Abstract
The utilisation of magnesium oxide-based binders (M) as an alternative to hydrated calcium silicate materials is a promising avenue for binding methodologies. However, the efficacy of using silica fume (S) as a co-binder with magnesium oxide in sulphate soil stabilisation, along with their ideal blending ratio, has yet to be unveiled. Therefore, an array of artificial sulphate soil specimens was fabricated, each featuring varying combinations of magnesium oxide and silica fume. These specimens were subsequently subjected to comprehensive testing, including unconfined compressive strength (UCS) test, linear expansion test, thermogravimetric analysis, and X-ray diffraction analysis. The outcomes demonstrated that the co-utilisation of silica fume and magnesium oxide significantly improves the compressive strength and linear expansion of sulphate soil, and such an improvement was more efficacious at a stoichiometric amount of 5% magnesium oxide and 5% silica fume (5M5S). This outperforming threshold, characterised by the highest UCS (1834 kN/m2) and minimal expansion (0.2%), occurred through the consumption of surplus brucite and the formation of further magnesium silicate hydrate.
1. Introduction
In engineering practice, expansive soil is typically gauged as problematic and weak worldwide [1] due to its inherent weaknesses, including spontaneous swelling and shrivelling properties [2,3,4,5]. For this reason, most construction sites have implemented chemical soil stabilisation to reinforce stability and robustness against loading [6,7,8]. This is typically achieved by using a calcium-based stabiliser (cement and lime) at pre-defined proportions [1,7,9,10]. However, in the presence of sulphate, calcium-based soil treatment has proven to be counterproductive or even detrimental [11,12,13], as the soil’s swell–shrink behaviour is exacerbated due to the nucleation and evolution of ettringite [14,15], thereby jeopardising the engineering structures built above them. Apart from that, calcium-based stabilisers induce some environmental issues, such as substantial greenhouse gas emissions emitted to the atmosphere [16,17], the high energy consumption of their production [16,18], and the exploitation of raw materials for cement production [10,19]. Hence, it is essential to develop an alternative and more sustainable binder to remediate sulphate soils [6].
Recently, some by-product materials such as silica fume, S (from the silicon and ferrosilicon industries), and ground granulated blast-furnace slag, GGBS (from the steel industry), among others [20,21,22], have been employed as substitutes for calcium-based stabilisers in sulphate soil stabilisation [5] in order to curtail the inherent weaknesses of calcium-based stabilisers [16,23]. Among these by-products, silica fume, with a total annual production of 1 million tons around the world [24], is a promising avenue in binding sulphate soil, since it can promote better densification and interlocking of the soil matrix [14,25]. This occurs through the complete consumption of surplus calcium hydroxide in the system and the formation of calcium-silicate-hydrates (C-S-H) over calcium-aluminate-hydrates (C-A-H) [14], all of which can result in reduced permeability, enhanced volume stability, and superior strength [25]. Besides the above geo-technical advantages, silica fume has an economic benefit [26] due to its lower cost relative to cement (40% cheaper than Portland cement) [24] and an environmental benefit because there are no emissions associated with its production [7,27].
The utilisation of silica fume is also a recent engineering development offering a wide range of geo-technical and environmental advantages over the use of calcium-based stabilisers and GGBS-activated lime. In this context, research studies by [24,25] reported a reduction in the plasticity index of dispersive soil by the incorporation of silica fume. Ebailila et al. [25] established that, at a fixed binder content of 10 wt%, the use of silica fume (S) with lime (L) in sulphate soil stabilisation at a blending ratio of 3L-7S yielded a lower swelling magnitude (4%) relative to the addition of lime alone (32%) and a binary blend of 3L-7GGBS (7%). Moayyeri et al. [28] concluded that, after soaking in water, the use of 3% lime and 3% silica fume in gypseous soil (with a gypsum content of 50%) yielded higher compressive strength relative to their sole addition. However, there is a gap in the literature about the co-utilisation of silica fume and magnesium oxide in sulphate soil; therefore, a study shedding light on such a hybrid binder and unveiling its effect on the physico-mechanical and microstructural performance of sulphate-bearing soil is needed.
