Abstract
Magnetically hard-soft (100-x) SrFe12O19-x wt % La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 nanocomposites were synthesized via a one-pot auto-combustion technique using nitrate salts followed by heat treatment in air at 950 °C. X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM) were used to characterize the structural and magnetic properties of the samples. XRD spectra revealed the formation of a mixture of ferrite and magnetite phases without any trace of secondary phases in the composite. Microstructural images show the proximity grain growth of both phases. The room temperature hysteresis loops of the samples showed the presence of exchange-coupling between the hard and soft phases of the composite. Although saturation magnetization reduced by 41%, the squareness ratio and coercivity of the nanocomposite improved significantly up to 6.6% and 81.7%, respectively, at x = 40 wt % soft phase content in the nanocomposite. The enhancement in squareness ratio and coercivity could be attributed to the effective exchange-coupling interaction, while the reduction in saturation magnetization could be explained on the basis of atomic intermixing between phases in the system. Overall, these composite particles exhibited magnetically single-phase behavior. The adopted synthesis method is low cost and rapid and results in pure crystalline nanocomposite powder. This simple method is a promising way to tailor and enhance the magnetic properties of oxide-based hard-soft magnetic nanocomposites.
1. Introduction
Composites with magnetically hard and soft phases can improve magnetic properties because of the presence of high exchange-coupling of both phases. The composite attributes of the high saturation magnetization of the soft phase and the high coercivity of the hard phase increases; consequently, the squareness ratio (Mr/Ms) of the nanocomposite increases. Following the success of the observed phenomenon of exchange-coupling in the metallic hard-soft systems, efforts have been directed to studying the exchange-coupling phenomenon in oxide-based hard-soft composite magnets. These rare-earth-free exchange-coupled oxide composite magnets are economical, show oxidation resistance, have a high operating temperature, and are technologically important [1,2,3,4,5]. Recently, many studies on exchange-coupled hard-soft composites have been reported, where ferrites are used as a magnetically soft-phase, such as SrFe10Al2O19/NiZnFe2O4 [6], SrFe12O19/γ-Fe2O3 [7], CoFe2O4/Fe3O4 [8], BaFe12O19/Ni0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 [9], Fe3O4/BaCa2Fe16O27 [10], SrFe12O19/CoFe2O4 [11], SrFe10Al2O19/Co0.8Ni0.2Fe2O4 [12], and SrFe12O19/La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 [13]. However, the exchange-coupling phenomenon in many of these composites is not fully realized due to the intricate fabrication methods, microstructural and interfacial complexities, and the formation of secondary phases, factors which inhibit realization of full exchange-coupling between the hard-soft phases of composites [14,15]. The presence of incomplete exchange-coupling adversely affects the magnetic properties of the composite. Hence, it is important to obtain samples with no impurities and strong exchange-coupling interactions. The majority of reported methods for the synthesis of exchange-coupled composites are two-step methods: first the individual synthesis of hard and soft magnetic phase materials and later the exchange-coupling either via ball milling [16], chemical treatment [17], electroplating [18] or heat treatment [19]. To realize the exchange-coupling, it is required to achieve a high level of homogeneous mixing of the hard and soft phases, which is possible if the growth of both of these phases takes place together from a single reaction mixture. Thus, there is a need for the development and a systematic study of a simple method for the preparation of hard-soft composites.
As discussed above, many of the studies on exchange-coupled composites are focused on using spinel ferrites as a soft phase in the composite. The studies on using lanthanum manganite, LaSrMnO3 (LSMO), as a potential soft-phase in the exchange-coupled composite are limited. This study reports the preparation of hard-soft SrFe12O19 (Ms~59.66 emu/g and Hc~3.6 kOe)-La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 (Ms~52.42 emu/g and Hc~0.052 kOe) exchange-coupled nanocomposites using the auto-combustion synthesis technique. LSMO belonging to the hole-doped manganite family is known to be a potential candidate for technological applications as it has a ferromagnetic transition temperature TC~380 K and a large magnetic moment at room temperature. The auto-combustion synthesis method [20] is a unique combination of combustion and the chemical gelation processes. This method exploits the advantages of cheap precursors, simple preparation, and atomic-level diffusion and results in ultrafine, homogeneous, crystalline powder [21,22,23,24]. The combustion synthesis is also advantageous over the solid-state synthesis in terms of compositional homogeneity and the purity of the final product. Nitrate salts have been used in the synthesis, where during the combustion exothermic redox reactions associated with nitrate decomposition and fuel oxidation cause combustion. Gases such as N2, H2O, and CO2 evolve, favoring the formation of fine particle ashes after a few minutes [25]. The rapid evolution of a large volume of gases during the process limits the occurrence of agglomeration, thus leading to the formation of nanocrystalline powders.
