Abstract
This review aims to provide a practical update regarding the current role of tissue-based biomarkers in bladder cancer. Their prognostic and predictive role both in non-muscle-invasive (NMIBC) and in muscle-invasive disease (MIBC) has been reviewed with particular focus to their use in clinical practice. In summary, the literature on the prediction of disease recurrence in NMIBC is inconclusive, and there is little information on prediction of response to intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG). Concerning disease progression, external prospective validation studies suggest that FGFR3 mutation status and gene signatures may improve models that are based only on clinicopathologic information. In MIBC, tissue-based biomarkers are increasingly important, since they may predict the response to systemic chemotherapy and immunotherapy. In particular, the advent of molecular characterization promises to revolutionize the paradigm of decision-making in the treatment of MIBC. Molecular subtyping has been shown to improve the prediction of pathological stage at RC and to predict the response to systemic chemotherapy and immunotherapy. However, external and prospective validations are warranted to confirm these preliminary findings. Several different tissue-based biomarkers such as PD-1/PD-L1 expression, tumor mutational burden, and the analysis of tumor microenvironment, may in future play a role in selecting patients for systemic immunotherapy. However, to date, no pretreatment recommendations can be definitively made on the basis of any molecular predictors. In conclusion, despite the potential of tissue-based biomarkers, their use in bladder cancer should be limited to experimental settings.
Introduction
In recent years, there have been significant innovations in the treatment of bladder cancer (BCa). While most treatments are standardized, we are transitioning from the era of “one size fits all” into the era of “precision medicine,” in which treatments are personalized and tailored according to the particular characteristics of each patient and tumor. Biomarkers play an undeniable role in this setting, allowing patient risk stratification, predicting response to treatments, and paving the way for targeted therapies. In this non-systematic review, the technical aspects of tissue-based biomarkers, as well as their current role in terms of clinical utility, both in non-muscle invasive (NMIBC) and muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC), are reviewed.
Technical Aspects of Tissue-Based Biomarkers in Bladder Cancer
Several technical aspects should be considered when working with tissue specimens. First, there are important differences between using fresh, frozen, or formalin-fixed material. The use of fresh or fresh-frozen tissue, for example, enriches the quality of RNA-derived material as compared with formalin-fixed tissue [1]. Conversely, DNA is usually more stable, and unless long nucleic acids are required, DNA of sufficient quality for analysis can be obtained for the majority of the PCR-based methods in fresh, fresh-frozen, or formalin-fixed material.
Second, it is critical to consider that BCa is extremely heterogeneous. This is particularly evident in MIBC, in which tissue heterogeneity might be extremely high, with differential ratios between tumor and stromal cells among paraffin blocks, leading to very different results if microdissection is not performed. This may lead to significant differences when staining sections from different blocks. However, even when microdissection is performed, intratumoral heterogeneity may currently play a role in limiting the use of tissue-based biomarkers in BCa.
Third, sample handling is very important to preserve the quality of the specimen. In frozen material, it is important that freezing is performed within 30 minutes of the specimen’s removal. When working with paraffin- embedded tumors it is important that specimens are maintained no longer than 24 hours in formalin for fixation and that blocks are well orientated to be cut within that time [2,3].
Finally, the use of controls is mandatory. A comparison with normal urothelium should always be performed in any experiment at the DNA, RNA, or protein level [4]. This is not always possible for BCa because of the field effect of carcinogenesis so adjacent “normal” may be best alternative control.
Tissue-Based Biomarkers in Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
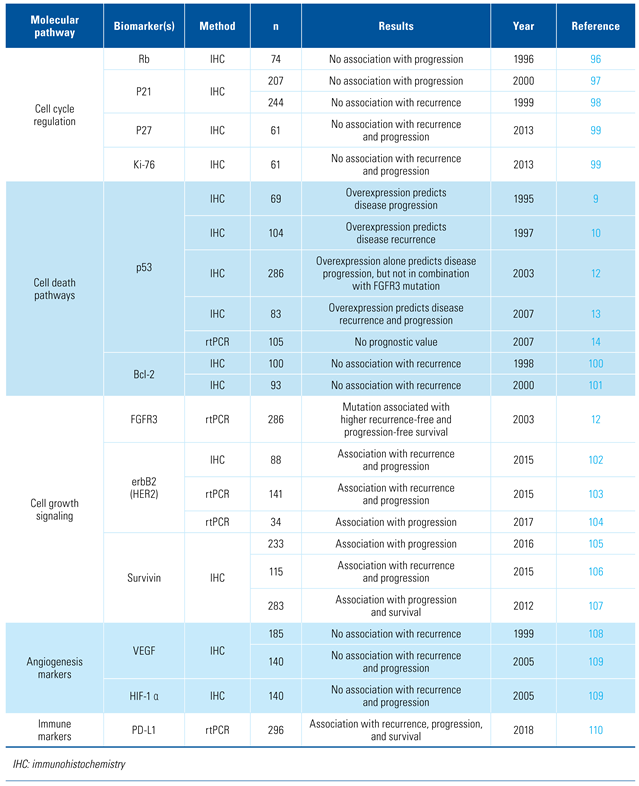
In general, prognostic information for patients with NMIBC is highly desirable, because guidance for further treatment and follow-up is urgently needed. So far, this information relies exclusively on clinico-pathological parameters [5,6,7,8]. Since there is a broad range of recurrence and progression rates even when applying European Association of Urology (EAU) or American Urology Association (AUA) risk stratification, there is need to refine prediction of rates to help inform treatment and surveillance decisions. Key prognostic biomarkers for disease recurrence and progression in NMIBC are listed in Table 1 and are briefly described below.

Table 1.
Prognostic biomarkers in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.
Prognostic markers for disease recurrence
The p53 tumor suppressor gene is probably the first molecular alteration that has been extensively studied, but there have been conflicting results regarding association with prognosis [9,10,11,12,13,14]. Using p53 as a single marker has issues due to multiple cell cycle regulators that may have overlapping roles. Considering the biological diversity of NMIBC along with its intratumoral heterogeneity, the research focus in tissue marker research has shifted from the investigation of single alterations to consideration of combined alterations, including gene classifiers for discrimination between recurrent and non-recurrent NMIBC, with promising results [13,15,16,17]. Nevertheless, a large international retrospective validation study including 404 patients investigating a 26-gene signature found no association with tumor recurrence [18].
FGFR3 mutations have been correlated with the prognosis of patients with NMIBC. A retrospective multicentre study investigated the prognostic potential of FGFR3 status and 3 molecular markers (MIB-1, P53, and P27kip1) showed that the combination of FGFR3 and MIB-1 was able to independently predict disease recurrence [12]. More recently, dysregulation of several miRNAs has been suggested to predict tumor recurrence [19,20,21]; however, validation and prospective assessment are lacking.
