Abstract
Surgery with either partial or radical nephrectomy remains the standard of care for localized primary renal cell carcinoma (RCC). However, most RCCs are detected in an older age group, and some may have multiple comorbidities that preclude surgery. Thermal ablation (TA) with radiofrequency ablation (RFA), cryoablation (CA), or microwave ablation (MWA) is considered an alternative to extirpative surgical procedures for select patients with small renal tumors. There is more than 90% post-ablation local control in carefully selected patients with reported complication rates of less than 10%. Most thermal ablation require only a single procedure. More recently, stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy (SABR) has emerged as an attractive noninvasive treatment modality for elderly patients with comorbidities and localized RCC. It has shown more than 90% local control rates for both small and relatively larger tumors (> 4 cm). Modest post-SABR renal function decline has been observed. Despite most patients presenting with mild or moderate chronic kidney disease there is less than a 5% chance of progression to end-stage renal disease. This article aims to summarize the key evidence and ablative treatment’s optimal patient selection, efficacy, and toxicity.
Introduction
Surgery is the standard of care for primary localized renal cell carcinoma (RCC); however, many patients in this population have comorbidities that render them at high risk for complications from both anesthesia and surgery. Moreover, partial (PN) or radical nephrectomy (RN) is associated with a potential risk for long-term impairment of renal function and chronic kidney disease (CKD)[1,2,3]. In patients where surgery is contraindicated, active surveillance (AS) is commonly used, particularly in patients with multiple comorbidities, tumor size of less than 2 cm, and tumor growth kinetics of less than 5 mm/year[4].
For patients with small renal masses (SRMs) who are not considered good candidates for surgery or have declined surgery and are not candidate for AS, thermal ablation (TA) has been endorsed by multiple international guidelines as a safe and effective alternative[5,6]. More recently, stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR), a form of hypofractionated radiation, has emerged as an alternative noninvasive treatment option for patients who are not suitable for surgery. The European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) guidelines have endorsed SABR as a treatment option for patients considered unsuitable or who have declined other treatment options[6]. The 2022 National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) version 1.0 Kidney Cancer guidelines state, “SABR may be considered for medically inoperable patients with stage I kidney cancer (category 2B) [and patients] with stage II/III kidney cancer (category 3)”[7].
The aim of this article is to review the role of ablative therapies (TA/SABR) for localized primary kidney cancer. It will also report and summarize each modality’s optimal patient selection, efficacy, and toxicity.
Thermal Ablation
TA refers to the local application of thermal energy to a tumor[8]. When TA is applied to a renal tumor, the thermal energy is delivered directly into the tumor via an antenna or probe inserted through an imageguided percutaneous approach or surgically via an open or laparoscopic approach. Renal tumors can be ablated via application of extreme heat (radiofrequency [RFA], microwave [MWA]) or cooling ablation (CA); the advantages and disadvantages of each system are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Advantages and disadvantages between ablative technologies.
Small (T1) localized renal tumors are well suited for ablation because of their rounded shape and relative isolation from temperature-sensitive structures in the retroperitoneum[9]. Given the in situ nature of the treatment, evaluation of treatment efficacy relies on continued surveillance via computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Indications and Patient Selection
Historically, TA has been reserved for patients who are considered poor surgical candidates due to renal insufficiency or a high burden of comorbid conditions. International guidelines now support consideration of TA in treating patients with a renal tumor of < 3 cm as a primary treatment[10,11,12]. TA is also considered an effective treatment for patients with a solitary kidney, renal insufficiency, multiple tumors, or hereditary tumors.
Ablation is the treatment of choice in patients with compromised renal function where dialysis and/or nephrectomy are not desired[10,12]. Percutaneous TA has the advantage of avoiding the temporary vascular clamping, which is required during PN[13,14]. Also, the sphere-shaped ablation zone can be adjusted to minimize unnecessary damage to the normal renal parenchyma.
An appropriate patient selection for TA can generate oncologic outcomes comparable to those of nephron-sparing surgery, with the added benefit of better preservation of renal function[15,16,17,18].
Technical Considerations
The effect of ablative therapies varies across tumors. Tumor size is one of the most important factors; RFA and MWA have excellent outcomes for masses of < 3 cm. Masses measuring 3 to 4 cm or larger may need repeated treatment or multiple probes[19,20,21,22]. Microwave ablation should theoretically be able to treat larger tumors efficiently given the physics behind the larger active heating zone. Although T1b tumors have been treated with secondary efficacy rates of up to 95%, current reports are limited by small samples (the largest series included 56 patients)[23,24,25]. High-output centers have reported good tumor control with single-session treatment for larger tumors using CA[26,27]. However, the upper size limit at which complete ablation can be expected remains to be defined. Moreover, larger tumors also have an increased risk for hemorrhage with TA modalities.
Centrally located tumors are at increased risk for treatment failure as proximity to the larger hilar vessels washes out the extreme temperature gradients generated during ablation procedures, which is necessary for cell death[19,28]. CA appears to provide better oncologic outcomes for centrally located tumors than RFA[29,30]. RFA for central tumors is associated with low rate of complications but with severe sequelae, such as ureteropelvic junction obstruction, urinoma, and proximal ureteral stricture[31,32]. The early reports of CA appear to show that CA safe, with fewer complications than those reported with RFA[30,33].
The insulative properties of the surrounding retroperitoneal fat and the greater distance to large hilar vessels render exophytic tumors easier to ablate in a single session[19,20]. Endophytic tumors are surrounded by renal parenchyma, through which temperature gradients may dissipate more rapidly, resulting in increased risk for treatment failure[34,35].
