2022 WUOF/SIU International Consultation on Urological Diseases: Imaging of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:Introduction
Detection and Diagnosis
Imaging Features of Common Subtypes of RCC
Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinom
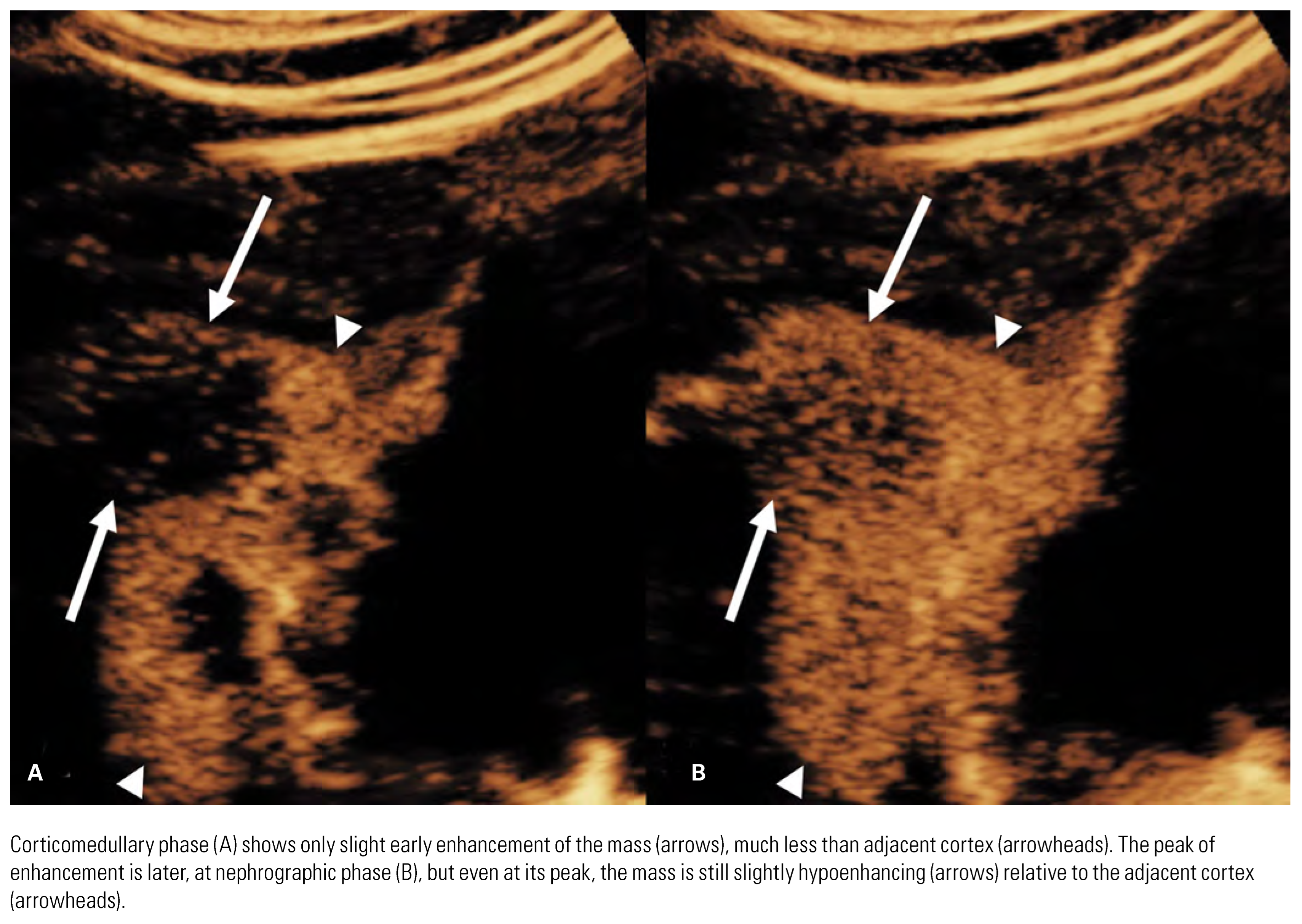
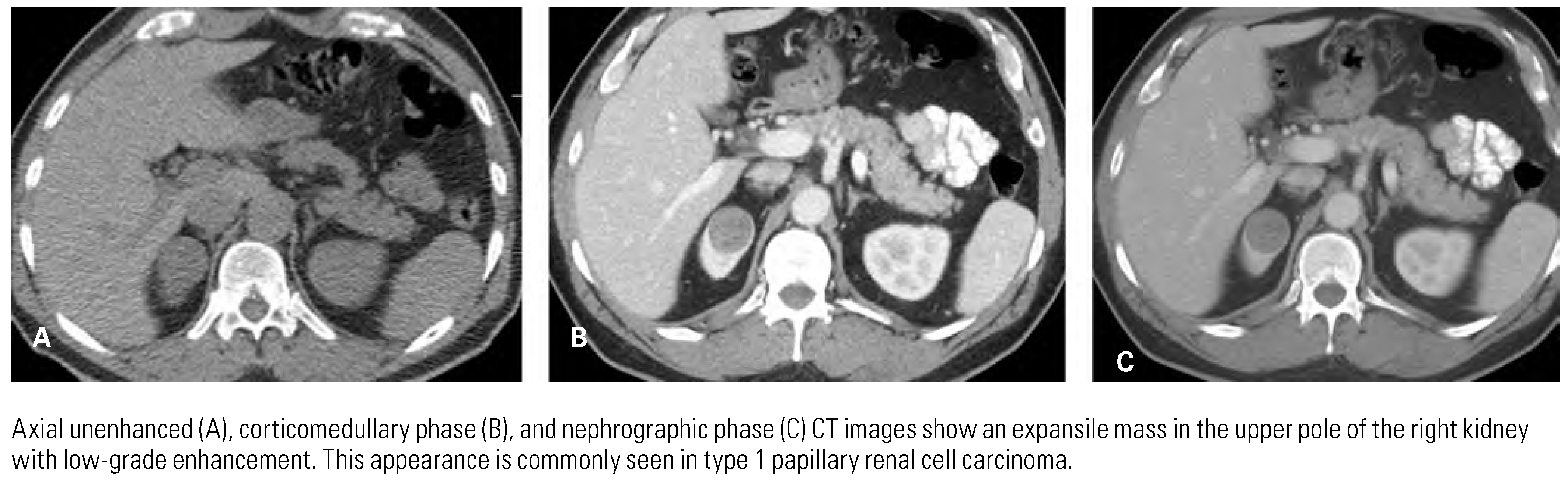
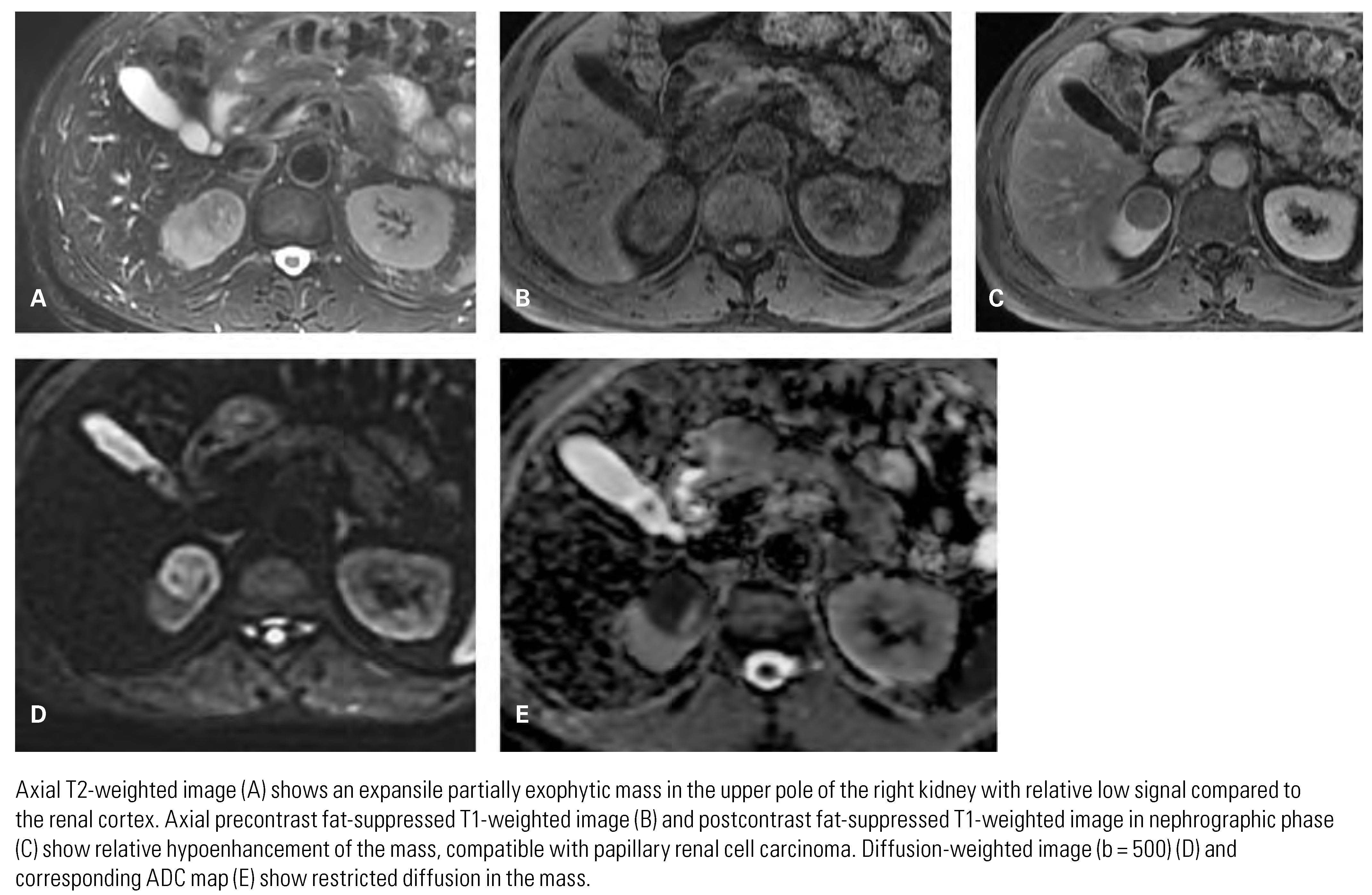
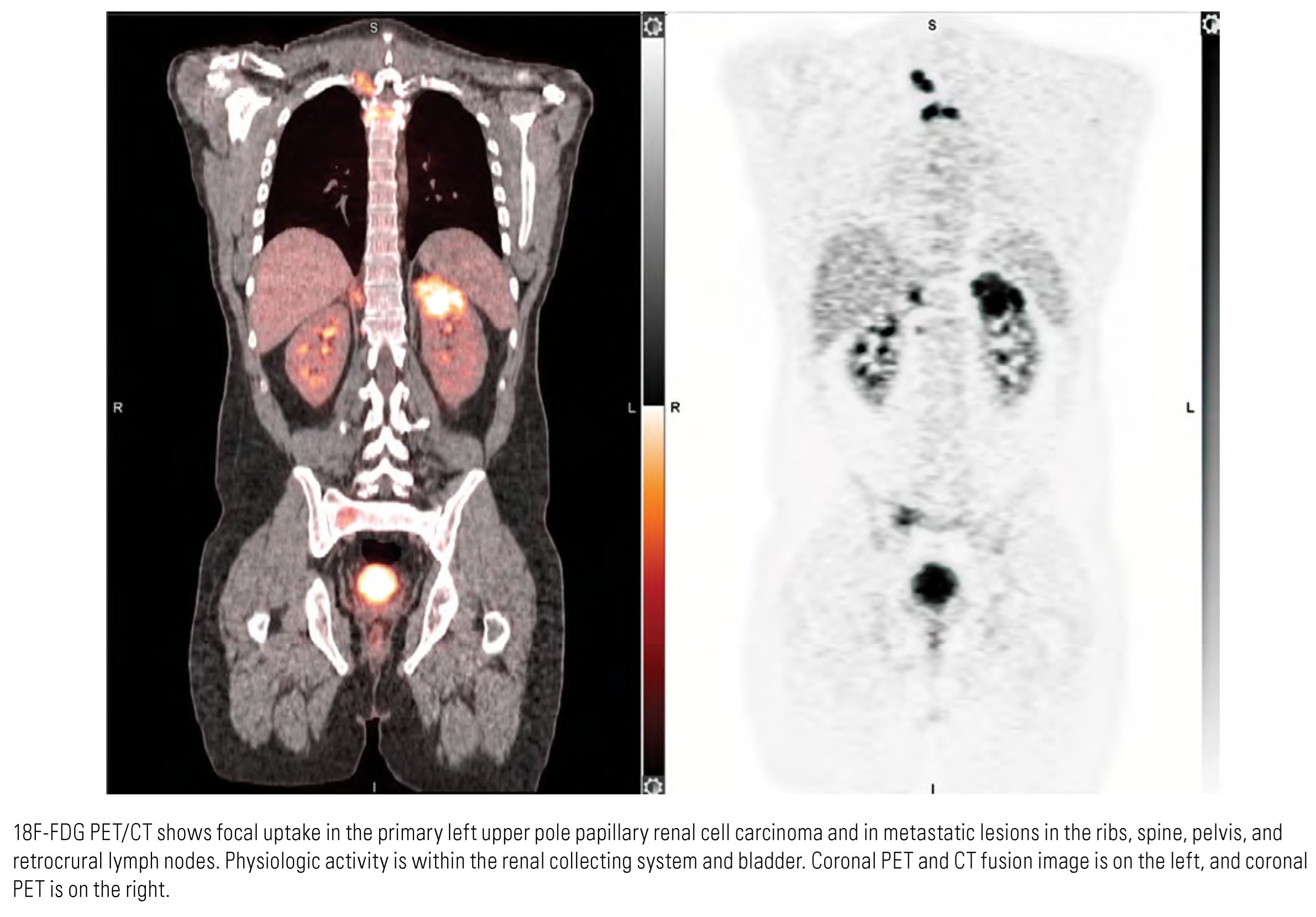
Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma
Differentiation of RCC from Benign Renal Tumors
Differentiation of Subtypes of RCC
Grading of RCC
Staging
Evaluation of Primary Tumor
Evaluation of Nodes and Distant Metastases
Imaging in Follow-Up
Imaging-Assisted Interventions
Future Directions
Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AML | angiomyolipoma |
| AUA | American Urological Association |
| CAIX | carbonic anhydrase IX |
| ccRCC | clear cell renal cell carcinoma |
| CEUS | contrast-enhanced US |
| chRCC | chromophobe renal cell carcinoma |
| CT | computed tomography |
| FDG | 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| PET/CT | positron emission tomography/computed tomography |
| pRCC | papillary renal cell carcinoma |
| PSMA | prostate-specific membrane antigen |
| RCC | renal cell carcinoma |
| SUVmax | maximum standardized uptake value |
| US | ultrasound |
References
- Moch, H.; Cubilla, A.L.; Humphrey, P.A.; Reuter, V.E.; Ulbright, T.M. The 2016 WHO classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs – Part A: renal, penile, and testicular tumours. Eur Urol. 2016, 70, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.J.; Nikolaidis, P.; Khatri, G.; Dogra, V.S.; Ganeshan, D.; Goldfarb, S.; et al. ACR appropriateness criteria® indeterminate renal mass. J Am Coll Radiol. 2020, 17, S415–S428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, C.; Ziegelmuller, B.; Ljungberg, B.; Bensalah, K.; Bex, A.; Canfield, S.; et al. Imaging in suspected renal-cell carcinoma: systematic review. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2019, 17, e345–e355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.Y.; Lu, Q.; Huang, B.J.; Ma, J.J.; Yan, L.X.; Wen, J.X.; et al. Contrast- enhanced ultrasonography for evaluation of cystic renal mass: in comparison to contrast-enhanced CT and conventional ultrasound. Abdom Imaging. 2014, 39, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.K.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.H.; Ko, K.; Lee, H.M.; Choi, H.Y. Assessment of cystic renal masses based on Bosniak classification: comparison of CT and contrast-enhanced US. Eur J Radiol. 2007, 61, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantisani, V.; Bertolotto, M.; Clevert, D.A.; Correas, J.M.; Drudi, F.M.; Fischer, T.; et al. EFSUMB 2020 proposal for a contrast-enhanced ultrasound- adapted Bosniak cyst categorization – position statement. Ultraschall Med. 2021, 42, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, S.C.; Clark, P.E.; Chang, S.S.; Karam, J.A.; Souter, L.; Uzzo, R.G. Renal mass and localized renal cancer: evaluation, management, and follow-up: AUA guideline: Part I. J Urol. 2021, 206, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungberg, B.; Albiges, L.; Abu-Ghanem, Y.; Bedke, J.; Capitanio, U.; Dabestani, S.; et al. European association of urology guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: the 2022 update. Eur Urol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Jonasch, E.; Agarwal, N.; Alva, A.; Baine, M.; Beckermann, K.; et al. Kidney cancer, version 3.2022, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2022, 20, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, R.; Narain, T.A.; Singh, U.P.; Srivastava, A. Role of positron emission tomography/computed tomography in the evaluation of renal cell carcinoma. Indian J Urol. 2021, 37, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgan, C.M.; Sanyal, R.; Lockhart, M.E. Ultrasound of renal masses. Radiol Clin North Am. 2019, 57, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, M.; King, K.G.; Gill, I.S.; Pham, V.; Grant, E.; Duddalwar, V.A. Contrast- enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) of cystic and solid renal lesions: a review. Abdom Imaging. 