Abstract
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a heterogeneous syndrome estimated to affect approximately 10% to 15% of men and women globally. OAB not only negatively impacts quality of life but also results in a significant financial burden to both patients and health systems. Therefore, it is crucial that OAB is properly addressed. This manuscript provides a general review of the diagnostic algorithm for OAB and treatment per the AUA/SUFU guidelines, and an overview of new developments in OAB therapy. Given the wide array of therapeutic options that currently exist and those that are currently under development, there is tremendous opportunity to treat OAB successfully and positively affect our patients’ lives.
Introduction
Impact of Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder (OAB) affects approximately 10% to 15% of men and women, with some estimates placing prevalence as high as 27% for men and 43% for women [1,2,3]. Individuals with OAB have been shown to have poorer quality of life, higher rates of depression, and decreased rates of sexual fulfillment when compared with individuals who do not have OAB [4]. In a cohort of several North American and Western European nations, OAB-related expenses amounted to. €1.2 billion per year [5]. With the high prevalence of OAB, the aging population, and the associated cost to the system, proper management of OAB is essential. This manuscript provides an overview of current treatment options and a discussion regarding new developments in advanced therapies.
Defining Overactive Bladder
OAB was first described as a clinical entity in the late 1980s [6]. The American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine and Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) OAB guidelines acknowledge the challenges in defining OAB, as reflected by the number of statements that are based upon expert opinion rather than scientific publications. Joint work by the International Urogynecological Association (IUGA) and International Continence Society (ICS) defines OAB as “urinary urgency, usually accompanied by frequency and nocturia, with or without urgency urinary incontinence (UUI), in the absence of urinary tract infection (UTI) or other obvious pathology” [7]. Figure 1 shows an algorithm proposed by the authors to guide the evaluation of patients with OAB symptoms. While not a guideline, this pathway can offer clinicians, particularly those not familiar with OAB management, a structured approach to managing these patients.
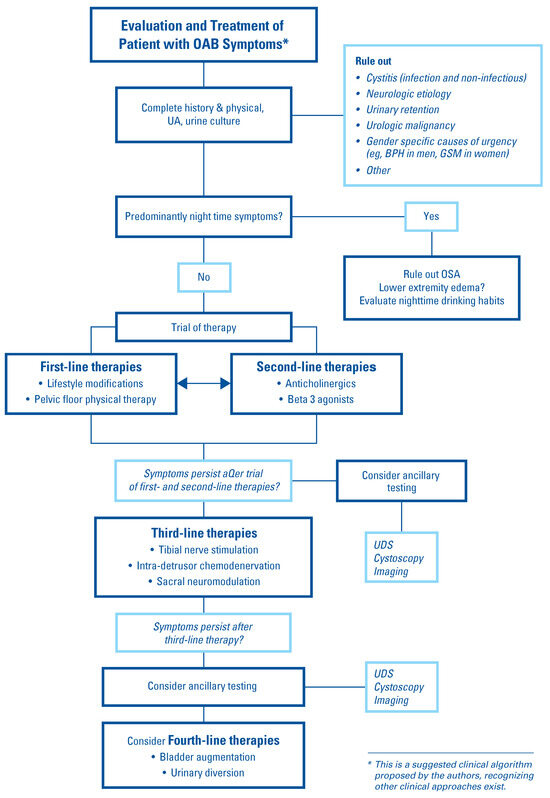
Figure 1.
Suggested clinical algorithm for management of OAB.
Methods
A comprehensive literature search was performed using PubMed regarding (1) the pathophysiology of OAB, (2) treatment options for OAB, and (3) special considerations with respect to OAB management. Approach to treatment is presented per the AUA/SUFU guidelines, summarizing lifestyle modifications (first- line), pharmacotherapy (second-line), and surgical and interventional therapies (third-line), and concluding with a discussion regarding new treatment developments in advanced therapies.
Pathophysiology
Several etiologies for OAB have been defined: (1) myogenic detrusor overactivity (DO), (2) overactive signaling by the central nervous system (CNS) causing micturition (neurogenic), and (3) alterations within the urothelium of the lower urinary tract [8,9]. The myogenic hypothesis attributes DO to changes within the bladder smooth muscle that result in increased excitability and spontaneous contraction [10]. In vivo tissue studies have suggested that structural changes within the detrusor muscle in OAB could allow for increased conduction of electrical impulses with resultant contraction among a large proportion of muscles cells [11].
In the neurogenic hypothesis, bladder overactivity is attributed to increased neuroplasticity within the CNS [12]. Maladaptive sensory signaling from pelvic sensory nerves can instigate DO and precipitate OAB [13]. Two neurotrophins, specifically brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and nerve growth factor (NGF), have been implicated in OAB. These are modulators of neural plasticity, and individuals with OAB symptoms have demonstrated detectable amounts of these molecules in their urine [14,15,16,17]. Additionally, individuals with OAB exhibit varying degrees of functional connectivity in the cortex on functional MRI (fMRI) studies [18,19], and interestingly, sacral neuromodulation has been demonstrated to cause cerebral activity on fMRI [20], emphasizing the role of CNS function in OAB.
Regarding the urothelial hypothesis, research in rat models indicates that chronic urothelial injury, as modeled by intravesical injection of protamine sulfate into rats, can cause increased urinary frequency and decreased voided volumes [21]. A related hypothesis postulates that OAB symptoms may also be urethrogenic, that is, arising from the urethra [22]. Specifically, low urethral tone and subsequent stress urinary incontinence (SUI) or contact of urine with the proximal urethra can stimulate the proximal urethral afferent nerves that can initiate micturition via the urethrovesical reflex and, in some cases, cause symptoms of OAB. Newer areas of exploration for OAB pathophysiology include the role of sex hormones, mood disorders, and the effect of the urinary microbiome [23].
