The Influence of Accumulated Radiolysis Products on the Mechanisms of High-Temperature Degradation of Two-Component Lithium-Containing Ceramics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
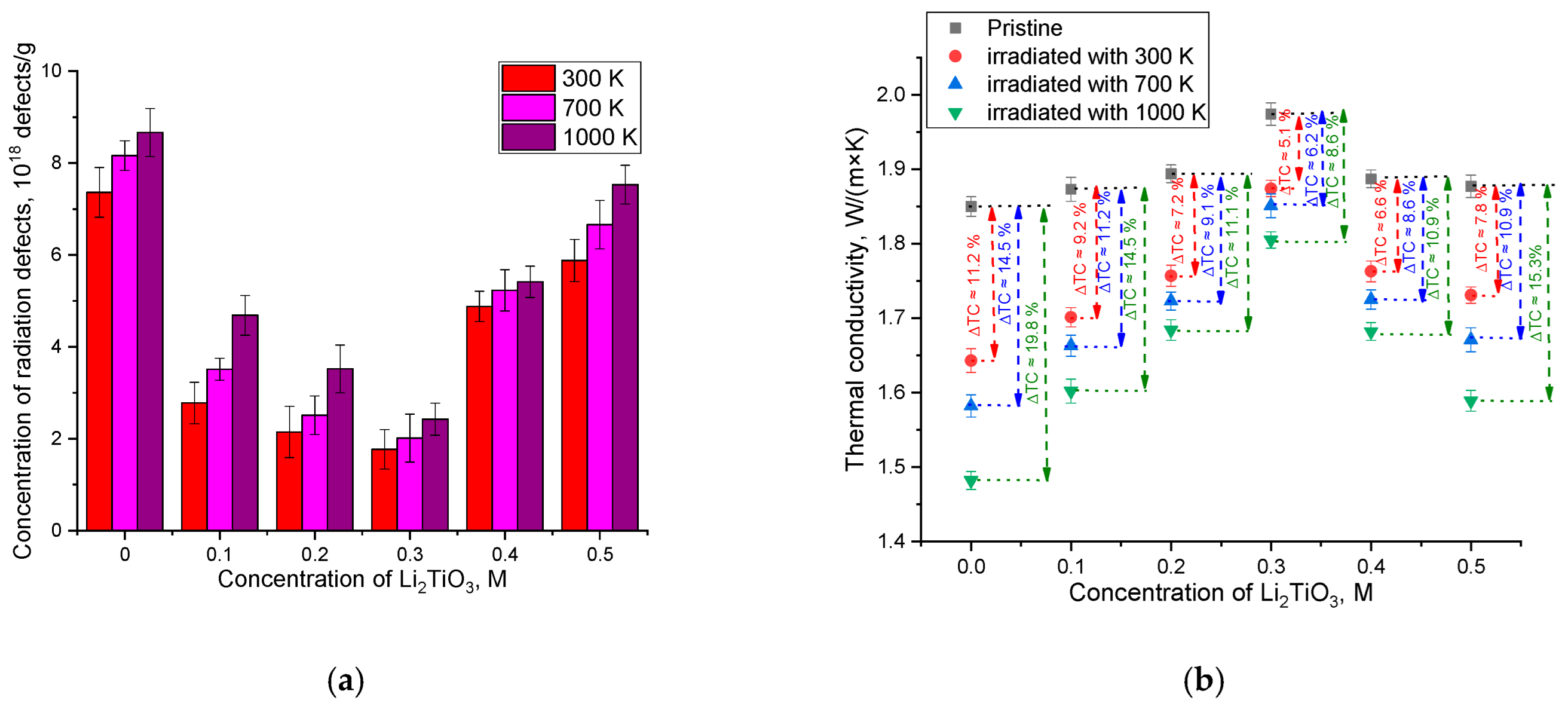
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanaor, D.A.; Kolb, M.H.; Gan, Y.; Kamlah, M.; Knitter, R. Solution based synthesis of mixed-phase materials in the Li2TiO3–Li4SiO4 system. J. Nucl. Mater. 2015, 456, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Wang, C.; Gu, S.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Luo, G.N. Effect of annealing on microstructure and thermal conductivity of Li2TiO3 and Li4SiO4. Nucl. Mater. Energy 2022, 31, 101191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, M.; Shrivastava, A.; Patel, H.A. Fabrication methods for lithium based ceramic material development-A Review. Invertis J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 10, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, G.; Yang, M.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, C. Modeling of tritium release behavior of biphasic Li2TiO3–Li4SiO4 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 22421–22429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qi, J.; Guo, H.; Chen, R.; Yang, M.; Gong, Y.; Lu, T. Influence of helium ion radiation on the nano-grained Li2TiO3 ceramic for tritium breeding. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 28357–28366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Chen, R.; Yang, M.; Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Shi, Y.; Lu, T. Fast fabrication of high quality Li2TiO3–Li4SiO4 biphasic ceramic pebbles by microwave sintering: In comparison with conventional sintering. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 19022–19026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tīliks, J.; Ķizāne, G.; Vitiņš, A.; Vītiņš, Ģ.; Meistars, J. Physicochemical processes in blanket ceramic materials. Fusion Eng. Des. 2003, 69, 519–522. [Google Scholar]
