Microstructural Evolution of Antarctic Ice with the Rising Atmospheric CO2: A Longitudinal Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Mechanism and Implications
4.2. Study Justification and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicklin, G. The colonial and extracolonial bordering of Antarctica. In Colonialism and Antarctica: Attitudes, Logics, and Practices; Roberts, P., Mancilla, A., Eds.; Manchester University Press: Manchester, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Nicklin, G. The implied border mechanisms of Antarctica: Arguing the case for an Antarctic borderscape. Borderl. J. 2020, 19, 27–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, K. What is Antarctica? Geography 2024, 109, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A. Antarctica without Borders. Issues 2012, 100, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Karacan, D.B.; Ozsoy, B.; Okay, D.Z. Scientific research and collaboration in Antarctica: Türkiye’s engagement from a science diplomacy perspective. Polar Sci. 2024, 39, 101035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farman, J.C.; Gardiner, B.G.; Shanklin, J.D. Large losses of total ozone in Antarctica reveal seasonal ClOx/NOx interaction. Nature 1985, 315, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlighem, M.; Rignot, E.; Binder, T.; Blankenship, D.; Drews, R.; Eagles, G.; Eisen, O.; Ferraccioli, F.; Forsberg, R.; Fretwell, P.; et al. Deep glacial troughs and stabilizing ridges unveiled beneath the margins of the Antarctic ice sheet. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.; Phillips, T.; Hosking, J.S.; Marshall, G.J.; Bracegirdle, T.J. Future projections of temperature and precipitation for Antarctica. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 014029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauska, T.K. Ice core records of atmospheric carbon dioxide. In Encyclopedia of Quaternary Science, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Prior, D.J.; Han, Y.; Qi, C.; Han, H.; Ju, H.T. Microstructures and Fabric Transitions of Natural Ice from the Styx Glacier, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Minerals 2020, 10, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüthi, D.; Le Floch, M.; Bereiter, B.; Blunier, T.; Barnola, J.-M.; Siegenthaler, U.; Raynaud, D.; Jouzel, J.; Fischer, H.; Kawamura, K.; et al. High-resolution carbon dioxide concentration record 650,000–800,000 years before present. Nature 2008, 453, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, R.; Harwood, D.; Florindo, F.; Sangiorgi, F.; Tripati, R.; von Eynatten, H.; Gasson, E.; Kuhn, G.; Tripati, A.; DeConto, R.; et al. Antarctic ice sheet sensitivity to atmospheric CO2 variations in the early to mid-Miocene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3453–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskoković, V. Ion-Doped Hydroxyapatite: An Impasse or the Road to Follow? Ceramics International 2020, 46, 11443–11465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskoković, V. An Odyssey at the Interface—A Study in the Stream of Consciousness. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 5150–5160. [Google Scholar]
- Uskoković, V. The Samsonov Configurational Model: Instructive Historical Remarks and Extension of Its Application to Substituted Hydroxyapatite. Comments Inorg. Chem. 2023, 43, 106–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, C.D.; Piper, S.C.; Bacastow, R.B.; Wahlen, M.; Whorf, T.P.; Heimann, M.; Meijer, H.A.I. Global aspects. In Exchanges of Atmospheric CO2 and 13CO2 with the Terrestrial Biosphere and Oceans from 1978 to 2000; SIO Reference Series, No. 01–06; Scripps Institution of Oceanography: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; 88p. [Google Scholar]
- Uskoković, V. Entering the Era of Nanoscience: Time to Be So Small. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 1441–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qian, Z.; Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, J. Effect of Grain Size on the Uniaxial Compressive Strength of Ice Forming with Different Wind Speeds in a Cold Laboratory. Water 2024, 16, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currier, J.H.; Schulson, E.M. The tensile strength of ice as a function of grain size. Acta Metall. 1982, 30, 1511–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiscombe, W.J.; Warren, S.G. A model for the spectral albedo of snow, 1. Pure snow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 2712–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenfell, T.C.; Warren, S.G.; Mullen, P.C. Reflection of solar radiation by the Antarctic snow surface at ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared wavelengths. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 18669–18684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maykut, G.A. The surface heat and mass balance. In The Geophysics of Sea Ice; Untersteiner, N., Ed.; NATO ASI Ser., Ser. B.; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1986; Volume 146, pp. 395–463. [Google Scholar]
- Khuller, A.R.; Warren, S.G.; Christensen, P.R.; Clow, G.D. Potential for photosynthesis on Mars within snow and ice. Commun Earth Env. 2024, 5, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.R.; Iverson, N.R. A permeameter for temperate ice: First results on permeability sensitivity to grain size. J. Glaciol. 2022, 68, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, C.; Mampearachchi, W.K. Effect of surface texture, size ratio and large particle volume fraction on packing density of binary spherical mixtures. Granul. Matter 2020, 22, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenfell, T.C.; Warren, S.G. Representation of a nonspherical ice particle by a collection of independent spheres for scattering and absorption of radiation. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 31697–31709. [Google Scholar]
- Beers, T.M.; Sneed, S.B.; Mayewski, P.A.; Kurbatov, A.V.; Handley, M.J. Triple Junction and Grain Boundary Influences on Climate Signals in Polar Ice. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.14268v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, E.W.; Mulvaney, R.; Oates, K. The location of impurities in Antarctic ice. Ann. Glaciol. 1988, 11, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, H.; Maeno, N. Studies on structures and physical properties of snow on Mizuho Plateau, Antarctica. Ann. Glaciol. 1985, 6, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lu, S.; Zhang, N.; Wang, D.; Shi, G.; Ma, T.; Ma, H.; An, C.; Li, Y. Spatial Variations of Fabric and Microstructure of Blue Ice Cores at the Shear Margin of Dalk Glacier, Antarctica. Water 2023, 15, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonell, S.; Fernandoy, F.; Villar, P.; Hammann, A. Stratigraphic Analysis of Firn Cores from an Antarctic Ice Shelf Firn Aquifer. Water 2021, 13, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skatulla, S.; Audh, R.R.; Cook, A.; Hepworth, E.; Johnson, S.; Lupascu, D.C.; MacHutchon, K.; Marquart, R.; Mielke, T.; Omatuku, E.; et al. Physical and mechanical properties of winter first-year ice in the Antarctic marginal ice zone along the Good Hope Line. Cryosphere 2022, 16, 2899–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, P.