In summary, the role of molecular markers in the prognostication of disease recurrence in NMIBC seems limited, not only for technical reasons but also because clinical parameters (eg, multiplicity, tumor size, incomplete TUR) have a substantial effect on this event and mitigate the impact of biomarkers [12]. Furthermore, most patients with NMIBC, especially those with high- risk disease, undergo treatment, and response to therapy will impact the likelihood of recurrence significantly.
Prognostic markers for disease progression
Progression of disease is defined as a recurrence with a worsening stage or grade of disease. p53 alteration is one of the first and certainly most frequently studied markers in this context. Most of these studies, including a combined analysis of 23 studies [22], reported a correlation between p53 overexpression and tumor progression. However, as p53 alterations are closely related to tumor grade, stage, and other molecular changes, the independent prognostic value of this parameter remains a matter of controversy [11,12,13]. Immunohistochemical p53 overexpression has also been tested in combination with other alterations, frequently related to cell cycle regulation. In one prospective study every patient with high-grade NMIBC underwent immunohistochemical staining for 5 biomarkers (p21, p27, p53, KI-67, and cyclin E1) no differences were found in progression or survival based on the number of altered markers [23].
A molecular grading based on the combination of FGFR3 mutation together with MIB-1 expression is significantly associated with disease progression. A large prospective study of 1239 patients from the same group demonstrated that molecular grading based on FGFR3 mutational status and methylation of GATA2 was able to improve the EAU NMIBC risk score in predicting tumor progression [24].
The development of gene classifiers and subtyping using microarrays is another option for combining molecular information [25,26]. In a large prospective Scandinavian-based trial of 1224 patients, Dyrskjøt et al. demonstrated that the results of a 12-gene real-time qualitative PCR assay yielded independent prognostic information on tumor progression [27]. Nevertheless, with a 66% sensitivity and specificity to predict tumor progression as a stand-alone assay, it becomes obvious that, at this stage, information obtained by molecular markers is not sufficient and needs to be integrated with established clinicopathologic variables.
Predictive markers for response to intravesical therapy
Various tissue-based biomarkers have been evaluated for prediction of response to intravesical bacillus Calmette- Guérin (BCG) therapy. To date, the best evidence comes from a validation study based on 2 Nordic multicenter trials comparing treatment with BCG and other intravesical adjuvant therapies [28]. In this report, ezrin, CK20, and Ki-67 have been analyzed in a tissue microarray: unfortunately, none of the variables correlated with disease recurrence, and only tumor multifocality was associated with disease progression.
Several studies demonstrated a clinical utility in combining gene expression signatures with clinico-pathologic features [29]. Pietzak et al. demonstrated that patients with NMIBC had a high prevalence of alterations to DNA damage repair genes and that mutations in ARID1A are associated with an increased risk of recurrence following BCG therapy [30]. Moreover, total mutational burden has been associated with disease progression in a small retrospective study of 25 patients treated with BCG [31].
Following the advent of immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors also in the NMI setting (recently, according to the results of the Keynote-057 trial [32], the use of pembrolizumab in patients with BCG-unresponsive Cis has been approved by the FDA), the role of potential immune markers (ie, PD-1 and PD-L1 mRNA expression) to predict response to BCG has been investigated with promising results. However, it should be underlined that these findings need to be externally validated before they could be considered for clinical practice. Finally, in the context of immunological markers, Pichler et al. studied the association between recurrence-free survival and the count of CD4, GATA3, tumor-associated macrophages, Tregs, and T-bet+ T cells in the malignant tissue samples prior to BCG therapy [33]. They found that CD4+ and GATA3+ T cells were predictors of prolonged recurrence-free survival, while the predictors of shorter recurrence-free survival were TAMs, Tregs, and T-bet+ T cells.
Tissue-Based Biomarkers in Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer
Prediction of Oncological Outcomes
The standard treatment for patients with MIBC is radical cystectomy (RC) with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC). However, despite the administration of adequate therapy and the recent development of new treatment strategies such as trimodal therapy (TMT) or targeted therapies, MIBC remains an aggressive disease characterized by a generally unfavorable prognosis [34,35]. There are significant challenges in accurately staging the disease and insufficient ability using clinical/ pathological factors alone to predict recurrence and progression, and an inability to predict response to systemic therapies and radiotherapy. The consequence is that many patients are either undertreated, overtreated, or given therapies that are unlikely to benefit the patient.
Understanding the molecular pathology and biology of BCa could be useful to improve patients’ stratification and decision-making. Recently, several reports have focused their attention on molecular biomarkers as diagnostic and prognostic tools in MIBC, although their application in clinical practice remains, to date, unclear.
Prediction of disease stage at radical cystectomy
An accurate prediction of disease stage at diagnosis is of fundamental importance to risk-stratification and to select patients for neoadjuvant systemic therapies. Understaging disease after initial TURBT is over 40% despite examination under anesthesia and cross sectional imaging [36]. As such improving staging at diagnosis is important to appropriately treat patients. Several tissue-based biomarkers have been investigated for this purpose and have been integrated into predictive models. Mitra et al. firstly developed a pre-cystectomy decision model to predict pathological upstaging and oncological outcomes in cT2 patients undergoing RC [37]. This model was based on clinicopathologic variables such as the preoperative presence of hydronephrosis, evidence of deep muscolaris propria invasion and LVI as well as tumor growth pattern and count. Subsequently, Shariat et al. tested the accuracy of a preoperative panel of tissue-based biomarkers (p53, p21, p27, Ki67, and cyclin E1); the number of altered biomarkers was able to predict T-stage upstaging but not T- and/or N-stage upstaging; however, the accuracy of the model in the prediction of the T-stage upstaging was low (62%) [38]. Recently, a genomic subtyping classifier was used to evaluate pathological upstaging in a multi-institutional cohort of patients with cT1-T2 BCa treated with RC [39]. Luminal tumors showed a lower rate of upstaging to non-organ confined disease compared to non-luminal ones (34% versus 51%). Pending external validation, molecular characterization promises to transform the paradigm of BCa risk-stratification, thus paving the way to an even more personalized approach.
Prediction of oncological outcomes after radical cystectomy alone
There has been an interest in predicting the likelihood of recurrence in patients who underwent RC alone. These patients may benefit from adjuvant therapies such as chemotherapy [40] and multiple trials are evaluating the value of adjuvant checkpoint inhibitors. Key biomarkers evaluated for prediction of oncological outcomes are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Prognostic biomarkers after radical cystectomy alone in muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
Currently, p53 is the most studied prognostic biomarker in patients treated with RC, with conflicting results reported in the literature. In patients with BCa confined to the bladder, p53 has been associated with progression and survival, independently of tumor grade, stage, and lymph node status [41].
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is a tyrosine kinase transmembrane receptor involved in cycle cell regulation and cell proliferation. Its overexpression was associated with adverse pathological features at RC but its relationship with long-term oncological outcomes remains controversial [42,43].
