Abstract
Introduction and Objectives: Multimorbidity, defined as the coexistence of two or more chronic conditions, poses significant challenges in healthcare by affecting patient outcomes and increasing costs. This study aimed to evaluate multimorbidity’s impact on patients with genitourinary cancer (GUC) in Chile, focusing on prevalent comorbidities, their combinations, and their association with hospitalization severity. Materials and Methods: A retrospective, population-based study was conducted using data from the Fondo Nacional de Salud (FONASA) in Chile, including patients with bladder, prostate, kidney, and testicular cancer between 2019 and 2021. Diagnosis-related group (DRG) data were used to analyze comorbidity prevalence, hospitalization type (elective vs. emergency), severity (moderate/major vs. minor/none), length of stay, and associated costs. Results: Among 4,028,597 hospital events, 11.6% were related to GUC, involving 18,792 patients. Multimorbidity was present in 67.3% of patients, with hypertension and diabetes being the most common comorbidities. These patients accounted for 69.1% of total GUC care costs. Hospital mortality was higher in multimorbid patients (7.5% vs. 3.7%; p < 0.001), who also had longer stays (mean 8 vs. 5 days). Most patients were admitted electively (60.3%), while 39.7% were admitted through the emergency room. Patients with multimorbidity had higher rates of moderate/major severity hospitalizations compared to those without (56.1% vs. 32.5%; p < 0.001). Conclusions: In Chile, multimorbidity among GUC patients is linked to increased costs, longer hospital stays, higher mortality, and greater hospitalization severity. Comprehensive care strategies are needed to improve outcomes and reduce healthcare system burdens.
1. Introduction
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines multimorbidity as “the presence of two or more health conditions” [1]. Multimorbidity is distinct from the related concept of comorbidity, which refers to the combined effects of additional conditions in relation to the index condition in an individual. In contrast, care for multimorbidity is patient-centered, and does not routinely give priority to any single condition, although in clinical care, patients and clinicians will usually focus on the most pressing problems that the patient is experiencing.
Compared to people with a single chronic condition, people with multimorbidity are more likely to die prematurely, be admitted to hospital, and have an increased length of stay.
This phenomenon presents a growing global challenge, with substantial effects on individuals, families, healthcare systems, and society. In socioeconomically disadvantaged communities, multimorbidity occurs a decade earlier, and is associated with premature death, poorer function and quality of life, depression, polypharmacy, and increased demand for medical care [2]. It is estimated that caring for patients with multimorbidity accounts for 78% of healthcare expenditures in the US [3]. A study of Medicare beneficiaries revealed that 64% of individuals had two or more health conditions, and 24% had four or more health conditions [4]. Regarding its impact on cancer, multimorbidity delays diagnosis, reduces the likelihood of implementing curative treatment, results in a higher rate of complications, and decreases quality of life and survival [5].
Genitourinary cancer (GUC), which includes prostate, kidney, bladder, and testicular neoplasms, is common, with detection increasing with age [6]. By 2020, prostate cancer was the second most common cancer worldwide (307 per 100,000), and bladder cancer was the thirteenth most common (56 per 100,000) [7]. In Chile, prostate cancer is the most frequent malignant neoplasm in men (23.9%). Kidney cancer ranked seventh, while testicular cancer was the sixth most diagnosed cancer in men [8]. Additionally, GUC carries a high financial burden. For example, the global cost of bladder cancer in the US was $5 billion in 2020 [9]. Thus, it is crucial to understand the extent of multimorbidity in GUC and its clinical and financial impacts.
The objective of this study is to characterize multimorbidity and determine the most clinically and financially impactful combinations of comorbidities in patients with GUC in Chile.
2. Material and Methods
This was a descriptive, retrospective, population-based study of patients with GUC, evaluating comorbidities and their respective costs for the National Health Fund (FONASA) in Chile. The Chilean healthcare system is structured by two main sectors: a public sector, managed by the National Health Fund (Fondo Nacional de Salud, FONASA), and a private sector, represented by private health insurance institutions (Instituciones de Salud Previsional, ISAPREs).
FONASA is a public agency that manages state health funds for its beneficiary population, which represents 79.6% of the population (87.8% in individuals > 65 years) [10,11]. FONASA is funded primarily through employer contributions and government subsidies, and focuses on delivering healthcare to individuals with lower incomes and greater healthcare needs.
The diagnosis-related group (DRG) databases include all hospital events in the country’s 68 public health centers of medium and high complexity. This information includes the data using which FONASA estimates the cost and payment mechanism for each hospital event for the public health system’s population. The DRG-based payment mechanism accounts for 70% of FONASA’s total expenditure [10,11].
