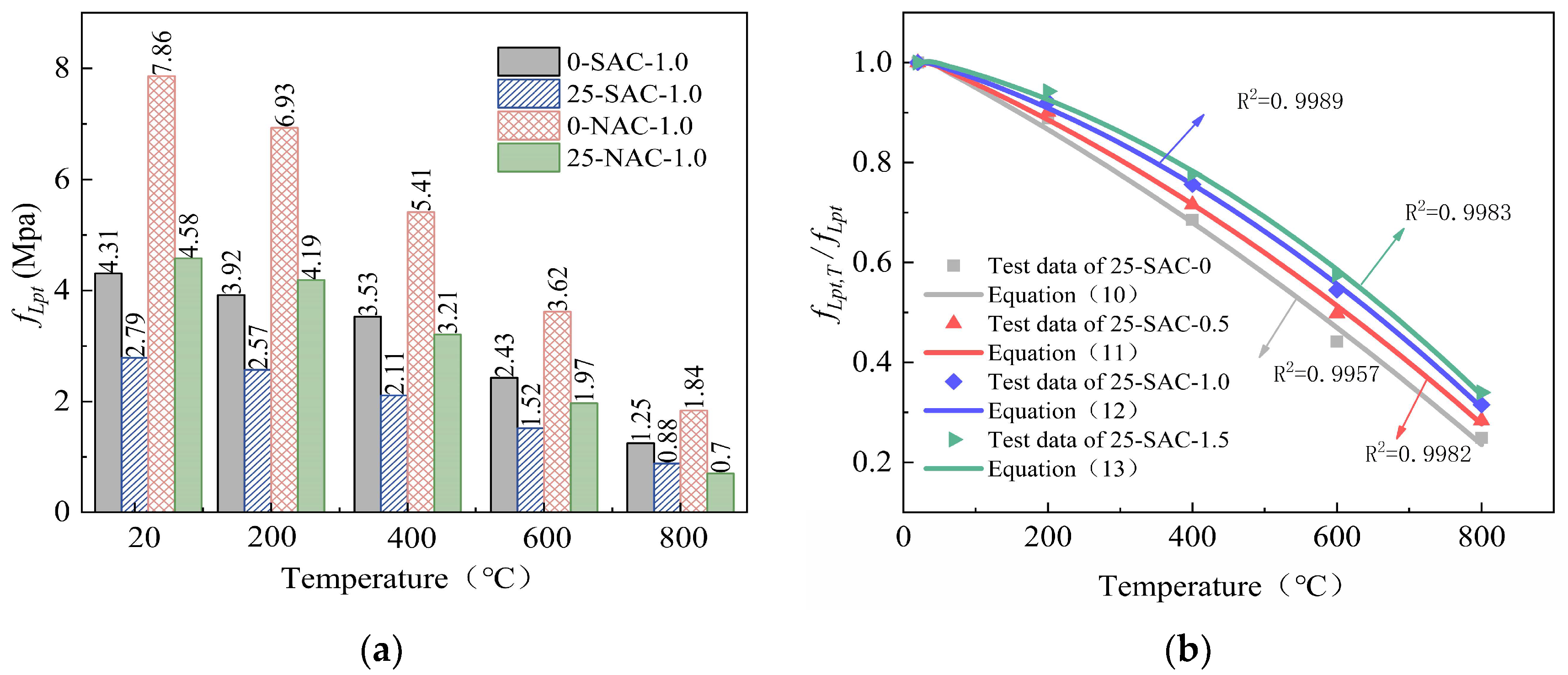
| 0 | SAC-1.0 | 4.31 | 3.92 | 3.53 | 2.43 | 1.25 |
| 0 | SAC-1.5 | 4.48 | 4.23 | 4.11 | 2.51 | 1.27 |
| 0 | NAC-0 | 7.18 | 6.17 | 4.63 | 2.94 | 1.53 |
| 0 | NAC-0.5 | 7.42 | 6.46 | 5.08 | 3.33 | 1.72 |
| 0 | NAC-1.0 | 7.86 | 6.93 | 5.41 | 3.62 | 1.84 |
| 0 | NAC-1.5 | 8.04 | 7.13 | 5.73 | 3.91 | 1.87 |
| 25 | SAC-0 | 1.97 | 1.75 | 1.35 | 0.87 | 0.49 |
| 25 | SAC-0.5 | 2.43 | 2.19 | 1.74 | 1.21 | 0.69 |
| 25 | SAC-1.0 | 2.79 | 2.57 | 2.11 | 1.52 | 0.88 |
| 25 | SAC-1.5 | 2.97 | 2.80 | 2.31 | 1.71 | 1.01 |
| 25 | NAC-0 | 4.16 | 3.67 | 2.59 | 1.53 | 0.55 |
| 25 | NAC-0.5 | 4.32 | 3.91 | 2.85 | 1.79 | 0.65 |
| 25 | NAC-1.0 | 4.58 | 4.19 | 3.21 | 1.97 | 0.70 |
| 25 | NAC-1.5 | 4.69 | 4.37 | 3.43 | 2.13 | 0.72 |
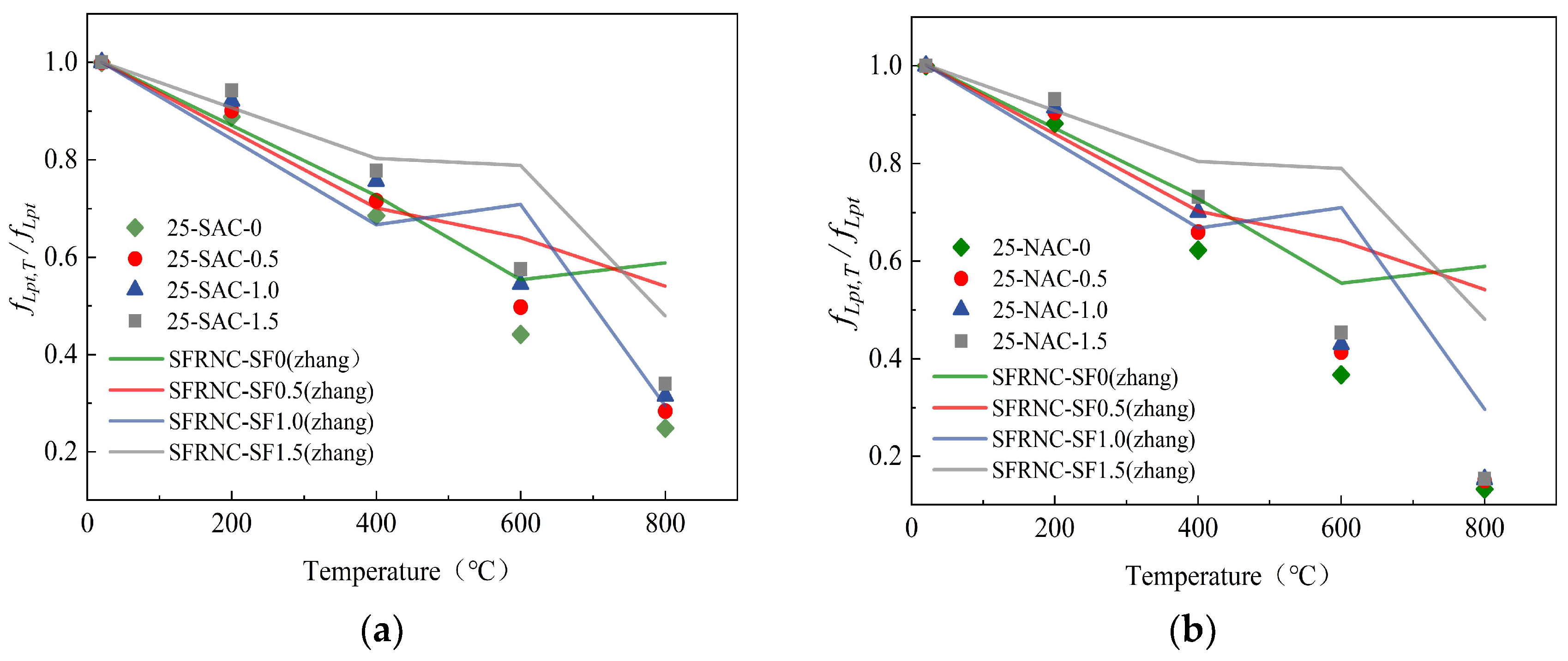
Table 8.
The fitting formulas for the cube splitting tensile strength of SFSAC.
Table 8.
The fitting formulas for the cube splitting tensile strength of SFSAC.
| Steel Fiber Content | Split Tensile Strength Fitting Formula | R2 |
|---|
| VSF = 0% | | (10) | 0.9957 |
| VSF = 0.5% | | (11) | 0.9982 |
| VSF = 1.0% | | (12) | 0.9989 |
| VSF = 1.5% | | (13) | 0.9983 |
Table 9.
Elastic modulus after freeze-thaw and then high temperature for each group of test blocks (GPa).