The retinoblastoma protein (RB1) is a tumor suppressor gene, which acts as a negative regulator of cell cycle progression and has been proved to be dysregulated in several cancers. The loss of RB1 expression is an adverse prognostic biomarker in MIBC [44,45]. Inactivating RB1 mutation results in a lower expression of FGFR3 levels and is associated with worse cancer- specific mortality (CSM) [46].
Survivin, an inhibitor of apoptosis, was found to be associated with disease recurrence (HR 1.7, P = 0.04), CSM (HR 1.7, P = 0.03), and all-cause mortality (HR 1.7, P = 0.04) in 222 consecutive patients treated with RC after accounting for the effects of standard prognosticators [47]. These results have been externally validated and survivin status has been incorporated in a nomogram for the prediction of outcomes in patients with pT1-3N0M0 disease: the addition of survivin improved the accuracy of the model over standard clinicopathologic features for prediction of disease recurrence and CSM.
Despite these findings, the role of these biomarkers in clinical practice as single markers remains limited, mainly due to their unsatisfactory accuracy. Models based on the assessment of multiple markers (p53, p21, RB, cyclin E1, and p27) showed higher predictive accuracy compared to those based on single markers [48,49,50]. A prospective study of 216 patients treated with RC who underwent immunohistochemical staining for p53, p21, p27, cyclin E1, and Ki-67 found that in a multivariable model adjusting for the effects of standard prognosticators, only LVI and number of altered biomarkers were independent predictors of recurrence and CSM [51].
As already before mentioned, BCa molecular characterization is acquiring increasing importance in the prediction of prognosis in patients with MIBC. Recently, a consensus classification has been provided. Compared to luminal papillary tumors that were taken as reference, luminal non-specified and stroma-rich tumors showed similar outcomes while luminal unstable, basal/squamous, and neuroendocrine-like subtypes were associated with worse survival, with the latter representing the class with the worst prognosis (HR 2.18, P < 0.05). Moreover, this classification, besides providing a promising tool for risk-stratification, suggests possible therapeutic implications such as those related to targeted therapies, thereby representing a milestone for MIBC classification.
Prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy
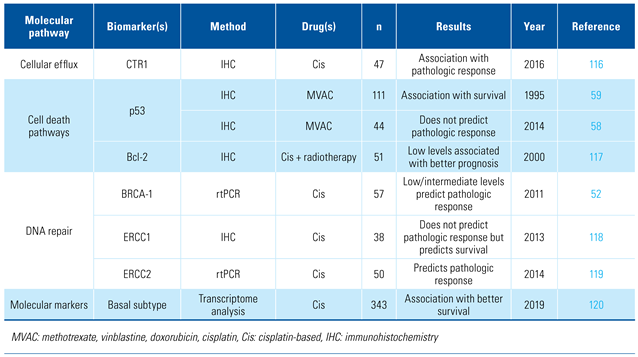
Key biomarkers investigated for prediction of response to NAC are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Biomarkers associated with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Cisplatin acts as an alkylating agent and interferes with DNA replication and gene transcription. This DNA-damage is repaired by 2 pathways: the first includes BRCA1, BRCA2, and RADS51 genes while the second involves the nucleotide excision repair NER, and includes several genes such as ERCC1-5, CDK7, DDB1-2, XPA. Alteration of these pathways has been suggested to affect the response to cisplatin-based chemotherapy. The breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 (BRCA1) modulates chemoresistance encoding a nuclear protein that responds to DNA damage with several different mechanisms. Patients with low/intermediate BRCA1 levels were found to have a significantly higher pathological response at RC compared to patients with high BRCA1 levels (66% versus 22%, P = 0.01) [52]. The excision repair cross-complementing 1 (ERCC1) is involved in DNA repair and DNA recombination: it was found associated with cisplatin resistance different tumors [53,54,55], whereas its role in BCa remains debated [56]. Genomic alterations in the DNA repair- associated genes ATM, RB1, and FANCC were found to be predictors of response (87% sensitivity, 100% specificity) and better OS after MVAC chemotherapy for MIBC [57,58]. Regarding the ability of p53 mutation to predict response to NAC, conflicting results have been reported [58,59].
Recent studies evaluated the role of molecular profiles for decision-making and counseling of patients treated with NAC and RC. While there is some evidence that different tumor subtypes (basal, luminal, p53-like) are associated with different patterns of response to NAC [60], in the recently developed international consensus about the molecular classification of MIBC [61] no significant association between the consensus classes and oncologic outcomes in patients treated with NAC was found.
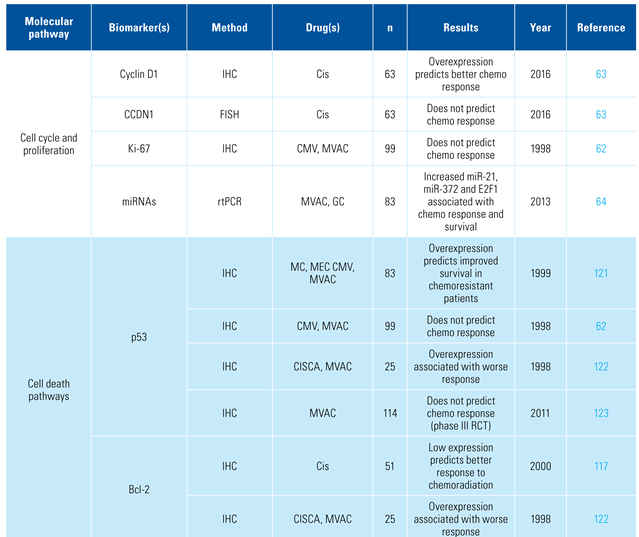
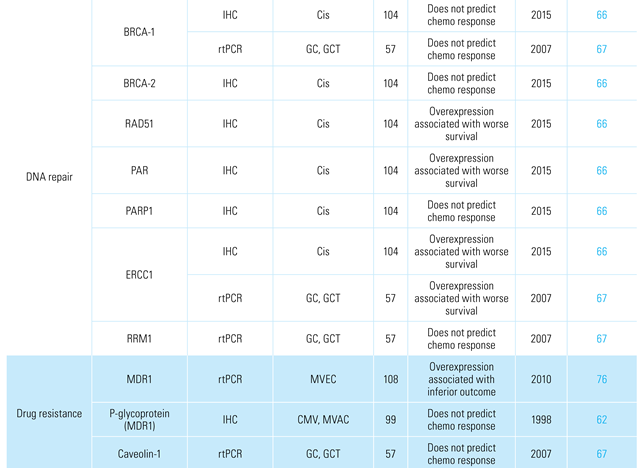
Prediction of response to systemic chemotherapy
Several cell cycle regulators and markers of proliferation have been evaluated as predictors of chemotherapy response [62,63]. Alongside this, a combination of regulatory RNAs and transcription factors has shown to be predictive in metastatic BCa patients treated with cisplatin-based therapy [64]. However, there is yet to be a clinically validated role for them as predictive markers.