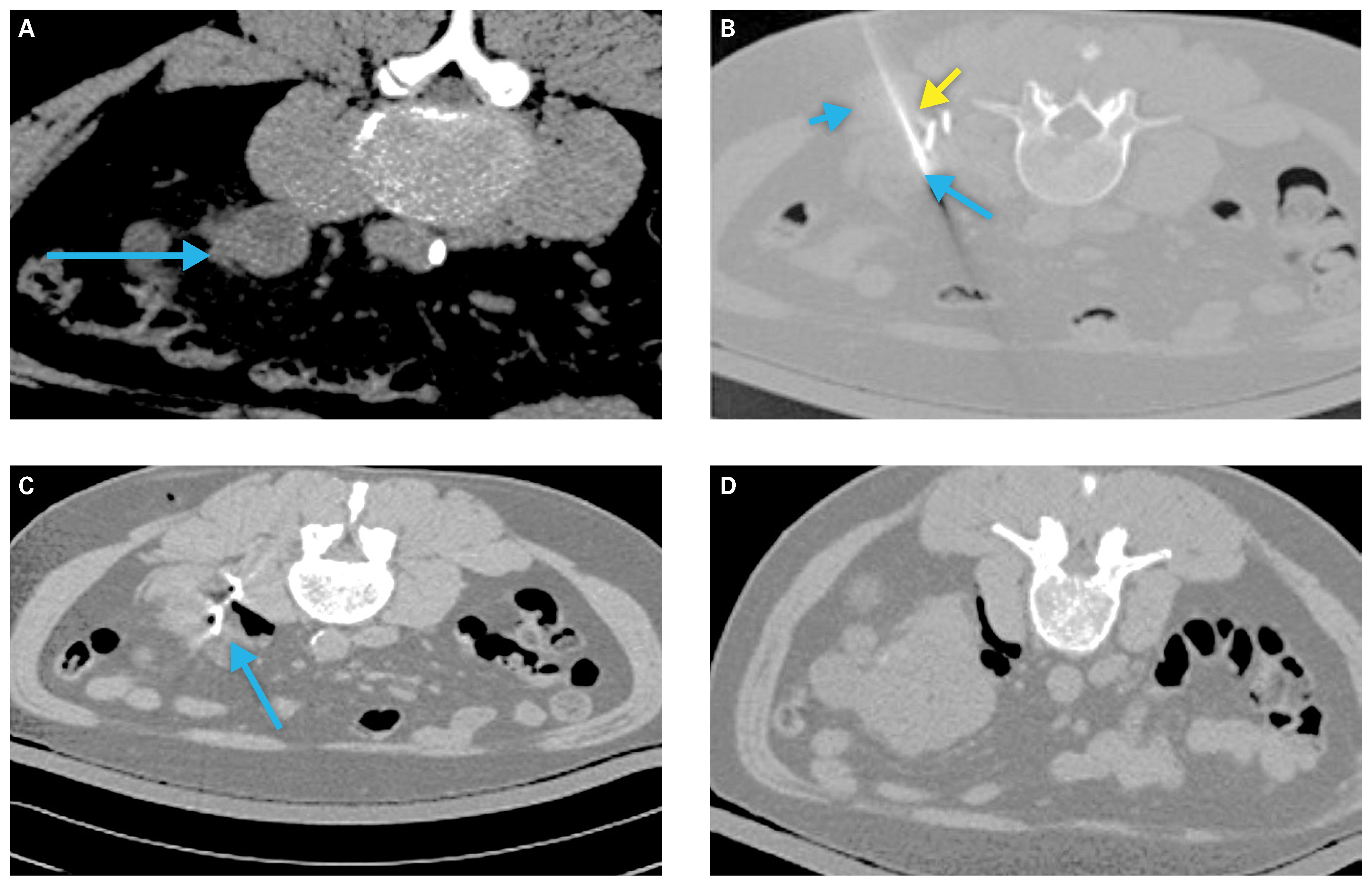
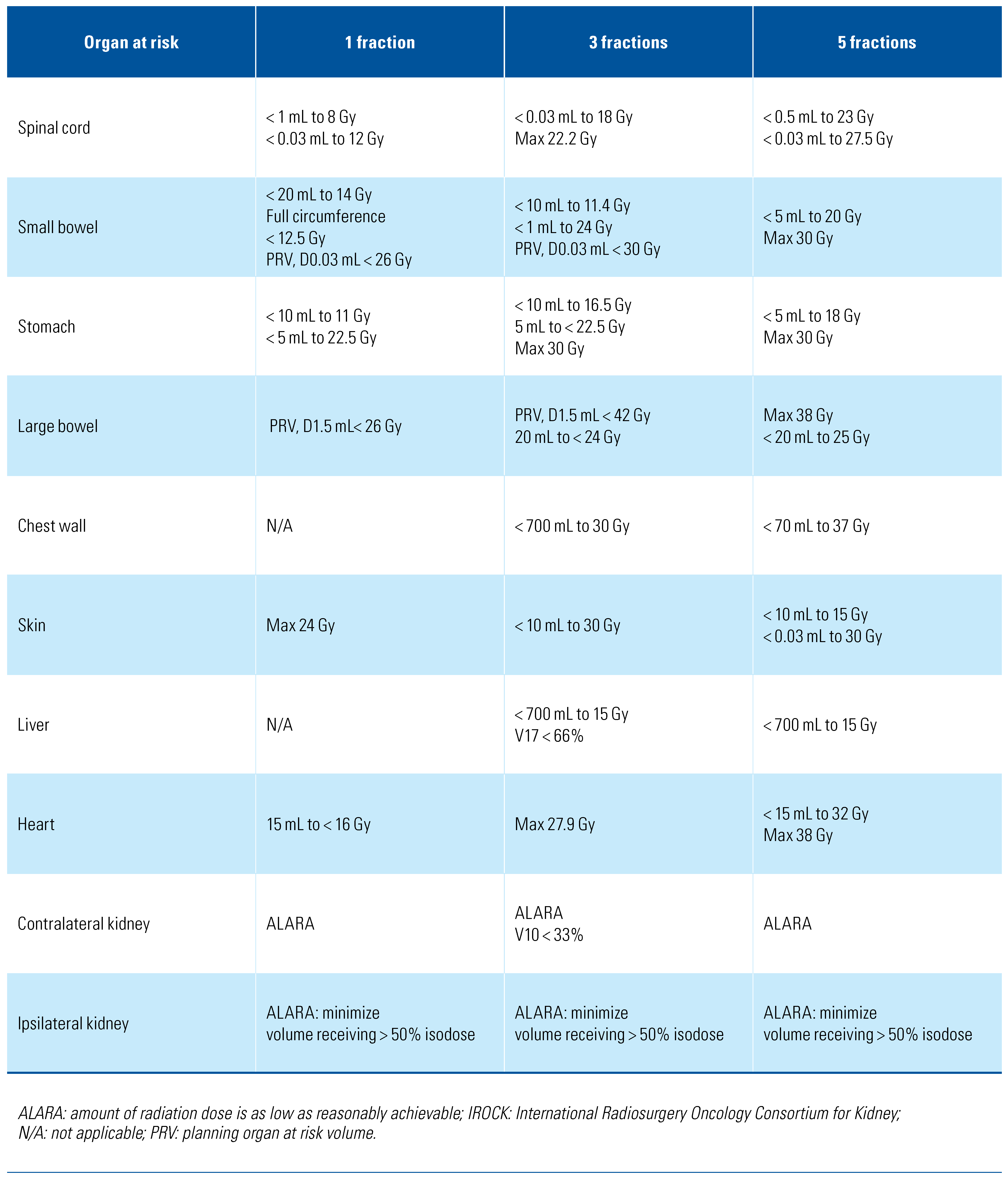
Hydrodissection via saline instillation and intentional patient positioning can increase the distance between adjacent structures and the tumor target[34] (Figure 1). Retrograde pyeloperfusion can be similarly used to protect the ureter and ureteropelvic junction from thermal injury, with resultant risk for perforation, urine leak, and/or subsequent stricture[34]. Renal tumor scoring systems can aid preprocedural planning and tumor selection[36,37].
Figure 1.
Example of a patient requiring tissue displacement prior to ablation.
To summarize, a small (< 3 cm) exophytic tumor, with a minimum of 1 cm distance from the adjacent anatomic structures represents ideal morphologic characteristics for tumor ablation.
Preprocedural Planning
Before TA, patient evaluation should include relevant comorbidities, risk factors for RCC, familial history of hereditary RCC syndromes, and blood workup including coagulative profile and renal function[38]. The American Urological Association/ Society of Urologic Oncology (AUA/SUO) guidelines recommend renal mass biopsy prior to TA to characterize the tumor histology, subsequently informing posttreatment surveillance[10].
Percutaneous ablation can be performed under either general anesthesia or conscious sedation. Image-guided percutaneous techniques are preferred over laparoscopic approaches due to a lower risk for associated complications, shorter hospitalization and operative times, reduced morbidity, reduced opioid analgesic requirement, and faster recovery time[15,16,39,40,41].
Preprocedural imaging aims to evaluate the feasibility of ablation, access site, the number of probes needed, the tumor’s location relative to other structures, and the need for any ancillary procedures[42,43]. CT is most commonly the modality of choice for both procedural planning and probe placement at the time of treatment. MRI can be used but is more expensive and technically demanding. Ultrasound alone allows for direct monitoring during probe placement; however, it may be limited in its ability to visualize adjacent structures, and thus is commonly used in combination with CT[43,44].