Official FONASA DRG databases for the years 2019–2021, encompassing 4,028,597 hospitalization events, were used. The DRG databases include hospitalizations of the population exclusively belonging to the public health system. All patients with bladder cancer (BC) (ICD-10 C67), prostate cancer (PC) (ICD-10 C61), testicular cancer (TC) (ICD-10 C62), and kidney cancer (KC) (ICD-10 C64) were included, corresponding to 25,358 individuals with GUC. The most prevalent comorbidities were analyzed. The cost associated with FONASA was calculated by multiplying the base price of each hospital by the DRG weight for each hospitalization [10,11]. The variable “type of admission” was used to define records corresponding to emergency or elective admissions. The variable “Severity” was used to determine the severity of the hospitalization event, and was determined by how deviate from the normal the course of the disease was, measured by the amount of resource use in that event in comparison with others with the same characteristics [10,11]. The information used corresponded to official secondary data sources. Individuals’ identities were encrypted with a code (ID), thus not violating the requirements outlined by Law 19.628 for the protection of private life and the use of sensitive data in Chile.
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS v29.0.0. Continuous variables were analyzed using Mann–Whitney U tests due to their non-normal distribution, as verified by the Shapiro–Wilk test. Categorical variables were analyzed using Chi-square tests. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
Of the total hospital events (n = 4,028,597), 5% were related to cancer (n = 218,209), of which 11.6% were related to GUC (n = 25,358), representing a total of 18,792 patients. Multimorbidity was present in 67.3% of patients (two or more comorbidities) (Figure 1).
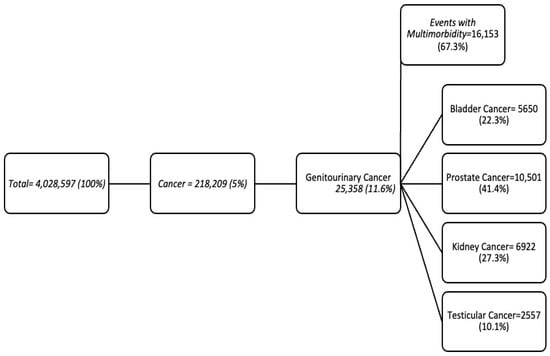
Figure 1.
Official FONASA diagnosis-related group (DRG) databases for the years 2019–2021, encompassing 4,028,597 hospitalization events and filtered by CIE-10 diagnosis.
A significant proportion of patients (72.5%) were within working age. In terms of gender, all the tumor types predominantly occurred in males, with the proportion of male occurrence reaching 73.9% for bladder cancer and 63.6% for kidney cancer. The sociodemographic variables are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Sociodemographic variables.
The total cost of GUC was $67,513,129 USD. Patients with multimorbidity accounted for 69.1% of the total cost. The cost descriptions, in USD, are detailed in Table 2. The most frequent comorbidities were hypertension (HTN) (43.9%) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2) (19%). The most prevalent combined comorbidities were hypertension with diabetes mellitus (13.4%) and hypertension with chronic kidney disease (CKD) (6.9%). The comorbidities by type of GUC and their distribution are listed in Table 3.

Table 2.
Cost by type of genitourinary cancer and comparation by multimorbidity.

Table 3.
List of comorbidities with genitourinary cancer and their frequencies.
Most patients were admitted electively (60.3%), while 39.7% were admitted through the emergency room (ER). The differences between the main comorbidities are detailed in Table 4. The prevalence of comorbidities by admission type is detailed in Figure 2.

Table 4.
Comorbidity frequency by type of admission in all events.
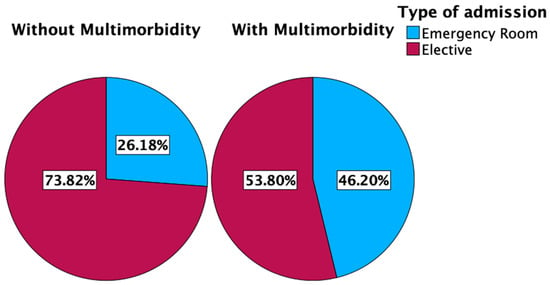
Figure 2.
Differences in type of admission in patients with multimorbidity and without multimorbidity. The admission of patients with multimorbidity had 20% more.