The most promising class of predictive markers thus far for chemotherapeutic response is represented by those involved in DNA damage detection and repair (ie, BRCA-1, BRCA-2, RAD51, PAR, PARP1, ERCC1, ERCC2, and RRM1). In a study of patients with advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer receiving platinum-based palliative chemotherapy, 341 genes including 34 DNA damage response (DDR)-associated genes were evaluated [65]. Patients with DDR gene alterations had significantly longer progression-free and OS than patients with wild-type DDR genes. In the setting of advanced urothelial carcinoma, overexpression of ERCC1, RAD51, and PAR has been correlated with worse survival for patients treated with first-line platinum combination chemotherapy [66,67].
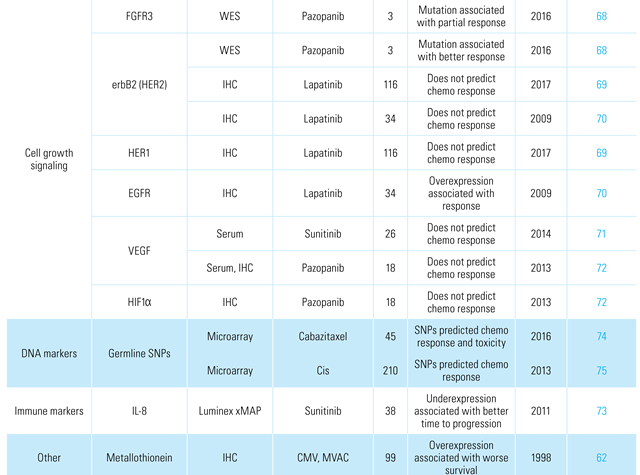
Aberrations of growth factors and their associated tyrosine kinase receptors can result in an abnormal increase in the rate of transduction of growth signals, thereby leading to uncontrolled cellular proliferation and tumor formation. Such kinases are the targets of several new systemic therapies in oncology. Several tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been tried in BCa including lapatinib (inhibits EGFR and HER2/neu pathways), and pazopanib (inhibits FGF, PDGF, and VEGF pathways). While these drugs appear to have limited activity in BCa, the possibility of biomarker enrichment for response has been assessed with mixed results [68,69,70,71,72].
Several other factors have been assessed for their ability to predict chemotherapy response, including immunological markers [73], germline and somatic DNA mutations [74,75], as well as drug transport genes [62,76]. Several of these factors are summarized in Table 4.

Table 4.
Biomarkers associated with systemic chemotherapy and immunotherapy response.
Prediction of response to systemic immunotherapy
The advent of systemic immunotherapy in the management of advanced BCa represents a quantum leap over the last few years, especially in patients refractory to cisplatin-based therapies. Several immune checkpoint inhibitors have shown promising activity, including agents targeting PD-1 receptor and its ligand PD-L1, and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4). While these developments are promising, a majority of patients still do not respond to treatment [77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84], resulting in a significant financial burden and potential treatment-related side effects. This highlights the need for appropriate biomarkers to aid in selecting patients who are most likely to benefit from checkpoint targeting therapy. While several biomarkers have been explored in the context of these clinical trials, no pretreatment recommendations can be definitively made at this point based on any molecular predictors, since a significant proportion of patients do respond to treatment despite testing negative for a biomarker. Nevertheless, biomarker-based selection for immunotherapy remains an area of active interest that is likely to further develop in the years to come.
PD-L1 expression has been associated with higher tumor grade, worse outcomes, and decreased postoperative survival [85,86]. In the IMvigor210 trial, a higher PD-L1 expression score was associated with a higher response rate [77]. In contrast, the CheckMate 275 trial showed meaningful responses to nivolumab, irrespective of PD-L1 expression levels [78]. Lack of standardized testing and evaluation of PD-L1 may be partially responsible for these discrepancies. Additionally, PD-L1 expression has been variously assessed: on tumor-infiltrating immune cells in the IMvigor210 trial [77], on tumor cells in the CheckMate 275 trial [78], and on both tumor cells and immune cells in the durvalumab trial [84]. Furthermore, there are variations in percentage cutoffs used to define the high and low expression. Finally, PD-L1 expression is dynamic, and a single biopsy is unlikely to provide a complete assessment of status for the entire duration of disease. Therefore, evaluation of the predictive value of PD-L1 positivity is difficult, and correlations with response to treatment or survival vary between trials.
Despite these discrepancies, both pembrolizumab and atezolizumab are approved by the FDA and the EMA for first-line treatment in cisplatin-ineligible patients only in case of positive PD-L1 status on the basis of unpublished results from ongoing phase II trials. Patients with negative PD-L1 expression should be treated with chemotherapy-based combinations.
Exploratory analyses from the cisplatin pre-treated arm of the IMvigor210 trial showed that molecular subtypes were independently associated with response to atezolizumab treatment [77]. PD-L1 immune cell prevalence was highly enriched in the basal subtype versus the luminal subtype (60% versus 23%, P < 0.001). Response to atezolizumab occurred in all subtypes but was significantly higher in luminal cluster II than in other subtypes [77]. Conversely, in CheckMate 275, the basal-1 subtype had the highest proportion of responders [78]. These discrepancies may be partially attributable to the fact that both trials allowed biopsy specimens from the primary tumor, lymph nodes, or metastatic lesions for subtyping, which may lead to inaccurate tumor classification. Until further details emerge, molecular classification may not be a reproducible predictive biomarker for immunotherapy.
The role of neoadjuvant therapy with checkpoint inhibitors is also gaining interest. The PURE-01 study evaluated the activity of preoperative pembrolizumab (NCT02736266) administered in T2-4aN0M0 MIBC patients [87]. In total, 114 patients were enrolled, and the pT0 rate was 37% (95% CI 28 to 46) while pT ≤ 1 rate was 55% (95% CI 46 to 65). On multivariable analysis, tumor mutational burden and PD-L1 combined positive score were associated with both the pT0 and the pT ≤ 1 response, regardless of tumor histology. A separate study using RNA sequencing found that the Immune190 signature was significant for complete response on multivariable logistic regression analyses in PURE-01, but not in a cohort of patients who underwent NAC and RC [88]. Hallmark signatures for interferon gamma (IFNγ; OR 1.11, P = 0.004) and IFNα response (OR 1.07, P = 0.006) were also associated with complete response for PURE-01, but not for NAC (IFNγ: OR 0.99, P = 0.9 and IFNα: OR 0.99, P = 0.8). Basal subtypes (across classifications) with higher Immune190 scores showed 100% 2-year progression-free survival after pembrolizumab therapy.
High mutational load may be associated with better response to immunotherapy [77]. However, there is currently no standardized definition of mutation burden relative to the depth of sequencing performed. Targeted sequencing panels may also not adequately cover gene fusions, truncations, and translocations. Further, germline variants may not be silenced by informatics techniques that filter common germline single-nucleotide polymorphisms. These challenges currently limit the use of tumor mutational burden as a predictive biomarker for immunotherapy.