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z. Flexural and compressive strength of the landfast sea ice in the Prydz Bay, East Antarctic. Cryosphere 2022, 16, 1941–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Audh, R.R.; de Jager, W.; Matlakala, B.; Vichi, M.; Womack, A.; Rampai, T. Physical and morphological properties of first-year Antarctic sea ice in the spring marginal ice zone of the Atlantic-Indian sector. J. Glaciol. 2023, 69, 1351–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.E.; Negrini, M.; Prior, D.J.; Mulvaney, R.; Still, H.; Bowman, M.H.; Craw, L.; Fan, S.; Hubbard, B.; Hulbe, C.; et al. Microstructure and Crystallographic Preferred Orientations of an Azimuthally Oriented Ice Core from a Lateral Shear Margin: Priestley Glacier, Antarctica. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 702213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, R.; Fujita, S.; Kawamura, K.; Oyabu, I.; Nakazawa, F.; Motoyama, H.; Aoki, T. Spatial distribution of vertical density and microstructure profiles in near-surface firn around Dome Fuji, Antarctica. Cryosphere 2024, 18, 425–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, D.E.; Hörhold, M.; Kipfstuhl, S.; Freitag, J. Microstructure of Snow and Its Link to Trace Elements and Isotopic Composition at Kohnen Station, Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolshunov, A.V.; Vasilev, D.A.; Dmitriev, A.N.; Ignatev, S.A.; Kadochnikov, V.G.; Krikun, N.S.; Serbin, D.V.; Shadrin, V.S. Results of complex experimental studies at Vostok station in Antarctica. J. Min. Inst. 2023, 263, 724–741. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsen, T.; Birnbaum, G.; Ehrlich, A.; Freitag, J.; Heygster, G.; Istomina, L.; Kipfstuhl, S.; Orsi, A.; Schäfer, M.; Wendisch, M. Comparison of different methods to retrieve optical-equivalent snow grain size in central Antarctica. Cryosphere 2017, 11, 2727–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calonne, N.; Montagnat, M.; Matzl, M.; Schneebeli, M. The layered evolution of fabric and microstructure of snow at Point Barnola, Central East Antarctica. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 460, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, M.; Löwe, H.; Schneebeli, M. Density, specific surface area, and correlation length of snow measured by high-resolution penetrometry. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2015, 120, 346–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadic, R.; Schneebeli, M.; Bertler, N.A.N.; Schwikowski, M.; Matzl, M. Extreme snow metamorphism in the Allan Hills, Antarctica, as an analogue for glacial conditions with implications for stable isotope composition. J. Glaciol. 2015, 61, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pirazzini, R.; Räisänen, P.; Vihma, T.; Johansson, M.; Tastula, E.-M. Measurements and modelling of snow particle size and shortwave infrared albedo over a melting Antarctic ice sheet. Cryosphere 2015, 9, 2357–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, G.A.; Fedotov, V.I.; Cherepanov, N.V. Some features of sea ice formation in Antarctic coastal waters. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2013, 38, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, A.R.; Gough, A.J.; Langhorne, P.J.; Robinson, N.J.; Stevens, C.L.; Williams, M.M.J.; Haskell, T.G. The seasonal appearance of ice shelf water in coastal Antarctica and its effect on sea ice growth. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116, C11032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallet, J.-C.; Domine, F.; Savarino, J.; Dumont, M.; Brun, E. The growth of sublimation crystals and surface hoar on the Antarctic plateau. Cryosphere 2014, 8, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallet, J.-C.; Domine, F.; Arnaud, L.; Picard, G.; Savarino, J. Vertical profiles of the specific surface area of the snow at Dome C, Antarctica. Cryosphere Discuss. 2010, 4, 1647–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, S.; Okuyama, J.; Hori Hondoh, T. Metamorphism of stratified firn at Dome Fuji, Antarctica: A mechanism for local insolation modulation of gas transport conditions during bubble close off. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, F03023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, D.E.; Langhorne, P.J.; Robinson, N.J.; Haskell, T.G.; Frew, R. Observation and modeling of platelet ice fabric in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saruya, T.; Fujita, S.; Iizuka, Y.; Miyamoto, A.; Ohno, H.; Hori, A.; Shigeyama, W.; Hirabayashi, M.; Goto-Azuma, K. Development of crystal orientation fabric in the Dome Fuji ice core in East Antarctica: Implications for the deformation regime in ice sheets. Cryosphere 2022, 16, 2985–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, J.; Kipfstuhl, S.; Faria, S.H. The connectivity of crystallite agglomerates in low-density firn at Kohnen station, Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica. Ann. Glaciol. 2008, 49, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucker, L.; Picard, G.; Arnaud, L.; Barnola, J.-M.; Schneebeli, M.; Brunjail, H.; Lefebvre, E.; Fily, M. Modeling time series of microwave brightness temperature at Dome C, Antarctica, using vertically resolved snow temperature and microstructure measurements. J. Glaciol. 2011, 57, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alencar, A.S.; Evangelista, H., Jr.; Simões, J.C.; Felzenszwalb, I.; Setzer, A.; Passos, H.R. On the potential of glaciochemical analysis of Joinville Island firn core for the sea ice reconstruction around the northern Antarctic Peninsula. An. Da Acad. Bras. De Cienc. 2024, 96 (Suppl. S2), e20230751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Qin, D.; Ren, J.; Kang, J.; Li, Z. Structure, salinity and isotopic composition of multi-year landfast sea ice in Nella Fjord, Antarctica. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2007, 49, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärkäs, E.; Martma, T.; Sonninen, E. Physical properties and stratigraphy of surface snow in western Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica. Polar Res. 2005, 24, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rasmus, K.; Granberg, H.; Kanto, K.; Kärkäs, E.; Lavoie, C.; Leppäranta, M. Seasonal Snow in Antarctica Data Report; Report Series in Geophysics No. 47; University of Helsinki: Helsinki, Finland, 2003. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Gow, A.J.; Meese, D.A.; Bialas, R.W. Accumulation variability, density profiles and crystal growth trends in ITASE firn and ice cores from West Antarctica. Ann. Glaciol. 2004, 39, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, M.R.; Shultz, E.F.; Perron, F.E., Jr. Snow and firm permeability at Siple Dome, Antarctica. Ann. Glaciol. 2000, 31, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, M.; Fily, M.; Frezzotti, M.; Genthon, C.; Oerter, H.; Winther, J.G. Snow grain-size measurements in Antarctica. J. Glaciol. 