Table 9.
Elastic modulus after freeze-thaw and then high temperature for each group of test blocks (GPa).
Characteristic
Index | Number of Freezing and Thawing | Groups | Temperature (°C) |
|---|
| 20 | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 |
|---|
| Ec (Gpa) | 0 | SAC-0 | 20.358 | 16.393 | 11.880 | 6.303 | 2.598 |
| 0 | SAC-0.5 | 20.828 | 16.521 | 11.990 | 6.397 | 2.667 |
| 0 | SAC-1.0 | 21.116 | 17.179 | 12.486 | 6.106 | 2.491 |
| 0 | SAC-1.5 | 20.768 | 17.161 | 12.033 | 6.171 | 2.475 |
| 0 | NAC-0 | 29.898 | 21.822 | 12.370 | 3.908 | 0.228 |
| 0 | NAC-0.5 | 30.777 | 22.758 | 12.783 | 3.950 | 0.289 |
| 0 | NAC-1.0 | 30.400 | 22.196 | 12.788 | 3.648 | 0.264 |
| 0 | NAC-1.5 | 30.799 | 22.586 | 12.987 | 4.051 | 0.250 |
| 25 | SAC-0 | 13.735 | 10.359 | 5.007 | 2.670 | 0.841 |
| 25 | SAC-0.5 | 13.863 | 10.288 | 5.134 | 2.791 | 0.769 |
| 25 | SAC-1.0 | 13.925 | 10.581 | 5.001 | 2.775 | 0.853 |
| 25 | SAC-1.5 | 14.170 | 10.718 | 5.174 | 2.850 | 0.809 |
| 25 | NAC-0 | 23.765 | 16.244 | 6.382 | 2.139 | 0.095 |
| 25 | NAC-0.5 | 24.506 | 17.020 | 6.624 | 2.336 | 0.046 |
| 25 | NAC-1.0 | 24.195 | 16.676 | 6.367 | 2.168 | 0.065 |
| 25 | NAC-1.5 | 24.290 | 17.082 | 6.598 | 2.195 | 0.071 |
Table 10.