2015, 40, 1982–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, K.G. Use of contrast ultrasound for renal mass evaluation. Radiol Clin North Am. 2020, 58, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.R.; Ngo, L.; Genega, E.M.; Atkins, M.B.; Finn, M.E.; Rofsky, N.M.; et al. Renal cell carcinoma: dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging for differentiation of tumor subtypes – correlation with pathologic findings. Radiology. 2009, 250, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, M.R.; Glickman, J.N.; Zou, K.H.; Teo, S.Y.; Mortele, K.J.; Rocha, M.S.; et al. Renal cell carcinoma: t1 and t2 signal intensity characteristics of papillary and clear cell types correlated with pathology. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009, 192, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eilenberg, S.S.; Lee, J.K.; Brown, J.; Mirowitz, S.A.; Tartar, V.M. Renal masses: evaluation with gradient-echo Gd-DTPA-enhanced dynamic MR imaging. Radiology. 1990, 176, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlo, C.A.; Donati, O.F.; Burger, I.A.; Zheng, J.; Moskowitz, C.S.; Hricak, H.; et al. MR imaging of renal cortical tumours: qualitative and quantitative chemical shift imaging parameters. Eur Radiol. 2013, 23, 1738–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsili, A.C.; Argyropoulou, M.I.; Gousia, A.; Kalef-Ezra, J.; Sofikitis, N.; Malamou- Mitsi, V.; et al. Renal cell carcinoma: value of multiphase MDCT with multiplanar reformations in the detection of pseudocapsule. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012, 199, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, C.; El Ghali, S.; Buy, X.; Lindner, V.; Lang, H.; Saussine, C.; et al. Significance of the pseudocapsule on MRI of renal neoplasms and its potential application for local staging: a retrospective study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005, 184, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Kim, T.K.; Ahn, H.J.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, K.R.; Cho, K.S. Differentiation of subtypes of renal cell carcinoma on helical CT scans. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002, 178, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvidat, C.; Eiss, D.; Verkarre, V.; Merran, S.; Correas, J.M.; Mejean, A.; et al. Renal papillary carcinoma: CT and MRI features. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2014, 95, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimitsu, K.; Kakihara, D.; Irie, H.; Tajima, T.; Nishie, A.; Asayama, Y.; et al. Papillary renal carcinoma: diagnostic approach by chemical shift gradient-echo and echo-planar MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2006, 23, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, I.; Sun, M.R.; Spencer, M.; Genega, E.M.; Olumi, A.F.; Dewolf, W.C.; et al. MR imaging of renal masses: correlation with findings at surgery and pathologic analysis. Radiographics. 2008, 28, 985–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egbert, N.D.; Caoili, E.M.; Cohan, R.H.; Davenport, M.S.; Francis, I.R.; Kunju, L.P.; et al. Differentiation of papillary renal cell carcinoma subtypes on CT and MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013, 201, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Hindman, N.; Fitzgerald, E.F.; Niver, B.E.; Melamed, J.; Babb, J.S. MRI features of renal oncocytoma and chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010, 195, W421–W427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, S.P.; Johnson, P.T.; Allaf, M.E.; Netto, G.; Fishman, E.K. Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma: multiphase MDCT enhancement patterns and morphologic features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013, 201, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, W.; Chen, W.; Wang, S. Comparative study of CT appearances in renal oncocytoma and chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Acta Radiol. 