The study reports a systematic investigation of the effect of varying soft phase content, x, in SrFe12O19 (SFO)–x wt % La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 (LSMO) nanocomposite on the overall magnetic property of the nanocomposite. The exchange-coupled nanocomposite was successfully prepared via an auto-combustion technique as they exhibit smooth hysteresis loops with high Mr/Ms and coercivity values.
2. Experimental
Magnetically hard-soft (100-x) SrFe12O19 (SFO)-x wt % La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 (LSMO) (x = 0, 10, 20, 30, 40) composites were prepared via a one-pot auto combustion method using nitrate salts [8,26]. According to the composition of the hard-soft composite, two mixtures were prepared separately. The stoichiometry weight of precursors used for the synthesis of (100-x) SrFe12O19-x wt % La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 composites are listed in Table 1. For SrFe12O19, stoichiometric amounts of Sr(NO3)2 and Fe(NO3)3.9H2O were dissolved in a minimum amount of deionized water (100 mL for 0.1 mol of Fe+3) by stirring on a hotplate at 60 °C. Citric acid was dissolved into the nitrate solutions to give a molar ratio of metal ions to citric acid of 1:1. The solutions were then allowed to cool down for several minutes, until room temperature was reached. The pH of the solution was maintained at 6.5 using an NH4OH solution. On the other hand, according to the composition of x wt % LSMO, a stoichiometric amount of La(NO3)2, Sr(NO3)2, and Mn(NO3)2 were dissolved in a minimum amount of deionized water. These two solutions of hard and soft phases were mixed and stirred magnetically 30 min before heating the solution on a hotplate at 95 °C. The solution was heated until a viscous gel was formed. Instantaneously, gel ignited with the formation of large amounts of gas, resulting in a lightweight voluminous powder. The resulting ‘‘precursor’’ powder was calcined at 950 °C for 12 h to obtain (100-x) SFO-x wt % LSMO composite powder.

Table 1.
Stoichiometry weight in gram of precursors used for the synthesis of (100-x) SFO-x wt % LSMO composites.
The crystal phases of the synthesized powders were determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD, Bruker D8 Advance, Germany) using Cu Kα (λ = 1.5406 Å) as the radiation source (40 kV, step size 0.02, scan rate 0.2 min/step, 20° ≤ 2θ ≤ 70°). The particle morphology of the composite was investigated using a transmission electron microscope (TEM) (JEOL JEM-1200). Magnetic hysteresis loops of powder samples were obtained using a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) at room temperature with a sweeping magnetic field within ±12 kOe.
3. Result and Discussion
Figure 1 shows the room temperature XRD pattern of SFO–LSMO composites. Analysis of the room-temperature XRD pattern of the composite reveals the presence of a distinct pure and single-phase perovskite-based structure LSMO and hexaferrite SFO. All patterns are in accordance with the ICCD numbers (SFO: 033-1340 and LSMO: 050-0298). No trace of secondary phase was detected within the sensitivity limit of the experiment. This indicates that the modified auto-combustion method to synthesize SFO–LSMO did not change the magnetoplumbite structure of SrFe12O19 and the cubic perovskite-like structure of LSMO nanoparticles. Hence, it is understandable that the LSMO and SFO phases are compatible because these two phases can coexist without forming secondary phases. The XRD pattern was indexed by a rhombohedral lattice with the space group R3c for LSMO and hexagonal ferrite with the space group of P63/mmm for SFO. The intensity ratio of the strongest peak of SFO and LSMO was defined as α = ISFO(110)/ILSMO(104), where ISFO(110) and ILSMO(104) are peak intensity for (110) and (104) peaks of SFO and LSMO, respectively. The values of α for 10%, 20%, 30%, and 40% wt % LSMO composites are 4.59, 1.83, 1.15, and 0.06 in Figure 1, respectively. As expected, the relative intensity of the diffraction peaks from LSMO in the composites increases with the increase in LSMO content. In addition, phase fraction was also calculated using an intensity ratio. Bruker DIFFRAC.DQUANT software was used