2002, 48, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Haas, C.; Thomas, D.N.; Bareiss, J. Surface properties and processes of perennial Antarctic sea ice in summer. J. Glaciol. 2001, 47, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massom, R.A.; Lytle, V.I.; Worby, A.P.; Allison, I. Winter snow cover variability on East Antarctic sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 24837–24855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnati, A. Some observations on snowpack features in Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Geogr. Fis. Dinam. Quat. 1997, 20, 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, C. The seasonal cycle of ERS scatterometer signatures over perennial Antarctic sea ice and associated surface ice properties and processes. Ann. Glaciol. 2001, 33, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, M.; Morris, K.; Massom, R. The winter snow cover of the West Antarctic pack ice: Its spatial and temporal variability. In Antarctic Sea Ice: Physical Processes, Interactions and Variability; Jeffries, M.O., Ed.; Antarctic Research Set: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; Volume 74, pp. 19–40. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, O.; Shimada, W.; Narita, H.; Miyamoto, A.; Tayuki, K.; Hondoh, T.; Kawamura, T.; Fujita, S.; Shoji, H.; Enomoto, H.; et al. Preliminary discussion of physical properties of the Dome Fuji shallow ice core in 1993, Antarctica. In Proceedings of the NIPR Symposium on Polar Meteorology and Glaciology, Tokyo, Japan, 13–14 October 1997; Volume 11, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Worby, A.P.; Massom, R.A. The Structure and Properties of Sea Ice and Snow Covering East Antarctic Pack Ice; Research Report No. 7; Antarctic CRC: Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, 1995; 191p. [Google Scholar]
- Massom, R.A.; Drinkwater, M.R.; Haas, C. Winter snow cover on sea ice in the Weddell Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 1101–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, M.O.; Shaw, R.A.; Veazey, K.M.A.L.; Krouse, H.R. Crystal structure, stable isotopes and development of sea ice in the Ross, Amundsen, and Bellingshausen seas, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walden, V.P.; Warren, S.G.; Tuttle, E. Atmospheric Ice Crystals over the Antarctic Plateau in Winter. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2003, 42, 1391–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veazey, A.L.; Jeffries, M.O.; Morris, K. Small-scale variability of physical properties and structural characteristics of Antarctic fast ice. Ann. Glaciol. 1994, 20, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Iwai, K. Three dimensional fine structures of bullet-type snow crystals and their growth conditions observed at Syowa Station, Antarctica. J. Jpn. Soc. Snow Ice 1999, 61, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, M.O.; Weeks, W.F. Structural characteristics and development of sea ice in the western Ross Sea. Antarct. Sci. 1992, 5, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, H.; Muramoto, K.; Shiina, T.; Endoh, T.; Kitano, K. Z-R relation for graupels and aggregates observed at Syowa Station, Antarctica. Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar Meteorol. Glaciol. 1992, 5, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka, M.; Ohta, Y.; Nishitsuji, A.; Sakaguchi, T.; Wada, M. A method of measuring snow particle size from video images for meteorological radar observations. Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar Meteorol. Glaciol. 1995, 9, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Tison, J.L.; Haren, J. Isotopic, chemical and crystallographic characteristics of first-year sea ice from Breid Bay (Princess Ragnhild Coast-Antarctica). Antarct. Sci. 1989, 1, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, R.B.; Bentley, C.R. Ice-core analysis on the Siple Coast of West Antarctica. Ann. Glaciol. 1988, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahe, Q.; Young, N.W.; Thwaites, R.J. Growth rate of crystals within the surface-snow/firn layer in Wilkes Land, East Antarctica. Ann. Glaciol. 1988, 11, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Urabe, N.; Inoue, M. Mechanical properties of Antarctic Sea ice. J. Offshore Mech. Arct. Eng. 1988, 110, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.A. Basic properties of Antarctic sea ice as revealed by textural analysis of ice cores. Ann. Glaciol. 1988, 10, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wada, M.; Gonda, T. Snow crystals of hollow-prism type observed at Mizuho Station, Antarctica. Antarct. Rec. 1985, 86, 1–8. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Duval, P.; Lorius, C. Crystal size and climatic records down to the last Ice Age from Antarctic ice. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1980, 48, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, T. Atmospheric ice crystals at the South Pole in summer. Antarct. J. 1978, 13, 174–175. [Google Scholar]
- Iwai, K. Morphological features of combination of bullet-type snow crystals observed at Syowa Station, Antarctica. Mem. Natl. Inst. Polar Res. 1986, 45, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, K.; Hogan, A.W. Properties of diamond dust type ice crystals observed in summer season at Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station, Antarctica. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1978, 57, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hogan, A.W. Summer ice crystal precipitation at the South Pole. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1974, 14, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, R.A. Crystallographic Studies of Sea Ice in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica; Technical Report R-494; US Naval Civil Engineering Laboratory: Port Hueneme, CA, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, H. “Long prism” crystals observed in the precipitation in Antarctica. J. Meteor. Soc. Jpn. Ser II. 1963, 41, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.W.; Peters, G.P.; Gasser, T.; Andrew, R.M.; Schwingshackl, C.; Gütschow, J.; Houghton, R.A.; Friedlingstein, P.; Pongratz, J.; Le Quéré, C. National contributions to climate change due to historical emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide since 1850. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inman, M. Carbon is forever. Nat. Clim. Change 2008, 1, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Buehler, M.J. Carbon dioxide enhances fragility of ice crystals. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Prior, D.J.; Pooley, B.; Bowman, H.; Davidson, L.; Wallis, D.; Piazolo, S.; Qi, C.; Goldsby, D.L.; Hager, T.F. Grain growth of natural and synthetic ice at 0 °C. Cryosphere 2023, 17, 3443–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushbrain. Freezing Carbonated Sparkling Water vs. Distilled Water. Science Buddies. 31 January 2005. Available online: www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/ask-an-expert/viewtopic.php?t=392 (accessed on 18 February 2025).