Peri- and Post-Procedural Complications
TA is considered a safe procedure with very few complications (7.4%) compared to surgery (11%)[15]. The incidence of significant complications after TA is lower than following surgery (2.3% vs. 5%)[15,45].
Complications during ablation of renal tumors include the following:
- Post-ablation syndrome: A transient and self-limiting constellation of symptoms experienced following TA characterized by fever, nausea, vomiting, and malaise. Larger volumes of necrosis may prolong symptoms. Fewer than 10% of patients experience the full spectrum of symptoms, while 60% report flu-like symptoms within the first 10 days following ablation[46].
- Bleeding: Most commonly, TA-associated bleeding is minor (6%), while massive hemorrhage requiring transfusion is extremely rare (< 1% of cases) [19,43,47]. Some tumors may require pretreatment embolization, most often in the context of highly complex tumors[43,47,48].
- Hematuria: This is a rare side effect of TA (0.5–1%) that generally spontaneously resolves within 12 to 24 hours of treatment[43]. If hematuria persists, thermal damage to the pelvicalyceal system should be suspected. In the case of hydronephrosis due to clot obstruction, placement of a ureteric stent and/or manual irrigation of the bladder may be necessary.
- Ureteric/Collecting System Injury: This complication is associated with treatment of central tumors. Although rare (1%–3% of cases[43]), injury can result in ureteric strictures, urine leak, urinoma, or formation of a urinary fistula[40,43,47], which may present in a delayed fashion (weeks to months following treatment).
- Neuropraxia: Nerve injury (1%–3%) can occur following ablation of tumors close to the psoas muscle, or intercostal or lumbar nerves[43]. One study found that nerve injury resolved in 90% of affected patients within 6 months of treatment[47].
Other rare complications include bowel perforation[43], infection[43,49], pneumothorax, skin burn or freeze at the site of entry, and tumor seeding along the entry site[9,41,47].
Evidence Synthesis
Local Tumor Control
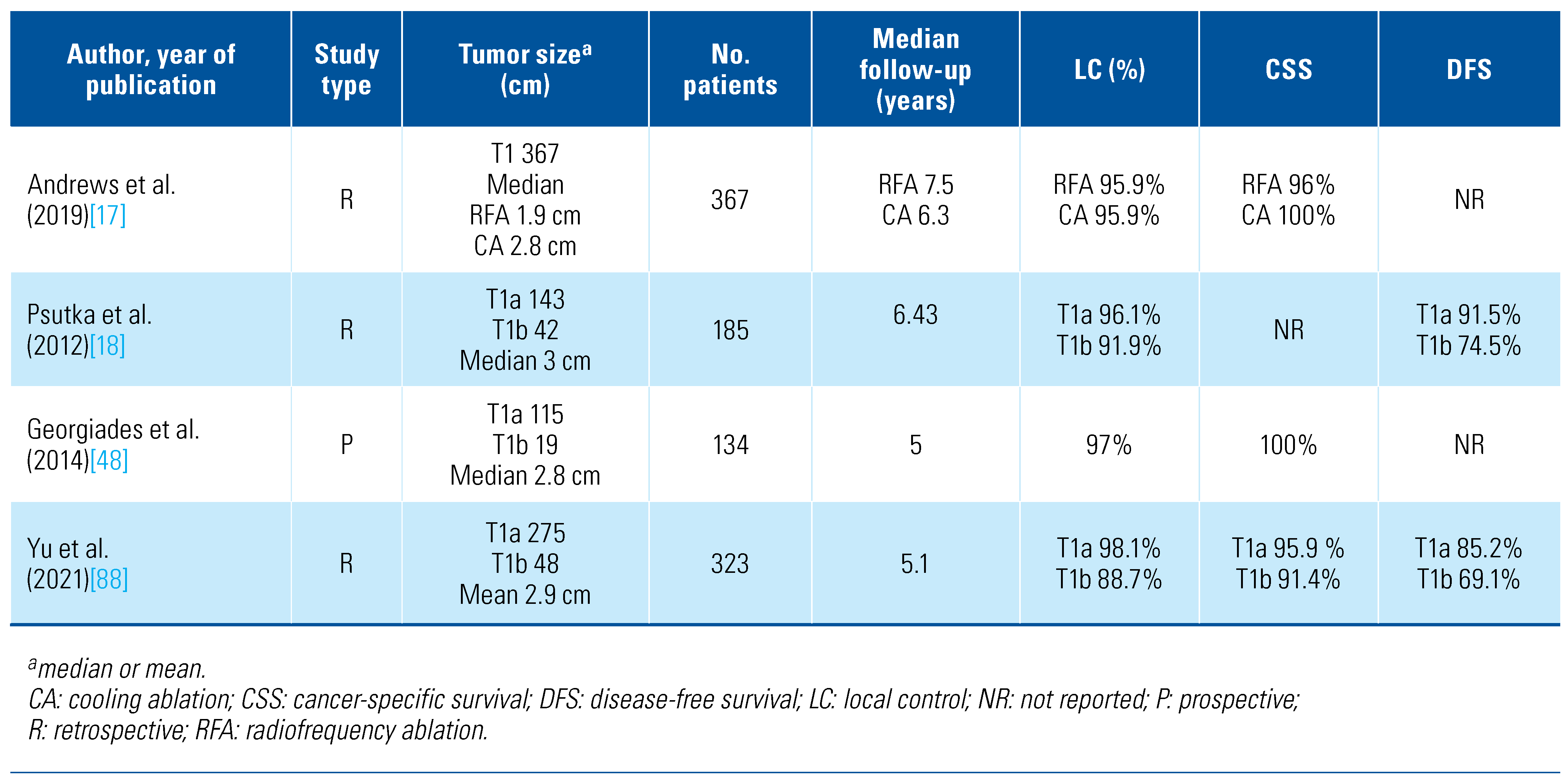
Current literature suggests that careful patient and tumor selection can result in the successful ablation of nearly all renal tumors, with low recurrence rates over short and intermediate follow-up. To date, however, TA has not been compared against surgery in a randomized controlled trial. The available (retrospective) data is limited by selection bias, institutional practices, and local expertise, impacting generalizability of TA across centers, providers, and patients. The sum of the comparative efficacy data suggests comparable oncologic and safety outcomes between TA and radical or partial nephrectomy for T1a disease[50]. The largest-cohort studies of the long-term oncologic results following ablation are reported in Table 2.

Table 2.
Long-term cohort studies of percutaneous thermal ablation of T1 renal tumors.
Comparative Studies
In a retrospective review of 1424 RCC patients (367 treated with RFA or CA; 1055 with PN), there was no difference in the clinical outcome of T1a disease, with 5-year CSS of 96%, 100%, and 99% for RFA, CA, and PN, respectively. However, a higher death rate from RCC was observed for CA compared to PN in this subset. For 376 cT1b patients, 5-year CSS was lower for CA compared to PN (91% vs. 98%, respectively). Despite the limitations associated with the retrospective analysis design and risk of selection bias, the authors concluded that any clinically significant difference between ablation and PN of cT1a tumors was unlikely but encouraged further research regarding the oncologic efficacy of CA for cT1b tumors[17].
In a systematic review and meta-analysis of 107 studies, Pierorazio et al. compared the effectiveness of AS, TA, and RN or PN for T1 tumors. They reported an increased incidence of local recurrence following a single ablation session but no difference when secondary ablations were considered. TA was associated with less perioperative morbidity and complications compared to PN. There was no difference in the CSS across the different management options[50]. Katsanos et al. reported similar findings as well[15].