Finally, the tumor microenvironment may play a role in predicting response to therapy [89]. CheckMate 275 found that the highest CXCL9 or CXCL10 expression was observed in nivolumab responders [78]. The same findings were reported by analyzing the cohort of cisplatin-pretreated patients of the IMvigor210 trial [77]. Immune markers investigated for the prediction of response to systemic immunotherapy are summarized in Table 4.
Prediction of response to radiotherapy
In the modern era, radiotherapy is generally administered in the context of organ preservation therapy in BCa. With careful patient selection, TMT yields oncological outcomes and quality of life comparable to RC in MIBC [90,91,92]. However, those who do not achieve complete response may undergo salvage cystectomy, with unfavorable oncological outcomes [93,94]. It is therefore imperative to carefully select patients who may be the optimal candidates for TMT. Several studies have looked at biomarkers that can predict response to TMT; the logic for evaluation of these biomarkers is generally based on their ability to predict response to the radiotherapy aspect of TMT.
Several different biomarkers such as cellular proliferation markers (ie, Ki-67), cell cycle regulators (ie, p53, Bcl-2, Bax, Bad), cell growth factors (ie, HER2/ neu), and DNA damage repairs genes have been studied for this purpose. However, because of conflicting results between studies or lack of external validations, none of these markers is currently available for clinical practice. Important biomarkers that are predictive of response to radiotherapy in the context of TMT are listed in Table 5.

Table 5.
Biomarkers associated with radiotherapy response.
Tissue-based biomarkers and target therapies
Biomarkers are important not only because of their ability to predict outcomes or response to therapy but also, and more importantly, because they could act as potential targets for biomarkers-directed therapies.
This is the case of erdafitinib, the first FDA-approved oral pan-fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) kinase inhibitor that binds to 4 FGFRs (FGFR-1 to -4), leading to decreased cell signaling and cellular apoptosis. The efficacy of erdafitinib (Balversa) has been tested in 99 patients with advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer progressing after at least one cycle of chemotherapy with FGFR2 or FGFR3 alterations [95]. The overall response was 40%, with 3% of patients experiencing complete response and 37% experiencing partial response. Of note, response was observed also in patients previously treated with systemic immunotherapy (response rate of 59% in this subgroup of patients).
Following these promising results, FGFR3 inhibitors (eg, infigratinib) are currently under investigation in the adjuvant setting after RC (EudraCT 2019-003248-63).
Conclusions
Reviewing the literature on the utility of tissue-based biomarkers in BCa through the last 2 decades, it appears obvious that the focus of research has moved from immunohistochemical analysis and tumor-related phenotypic changes to the analysis of genetic alterations. Furthermore, a trend towards marker combinations and genetic classifiers, mostly combining these findings with clinical parameters, is observed.
In summary, the literature on the prediction of disease recurrence in NMIBC is inconclusive, and little information is available for prediction of response to intravesical BCG. Concerning disease progression, external prospective validation studies suggest that mutational FGFR3 status and gene signatures may improve models on the basis of clinicopathologic information.
In MIBC, tissue-based biomarkers are increasing their importance since they may predict the response to systemic chemotherapy and immunotherapy. The advent of molecular characterization carries the promise to revolutionize the paradigm of decision-making in the treatment of MIBC, especially in these years characterized by the advent of systemic immunotherapy.
Prospective studies in well-defined patient cohorts and with clinically meaningful endpoints are needed for retrieving definitive conclusions about the utility of tissue-based biomarkers in BCa. Until then, their role, despite their promising value, should be limited to experimental settings.
Conflicts of Interest
None declared.
Abbreviations
| AUA | American Urological Association |
| BCa | bladder cancer |
| CSM | cancer-specific mortality |
| EAU | European Association of Urology |
| MIBC | muscle invasive disease |
| NAC | neoadjuvant chemotherapy |
| NMIBC | non-muscle invasive bladder cancer |
| RC | radical cystectomy |
References
- Sanchez-Carbayo, M.; Saint, F.; Lozano, J.J.; Viale, A.; Cordon-Cardo, C. Comparison of gene expression profiles in laser-microdissected, nonembedded, and OCT-embedded tumor samples by oligonucleotide microarray analysis. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 2096–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebrian, V.; Alvarez, M.; Aleman, A.; Palou, J.; Bellmunt, J.; Gonzalez-Peramato, P.; et al. Discovery of myopodin methylation in bladder cancer. J. Pathol. 2008, 216, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleman, A.; Cebrian, V.; Alvarez, M.; Lopez, V.; Orenes, E.; Lopez-Serra, L.; et al. Identification of PMF1 methylation in association with bladder cancer progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 8236–8243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orenes-Piñero, E.; Barderas, R.; Rico, D.; Casal, J.I.; Gonzalez-Pisano, D.; Navajo, J.; et al. Serum and tissue profiling in bladder cancer combining protein and tissue arrays. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babjuk, M.; Burger, M.; Compérat, E.M.; Gontero, P.; Mostafid, A.H.; Palou, J.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Non-muscle- invasive Bladder Cancer (TaT1 and Carcinoma In Situ) - 2019 Update. Eur. Urol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambier, S.; Sylvester, R.J.; Collette, L.; Gontero, P.; Brausi, M.A.; van Andel, G.; et al. EORTC nomograms and risk groups for predicting recurrence, progression, and disease-specific and overall survival in non-muscle-invasive stage Ta-T1 urothelial bladder cancer patients treated with 1-3 years of maintenance bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, R.J.; van der Meijden, A.P.M.; Oosterlinck, W.; Witjes, J.A.; Bouffioux, C.; Denis, L.; et al. Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: A combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur. Urol. 2006, 49, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Gomez, J.; Madero, R.; Solsona, E.; Unda, M.; Martinez- Piñeiro, L.; Gonzalez, M.; et al. Predicting nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer recurrence and progression in patients treated with bacillus Calmette-Guérin: The CUETO scoring model. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 2195–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serth, J.; Kuczyk, M.A.; Bokemeyer, C.; Hervatin, C.; Nafe, R.; Tan, H.K.; et al. p53 immunohistochemistry as an independent prognostic factor for superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Br. J. Cancer 1995, 71, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorreuther, R.; Hake, R.; Borchmann, P.; Lukowsky, S.; Thiele, J.; Engelmann, U. Expression of immunohistochemical markers (pcna, ki-67,486p and p53) on paraffin sections and their relation to the recurrence rate of superficial bladder tumors. Urol. Int. 1997, 59, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malats, N.; Bustos, A.; Nascimento, C.M.; Fernandez, F.; Rivas, M.; Puente, D.; et al. P53 as a prognostic marker for bladder cancer: A meta- analysis and review. Lancet Oncol. 