OAB Treatment
Guidelines
The AUA/SUFU OAB guidelines provide a framework clinicians can use to diagnose and stratify patients with OAB. As acknowledged in the guidelines, there is a lack of evidence-based publications in the current literature regarding the diagnosis of OAB. A clinical principle in the guidelines suggests that the initial evaluation for uncomplicated OAB requires only a thorough history and physical examination and a urinalysis to rule out conditions that may mimic OAB, such as urinary tract infection or malignancy. Use of adjunct tests such as urine cultures or post-void residuals can be incorporated as deemed necessary. The guidelines also clarify that UDS, cystoscopy, and renal imaging are not indicated in the initial workup. Clinicians should also consider how OAB symptoms may manifest in select populations, such as men with benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) or women with genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM).
The guidelines stratify OAB treatment into several tiers: first-line (behavioral and non-pharmacologic), second-line (pharmacologic therapy), third-line (surgical and interventional therapies) and fourth-line (urinary diversion or bladder augmentation) [1]. This discussion focuses on the first 3 tiers.
First-Line Therapy
First-line therapy for OAB includes low-risk behavioral interventions, although much of the data supporting these therapies is drawn from non-randomized controlled trials (RCT). In a study of pelvic floor biofeedback for OAB symptoms in women, 9 weeks of EMG-based biofeedback for pelvic floor muscle therapy resulted in significant symptom improvement [24]. A review exploring the role of pelvic floor muscle therapy traditionally used for SUI found the use of similar regimens in patients who had urinary urgency and OAB symptoms effectively reduced symptoms [25].
In a comprehensive review regarding urinary symptoms in overweight and obese women, weight loss showed no benefit in the reduction of urinary urgency [26]. However, in a cohort of morbidly obese patients who underwent laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, patients experienced a significant improvement in OAB symptoms as measured by a 3-day voiding diary and improvement on the OAB short form questionnaire. The mean reduction in BMI following surgery was 9 kg/m2, suggesting that the magnitude of weight loss to reduce symptoms may be unattainable for many patients [27].
Smoking and dietary habits, particularly consumption of carbonated beverages, alcohol, and caffeine, can cause OAB symptoms. Accordingly, lifestyle modifications aimed at reducing smoking and dietary triggers can result in an improvement of OAB [28]. Finally, an association between functional constipation and OAB has been shown [29,30,31], but these studies do not specifically report on the effect of treating constipation and relief of OAB.
Second-Line Therapy
Anticholinergics
Anticholinergics are a well-established pharmacotherapy for OAB [1]. There are 5 described subtypes of muscarinic receptors, of which M2 and M3 are found in highest concentration within the bladder. While the M2 receptor is predominant in the bladder, the M3 receptors are most strongly associated with micturition control [32]. A review examining the effectiveness of anticholinergics versus behavioral therapy concluded that anticholinergics outperformed non-pharmacologic interventions for improvement in OAB symptoms [33].
While dry mouth and constipation are the most frequent side effects of anticholinergic medications, cognitive side effects can be profound, particularly amongst older individuals. The rates of discontinuation of anticholinergics in trial settings have been shown to be as high 80% [34]. In a case– control study conducted in the United Kingdom, anticholinergic exposure was associated with dose-dependent increased odds of developing dementia [35]. This relationship has been well documented and demonstrated, particularly in older individuals [36,37,38]. At a molecular level, trospium’s bulky quaternary amine structure limits its penetration across the blood–brain barrier, thereby reducing unwanted cognitive effects [39,40].
Beta-3 agonists
Beta-3 agonists represent a newer class of OAB medication. Studies have demonstrated that mirabegron is equally efficacious as anticholinergics in their reduction of OAB symptoms [41,42,43]. Potential side effects include hypertension and cardiac arrythmia [44]. In a study examining the safety profile of mirabegron, there was a slight increase in hypertension with this drug compared with placebo and only among individuals over 75 (7% versus 5%) [45]. The absence of hypertension risk has also been reaffirmed on meta-analysis [46]. In an observational study from the UK, improvements in both quality of life and health status were seen for patients on mirabegron, with over 50% persisting on the drug at 12 months [47].
Recently approved, vibegron is a novel beta-3 agonist that has also shown efficacy in placebo-controlled studies including reduction of micturition episodes and urge incontinence episodes [48,49]. Furthermore, recent RCT data showed no difference in the rates of hypertension between patients on vibegron versus placebo [50].
Despite a higher per-pill cost of beta-3 agonists, recent studies have demonstrated a similar cost-effectiveness between beta-3 agonists and anticholinergics. This increased cost-effectiveness has been attributed to decreased discontinuation of beta-3 agonists, leading to improved quality of life, decreased need for third-line therapies, and decreased health care use due to adverse events [51,52,53,54].
Third-Line Therapy
Third-line therapies represent a rapidly growing category of OAB treatment, although they remain underutilized [55]. Existing third-line therapies include bladder chemodenervation with onabotulinumtoxinA (BTX), percutaneous tibial nerve modulation (PTNM), and sacral neuromodulation (SNM).
Bladder chemodenervation with onabotulinumtoxinA
Chemodenervation involves the prevention of pre- synaptic release of acetylcholine (ACh) thereby averting excitation of ACh-dependent smooth muscle within the detrusor and reducing bladder contractions [56]. Data also suggest that the toxin may decrease sensory input during bladder filling via its effect on ATP-regulated signaling mechanisms [56,57,58].