As no study on the co-utilisation of magnesium oxide and silica fume as stabilising agents for sulphate-bearing soils has been documented so far, this research study is anticipated to lay the base of this area and pave the way to an alternative pragmatic solution for ettringite-induced heave in sulphate-bearing soil. This study aims to examine the co-effect of magnesium oxide and silica fume on the physico-mechanical and microstructure properties of artificially sulphate-amended kaolin using multi-scale analyses, including UCS, linear expansion, derivative thermogravimetric, and x-ray diffraction analysis. The outcomes of the experiments demonstrate that the co-utilisation of silica fume and magnesium oxide significantly improves the UCS and linear expansion of sulphate soil, and such an improvement was more efficacious at a stoichiometric amount of 5M5S. These outcomes are important and are practically relevant to all geotechnical engineers involved in the development of a sustainable, low-carbon binder for sulphate soil stabilisation, as they provide a novel, practical solution to counteract strength deterioration and volume increase associated with sulphate soil stabilised with a lime.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Sulphate-Bearing Soil
The sulphate-bearing soil used in the laboratory experiments was an artificial blend of industrial soil (kaolin, K) and one source of sulphate (gypsum, G). K was supplied by Potterycrafts Ltd., Stoke-on-Trent, UK, while G was sourced from Fisher Scientific Ltd., Loughborough, Leicester, UK. The K appeared as a white powder with a liquid limit of 56.7% and plastic limit of 33.3%, from which the soil was classified as a medium graded sandy silt with high plasticity (23.4). The oxide composition of K, obtained by X-ray fluorescence analysis, is summarised in Table 1. The physical properties and particle size distribution of K and G are delineated in Table 2 and Figure 1, respectively.

Table 1.
Oxide composition of kaolin, magnesium oxide, and silica fume.

Table 2.
Some physical properties for the kaolin, magnesium oxide, and silica fume.
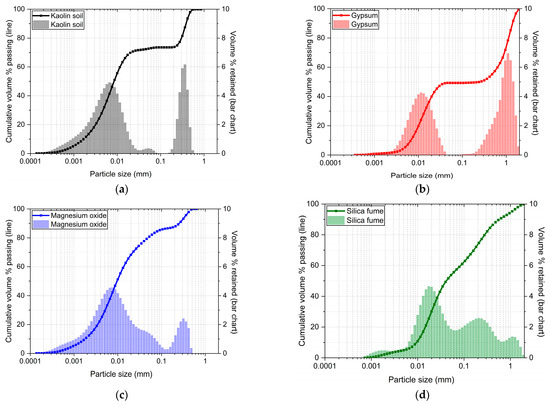
Figure 1.
The granulometric distribution curves of (a) kaolin, (b) gypsum, (c) magnesium oxide, and (d) silica fume.
2.1.2. Binder
Two types of cementitious materials, i.e., magnesium oxide (M) and silica fume (S), were used in this study to form a binary-blend binder. M was purchased from Fisher Scientific Ltd., Loughborough, Leicester, UK, whereas S (commercially undensified microsilica 971) was supplied by Tarmac Cement and Lime Company, Buxton Lime and Powders, Derbyshire, Derby, UK. The oxide compositions of M and S (see Table 1), as obtained by X-ray fluorescence analysis (XRF), were found to be dominated by magnesium oxide (98%) and silicon dioxide (98.4%), respectively.
2.2. Mix Proportions
A total of six mix compositions of stabilised sulphate-bearing soil—consisting of one control mix (with no silica fume) and five binary-blend cases—were designed in this study (see Table 3). The control mix was made of 90% artificial sulphate kaolin (K9G) and 10 wt% magnesium oxide (10M0S), while the subsequent mixes were constructed by replacing magnesium oxide with silica fume at different blending ratios (M:S) of 9:1, 7:3, 5:5, and 3:7. This was to establish the outperforming threshold, beyond which the incorporation of silica fume does not influence the phyisco-mechanical properties of the artificial sulphate soil. In each of the designed mixes, the binder content and moisture content were set at a fixed ratio of 10 wt% and 31 wt% by weight of the dry raw materials, respectively. This allowed for an unbiased comparison of the influence of silica fume content on the artificially amended sulphate soil, and ensured the specimens were made at a comparable densification.

Table 3.
Mix design of kaolin specimens stabilised with magnesium oxide and silica fume.
2.3. Sample Preparation
A total of eleven specimens were made for each of the mix compositions outlined in Table 3, two of which were used for swelling and nine of which were used for strength investigation. For each specimen, the preparation was carried out by blending the solid raw materials thoroughly in a mechanical mixer for 3 min, whereupon the predetermined water was added, and the mixing was continued for a further 3 min. Upon gaining a homogeneous mixture, the semi-paste mixture was poured into a 2-piece cylinder-shaped mould with dimensions of 50 mm in diameter by 100 mm in height and compacted using a hydraulic jack. Thereafter, the specimen was extruded using a plunger, labelled, encased in several runs of cling film to preserve moisture, and immediately stored in a hermetically airtight plastic container at a temperature of 20 ± 2 °C and humidity of 90% until the testing date.