- Zhu, Z.W.; Sun, D.W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.F.; Cheng, L.N. Effects of micro-nano bubbles on the nucleation and crystal growth of sucrose and maltodextrin solutions during ultrasound-assisted freezing process. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 92, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Liu, B. Effect of ultrasound on the nucleation temperature of water with varied air contents. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2019, 207, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.G.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Sun, J.; Gao, Z. Infusion of CO2 in a solid food: A novel method to enhance the low-frequency ultrasound effect on immersion freezing process. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 35, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Jia, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Mo, S. Supercooling of water controlled by nanoparticles and ultrasound. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.M.; Truong, T.; Prakash, S.; Bansal, N.; Bhandari, B. Impact of incorporation of CO2 on the melting, texture and sensory attributes of soft-serve ice cream. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 109, 104789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskoković, V. Revisiting the Fundamentals in the Design and Control of Nanoparticulate Colloids in the Frame of Soft Chemistry. Rev. J. Chem. 2013, 3, 271–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Palmer Station Antarctica LTER; Ducklow, H.; Karl, D. Dissolved Inorganic Carbon and Alkalinity of Discrete Water Column Samples, Collected Aboard PALMER LTER Annual Cruises of the Western Antarctic Peninsula, 1993–2019; ver 8; Environmental Data Initiative: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libbrecht, K. The Formation of Snow Crystals. Am. Sci. 2007, 95, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, V.A.; Kolbe, J.L.; Opperhauser, H. Effect of pH on the growth of Mg(OH)2 crystals in an aqueous environment at 60 °C. J. Cryst. Growth 1977, 41, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskoković, V.; Wu, L.; Habelitz, S. Biomimetic Precipitation of Uniaxially Grown Calcium Phosphate Crystals from Full-Length Human Amelogenin Sols. J. Bionic Eng. 2011, 8, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Uskoković, V.; Batarni, S.S.; Schweicher, J.; King, A.; Desai, T.A. Effect of Calcium Phosphate Particle Shape and Size on their Antibacterial and Osteogenic Activity in the Delivery of Antibiotics in vitro. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 2422–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, T.; Matijević, E. Formation of uniform spherical magnetite particles by crystallization from ferrous hydroxide gels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1980, 74, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-J.; Fang, W.-S.; Liu, Y.-M.; Li, F.-M.; Chen, P.; Chen, Y. Heterostructured Pd/PdO nanowires for selective and efficient CO2 electroreduction to CO. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 70, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, R. Climate Change: Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide. Climate.gov (9 April 2024). Available online: https://www.climate.gov/news-features/understanding-climate/climate-change-atmospheric-carbon-dioxide (accessed on 18 February 2025).
- Libbrecht, K.G. Morphogenesis on Ice: The Physics of Snow Crystals. Eng. Sci. 2001, 1, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Nakaya, U. Formation of snow-crystals in the mountains and in the laboratory in Japan (A sound film). Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1940, 21, 97–99. [Google Scholar]
- Libbrecht, K.G. Toward a Comprehensive Model of Snow Crystal Growth Dynamics: 1. Overarching Features and Physical Origins. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1211.5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Lv, L.; Zhong, H. Effect of CO2 on the heterogeneous condensation of water vapor on insoluble fine particles. Powder Technol. 2022, 408, 117728. [Google Scholar]