- Tolstolutskaya, G.D.; Karpov, S.A.; Ruzhytskiy, V.V.; Nikitin, A.V. Ion-implanted deuterium release behavior from Li-based advanced ceramics. Probl. At. Sci. Technol. 2022, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ryskulov, A.E.; Ivanov, I.A.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Konuhova, M. The effect of residual mechanical stresses and vacancy defects on the diffusion expansion of the damaged layer during irradiation of BeO ceramics. Opt. Mater. X 2024, 24, 100375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, U.Y. Future of hydrogen as an alternative fuel for next-generation industrial applications; challenges and expected opportunities. Energies 2022, 15, 4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Sun, F.; Hirata, S.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Oya, Y. Effect of neutron dose on the tritium release behavior of Li2TiO3–0.5 Li4SiO4 biphasic ceramic. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 4363–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Sena, A.; Ying, A.; Abdou, M. Effective thermal conductivity of lithium ceramic pebble beds for fusion blankets: A review. Fusion Sci. Technol. 2005, 47, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhao, L.; Ran, G.; Gong, Y.; Wang, H.; Peng, S.; Xiao, C.; Chen, X.; Lu, T. Tritium release behavior of Li2TiO3 and 2Li2TiO3-Li4SiO4 biphasic ceramic pebbles fabricated by microwave sintering. Fusion Eng. Des. 2021, 168, 112390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotomin, E.; Kuzovkov, V.; Popov, A.I.; Maier, J.; Vila, R. Anomalous kinetics of diffusion-controlled defect annealing in irradiated ionic solids. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanfukuji, A.; Zhou, Q.; Oya, Y. Effects of lead addition on tritium recovery for advanced Li2TiO3-Li4SiO4 mixed breeder material. J. Nucl. Mater. 2024, 597, 155141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, N.; Fukuda, S.; Nakajima, T.; Ogawa, H.; Fujimura, Y.; Taguchi, T. Ion tracks and nanohillocks created in natural zirconia irradiated with swift heavy ions. Materials 2024, 17, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunami, N.; Sataka, M.; Okayasu, S.; Tsuchiya, B. Modification of Cu Oxide and Cu Nitride Films by Energetic Ion Impact. Quantum Beam Sci. 2024, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snopiński, P.; Barlak, M.; Nowakowska-Langier, K. Ar+ Ion Irradiation Response of LPBF AlSi10Mg Alloy in As-Built and KOBO-Processed Conditions. Symmetry 2024, 16, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Xue, L.; Li, H.; Yan, Y. Synthesis of the biphasic mixture of Li2TiO3-Li4SiO4 and its irradiation performance. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 4107–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroni, C.; Olsen, T.; Wharry, J.P.; Xiong, H. Irradiation-induced amorphous-to-crystalline phase transformations in ceramic materials. Materials 2022, 15, 5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Tracy, C.L.; Zhang, F.; Park, C.; Trautmann, C.; Tkachev, S.N.; Lang, M.; Mao, W.L.; Ewing, R.C. Radiation-induced disorder in compressed lanthanide zirconates. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 6187–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, M.H.H.; Mukai, K.; Knitter, R.; Hoshino, T. Li4SiO4 based breeder ceramics with Li2TiO3, LiAlO2 and LiXLaYTiO3 additions, part I: Fabrication. Fusion Eng. Des. 2017, 115, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulsartov, T.; Zaurbekova, Z.; Knitter, R.; Chikhray, Y.; Kenzhina, I.; Askerbekov, S.; Kizane, G. Reactor experiments on irradiation of two-phase lithium ceramics Li2TiO3/Li4SiO4 of various ratios. Fusion Eng. Des. 2023, 197, 114035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Kang, K.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Ren, S.; Zhang, G. Fabrication of fine-grained Li2TiO3 ceramic with enhanced performance using high-energy ball milling. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol 2024, 21, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Gu, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhu, X. Research on the preparation, electrical and mechanical properties of γ-LiAlO2 ceramics. J. Nucl. Mater. 2004, 329, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, H.; Xu, P.; Tu, B.; Zong, X.; Zheng, K.; Fu, Z. Crystal structure and bond-valence investigation of nitrogen-stabilized LiAl5O8 spinels. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 62, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.J.; Mazumder, R.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Chaudhuri, P. Fabrication and characterization of Li4SiO4-Li2TiO3 composite ceramic pebbles using extrusion and spherodization technique. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 5174–5183. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Zhuo, L.; Zhang, G. In-situ generation of Li2TiO3/Li2SiO3 particles in Li4SiO4 using TiO2 addition for grain refinement and improved thermal cycling stability. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 42976–42985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikhray, Y.; Askerbekov, S.; Knitter, R.; Kulsartov, T.; Shaimerdenov, A.; Aitkulov, M.; Zarins, A. Studies of irradiated two-phase lithium ceramics Li4SiO4/Li2TiO3 by thermal desorption spectroscopy. Nucl. Mater. Energy 2024, 38, 101621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Gu, S.; Nakata, M.; Zhou, H.; Oya, Y.; Luo, G.N. Comparison of tritium release behavior in Li2TiO3 and promising core-shell Li2TiO3–Li4SiO4 biphasic ceramic pebbles. J. Nucl. Mater. 2020, 539, 152330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, D.R.; Chaudhuri, P.; Swaminathan, N. Primary radiation damages in Li2TiO3 and Li4SiO4: A comparison study using molecular dynamics simulation. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 2022, 177, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, E.; Hernández, T. The effect of γ-radiation in Li4SiO4 ceramic breeder blankets. Fusion Eng. Des. 2015, 90, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Liu, L.; Qi, J.; Yang, M.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Zhang, G.; Lu, T. A comprehensive study on Li4Si1−xTixO4 ceramics for advanced tritium breeders. J. Adv. Ceram. 2020, 9, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenzhina, I.E.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Chikhray, Y.; Kulsartov, T.; Zaurbekova, Z.; Begentayev, M.; Askerbekov, S. Study of gas swelling processes under irradiation with protons and He2+ ions in Li4SiO4–Li2TiO3 ceramics. Crystals 2023, 13, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenzhina, I.E.