2016, 57, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monn, M.F.; Gellhaus, P.T.; Patel, A.A.; Masterson, T.A.; Tann, M.; Boris, R.S. Can radiologists and urologists reliably determine renal mass histology using standard preoperative computed tomography imaging? J Endourol. 2015, 29, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesavre, A.; Correas, J.M.; Merran, S.; Grenier, N.; Vieillefond, A.; Helenon, O. CT of papillary renal cell carcinomas with cholesterol necrosis mimicking angiomyolipomas. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003, 181, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindman, N.; Ngo, L.; Genega, E.M.; Melamed, J.; Wei, J.; Braza, J.M.; et al. Angiomyolipoma with minimal fat: can it be differentiated from clear cell renal cell carcinoma by using standard MR techniques? Radiology. 2012, 265, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilauro, M.; Quon, M.; McInnes, M.D.; Vakili, M.; Chung, A.; Flood, T.A.; et al. Comparison of contrast-enhanced multiphase renal protocol CT versus MRI for diagnosis of papillary renal cell carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016, 206, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasiwimonphan, K.; Takahashi, N.; Leibovich, B.C.; Carter, R.E.; Atwell, T.D.; Kawashima, A. Small (<4cm) renal mass: differentiation of angiomyolipoma without visible fat from renal cell carcinoma utilizing MR imaging. Radiology. 2012, 263, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galmiche, C.; Bernhard, J.C.; Yacoub, M.; Ravaud, A.; Grenier, N.; Cornelis, F. Is multiparametric MRI useful for differentiating oncocytomas from chromophobe renal cell carcinomas? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017, 208, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee-Felker, S.A.; Felker, E.R.; Tan, N.; Margolis, D.J.A.; Young, J.R.; Sayre, J.; et al. Qualitative and quantitative MDCT features for differentiating clear cell renal cell carcinoma from other solid renal cortical masses. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014, 203, W516–W524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.R.; Coy, H.; Kim, H.J.; Douek, M.; Lo, P.; Pantuck, A.J.; et al. Performance of relative enhancement on multiphasic MRI for the differentiation of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) from papillary and chromophobe RCC subtypes and oncocytoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017, 208, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.K.; Zhang, A.; Pandharipande, P.V.; Chandarana, H.; Braithwaite, R.S.; Littenberg, B. DWI for renal mass characterization: systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test performance. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015, 205, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Y.; et al. Angiomyolipoma with minimal fat: differentiation from clear cell carcinoma by texture analysis on CT images. Acad Radiol. 2015, 22, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, F.U.; Canvasser, N.E.; Xi, Y.; Pinho, D.F.; Costa, D.N.; Diaz de Leon, A.; et al. Diagnostic performance and interreader agreement of a standardized MR imaging approach in the prediction of small renal mass histology. Radiology. 2018, 287, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, E.; Capitanio, U.; Kutikov, A.; Oosterwijk, E.; Pedrosa, I.; Rowe, S.P.; et al. Novel imaging methods for renal mass characterization: a collaborative review. Eur Urol. 2022, 81, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Huo, L.; Li, F.; et al. Clinical utility of FDG PET/CT for primary and recurrent papillary renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Imaging. 2021, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikpanah, M.; Paschall, A.K.; Ahlman, M.A.; Civelek, A.C.; Farhadi, F.; Mirmomen, S.M.; et al. 18Fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography for differentiation of renal tumors in hereditary kidney cancer syndromes. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021, 46, 3301–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, R.; Abe, K.; Kondo, T.; Tanabe, K.; Sakai, S. Clinical role of early dynamic FDG-PET/CT for the evaluation of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Radiol. 2016, 26, 1852–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, R.; Nozaki, S.; Kondo, T.; Nagashima, Y.; Abe, K.; Sakai, S. Evaluation of renal cell carcinoma histological subtype and Fuhrman grade using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/ computed tomography. Eur Radiol. 2017, 27, 4866–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficarra, V.; Righetti, R.; Martignoni, G.; D’Amico, A.; Pilloni, S.; Rubilotta, E.; et al. Prognostic value of renal cell carcinoma nuclear grading: multivariate analysis of 333 cases. Urol Int. 2001, 67, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, I.; Chou, M.T.; Ngo, L.; Baroni, R.H.; Genega, E.M.; Galaburda, L.; et al. MR classification of renal masses with pathologic correlation. Eur Radiol. 2008, 18, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelis, F.; Tricaud, E.; Lasserre, A.S.; Petitpierre, F.; Bernhard, J.C.; Le Bras, Y.; et al. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for the differentiation of low and high grade clear cell renal carcinoma. Eur Radiol. 2015, 25, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schieda, N.; Thornhill, R.E.; Al-Subhi, M.; McInnes, M.D.; Shabana, W.M.; van der Pol, C.B.; et al. Diagnosis of sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma with CT: evaluation by qualitative imaging features and texture analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.R.; Young, J.A.; Margolis, D.J.A.; Sauk, S.; Sayre, J.; Pantuck, A.J.; et al. Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma and collecting duct carcinoma: discrimination from common renal cell carcinoma subtypes and benign RCC mimics on multiphasic MDCT. Acad Radiol. 2017, 24, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindman, N.M.; Bosniak, M.A.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Lee-Felker, S.; Melamed, J. Multilocular cystic renal cell carcinoma: comparison of imaging and pathologic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012, 198, W20–W26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, S.; Zuo, C.; Ren, F. FDG PET/CT and CT findings of renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Arora, G.; Nayak, B.; Sharma, A.; Singh, G.; Kumari, K.; et al. Semi- quantitative F-18-FDG PET/computed tomography parameters for prediction of grade in patients with renal cell carcinoma and the incremental value of diuretics. Nucl Med Commun. 2020, 41, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, W.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Liao, X.; et al. 2-[18F]FDG PET/CT parameters associated with WHO/ISUP grade in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021, 48, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coy, H.; Young, J.R.; Pantuck, A.J.; Douek, M.L.; Sisk, A.; Magyar, C.; et al. Association of tumor grade, enhancement on multiphasic CT and microvessel density in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2020, 45, 3184–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.; Suh, C.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, S.H. Diagnostic performance of DWI for differentiating high- from low-grade clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017, 209, W374–W381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, E.; Li, Z.; Ma, C.; Li, Q.; Lei, Y.; Lan, Y.; et al. Predicting the ISUP grade of clear cell renal cell carcinoma with multiparametric MR and multiphase CT radiomics. Eur Radiol. 2020, 30, 2912–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, H.; Han, W.; Wang, M.; et al. 18F-FDG texture analysis predicts the pathological Fuhrman nuclear grade of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021, 46, 5618–5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.B. AJCC Cancer staging manual, 8th Edition. Springer Nature Switzerland AG; 2017.