for the quantitative phase analysis from the X-ray diffraction data. It uses one or more diffraction peaks instead of the entire diffraction pattern to establish calibrations from standard reference samples. Due to overlapping peaks of SFO and LSMO, three peaks of SFO at 31.03 (110), 34.19 (114), and 37.15 (203) and one distinct peak of LSMO at 46.87 (024) were used in the calculation. The calculated phase fractions are 10.58%%, 14.34%, 28.20%, and 43.34% for x = 10, 20, 30, and 40 wt % samples, respectively. The calculated phase fractions are close to the assumed values of the composition of the composite. The broadness with the full-width-at-half-maximum (FWHM) of a characteristic XRD peak implies the formation of nanocrystals. The crystallite size was calculated using the Scherrer formula D = kλ/βcosθ, where D is the average crystallite size, λ is the wavelength of X-ray used (1.5406 Å), k is a constant (shape factor ~0.9), θ is the angle of diffraction, and β is the FWHM [27]. The average crystallite size was measured for individual phase using (107), (203), (206), and (220) peaks for SFO and (012) and (202) peaks for LSMO. The lattice parameters for SFO and LSMO were obtained using Rietveld refinement, and crystallite size using Scherrer’s formula are listed in Table 2 for varying x values of the composite. A distinct difference in the growth pattern of hard and soft phases was observed in the composite. The crystallite size of the hard phase was observed to increase from 35 to 40 nm (x = 40 wt %) while that of the soft phase decreased from 34 to 20 nm (x = 40 wt %). The difference in crystallite growth could be due to the presence of two distinct phases with limited mutual solubility in the composites. For a two-phase system with limited solubility, ionic diffusion is usually via a long range [28]. Since the long-range diffusion of atoms and hence the grain boundary migration is different for two phases, the grain growth is also different. Interestingly, the unit cell volume of SFO increases (from 684.7 to 687.4 Å3), while that of LSMO decreases (from 385.2 to 378.6 Å3) with the increase in the soft-phase content at x = 40 wt % in the composite. There does exist a possibility of ion migration between SFO and LSMO. Most likely the inter-diffusion of Fe3+(rionic~0.645 Å) and Mn3+ (rionic~0.645 Å) having comparable ionic radii will not affect the lattice parameter of either phase (Table 3). On the other hand, substitution for Sr2+ (rionic~1.18 Å) in SFO with La3+ (rionic~1.03 Å) from LSMO could expand the unit cell of SFO [29] due to charge compensation resulting from the conversion of Fe3+ (rionic~0.645 Å) to Fe2+ (rionic~0.78 Å). With a fractional migration of La3+ out of LSMO, a concomitant reduction in its lattice volume is expected. It is also clear from Table 3 that the c parameter changes more than the a parameter in both components, which may be due to the cross substitution between LSMO and SFO based on the ionic radii while forming the composite.
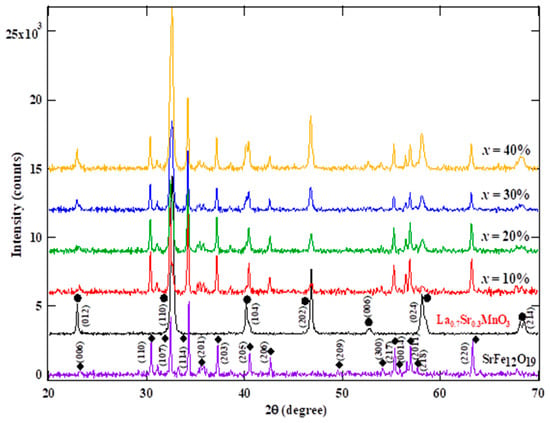
Figure 1.
XRD pattern of (100-x) SFO-x wt % LSMO.

Table 2.
Lattice parameters and volume obtained from the refinement of XRD data and crystallite size calculated using Scherrer’s formula for (100-x) SFO-x wt % LSMO composites.

Table 3.
Effective ionic radii (Å) adopted in the present study [30].
A representative TEM micrograph of the SFO-40 wt % LSMO composite is shown in Figure 2. This micrograph shows that the grain shapes of LSMO have a round shape, whereas SFO grains have unique hexagonal facets. It is believed that the darker particles are LSMO and the brighter hexagonal facet particles are of SFO, as LSMO contains heavier elements such as La and Sr than SFO. The grain size of LSMO is very different from that of SFO, and grains are in close contact where smaller LSMO particles have grown on the surface of the relatively large SFO plates in the composite. This observation is in confirmation to the earlier reports on LSMO-SFO prepared via solid-state reaction [31,32]. This proximity of LSMO and SFO particles could facilitate effective exchange-coupling between hard and soft phases, as discussed below.
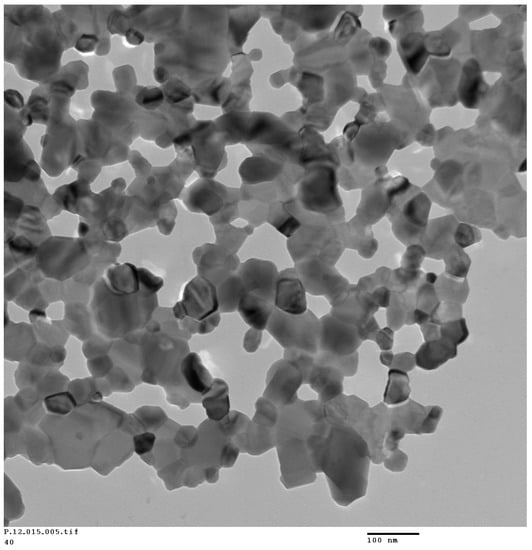
Figure 2.
