Late Holocene Abrupt Changes in the Fluvial Dynamics of the Tiber Valley Catchment (Rome, Italy): An Impact of the 4.2 Event?
Abstract
1. Introduction
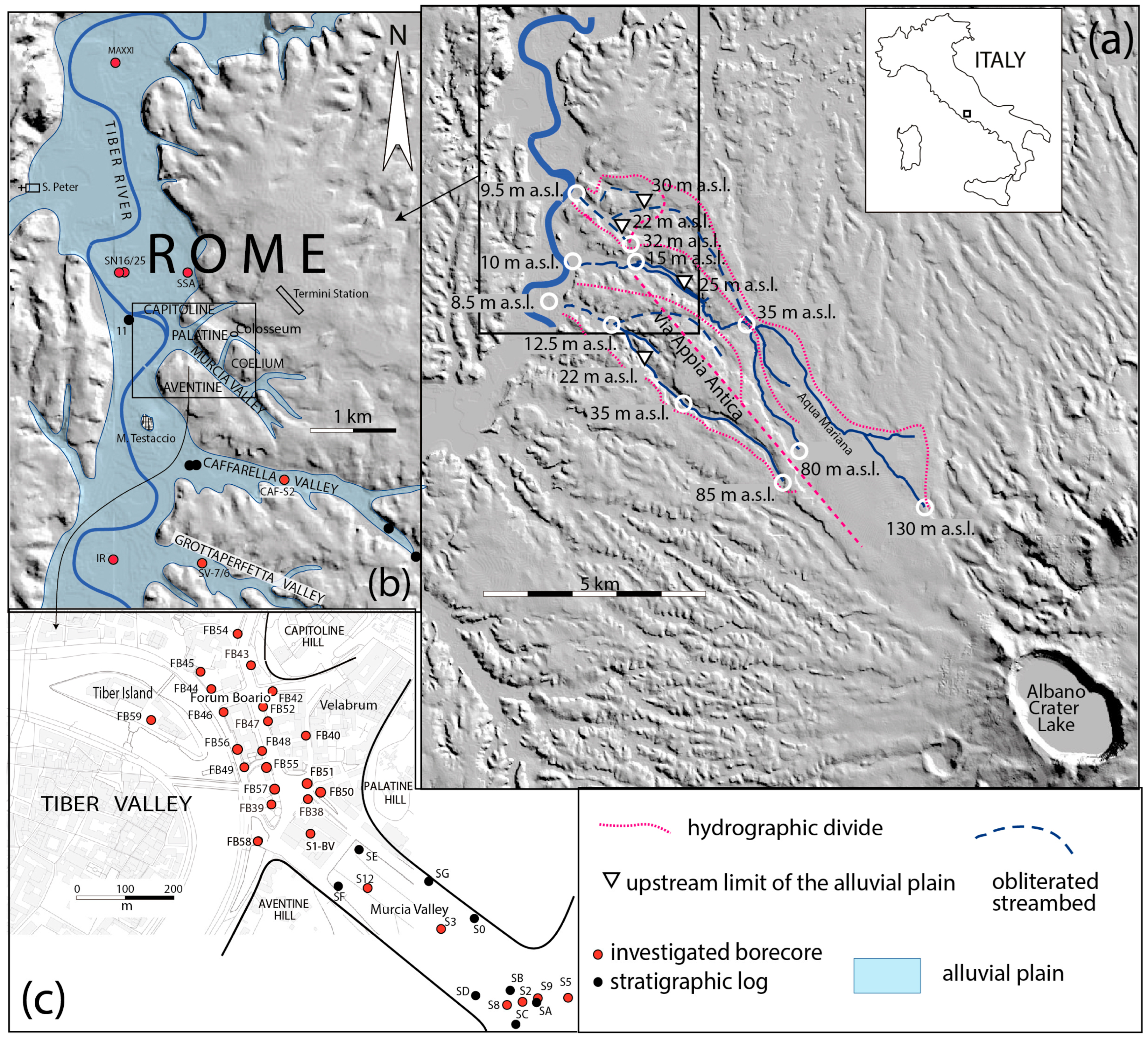
2. Geologic Setting
3. Materials and Methods
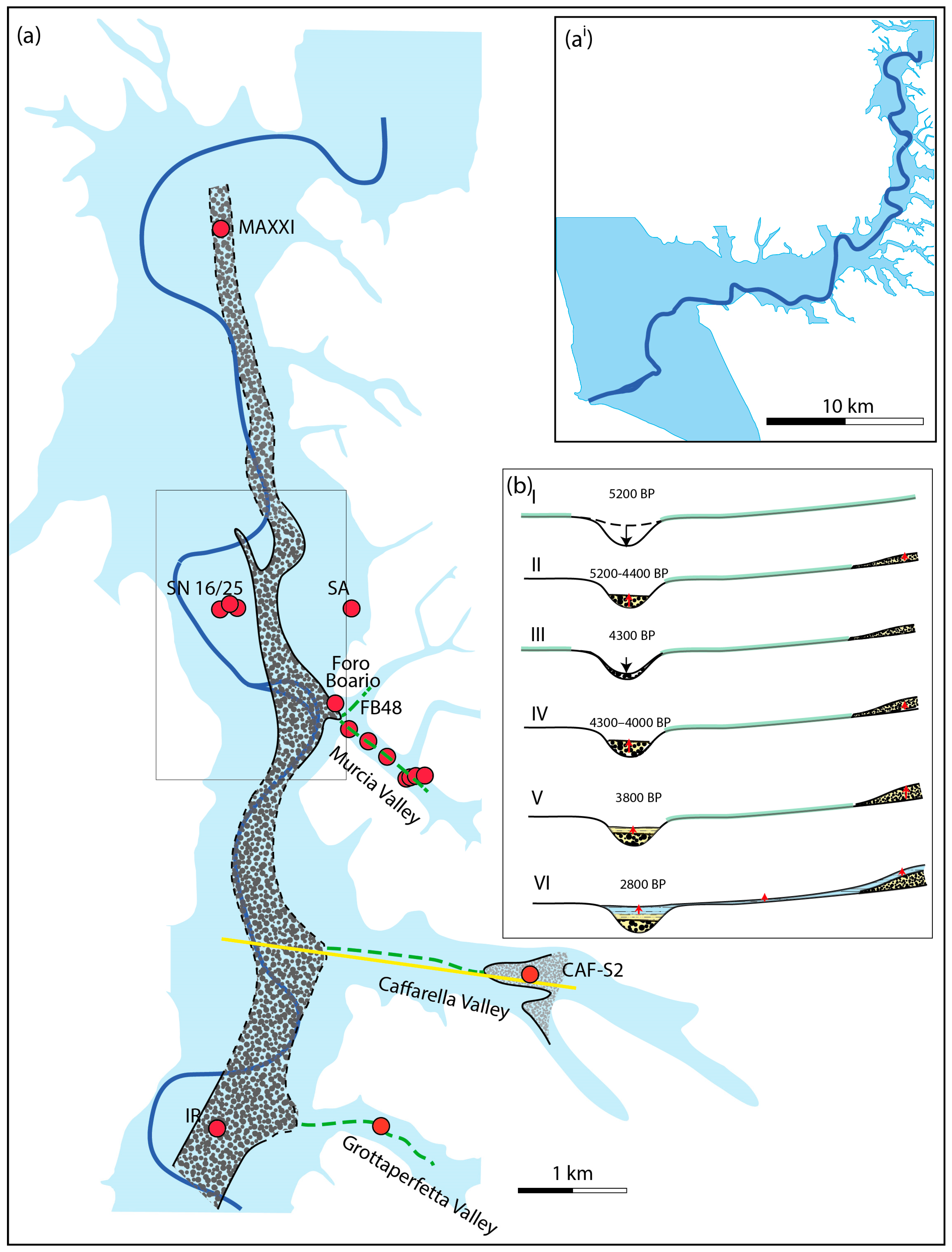
- one 35 m deep borehole (CAF-S2) drilled in the Caffarella Valley (Figure 1) aimed at recovering the complete post-glacial alluvial succession, drilled by Fondazione Amici di Italia Fenice as part of a Geological Monograph Project on the Caffarella Valley and with the permission of the Ente Regionale Parco dell’Appia antica and of the Parco Archeologico dell’Appia antica;