BTX is administered cystoscopically with injections distributed throughout the bladder [59,60]. Complete resolution of urinary incontinence has been shown to be higher amongst those receiving BTX (27%) compared with those on anticholinergics (13%) [61]. BTX also outperforms placebo for the reduction of OAB symptoms, with 2.95 fewer daily UUI episodes compared with 1 fewer observed with a placebo after 12 weeks of treatment [58]. BTX injection also appears to be of therapeutic value for all patients with idiopathic OAB, regardless of whether DO is present on pretreatment urodynamics [62]. One of the potential risks of BTX is urinary retention. However, the definition of retention is not standardized across the BTX reports, and this has contributed to the widely variable (2% to 35%) rates reported in the literature. The risk of retention appears to be dose-dependent [63,64,65,66]. Studies have demonstrated a median of 7.6 months of symptom relief following BTX injection [67]. There are data suggesting that the production of neutralizing antibodies can result in tachyphylaxis with successive treatments with BTX. However, this risk has been drastically lowered with newer formulation of the toxin [68].
Percutaneous tibial nerve modulation
Performed in the clinic setting, PTNM involves 12 weekly in-office sessions during which a 34-gauge needle is placed cephalad to the medial malleolus and posterior to the tibia. The posterior tibial nerve is stimulated at varying frequencies with an external generator. The hypothesized mechanism of action involves modulation of bladder contraction via both afferent and efferent pathways of the tibial nerve [69,70].
PTNM has shown success in patients with refractory OAB. In a study of patients undergoing a 12-week study course, a 25% reduction in mean daytime urinary urgency, a 35% reduction in number UUI episodes, and a 21% reduction in nighttime frequency was reported [71]. Adverse effects of PTNM are rare and include bruising, pain, and bleeding at the needle site [59]. PTNM therefore remains a well-tolerated and efficacious option for the treatment of OAB. Despite this, there remains a high drop-out rate, with retrospective data indicating an over 40% discontinuation rate [72], similar to the drop-out rates reported with BTX. Only 40% to 60% of patients receive a second injection, with subsequent treatments decreasing even further [73,74,75].
The updated OAB guidelines include a specific statement that the guidelines do not represent a step- by-step algorithm that must be followed in successive order. Consequently, a study that showed success with PTNM in drug-naïve OAB patients was of interest. In a single-arm study of drug-naïve OAB patients with >3 UUI episodes a day, 78% of patients saw a 50% reduction in their UUI episodes, with 40% achieving complete continence [76].
Sacral neuromodulation
Sacral neuromodulation is an operative procedure, performed in 2 stages. During the first stage, a tined lead connected to an external generator is inserted into the S3 foramina. If the patient experiences a ≥ 50% improvement in their symptoms during the 1 to 2 week trial period, a permanent impulse generator (IPG) is inserted into a subcutaneous pocket low back/upper buttock [77]. Alternatively, the first stage can be done in the office setting as a peripheral nerve evaluation with temporary bilateral leads, with or without fluoroscopic guidance. If successful, the lead and IPG can subsequently be placed in a single procedure.
SNM has been shown to be well tolerated and more efficacious than standard medical therapy. In a study comparing SNM with anticholinergic medical therapy, 76% of the SNM arm experienced therapeutic success (≥ 50% improvement) compared with 49% of the medical arm [78]. While the ROSETTA trial suggested a slight advantage of BTX over SNM in reducing OAB symptoms, this trial used an unconventional 200-unit dose of BTX, as opposed to the accepted 100 units for idiopathic OAB [79]. This initial advantage of BTX was not noted at 2 years. In the 2-year follow-up, 72% of patients randomized to BTX had required a second injection, with half of these individuals requiring a third [80].
In a retrospective analysis of state claims data, 38% of all patients who undergo SNM implantation undergo a lead revision within 5 years of their initial lead implantation, approximately two-thirds for device malfunction and the remaining third for treatment failure [81]. Another consideration with SNM is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) compatibility. In mid-2020, a full-body MRI-compatible lead became FDA-approved and available for implantation; patients can safely undergo a full-body MRI with a 1.5 or 3 Tesla magnet for up to 30 minutes without a rest period. However, it is important to consider the implications of the leads placed before the availability of the new leads, with which patients should not undergo MRI below the neck. A review examining neuromodulation, both PTNS and SNM, for OAB found that overall SNM was both well tolerated and effective in improving OAB symptoms. There are no long-term data describing PTNS success against SNM [82].
New technologies in third-line therapy
New chemodenervation options are being studied. Data suggest that chimeric alternatives to the BTX toxin, such as the BoNT/BMY-WW toxin have stronger affinity for nerve terminal binding, which modulates bladder effects [83]. Intravesical instillation of BTX mixed with hydrogel to promote a slower release of drug without the need for injection has been demonstrated to be well tolerated in interstitial cystitis patients [84]. While BTX hydrogel is still in the trial phase as part of the APOLLO study, the potential to deliver BTX “topically” via urinary catheter as opposed to via cystoscopic injections could significantly enhance the ease of delivery [85].
New technologies for PTNM are also in development. The eCoin is an implantable device, approximately the size of a nickel, that is placed along the course of the patient’s posterior tibial nerve. It can be placed in the office setting and implantation minimizes the need for weekly visits. During clinical trials, 68% of subjects demonstrated at least 50% reduction in UUI episodes at 48 weeks [86]. Another investigational technology is the StimGuard device. An internal lead is placed near the posterior tibial nerve, which can be stimulated with an external device that remains with the patient. The ongoing PROTECT trial is a multicenter RCT designed to evaluate StimGuard for non-inferiority of versus traditional SNM for OAB [87].