- Vikram, R.; Beland, M.D.; Blaufox, M.D.; Moreno, C.C.; Gore, J.L.; Harvin, H.J.; et al. ACR appropriateness criteria renal cell carcinoma staging. J Am Coll Radiol. 2016, 13, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallscheidt, P.J.; Bock, M.; Riedasch, G.; Zuna, I.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Autschbach, F.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of staging renal cell carcinomas using multidetector-row computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging: a prospective study with histopathologic correlation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2004, 28, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, C.; Kruessell, M.; Gindele, A.; Brochhagen, H.G.; Gossmann, A.; Landwehr, P. Imaging of renal lesions: evaluation of fast MRI and helical CT. Br J Radiol. 2003, 76, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.C.; Uzzo, R.G.; Karam, J.A.; Chang, S.S.; Clark, P.E.; Souter, L. Renal mass and localized renal cancer: evaluation, management, and follow- up: AUA guideline: Part II. J Urol. 2021, 206, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerety, E.L.; Lawrence, E.M.; Wason, J.; Yan, H.; Hilborne, S.; Buscombe, J.; et al. Prospective study evaluating the relative sensitivity of 18F-NaF PET/CT for detecting skeletal metastases from renal cell carcinoma in comparison to multidetector CT and 99mTc-MDP bone scintigraphy, using an adaptive trial design. Ann Oncol. 2015, 26, 2113–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkassem, A.A.; Allen, B.C.; Sharbidre, K.G.; Rais-Bahrami, S.; Smith, A.D. Update on the role of imaging in clinical staging and restaging of renal cell carcinoma based on the AJCC 8th edition, from the AJR special series on cancer staging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021, 217, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffrey, N.N.; Douek, N.; Guo, D.Y.; Patel, M.I. Discrepancy between radiological and pathological size of renal masses. BMC Urol. 2011, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolster, F.; Durcan, L.; Barrett, C.; Lawler, L.P.; Cronin, C.G. Renal cell carcinoma; accuracy of multidetector computed tomography in the assessment of renal sinus fat invasion. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2016, 40, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, A.; Yoshida, K.; Obokata, M.; Inoue, D.; Yoneda, N.; Kadono, Y.; et al. Urinary collecting system invasion on multiphasic CT in renal cell carcinomas: prevalence, characteristics, and clinical significance. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021, 46, 2090–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedgire, S.S.; Elmi, A.; Nadkarni, N.D.; Cao, K.; McDermott, S.; Harisinghani, M.G. Preoperative evaluation of perinephric fat invasion in patients with renal cell carcinoma: correlation with pathological findings. Clin Imaging. 2013, 37, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, M.; Sun, M.; Jeldres, C.; Shariat, S.F.; Trinh, Q.D.; Briganti, A.; et al. Distribution of metastatic sites in renal cell carcinoma: a population- based analysis. Ann Oncol. 2012, 23, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, N.; Gore, M.E.; Sohaib, S.A. Imaging in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007, 189, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, A.; Ravery, V. European Society of Oncological Urology. Preoperative imaging in renal cell cancer. World J Urol. 2004, 22, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadayoni, A.; Paschall, A.K.; Malayeri, A.A. Assessing lymph node status in patients with kidney cancer. Transl Androl Urol. 2018, 7, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungberg, B.; Alamdari, F.I.; Rasmuson, T.; Roos, G. Follow-up guidelines for nonmetastatic renal cell carcinoma based on the occurrence of metastases after radical nephrectomy. BJU Int. 1999, 84, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, S.H.; Prezzi, D.; Kelly-Morland, C.; Goh, V. Imaging for the diagnosis and response assessment of renal tumours. World J Urol. 2018, 36, 1927–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Shen, G.; Liu, B.; Yang, Y.; Ren, P.; Kuang, A. Diagnostic performance of 18F-FDG PET or PET/CT in restaging renal cell carcinoma: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Nucl Med Commun. 