14C Dating
4. Results
4.1. CAF-S2 Borehole Stratigraphy
4.2. 14C Dating
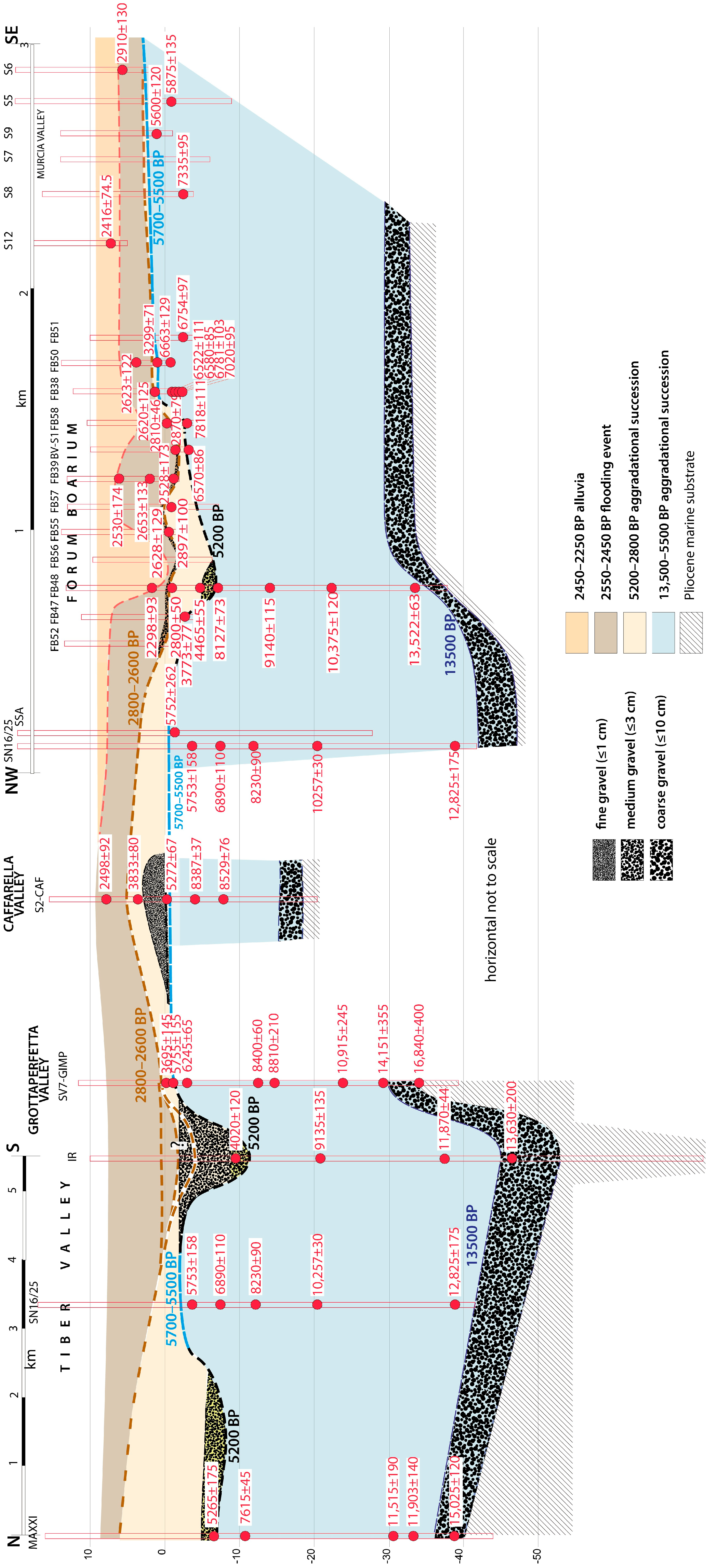
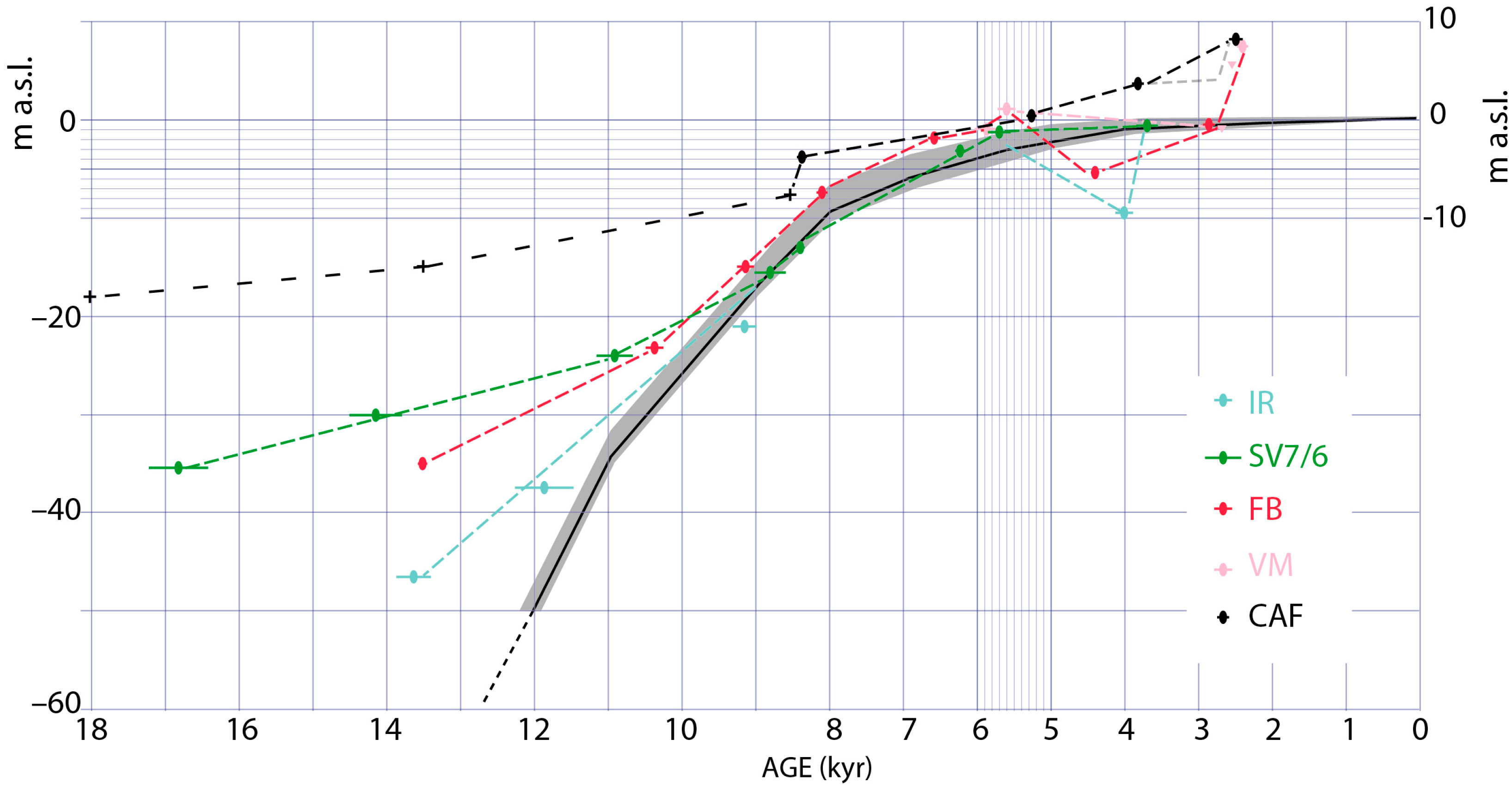
4.3. Chronostratigraphic Reconstruction
- Basal gravel layer (~18.0–13.0 ka). Coarse (Ø ≤ 10 cm) gravel constituted by mainly limestone and chert, and subordinated pyroclastic, well-rounded pebbles, in sandy matrix.
- Pre-Bronze Age alluvial succession (~13.0–5.3 ka). Grey clay with diffused organic material (peat layers, charred wood, and vegetal remains), subordinated sand.
- Bronze–Iron Age alluvial succession (~4.5–2.8 ka). Yellow sandy clay and silt, with rare organic-rich mm-thick layers, with medium sized gravel (Ø ≤ 5 cm) at the base.
- 6th Century alluvial succession (~2.55–2.45 ka). Light grey to yellowish clay, sometimes thinly laminated, devoid of anthropic and organic material, with a ~10 cm thick layer of fine gravel (Ø ≤ 2 cm) including sub-angular tuff and ceramic fragments at the base.
- Early Republican to Modern Age alluvial succession (<2.45 ka). Heterogeneous yellow to brown sandy clay sediments, including frequent fragments of anthropic materials.