2005, 6, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rhijn, B.W.G.; Vis, A.N.; van der Kwast, T.H.; Kirkels, W.J.; Radvanyi, F.; Ooms, E.C.M.; et al. Molecular grading of urothelial cell carcinoma with fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 and MIB-1 is superior to pathologic grade for the prediction of clinical outcome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 1912–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariat, S.F.; Ashfaq, R.; Sagalowsky, A.I.; Lotan, Y. Predictive value of cell cycle biomarkers in nonmuscle invasive bladder transitional cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2007, 177, 481–487; discussion 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moonen, P.M.J.; van Balken-Ory, B.; Kiemeney, L.A.L.M.; Schalken, J.A.; Witjes, J.A. Prognostic value of p53 for high risk superficial bladder cancer with long-term followup. J. Urol. 2007, 177, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhateeb, S.S.; Neill, M.; Bar-Moshe, S.; Van Rhijn, B.; Kakiashvili, D.M.; Fleshner, N.; et al. Long-term prognostic value of the combination of EORTC risk group calculator and molecular markers in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients treated with intravesical Bacille Calmette-Guérin. Urol. Ann. 2011, 3, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breyer, J.; Wirtz, R.M.; Otto, W.; Erben, P.; Kriegmair, M.C.; Stoehr, R.; et al. In stage pT1 non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC), high KRT20 and low KRT5 mRNA expression identify the luminal subtype and predict recurrence and survival. Virchows Arch. 2017, 470, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, O.T.M.; Furuya, H.; Pagano, I.; Shimizu, Y.; Hokutan, K.; Dyrskjøt, L.; et al. Association of MMP-2, RB and PAI-1 with decreased recurrence- free survival and overall survival in bladder cancer patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 99707–99721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyrskjøt, L.; Zieger, K.; Real, F.X.; Malats, N.; Carrato, A.; Hurst, C.; et al. Gene expression signatures predict outcome in non-muscle-invasive bladder carcinoma: A multicenter validation study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3545–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, A.S.; Karagas, M.R.; Schroeck, F.R.; Marsit, C.J.; Schned, A.R.; Pettus, J.R.; et al. MicroRNA dysregulation and non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer prognosis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2019, 28, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanca, A.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, A.; Requena, M.J.; Carrasco-Valiente, J.; Gomez-Gomez, E.; Cheng, L.; et al. Expression of miR-100 and miR-138 as prognostic biomarkers in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. APMIS 2019, 127, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikrika, F.D.; Avgeris, M.; Levis, P.K.; Tokas, T.; Stravodimos, K.; Scorilas, A. miR-221/222 cluster expression improves clinical stratification of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (TaT1) patients’ risk for short-term relapse and progression. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2018, 57, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goebell, P.J.; Groshen, S.L.; Schmitz-Drager, B.J. Guidelines for development of diagnostic markers in bladder cancer. World J. Urol. 2008, 26, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passoni, N.; Gayed, B.; Kapur, P.; Sagalowsky, A.I.; Shariat, S.F.; Lotan, Y. Cell-cycle markers do not improve discrimination of EORTC and CUETO risk models in predicting recurrence and progression of non-muscle-invasive high-grade bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2016, 34, 485.e7–485.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kessel, K.E.M.; van der Keur, K.A.; Dyrskjøt, L.; Algaba, F.; Welvaart, N.Y.C.; Beukers, W.; et al. Molecular markers increase precision of the European Association of Urology non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer progression risk groups. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.Z.; Rouanne, M.; Tan, K.T.; Huang, R.Y.J.; Thiery, J.P. Molecular subtypes of urothelial bladder cancer: Results from a meta-cohort analysis of 2411 tumors. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, F.; Jia, C.; Liu, M.; Nan, Y.; Qu, L.; et al. Comprehensive gene expression analysis in NMIBC using RNA-seq reveals new therapy strategies. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyrskjøt, L.; Reinert, T.; Algaba, F.; Christensen, E.; Nieboer, D.; Hermann, G.G.; et al. Prognostic impact of a 12-gene progression score in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A prospective multicentre validation study. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmström, P.-U.; Hemdan, T.; Segersten, U. Validation of the ezrin, CK20, and Ki-67 as potential predictive markers for BCG instillation therapy of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 532.e1–532.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alameddine, M.; Kineish, O.; Ritch, C. Predicting response to intravesical therapy in non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus 2018, 4, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietzak, E.J.; Bagrodia, A.; Cha, E.K.; Drill, E.N.; Iyer, G.; Isharwal, S.; et al. Next-generation sequencing of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer reveals potential biomarkers and rational therapeutic targets. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeks, J.J.; Carneiro, B.A.; Pai, S.G.; Oberlin, D.T.; Rademaker, A.; Fedorchak, K.; et al. Genomic characterization of high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 75176–75184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balar, A.V.; Kulkarni, G.S.; Uchio, E.M.; Boormans, J.; Mourey, L.; Krieger, L.E.M.; et al. Keynote 057: Phase II trial of Pembrolizumab (pembro) for patients (pts) with high-risk (HR) nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) unresponsive to bacillus calmette-guérin (BCG). J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 350–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, R.; Gruenbacher, G.; Culig, Z.; Brunner, A.; Fuchs, D.; Fritz, J.; et al. Intratumoral Th2 predisposition combines with an increased Th1 functional phenotype in clinical response to intravesical BCG in bladder cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, C.; Mistretta, F.A.; Knipper, S.; Pecoraro, A.; Tian, Z.; Shariat, S.F.; et al. How cancer-specific mortality changes over time after radical cystectomy: Conditional survival of patients with nonmetastatic urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mari, A.; Campi, R.; Tellini, R.; Gandaglia, G.; Albisinni, S.; Abufaraj, M.; et al. Patterns and predictors of recurrence after open radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: A comprehensive review of the literature. World J. Urol. 2018, 36, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariat, S.F.; Palapattu, G.S.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Rogers, C.G.; Vazina, A.; Bastian, P.J.; et al. Discrepancy between clinical and pathologic stage: Impact on prognosis after radical cystectomy. Eur. Urol. 2007, 51, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.P.; Skinner, E.C.; Miranda, G.; Daneshmand, S. A precystectomy decision model to predict pathological upstaging and oncological outcomes in clinical stage T2 bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2013, 111, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, S.F.; Passoni, N.; Bagrodia, A.; Rachakonda, V.; Xylinas, E.; Robinson, B.; et al. Prospective evaluation of a preoperative biomarker panel for prediction of upstaging at radical cystectomy. BJU Int. 2014, 113, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotan, Y.; Boorjian, S.A.; Zhang, J.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; Porten, S.P.; Wheeler, T.; et al. Molecular subtyping of clinically localized urothelial carcinoma reveals lower rates of pathological upstaging at radical cystectomy among luminal tumors. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leow, J.J.; Martin-Doyle, W.; Rajagopal, P.S.; Patel, C.G.; Anderson, E.M.; Rothman, A.T.; et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for invasive bladder cancer: A 2013 updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Eur. Urol. 2014, 66, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esrig, D.; Elmajian, D.; Groshen, S.; Freeman, J.A.; Stein, J.P.; Chen, S.C.; et al. Accumulation of nuclear p53 and tumor progression in bladder cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, F.; Moschini, M.; Haitel, A.; Wirth, G.J.; Gust, K.M.; Briganti, A.; et al. The effect of HER2 status on oncological outcomes of patients with invasive bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2016, 34, 533.e1–533.