TEM micrograph of the SFO-40 wt % LSMO composite.
Figure 3 shows the RT hysteresis loops of (100-x) SFO-x wt % LSMO calcined at 950 °C. The hysteresis loops show the characteristic behavior of hard magnets with a high coercive field (Hc). The LSMO hysteresis loop corresponds to the soft magnet with Ms~52.42 emu/g, Mr~8.72 emu/g, and Hc~52 Oe, while SFO displays a characteristic loop of a hard magnet with Ms~59.66 emu/g, Mr~33.37 emu/g, and Hc~3.63 kOe. For all soft-phase content, hysteresis loops of the composite system are smooth and without any kink, indicating effective interphase exchange-coupling between phases, which results in cooperative magnetization switching of the two phases. If these phases were not exchange-coupled properly, then the demagnetization loops would show a superimposition of two loops corresponding to the hard and soft phases. Often a kink is observed in the demagnetizing loops, signifying the presence of decoupled phases in the composite [12,14,33].
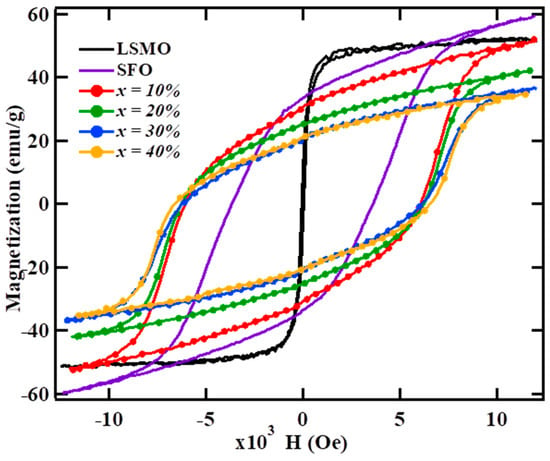
Figure 3.
Room temperature hysteresis loop of the (100-x) SFO-x wt % LSMO composite.
The magnetic parameters, saturation magnetization Ms, coercivity Hc, and the Mr/Ms squareness ratio extracted from hysteresis loops are given in Table 4. With the increase in LSMO content, the Ms value of the composite was observed to decrease. The hard-soft composite with 40 wt % LSMO shows a 41.5% decrease in Ms (~34.93 emu/g) and a 6.6% increase in the Mr/Ms (~0.6) value, as compared to that of SrFe12O19 (Ms~59.6 emu/g, Mr/Ms~0.56). In accordance with the theoretical calculation of the remanence, Mr, the dependence on the soft phase content [34], the Mr/Ms value of the SFO–LSMO composite showed a moderate increase in value with the increase in the soft phase content, as shown in Figure 4. Since the anisotropy field of the soft magnetic phase is small, the magnetizations in soft grains rotate out of the easy axis easily and align parallel to the easy directions of the neighboring hard magnetic grains owing to the contribution of intergrain exchange-coupling. As a result, Mr increases with the increase of the soft phase content. This result further corroborates the claim for the presence of exchange-coupling between hard-soft phases in the present composite. As per the Stoner–Wohlfarth prediction [35], in a non-interacting ensemble of single-domain grains with uniaxial magnetocrystalline anisotropy and isotropic distribution of easy axes, Mr/Ms = 0.5. However, if neighboring grains are coupled through exchange interaction, interfacial magnetic moments of the soft grains are aligned parallel to the magnetic moments of the hard ones resulting in Mr > 0.5 Ms. In a two-phase system, the remanence enhancement owing to exchange interaction between hard-soft phases is highly effective. As compared to pure SrFe12O19, a 6.6% enhancement in Mr/Ms value was observed in the present composite with x = 40 wt %. It is important to point out that, for an isotropic magnet with a 10 nm homogenous grain size, the theoretically predicted value of Mr/Ms~0.72 [36]. Thus, the high value of Mr/Ms~0.6 obtained for 40 wt % LSMO show a moderate exchange-coupling between hard-soft phases in the composite. However, an increase in Mr of isotropic powders can also respond to other effects, such as magnetic alignment, which is not evaluated in this work. The observed enhancement in Mr/Ms in the present composite was observed to be higher than the values reported in the literature for the similar composites prepared via solid-state reaction [30,31]. This could be attributed to the effectiveness of the auto combustion technique in achieving the effective growth of fine crystalline grains of respective phases in proximity, as discussed above.