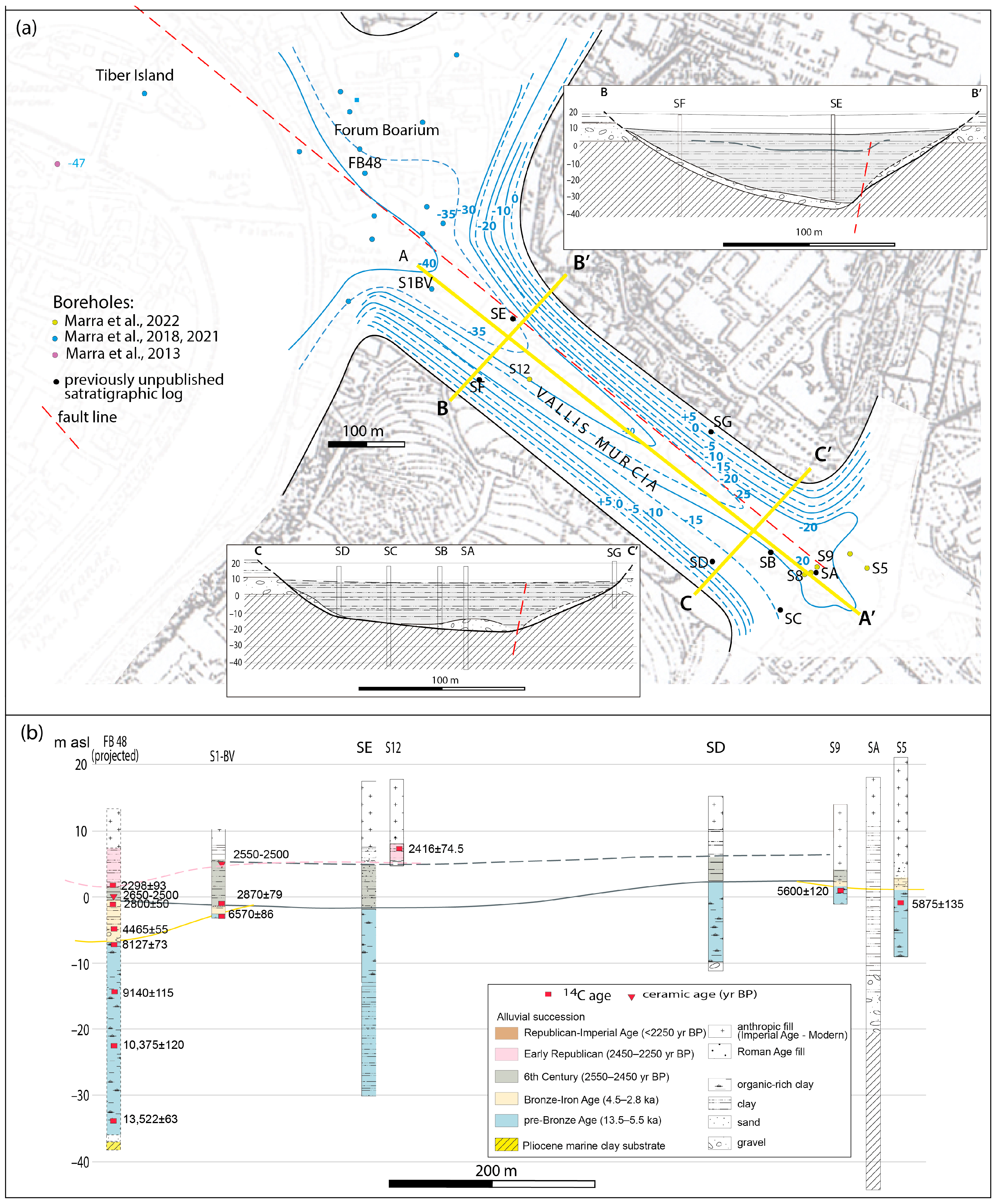
4.3.1. Murcia Valley
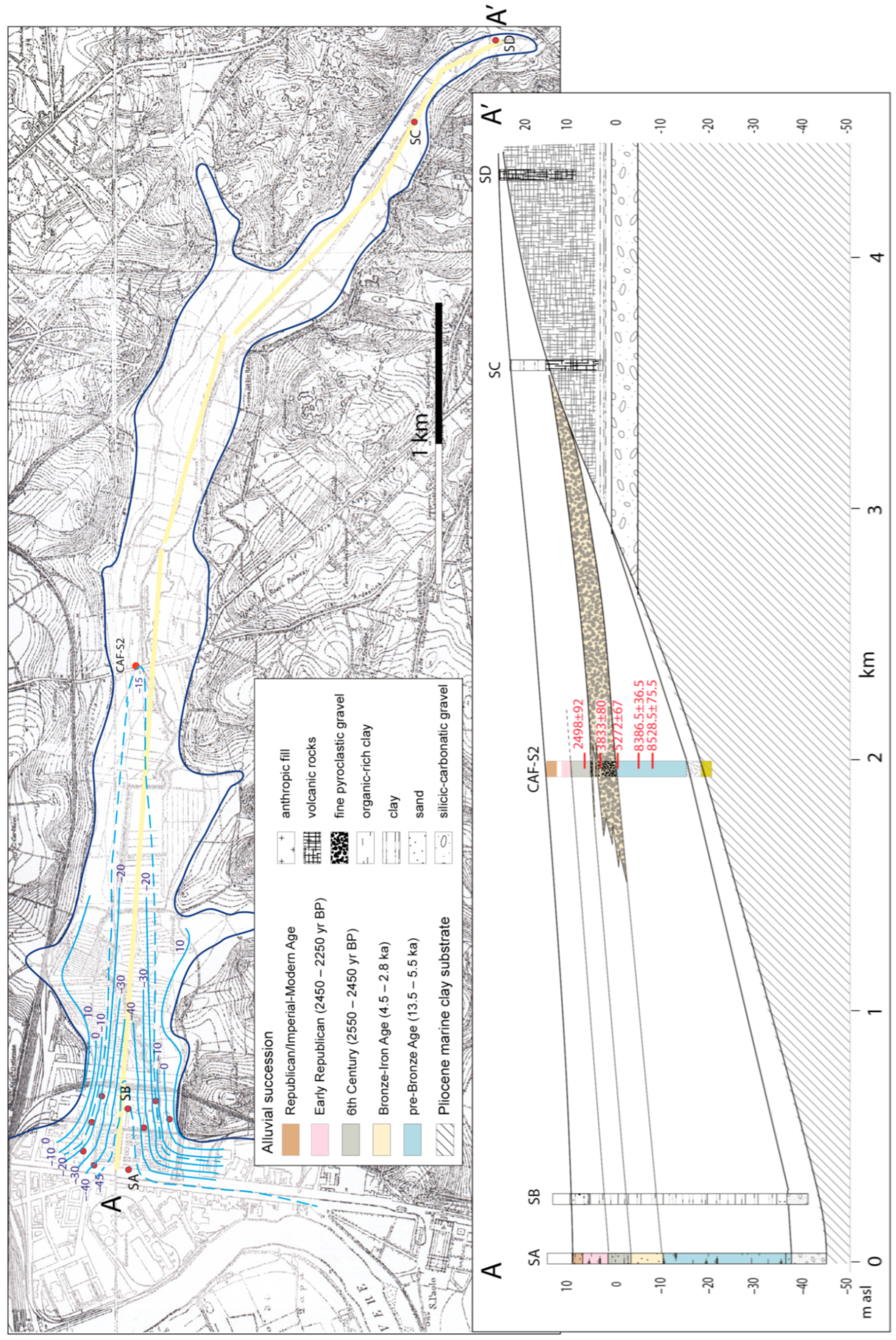
4.3.2. Caffarella Valley
4.3.3. Grottaperfetta Valley
5. Discussion
5.1. Reconstruction of the Aggradational Phases and Correlation with the Main Tiber Valley
5.1.1. Mid-Holocene Erosional Phase
5.1.2. The 4.2 ka Event
5.1.3. 6th Century Overflooding Phase
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amorosi, A.; Milli, S. Late Quaternary depositional architecture of Po and Tevere river deltas (Italy) and worldwide comparison with coeval deltaic successions. Sed. Geol. 2001, 144, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkowska, K.; Dzieduszyńska, D. Local evidence of landform evolution vs. global changes—A case of younger dryas study in the upper Ner valley system, Central Poland. Geogr. Pol. 2011, 84, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, J.; Busschers, F.S.; Stouthamer, E. Fluvial Evolution of the Rhine during the Last Interglacial-Glacial Cycle in the Southern North Sea Basin: A Review and Look Forward. Quat. Int. 2015, 357, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalicki, T.; Frączek, M.; Przepióra, P.; Kusztal, P.; Kłusakiewicz, E.; Malęga, E. Late Quaternary geomorphology and geoarchaelogy in the rivers of the Holy Cross Mountains region, Central Europe. Quat. Res. 2019, 91, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalicki, T.; Chwałek, S.; Przepióra, P.; Frączek, M.; Kusztal, P.; Chrabąszcz, M.; Puntos, C.K. Sediments and age of terraces and floodplains of the Ezousas River in SW Cyprus. Acta Geobalcanica 2020, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Bozzano, F.; Cinti, F.R. Chronostratigraphic and lithologic features of the Tiber River sediments (Rome, Italy): Implications on the Post-glacial sea-level rise and Holocene climate. Glob. Planet. Change 2013, 107, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J.; Marriner, N.; Morhange, C. Human Influence and the Changing Geomorphology of Mediterranean Deltas and Coasts over the Last 6000 Years: From Progradation to Destruction Phase? Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 139, 336–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchi, M.; Marriner, N.; Morhange, C.; Spada, G.; Fontana, A.; Rovere, A. Multiproxy assessment of Holocene relative sea-level changes in the western Mediterranean: Sea-level variability and improvements in the definition of the isostatic signal. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 155, 172–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorosi, A.; Bruno, L.; Campo, B.; Morelli, A.; Rossi, V.; Scarponi, D.; Hong, W.; Bohacs, K.M.; Drexler, T.M. Global Sea-Level Control on Local Parasequence Architecture from the Holocene Record of the Po Plain, Italy. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 87, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, A.; Marra, F.; Motta, L.; Nicosia, C.; Pescio, S.; Terrenato, N. Natural and anthropic influences on the transformation of the landscape in archaic Rome during the 6th c BCE. JAS Rep. 2025, 62, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milli, S.; Mancini, M.; Moscatelli, M.; Stigliano, F.; Marini, M.; Caginato, G.P. From river to shelf, anatomy of a high-frequency depositional sequence: The Late Pleistocene to Holocene Tiber depositional sequence. Sedimentology 2016, 63, 1886–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Frepoli, A.; Gioia, D.; Schiattarella, M.; Tertulliani, A.; Bini, M.; De Luca, G.; Luppichini, M. A morpho-structural approach to the study of earthquakes in Rome. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 2445–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazza, A.; Lanzini, M.; Rosa, C.; Salucci, R. Caratteri stratigrafici, idrogeologici e geotecnici delle alluvioni tiberine nel settore del centro storico di Roma. Il Quat. 1999, 12, 215–235. [Google Scholar]
- Bozzano, F.; Caserta, A.; Govoni, A.; Marra, F.; Martino, S. Static and dynamic characterization of alluvial deposits in the Tiber River Valley: New data for assessing potential ground motion in the City of Rome. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2008, 113, BO1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Moscatelli, M.; Stigliano, F.P.; Cavinato, G.P.; Milli, S.; Pagliaroli, A.; Simionato, M.; Brancaleoni, R.; Cipolloni, I.; Coen, G.; et al. The Upper Pleistocene-Holocene fluvial deposits of the Tiber River in Rome (Italy): Lithofacies, geometries, stacking pattern and chronology. J. Med. Earth Sci. 2013, 5, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Marra, F.; Motta, L.; Brock, A.; Macrì, P.; Florindo, F.; Sadori, L.; Terrenato, N. Rome in its setting. Post-glacial aggradation history of the Tiber River alluvial deposits and tectonic origin of the Tiber Island. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marra, F.; Brock, A.; Florindo, F.; Macrì, P.; Motta, L.; Nicosia, C.; Terrenato, N. Faults and Fluvial Dynamism affecting the Tiber River in Prehistoric Rome. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2021, 111, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belluomini, G.; Iuzzolini, P.; Manfra, L.; Mortari, R.; Zalaffi, M. Evoluzione recente del delta del Tevere. Geol. Rom. 1986, 25, 213–234. [Google Scholar]
- Bellotti, P.; Calderoni, G.; Carboni, M.G.; Di Bella, L.; Tortora, P.; Valeri, P. Late Quaternary landscape evolution of the Tiber River delta plain (Central Italy): New evidence from pollen data, biostratigraphy and 14C dating. Zeit. Geomorph. 2007, 51, 505–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersani, P.; Bencivenga, M. Le Piene del Tevere a Roma dal V secolo a.C. all’anno 2000; Presidenza del Consiglio dei Ministri: Rome, Italy, 2003; pp. 4–9.