While traditional SNM devices require a stepwise procedure to insert the leads and subsequently a permanent IPG, the AHLeveeS System from Neuspera Medical Inc. provides an alternative approach. This new device is a miniature implantable stimulator that can be placed into the S3 foramen and differs from the existing SNM technology in that in lieu of an internal IPG, the AHLeveeS System uses an external wireless generator. The use of this device in a small pilot study was seen to produce physiologic responses consistent with adequate stimulation of the S3 nerve root foramina, including bellows and great toe plantarflexion [88]. Table 1 shows the major third-line therapies and the corresponding emerging technologies for OAB.

Table 1.
Third-line therapies for OAB and future directions.
Definition of Success for Interventions
As the presentation of OAB is heterogenous, defining success in the management of OAB can be challenging. A systematic review published in 2014 sought to assess what current research uses to define success in OAB trials. In this review, number of UUI episodes was the most common metric used to assess treatment efficacy, with treatment response defined as a reduction in UUI episodes of between 50% and 100% from baseline. Other symptom-based markers of treatment response were number of urgency episodes per day, voids per day, and changes in urodynamic parameters [89]. The adoption of patient-reported outcomes (PROs) has increased in biomedical and clinical research, and PRO tools are now more commonly used in OAB research [90,91]. The use of PROs as opposed to disease-oriented or symptom-based endpoints can provide a standardized means of communicating symptoms between patients and their physicians in the preoperative setting, thereby facilitating improved expectation and goal-setting before medical or surgical intervention for OAB [92].
Special Clinical Considerations
Nocturia
Nocturia, defined as needing to awaken at least one or more times per night to void, is one of the most common lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) [93]. While nocturia can be related to urologic disorders such as OAB or BPH, a variety of non-urologic conditions can also cause nocturia. Among these are diabetes, heart failure, and sleep apnea [60,93,94]. In patients with nocturia-predominant OAB symptoms, urologists should investigate possible alternative diagnoses that may explain a patient’s symptoms. In patients with bothersome nocturia, 24-hour urine testing to evaluate for nocturnal polyuria should be considered, as should referral for sleep studies in patients who have a history of snoring or obstructive sleep apnea.
Considerations for Neurogenic Bladder
LUTS and OAB-like symptoms are highly prevalent in individuals with neurologic conditions, such as stroke or multiple sclerosis [95]. Up to 80% of MS patients will have bladder dysfunction in their lifetime, with 10% of all MS patients demonstrating urinary symptoms as the initial manifestation [96]. The approach to patients with neurogenic bladder can mirror the approach to those without neurologic disease, starting with first- and second-line therapies and escalating to advanced therapies [97]. Pharmacotherapy, particularly anticholinergics, have been shown efficacious in managing OAB amongst those with neurogenic bladder, although higher doses are often required [98]. While BTX is the only FDA-approved therapy for neurogenic bladder, it should be noted that some studies have demonstrated that neuromodulation provides benefit to neurogenic patients with refractory OAB [99].
Sex Differences in Overactive Bladder Management
The genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM), previously referred to as vulvovaginal atrophy, refers to all collective genitourinary symptoms associated with a decreasing level of estrogen in perimenopausal women [100]. Twenty percent of postmenopausal women report severe urinary urgency, and nearly 50% of these women have some form of urinary incontinence [101]. Both topical therapies, such as vaginal estrogen, and non-topical options, such as selective estrogen receptor modulators (ospemifene and lasofoxifene in particular), have been shown to improve urinary symptoms among women with GSM [99,100,102]. At the authors’ institutions, women with GSM and a history of breast or gynecological malignancy are frequently treated with local estrogen following consultation with their oncologist and shared-decision making with the patient.
While OAB prevalence is approximately equal between men and women, women are more likely to present with UUI [103]. As alluded to in the AUA/SUFU guidelines, men presenting with OAB-like symptoms should be screened for BPH [1]. However, OAB is still common among men with BPH, with up to 75% of men with BPH having clinical symptoms of OAB or DO on UDS [104]. Therefore, clinicians should consider a concomitant diagnosis of OAB in men with persistent LUTS despite treatment for BPH. In general, although sex-specific factors should be considered in any approach to OAB evaluation, treatment should be patient-specific based on both the presenting symptoms and patient goals of care.
Conclusions
OAB is a complex clinical syndrome that can have a serious impact on patient quality of life. From lifestyle modifications to implantable devices, the wide spectrum of available OAB therapies provides clinicians a large armamentarium to help alleviate OAB symptoms for their patients. This review explores various treatment modalities for OAB along with recent developments, with a particular emphasis on third-line therapies. Despite their high-efficacy rates compared to first- and second-line therapies, third-line treatments for OAB continue to be underutilized. In recent years, however, there has been a rapid growth and development of novel therapies. These new technologies allow for more patient-centered and tailored approaches to managing OAB symptoms, making it an exciting time to be a clinician treating OAB.
Conflicts of Interest
None declared.