2017, 38, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, S. Role of F-18 FDG PET/CT in the follow-up of asymptomatic renal cell carcinoma patients for postoperative surveillance: based on conditional survival analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022, 148, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alongi, P.; Picchio, M.; Zattoni, F.; Spallino, M.; Gianolli, L.; Saladini, G.; et al. Recurrent renal cell carcinoma: clinical and prognostic value of FDG PET/CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016, 43, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayani, I.; Avril, N.; Bomanji, J.; Chowdhury, S.; Rockall, A.; Sahdev, A.; et al. Sequential FDG-PET/CT as a biomarker of response to sunitinib in metastatic clear cell renal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6021–6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamimoto, R.; Barkhodari, A.; Harshman, L.; Srinivas, S.; Quon, A. Prognostic value of quantitative metabolic metrics on baseline pre-sunitinib FDG PET/CT in advanced renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 2016, 11, e0153321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Cho, A.; Yun, M.; Choi, Y.D.; Rha, S.Y.; Kang, W.J. Prognostic value of pretreatment metabolic tumor volume and total lesion glycolysis using 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor- targeted agents. Clin Nucl Med. 2017, 42, e235–e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, P.R.; Wei, W.; Ernst, R.D.; Bathala, T.K.; Reading, R.M.; Wood, C.G.; et al. Intraoperative sonography during open partial nephrectomy for renal cell cancer: does it alter surgical management? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014, 203, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, N.; Luo, Y.; Yu, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Role of intraoperative ultrasound in robotic-assisted radical nephrectomy with inferior vena cava thrombectomy in renal cell carcinoma. World J Urol. 2020, 38, 3191–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, N.; Bjurlin, M.A.; Rostami, P.; Chandarana, H.; Huang, W.C. Three- dimensional printing and augmented reality: enhanced precision for robotic assisted partial nephrectomy. Urology. 2018, 116, 227–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, J.C.; Isotani, S.; Matsugasumi, T.; Duddalwar, V.; Hung, A.J.; Suer, E.; et al. Personalized 3D printed model of kidney and tumor anatomy: a useful tool for patient education. World J Urol. 2016, 34, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campi, R.; Stewart, G.D.; Staehler, M.; Dabestani, S.; Kuczyk, M.A.; Shuch, B.M.; et al. Novel liquid biomarkers and innovative imaging for kidney cancer diagnosis: what can be implemented in our practice today? A systematic review of the literature. Eur Urol Oncol. 2021, 4, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussel, E.; Capitanio, U.; Kutikov, A.; Oosterwijk, E.; Pedrosa, I.; Rowe, S.P.; et al. Novel imaging methods for renal mass characterization: a collaborative review. Eur Urol. 2022, 81, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagreiya, H.; Akhbardeh, A.; Li, D.; Sigrist, R.; Chung, B.I.; Sonn, G.A.; et al. Point shear wave elastography using machine learning to differentiate renal cell carcinoma and angiomyolipoma. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019, 45, 1944–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Kang, Q.; Xu, B.; Shi, Z.; Guo, H.; Wei, Q.; et al. Fat poor angiomyolipoma differentiation from renal cell carcinoma at 320-slice dynamic volume CT perfusion. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018, 43, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Huang, X.; Bai, L.; Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Zhou, J. Differential diagnosis of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma and papillary renal cell carcinoma with dual-energy spectral computed tomography. Acta Radiol. 