- Aldrete, G.S. Floods of the Tiber in Ancient Rome; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Leonardi, R.; Pracchia, S.; Bonaguro, S.; Laudato, M.; Saviane, N. Sondaggi lungo la tratta T2. Caratteri ambientali e aspetti topografici del Campo Marzio in epoca romana. Boll. d’Arte 2010, 1, 82–92. [Google Scholar]
- Brock, A.; Motta, L.; Terrenato, N. On the Banks of the Tiber: Opportunity and Transformation in Early Rome. J. Rom. Stud. 2021, 111, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, F.R.; Marra, F.; Bozzano, F.; Cara, F.; Di Giulio, G.; Boschi, E. Tectonostratigraphic investigations within a highly urbanized area: The case of the Grottaperfetta valley in the city of Rome (Italy). Ann. Geoph. 2008, 51, 849–865. [Google Scholar]
- Luberti, G.M.; Marra, F.; Florindo, F. A review of the stratigraphy of Rome (Italy) according to geochronologically and paleomagnetically constrained aggradational successions, glacio-eustatic forcing and volcano-tectonic processes. Quat. Int. 2017, 438, 40–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellotti, P.; Chiocchini, U.; Cipriani, N.; Milli, S. I sistemi deposizionali nei sedimenti clastici pleistocenici affioranti nei dintorni di Ponte Galeria (sud ovest di Roma). Boll. Della Soc. Geol. Ital. 1994, 112, 924–941. [Google Scholar]
- Marra, F.; Florindo, F.; Karner, D.B. Paleomagnetism and geochronology of early Middle Pleistocene depositional sequences near Rome: Comparison with the deep sea d18O climate record. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1998, 159, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Florindo, F. The subsurface geology of Rome: Sedimentary processes, sea-level changes and astronomical forcing. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 136, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccerillo, A. Cenozoic Volcanism in the Tyrrhenian Sea Region; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; 399p. [Google Scholar]
- Fornaseri, M.; Scherillo, A.; Ventriglia, U. La Regione Vulcanica dei Colli Albani: Il Vulcano Laziale; Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (C.N.R.): Rome, Italy, 1963; 561p. [Google Scholar]
- Mattias, P.P.; Ventriglia, U. La regione vulcanica dei monti Sabatini e Cimini. Mem. Soc. Geol. It. 1970, 95, 831–849. [Google Scholar]
- De Rita, D.; Funiciello, R.; Parotto, M. Geological Map of the Colli Albani Volcanic Complex; Progetto Finalizzato Geodinamica CNR: Rome, Italy, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Karner, D.B.; Marra, F.; Renne, P. The history of the Monti Sabatini and Alban Hills volcanoes: Groundwork for assessing volcanic-tectonic hazards for Rome. J. Volcanol. Geoth. Res. 2001, 107, 185–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, G.; De Benedetti, A.A.; Diana, A.; Diano, G.; Gaudioso, F.; Marasco, F.; Miceli, M.; Mollo, S.; Cas, R.A.F.; Funiciello, R. The Colli Albani mafic caldera (Roma, Italy): Stratigraphy, structure and petrology. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2006, 155, 49–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Karner, D.B.; Freda, C.; Gaeta, M.; Renne, P.R. Large mafic eruptions at the Alban Hills Volcanic District (Central Italy): Chronostratigraphy, petrography and eruptive behavior. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2009, 179, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Sottili, G.; Gaeta, M.; Giaccio, B.; Jicha, B.; Masotta, M.; Palladino, D.M.; Deocampo, D. Major explosive activity in the Sabatini Volcanic District (central Italy) over the 800–390 ka interval: Geochronological—Geochemical overview and tephrostratigraphic implications. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 94, 74–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaeta, M.; Freda, C.; Marra, F.; Arienzo, I.; Gozzi, F.; Jicha, B.; Di Rocco, T. Paleozoic metasomatism at the origin of Mediterranean ultrapotassic magmas: Constraints from time-dependent geochemistry of Colli Albani volcanic products (Central Italy). Lithos 2016, 244, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Rosa, C. Stratigrafia e assetto geologico dell’area romana—In: La geologia di Roma: Il centro storico. Mem. Descr. Carta Geol. D’It. 1995, 50, 49–118. [Google Scholar]
- Funiciello, R.; Giordano, G.; Mattei, M. Carta geologica del Comune di Roma. Scala 1:50000. In La Geologia di Roma dal Centro Storico alla Periferia; Memorie descrittive della Carta Geologica d’Italia; ISPRA: Rome, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Karner, D.B.; Marra, F. Correlation of Fluviodeltaic Aggradational Sections with Glacial Climate History: A Revision of the Classical Pleistocene Stratigraphy of Rome. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1998, 110, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karner, D.B.; Marra, F.; Florindo, F.; Boschi, E. Pulsed uplift estimated from terrace elevations in the coast of Rome: Evidence for a new phase of volcanic activity? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 188, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Florindo, F.; Anzidei, M.; Sepe, V. Paleo-surfaces of glacio- eustatically forced aggradational successions in the coastal area of Rome: Assessing interplay between tectonics and sea-level during the last ten interglacials. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 148, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Bahain, J.