Abbreviations
| AUA | American Urological Association |
| BPH | benign prostatic hypertrophy |
| BTX | onabotulinumtoxinA |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| DO | detrusor overactivity |
| GSM | genitourinary syndrome of menopause |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| OAB | overactive bladder |
| PRO | patient-reported outcomes |
| RCT | randomized control trial |
| SNM | sacral neuromodulation |
| SUFU | Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine, and Urogenital Reconstruction |
| SUI | stress urinary incontinence |
| UDS | urodynamics |
| US | ultrasound |
| UTI | urinary tract infection |
| UUI | urge urinary incontinence |
References
- Gormley, E.; Lightner, D.; Burgio, K.; Chai, T.; Clemens, J.; Culkin, D.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline. J Urol. 2012, 188 (Suppl. 6). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, D.; Milsom, I.; Hunskaar, S.; Reilly, K.; Kopp, Z.; Herschorn, S.; et al. Population-based survey of urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, and other lower urinary tract symptoms in five countries: Results of the EPIC study. Eur Urol. 2006, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, W.; Van Rooyen, J.; Cundiff, G.; Abrams, P.; Herzog, A.; Corey, R.; et al. Prevalence and burden of overactive bladder in the United States. World J Urol. 2003, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyne, K.; Sexton, C.; Irwin, D.; Kopp, Z.; Kelleher, C.; Milsom, I. The impact of overactive bladder, incontinence and other lower urinary tract symptoms on quality of life, work productivity, sexuality and emotional well-being in men and women: Results from the EPIC study. BJU Int. 2008, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, D.; Mungapen, L.; Milsom, I.; Kopp, Z.; Reeves, P.; Kelleher, C. The economic impact of overactive bladder syndrome in six Western countries. BJU Int. 2009, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikkinen, K.; Auvinen, A. Does the imprecise definition of overactive bladder serve commercial rather than patient interests? Eur Urol. 2012, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haylen, B.; de Ridder, D.; Freeman, R.; Swift, S.; Berghmans, B.; Lee, J.; et al. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for female pelvic floor dysfunction. Int Urogynecol J. 2010, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, E.; Lin, W.-Y.; Lee, W.-C.; Chuang, Y.-C. Pathophysiology of overactive bladder. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2012, 4, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wein, A.; Rackley, R. Overactive bladder: A better understanding of pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. J Urol. 2006, 175 Pt 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brading, A. A myogenic basis for the overactive bladder. Urology. 1997, 50 (Suppl. 6A). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haferkamp, A.; Dörsam, J.; Elbadawi, A. Ultrastructural diagnosis of neuropathic detrusor overactivity: Validation of a common myogenic mechanism. Adv Exp Med Biol. [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, N. Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and bladder afferent activity. Neurourol Urodyn. 2007, 26 (Suppl. 6). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, B.; Kosaka, A.; Knight, G.; Chang, T.; Ford, A.; Rymer, J.; et al. P2X receptors and their role in female idiopathic detrusor instability. J Urol. 2002, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes-Lopes, T.; Pinto, R.; Barros, S.C.; Botelho, F.; Silva, C.M.; Cruz, C.D.; et al. Urinary neurotrophic factors in healthy individuals and patients with overactive bladder. J Urol. 2013, 189, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochodnicky, P.; Cruz, C.D.; Yoshimura, N.; Cruz, F. Neurotrophins as regulators of urinary bladder function. Nat Rev Urol. 2012, 9, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, B.; Lopes, T.; Pinto, R.; Cruz, F.; Cruz, C. Neurotrophins in the lower urinary tract: Becoming of age. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2011, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes-Lopes, T.; Carvalho-Barros, S.; Cruz, C.-D.; Cruz, F.; Martins-Silva, C. Biomarkers in overactive bladder: A new objective and noninvasive tool? Adv Urol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zuo, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, B.; Gu, H. Intra- and inter-resting- state networks abnormalities in overactive bladder syndrome patients: An independent component analysis of resting-state fMRI. World J Urol. 2020, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, B.; Gu, H.; Chen, J. Abnormal brain functional connectivity strength in the overactive bladder syndrome: A resting-state fMRI study. Urology. 2019, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissbart, S.; Bhavsar, R.; Rao, H.; Wein, A.; Detre, J.; Arya, L.; et al. Specific changes in brain activity during urgency in women with overactive bladder after successful sacral neuromodulation: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Urol. 2018, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shioyama, R.; Aoki, Y.; Ito, H.; Matsuta, Y.; Nagase, K.; Oyama, N.; et al. Long-lasting breaches in the bladder epithelium lead to storage dysfunction with increase in bladder PGE2 levels in the rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008, 295, R714–R718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Fraser, M.; Ozawa, H.; Yokoyama, O.; Yoshiyama, M.; De Groat, W.; et al. Urethral afferent nerve activity affects the micturition reflex; implication for the relationship between stress incontinence and detrusor instability. J Urol. 1999, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyronnet, B.; Mironska, E.; Chapple, C.; Cardozo, L.; Oelke, M.; Dmochowski, R.; et al. A comprehensive review of overactive bladder pathophysiology: On the way to tailored treatment. Eur Urol. 2019, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voorham, J.; De Wachter, S.; Van den Bos, T.; Putter, H.; Lycklama À Nijeholt, G.; Voorham-van der Zalm, P. The effect of EMG biofeedback assisted pelvic floor muscle therapy on symptoms of the overactive bladder syndrome in women: A randomized controlled trial. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgio, K. Update on behavioral and physical therapies for incontinence and overactive bladder: The role of pelvic floor muscle training. Curr Urol Rep. 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdany, T.; Jakus-Waldman, S.; Jeppson, P.; Schimpf, M.; Yurteri-Kaplan, L.; Ferzandi, T.; et al. American Urogynecologic Society systematic review: The impact of weight loss intervention on lower urinary tract symptoms and urinary incontinence in overweight and obese women. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palleschi, G.; Pastore, A.; Rizzello, M.; Cavallaro, G.; Silecchia, G. Carbone Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy effects on overactive bladder symptoms. J Surg Res. 2015, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallosso, H.; McGrother, C.; Matthews, R.; Donaldson, M. The association of diet and other lifestyle factors with overactive bladder and stress incontinence: A longitudinal study in women. BJU Int. 2003, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyne, K.S.; Cash, B.; Kopp, Z.; Gelhorn, H.; Milsom, I.; Berriman, S.; et al. The prevalence of chronic constipation and faecal incontinence among men and women with symptoms of overactive bladder. BJU Int. 2011, 107, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, T.; Tomita, M.; Nakazawa, A.; Sakai, G.; Funakoshi, S.; Komatsuda, A.; et al. female functional constipation is associated with overactive bladder symptoms and urinary incontinence. Biomed Res Int. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, G.E.; Dourado, E.R.; Alves, D.N.; Araujo, M.Q.; Mendonça, N.S.P.; Barroso Junior, U. Functional constipation and overactive bladder in women: A population-based study. Arq Gastroenterol. 2018, 55 (Suppl. 1), 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K. Antimuscarinics for treatment of overactive bladder. Lancet Neurol. 2004, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhasso, A.; McKinlay, J.; Patrick, K.; Stewart, L. Anticholinergic drugs versus non-drug active therapies for overactive bladder syndrome in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, C.C.; Notte, S.M.; Maroulis, C.; Dmochowski, R.R.; Cardozo, L.; Subramanian, D.; et al. Persistence and adherence in the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome with anticholinergic therapy: A systematic review of the literature. Int J Clin Pract. 2011, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coupland, C.A.C.; Division of Primary Care, U.o.N.; Nottingham England Hill, T.; et al. Anticholinergic drug exposure and the risk of dementia: A nested case-control study. JAMA Intern Med. 2020, 179, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrière, I.; Fourrier-Reglat, A.; Dartigues, J.; Rouaud, O.; Pasquier, F.; Ritchie, K.; et al. Drugs with anticholinergic properties, cognitive decline, and dementia in an elderly general population: The 3-city study. Arch Internal Med. 2009, 169, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessen, F.; Kaduszkiewicz, H.; Daerr, M.; Bickel, H.; Pentzek, M.; Riedel-Heller, S.; et al. Anticholinergic drug use and risk for dementia: Target for dementia prevention. Eur Arch Ppsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2010, 260 (Suppl. 2), S111–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, S.; Anderson, M.; Dublin, S.; Hanlon, J.; Hubbar, R.; Walker, R.; et al. Cumulative use of strong anticholinergic medications and incident dementia. JAMA Intern Med. 2015, 175, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staskin, D. Trospium chloride: Distinct among other anticholinergic agents available for the treatment of overactive bladder. Urol Clin North Am. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geller, E.; Dumond, J.; Bowling, J.; Khandelwal, C.; Wu, J.; Busby-Whitehead, J.; et al. Effect of trospium chloride on cognitive function in women aged 50 and older: A randomized trial. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg. 2017, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapple, C.; Cardozo, L.; Nitti, V.; Siddiqui, E.; Michel, M. Mirabegron in overactive bladder: A review of efficacy, safety, and tolerability. Neurourol Urodyn. 2014, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.; Lee, K.; Na, Y.; Sood, R.; Nakaji, S.; Kubota, Y.; et al. Results of a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo- and active- controlled, multicenter study of mirabegron, a β3-adrenoceptor agonist, in patients with overactive bladder in Asia. Neurourol Urodyn. 2015, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagg, A.; Cardozo, L.; Nitti, V.; Castro-Diaz, D.; Auerbach, S.; Blauwet, M.; et al. The efficacy and tolerability of the β3-adrenoceptor agonist mirabegron for the treatment of symptoms of overactive bladder in older patients. Age Ageing. 2014, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zong, H.; Yang, C.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Y. The efficacy and safety of mirabegron in treating OAB: A systematic review and meta-analysis of phase III trials. Int Urol Nephrol. 2014, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapple, C.; Cruz, F.; Cardozo, L.; Staskin, D.; Herschorn, S.; Choudhury, N.; et al. Safety and efficacy of mirabegron: Analysis of a large integrated clinical trial database of patients with overactive bladder receiving mirabegron, antimuscarinics, or placebo. Eur Urol. 2020, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Chen, T.; Chang, H.; Juan, Y.; Huang, W.; Pan, H.; et al. Mirabegron is alternative to antimuscarinic agents for overactive bladder without higher risk in hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Urol. 2018, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, S.; Choudhury, N.; Huang, M.; Stari, A.; Nazir, J.; Freeman, R. Quality of life in patients aged 65 years and older with overactive bladder treated with mirabegron across eight European countries: Secondary analysis of BELIEVE. Int J Urol. 2019, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y. The efficacy and safety of vibegron in treating overactive bladder: A systematic review and pooled analysis of randomized controlled trials. Neurourol Urodyn. 2020, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Takeda, M.; Gotoh, M.; Nagai, S.; Kurose, T. Vibegron, a novel potent and selective β3-adrenoreceptor agonist, for the treatment of patients with overactive bladder: A randomized, double-blind, placebo- controlled phase 3 study. Eur Urol. 2018, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staskin, D.; Frankel, J.; Varano, S.; Shortino, D.; Jankowich, R.; Paul, N.; et al. International phase iii, randomized, double-blind, placebo and active controlled study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of vibegron in patients with symptoms of overactive bladder: EMPOWUR. J Urol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, J.; Maman, K.; Neine, M.; Briquet, B.; Odeyemi, I.; Hakimi, Z.; et al. Cost- effectiveness of mirabegron compared with antimuscarinic agents for the treatment of adults with overactive bladder in the United Kingdom. Value Health. 