2.4. Testing Method
2.4.1. Unconfined Compression Strength (UCS)
The UCS test was conducted in adherence with the specifications outlined in BS 1924-2 and BS EN ISO 17892–7: 2018 [29,30] using a Hounsfield machine, obtained from Hounsfield Testing Machine Ltd, Unit 6/Perry wood Business Park, Honey Crook Lane, Redhill, Surrey, England, UK. A triplet of three cylindrical specimens, with dimensions of 50 mm diameter by 100 mm height, was axially compressed at a constant loading ratio of 2 mm/min after the respective prescribed curing ages of 7, 14, and 90 days. Upon the collapse of the specimen, small chunks of the broken specimens were milled, sieved, and dried in a desiccator at a temperature of 40 °C with the aid of silica gel to quench/terminate the hydration reaction in preparation for the analytical tests.
2.4.2. Swelling
In line with previous studies [14,25], the swelling test was conducted by means of linear expansion method using Perspex cells, in adherence with BS EN 13286-49: 2004 [31]. After 7 days of moist curing, 10 mm of the upper and bottom sides of two specimens per mix were unwrapped and positioned into a separate Perspex cell with two porous discs: one at the top and one at the bottom of the specimen to facilitate the vertical upward percolation of water within the specimens. Thereafter, the Perspex cells were covered with a lid fitted with a digital dial gauge, and the water was injected through the upper inlet using a syphon until the 10 mm bottom part of the specimen was inundated with water. Hence, the vertical linear deformation (dial gauge reading) was recorded on an irregular interval (most likely a semiweekly basis) for a prolonged soaking period of 200 days, during which the water level was kept constant to avoid the specimen’s evaporation. Finally, the mean ratio of the vertical linear deformation to the original height of the specimen was determined at the end of each interval and reported as the representative swelling.
2.4.3. Mineralogical Investigation
Three major analytical tests, i.e., derivative thermogravimetric (DTG), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis, were performed in this study to pinpoint the change in sulphate-bearing soil in response to variation in the binary blend of magnesium oxide and silica fume. The DTG test was conducted on a powdered portion of small chunks of the 7 UCS specimens by means of a TA Instruments TGA55 kit, which was manufactured by Waters Ltd and obtained from the TA Instruments, a subsidiary of Waters Ltd, Cheshire, UK. The DTG analysis was operated from 40 °C up to 1000 °C through a flow of argon gas at a flow rate of 20 °C/min. The XRD analysis was performed on a powdered portion of small chunks of the 90 UCS specimens using a STOE powder diffraction system. The XRD scans were acquired through a commercial service at the University of Bath, using Cu-Kα radiation at an angle scan (2θ) ranging from 10 to 84, a step size of 0.015°, and a wavelength (λ) of 1.54 Å. The SEM analysis was performed on a powdered portion of 90 UCS specimens using a field emission electron microscope at a lower accelerating voltage of 5 kV.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Derivative Thermogravimetric Analysis (DTG)
The 7-day thermal decomposition of specimens amended with varying proportions of M and S, determined by DTG analysis, is delineated in Figure 2. The 7-day DTG diagrams are primarily composed of two or three main endothermic peaks: the first peak occurs between 100 and 150 °C owing to the dehydration of gypsum [25], the second peak occurs between 350 and 450 °C due to the decomposition of surplus magnesium hydroxide [32], and the third peak occurs between 450 and 750 °C on account of kaolinite mineral dehydroxylation [14]. The gypsum peak height appeared stable in all the 7-day DTG diagrams, suggesting the non-participation of gypsum in the reaction between soil and magnesium oxide. In contrast, the height of the magnesium oxide peak experienced a gradual drop as the silica fume content increased to up to 50 wt% the binder.
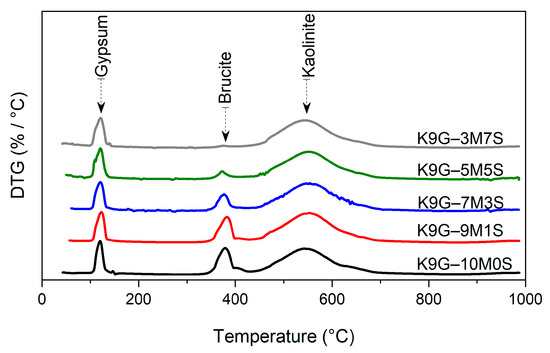
Figure 2.