Table 4.
Room temperature magnetic parameters of (100-x) SFO-x wt % LSMO composites obtained from M vs. H loops.
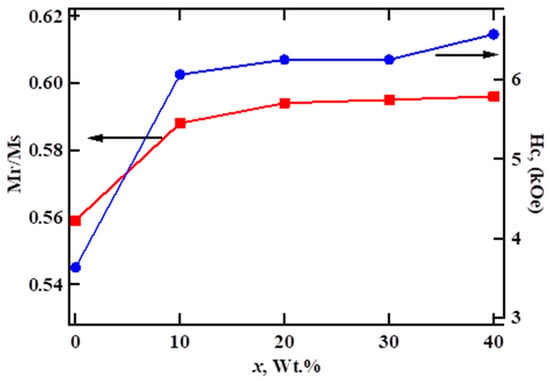
Figure 4.
Squareness ratio Mr/Ms and coercivity Hc as a function of x in a (100-x) SFO-x wt % LSMO composite.
The measured Ms values of the composite are listed in Table 4. It is observed that the Ms values decrease with the increase in the soft content of the composite. This decrease in MS in the composite, in spite of the increase in the soft phase with having higher Ms values than the hard phase, could be the result of interatomic diffusion and inter-substitution between Mn in LSMO and Fe in SFO as discussed above. It has been reported earlier that Fe substitution to Mn sites of LSMO (La0.67Sr0.33Mn1−xFexO3) [37] and Mn substitution at the Fe site (SrFe12−xMnxO19) has brought a reduction in the Ms values [31]. Ideally, the saturation magnetization of the composite consisting of hard and soft phases can be measured as [15,38]
where Ms,hard is the saturation magnetization of hard-phase SFO, Ms,soft is the saturation magnetization of soft-phase LSMO, and fs is the weight fraction of the soft phase in the composite. The measured value of 34.93 emu/g for the Ms of the composite with 40 wt % LSMO is about 38% lower than that predicted by Equation (1). Most likely, the intermixing of atoms, as discussed above, could be the factor for the observed deviation in the Ms value as compared to that of projected by Equation (1). Furthermore, this intermixing can lead to the formation of the amorphous region near the interfaces between the soft-hard phases and make the areas of crystalline regions smaller. The amorphous region corresponds to the paramagnetic response due to the disorder on the arrangement, leading to the decrease in Ms. Additionally, the effect of surface defects such as spin canting or non-collinear magnetic ordering on the magnetic properties of the nanoparticle cannot be avoided [39]. The magnetic ion spins align in different angles with respect to the easy axis of magnetization (c-axis for M structure ferrites). When canted spin occurs, it gives suppressions of exchange interaction strength and promotes lower MS.
M = Ms,hard (1 − fs) + Ms,soft × fs
From Figure 4, it is seen that coercivity (Hc) increases with the content of the soft LSMO phase in the composite. An overall 80% increase in Hc value (6569 Oe) of x = 40 wt % composite as compared to that of Hc value (3633 Oe) of SFO is observed. In earlier reported studies of hard-soft exchange-coupled composites, the coercivity was observed to be lower than the hard-phase compound. This means that, by increasing the reverse field, the soft phase domain walls move toward the interface between the soft and hard phases and exceed into the hard phase and cause magnetization reverse to that phase. Therefore, the coercivity of the samples decreases in comparison to the hard phase region [40,41]. Considering the small size and proximity of hard-soft phases (Figure 2), it is possible that the volume fraction of the hard phase is enough to exert exchange force on magnetization in a soft grain of SFO, thus preventing the magnetization in soft grains from reversal with the applied field reversal. Furthermore, with the increase in the soft phase content, the coupling between magnetization inside different hard grains is not very strong, because direct coupling is prevented by the presence of the soft grain and because the indirect coupling through the soft grain is prevented by a small value of soft–soft exchange constant [42]. Therefore, the coercivity increases with the increased volume of the soft phase. With this observation, the absence of a pinning interfacial layer, a layer that is detrimental to the coercivity enhancement, can be hypothesized. Considering the auto-combustion synthesis process adapted here, where compound formation occurs with the rapid diffusion of ions, it can be safely assumed that the as-synthesized composites are devoid of interfacial pinning layers.
The switching field distribution, dM/dH vs. H curve is a characteristic feature of interphase exchange-coupling, as shown in Figure 5. The distribution of the switching field shows a narrow dM/dH peak and corresponds to a narrow crystallite size distribution [43,44]. Generally, two distinct maxima are expected for an uncoupled hard and soft phase mixture if the coupling between the hard and soft phases is weak. The width of these dM/dH peaks can be interpreted as an estimation of the efficiency of hard/soft inter-phase exchange-coupling: the narrower the peak, the better the exchange-coupling between the soft and hard phase. Furthermore, the large peaks and the long tails testify about the percentage of crystallites, which are not well coupled by exchange to the hard phase. It is evident from Figure 5 that the width of dM/dH peaks decreases with an increase in LSMO content in the composite, which indicates increasingly effective exchange-coupling between the hard-soft phases of the composite.