2015, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielage, R.; Perk, S.; Campbell, N.; Klein, T.; Posta, L.; Yuran, T.; et al. Mirabegron for the treatment of overactive bladder: Cost- effectiveness from US commercial health-plan and Medicare Advantage perspectives. J Med Econ. 2016, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perk, S.; Wielage, R.; Campbell, N.; Klein, T.; Perkins, A.; Posta, L.; et al. Estimated budget impact of increased use of mirabegron, a novel treatment for overactive bladder. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogaing, C.; Mossa, A.; Campeau, L. Are beta 3 adrenergic agonists now the preferred pharmacologic management of overactive bladder? Curr Urol Rep. 2020, 21, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskowitz, D.; Adelstein, S.; Lucioni, A.; Lee, U.; Kobashi, K. Use of third line therapy for overactive bladder in a practice with multiple subspecialty providers-are we doing enough? J Urol. 2018, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vianello, A.; Proietti, S.; Giannantoni, A. Effect of botulinum neurotoxin on the urinary bladder: Novel insights on mechanism of action. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2010, 62, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dolly, J.; Aoki, K. The structure and mode of action of different botulinum toxins. Eur J Neurol. 2006, 13 (Suppl. 4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, V.; Daly, D.; Liaskos, M.; McKay, N.; Sellers, D.; Chapple, C.; et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA significantly attenuates bladder afferent nerve firing and inhibits ATP release from the urothelium. BJU Int. 2013, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emami, M.; Shadpour, P.; Kashi, A.; Choopani, M.; Zeighami, M. Abobotulinum—A toxin injection in patients with refractory idiopathic detrusor overactivity: Injections in detrusor, trigone and bladder neck or prostatic urethra, versus detrusor—Only injections. Int Braz J Urol. 2017, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenstein, L.; Kenton, K.; Brubaker, L.; Pillar, G.; Undevia, N.; Mueller, E.; et al. The relationship between obstructive sleep apnea, nocturia, and daytime overactive bladder syndrome in women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, A.; Brubaker, L.; Richter, H.; Nygaard, I.; Paraiso, M.F.R.; Menefee, S.A.; et al. Anticholinergic therapy vs. onabotulinumtoxina for urgency urinary incontinence. N Engl J Med. 2012, 367, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovner, E.; Kennelly, M.; Schulte-Baukloh, H.; Zhou, J.; Haag-Molkenteller, C.; Dasgupta, P. Urodynamic results and clinical outcomes with intradetrusor injections of onabotulinumtoxinA in a randomized, placebo-controlled dose-finding study in idiopathic overactive bladder. Neurourol Urodyn. 2011, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborn, D.J.; Kaufman, M.R.; Mock, S.; Guan, M.J.; Dmochowski, R.R.; Reynolds, W.S. Urinary retention rates after intravesical onabotulinumtoxinA injection for idiopathic overactive bladder in clinical practice and predictors of this outcome. Neurourol Urodyn. 2015, 34, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, M.K.; Amundsen, C.L.; Perevich, M.; Liu, F.; Webster, G.D. Outcome of a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial of botulinum A toxin for refractory overactive bladder. J Urol. 2009, 181, 2608–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmochowski, R.; Chapple, C.; Nitti, V.; Chancellor, M.; Everaert, K.; Thompson, C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of onabotulinumtoxinA for idiopathic overactive bladder: A double-blind, placebo controlled, randomized, dose ranging trial. J Urol. 2010, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowson, C.; Watkins, J.; Khan, M.; Dasgupta, P.; Sahai, A. Repeated botulinum toxin type A injections for refractory overactive bladder: Medium-term outcomes, safety profile, and discontinuation rates. Eur Urol. 2012, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitti, V.; Ginsberg, D.; Sievert, K.; Sussman, D.; Radomski, S.; Sand, P.; et al. Durable efficacy and safety of long-term onabotulinumtoxina treatment in patients with overactive bladder syndrome: Final results of a 3.5-year study. J Urol. 2016, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Patterson, J.; Chapple, C. Botulinum toxin injections for neurogenic and idiopathic detrusor overactivity: A critical analysis of results. Eur Urol. 2006, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statskin, D.; Peter, K.; MacDiarmid, S.; Shore, N.; deGroat, W.C. Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation: A clinically and cost effective addition to the overactive bladder algorithm of care. Curr Urol Rep. 2012, 13, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaziev, G.; Topazio, L.; Iacovelli, V.; Asimakopoulos, A.; Di Sant, A.; De Nunzio, C.; et al. Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS) efficacy in the treatment of lower urinary tract dysfunctions: A systematic review. BMC Urol. 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govier, F.; Litwiller, S.; Nitti, V.; Kreder, K.; Rosenblatt, P. Percutaneous afferent neuromodulation for the refractory overactive bladder: Results of a multicenter study. J Urol. 2001, 165, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Dorsthorst, M.; Heesakkers, J.; van Balken, M. Long-term real-life adherence of percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation in over 400 patients. Neurourol Urodyn. 2020, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldred-Evans, D.; Sahai, A. Medium- to long-term outcomes of botulinum toxin A for idiopathic overactive bladder. Therapeutic Adv Urol. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Du, C.; Donahue, R.; Lucioni, A.; Kobashi, K.; Lee, U. Majority of onabotulinumtoxina-naive patients with idiopathic overactive bladder do not repeat chemodenervation: Factors affecting patient dropout after initial treatment with 100 units. J Urol. 2020, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, J.; Nguyen, A.; Du, C.; Wang, Q.; Hung, M.; Weissbart, S.; et al. Patients have poor compliance with repeat onabotulinumtoxin a injections for overactive bladder. J Urol. 2018, 199 (Suppl. 4S), e646–e647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobashi, K.; Nitti, V.; Margolis, E.; Sand, P.; Siegel, S.; Khandwala, S.; et al. A prospective study to evaluate efficacy using the nuro percutaneous tibial neuromodulation system in drug-naïve patients with overactive bladder syndrome. Urology. 