Negative Hydrogen and Deuterium Ion Density in a Low Pressure Plasma in Front of a Converter Surface at Different Work Functions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Negative Ion Formation in Low Pressure Plasmas
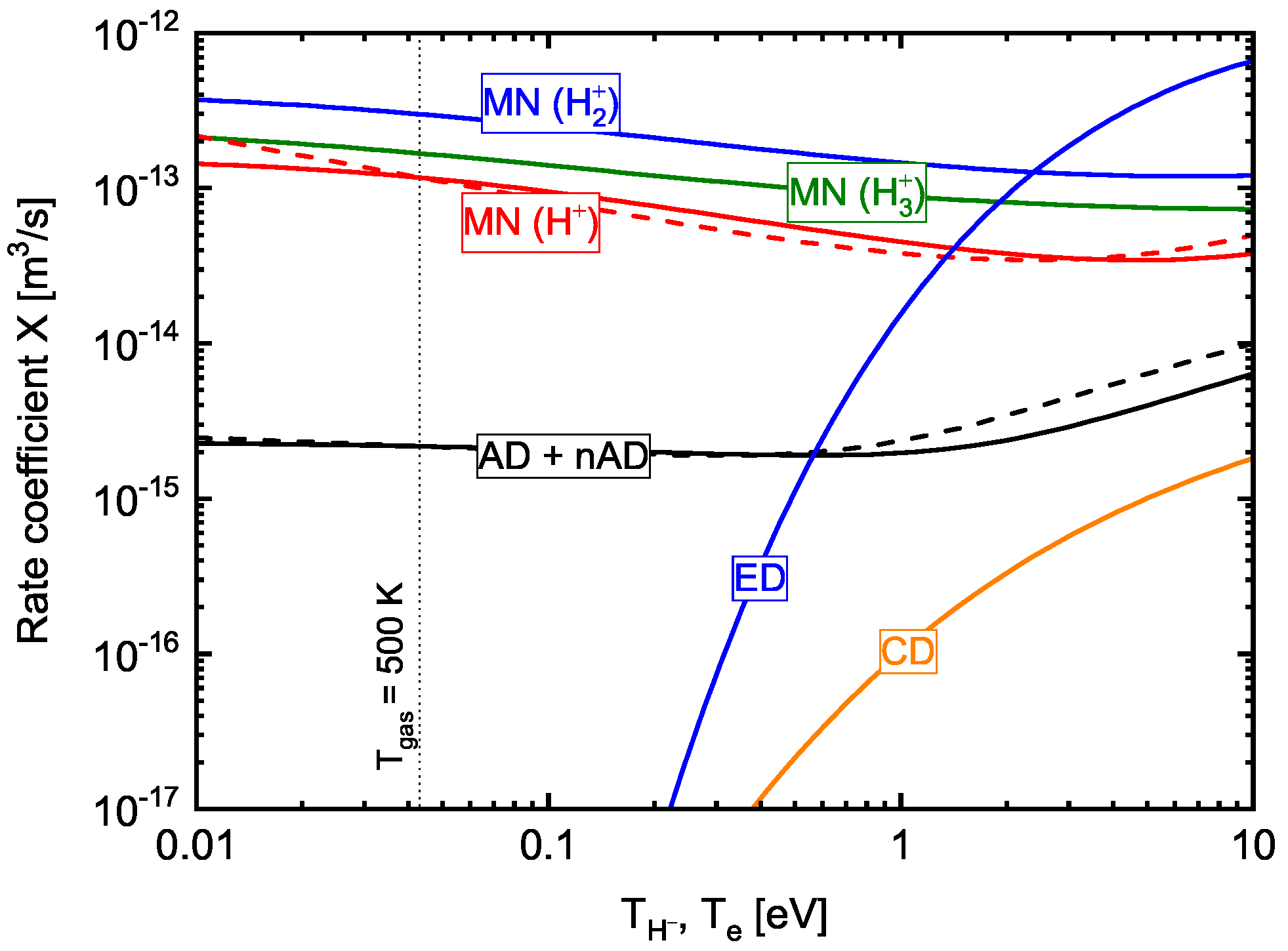
2.1. Volume Formation
2.2. Surface Formation
2.3. Destruction Mechanisms
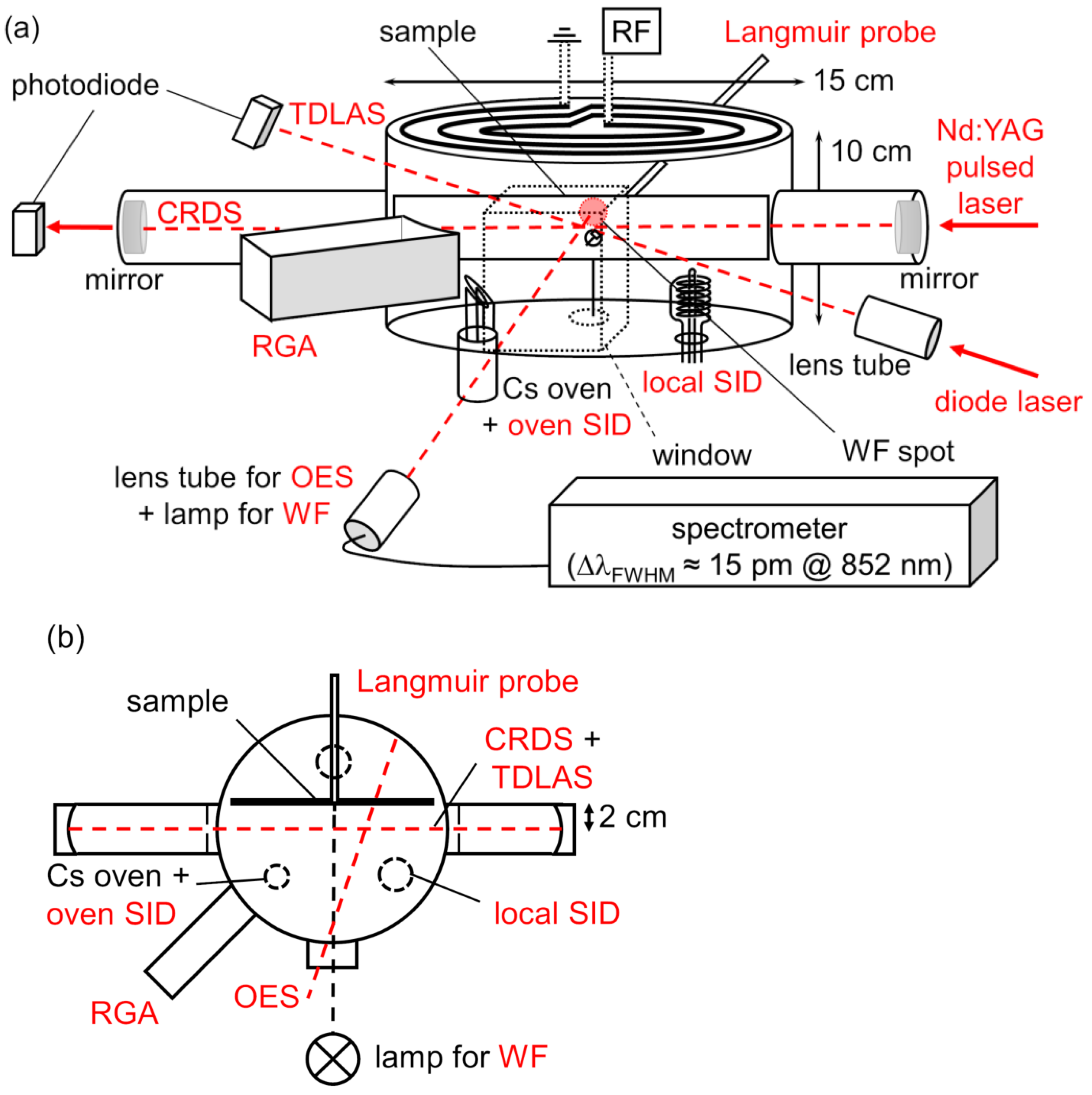
3. Experimental Setup
3.1. Diagnostics
3.2. Measurement Procedure
3.3. Modelling of the H Volume Processes
4. Results and Discussion
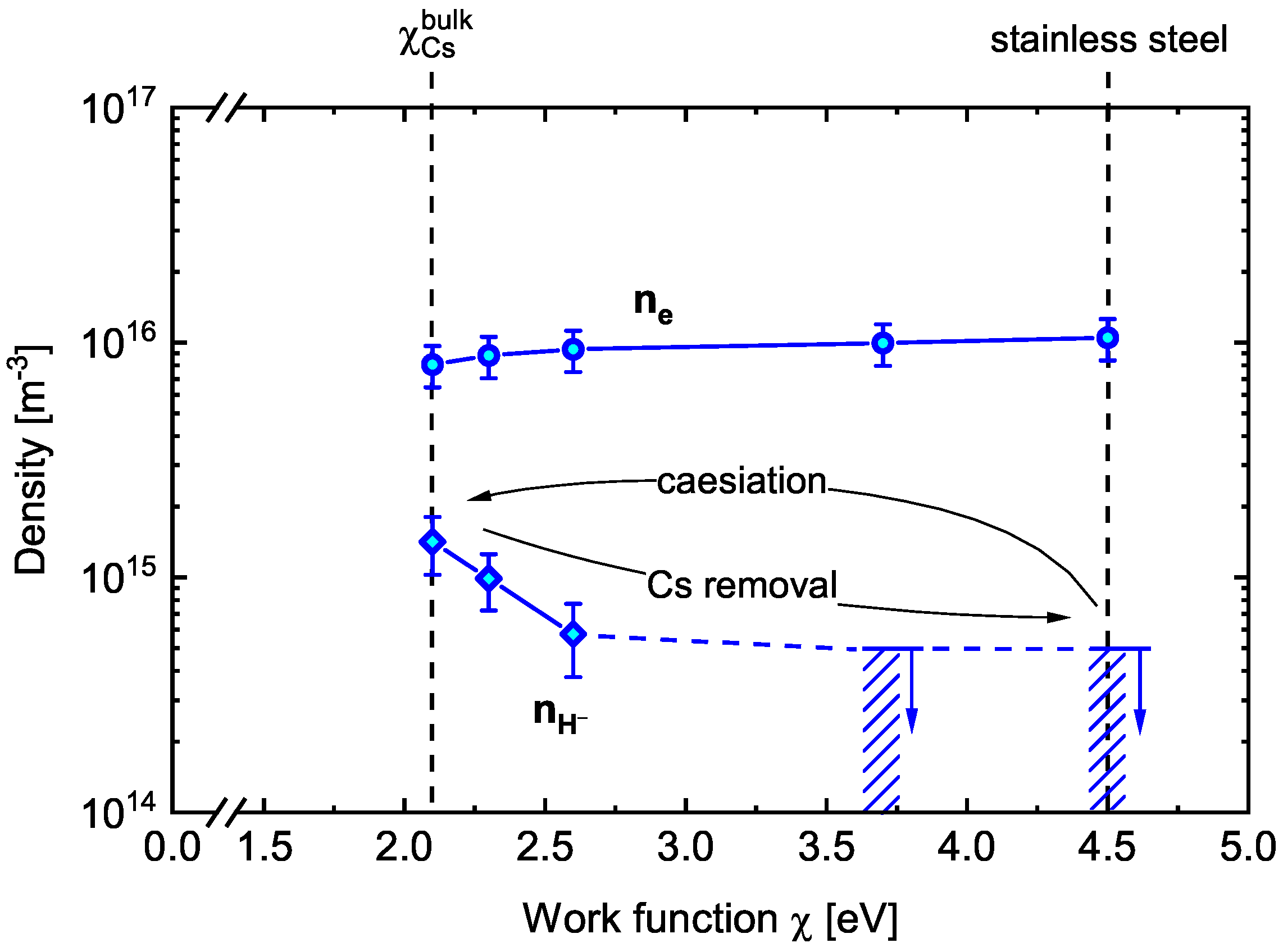
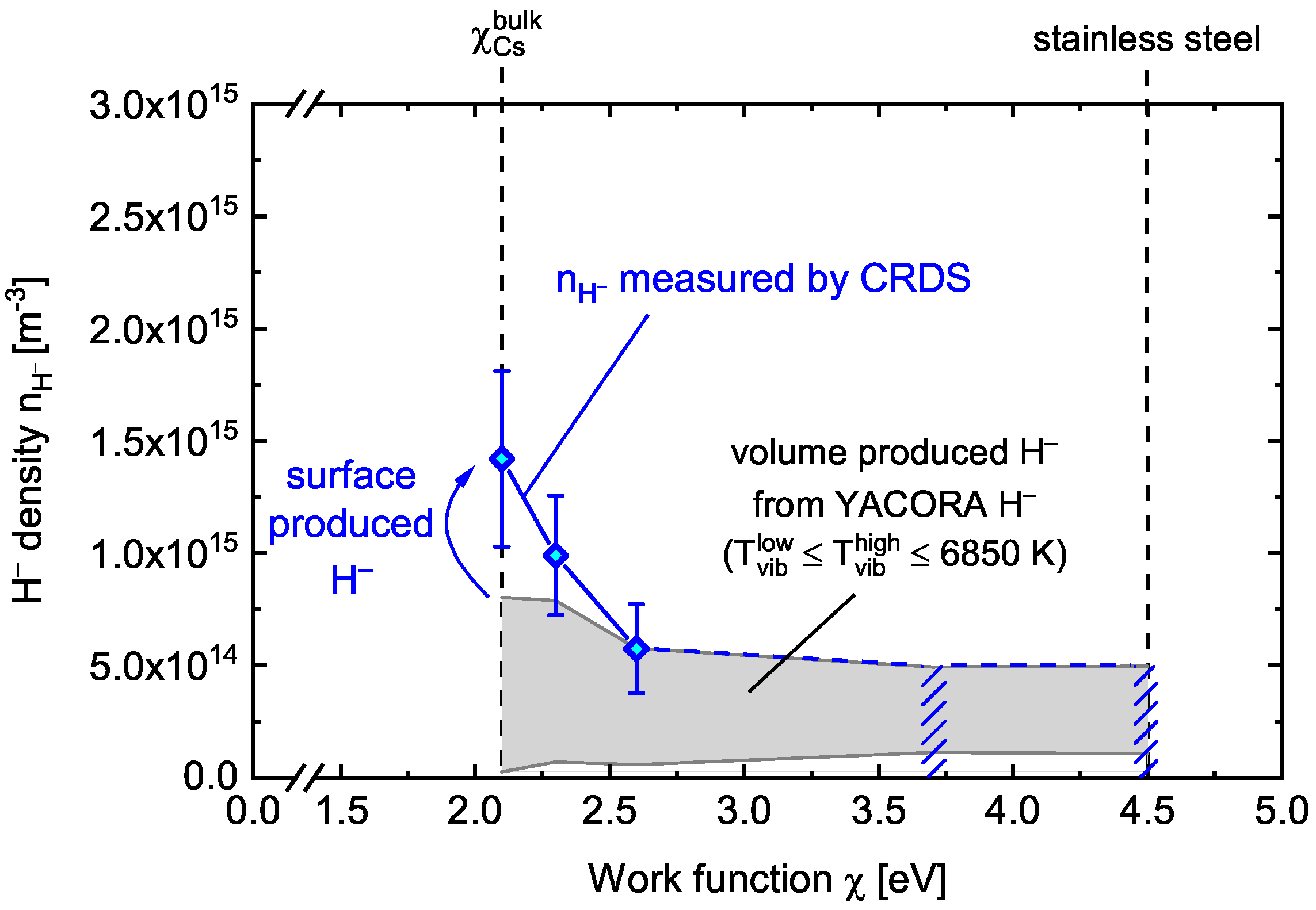
4.1. Correlation between Work Function and H− Density
4.2. Comparison between H and D Plasmas
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IAEA. ITER Technical Basis; ITER EDA Documentation Series 24; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hemsworth, R.; Decamps, H.; Graceffa, J. Status of the ITER heating neutral beam system. Nucl. Fusion 2009, 49, 045006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemsworth, R.S.; Boilson, D.; Blatchford, P. Overview of the design of the ITER heating neutral beam injectors. New J. Phys. 2017, 19, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacal, M.; Wada, M. Negative hydrogen ion production mechanisms. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2015, 2, 021305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelson, H.B. The work function of the elements and its periodicity. J. Appl. Phys. 1977, 48, 4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudnikov, V. Forty years of surface plasma source development. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 83, 02A708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, B.; Fantz, U.; Kraus, W. Towards large and powerful radio frequency driven negative ion sources for fusion. New J. Phys. 2017, 19, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantz, U.; Hopf, C.; Wünderlich, D. Towards powerful negative ion beams at the test facility ELISE for the ITER and DEMO NBI systems. Nucl. Fusion 2017, 57, 116007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, W.; Wünderlich, D.; Fantz, U. Deuterium results at the negative ion source test facility ELISE. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 052102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, C.; Mimo, A.; Lindauer, M. Improved understanding of the Cs dynamics in large H− sources by combining TDLAS measurements and modeling. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 2011, 060001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofaro, S.; Friedl, R.; Fantz, U. Correlation of Cs flux and work function of a converter surface during long plasma exposure for negative ion sources in view of ITER. Plasma Res. Express 2020, 2, 035009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumori, K.; Nakano, H.; Kisaki, M. Spatial distribution of the charged particles and potentials during beam extraction in a negative-ion source. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 83, 02B116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wünderlich, D.; Riedl, R.; Bonomo, F. Achievement of ITER-relevant accelerated negative hydrogen ion current densities over 1000 s at the ELISE test facility. Nucl. Fusion 2019, 59, 084001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimo, A.; Nakano, H.; Wimmer, C.; Wünderlich, D.; Fantz, U.; Tsumori, K. Cavity ring-down spectroscopy system for the evaluation of negative hydrogen ion density at the ELISE test facility. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 91, 013510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wünderlich, D.; Gutser, R.; Fantz, U. PIC code for the plasma sheath in large caesiated RF sources for negative hydrogen ions. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2009, 18, 045031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantz, U.; Schiesko, L.; Wünderlich, D.; the NNBI Team. A comparison of hydrogen and deuterium plasmas in the IPP prototype ion source for fusion. AIP Conf. Proc. 2013, 1515, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomin, M. Application of Collisional Radiative Models for Atomic and Molecular Hydrogen to a Negative Ion Source for Fusion. Master’s Thesis, University of Padova, Padova, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Friedl, R.; Fantz, U. Influence of H2 and D2 plasmas on the work function of caesiated materials. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 083304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardsley, J.N.; Wadehra, J.M. Dissociative attachment and vibrational excitation in low-energy collisions of electrons with H2 and D2. Phys. Rev. A 1979, 20, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, E.; Denifl, S.; Čadež, I.; Markelj, S.; Mason, N.J. Dissociative Electron Attachment Cross Sections for H2 and D2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 243201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isenberg, J.D.; Kwon, H.J.; Seidl, M. Surface production of H− ions by backscattering of H+ and ions in the 3–50 eV ion energy range. AIP Conf. Proc. 1992, 287, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, M.; Cui, H.L.; Isenberg, J.D. Negative surface ionization of hydrogen atoms and molecules. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasser, B.; Wunnik, J.N.M.v.; Los, J. Theoretical models of the negative ionization of hydrogen on clean tungsten, cesiated tungsten and cesium surfaces at low energies. Surf. Sci. 1982, 118, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørskov, J.K.; Lundqvist, B.I. Secondary-ion emission probability in sputtering. Phys. Rev. B 1979, 19, 5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, N.D.; Nørskov, J.K. The Theory of Ionization Probability in Sputtering. Phys. Scr. 1983, T6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.L. Resonant charge transfer in the scattering of hydrogen atoms from a metal surface. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1991, 9, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnychuk, S.T.; Seidl, M. Reflection of hydrogen atoms from alkali and alkaline earth oxide surfaces. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1991, 9, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.S.; Seidl, M. Surface production of H− ions by hyperthermal hydrogen atoms. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1992, 61, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janev, R.K.; Reiter, D.; Samm, U. Collision Processes in Low-Temperature Hydrogen Plasmas; Berichte des Forschungszentrums Jülich; Forschungszentrum Jülich: Jülich, Germany, 2003; Volume 4105. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, K.A.; Bruhns, H.; Cížek, M. Isotope effect for associative detachment: H(D)− + H(D) → H2(D2) + e−. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 86, 032714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huq, M.S.; Doverspike, L.D.; Champion, R.L. Electron detachment for collisions of H− and D− with hydrogen molecules. Phys. Rev. A 1983, 27, 2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantz, U.; Friedl, R.; Fröschle, M. Controllable evaporation of cesium from a dispenser oven. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 83, 123305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, R.; Fantz, U. Influence of cesium on the plasma parameters in front of the plasma grid in sources for negative hydrogen ions. AIP Conf. Proc. 2013, 1515, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantz, U.; Falter, H.; Franzen, P. Spectroscopy—A powerful diagnostic tool in source development. Nucl. Fusion 2006, 46, S297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, R.; Fantz, U. Fundamental studies on the Cs dynamics under ion source conditions. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 02B109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, R.H. The Analysis of Photoelectric Sensitivity Curves for Clean Metals at Various Temperatures. Phys. Rev. 1931, 38, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, R. Enhancing the accuracy of the Fowler method for monitoring non-constant work functions. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 043901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wünderlich, D.; Fantz, U. Evaluation of State-Resolved Reaction Probabilities and Their Application in Population Models for He, H, and H2. Atoms 2016, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauner, D.; Kurutz, U.; Fantz, U. Comparison of measured and modelled negative hydrogen ion densities at the ECR-discharge HOMER. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 1655, 020017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurutz, U.; Friedl, R.; Fantz, U. Investigations on Cs-free alternatives for negative ion formation in a low pressure hydrogen discharge at ion source relevant parameters. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2017, 59, 075008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacal, M.; Berlemont, P.; Bruneteau, A.M. Measurement of the H− thermal energy in a volume ion source plasma. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 70, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiura, M.; Sasao, M.; Bacal, B. H− laser photodetachment at 1064, 532, and 355 nm in plasma. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, M.A.; Lichtenberg, A.J. Principles of Plasma Discharges and Materials Processing, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cristofaro, S.; Friedl, R.; Fantz, U. Negative Hydrogen and Deuterium Ion Density in a Low Pressure Plasma in Front of a Converter Surface at Different Work Functions. Plasma 2021, 4, 94-107. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma4010007
Cristofaro S, Friedl R, Fantz U. Negative Hydrogen and Deuterium Ion Density in a Low Pressure Plasma in Front of a Converter Surface at Different Work Functions. Plasma. 2021; 4(1):94-107. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma4010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleCristofaro, Sofia, Roland Friedl, and Ursel Fantz. 2021. "Negative Hydrogen and Deuterium Ion Density in a Low Pressure Plasma in Front of a Converter Surface at Different Work Functions" Plasma 4, no. 1: 94-107. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma4010007
APA StyleCristofaro, S., Friedl, R., & Fantz, U. (2021). Negative Hydrogen and Deuterium Ion Density in a Low Pressure Plasma in Front of a Converter Surface at Different Work Functions. Plasma, 4(1), 94-107. https://doi.org/10.3390/plasma4010007