Selection bias is likely to contribute to some of these findings; for example, surgery is often favored for healthier patients and ablation for patients with a high burden of comorbidity or limited projected life expectancy. However, current data suggests that TA can be considered a practical alternate approach to surgery in small T1a tumors, and sometimes for larger tumors in patients unsuitable for or at higher risk from partial nephrectomy.
Several groups report a significantly lower cost for ablation (up to a third) than for surgery[51,52,53]. These cost-savings are the short procedure time, outpatient nature, limited ancillary perioperative costs, and lower complication rate[51,52]. Theoretically, when considering the occasional need for retreatment post-TA, TA may contribute to additional expense due to further treatments. Some data support that radiofrequency ablation is still less expensive than nephron-sparing surgery[54]. However, the authors concluded that future studies are necessary before using the analysis for policy-level decision-making. Furthermore, the analysis was limited to short-term cost-effectiveness.
Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR)
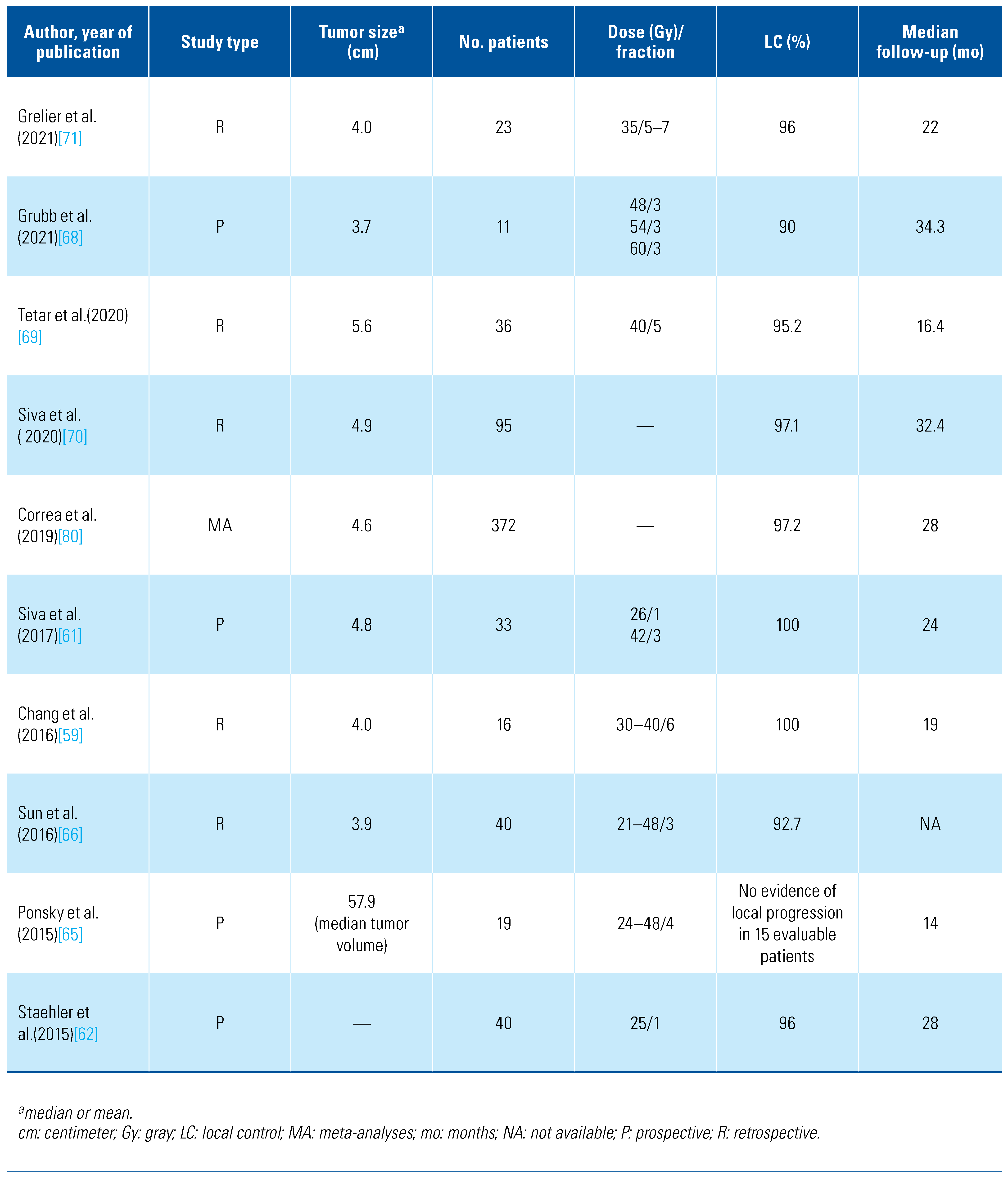
Preclinical studies on mouse models with implanted human RCC cell lines and in vitro cell culture indicate that the entrenched dogma of radioresistance of RCC may not be relevant in the era of high doses per fraction, which can be safely delivered with the advent of SABR[55,56]. These reports were reinforced by excellent local control (LC) rates using SABR in patients with extracranial metastatic RCC[57]. Since then, multiple retrospectives and prospective phase 1 and 3 studies have demonstrated the feasibility, safety, and efficacy of SABR[58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73]. The results of selected published studies are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Summary of selective Studies evaluating SABR for the treatment of primary renal cell carcinoma.
Patient Selection for SABR
Current published studies have evaluated the safety and efficacy of SABR in patients with localized RCC who are inoperable, those who refuse surgery, and those with baseline CKD and high risk for renal replacement therapy with PN or RN. SABR has the advantage of being a noninvasive treatment that does not require anesthesia or sedation. Therefore, it may be a more suitable option for older and/or more frail patients, those requiring ongoing anticoagulation, or those with multiple competing comorbidities that would place them at unacceptably high risk from anesthesia, surgery, or TA. Furthermore, SABR has the added advantage of having minimal impact on quality of life, which reverted to baseline at subsequent follow-up in a study in older and frail patients[74].
The treatment options are limited for patients with tumors measuring ≥4 cm in maximal diameter, who are not surgical candidates. TA is not suitable for patients with T1b RCC due to the increased risk for local recurrence and complications[5,6]. In this subset of patients with T1b disease, SABR has shown excellent outcomes and can be an attractive approach[69,70].
Treatment of RCC in a patient with a solitary kidney is a challenging clinical scenario. PN, if feasible, remains the standard of care for renal masses in patients with a solitary kidney. However, ablative treatments are a good alternative for patients where PN is not possible due to tumor location or size. In challenging scenarios with RCC in a single kidney where other nephron-sparing approaches (PN, TA) are not technically or medically feasible, SABR has shown excellent tumor-related outcomes while avoiding the lifelong need for dialysis[58,75].