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Tolenova, A.; Begentayev, M.; Askerbekov, S. The connection between the accumulation of structural defects caused by proton irradiation and the destruction of the near-surface layer of Li4SiO4–Li2TiO3 ceramics. Opt. Mater. X 2024, 24, 100367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlimas, D.I.; Borgekov, D.B.; Kozlovskiy, A.L. Application of EPR spectroscopy method for comparative analysis of structural damage accumulation kinetics in two-phase lithium-containing ceramics. Opt. Mater. X 2025, 25, 100387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abyshev, B.K.; Giniyatova, S.G.; Kozlovskiy, A.L. Effect of irradiation temperature on the mobility of structural and vacancy defects in the damaged layer of Li2ZrO3 ceramics. Opt. Mater. X 2024, 24, 100376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griscom, D.L. Nature of defect centers in glass: E’ centers in SiO2. J. Non Cryst. Solids 1980, 40, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antuzevics, A.; Zarins, A.; Ansone, A.; Cipa, J.; Kizane, G.; Leys, J.M.; Knitter, R. Thermal properties of paramagnetic radiation-induced defects in lithium orthosilicate containing breeder material. J. Nucl. Mater. 2022, 565, 153713. [Google Scholar]
- Ollier, N.; Reghioua, I.; Cavani, O.; Mobasher, M.; Alessi, A.; Le Floch, S.; Skuja, L. Probing densified silica glass structure by molecular oxygen and E’center formation under electron irradiation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashkovtsev, R.I.; Pan, Y. EPR study of new E’ centers in neutron-irradiated α-quartz. EPL 2018, 124, 54001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarins, A.; Valtenbergs, O.; Kizane, G.; Supe, A.; Knitter, R.; Kolb, M.H.; Conka, D. Formation and accumulation of radiation-induced defects and radiolysis products in modified lithium orthosilicate pebbles with additions of titanium dioxide. J. Nucl. Mater. 2016, 470, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leys, J.M.; Zarins, A.; Cipa, J.; Baumane, L.; Kizane, G.; Knitter, R. Radiation-induced effects in neutron-and electron-irradiated lithium silicate ceramic breeder pebbles. J. Nucl. Mater. 2020, 540, 152347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supe, A.; Kizane, G.; Knitter, R.; Reinholds, I.; Vitins, A.; Tilika, V.; Baumane, L. Radiolysis of Slightly Overstoichiometric Lithium Orthosilicate Pebbles. Rigas Teh. Univ. Zinat. Raksti 2010, 22, 100. [Google Scholar]