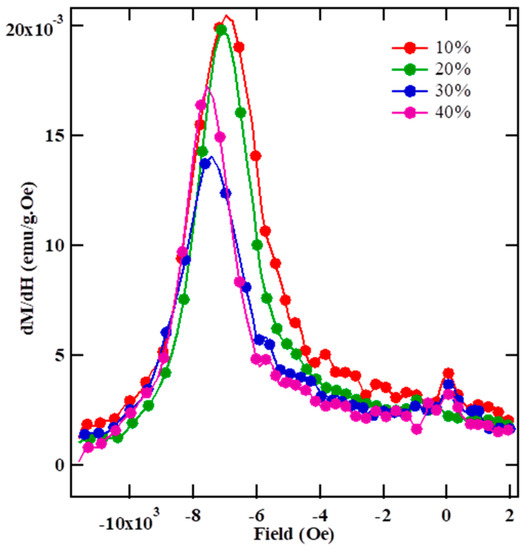
Figure 5.
Room temperature dM/dH curves of (100-x) SFO- x wt % LSMO composite.
The magnetic behavior of the hard-soft system is usually understood as a combination of the intrinsic parameters of the hard and soft phases. Usually, a soft phase material is viewed with low anisotropy, K (which results in a small HC) with a large saturation magnetization, MS, while a hard material is taken as a material with a large K and a moderate MS. In exchange-coupled hard-soft thin film systems, the magnetization switching behavior and thus the hysteresis loops have been demonstrated to show the strong dependence on the dimensions of the soft phase [45]. For a thin tsoft there is a critical thickness below which the soft phase is rigidly coupled to the hard phase, and the two phases reverse at the same nucleation field, HN, resulting in a rectangular hysteresis loop. Generally, the critical dimension (Dcr) of the soft magnetic phase for the exchange-coupling can be quantified as twice that of the exchange-coupling distance, δ = (A/K1)1/2, where A is the exchange stiffness and K1 the magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant. For composites, A and K1 can be described as the effective exchange stiffness and effective anisotropy constant, respectively [46]. As per Sun et al. [47], the exchange-coupling in a composite system is observed where the hard grain and soft grain sizes are around 40 and 15 nm, respectively. In the present work, the estimated grain sizes for the hard and soft phase are around 40 and 27 nm, respectively, which is comparable with the theoretical value predicted by Sun et al. [47]. Although the calculated δ is around 8.6 nm for SrFe12O19 [48], it could be different in the present composite system where inter-substitution has likely occurred. Considering the observed smooth hysteresis loops of the composite, it is safe to assume that the most of LSMO grains with a diameter of 27 nm are magnetically coupled by adjacent SFO. Thus, the new proposed Dcr could be ~27 nm in the prepared SFO–LSMO composite system.
Another important observation to notice is that, although Mr/Ms values are improved, the Mr value of the composite decreased with the increase in LSMO content. Indeed, strong exchange interaction is observed in the exchange-coupled composite, but the exchange interaction cannot suppress dipolar interactions in the center of the large soft magnetic region because of the limited range of the exchange interaction (δ~8.6 nm). Furthermore, the connected soft grains may form a large soft magnetic or amorphous region. This leads to the appearance of the reversed domain in the soft-phase for a magnet with a large size and volume fraction. Thus, Mr decreases with an increase in the soft phase content in the composite [33].
4. Conclusions
In summary, the study reports a simple and scalable synthesis route to produce a magnetic exchange-coupled composite, consisting of magnetically hard SFO and soft LSMO phases. The chemical synthesis ensures a fine mixing of nanoscale grains and creates an intimate interface, which is necessary for magnetic exchange-coupling. The coercivity of the nanocomposite improved significantly ~6.6 kOe (81.7%), more than SrFe12O19 (3.6 kOe), at x = 40 wt % soft phase content. The presence of smooth hysteresis loops with enhanced Mr/Ms and coercivity values clearly indicates exchange-coupled magnetic behavior of the composite. The observed weakening of magnetization of the composite could be attributed to the inter-diffusion of ions, while Mr deterioration may result from the increased dipolar interaction between soft-phase particles with the increased LSMO content. The smooth demagnetizing loops of the composites demonstrate the attractiveness of the auto-combustion method in producing well exchange-coupled composites. This simple method seems to be a promising way to tailor and enhance the magnetic properties of oxide-based soft-hard magnetic composites.