Technical Consideration
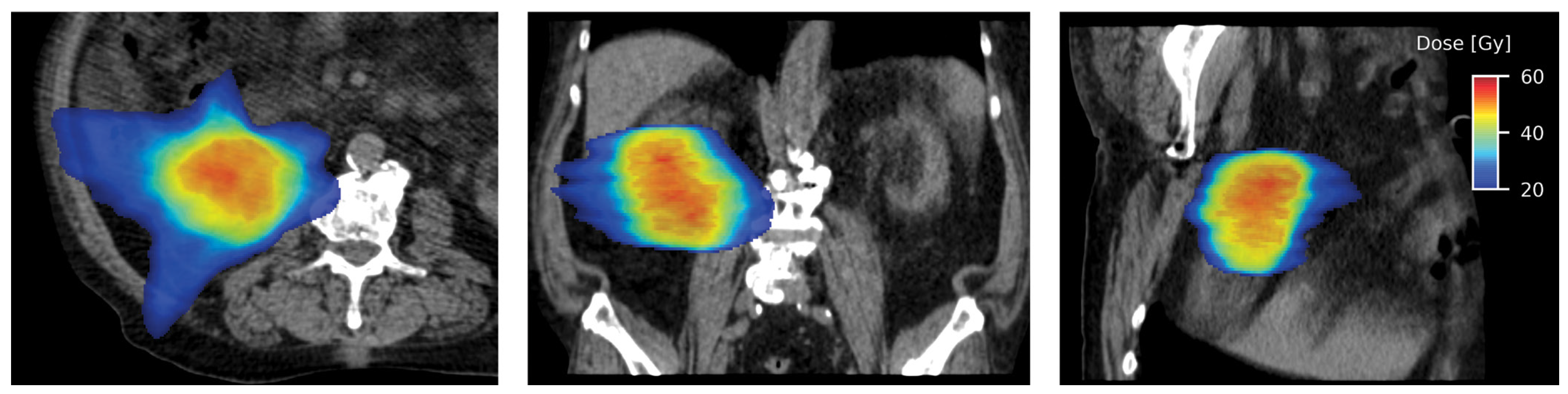
Different treatment units are used to deliver SABR to primary RCC[61,62,65,69,73]. Irrespective of the treatment system used, respiratory motion management is essential for treatment planning and delivery, due to the motion of kidneys with respiration[76]. The most commonly used technique in linear accelerator-based treatment is the internal target volume (ITV) concept, where a thin-cut 4-dimensional CT (4D-CT) is obtained during simulation. Respiratory gating or tumor tracking using implanted fiducial markers may be used to allow for a reduction in ITV, and this is usually incorporated into the delivery of SABR using CyberKnife. A typical linear accelerator-based SABR plan is shown in Figure 2.
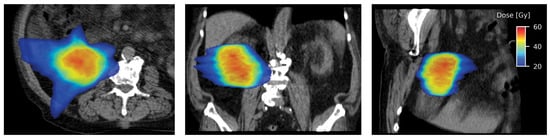
Figure 2.
Axial (left), coronal (middle), and sagittal sections (right) showing highly conformal radiation dose distribution with a typical SABR plan.
Target volumes for SABR are defined as per the International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements report (ICRU) 91[77], which has been suggested previously by the International Radiosurgery Oncology Consortium for Kidney (IROCK) consensus statement as well[78]. Similarly, the IROCK group recommended organs at risk (OARs) with acceptable dose constraints, adapted and summarized in Table 4[78]. The IROCK consensus statement recommended 25–26 Gy, 35–45 Gy, and 40–50 Gy in 1, 3, and 5 fractions, respectively[78].

Table 4.
Suggested SABR dose constraints. Adapted from IROCK Consensus Statement, Siva S et al. Future Oncol. 2016;12(5):637-645[78].
Clinical Evidence for SABR in Localized Primary RCC
Multiple prospective and retrospective studies have reported encouraging results with SABR in patients with localized RCC. In the largest reported prospective case-control study, Staehler et al. treated 40 patients with renal masses who were anticipated to require dialysis if they underwent nephrectomy with a single fraction of 25 Gy[62]. After a median follow-up of 28 months, the authors reported an LC of 96%, with a minimal decline in renal function. In a prospective phase 1 trial (FASTRACK) of 33 patients with a median tumor size of 4.8 cm (range, 2.1–7.9), freedom from local progression, distant progression, and overall survival (OS) at 2 years were 100%, 89%, and 92%, respectively[61]. Treatmentrelated grade 1–2 toxicities (flank pain, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) occurred in 26 of 33 patients (78%), and grade 3 fatigue occurred in only one patient. While early results of prospective studies are promising, these studies have some inherent limitations: (1) the small number of patients treated, (2) the lack of longterm follow-up, and (3) the varying dose fractionation schemes.
In a pooled analysis involving 223 patients with a mean tumor size of 4.4 cm, the IROCK group reported LC, cancer-specific survival (CSS), and progression-free survival (PFS) rates of 97.8%, 91.9%, and 65.4% at 4 years[79]. In another series of 95 patients with cT1b (> 4 cm tumor size) localized RCC treated with SABR, Siva et al. (2020) reported CSS, OS, and PFS rates of 96.1%, 83.7%, and 81.0% at 2 years and 91.4%, 69.2%, and 64.9% at 4 years, respectively[70]. At 4 years, local, distant, and any failure rates were 2.9%, 11.1%, and 12.1%, respectively. A systematic review and meta-analyses published in 2019 involving 372 patients with localized RCC (median size, 4.6 cm) involving 26 studies (11 of which were prospective) reported that the random effect estimates for LC were 97.2% with SABR[80]. The grade 1, 2, and 3–4 toxicity rates were 37.5%, 8.8%, and 1.5% (95% CI, 0–4.3%), respectively.
Prospective studies have used a range of dose fractionation regimens. The prospective dose-escalation studies evaluated doses ranging from 21 to 60 Gy in 3 fractions[68,81,82] and 24 to 48 Gy in 4 fractions[65]. They showed dose escalation to 60 Gy in 3 and 48 Gy in 4 fractions without dose-limiting toxicity. The ongoing phase 2 study TROG 15.03 (FASTRACK II) evaluates 26 Gy in 1 fraction for tumors of ≤ 4 cm and 42 Gy in 3 fractions for tumors of > 4 cm in size[83].
Response Evaluation
Currently, the interpretation of post-SABR response and identification of characteristics that coincide with treatment response or recurrence remain a key challenge. LC post-SABR is currently measured using the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) by either CT or MRI. Currently, lack of growth and subsequent slow regression in size is thought to represent a successful response to treatment. Given that small RCCs are associated with slow growth kinetics, radiographic responses following SABR are also attenuated. In a study of 40 patients, Sun et al. reported an average regression of 0.37 cm in the maximum dimension of RCC per year[66]. Unlike TA, where the absence of contrast enhancement post-procedure assesses the response, there are no significant changes in contrast enhancement after SABR[66]. Early results of functional MRI (fMRI) have shown some promise in detecting early response to SABR[84]; however, further exploration is warranted to validate the role of fMRI in characterizing the efficacy of SABR.
Routine post-SABR biopsy should be considered experimental. In a recent prospective study involving 11 patients with dose escalation to 60 Gy in 3 fractions, 5 of 5 posttreatment biopsies in the expansion cohort were positive by hematoxylin and eosin staining[68]. However, there was no radiological progression in subsequent follow-up. Moreover, staining of Ki-67, a nuclear protein associated with cell proliferation, was negative in the post-biopsy samples, confirming that cell viability on microscopy does not necessarily indicate ongoing active cell proliferation.
Renal Function Post-SABR
Given that many patients with RCC are at risk for longterm CKD following treatment, concerns exist regarding the impact of SABR on renal function. The published literature demonstrates a mild to moderate decrease in baseline renal function following SABR. In the IROCK pooled analysis of 223 patients (mean tumor size, 4.4 cm) treated with renal SABR, the average glomerular filtration rate (GFR) decreased by ~5.5 mL/minute after SABR, with 6 patients requiring dialysis[79]. Similarly, a systematic review and meta-analyses involving 372 patients showed a post-SABR GFR change of -7.7mL/ min from baseline[80]. Though the renal function decline is subclinical in published studies, patients with CKD 4–5 at baseline undergoing SABR should be counseled regarding ESRD risk following treatment and the potential need for renal replacement therapy[59].