Patients with multimorbidity had a 56.1% rate of moderate/major severity hospitalizations, while those without multimorbidity had a 32.5% rate, with an in-hospital mortality rate of 7.5% for the former and 3.7% for the latter (p < 0.001). Additionally, only 5% of patients with multimorbidity had a hospitalization without severity. The severity details are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Severity * of hospitalization event, according to multimorbidity.
Finally, the mean length of stay was 5 days for patients without multimorbidity (DS = 7), with a total of 26,752 bed-days, while it was significantly higher for those with multimorbidity (mean = 8 days; DS = 12; bed-day = 89,960; p < 0.001).
4. Discussion
This study represents the first attempt to graphically depict the impact of multimorbidity on hospitalizations for genitourinary cancer (GUC). Our results indicate that patients with multimorbidity have significantly higher rates of hospital mortality (7.5% vs. 3.7%; p < 0.001), a greater proportion of emergency admissions (46.2% vs. 26.2%; p < 0.001), and longer hospital stays (8 vs. 5 days). These findings underline the substantial impact of multimorbidity on the management and outcomes of GUC, a trend that has been increasingly recognized in global oncology practice [4,5].
Our descriptive, population-based study is grounded in the analysis of the FONASA DRG database, which aggregates information from 70% of hospital discharges in Chile [10,11]. This extensive dataset allows for a comprehensive examination of the healthcare burden associated with GUC and multimorbidity within the Chilean public health system, revealing demographic patterns that are consistent with the WHO Global Cancer Observatory records [12], such as a higher prevalence of GUC among males and individuals aged 65 to 81 years [7].
Our series revealed a higher comorbidity rate in prostate cancer patients compared to the literature. A recent retrospective study in the US analyzed the relationship of comorbidity with prostate cancer, concluding that 51% had at least one associated disease, with hypertension being the most prevalent (42%), followed by hypercholesterolemia (24%) and diabetes mellitus (12%) [5]. Our findings suggest that the burden of comorbidities in Chilean patients may be higher, potentially influenced by health access, lifestyle factors, and socioeconomic conditions.
The impact of comorbidities on early detection and treatment is particularly profound in prostate cancer, where older age correlates with a higher likelihood of comorbid conditions [4]. Previous data emphasize that comorbidities can delay diagnosis and reduce the likelihood of receiving curative treatment, especially in resource-limited settings [5,13,14,15]. The lower influence of comorbidities on treatment decisions in high-volume centers further emphasizes the role of healthcare infrastructure in managing these complex cases [16].
A high prevalence of multimorbidity is associated with lower quality of life and lower socioeconomic status [17], making it important to recognize patients that are at risk for multimorbidity, in order to implement interventions that can improve clinical outcomes. In our series, 67.3% of patients had multimorbidity, leading to poorer clinical outcomes. Prevention and identification programs focusing on multimorbidity could be key to enhancing GUC treatment outcomes in Chile, where healthcare resources are often constrained. Future research should continue to explore the intricate relationships between multimorbidity, cancer outcomes, and healthcare costs, with an emphasis on developing cost-effective, integrated care models that are tailored to different healthcare settings [9].
Several factors must be considered when interpreting the results. The analysis is based on data from the FONASA DRG database, which is comprehensive, yet limited to the public healthcare system. As such, the findings might not be fully generalizable to patients receiving care in the private system, where different resources and demographics may influence outcomes. Nonetheless, since FONASA covers a significant portion of the population, particularly among the elderly and socioeconomically disadvantaged, this study provides an important perspective on public health challenges in Chile. The descriptive and retrospective nature of the study, which relies on existing administrative data, presents additional considerations. While this approach allows for the inclusion of a large, representative sample, it also introduces potential limitations in the accuracy and completeness of comorbidity records. Misclassification or under-reporting of conditions may affect the observed associations between multimorbidity and hospital outcomes. Moreover, the focus on hospitalizations may omit crucial aspects of patient care management in outpatient settings, where many chronic conditions are treated. This focus could result in an underestimation of the true burden of multimorbidity on the healthcare system, as the study does not capture the full continuum of care required by these patients.
When analyzing healthcare costs, it is essential to acknowledge the significant differences between countries, driven by variations in healthcare system structures, funding mechanisms, and cost drivers. For example, factors such as labor costs, pharmaceutical pricing, and the organization of hospital services vary widely, and can influence the interpretation and generalizability of cost analyses across settings [18].
Finally, while this study identifies significant associations between multimorbidity and adverse in-hospital outcomes, it does not explore the causal mechanisms underlying these relationships.