- Zarins, A.; Antuzevics, A.; Kizane, G.; Leys, J.M.; Knitter, R. Simulations of complex electron paramagnetic resonance spectra for radiation-induced defect centres in advanced ceramic breeder pebbles. Nucl. Mater. Energy 2023, 35, 101458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Shi, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, R.; Ye, D.; Shi, Q.; Lu, T. Characterization of cation disorder and oxygen vacancies in Li-rich Li2TiO3. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 105, 6407–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, H.; Xiang, M.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, Q. Influence of ion irradiations on the microstructure in the tritium breeder material Li2TiO3. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2019, 450, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Laan, J.G.; Kawamura, H.; Roux, N.; Yamaki, D. Ceramic breeder research and development: Progress and focus. J. Nucl. Mater. 2000, 283, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Zhao, L.; Qin, Y.; Ran, G.; Gong, Y.; Wang, H.; Xiao, C.; Chen, X.; Lu, T. Tritium release property of Li2TiO3-Li4SiO4 biphasic ceramics. J. Nucl. Mater. 2020, 538, 152268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Xiong, Q.; Zhou, J.; Li, S.; Hirata, S.; Oya, Y. Preparation of Li2TiO3-Li4SiO4-Pb tritium breeding ceramic and its mechanical properties. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 26742–26749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Togari, A.; Nakata, M.; Zhao, M.; Sun, F.; Xu, Q.; Oya, Y. Release kinetics of tritium generation in neutron irradiated biphasic Li2TiO3–Li4SiO4 ceramic breeder. J. Nucl. Mater. 2019, 522, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertz, J. Electron Spin Resonance: Elementary Theory and Practical Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Heuser, J.M.; Zarins, A.; Baumane, L.; Kizane, G.; Knitter, R. Radiation stability of long-term annealed bi-phasic advanced ceramic breeder pebbles. Fusion Eng. Des. 2019, 138, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarins, A.; Supe, A.; Kizane, G.; Knitter, R.; Baumane, L. Accumulation of radiation defects and products of radiolysis in lithium orthosilicate pebbles with silicon dioxide additions under action of high absorbed doses and high temperature in air and inert atmosphere. J. Nucl. Mater. 