The 7 days of thermal decomposition of specimens stabilised with 10 wt% magnesium oxide-silica fume (M-S) blends at 7 days of moist curing.
The detection of brucite in the DTG curves of K9G–9M1S, K9G–7M3S, and K9G–5M5S is a sign of the incomplete consumption of brucite through the initial 7-day moist-curing period. This surplus supply of brucite is a possible reason for why specimens rich in magnesium oxide experienced a higher swelling magnitude, which was due to natural expansion and the inability of brucite to provide any binding within the system [33], therefore reducing the cohesion of the system [22] and the dissolution of soil particles [34]. Consequently, this diminished the amount of silicon and aluminium liberated during fabric modification, which is responsible for the initiation of the pozzolanic reaction, thereby delaying the pozzolanic reaction [35]. On further addition of silica fume (3M-7S), the magnesium hydroxide completely disappeared when 70% of the binder was replaced with silica fume, as represented by the thermal diagram of K9G–3M7S. This is a sign of the increased utilisation of magnesium hydroxide (brucite) in the hydration reaction, highlighting the complete consumption of magnesium hydroxide during the initial 7-day curing period via fabric modification, thus no trace of magnesium hydroxide remained for the evolution of the pozzolanic reactions. This was probably because of the higher pozzolanicity of silica fume [36], which can work as seeds, promoting more nucleation sites and accelerating the consumption of brucite. Hence, a lower degree of strength gain associated with fabric modification and pozzolanic hydrates would occur, as represented by 7M-3S (see Section 3.3).
3.2. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
The X-ray diffractograms of the artificial sulphate-bearing specimens—stabilised with addition of solely magnesium oxide (10M) or a binary blend of magnesium oxide and silica fume (5M5S) at (a) 90 days of moist curing or (b) 200 days of soaking—are shown in Figure 3, along with (c) the typical XRD patterns of kaolinite, ettringite, brucite, and gypsum obtained from the open-source integrated database of Roman spectra, X-ray diffraction and chemistry data for minerals (RRUFF).
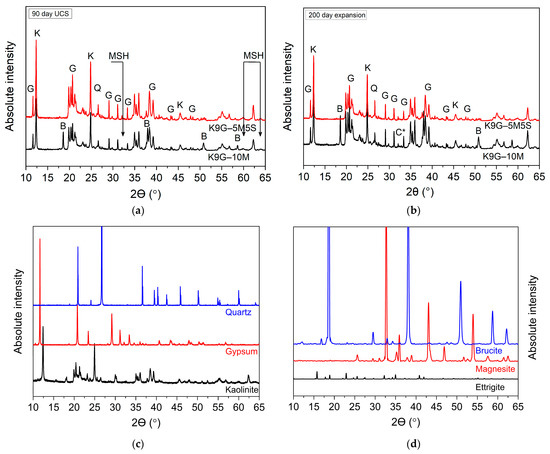
Figure 3.
X-ray diffractions of specimens stabilised with 10 wt% magnesium oxide–silica fume (M–S) blends at (a) 90 days of moist curing and (b) 200 days of water soaking, in comparison with the standard XRD patterns of (c) kaolinite, gypsum, and quartz, as well as (d) brucite, magnesite, and ettringite.
As elaborated in Figure 3, the main minerals detected in the XRD patterns of both specimens are kaolinite, K; gypsum, G; quartz, Q; brucite, B; magnesium carbonate, C*; and magnesium silicate hydrate, MSH. In the case of specimens stabilised with magnesium oxide only, the intensity of brucite reflection—under both curing cases—appeared sharper at 2θ = 18.6°, 38°, 50.8°, and 58.6°, the appearance of which is a clue that extra magnesium oxide is being used in the system. This was accompanied by the detection of magnesium carbonate at a diffraction angle of 2θ = 33°, matching the XRD pattern reported elsewhere [32,37,38]. As for the binary-blend-based specimen (5M5S), brucite was not detected, while the intensity of the magnesium silicate hydrate reflection (MSH) at 2θ = 32.5°, 60°, and 64°, as reported by [39,40], was slightly increased, which is reflected in the DTG curve and confirms the pozzolanic reaction. Eventually, no signs of diffraction of ettringite and periclase (MgO) were detected in all the X-ray diffractograms, supporting the DTG observations and implying the moisture content used for specimen fabrication was sufficient for MgO hydration. The absence of ettringite minerals in both 10M0S and 5M5S was also confirmed by the SEM photographs, as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
The SEM photographs of kaolin specimens stabilised with 10M0S (a) and 5M5S (b) at 90 days of moist curing.