Future Perspectives
One ongoing, prospective, randomized pilot trial (NCT03811665) compares SABR with RFA to manage SRMs. However, there are always challenges in completing large, randomized trials comparing different interventional modalities. One way to counteract these difficulties can be to conduct comparative studies using existing datasets and establish prospective registries. Considering encouraging results with a combination of SABR and MWA in patients with larger (> 5 cm) RCCs[85], an ongoing prospective clinical trial is exploring the safety and efficacy of this combination in patients with RCCs of > 4 cm (NCT02782715).
Evidence supports that SABR and TA also have potent immunomodulatory effects[86,87]. It will be interesting to combine ablative treatments, SABR or TA, with immunotherapies to optimize immune response to improve long-term outcomes. One trial (NCT05024318) assesses SABR with or without pembrolizumab in patients with T1B-T3, N0 or N1, 0 or low-volume M1 RCC before nephrectomy.
Take-Home Messages
- Patients with a newly diagnosed, localized renal mass should undergo a detailed assessment, including history focusing on comorbidity burden, physical examination, renal function assessment, and appropriate comprehensive tumor staging imaging. In patients considering TA or SABR, renal mass biopsy is recommended to characterize the histology of the tumor.
- Each case should be discussed in a multidisciplinary team meeting consisting of a urologist, interventional radiologist, and radiation oncologist, including a central imaging review.
- Ablative treatments, including TA or SABR, can be considered in patients at high risk for adverse outcomes following surgery who decline surgery and in whom AS is not optimal. Local expertise should be considered for decision-making.
- SRMs less than 4 cm (ideally < 3 cm), predominantly exophytic and distant to the renal hilum, should be considered for TA preferentially to SABR.
- Tumors measuring more than 4 cm (ideally > 3 cm), predominantly endophytic and centrally located, could be considered preferentially for SABR over TA.
- Ongoing imaging at regular specified intervals is essential to monitor the treatment outcome.
Acknowledgments
Muhammad Ali is a PhD candidate who is supported through an Australian Government Research Training Program (RTP) scholarship. Shankar Siva is funded by the Cancer Council Victoria Colebatch fellowship.
Competing Interests
None declared.
Abbreviations
| AS | active surveillance |
| CA | cooling ablation |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| CSS | cancer-specific survival |
| CT | computed tomography |
| IROCK | International Radiosurgery Oncology Consortium for Kidney |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| MWA | microwave ablation |
| PN | partial nephrectomy |
| RCC | renal cell carcinoma |
| RFA | radiofrequency ablation |
| RN | radical nephrectomy |
| SABR | stereotactic ablative radiotherapy |
| SMRs | small renal masses |
| TA | thermal ablation |
References
- Siegel, R.; Naishadham, D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2013, 63, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirjian, S.; Lane, B.R.; Derweesh, I.H.; Takagi, T.; Fergany, A.; Campbell, S.C. Chronic kidney disease due to surgical removal of nephrons: Relative rates of progression and survival. J. Urol. 2014, 192, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.P.; Thompson, R.H.; Boorjian, S.A.; Weight, C.J.; Han, L.C.; Murad, M.H.; et al. Comparative effectiveness for survival and renal function of partial and radical nephrectomy for localized renal tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Urol. 2012, 188, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, S.C.; Uzzo, R.G.; Karam, J.A.; Chang, S.S.; Clark, P.E.; Souter, L. Renal mass and localized renal cancer: Evaluation, management, and follow-up: AUA Guideline: Part II. J. Urol. 2021, 206, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Assocation of Urology (EAU). Guidelines on Renal Cell Cacrcinoma. Available online: https://uroweb.org/guideline/renal-cellcarcinoma/#7 (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- Escudier, B.; Porta, C.; Schmidinger, M.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Bex, A.; Khoo, V.; et al. Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up†. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Kidney Cancer (Version 2. 2022). Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/kidney.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- Ahmed, M.; Solbiati, L.; Brace, C.L.; Breen, D.J.; Callstrom, M.R.; Charboneau, J.W.; et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: Standardization of terminology and reporting criteria--a 10-year update. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 1691–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breen, D.J.; Railton, N.J. Minimally invasive treatment of small renal tumors: Trends in renal cancer diagnosis and management. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2010, 33, 896–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.; Uzzo, R.G.; Allaf, M.E.; Bass, E.B.; Cadeddu, J.A.; Chang, A.; et al. Renal mass and localized renal cancer: AUA Guideline. J. Urol. 2017, 198, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finelli, A.; Ismaila, N.; Bro, B.; Durack, J.; Eggener, S.; Evans, A.; et al. Management of small renal masses: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungberg, B.; Albiges, L.; Abu-Ghanem, Y.; Bensalah, K.; Dabestani, S.; Fernández-Pello, S.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: The 2019 update. Eur Urol. 2019, 75, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginzburg, S.; Uzzo, R.; Walton, J.; Miller, C.; Kurz, D.; Li, T.; et al. Residual parenchymal volume, not warm ischemia time, predicts ultimate renal functional outcomes in patients undergoing partial nephrectomy. Urology 2015, 86, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Bang, J.K.; Park, H.K.; Ahn, H. Factors influencing renal function reduction after partial nephrectomy. J. Urol. 2009, 181, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsanos, K.; Mailli, L.; Krokidis, M.; McGrath, A.; Sabharwal, T.; Adam, A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of thermal ablation versus surgical nephrectomy for small renal tumours. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2014, 37, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta Ruiz, V.; Batelsson, S.; Onkamo, E.; Wernroth, L.; Nilsson, T.; Lonnemark, M.; et al. Split renal function after treatment of small renal masses: Comparison between radiofrequency ablation and laparoscopic partial nephrectomy. Acta Radiol. 2020, 284185120956281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, J.R.; Atwell, T.; Schmit, G.; Lohse, C.M.; Kurup, A.N.; Weisbrod, A.; et al. Oncologic outcomes following partial nephrectomy and percutaneous ablation for cT1 renal masses. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psutka, S.P.; Feldman, A.S.; McDougal, W.S.; McGovern, F.J.; Mueller, P.; Gervais, D.A. Long-term oncologic outcomes after radiofrequency ablation for T1 renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gervais, D.A.; McGovern, F.J.; Arellano, R.S.; McDougal, W.S.; Mueller, P.R. Radiofrequency ablation of renal cell carcinoma: Part 1, Indications, results, and role in patient management over a 6-year period and ablation of 100 tumors. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 185, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wah, T.M.; Irving, H.C.; Gregory, W.; Cartledge, J.; Joyce, A.D.; Selby, P.J. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of renal cell carcinoma (RCC): Experience in 200 tumours. BJU Int. 2014, 113, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, B.M.; Prevoo, W.; Meier, M.A.J.; Bex, A.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Klompenhouwer, E.G.; et al. Percutaneous microwave ablation of histologically proven T1 renal cell carcinoma. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2020, 43, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagoria, R.J.; Traver, M.A.; Werle, D.M.; Perini, M.; Hayasaka, S.; Clark, P.E. Oncologic efficacy of CT-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of renal cell carcinomas. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 189, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Z.G.; Liu, F.Y.; Li, Q.Y.; He, G.Z.; et al. A multicenter 10-year oncologic outcome of ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation of clinical T1 renal cell carcinoma: Will it stand the test of time? Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atwell, T.D.; Vlaminck, J.J.; Boorjian, S.A.; Kurup, A.N.; Callstrom, M.R.; Weisbrod, A.J.; et al. Percutaneous cryoablation of stage T1b renal cell carcinoma: Technique considerations, safety, and local tumor control. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Huang, Y.; et al. Thermal ablation assisted laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for clinical T1b renal tumors. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2022, 31, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atwell, T.D.; Farrell, M.A.; Leibovich, B.C.; Callstrom, M.R.; Chow, G.K.; Blute, M.L.; et al. Percutaneous renal cryoablation: Experience treating 115 tumors. J. Urol. 2008, 179, 2136–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breen, D.J.; Bryant, T.J.; Abbas, A.; Shepherd, B.; McGill, N.; Anderson, J.A.; et al. Percutaneous cryoablation of renal tumours: Outcomes from 171 tumours in 147 patients. BJU Int. 2013, 112, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta Ruiz, V.; Lonnemark, M.; Brekkan, E.; Dahlman, P.; Wernroth, L.; Magnusson, A. Predictive factors for complete renal tumor ablation using RFA. Acta Radiol. 2016, 57, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinshaw, J.L.; Lubner, M.G.; Ziemlewicz, T.J.; Fred, T.; Lee, J.; Brace, CL. Percutaneous tumor ablation tools: Microwave, radiofrequency, or cryoablation–what should you use and why? RadioGraphics. 2014, 34, 1344–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, M.D.; Kim, C.Y.; Tsivian, M.; Suberlak, M.N.; Sopko, D.R.; Polascik, T.J.; et al. Percutaneous cryoablation of renal lesions with radiographic ice ball involvement of the renal sinus: Analysis of hemorrhagic and collecting system complications. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.B.; Saboorian, M.H.; Duchene, D.A.; Ogan, K.; Cadeddu, J.A. Nephrectomy after radiofrequency ablation-induced ureteropelvic junction obstruction: Potential complication and long-term assessment of ablation adequacy. Urology 2003, 62, 351–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; Solomon, S.B.; Su, L.M.; Matsumoto, E.D.; Kavoussi, L.R.; Nakada, S.Y.; et al. Defining the complications of cryoablation and radio frequency ablation of small renal tumors: A multi-institutional review. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 874–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warlick, C.A.; Lima, G.C.; Allaf, M.E.; Varkarakis, I.; Permpongkosol, S.; Schaeffer, E.M.; et al. Clinical sequelae of radiographic iceball involvement of collecting system during computed tomography-guided percutaneous renal tumor cryoablation. Urology 2006, 67, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmit, G.D.; Kurup, A.N.; Weisbrod, A.J.; Thompson, R.H.; Boorjian, S.A.; Wass, C.T.; et al. ABLATE: A renal ablation planning algorithm. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsivian, M.; Lyne, J.C.; Mayes, J.M.; Mouraviev, V.; Kimura, M.; Polascik, T.J. Tumor size and endophytic growth pattern affect recurrence rates after laparoscopic renal cryoablation. Urology 2010, 75, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutikov, A.; Uzzo, R.G. The R. E. N. A. L. nephrometry score: A comprehensive standardized system for quantitating renal tumor size, location and depth. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahan, J.C.; Richter, M.D.; Seideman, C.A.; Trimmer, C.; Chan, D.; Weaver, M.; et al. The Performance of a modified RENAL nephrometry score in predicting renal mass radiofrequency ablation success. Urology 2015, 85, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, L.J.; Hong, K. Renal Ablation Techniques: State of the Art. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 205, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finley, D.S.; Beck, S.; Box, G.; Chu, W.; Deane, L.; Vajgrt, D.J.; et al. Percutaneous and laparoscopic cryoablation of small renal masses. J. Urol. 2008, 180, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, G.C.; Tuncali, K.; Tatli, S.; Morrison, P.R.; Silverman, S.G. Comparison of percutaneous and surgical approaches to renal tumor ablation: Metaanalysis of effectiveness and complication rates. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2008, 19, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta Ruiz, V.; Ladjevardi, S.; Brekkan, E.; Haggman, M.; Lonnemark, M.; Wernroth, L.; et al. Periprocedural outcome after laparoscopic partial nephrectomy versus radiofrequency ablation for T1 renal tumors: A modified R. E. N. A. L nephrometry score adjusted comparison. Acta Radiol. 2019, 60, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Solbiati, L.; Brace, C.L.; Breen, D.J.; Callstrom, M.R.; Charboneau, J.W.; et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: Standardization of terminology and reporting criteria-a 10-year update. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 1691–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krokidis, M.E.; Orsi, F.; Katsanos, K.; Helmberger, T.; Adam, A. CIRSE guidelines on percutaneous ablation of small renal cell carcinoma. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2017, 40, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Hashimi, F.; Lyrdal, D.; Lundstam, S.; Hellstrom, M. Improved outcome with combined US/CT guidance as compared to US guidance in percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of small renal masses. Acta Radiol. 2015, 56, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Covarrubias, D.; Uppot, R.; Arellano, R.S. Image-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of central renal cell carcinoma: Assessment of clinical efficacy and safety in 31 tumors. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 1643–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Bambrook, J.; Bhambra, B.; Smith, J.; Cartledge, J.; Ralph, C.; et al. Incidence of post-ablation syndrome following image-guided percutaneous cryoablation of renal cell carcinoma: A prospective study. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 41, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwell, T.D.; Carter, R.E.; Schmit, G.D.; Carr, C.M.; Boorjian, S.A.; Curry, T.B.; et al. Complications following 573 percutaneous renal radiofrequency and cryoablation procedures. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiades, C.S.; Rodriguez, R. Efficacy and safety of percutaneous cryoablation for stage 1A/B renal cell carcinoma: Results of a prospective, single-arm, 5-year study. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2014, 37, 1494–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, D.; vanSonnenberg, E.; Kang, P. Infectious outcomes from renal tumor ablation: Prophylactic antibiotics or not? Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2018, 41, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierorazio, P.M.; Johnson, M.H.; Patel, H.D.; Sozio, S.M.; Sharma, R.; Iyoha, E.; et al. Management of renal masses and localized renal cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Urol. 2016, 196, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castle, S.M.; Gorbatiy, V.; Avallone, M.A.; Eldefrawy, A.; Caulton, D.E.; Leveillee, R.J. Cost comparison of nephron-sparing treatments for cT1a renal masses. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2013, 31, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcher, A.; Sun, M.; Dell’Oglio, P.; Trudeau, V.; Boehm, K.; Schiffmann, J.; et al. Mortality, morbidity and healthcare expenditures after local tumour ablation or partial nephrectomy for T1A kidney cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 43, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Leow, J.J.; Levy, A.C.; Chang, S.L.; Gelpi, F.H. Cost-effectiveness of management options for small renal mass: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandharipande, P.V.; Gervais, D.A.; Mueller, P.R.; Hur, C.; Gazelle, G.S. Radiofrequency ablation versus nephron-sparing surgery for small unilateral renal cell carcinoma: Cost-effectiveness analysis. Radiology 2008, 248, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, S.; Trisler, K.; Wessels, B.W.; Knox, S.J. Radiobiologic studies of radioimmunotherapy and external beam radiotherapy in vitro and in vivo in human renal cell carcinoma xenografts. Cancer 1997, 80 (Suppl. 12), 2519–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, L.; Stanfield, J.L.; Cho, L.C.; Chang, C.H.; Forster, K.; Kabbani, W.; et al. Efficacy of ablative high-dose-per-fraction radiation for implanted human renal cell cancer in a nude mouse model. Eur. Urol. 2006, 50, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothari, G.; Foroudi, F.; Gill, S.; Corcoran, N.M.; Siva, S. Outcomes of stereotactic radiotherapy for cranial and extracranial metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review. Acta Oncol. 2015, 54, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svedman, C.; Karlsson, K.; Rutkowska, E.; Sandström, P.; Blomgren, H.; Lax, I.; et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy of primary and metastatic renal lesions for patients with only one functioning kidney. Acta Oncol. 