2020, 61, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; et al. Analysis of dual energy spectral CT and pathological grading of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). PLoS One. 2018, 13, e0195699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoharan, D.; Netaji, A.; Diwan, K.; Sharma, S. Normalized dual-energy iodine ratio best differentiates renal cell carcinoma subtypes among quantitative imaging biomarkers from perfusion CT and dual-energy CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Wiele, C.; Sathekge, M.; de Spiegeleer, B.; de Jonghe, P.J.; Beels, L.; Maes, A. PSMA-targeting positron emission agents for imaging solid tumors other than non-prostate carcinoma: a systematic review. Int J Mol Sci. 2019, 20, 4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Yu, H.; Wu, Y.; Lin, M.; Gao, J.; et al. Comparison of 18F-DCFPyL and 18F-FDG PET/computed tomography for the restaging of clear cell carcinoma: preliminary results of 15 patients. Nucl Med Commun. 2020, 41, 1299–12305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkx, R.I.J.; Lobeek, D.; Konijnenberg, M.; Jimenez-Franco, L.D.; Kluge, A.; Oosterwijk, E.; et al. Phase I study to assess safety, biodistribution and radiation dosimetry for 89Zr-girentuximab in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021, 48, 3277–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoeff, S.R.; van Es, S.C.; Boon, E.; van Helden, E.; Angus, L.; Elias, S.G.; et al. Lesion detection by [89Zr]Zr-DFO-girentuximab and [18F]FDG-PET/ CT in patients with newly diagnosed metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019, 46, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muselaers, C.H.J.; Boers-Sonderen, M.J.; van Oostenbrugge, T.J.; Boerman, O.C.; Desar, I.M.E.; Stillebroer, A.B.; et al. Phase 2 study of lutetium 177-labeled anti-carbonic anhydrase IX monoclonal antibody girentuximab in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2016, 69, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.P.; Katlariwala, P.; Murad, M.H.; Abele, J.; McInnes, M.D.F.; Low, G. Diagnostic accuracy of 99mTc-sestamibi SPECT/CT for detecting renal oncocytomas and other benign renal lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2020, 45, 2532–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Ibarrola, R.; Hein, S.; Reis, G.; Gratzke, C.; Miernik, A. Current and future applications of machine and deep learning in urology: a review of the literature on urolithiasis, renal cell carcinoma, and bladder and prostate cancer. World J Urol. 2020, 38, 2329–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coy, H.; Hsieh, K.; Wu, W.; Nagarajan, M.B.; Young, J.R.; Douek, M.L.; et al. Deep learning and radiomics: the utility of Google TensorFlowTM Inception in classifying clear cell renal cell carcinoma and oncocytoma on multiphasic CT. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2019, 44, 2009–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, F.Y.; Varghese, B.A.; Cen, S.Y.; Hwang, D.H.; Lei, X.; Desai, B.; et al. Shape and texture-based radiomics signature on CT effectively discriminates benign from malignant renal masses. Eur Radiol. 2021, 31, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, I.L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, R.; Chang, M.; Purkayastha, S.; Chang, K.; et al. Deep learning to distinguish benign from malignant renal lesions based on routine MR imaging. Clin Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1944–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendrami, C.L.; McCarthy, R.J.; Villavicencio, C.P.; Miller, F.H. Predicting common solid renal tumors using machine learning models of classification of radiologist-assessed magnetic resonance characteristics. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2020, 45, 2797–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.M.Y.; Shi, B.; Xue, H.D.; Ganeshan, B.; Sun, H.; Jin, Z.Y. Can quantitative CT texture analysis be used to differentiate subtypes of renal cell carcinoma? Clin Radiol. 