3.3. Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS)
The UCS trends of kaolin specimens stabilised with different binary blends of magnesium oxide and silica fume over a prolonged moist-curing period of 90 days are elaborated on in Figure 5. Overall, the observation revealed that the strength trajectory for all the formulations epitomises a typical soil stabilisation trend, where the strength increases as the curing age increases. This strength increase can typically be assigned to two main factors: fabric modification due to cation exchange and flocculation–agglomeration of soil particles and the interlocking of the soil matrix due to the formation of hydrates through a pozzolanic reaction between the soil and binder [41,42]. On the substitution of magnesium oxide with silica fume, the strength increased correspondingly as the silica fume content increased up to a certain dosage of 5M:5S. This optimal dosage yielded about a two-fold strength increase, as represented by the increase from 927 kN/m2 for K9G–10M0S to the highest point of 1834 kN/m2 for K9G–5M5S. This strength outperformance could be credited to two key reasons: the complete consumption of magnesium oxide (as detected by XRD) and the formation of further magnesium silicate hydrates [43]. The complete depletion of magnesium oxide improves the strength by overcoming the negative impact of brucite on the cohesion of the system, while the continuation of hydration contributes to better densification, interlocking, and pore-blocking effects, all of which reinforce robustness against loading [36,41].
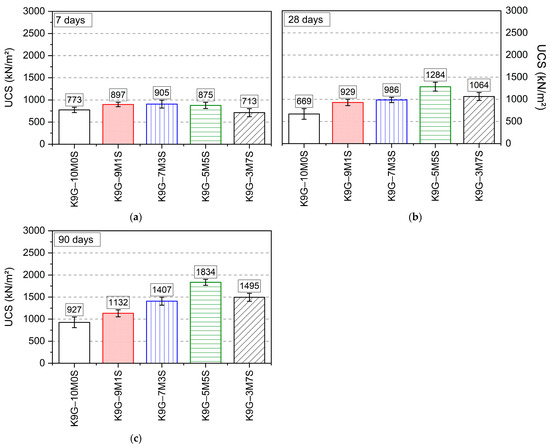
Figure 5.
The UCS performance of kaolin specimens stabilised with 10 wt% magnesium oxide-silica fume (M-S) blends at a curing age of (a) 7 days, (b) 28 days, and (c) 90 days.
However, upon further addition of silica fume (70%), the strength improvement was negatively impacted, with the strength dwindling to 1495 kN/m2 for K9G–3M7S, representing a 20% strength reduction relative to the threshold for K9G–5M5S. The reason for this strength reduction may be ascribed to the deficiency of magnesium oxide content and the abundance of silica fume content within the system, along with its associated pozzolanic activity. That is, the provision of a higher quantity (7%) of highly reactive materials (silica fume) would have promoted more reactive and attractive nucleation sites for hydration [36]. This therefore affected the short-term reaction (soil–binder reaction) by causing a faster depletion of magnesium oxide, thus promoting a lesser degree of fabric modification (cation exchange and flocculation–agglomeration of soil particles) and a more poorly interlocked system. The poorer interlocking then induced a lower degree of strength gain associated with fabric modification. To summarize, silica fume has the potential to substitute up to 70% of the magnesium oxide in sulphate soil stabilisation with no compromise in strength, but 50% is the optimal substitution proportion for strength performance.
3.4. Linear Expansion
The swelling trajectories of kaolin specimens ameliorated by various blends of magnesium oxide and silica fume over a 200-day soaking period are shown in Figure 6. In general, regardless of the binder composition, all the formulations exhibited minor swelling during the initial 20 days of soaking, before plateauing out at approximately the same level throughout the rest of the soaking period.

Figure 6.
The swelling plots of kaolin specimens stabilised with 10 wt% magnesium oxide-silica fume (M-S) blends over a 200-day water soaking period.