2012, 429, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Koyanagi, T.; Bhattacharya, A.; Wang, L.; Katoh, Y.; Hu, X.; Zinkle, S.J. Neutron irradiation-induced microstructure damage in ultra-high temperature ceramic TiC. Acta Mater. 2020, 186, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinkle, S.J. Effect of H and He irradiation on cavity formation and blistering in ceramics. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2012, 286, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, T.; Liu, F.; Chen, C.; Zhou, P.; He, C. Influence of implantation and annealing temperatures on the irradiation damage in He2+ ion implanted 6H-SiC. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2025, 560, 165611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Cao, Z.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, J.; Wu, D. He irradiation-induced lattice distortion and surface blistering of Gd2Zr2O7 defect-fluorite ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 103, 3425–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Trocellier, P.; Brimbal, D.; Vaubaillon, S. An experimental study of helium diffusion and helium induced microstructural evolution in ion implanted polycrystalline titanium nitride. Acta Mater. 2016, 121, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

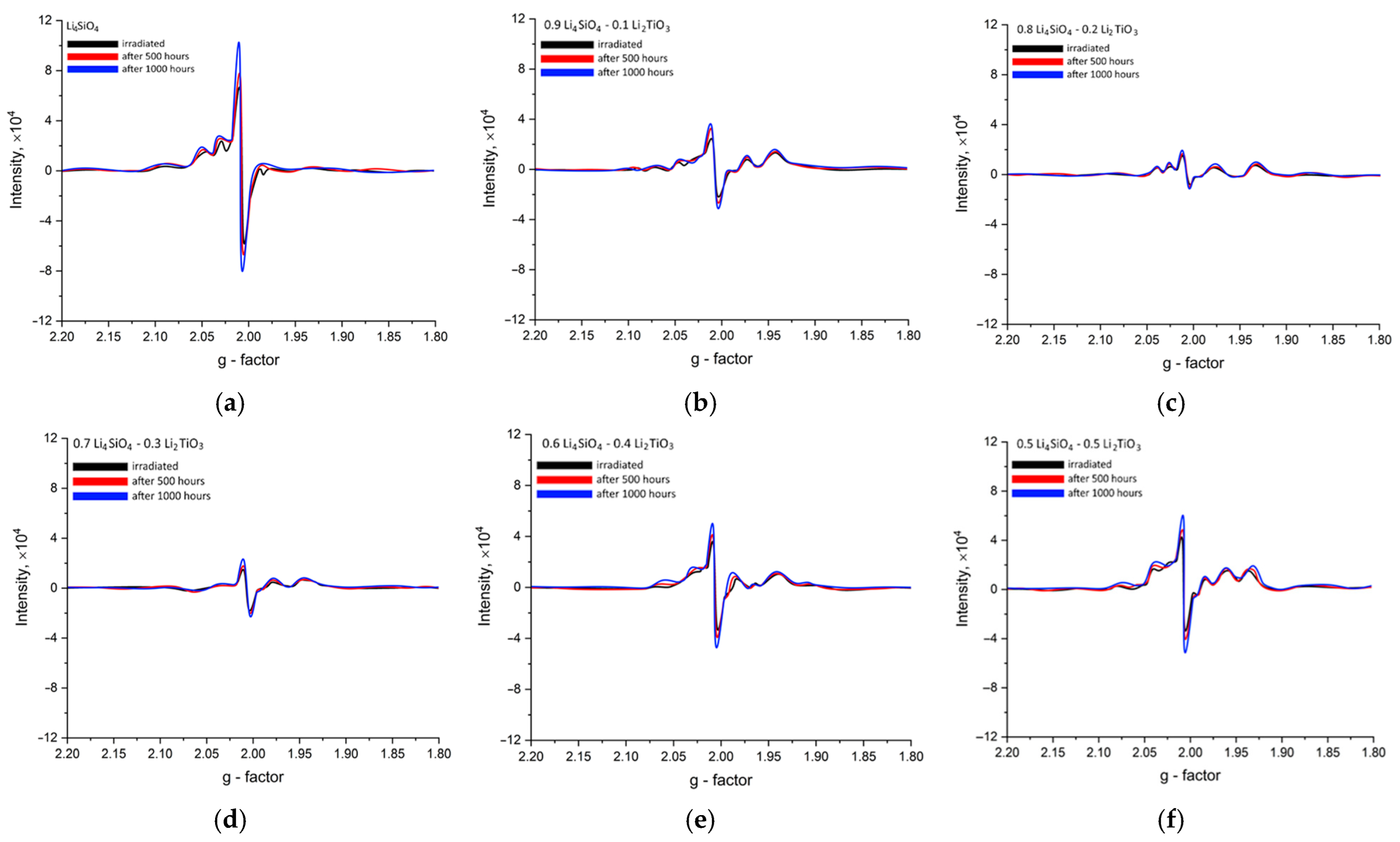
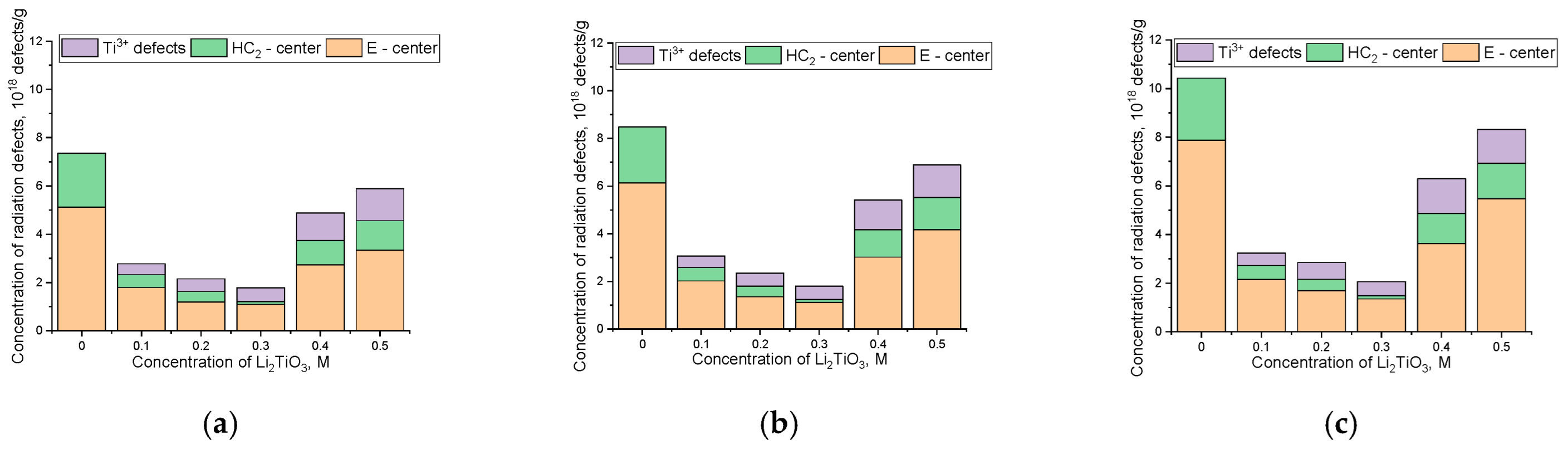
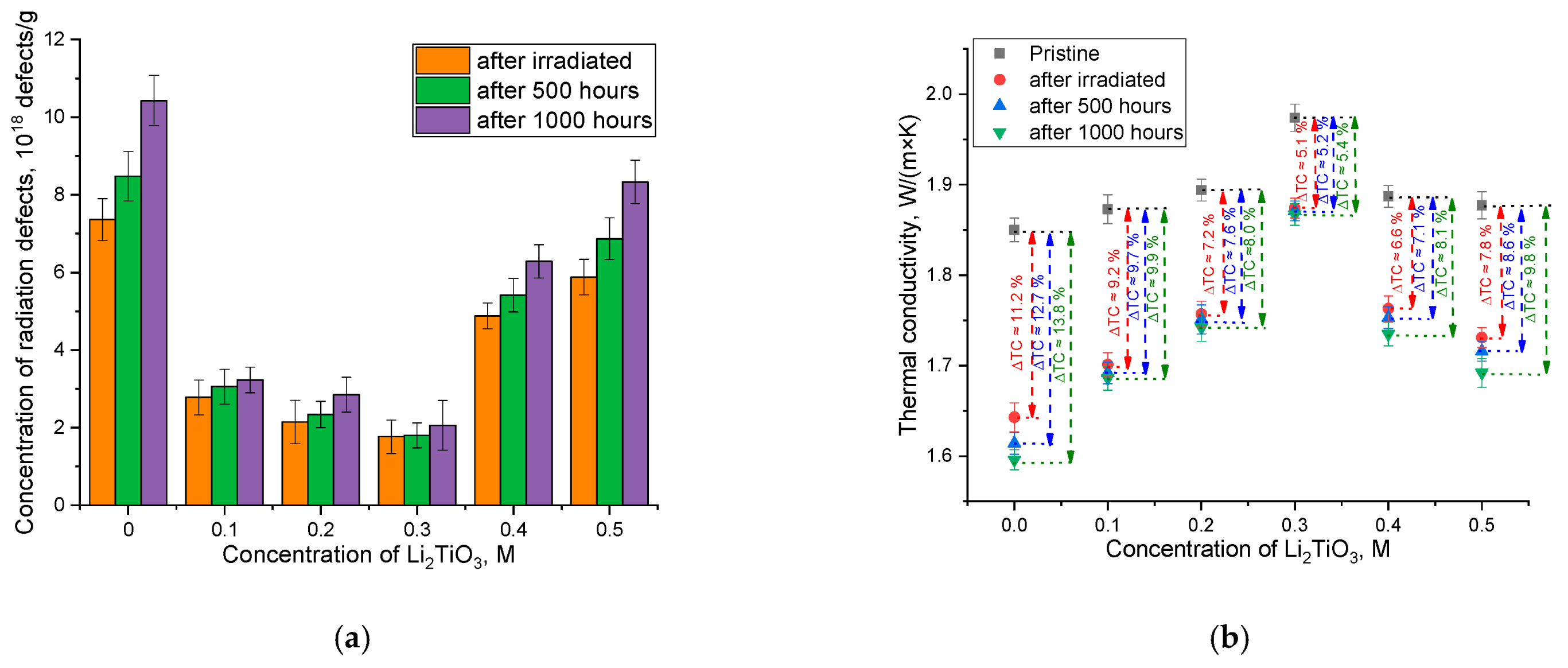
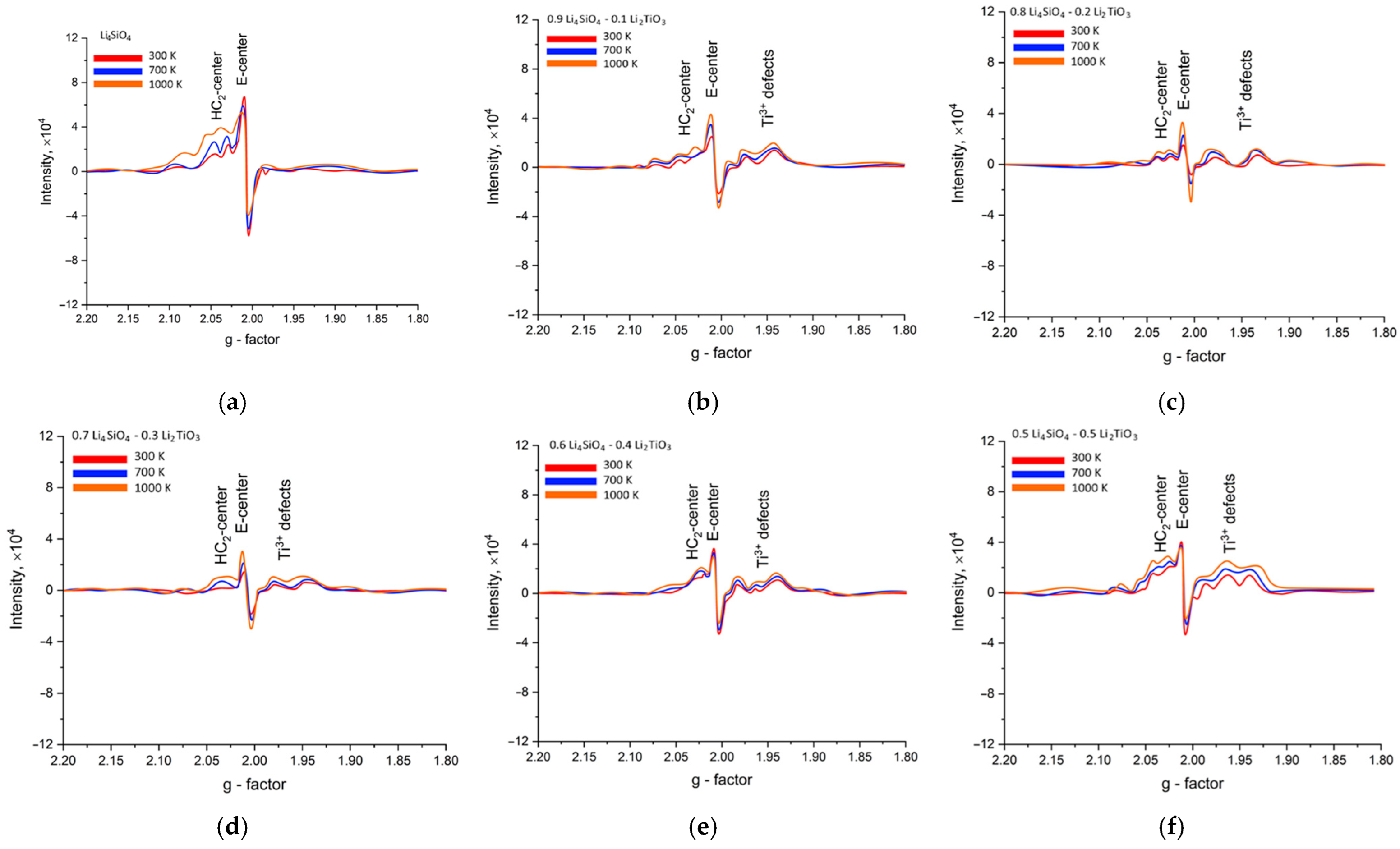

| Parameter | Concentration of Li2TiO3 in Ceramics, M | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | |
| Hardness, HV | 690 ± 15 | 715 ± 13 | 768 ± 14 | 822 ± 17 | 803 ± 14 | 786 ± 16 |
| Crush load, N | 42.1 ± 0.2 | 46.4 ± 0.3 | 50.2 ± 0.4 | 57.6 ± 0.3 | 53.2 ± 0.2 | 49.3 ± 0.5 |
| Thermal conductivity, W/(m × K) | 1.85 ± 0.02 | 1.87 ± 0.01 | 1.89 ± 0.02 | 1.97 ± 0.03 | 1.88 ± 0.02 | 1.87 ± 0.01 |
| Parameter | Concentration of Li2TiO3 in Ceramics, M | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | |
| E-center (g-factor~2.002–2.005) | Oxygen vacancies; the intensity of the singlet band is quite large. | The decrease in the intensity of the singlet band is due to the increase in the stability of two-component ceramics to disordering processes caused by irradiation. | ||||
| HC2-center (g-factor~2.020–2.025) | The weakening of the signals of HC2 centers is due to the higher stability of TiO6 octahedra to radiation damage and the higher radiation resistance of titanates compared to silicates. | |||||
| Ti3+ defects (g-factor~~1.94–1.98) | none | The intensity increases as Li2TiO3 concentration grows in the ceramics’ composition. | ||||
| Si4+-defects (g-factor~~2.01–2.015) | Oxygen vacancies in SiO4-tetrahedra | As the Li2TiO3 concentration in the ceramics grows, the intensity of the spectral band characteristic of this type of defect reduces, which indicates an increase in the stability of the ceramics to radiation damage. | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kenzhina, I.E.; Askerbekov, S.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Tolenova, A.; Piskunov, S.; Popov, A.I. The Influence of Accumulated Radiolysis Products on the Mechanisms of High-Temperature Degradation of Two-Component Lithium-Containing Ceramics. Ceramics 2025, 8, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8030099
Kenzhina IE, Askerbekov S, Kozlovskiy AL, Tolenova A, Piskunov S, Popov AI. The Influence of Accumulated Radiolysis Products on the Mechanisms of High-Temperature Degradation of Two-Component Lithium-Containing Ceramics. Ceramics. 2025; 8(3):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8030099
Chicago/Turabian StyleKenzhina, Inesh E., Saulet Askerbekov, Artem L. Kozlovskiy, Aktolkyn Tolenova, Sergei Piskunov, and Anatoli I. Popov. 2025. "The Influence of Accumulated Radiolysis Products on the Mechanisms of High-Temperature Degradation of Two-Component Lithium-Containing Ceramics" Ceramics 8, no. 3: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8030099
APA StyleKenzhina, I. E., Askerbekov, S., Kozlovskiy, A. L., Tolenova, A., Piskunov, S., & Popov, A. I. (2025). The Influence of Accumulated Radiolysis Products on the Mechanisms of High-Temperature Degradation of Two-Component Lithium-Containing Ceramics. Ceramics, 8(3), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics8030099