2008, 47, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.H.; Cheung, P.; Erler, D.; Sonier, M.; Korol, R.; Chu, W. Stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy for primary renal cell carcinoma in non-surgical candidates: Initial clinical experience. Clin. Oncol. (R Coll Radiol.) 2016, 28, e109–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.H.; Huang, W.Y.; Chao, H.L.; Lin, K.T.; Jen, Y.M. Novel application of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy using CyberKnife® for early-stage renal cell carcinoma in patients with pre-existing chronic kidney disease: Initial clinical experiences. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siva, S.; Pham, D.; Kron, T.; Bressel, M.; Lam, J.; Tan, T.H.; et al. Stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy for inoperable primary kidney cancer: A prospective clinical trial. BJU Int. 2017, 120, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehler, M.; Bader, M.; Schlenker, B.; Casuscelli, J.; Karl, A.; Roosen, A.; et al. Single fraction radiosurgery for the treatment of renal tumors. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svedman, C.; Sandström, P.; Pisa, P.; Blomgren, H.; Lax, I.; Kälkner, K.M.; et al. A prospective phase II trial of using extracranial stereotactic radiotherapy in primary and metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Acta Oncol. 2006, 45, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, D.; Thompson, A.; Kron, T.; Foroudi, F.; Kolsky, M.S.; Devereux, T.; et al. Stereotactic ablative body radiation therapy for primary kidney cancer: A 3-dimensional conformal technique associated with low rates of early toxicity. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponsky, L.; Lo, S.S.; Zhang, Y.; Schluchter, M.; Liu, Y.; Patel, R.; et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for poor surgical candidates with localized renal cell carcinoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 117, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.R.; Brook, A.; Powell, M.F.; Kaliannan, K.; Wagner, A.A.; Kaplan, I.D.; et al. Effect of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy on the Growth Kinetics and Enhancement Pattern of Primary Renal Tumors. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 206, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaidar-Person, O.; Price, A.; Schreiber, E.; Zagar, T.M.; Chen, R.C. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for large primary renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer. 2017, 15, e851–e854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubb, W.R.; Ponsky, L.; Lo, S.S.; Kharouta, M.; Traughber, B.; Sandstrom, K.; et al. Final results of a dose escalation protocol of stereotactic body radiotherapy for poor surgical candidates with localized renal cell carcinoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 155, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetar, S.U.; Bohoudi, O.; Senan, S.; Palacios, M.A.; Oei, S.S.; Wel, A.M.V.; et al. The role of daily adaptive stereotactic mr-guided radiotherapy for renal cell cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siva, S.; Correa, R.J.M.; Warner, A.; Staehler, M.; Ellis, R.J.; Ponsky, L.; et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for ≥t1b primary renal cell carcinoma: A report from the International Radiosurgery Oncology Consortium for Kidney (IROCK). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 108, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grelier, L.; Baboudjian, M.; Gondran-Tellier, B.; Couderc, A.L.; McManus, R.; Deville, J.L.; et al. Stereotactic Body radiotherapy for frail patients with primary renal cell carcinoma: Preliminary results after 4 years of experience. Cancers 2021, 13, 3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senger, C.; Conti, A.; Kluge, A.; Pasemann, D.; Kufeld, M.; Acker, G.; et al. Robotic stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for renal cell carcinoma in patients with impaired renal function. BMC Urol. 2019, 19, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomiya, T.; Tsuji, H.; Hirasawa, N.; Kato, H.; Kamada, T.; Mizoe, J.; et al. Carbon ion radiation therapy for primary renal cell carcinoma: Initial clinical experience. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 72, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminath, A.; Cheung, P.; Glicksman, R.M.; Donovan, E.K.; Niglas, M.; Vesprini, D.; et al. Patient-reported quality of life following stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary kidney cancer—Results from a prospective cohort study. Clin. Oncol. (R Coll Radiol.) 2021, 33, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, R.J.M.; Louie, A.V.; Staehler, M.; Warner, A.; Gandhidasan, S.; Ponsky, L.; et al. Stereotactic radiotherapy as a treatment option for renal tumors in the solitary kidney: A multicenter analysis from the IROCK. J. Urol. 2019, 201, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siva, S.; Pham, D.; Gill, S.; Bressel, M.; Dang, K.; Devereux, T.; et al. An analysis of respiratory induced kidney motion on four-dimensional computed tomography and its implications for stereotactic kidney radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, L.; Andratschke, N.; Blanck, O.; Brunner, T.B.; Combs, S.E.; Grosu, A.L.; et al. ICRU report 91 on prescribing, recording, and reporting of stereotactic treatments with small photon beams : Statement from the DEGRO/DGMP working group stereotactic radiotherapy and radiosurgery. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2019, 195, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siva, S.; Ellis, R.J.; Ponsky, L.; Teh, B.S.; Mahadevan, A.; Muacevic, A.; et al. Consensus statement from the International Radiosurgery Oncology Consortium for Kidney for primary renal cell carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2016, 12, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, S.; Louie, A.V.; Warner, A.; Muacevic, A.; Gandhidasan, S.; Ponsky, L.; et al. Pooled analysis of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for primary renal cell carcinoma: A report from the International Radiosurgery Oncology Consortium for Kidney (IROCK). Cancer. 2018, 124, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, R.J.M.; Louie, A.V.; Zaorsky, N.G.; Lehrer, E.J.; Ellis, R.; Ponsky, L.; et al. The emerging role of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for primary renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. Focus. 2019, 5, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, I.; Redrosa, I.; Martin, C.; Collins, C.; Wagner, A. Results of a phase I dose escalation study of stereotactic radiosurgery for primary renal tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 78, S191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, S.; Wagner, A.; Kaplan, I. A phase 1 dose-escalation study of robotic radiosurgery in inoperable primary renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, S.; Chesson, B.; Bressel, M.; Pryor, D.; Higgs, B.; Reynolds, H.M.; et al. TROG 15. 03 phase II clinical trial of Focal Ablative STereotactic Radiosurgery for Cancers of the Kidney-FASTRACK II. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, H.M.; Parameswaran, B.K.; Finnegan, M.E.; Roettger, D.; Lau, E.; Kron, T.; et al. Diffusion weighted and dynamic contrast enhanced MRI as an imaging biomarker for stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy (SABR) of primary renal cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blitzer, G.C.; Wojcieszynski, A.; Abel, E.J.; Best, S.; Lee, F.T., Jr.; Hinshaw, J.L.; et al. Combining stereotactic body radiotherapy and microwave ablation appears safe and feasible for renal cell carcinoma in an early series. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2021, 19, e313–e318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.; Hoffend, N.C.; Abrams, S.I.; Schwaab, T.; Singh, A.K.; Muhitch, J.B. Radiation induces dynamic changes to the T cell repertoire in renal cell carcinoma patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 23721–23729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.F.; Dupuy, D.E. Thermal ablation of tumours: Biological mechanisms and advances in therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2014, 14, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Z.G.; Liu, F.Y.; Li, Q.Y.; He, G.Z.; et al. A multicenter 10-year oncologic outcome of ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation of clinical T1 renal cell carcinoma: Will it stand the test of time? Eur. Radiol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
This is an open access article under the terms of a license that permits non-commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. © 2022 The Authors. Société Internationale d'Urologie Journal, published by the Société Internationale d'Urologie, Canada.