5. Conclusions
Multimorbidity in genitourinary cancer has a high prevalence, and is associated with increased length of stay, costs, and mortality. This highlights the need for additional efforts to identify and manage this phenomenon.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: I.E., M.I.F. and I.D.; Methodology: I.E. and M.I.F.; Writing—original draft preparation: I.E., C.C., D.J. and I.R.; Writing—review & editing: I.E. and M.I.F.; Investigation: C.C. and D.J.; Data curation: I.D., I.E. and C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was conducted without specific funding from public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. All resources utilized in this research were provided by the authors and their affiliated institutions as part of their regular activities.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study did not require ethical approval.
Informed Consent Statement
This study did not require ethical consent.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset used in this study is publicly available and can be accessed through the following link: FONASA Open Data-GRD Database (https://www.fonasa.cl/sites/fonasa/datos-abiertos/bases-grd). The data is provided by FONASA under an open data policy, ensuring accessibility for research purposes.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gauld, R.; Blank, R.; Burgers, J.; Cohen, A.B.; Dobrow, M.; Ikegami, N.; Kwon, S.; Luxford, K.; Millett, C.; Wendt, C. The World Health Report 2008-Primary Healthcare: How Wide Is the Gap between Its Agenda and Implementation in 12 High-Income Health Systems? Healthc. Policy 2012, 7, 38–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skou, S.T.; Mair, F.S.; Fortin, M.; Guthrie, B.; Nunes, B.P.; Miranda, J.J.; Boyd, C.M.; Pati, S.; Mtenga, S.; Smith, S.M. Multimorbidity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2022, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogeli, C.; Shields, A.E.; Lee, T.A.; Gibson, T.B.; Marder, W.D.; Weiss, K.B.; Blumenthal, D. Multiple Chronic Conditions: Prevalence, Health Consequences, and Implications for Quality, Care Management, and Costs. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2007, 22, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, C.S.; Kvale, E.; Fisch, M.J. Multimorbidity: An Issue of Growing Importance for Oncologists. J. Oncol. Pract. 2011, 7, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarfati, D.; Koczwara, B.; Jackson, C. The Impact of Comorbidity on Cancer and Its Treatment. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, D.; Skinner, E. Genitourinary Cancer in the Elderly. Semin. Oncol. 2004, 31, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer Statistics for the Year 2020: An Overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra-Soto, S.; Petermann-Rocha, F.; Martínez-Sanguinetti, M.A.; Leiva-Ordeñez, A.M.; Troncoso-Pantoja, C.; Ulloa, N.; Diaz-Martínez, X.; Celis-Morales, C.; Parra-Soto, S.; Petermann-Rocha, F.; et al. Cáncer En Chile y En El Mundo: Una Mirada Actual y Su Futuro Escenario Epidemiológico. Rev. Med. Chil. 2020, 148, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, C.; Dinh, T.; Lee, J. The Health Economics of Bladder Cancer: An Updated Review of the Published Literature. Pharmacoeconomics 2014, 32, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FONASA. FONASA NOTA METODOLÓGICA Indicadores Panel FONASA; FONASA: Santiago, Chile, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- FONASA. FONASA Base de Datos GRD FONASA; FONASA: Santiago, Chile, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppie, T.M.; Serio, A.M.; Vickers, A.J.; Vora, K.; Dalbagni, G.; Donat, S.M.; Herr, H.W.; Bochner, B.H. Age-Adjusted Charlson Comorbidity Score Is Associated with Treatment Decisions and Clinical Outcomes for Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy for Bladder Cancer. Cancer 2008, 112, 2384–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.; Cheung, W.Y.; Atkinson, E.; Krzyzanowska, M.K. Impact of Comorbidity on Chemotherapy Use and Outcomes in Solid Tumors: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Tan, F.; Goovaerts, P.; Adunlin, G.; Ali, A.A.; Gwede, C.K.; Huang, Y. Impact of Comorbidities on Prostate Cancer Stage at Diagnosis in Florida. Am. J. Mens. Health 2016, 10, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, P.N.; Kil, P.J.M.; Hendrikx, A.J.M.; Janssen-Heijnen, M.L.G.; Crommelin, M.A.; Coebergh, J.W.W. Comorbidity in Patients with Prostate Cancer and Its Relevance to Treatment Choice. BJU Int. 1999, 84, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.A.; Gopal, D.P.; Chelala, C.; Zm, A.; Ullah, D.; Taylor, S.J. Review Article Multimorbidity in People Living with and beyond Cancer: A Scoping Review. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 13, 4346–4365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kurnot, J.A.; Kaye, D.R. Reducing Financial Toxicity in Bladder Cancer Care. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2024, 34, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Société Internationale d’Urologie. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).