- Kurniawan, E.A.D.; Fatmawati; Miswanto. Modeling of global warming effect on the melting of polar ice caps with optimal control analysis. AIP Conf. Proc. 2021, 2329, 040006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskoković, E.; Uskoković, T.; Wu, V.M.; Uskoković, V. …And All the World a Dream: Memory Effects Outlining the Path to Explaining the Strange Temperature-Dependency of Crystallization of Water, a.k.a. the Mpemba Effect. Subst. Int. J. Hist. Chem. 2020, 4, 59–117. [Google Scholar]
- Gow, A.J.; Williamson, T. Rheological implications of the internal structure and crystal fabrics of the West Antarctic ice sheet as revealed by deep core drilling at Byrd Station. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1976, 87, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerner, R.M.; Fisher, D.A. Discontinuous Flow, Ice Texture, and Dirt Content in the Basal Layers of the Devon Island Ice Cap. J. Glaciol. 1979, 23, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cuffey, K.M.; Paterson, W.S.B. The Physics of Glaciers, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Thorsteinsson, T.; Kipfstuhl, J.; Eicken, H.; Johnsen, S.J.; Fuhrer, K. Crystal size variations in Eemian-age ice from the GRIP ice core, central Greenland. Earth Planet. Sc. Lett. 1995, 131, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, R.B.; Woods, G.A. Impurity influence on normal grain growth in the GISP2 ice core, Greenland. J. Glaciol. 1996, 42, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Durand, G.; Weiss, J.; Lipenkov, V.; Barnola, J.; Krinner, G.; Parrenin, F.; Delmonte, B.; Ritz, C.; Duval, P.; Röthlisberger, R. Effect of impurities on grain growth in cold ice sheets. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, F01015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, E.W.; Legrand, M.R.; Wagenbach, D. Coastal Antarctic aerosol and snowfall chemistry. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 10927–10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertler, N.A.N.; Mayewski, P.A.; Barrett, P.J.; Sneed, S.B.; Handley, M.J.; Kreutz, K.J. Monsoonal circulation of the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Ross Sea region: Signal from the snow chemistry. Ann. Glaciol. 2004, 39, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Solomon, S.; Keys, J.G. Seasonal variations in Antarctic NO x chemistry. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 7971–7978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertler, N.; Mayewski, P.; Aristarain, A.; Barrett, P.; Becagli, S.; Bernardo, R.; Bo, S.; Xiao, C.; Curran, M.; Qin, D.; et al. Snow chemistry across Antarctica. Ann. Glaciol. 2005, 41, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, S.H.; Kipfstuhl, S.; Azuma, N.; Freitag, J.; Weikusat, I.; Murshed, M.M.; Kuhs, W.F. The Multiscale Structure of Antarctica Part I: Inland Ice. In The Physics of Ice Core Records; Hondoh, T., Ed.; Yoshioka Publishing, Co., Ltd.: Kyoto, Japan, 2009; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Oshima, K.; Yamazaki, K. Seasonal variation of moisture transport in polar regions and the relation with annular modes. Polar Meteorol. Glaciol 2004, 18, 30–53. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, P.A.; Budd, W.F. Calculation of Antarctic surface ice mass accumulation through atmospheric parameters. In Proceedings of the APOC and AMOS Joint Conference, Lorne, Victoria, Australia, 20–22 February 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Budd, W.F.; Reid, P.A.; Minty, L.J. Antarctic moisture flux and net accumulation from global atmospheric analyses. Ann. Glaciol. 1995, 21, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Furukawa, Y. Snow and Ice Crystal Growth. In Handbook of Crystal Growth, 2nd ed.; Nishinaga, T., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1061–1112. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Riche, F.; Montagnat, M.; Scheebeli, M. Evolution of crystal orientation in snow during temperature gradient metamorphism. J. Glaciol. 2013, 59, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, P.; Ashby, M.F.; Anderman, I. Rate-controlling processes in the creep of polycrystalline ice. J. Phys. Chem. 1983, 87, 4066–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, R.; Sun, S.; Bian, L.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, T. A one-dimensional heat transfer model of the Antarctic Ice Sheet and modeling of snow temperatures at Dome A, the summit of Antarctic Plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuffey, K.M.; Steig, E.J. Isotopic diffusion in polar firn: Implications for interpretation of seasonal climate parameters in ice-core records, with emphasis on central Greenland. J. Glaciol. 1998, 44, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Frezzotti, M.; Gandolfi, S.; Urbini, S. Snow megadunes in Antarctica: Sedimentary structure and genesis. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massom, R.A.; Eicken, H.; Haas, C.; Jeffries, M.O.; Drinkwater, M.R.; Sturm, M.; Worby, A.P.; Wu, X.; Lytle, V.I.; Ushio, S.; et al. Snow on Antarctic sea ice. Rev. Geophys. 2001, 39, 413–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cheng, B.; Vihma, T.; Yang, Q.; Hui, F.; Zhao, B.; Hao, G.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. Observation and thermodynamic modeling of the influence of snow cover on landfast sea ice thickness in Prydz Bay, East Antarctica. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2019, 168, 102869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzacher, W. Pack-ice studies in the Arctic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 1959, 64, 2357–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Average Humidity in Vostok Station. Weather & Climate. 2025. Available online: https://weather-and-climate.com/average-monthly-Humidity-perc,Vostok+Station-AQ,antarctica (accessed on 18 February 2025).
- Anonymous. Climate and Monthly Weather Forecast McMurdo, Antarctica. Weather Atlas. 2025. Available online: https://www.weather-atlas.com/en/antarctica/mcmurdo-climate (accessed on 18 February 2025).
- Treverrow, A.; Warner, R.C.; Budd, W.F.; Craven, M. Meteoric and marine ice crystal orientation fabrics from the Amery Ice Shelf, East Antarctica. J. Glaciol. 2010, 56, 877–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, J. Ice Growth and Platelet Crystals in Antarctica. Ph.D. Thesis, Victoria University of Wellington, Wellington, New Zealand, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Leppäranta, M. A review of analytical models of sea-ice growth. Atmos.-Ocean 1993, 31, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norikazu, M.; Ebinuma, T. Pressure sintering of ice and its implication to the densification of snow at polar glaciers and ice sheets. J. Phys. Chem. 1983, 87, 4103–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knepp, T.N.; Renkens, T.L.; Shepson, P.B. Gas phase acetic acid and its qualitative effects on snow crystal morphology and the quasi-liquid layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 7679–7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obbard, R.; Baker, I. The microstructure of meteoric ice from Vostok, Antarctica. J. Glaciol. 2007, 53, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraiwa, T.; Shoji, H.; Saito, T.; Yokoyama, K.; Watanabe, O. Structure and dielectric properties of surface snow along the traverse route from coast to Dome Fuji station, Queen Maud Land, Victoria. Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar Meteorol. Glaciol. 