2019, 74, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.; Li, N.; Niu, L.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Liu, F.; et al. CT texture analysis for the differentiation of papillary renal cell carcinoma subtypes. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2020, 45, 3860–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huhdanpaa, H.; Hwang, D.; Cen, S.; Quinn, B.; Nayyar, M.; Zhang, X.; et al. CT prediction of the Fuhrman grade of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC): towards the development of computer-assisted diagnostic method. Abdom Imaging. 2015, 40, 3168–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, J.; Wen, D.; Xi, Y.; Xia, Y.; Cai, Z.; Xu, W.; et al. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma: machine learning-based computed tomography radiomics analysis for the prediction of WHO/ISUP grade. Eur J Radiol. 2019, 121, 108738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bektas, C.T.; Kocak, B.; Yardimci, A.H.; Turkcanoglu, M.H.; Yucetas, U.; Koca, S.B.; et al. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma: machine learning-based quantitative computed tomography texture analysis for prediction of Fuhrman nuclear grade. Eur Radiol. 2019, 29, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinagare, A.B.; Vikram, R.; Jaffe, C.; Akin, O.; Kirby, J.; Huang, E.; et al. Radiogenomics of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: preliminary findings of the cancer genome atlas-renal cell carcinoma (TCGA-RCC) imaging research group. Abdom Imaging. 2015, 40, 1684–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlo, C.A.; Di Paolo, P.L.; Chaim, J.; Hakimi, A.A.; Ostrovnaya, I.; Russo, P.; et al. Radiogenomics of clear cell carcinoma: associations between CT imaging features and mutations. Radiology. 2014, 270, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursprung, S.; Beer, L.; Bruining, A.; Woitek, R.; Stewart, G.D.; Gallagher, F.A.; et al. Radiomics of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in renal cell carcinoma – a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol. 2020, 30, 3558–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
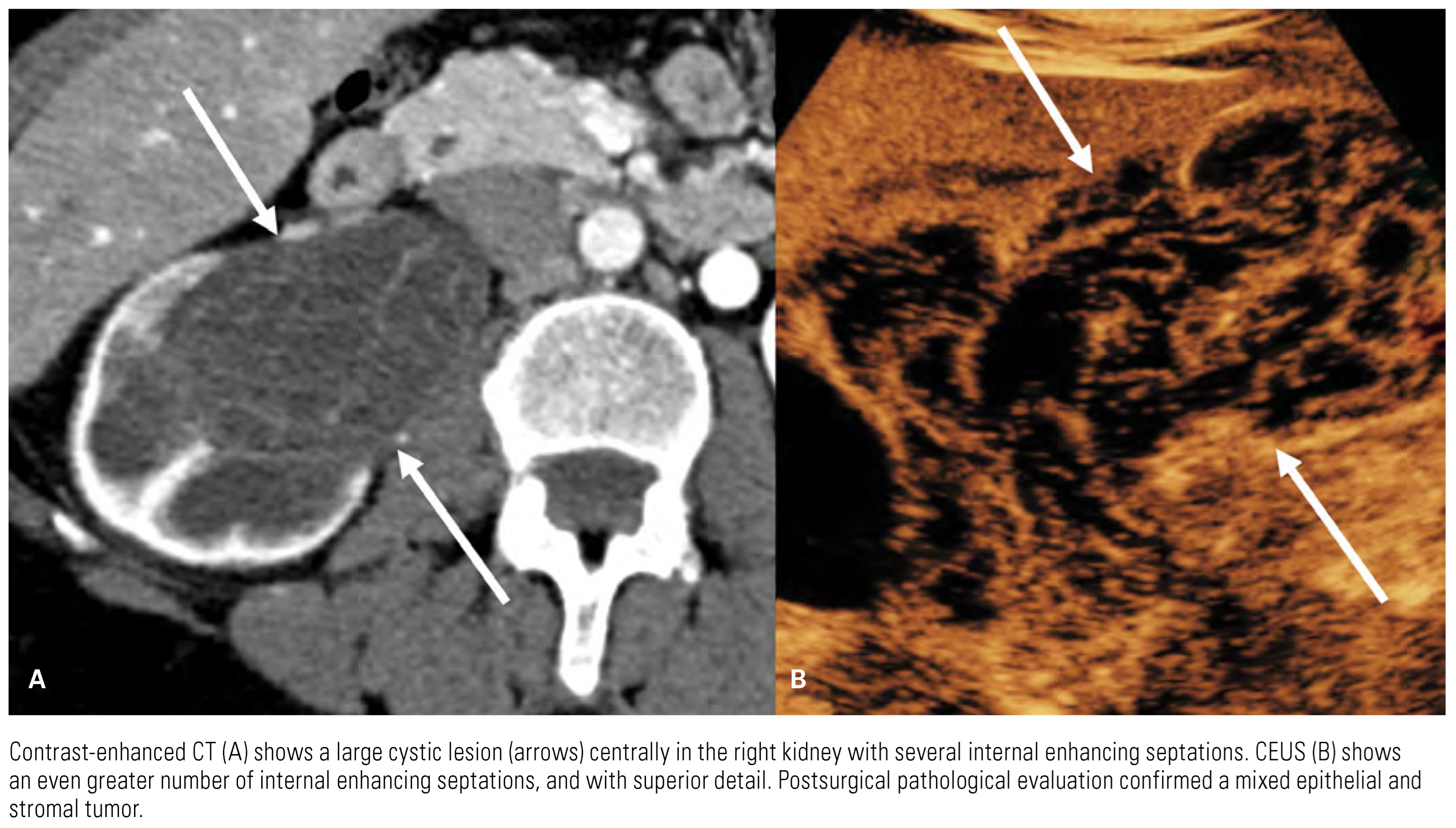
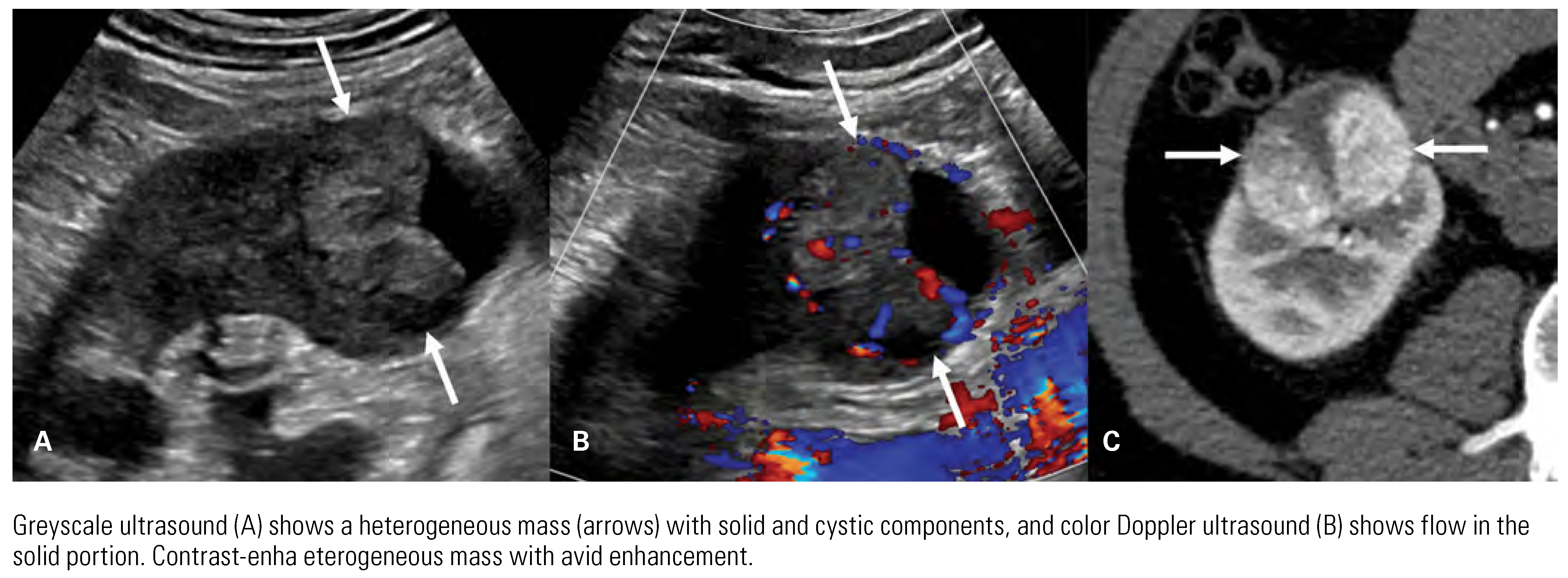


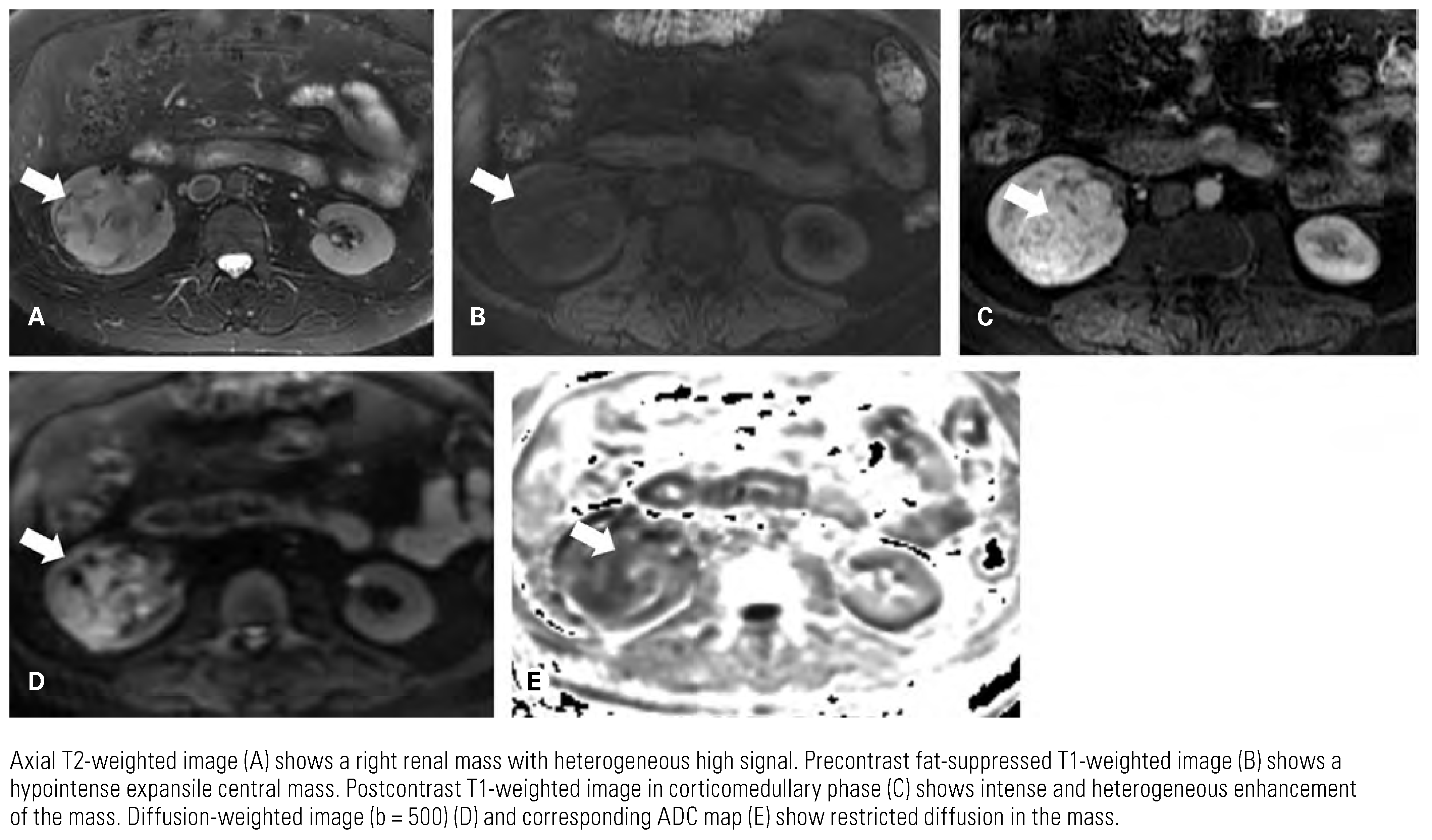
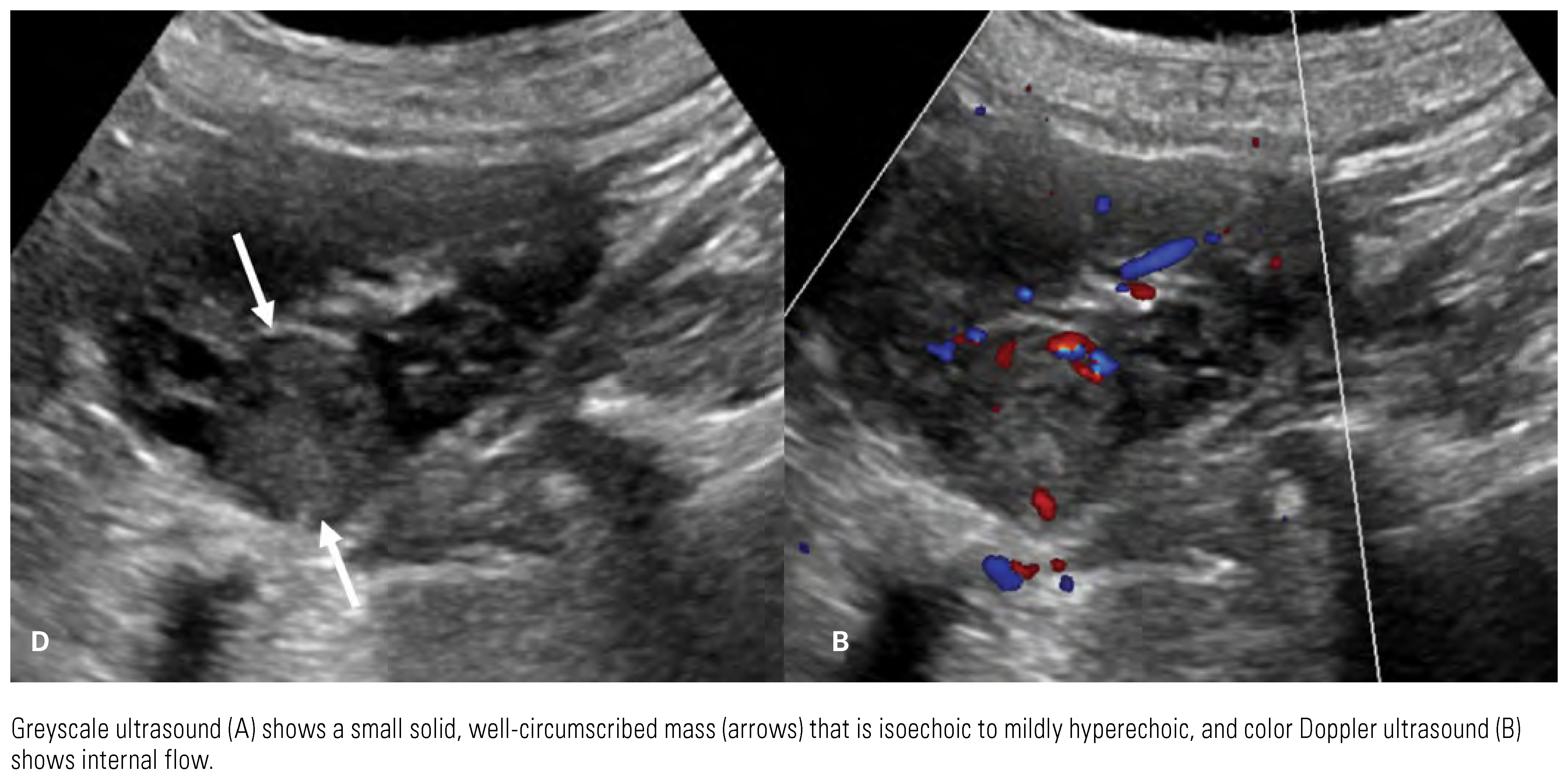

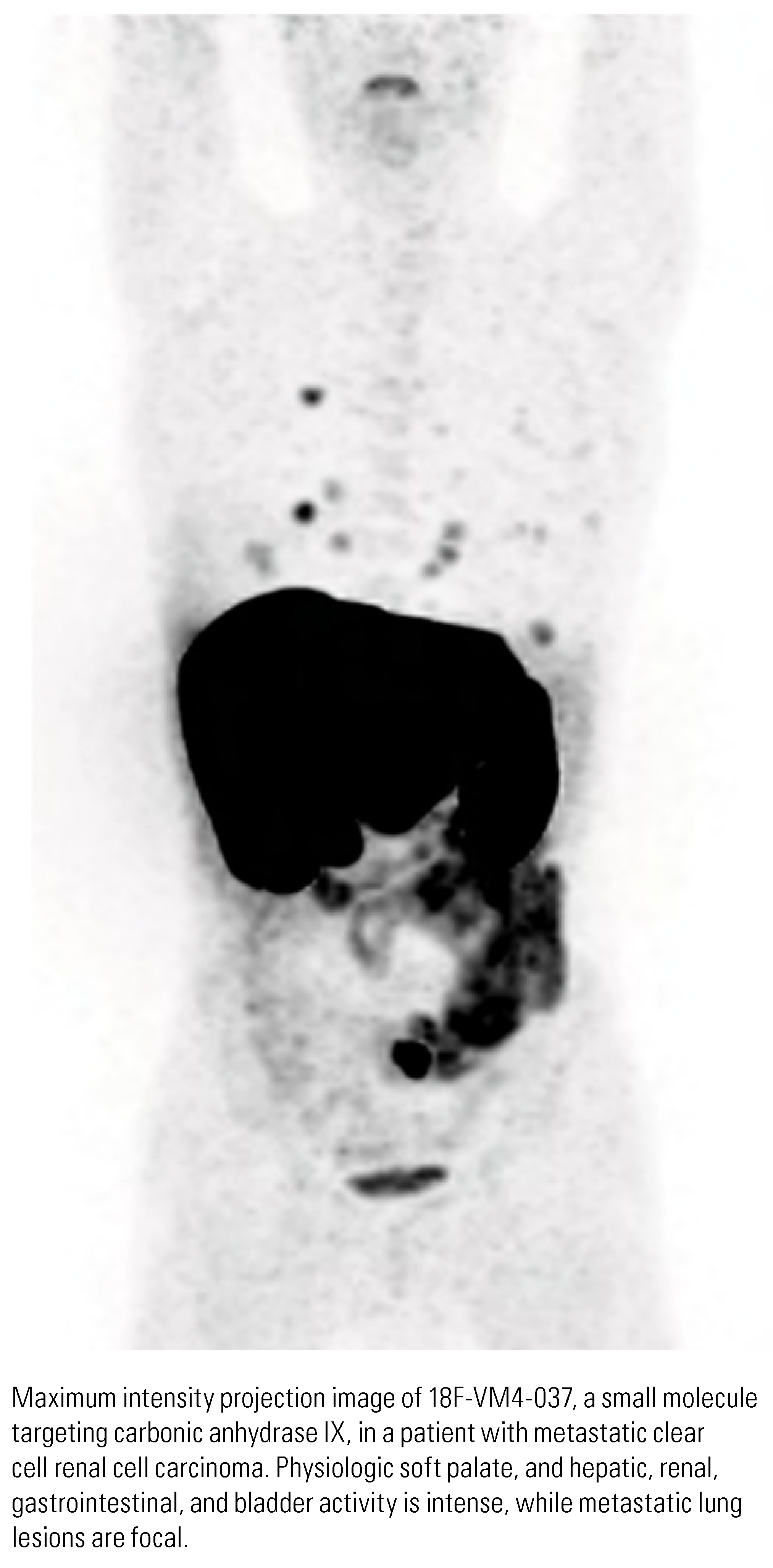
 |
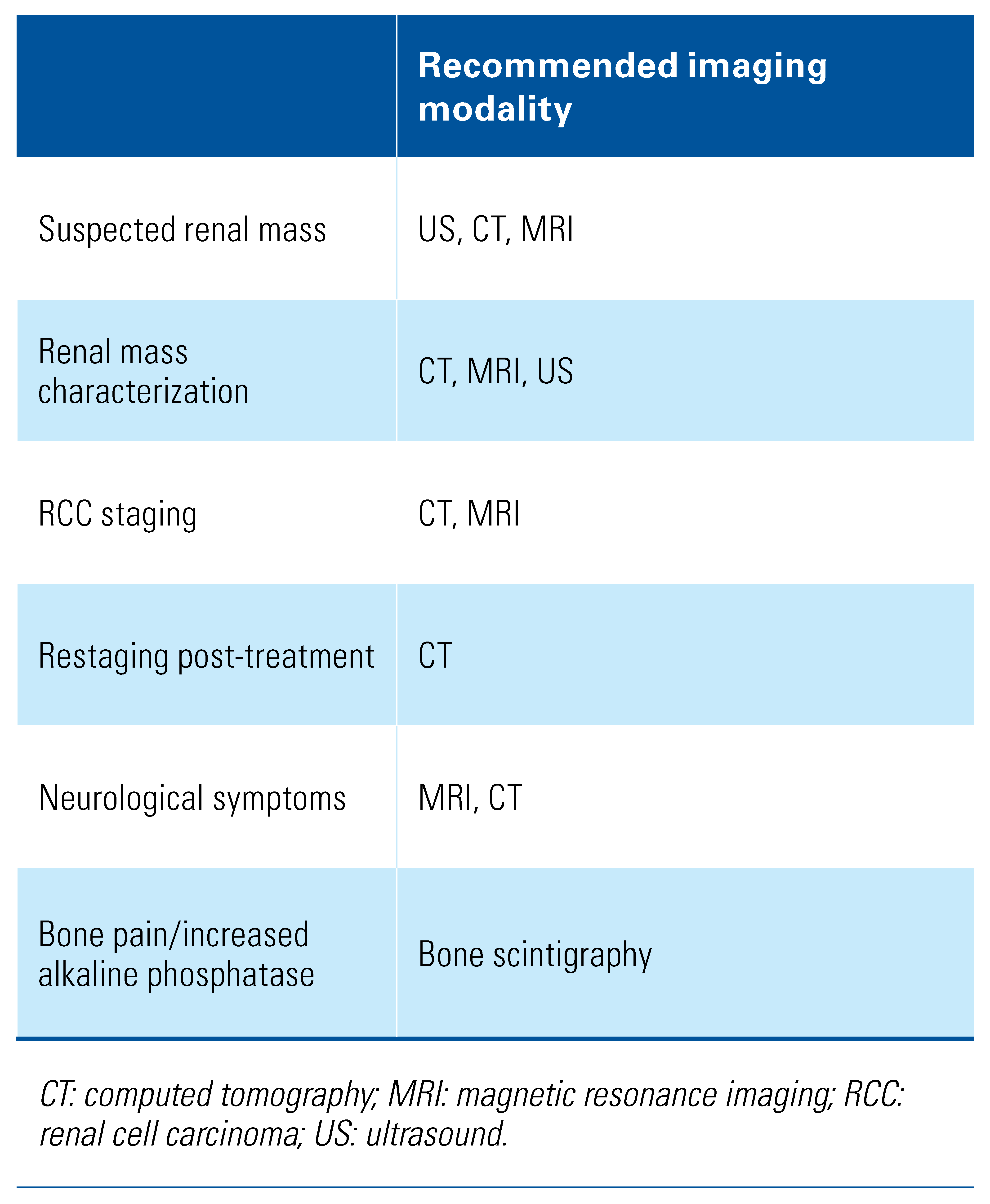 |
This is an open access article under the terms of a license that permits non-commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. © 2022 The Authors. Société Internationale d'Urologie Journal, published by the Société Internationale d'Urologie, Canada.
Share and Cite
Lee, W.-K.; Lindenberg, M.L.; Gonzalez, E.M.; Choyke, P.; King, K.G.; Vikram, R.; Duddalwar, V.A. 2022 WUOF/SIU International Consultation on Urological Diseases: Imaging of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Soc. Int. Urol. J. 2022, 3, 407-423. https://doi.org/10.48083/SDMV1045
Lee W-K, Lindenberg ML, Gonzalez EM, Choyke P, King KG, Vikram R, Duddalwar VA. 2022 WUOF/SIU International Consultation on Urological Diseases: Imaging of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Société Internationale d’Urologie Journal. 2022; 3(6):407-423. https://doi.org/10.48083/SDMV1045
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Wai-Kit, M. Liza Lindenberg, Esther Mena Gonzalez, Peter Choyke, Kevin G. King, Raghunandan Vikram, and Vinay A. Duddalwar. 2022. "2022 WUOF/SIU International Consultation on Urological Diseases: Imaging of Renal Cell Carcinoma" Société Internationale d’Urologie Journal 3, no. 6: 407-423. https://doi.org/10.48083/SDMV1045
APA StyleLee, W.-K., Lindenberg, M. L., Gonzalez, E. M., Choyke, P., King, K. G., Vikram, R., & Duddalwar, V. A. (2022). 2022 WUOF/SIU International Consultation on Urological Diseases: Imaging of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Société Internationale d’Urologie Journal, 3(6), 407-423. https://doi.org/10.48083/SDMV1045