-J.; Jicha, B.; Nomade, S.; Palladino, D.M.; Pereira, A.; Tolomei, C.; Voinchet, P.; Anzidei, M.; Aureli, D.; et al. Reconstruction of the MIS 5.5, 5.3 and 5.1 coastal terraces in Latium (central Italy): A re-evaluation of the sea-level history in the Mediterranean Sea during the Last Interglacial. Quat. Int. 2019, 525, 54–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Gaeta, M.; Jicha, B.R.; Nicosia, C.; Tolomei, C.; Ceruleo, P.; Florindo, F.; Gatta, M.; La Rosa, M.; Rolfo, M.F. MIS 9 to MIS 5 terraces along the Tyrrhenian Sea coast of Latium (central Italy): Assessing interplay between sea-level oscillations and tectonic movements. Geomorphology 2019, 346, 106843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Monte, M.; D’Orefice, M.; Luberti, G.M.; Marini, R.; Pica, A.; Vergari, F. Geomorphological classification of urban landscapes: The case study of Rome (Italy). J. Maps 2016, 12, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luberti, G.M.; Vergari, F.; Marini, R.; Pica, A.; Del Monte, M. Anthropogenic modifications to the drainage network of Rome (Italy): The case study of the Aqua Mariana. Alp. Mediterr. Quat. 2018, 31, 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Carpentieri, E.; de Rita, D.; della Monica, G.D. Geology of the Murcia valley and flood plain modifications in the construction of the Circus Maximus, Rome, Italy. Geoarchaeology 2015, 30, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Buonfiglio, M.; Motta, L. Holocene aggradation history of the Murcia alluvial valley: Insights on early Rome paleoenvironmental evolution. Quat. Int. 2022, 628, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strunk, A.; Olsen, J.; Sanei, H.; Rudra, A.; Larsen, N.K. Improving the reliability of bulk sediment radiocarbon dating. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 242, 106442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Rohling, E.J.; Florindo, F.; Jicha, B.; Nomade, S.; Pereira, A.; Renne, P.R. Independent 40Ar/39Ar and 14C age constraints on the last five glacial terminations from the aggradational successions of the Tiber River, Rome (Italy). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 449, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, J.D.; Hemingway, R.; Rohling, E.J.; Challenor, P.G.; Medina-Elizalde, M.; Lester, A.J. Sea-level probability for the last deglaciation: A statistical anal-ysis of far-field records. Glob. Planet. Change 2011, 79, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, M.; Zanchetta, G.; Perşoiu, A.; Cartier, R.; Català, A.; Cacho, I.; Dean, J.R.; Di Rita, F.; Drysdale, R.N.; Finnè, M.; et al. The 4.2 ka BP Event in the Mediterranean Region: An overview. Clim. Past 2019, 15, 555–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S.; Kanata Kobayashi, K.; Irizuki, T.; Akira Tsujimoto, A.; Rei Nakashima, R.; Haneda, Y.; Ishihara, Y. Coastal dynamics and sea-level change at 4 ka: A case study from the Wakayama Plain, Japan. Sed. Geol. 2025, 476, 106807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, H.M.; deMenocal, P.; Hemming, S.; Hemming, G.; Brown, F.H.; Guilderson, T.; Sirocko, F. Climate change and the collapse of the Akkadian empire: Evidence from the deep sea. Geology 2000, 28, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drysdale, R.N.; Zanchetta, G.; Hellstrom, J.C.; Maas, R.; Fallick, A.E.; Pickett, M.; Cartwright, I.; Piccini, L. Late Holocene drought responsible for the collapse of Old World civilizations is recorded in an Italian cave flowstone. Geology 2006, 34, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, Y.; Hodell, D.A.; Petrie, C.A. Abrupt weakening of the summer monsoon in northwest India 4100 yr ago. Geology 2014, 42, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, H. Global megadrought, collapse, and resilience in late 3rd millennium BC Mesopotamia. In 2200 BC—A Climatic Break-down as a Cause for the Collapse of the Old World? Meller, H., Arz, H.W., Jung, R., Risch, R., Eds.; Landesmuseum fur Vorgeschichte: Halle, Germany, 2015; pp. 35–52. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, H. Global megadrought, societal collapse and resilience at 4.2–3.9 ka BP across the Mediterranean and west Asia. Past Glob. Change Mag. 2016, 24, 62–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magny, M.; Vanniere, B.; Zanchetta, G.; Fouache, E.; Touchias, G.; Petrika, L.; Coussot, C.; Walter-Simonnet, A.-V.; Arnoud, F. Possible complexity of the climatic event around 4300–3800 cal. BP in the central and western Mediterranean. Holocene 2009, 19, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Railsback, L.B.; Liang, F.; Brook, G.A.; Riavo, N.; Voarintsoa, G.; Sletten, H.R.; Marais, E.; Hardt, B.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L. The timing, two-pulsed nature, and variable climatic expression of the 4.2 ka event: A review and new high-resolution stalagmite data from Namibia. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2018, 186, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayewski, P.E.; Rohling, J.; Stager, W.; Karlén, K.; Maasch, L.; Meeker, E.; Meyerson, F.; Gasse, S.; van Kreveld, K.; Holmgren, J.; et al. Holocene climate variability. Quat. Res. 2004, 62, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, H.; Beer, J.; Bütikofer, J.; Crowley, T.J.; Cubasch, U.; Flückiger, J.; Goosse, H.; Grosjean, M.; Joos, F.; Kaplan, J.O.; et al. Mid-to Late Holocene climate change: An overview. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2008, 27, 1791–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steig, E.J. Mid-Holocene climate change. Science 1999, 286, 1485–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzelt, G. Der zeitliche Ablauf und das Ausmass postglazialer Klimaschwankungen in den Alpen. In Dendrochronologie und Postglaziale Klimaschwankungen in Europa; Frenzel, B., Ed.; Steiner Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 1977; pp. 248–259. [Google Scholar]