Author Contributions
Data curation, Analysis, Methodology and Writing original draft preparation, J.N.D.; Data analysis, Rietveld analysis, D.N.; Revising/Editing the original draft, S.R.M.
Funding
The research was funded by NSF-CMMI: 1029780.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Asthana, S.; Nigam, A.K.; Bahadur, D. Magnetic and magnetotransport properties in (LaxSm1–x)2/3Sr1/3MnO3 (x = 1/3, 1/2 and 2/3) manganites. Phys. Stat. Sol. B 2006, 243, 1922–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, G.H.; Vansanten, J.H. Ferromagnetic compounds of manganese with perovskite structure. Physica 1950, 16, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, G.H. Magnetic compounds with perovskite structures IV Conducting and non-conducting compounds. Physica 1956, 22, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.P.; Lin, C.H. Fe/Sr ratio effect on magnetic properties of strontium ferrite powders synthesized by microwave-induced combustion process. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 386, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Mu, G.; Pan, X.; Gan, K.; Gu, M. Microwave absorption properties of SrFe12O19/ZnFe2O4 composite powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2007, 139, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, B.K.; Wang, L.; Mishra, S.R.; Nguyen, V.V.; Liu, J.P. Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Hard-Soft SrFe10Al2O19/NiZnFe2O4 Ferrite nanocomposites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 5272–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhong, W.; Gu, B.; Du, Y. Exchange-coupling interaction in nanocomposite SrFe12O19/γ-Fe2O3 permanent ferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 1028–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, R.; Shi, J.; Ruan, X. Synthesis and magnetic properties of hard magnetic (CoFe2O4)–soft magnetic (Fe3O4) nano-composite ceramics by SPS technology. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 1811–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Q. Preparation and magnetic properties of BaFe12O19/Ni0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 nanocomposite ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 3024–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Anil Kumar, P.S. Enhancement of (BH)max in a hard-soft- ferrite nanocomposite using exchange spring mechanism. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 073902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Patel, K.; Ren, S. Exchange-coupled ferrite nanocomposites through chemical synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 10354–10356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torkian, S.; Ghasemi, A. Energy product enhancement in sufficiently exchange-coupled nanocomposite ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 469, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Z.F.; Sun, Y.P.; Zhu, X.B.; Hao, C.Y.; Luo, X.; Yang, Z.R.; Dai, J.M.; Song, W.H. Electrical transport and magnetic properties in La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 and SrFe12O19 composite system. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 477, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, S.; Patra, M.K.; Vadera, S.R.; Ghosh, N.N. A Novel But Simple “One-Pot” Synthetic Route for Preparation of (NiFe2O4)x–(BaFe12O19)1−x Composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmanesh, A.; Seyyed Ebrahimi, S.A. Synthesis and magnetic properties of hard/soft SrFe12O19/Ni0.7Zn0.3Fe2O4 nanocomposite magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 3094–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; McCormick, P.G.; Street, R. Remanence enhancement in mechanically alloyed isotropic Sm7Fe93-nitride. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1993, 124, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.H.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, J.I.; Hur, N.H. Exchange-coupled magnetic nanocomposites of Sm (Co1− xFex)5/Fe3O4 with core/shell structure. Solid. State Commun. 2007, 141, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Bonder, M.J.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Fabrication of Sm–Co/Co (Fe) composites by electroless Co and Co–Fe plating. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 6498–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Breton, J.M.; Larde, R.; Chiron, H.; Pop, V.; Givord, D.; Isnard, O.; Chicinas, I. A structural investigation of SmCo5/Fe nanostructured alloys obtained by high-energy ball milling and subsequent annealing. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 085001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, J.N.; Wang, L.; Mishra, S.R.; Nguyen, V.V.; Liu, J.P. Synthesis and magnetic properties of SrFe12−x−yAlxCoyO19 nanocomposites prepared via autocombustion technique. J. Alloy Compd. 2014, 595, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, A.; Mukasyan, A.S.; Rogachev, A.S.; Manukyan, K.V. Solution Combustion Synthesis of Nanoscale Materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14493–14586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutka, A.; Mezinskis, G. Sol–Gel Auto-Combustion Synthesis of Spinel-Type Ferrite Nanomaterials. Front. Mater. Sci. 2012, 6, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadmanjiri, J.; Seyyed Ebrahimi, S.A. Influence of stoichiometry and calcination condition on the microstructure and phase constitution of NiFe2O4 powders prepared by sol-gel autocombustion method. Phys. Stat. Solidi (c) 2004, 1, 3414–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, D.; Fisher, W.; Rane, M.V. In-situ high-temperature X-ray diffraction studies of non-stoichiometric Ni–Zr substituted barium hexagonal ferrites prepared by citrate precursor route. Mater. Sci. Eng A 1998, 252, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, D.; Rajkumar, S.; Kumar, A. Influence of fuel ratios on auto combustion synthesis of barium ferrite nano particles. J. Chem. Sci. 2006, 118, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Rai, B.K.; Mishra, S.R.; Nguyen, V.V.; Liu, J.P. Physical and magnetic properties of highly aluminum doped strontium ferrite nanoparticles prepared by auto-combustion route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 2602–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D. Element of X-Ray Diffraction, 2nd ed.; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 1978; p. 102. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.N.; Chen, L.Q. Topological evolution during coupled grain growth and Ostwald ripening in volume-conserved 2-D two-phase polycrystals. Acta Mater. 1997, 45, 4145–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, F.N.T.; Miro, A.M.B.; De Jesús, F.S.; Serna, P.V.; Gonzalez, N.M.; Marcos, J.S. Crystal structure and magnetic properties of high Mn-doped strontium hexaferrite. J. Alloys. Compd. 2017, 695, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised Effective Ionic Radii and Systematic Studies of Interatomic Distances in Halides and Chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. 1976, A32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kang, Y.M. Magnetic coupling behaviors in M-type hexaferrite-perovskite manganese composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 439, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kang, Y.M.; Ur, S.C.; You, J.H.; Yoo, S.I. Structure and magnetic properties of La0.7Sr0.3MnO3(1−x)–SrFe12O19(x) composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 449, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, A.L.; Zuo, C.H.; Zhang, L.J.; Cao, C.X.; Deng, Y.; Xu, W.; Xie, M.F.; Ran, S.L.; Jin, C.G.; Liu, X.G. Magnetic properties, exchange-coupling and novel stripe domains in bulk SrFe12O19/(Ni,Zn)Fe2O4 composites. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 415004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, R.; He, S.; Shen, B. The role of dipolar interaction in nanocomposite permanent magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 302, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, E.C.; Wohlfarth, E.P. A Mechanism of Magnetic Hysteresis in Heterogeneous Alloys. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1948, 240, 599–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrefl, T.; Fidler, J.; Kronmuller, H. Remanence and Coercivity in isotropic nanocrystalline permanent magnets. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 49, 6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, S. Structure, magnetic, electrical transport and magnetoresistance properties of La0.67Sr0.33Mn1−xFexO3 (x = 0–0.15) doped manganite coatings. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 3679–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.W.; Cho, S.G.; Choa, Y.H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J. Synthesis and magnetic properties of nano Ba-hexaferrite/NiZn ferrite composites. Phys. Stat. Solidi A 2007, 204, 4141–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbandi, M.; Stromberg, F.; Landers, J.; Reckers, N.; Sanyal, B.; Keune, W.; Wende, H. Nanoscale size effect on surface spin canting in iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized by the microemulsion method. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 195001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Zhao, G.P.; Ran, N.; Peng, Y.; Morvan, F.J.; Wan, X.L. Deterioration of the coercivity due to the diffusion induced interface layer in hard/soft multilayers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakolinia, F.; Yousefi, M.; Afghahi, S.S.S.; Baghshahi, S.; Samadi, S. Synthesis of novel hard/soft ferrite composites particles with improved magnetic properties and exchange-coupling. Proc. Appl. Ceram. 2018, 12, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, H.; Kuma, J.; Kanai, Y. Effect of strength of intergrain exchange interaction on magnetic properties of nanocomposite magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1999, 35, 3235–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.W.; Zhang, D.H.; Li, W.; Li, X.M.; Zhang, J.C. Hard magnetic property and dM(H) plot for sintered NdFeB magnet. J. Magn. Magn. Matter. 2000, 208, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, D.; Ghimire, M.; Adhikari, H.; Lisfi, A.; Mishra, S.R. Synthesis and magnetic study of magnetically hard-soft SrFe12−yAlyO19−x Wt.% Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanocomposites. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 055602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, E.E.; Jiang, J.S.; Bader, S.D. Hard/soft magnetic heterostructures: model exchange-spring magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zeng, D.; Ramanujan, R.; Zhong, X.; Davies, H.A. Exchange interaction in rapidly solidified nanocrystalline RE–(Fe/Co)–B hard magnetic alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 07A736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gao, R.W.; Han, B.P.; Liu, M.; Han, G.B.; Feng, W.C. Exchange-coupling interaction, effective anisotropy and magnetic property of nano-magnetic materials. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2007, 17, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Wang, F.; Xia, A.; Zhang, L.; Li, T.; Jin, C.; Liu, X. A facile way to realize exchange-coupling interaction in hard/soft magnetic composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 417, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).