2019, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubsher, C.; Jansen, R.; Riggs, D.; Jackson, B.; Zaslau, S. Sacral nerve stimulation for neuromodulation of the lower urinary tract. Canadian J Urol. 2012, 19, 6480–6484. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, S.; Noblett, K.; Mangel, J.; Griebling, T.; Sutherland, S.; Bird, E.; et al. Results of a prospective, randomized, multicenter study evaluating sacral neuromodulation with InterStim therapy compared to standard medical therapy at 6-months in subjects with mild symptoms of overactive bladder. Neurourol Urodyn. 2015, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amundsen, C.; Richter, H.; Menefee, S.; Komesu, Y.; Arya, L.; Gregory, W.; et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA vs sacral neuromodulation on refractory urgency urinary incontinence in women: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amundsen, C.; Komesu, Y.; Chermansky, C.; Gregory, W.; Myers, D.; Honeycutt, E.; et al. Two-year outcomes of sacral neuromodulation versus onabotulinumtoxina for refractory urgency urinary incontinence: A randomized trial. Eur Urol. 2018, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chughtai, B.; Thomas, D.; Sun, T.; Sedrakyan, A. Failures of sacral neuromodulation for incontinence. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutolo, M.; Ammirati, E.; Heesakkers, J.; Kessler, T.; Peters, K.; Rashid, T.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sacral and percutaneous tibial neuromodulation in non-neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction and chronic pelvic pain: A systematic review of the literature. Eur Urol. 2018, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaker, H.; Zhang, S.; Diamond, D.; Dong, M. Beyond botulinum neurotoxin A for chemodenervation of the bladder. Curr Opin Urol. 2021, 31, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappaport, Y.; Zisman, A.; Jeshurun-Gutshtat, M.; Gerassi, T.; Hakim, G.; Vinshtok, Y.; et al. Safety and feasibility of intravesical instillation of botulinum toxin-a in hydrogel-based slow-release delivery system in patients with interstitial cystitis-bladder pain syndrome: A pilot study. Urology. 2018, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. APOLLO: The study of an investigational drug, patisiran (ALN-TTR02), for the treatment of transthyretin (TTR)- mediated amyloidosis. Full text view. 2021. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01960348 (accessed on 31 July 2021).
- Rogers, A.; Bragg, S.; Ferrante, K.; Thenuwara, C.; Peterson, D. Pivotal study of leadless tibial nerve stimulation with eCoin ® for urgency urinary incontinence: An open-label, single arm trial. J Urol. 2021, 206, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. CAN-Stim compared to SNS in treatment of urinary urgency incontinence with wireless neuromodulation technology—Full text view—Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02577302 (accessed on 30 July 2021).
- van Kerrebroeck, P.; Reekmans, M.; van Koeveringe, G.; Yeh, A.; Fayram, T.; Sharan, A.; et al. First-in-human implantation of a mid-field powered neurostimulator at the sacral nerve: Results from an acute study. Neurourol Urodyn. 2019, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, H.; Wyndaele, J.; Kaplan, S.; Wang, J.; Ntanios, F. Defining response and non-response to treatment in patients with overactive bladder: A systematic review. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, P.R.; Rajan, S.; Sudeepthi, B.L.; Abdul Nazir, C.P. Patient-reported outcomes: A new era in clinical research. Perspect Clin Res. 2011, 2, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Speight, J.; Barendse, S. FDA guidance on patient reported outcomes. BMJ. 2010, 340, c2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marschall-Kehrel, D.; Roberts, R.; Brubaker, L. Patient-reported outcomes in overactive bladder: The influence of perception of condition and expectation for treatment benefit. Urology. 2006, 68 (Suppl. 2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.P. Nocturia: Focus on etiology and consequences. Rev Urol. 2012, 14, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, B.; Gezmis, C.; Çetin, B.; Gönültas, S.; Gökmen, E.; Gürkan, O.; et al. Is obstructive sleep apnea syndrome related to nocturia? Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wein, A.; Dmochowski, R. Neuromuscular dysfunction of the lower urinary tract. In Campbell Walsh Wein Urology; Partin, A., Peters, C., Kavoussi, L., Dmchowski, R., Wein, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Aharony, S.; Lam, O.; Corcos, J. Evaluation of lower urinary tract symptoms in multiple sclerosis patients: Review of the literature and current guidelines. Can Urol Assoc J. 2017, 11, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurpad, R.; Kennelly, M. The evaluation and management of refractory neurogenic overactive bladder. Curr Urol Rep. 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennelly, M.; Devoe, W. Overactive bladder: Pharmacologic treatments in the neurogenic population. Rev in urology. 2008, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Sanford, M.; Suskind, A. Neuromodulation in neurogenic bladder. Transl Androl Urol. 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portamn, D.; LSGass, M.; Panel, V.A.T.C.C. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause: New terminology for vulvovaginal atrophy from the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health and the North American Menopause Society. J Sex Med. 2014, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kang, S.; Chung, Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, M. The recent review of the genitourinary syndrome of menopause. J Menopausal Med. 2015, 21, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavi, M.; Sciuga, V.; Giannini, A.; Vena, F.; D’oria, O.; Prata, G.; et al. Overactive bladder syndrome treatment with ospemifene in menopausal patients with vulvovaginal atrophy: Improvement of sexuality? Gynecol Endocrinol. 2018, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eapen, R.; Radomski, S. Gender differences in overactive bladder. Can J Urol. 2016, 23 (Suppl. 1), 2–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dmochowski, R. Overactive bladder in males. Therapeutic Adv Urol. 2009, 1, 209–221. [Google Scholar]
This is an open access article under the terms of a license that permits non-commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. © 2021 The Authors. Société Internationale d'Urologie Journal, published by the Société Internationale d'Urologie, Canada.