The sample with the sole addition of magnesium oxide (see K9G–10M0S) experienced a lower swelling percentage relative to the pure kaolin (6.2%), as tabulated in Table 2; nevertheless, it yielded the highest swelling magnitude of 1% among all the M-S formulations. In general, the swelling reduction induced by magnesium oxide is generally attributed to two major reactions, a short-term reaction (cation exchange and flocculation and agglomeration of soil particles) and long-term reaction (pozzolanic reaction between magnesium oxide and soil), all of which contribute to the formation of magnesium silicate hydrate, the interlocking of the system, and the stability of the soil matrix when soaked in water [14,25]. As for the higher swelling magnitude of 1% for the sample with sole addition of magnesium oxide among all the M-S formulations, this was probably due to the expansion and the inability of brucite to provide any binding within the system [33], therefore reducing the cohesion of the system [22] and inducing poorer interlocking.
Upon the substitution of magnesium oxide with silica fume, the swelling behaviour experienced a gradual drop as the substitution level increased up to an amount of 50%, representing a binder domination sequence similar to that of the UCS. In this context, the ultimate swelling magnitude dropped to the lowest value of 0.22% as represented by K9G–5M5S. This enhanced swelling was due to the complete consumption of surplus brucite and the formation of further magnesium silicate hydrates, as both promote proper cohesion and interlocking of the system and therefore improve the stability of soil under soaking conditions [36,44]. However, on further addition of silica fume, the swelling magnitude slightly increased to 0.3% for K9G–3M7S, representing an about 30% increase relative to the optimal value of 0.22% for its counterpart, K9G–5M5S. Similarly to UCS, this reverse trend was probably caused by the lack of magnesium oxide and the high concentration of silica fume, of which the latter promotes more reactive and competitive nucleation sites for hydration [36]. These reactive sites lead to faster consumption of magnesium oxide, less fabric modification, and relatively poorer interlocking, resulting in relatively less enhanced swelling.
4. Conclusions
The co-utilisation of magnesium oxide and silica fume as a blended binder for sulphate-bearing soil was assessed in this study using diverse tests, and the main outcomes can be summarised as follows:
- The UCS performance of sulphate soil stabilisation with silica fume as a co-additive to magnesium oxide revealed a steadily increasing strength trend as the silica fume content increased to a dosage of 5M:5S, beyond which such an increase was gradually countermanded.
- The outperforming threshold of the binary blend of magnesium oxide and silica fume for both unconfined compressive strength and linear expansion was achieved at an equal blend proportion of 5M:5S.
- The addition of silica fume in the magnesium oxide-based system improves expansion and strength through the consumption of brucite and formation of further magnesium silicate hydrates, both of which facilitate better densification, cohesion, and system interlocking.
- The co-utilisation of a binary blend of magnesium oxide and silica fume offers a practical solution to counteract strength loss and swelling increase in sulphate-bearing soil stabilised with a calcium-based stabiliser.
Overall, the outcomes of the experiments underscore the potential utilisation of a binary blend of magnesium oxide and silica fume as an effective stabilising agent for sulphate-bearing soils, particularly for enhancing their strength and ameliorating their expansion. However, further research using different natural sulphate-bearing soils and different sources of silicon dioxide is essential for validation and proper comprehension of the efficiency of such a binder blend.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.O., M.E., K.E. and J.K.; methodology, J.O., M.E., K.E. and J.K.; software, M.E. and K.E.; validation, J.O., M.E., K.E. and J.K.; formal analysis, M.E. and K.E.; investigation, M.E. and K.E.; resources, J.O., M.E., K.E. and J.K.; data curation, M.E. and K.E.; writing—original draft preparation, M.E. and K.E.; writing—review and editing, J.O. and J.K.; visualisation, J.O., M.E., K.E. and J.K.; supervision, J.K.; project administration, J.O., M.E., K.E. and J.K.; funding acquisition, J.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the Advanced Materials Testing Centre (AMTsC) within the School of Engineering at the University of South Wales for the administrative and technical support during the implementation of the laboratory experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| UCS | Unconfined Compressive Strength |
| MSH | Magnesium Silicate Hydrate |
| K | Kaolin |
| G | Gypsum |
| S | Silica Fume |
| M | Magnesium Oxide |
References