Peak strain after freeze-thaw and then high temperature for each group of test blocks.
Table 10.
Peak strain after freeze-thaw and then high temperature for each group of test blocks.
Characteristic
Index | Number of Freezing and Thawing | Groups | Temperature (°C) |
|---|
| 20 | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 |
|---|
| εcp | 0 | SAC-0 | 1911 | 2013 | 2731 | 3630 | 5343 |
| 0 | SAC-0.5 | 2134 | 2267 | 2819 | 3743 | 5473 |
| 0 | SAC-1.0 | 2320 | 2491 | 2924 | 4327 | 5667 |
| 0 | SAC-1.5 | 2439 | 3127 | 3281 | 4792 | 6191 |
| 0 | NAC-0 | 2013 | 2127 | 3573 | 5727 | 8591 |
| 0 | NAC-0.5 | 2238 | 2395 | 3769 | 5952 | 8863 |
| 0 | NAC-1.0 | 2385 | 2581 | 3863 | 6262 | 9040 |
| 0 | NAC-1.5 | 2519 | 3312 | 4104 | 6618 | 9365 |
| 25 | SAC-0 | 2731 | 2793 | 3461 | 5612 | 8035 |
| 25 | SAC-0.5 | 2814 | 2982 | 3637 | 5912 | 8173 |
| 25 | SAC-1.0 | 2873 | 3110 | 3716 | 6315 | 8341 |
| 25 | SAC-1.5 | 2923 | 3536 | 3842 | 7059 | 8917 |
| 25 | NAC-0 | 2245 | 2531 | 3913 | 6866 | 10,265 |
| 25 | NAC-0.5 | 2353 | 2833 | 4285 | 7120 | 11,263 |
| 25 | NAC-1.0 | 2504 | 3071 | 4483 | 7691 | 11,559 |
| 25 | NAC-1.5 | 2632 | 3473 | 4694 | 8371 | 12,007 |
Table 11.
Results of fitting of stress–strain curve parameters.
Table 11.
Results of fitting of stress–strain curve parameters.
| Groups | Temperature (°C) | Shape Parameters |
|---|
| n | R2 | α | R2 |
|---|
| SAC-0 | 20 | 2.981 | 0.9940 | 27.74 | 0.8937 |
| SAC-0 | 200 | 3.799 | 0.9963 | 12.00 | 0.9480 |
| SAC-0 | 400 | 40.08 | 0.9954 | 9.504 | 0.9379 |
| SAC-0 | 600 | 4.452 | 0.9950 | 8.178 | 0.9832 |
| SAC-0 | 800 | 13.33 | 0.9989 | 3.577 | 0.9873 |
| SAC-0.5 | 20 | 4.313 | 0.9823 | 10.81 | 0.9893 |
| SAC-0.5 | 200 | 7.366 | 0.9904 | 6.747 | 0.9714 |
| SAC-0.5 | 400 | 48.53 | 0.9882 | 18.72 | 0.9855 |
| SAC-0.5 | 600 | 3.560 | 0.9960 | 9.645 | 0.8588 |
| SAC-0.5 | 800 | 30.00 | 0.9793 | 3.603 | 0.9660 |
| SAC-1.0 | 20 | 4.508 | 0.9805 | 12.20 | 0.8185 |
| SAC-1.0 | 200 | 4.312 | 0.9963 | 6.038 | 0.9327 |
| SAC-1.0 | 400 | 29.34 | 0.9537 | 7.876 | 0.9957 |
| SAC-1.0 | 600 | 3.993 | 0.9943 | 13.66 | 0.9888 |
| SAC-1.0 | 800 | 319.7 | 0.9840 | 10.31 | 0.9836 |
| SAC-1.5 | 20 | 3.904 | 0.9848 | 4.958 | 0.9150 |
| SAC-1.5 | 200 | 3.941 | 0.9770 | 68.74 | 0.9517 |
| SAC-1.5 | 400 | 25.95 | 0.9753 | 18.00 | 0.8838 |
| SAC-1.5 | 600 | 4.685 | 0.9912 | 26.68 | 0.9638 |
| SAC-1.5 | 800 | 6.638 | 0.9922 | 3.809 | 0.9828 |