- Gasse, F. Hydrological changes in the African tropics since the Last Glacial Maximum. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2000, 19, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; Konig, K.A.; Thompson, R.; Kamenik, C. A multi proxy core study of the last 7000 years of climate and alpine land-use impacts on an Austrian mountain lake (Unterer Landschitzsee, Niedere Tauern). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2002, 187, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magny, M.; Haas, N. A major widespread climatic change around 5300 cal. yr BP at the time of the Alpine Iceman. J. Quat. Sci. 2004, 19, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitscke, S.; Demske, D.; Wünnemann, B.; Schundack, M.E. Groundwater discharge to a Gobi desert lake during Mid and Late Holocene dry periods. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2005, 225, 157–172. [Google Scholar]
- Carboni, M.G.; Conati Barbaro, C.; Manfredini, A. The Copper Age Settlement Le Cerquete-Fianello (Maccarese, Rome) a sedentary community in the lagoon environment of Maccarese (Rome). In Proceedings of the Atti del XIII Congresso U.I.S.P.P., Forlì, Italy, 8–14 September 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Di Rita, F.; Celant, A.; Magri, D. Holocene environmental instability in the wetland north of the Tiber delta (Rome, Italy): Sea-lake-man interactions. J. Paleolimnol. 2009, 44, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraudi, C. Evoluzione tardo-olocenica del delta del Tevere. It. J. Quat. Sci. 2004, 17, 477–492. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, L.; Bohacs, K.M.; Campo, B.; Drexler, T.M.; Rossi, V.; Sammartino, I.; Scarponi, D.; Hong, W.; Amorosi, A. Early Holocene transgressive palaeogeography in the Po coastal plain (northern Italy). Sedimentology 2017, 64, 1792–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorosi, A.; Barbieri, G.; Bruno, L.; Campo, B.; Drexler, T.M.; Hong, W.; Rossi, V.; Sammartino, I.; Scarponi, D.; Vaiani, S.C.; et al. Three-fold nature of coastal progradation during the Holocene eustatic highstand, Po Plain, Italy—Close correspondence of stratal character with distribution patterns. Sedimentology 2019, 66, 3029–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, B.; Barbieri, G.; Di Martino, A.; Hong, W.; Scarponi, D.; Vaiani, S.C.; Amorosi, A. Late Pleistocene to Holocene glacio-eustatic history as recorded in the Pescara paleovalley system (Central Italy, Adriatic basin). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 145, 105908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, E. Black Carbon in the Environment; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, H.; Witcher, R.; Di Giuseppe, H. The Changing Landscapes of Rome’s Northern Hinterland. In The British School at Rome’s Tiber Valley Project; Archaeopress Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cifani, G. Storia di una Frontiera. Dinamiche Territoriali e Gruppi Etnici Nella Media Valle Tiberina dalla Prima età del Ferro alla Conquista Romana; Archeologia del Territorio; Libreria dello Stato, Istituto Poligrafico e Zecca dello Stato: Rome, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
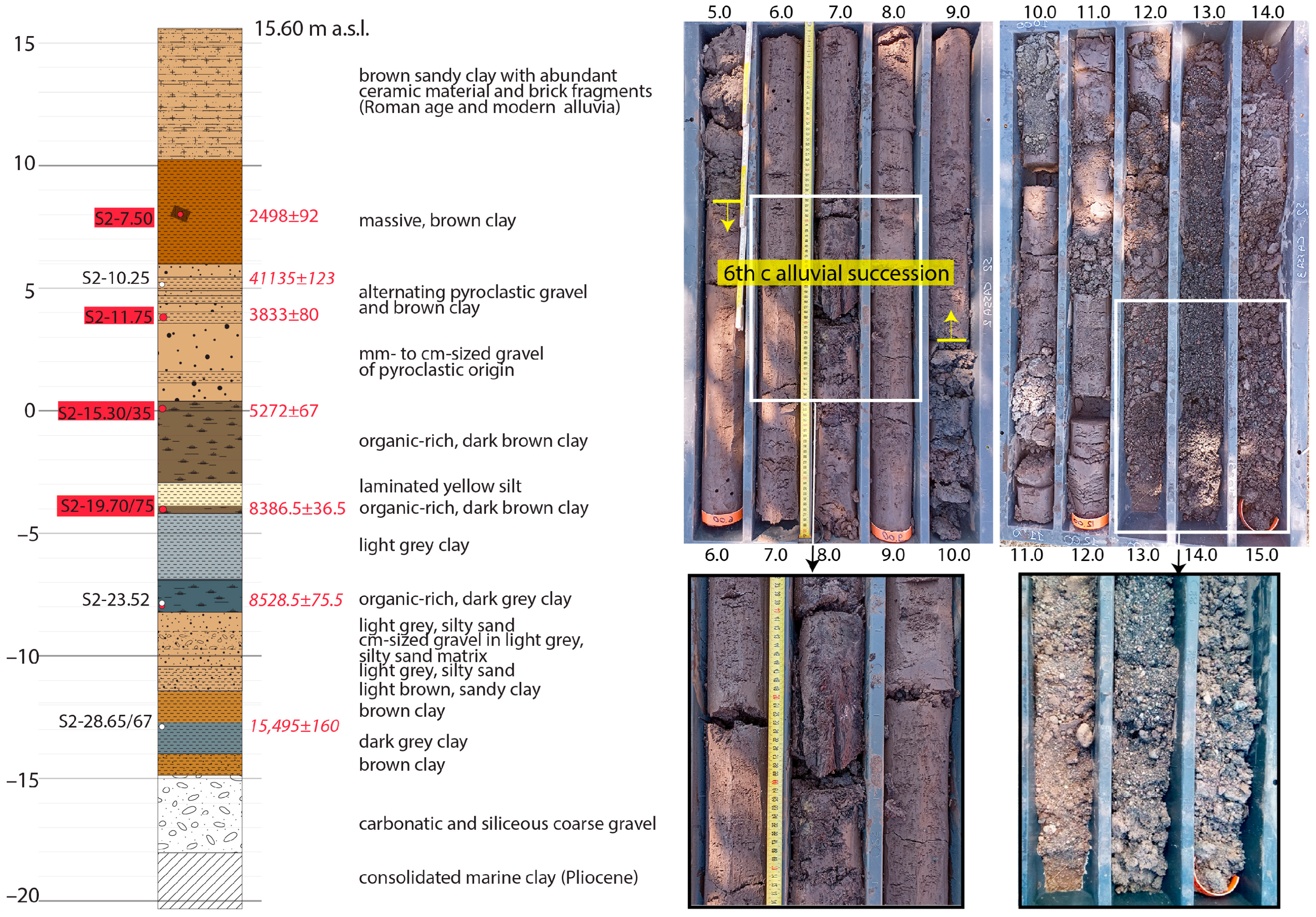

| Sample | Material | Conventional Radiocarbon Age | Calibrated Age (yr BP) | Adopted Age |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S2-7.50 | wood | 2440 ± 30 BP | (62.3%) 2540–2357 (22.3%) 2700–2633 (9.7%) 2617–2583 (1.1%) 2571–2562 | 2498 ± 92 |
| S2-10.25/30 | organic sediment | 3760 ± 30 BP | (64.8%) 4188–4076 (15.5%) 4236–4195 (15.2%) 4041–3990 | 4113 ± 123 * |
| S2-11.75 | seeds | 3510 ± 30 BP | (95.4%) 3872–3694 | 3833 ± 80 |
| S2-15.30/35 | plant material | 4470 ± 30 BP | (50.6%) 5289–5155 (35.5%) 5148–5025 (9.3%) 5014–4975 | 5272 ± 67 |
| S2-19.70/75 | organic sediment | 7590 ± 30 BP | (95.4%) 8423–8350 | 8386.5 ± 36.5 * |
| S2-23.52 | wood | 7780 ± 30 BP | (93.6%) 8604–8453 (1.8%) 8632–8621 | 8528.5 ± 75.5 |
| S2-28.65/67 | organic sediment | 12,920 ± 40 BP | (95.4%) 15,604–15,285 | 15,495 ± 160 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marra, F.; Rosa, C.; Florindo, F. Late Holocene Abrupt Changes in the Fluvial Dynamics of the Tiber Valley Catchment (Rome, Italy): An Impact of the 4.2 Event? Quaternary 2025, 8, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat8040059
Marra F, Rosa C, Florindo F. Late Holocene Abrupt Changes in the Fluvial Dynamics of the Tiber Valley Catchment (Rome, Italy): An Impact of the 4.2 Event? Quaternary. 2025; 8(4):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat8040059
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarra, Fabrizio, Carlo Rosa, and Fabio Florindo. 2025. "Late Holocene Abrupt Changes in the Fluvial Dynamics of the Tiber Valley Catchment (Rome, Italy): An Impact of the 4.2 Event?" Quaternary 8, no. 4: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat8040059
APA StyleMarra, F., Rosa, C., & Florindo, F. (2025). Late Holocene Abrupt Changes in the Fluvial Dynamics of the Tiber Valley Catchment (Rome, Italy): An Impact of the 4.2 Event? Quaternary, 8(4), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat8040059