1996, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Erbe, E.F.; Rango, A.; Foster, J.; Josberger, E.G.; Pooley, C.; Wergin, W.P. Collecting, shipping, storing, and imaging snow crystals and ice grains with low-temperature scanning electron microscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 62, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvaney, R.; Wolff, E.; Oates, K. Sulphuric acid at grain boundaries in Antarctic ice. Nature 1988, 331, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; van Donkelaar, A.; Hammer, M.S.; McDuffie, E.E.; Burnett, R.T.; Spadaro, J.V.; Chatterjee, D.; Cohen, A.J.; Apte, J.S.; Southerland, V.A.; et al. Reversal of trends in global fine particulate matter air pollution. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoll, N.; Bohleber, P.; Dallmayr, R.; Wilhelms, F.; Barbante, C.; Weikusat, I. The new frontier of microstructural impurity research in polar ice. Ann. Glaciol. 2023, 64, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, N.; Eichler, J.; Hörhold, M.; Shigeyama, W.; Weikusat, I. A Review of the Microstructural Location of Impurities in Polar Ice and Their Impacts on Deformation. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 8, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
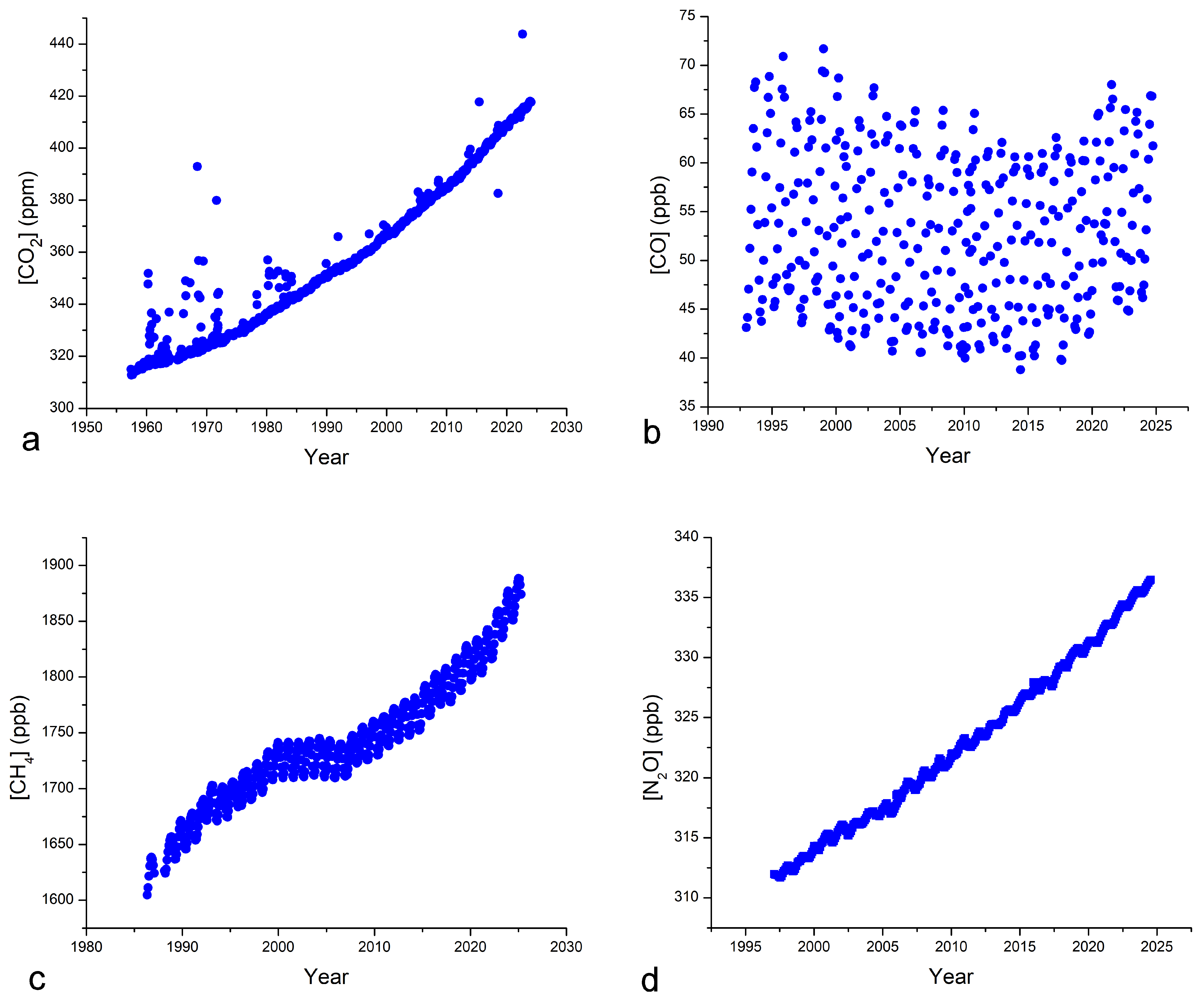
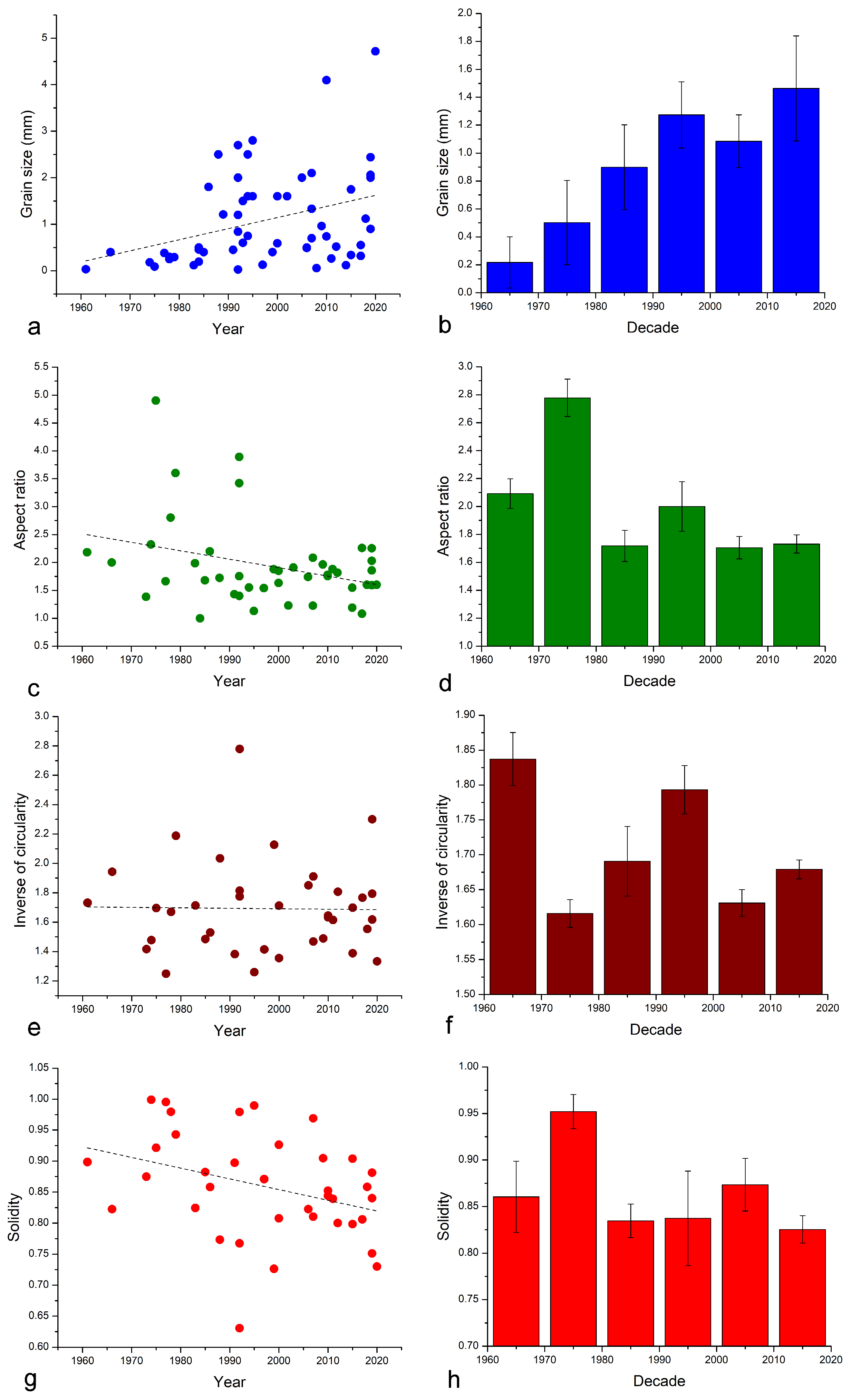
| Year of Sampling | Authors [Ref.] | Location | Coordinates | Altitude (masl) | Depth (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Lu et al. [30] | Dålk Glacier, East Antarctica | 69°24′0′′ S 76°20′0′′ E | 139–161 | 0.035 |
| 2019 | MacDonell et al. [31] | Müller Ice Shelf | 67°14′0′′ S 66°52′0′′ W | 19 | 0.6 |
| 2019 | Skatulla et al. [32] | Good Hope Line Transect | 58°8′16′′ S 0°0′16′′ W | 0 | 0.05 |
| 2019 | Wang et al. [33] | Prydz Bay | 69°12′0′′ S 76°18′0′′ E | 0 | 0.15 |
| 2019 | Johnson et al. [34] | Southern Ocean | 50°0′0′′ S 0°0′0′′ W–90°0′0′′ S 360°0′0′′ W | 0 | 0.55 |
| 2018 | Thomas et al. [35] | Priestley Glacier, Terra Nova Bay | 74°20′0′′ S 163°22′0′′ E | 80–2200 | 2.4 |
| 2017 | Inoue et al. [36] | Dome Fuji, Queen Maud Land | 77°47′17′′ S 39°3′14′′ E | 3764 | 0.1 |
| 2015 | Moser et al. [37] | Kohnen Station, Dronning Maud Land | 75°0′0′′ S 0°4′0′′ E | 2892 | 0.1 |
| 2015 | Bolshunov et al. [38] | Vostok Station Area | 78°27′50′′ S 106°50′ E | 3488 | 0.5 |
| 2014 | Carlsen et al. [39] | Kohnen Station | 75°0′0′′ S 0°4′0′′ E | 2892 | 0 |
| 2012 | Calonne et al. [40] | Point Barnola, Central East Antarctica | 75°42′0′′ S 123°15′0′′ E | 3236 | 0.2 |
| 2012 | Proksch et al. [41] | Kohnen Station | 75°0′0′′ S 0°7′0′′ E | 2892 | 0.015 |
| 2011 | Dadic et al. [42] | Allan Hills | 76°40′12′′ S 159°13′48′′ E | 1600–2100 | 0.2 |
| 2010 | Pirazzini et al. [43] | Aboa Station, Dronning Maud Land | 73°3′0′′ S 13°25′0′′ W | 200 | 0.2 |
| 2010 | Lebedev et al. [44] | Alasheev Gulf | 67°30′0′′ S 46°0′0′′ E | 0 | 0.25 |
| 2009 | Mahoney et al. [45] | McMurdo Sound | 77°39′30′′ S 165°0′0′′ E | 10 | 0.05 |
| 2009 | Gallet et al. [46] | Dome C | 75°6′0′′ S 123°21′0′′ E | 3233 | 0.01 |
| 2008 | Gallet et al. [47] | Dome C | 75°6′0′′ S 123°21′0′′ E | 3233 | 0.02 |
| 2007 | Fujita et al. [48] | Dome Fuji | 77°19′0′′ S 39°40′0′′ E | 3800 | 0–12.4 |
| 2007 | Dempsey et al. [49] | McMurdo Sound | 77°39′30′′ S 165°0′0′′ E | 10 | 0.55 |
| 2007 | Saruya et al. [50] | Dome Fuji | 77°19′0′′ S 39°42′0′′ E | 3800 | 0.5 |
| 2006 | Freitag et al. [51] | Kohnen Station | 75°0′0′′ S 0°8′0′′ E | 2892 | 1 |
| 2006 | Brucker et al. [52] | Dome C | 75°6′0′′ S 123°21′0′′ E | 3240 | 0.1 |
| 2005 | Alencar et al. [53] | Joinville Island | 63°15′18” S 55°38′21” W | 565 & 454 | 0.02 |
| 2003 | Tang et al. [54] | Nella Fjord | 69°22′0′′ S 76°20′0′′ E | 0.1 | |
| 2002 | Kärkäs et al. [55] | Riiser-Larsen ice shelf, Dronning Maud Land | 72°32′0′′ S 16°34′0′′ W–74°59′54′′ S 10°0′30′′ W | 30–2550 | 1.5 |
| 2000 | Rasmus et al. [56] | Amundsenisen, Högisen and Kvitkuven | 72°32′0′′ S 16°34′0′′ W–74°59′54′′ S 10°0′30′′ W | 40–2550 | 1.5 |
| 2000 | Gow et al. [57] | Byrd Station Area | 80°0′0′′ S 120°0′0′′ W | 935–1843 | 1–5 |
| 1999 | Albert et al. [58] | Siple Dome | 81°39′0′′ S 148°48′36′′ W | 730 | 0.1 |
| 1997 | Gay et al. [59] | Terra Nova Bay, Dumont d’Urville and Talos Dome | 68°36′0′′ S 137°43′12′′ E–75°9′36′′ S 123°13′48′′ E | 600–3470 | 0.08 |