- Khodabandeh, M.A.; Nagy, G.; Török, Á. Stabilization of Collapsible Soils with Nanomaterials, Fibers, Polymers, Industrial Waste, and Microbes: Current Trends. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 368, 130463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gharbawi, A.S.A.; Najemalden, A.M.; Fattah, M.Y. Expansive Soil Stabilization with Lime, Cement, and Silica Fume. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Leo, C.; Zeng, Q.; Fanna, D.J.; Hsi, J.; Karimi, R.; Fabbri, A.; Liyanapathirana, S.; Hu, P.; Alzghool, H. Efficacy of Expansive Soil Stabilisation Using Un-Calcinated Kaolinite-Based Alkali-Activated Binders. Clean. Mater. 2025, 16, 100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, J.R.; Islam, M.S. Characteristics of Compressed Stabilized Earth Block Fabricated with Sawdust Ash Based Geopolymer. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 101, 111840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Antunes, M.A.; Perlot, C.; Espuelas, S.; Marcelino, S.; Seco, A. Recent Developments in Stabilized Rammed Earth: Testing Protocols and the Recommendations for Standardization. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 106, 112436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthiban, D.; Vijayan, D.S.; Koda, E.; Vaverkova, M.D.; Piechowicz, K.; Osinski, P.; Duc, B. Van Role of Industrial Based Precursors in the Stabilization of Weak Soils with Geopolymer—A Review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaini, M.S.I.; Hasan, M.; Almuaythir, S.; Hyodo, M. Experimental Investigations on Physico-Mechanical Properties of Kaolinite Clay Soil Stabilized at Optimum Silica Fume Content Using Clamshell Ash and Lime. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulal, P.; Maharjan, S.; Timalsina, M.P.; Maharjan, Y.; Giri, A.; Tamang, A. Engineering Properties of Cement-Stabilized Compressed Earth Bricks. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 77, 107453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.Y.; Hossain, Z. Investigating the One-Dimensional Consolidation Properties of River Sludge Enhanced by Sustainable Additive Synergy for Eco-Friendly Stabilization. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 101, 111851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, H.; Su, J.; Wu, Z. Strength Performance and Enhancement Mechanism of Silty Sands Stabilized with Cement, Red Mud, and Phosphogypsum. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 73, 106762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldaood, A.; Bouasker, M.; Al-Mukhtar, M. Mechanical Behavior of Gypseous Soil Treated with Lime. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2021, 39, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnood, A. Soil and Clay Stabilization with Calcium- and Non-Calcium-Based Additives: A State-of-the-Art Review of Challenges, Approaches and Techniques. Transp. Geotech. 2018, 17, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehwailat, K.I.A.; Mohamad Ismail, M.A.; Ezreig, A.M.A. Novel Approach to the Treatment of Gypseous Soil-Induced Ettringite Using Blends of Non-Calcium-Based Stabilizer, Ground Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag, and Metakaolin. Materials 2021, 14, 5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebailila, M.; Kinuthia, J.; Oti, J. Suppression of Sulfate-Induced Expansion with Lime–Silica Fume Blends. Materials 2022, 15, 2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyo, E.U.; Abbey, S.J.; Ngambi, S.; Ganjian, E.; Coakley, E. Incorporation of a Nanotechnology-Based Product in Cementitious Binders for Sustainable Mitigation of Sulphate-Induced Heaving of Stabilised Soils. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 24, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H. Feasibility and Performance Assessment of Novel Framework for Soil Stabilization Using Multiple Industrial Wastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 449, 138228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, S.; Bogas, J.A.; Cruz, R.; Gomes, M.G. Eco-Recycled Cement’s Effect on the Microstructure and Hygroscopic Behaviour of Compressed Stabilised Earth Blocks. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimboe, A.G.; Abo, M.T.; Djobo, J.N.Y.; Tome, S.; Kaze, R.C.; Deutou, J.G.N. Lateritic Soil Based-Compressed Earth Bricks Stabilized with Phosphate Binder. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 31, 101465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasehchi, E.; Arjomand, M.A.; Alizadeh Elizei, M.H. Experimental Investigation of the Feasibility of Stabilizing Inshore Silty Sand Soil Using Geopolymer Based on Ceramic Waste Powder: An Approach to Upcycling Waste Material for Sustainable Construction. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e02979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seco, A.; del Castillo, J.M.; Espuelas, S.; Marcelino, S.; García, B. Sulphate Soil Stabilisation with Magnesium Binders for Road Subgrade Construction. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 23, 1840–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yi, Y.; Puppala, A.J. Suppressing Ettringite-Induced Swelling of Gypseous Soil by Using Magnesia-Activated Ground Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2020, 146, 06020008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choobbasti, A.J.; Kutanaei, S.S. Microstructure Characteristics of Cement-Stabilized Sandy Soil Using Nanosilica. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2017, 9, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskisar, T.; Rahat, E. Stabilization of Recycled and Pure Soils Using Mussel Shell Powder and Cement: Experimental Evaluation of Strength and Durability. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2025, 67, 102073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türköz, M.; Umu, S.U.; Öztürk, O. Effect of Silica Fume as a Waste Material for Sustainable Environment on the Stabilization and Dynamic Behavior of Dispersive Soil. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebailila, M.; Kinuthia, J.; Oti, J.; Al-Waked, Q. Sulfate Soil Stabilisation with Binary Blends of Lime–Silica Fume and Lime–Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag. Transp. Geotech. 2022, 37, 100888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Dash, H.K.; Samantaray, S. Effect of Silica Fume on Engineering Properties of Expansive Soil. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 5035–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, B.C.; Williams, R.P.; Lay, J.; Van Riessen, A.; Corder, G.D. Costs and Carbon Emissions for Geopolymer Pastes in Comparison to Ordinary Portland Cement. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1080–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayyeri, N.; Oulapour, M.; Haghighi, A. Study of Geotechnical Properties of a Gypsiferous Soil Treated with Lime and Silica Fume. Geomech. Eng. 2019, 17, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS 1924-2; Hydraulically Bound and Stabilized Materials for Civil Engineering Purposes—Part 2: Sample Preparation and Testing of Materials During and After Treatment. BSI Standards Limited: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 9780580974199.
- BS EN ISO 17892-7: 2018; Geotechnical Investigation and Testing-Laboratory Testing of Soil—Part 7: Unconfined Compression Test. BSI Standards Limited: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 178927:2017.
- BS EN 13286-49: 2004; Unbound and Hydraulically Bound Mixtures—Part 49: Accelerated Swelling Test for Soil Treated by Lime and/or Hydraulic Binder. BSI Standards Limited: London, UK, 2004; ISBN 0580435644.
- Jin, F.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Thermogravimetric Study on the Hydration of Reactive Magnesia and Silica Mixture at Room Temperature. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 566, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonat, C.; Unluer, C. Investigation of the Performance and Thermal Decomposition of MgO and MgO-SiO2 Formulations. Thermochim. Acta 2017, 655, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konan, K.L.; Peyratout, C.; Smith, A.; Bonnet, J.P.; Rossignol, S.; Oyetola, S. Comparison of Surface Properties between Kaolin and Metakaolin in Concentrated Lime Solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 339, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemeda, Y.C.; Deneele, D.; Ouvrard, G. Short-Term Lime Solution-Kaolinite Interfacial Chemistry and Its Effect on Long-Term Pozzolanic Activity. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 161, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Du, P.; Cheng, X. Effects of Nano-Silica on Hydration Properties of Tricalcium Silicate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, H.; Yu, H. Preparation and Properties of Modified Magnesium Oxysulfate Cement Derived from Waste Sulfuric Acid. Adv. Cement Res. 2016, 28, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonat, C.; Teo, W.W.; Unluer, C. Performance and Microstructure of MgO-SiO2 Concrete under Different Environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 184, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Vandeperre, L.J.; Cheeseman, C.R. Formation of Magnesium Silicate Hydrate (M-S-H) Cement Pastes Using Sodium Hexametaphosphate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 65, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zou, J.; Wang, B.; Wu, Z.; Jia, Y.; Cheeseman, C.R. Characterization of Magnesium Silicate Hydrate (MSH) Gel Formed by Reacting MgO and Silica Fume. Materials 2018, 11, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimiazar, J.; Sharifi Teshnizi, E.; O’Kelly, B.C.; Sadeghi, S.; Karimizad, N.; Yazdi, A.; Arjmandzadeh, R. Effect of Nano-Silica on Engineering Properties of Lime-Treated Marl Soil. Transp. Geotech. 2023, 43, 101123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, H.; Haoran, T.; Guojun, C.; Dongdong, M.; Kai, H.; Lulu, L.; Fengyun, W. Research on the Dynamic Fracture Characteristics and Constitutive Model of Cement-Metakaolin Stabilized Soil under Freeze-Thaw Cycle Conditions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 481, 141641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Miao, M.; Yan, P. Hydration Characteristics and Expansive Mechanism of MgO Expansive Agents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 183, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obuzor, G.N.; Kinuthia, J.M.; Robinson, R.B. Utilisation of Lime Activated GGBS to Reduce the Deleterious Effect of Flooding on Stabilised Road Structural Materials: A Laboratory Simulation. Eng. Geol. 2011, 122, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).