| 1995 | Haas et al. [60] | Bellingshausen, Amundsen & Weddell Seas | 68°0′0′′ S 20°0′0′′ W–78°0′0′′ S 125°0′0′′ W | 0 | 0.05 |
| 1995 | Massom et al. [61] | Indian & Western Pacific Oceans | 60°0′0′′ S 138°0′0′′ E–90°0′0′′ 142°0′0′′ E | 0 | 0 |
| 1994 | Cagnati [62] | Terra Nova Bay Region | 74°42′ S 164°8′ E | 0–2960 | 0.05 |
| 1994 | Haas et al. [63] | Weddell Sea | 70°0′0′′ S 60°0′0′′ W–78°0′0′′ S 20°0′0′′ W | 0 | 0 |
| 1994 | Sturm et al. [64] | Bellingshausen, Amundsen & Ross Seas | 68°0′0′′ S 109°0′0′′ W–78°0′0′′ S 171°0′0′′ W | 0 | 0 |
| 1993 | Watanabe et al. [65] | Dome Fiji | 77°19′0′′ S 39°40′0′′ E | 3810 | 0.8 |
| 1993 | Worby & Massom [66] | Indian & Western Pacific Oceans | 60°0′0′′ S 139°0′0′′—90°0′0′′ S 141°0′0′′ E & 60°0′0′′ S 144°0′0′′—90°0′0′′ S 150°0′0′′ E & | 0 | 0 |
| 1992 | Massom et al. [67] | Weddell Sea | 70°0′0′′ S 60°0′0′′ W–78°0′0′′ S 20°0′0′′ W | 0 | 0 |
| 1992 | Jeffries et al. [68] | Ross Sea, Amundsen Sea and Bellingshausen Sea | 68°0′0′′ S 57°0′0′′ W–78°0′0′′ S 160°0′0′′ W | 0 | 0.19 |
| 1992 | Walden et al. [69] | Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station | 90°0′0′′ S 45°0′0′′ E | 2804 | 0 |
| 1992 | Veazey et al. [70] | McMurdo Sound and Pine Island Bay | 77°52′35′′ S 166°45′47′′ E & 74°38′45′′ S 102°17′46′′ W | ≤10 | 0.18 and 0.27 |
| 1992 | Iwai [71] | Syowa Station | 69°00′15″ S 39°34′55″ E | 18 | 0 |
| 1991 | Jeffries & Weeks [72] | Ross Sea (Balleny Islands to Terra Nova Bay) | 71°17′0′′ S 170°14′0′′ E | 0 | 0.027 |
| 1989 | Konishi et al. [73] | Syowa Station | 69°00′15″ S 39°34′55′′ E | 18 | 0 |
| 1988 | Hatanaka et al. [74] | Syowa Station | 69°00′15′′ S 39°34′55′′ E | ||
| 1986 | Tison et al. [75] | Breid Bay | 70°13′0′′ S 23′47′0′′ E | 0 | 0.28 |
| 1985 | Alley & Bentley [76] | Siple Coast | 83°28′4′′ S 138°5′49” W | 335 | 0.1 |
| 1984 | Nishimura & Maeno [29] | Mizuho Plateau, East Antarctica | 71°30′0′′ S 39°0′0′′ E | 2230 | 0.5 |
| 1984 | Dahe et al. [77] | Law Dome & Casey Station, Wilkes Land | 66°16′5′′ S 110°31′3′′ E | 359 | 0.1 |
| 1984 | Urabe & Inoue [78] | Ongul Strait, Lutzow-Holm Bay | 69°1′0′′ S 39°35′0′′ E | 0 | 0.15 |
| 1983 | Lange [79] | Weddell Sea | 70°0′0′′ S 172°0′0′′ E–78°0′0′′ S 60°0′0′′ W | 0 | 0.4 |
| 1979 | Wada & Gonda [80] | Mizuho Station, East Antarctica | 70°41′57″ S 44°16′45″ E | 2230 | 0 |
| 1978 | Duval & Lorius [81] | Dome C | 74°39′0′′ S 124°10′0′′ E | 3240 | 0* |
| 1978 | Ohtake [82] | Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station | 90°0′0′′ S 45°0′0′′ E | 2804 | 0 |
| 1977 | Iwai [83] | Syowa Station | 69°00′15″ S 39°34′55′′ E | 18 | 0 |
| 1975 | Kikuchi & Hogan [84] | Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station | 90°0′0′′ S 45°0′0′′ E | 2804 | 0 |
| 1974 | Hogan [85] | Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station | 90°0′0′′ S 45°0′0′′ E | 2804 | 0.003 |
| 1966 | Paige [86] | Hut Point Peninsula, McMurdo Sound | 77°47′0′′ S 166°51′0′′ E | 143 | 0.50 |
| 1961 | Shimizu [87] | Byrd Station | 80°0′0′′ S 120°0′0′′ W | 1553 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uskoković, V. Microstructural Evolution of Antarctic Ice with the Rising Atmospheric CO2: A Longitudinal Meta-Analysis. Quaternary 2025, 8, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat8040057
Uskoković V. Microstructural Evolution of Antarctic Ice with the Rising Atmospheric CO2: A Longitudinal Meta-Analysis. Quaternary. 2025; 8(4):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat8040057
Chicago/Turabian StyleUskoković, Vuk. 2025. "Microstructural Evolution of Antarctic Ice with the Rising Atmospheric CO2: A Longitudinal Meta-Analysis" Quaternary 8, no. 4: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat8040057
APA StyleUskoković, V. (2025). Microstructural Evolution of Antarctic Ice with the Rising Atmospheric CO2: A Longitudinal Meta-Analysis. Quaternary, 8(4), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/quat8040057