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolenz, C.; Shariat, S.F.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Ashfaq, R.; Ho, R.; Sagalowsky, A.I.; et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 expression status provides independent prognostic information in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder. BJU Int. 2010, 106, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.J.; Datar, R.; Youssefzadeh, D.; George, B.; Goebell, P.J.; Stein, J.P.; et al. Combined effects of p53, p21, and pRb expression in the progression of bladder transitional cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordon-Cardo, C.; Wartinger, D.; Petrylak, D.; Dalbagni, G.; Fair, W.R.; Fuks, Z.; et al. Altered expression of the retinoblastoma gene product: Prognostic indicator in bladder cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1992, 84, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindgren, D.; Sjödahl, G.; Lauss, M.; Staaf, J.; Chebil, G.; Lövgren, K.; et al. Integrated genomic and gene expression profiling identifies two major genomic circuits in urothelial carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, S.F.; Ashfaq, R.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Saeedi, O.; Sagalowsky, A.I.; Lotan, Y. Survivin expression is associated with bladder cancer presence, stage, progression, and mortality. Cancer 2007, 109, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, S.F.; Ashfaq, R.; Sagalowsky, A.I.; Lotan, Y. Correlation of cyclin D1 and E1 expression with bladder cancer presence, invasion, progression, and metastasis. Hum. Pathol. 2006, 37, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, S.F.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Ashfaq, R.; Lerner, S.P.; Palapattu, G.S.; Cote, R.J.; et al. Multiple biomarkers improve prediction of bladder cancer recurrence and mortality in patients undergoing cystectomy. Cancer 2008, 112, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, S.F.; Chromecki, T.F.; Cha, E.K.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Sun, M.; Fradet, Y.; et al. Risk stratification of organ confined bladder cancer after radical cystectomy using cell cycle related biomarkers. J. Urol. 2012, 187, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotan, Y.; Bagrodia, A.; Passoni, N.; Rachakonda, V.; Kapur, P.; Arriaga, Y.; et al. Prospective evaluation of a molecular marker panel for prediction of recurrence and cancer-specific survival after radical cystectomy. Eur. Urol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, A.; Taron, M.; Gago, J.L.; Costa, C.; Sanchez, J.J.; Carrato, C.; et al. BRCA1 mRNA expression and outcome to neoadjuvant cisplatin- based chemotherapy in bladder cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britten, R.A.; Liu, D.; Tessier, A.; Hutchison, M.J.; Murray, D. ERCC1 expression as a molecular marker of cisplatin resistance in human cervical tumor cells. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 89, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabholkar, M.; Vionnet, J.; Bostick-Bruton, F.; Yu, J.J.; Reed, E. Messenger RNA levels of XPAC and ERCC1 in ovarian cancer tissue correlate with response to platinum-based chemotherapy. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, R.V.N.; Brabender, J.; Gandara, D.; Alberola, V.; Camps, C.; Domine, M.; et al. Low ERCC1 expression correlates with prolonged survival after cisplatin plus gemcitabine chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 2286–2291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Jacobus, S.; Bellmunt, J.; Qu, A.; Appleman, L.J.; Tretter, C.; et al. Neoadjuvant dose-dense methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin with pegfilgrastim support in muscle-invasive urothelial cancer: Pathologic, radiologic, and biomarker correlates. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plimack, E.R.; Dunbrack, R.L.; Brennan, T.A.; Andrake, M.D.; Zhou, Y.; Serebriiskii, I.G.; et al. Defects in DNA repair genes predict response to neoadjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy in muscle- invasive bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plimack, E.R.; Hoffman-Censits, J.H.; Viterbo, R.; Trabulsi, E.J.; Ross, E.A.; Greenberg, R.E.; et al. Accelerated methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin is safe, effective, and efficient neoadjuvant treatment for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Results of a multicenter phase II study with molecular correlates of response and toxicity. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1895–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, A.S.; Bajorin, D.F.; Reuter, V.E.; Herr, H.W.; Netto, G.; Zhang, Z.F.; et al. Prognostic value of p53 nuclear overexpression in patients with invasive bladder cancer treated with neoadjuvant MVAC. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Porten, S.; Kim, S.; Willis, D.; Plimack, E.R.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; et al. Identification of distinct basal and luminal subtypes of muscle-invasive bladder cancer with different sensitivities to frontline chemotherapy. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, A.; de Reyniès, A.; Allory, Y.; Sjödahl, G.; Robertson, A.G.; Seiler, R.; et al. A consensus molecular classification of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. SSRN Electron. J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, L.L.; Banerjee, D.; Khurana, R.J.; Pan, X.; Pflueger, R.; Tannock, I.F.; et al. The prognostic role of p53, metallothionein, P-glycoprotein, and MIB-1 in muscle-invasive urothelial transitional cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seiler, R.; Thalmann, G.N.; Rotzer, D.; Perren, A.; Fleischmann, A. CCND1/ CyclinD1 status in metastasizing bladder cancer: A prognosticator and predictor of chemotherapeutic response. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellmunt, J.; Zhou, C.W.; Mullane, S.A.; Werner, L.; Taplin, M.E.; Fay, A.P.; et al. Association of tumour microRNA profiling with outcomes in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma receiving first- line platinum-based chemotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, M.Y.; Bambury, R.M.; Zabor, E.C.; Jordan, E.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Boyd, M.E.; et al. DNA damage response and repair gene alterations are associated with improved survival in patients with platinum-treated advanced urothelial carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3610–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullane, S.A.; Werner, L.; Guancial, E.A.; Lis, R.T.; Stack, E.C.; Loda, M.; et al. Expression levels of DNA damage repair proteins are associated with overall survival in platinum-treated advanced urothelial carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin Cancer 2016, 14, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellmunt, J.; Paz-Ares, L.; Cuello, M.; Cecere, F.L.; Albiol, S.; Guillem, V.; et al. Gene expression of ERCC1 as a novel prognostic marker in advanced bladder cancer patients receiving cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinciroli, P.; Won, H.; Iyer, G.; Canevari, S.; Colecchia, M.; Giannatempo, P.; et al. Molecular signature of response to pazopanib salvage therapy for urothelial carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2016, 14, e81–e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Powles, T.; Huddart, R.A.; Elliott, T.; Sarker, S.J.; Ackerman, C.; Jones, R.; et al. Phase III, double-blind, randomized trial that compared maintenance lapatinib versus placebo after first-line chemotherapy in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 1/2-positive metastatic bladder cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novara, G.; De Marco, V.; Dalpiaz, O.; Galfano, A.; Bouygues, V.; Gardiman, M.; et al. Independent predictors of contralateral metachronous upper urinary tract transitional cell carcinoma after nephroureterectomy: Multi-institutional dataset from three European centers. Int. J. Urol. 2009, 16, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, P.D.; Daignault, S.; Tagawa, S.T.; Nanus, D.M.; Stadler, W.M.; Dreicer, R.; et al. Double-blind, randomized, phase 2 trial of maintenance sunitinib versus placebo after response to chemotherapy in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma. Cancer 2014, 120, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pili, R.; Qin, R.; Flynn, P.J.; Picus, J.; Millward, M.; Ho, W.M.; et al. A phase II safety and efficacy study of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor pazopanib in patients with metastatic urothelial cancer. Clin. Genitourin Cancer 2013, 11, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellmunt, J.; Gonzalez-Larriba, J.L.; Prior, C.; Maroto, P.; Carles, J.; Castellano, D.; et al. Phase II study of sunitinib as first-line treatment of urothelial cancer patients ineligible to receive cisplatin-based chemotherapy: Baseline interleukin-8 and tumor contrast enhancement as potential predictive factors of activity. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 2646–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, I.; Hagen, C.; Arranz, J.A.; Apellaniz-Ruiz, M.; Perez-Valderrama, B.; Sala, N.; et al. SNPs associated with activity and toxicity of cabazitaxel in patients with advanced urothelial cell carcinoma. Pharmacogenomics 2016, 17, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, D.J.; Vijai, J.; Hamilton, R.J.; Ostrovnaya, I.; Iyer, G.; Garcia-Grossman, I.R.; et al. Germline single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with response of urothelial carcinoma to platinum- based therapy: The role of the host. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2414–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.C.; Wild, P.; Leicht, C.; Bertz, S.; Danenberg, K.D.; Danenberg, P.V.; et al. MDR1 and ERCC1 expression predict outcome of patients with locally advanced bladder cancer receiving adjuvant chemotherapy. Neoplasia 2010, 12, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, J.E.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; Powles, T.; van der Heijden, M.S.; Balar, A.V.; Necchi, A.; et al. Atezolizumab in patients with locally advanced and metastatic urothelial carcinoma who have progressed following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy: A single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Retz, M.; Siefker-Radtke, A.; Baron, A.; Necchi, A.; Bedke, J.; et al. Nivolumab in metastatic urothelial carcinoma after platinum therapy (CheckMate 275): A multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellmunt, J.; de Wit, R.; Vaughn, D.J.; Fradet, Y.; Lee, J.L.; Fong, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab as second-line therapy for advanced urothelial carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balar, A.V.; Galsky, M.D.; Rosenberg, J.E.; Powles, T.; Petrylak, D.P.; Bellmunt, J.; et al. Atezolizumab as first-line treatment in cisplatin-ineligible patients with locally advanced and metastatic urothelial carcinoma: A single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; O’Donnell, P.H.; Massard, C.; Arkenau, H.T.; Friedlander, T.W.; Hoimes, C.J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of durvalumab in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma: Updated results from a phase 1/2 open-label study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, e172411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apolo, A.B.; Infante, J.R.; Balmanoukian, A.; Patel, M.R.; Wang, D.; Kelly, K.; et al. Avelumab, an anti-programmed death-ligand 1 antibody, in patients with refractory metastatic urothelial carcinoma: Results from a multicenter, phase Ib study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2117–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Callahan, M.K.; Bono, P.; Kim, J.; Spiliopoulou, P.; Calvo, E.; et al. Nivolumab monotherapy in recurrent metastatic urothelial carcinoma (CheckMate 032): A multicentre, open-label, two-stage, multi-arm, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1590–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massard, C.; Gordon, M.S.; Sharma, S.; Rafii, S.; Wainberg, Z.A.; Luke, J.; et al. Safety and efficacy of durvalumab (MEDI4736), an anti- programmed cell death ligand-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor, in patients with advanced urothelial bladder cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3119–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, J.; Wada, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Azuma, M.; Kikuchi, K.; Ueda, S. Overexpression of B7-H1 (PD-L1) significantly associates with tumor grade and postoperative prognosis in human urothelial cancers. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2007, 56, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boorjian, S.A.; Sheinin, Y.; Crispen, P.L.; Farmer, S.A.; Lohse, C.M.; Kuntz, S.M.; et al. T-cell coregulatory molecule expression in urothelial cell carcinoma: Clinicopathologic correlations and association with survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4800–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necchi, A.; Raggi, D.; Gallina, A.; Madison, R.; Colecchia, M.; Lucianò, R.; et al. Updated results of PURE-01 with preliminary activity of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab in patients with muscle-invasive bladder carcinoma with variant histologies. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necchi, A.; Raggi, D.; Gallina, A.; Ross, J.S.; Farè, E.; Giannatempo, P.; et al. Impact of molecular subtyping and immune infiltration on pathological response and outcome following neoadjuvant pembrolizumab in muscle-invasive bladder cancer [formula presented]. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarsheth, N.; Wicha, M.S.; Zou, W. Chemokines in the cancer microenvironment and their relevance in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efstathiou, J.A.; Spiegel, D.Y.; Shipley, W.U.; Heney, N.M.; Kaufman, D.S.; Niemierko, A.; et al. Long-term outcomes of selective bladder preservation by combined-modality therapy for invasive bladder cancer: The MGH experience. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacalone, N.J.; Shipley, W.U.; Clayman, R.H.; Niemierko, A.; Drumm, M.; Heney, N.M.; et al. Long-term outcomes after bladder-preserving tri-modality therapy for patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer: An updated analysis of the Massachusetts General Hospital experience. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploussard, G.; Daneshmand, S.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Herr, H.W.; James, N.D.; Rödel, C.M.; et al. Critical analysis of bladder sparing with trimodal therapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review. Eur. Urol. 2014, 66, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, F.; Numao, N.; Saito, K.; Masuda, H.; Fujii, Y.; Kawakami, S.; et al. Sensitivity to chemoradiation predicts development of metastasis in muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients. Urol. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, F.; Kihara, K. Selective bladder preservation with curative intent for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A contemporary review. Int. J. Urol. 2012, 19, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loriot, Y.; Necchi, A.; Park, S.H.; Garcia-Donas, J.; Huddart, R.; Burgess, E.; et al. Erdafitinib in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Têtu, B.; Fradet, Y.; Allard, P.; Veilleux, C.; Roberge, N.; Bernard, P. Prevalence and clinical significance of HER/2neu, p53 and Rb expression in primary superficial bladder cancer. J. Urol. 1996, 155, 1784–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liukkonen, T.; Lipponen, P.; Raitanen, M.; Kaasinen, E.; Ala-Opas, M.; Rajala, P.; et al. Evaluation of p21WAF1/CIP1 and cyclin D1 expression in the progression of superficial bladder cancer. Finbladder Group. Urol. Res. 2000, 28, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, C.; Moore, L.; Allard, P.; Larue, H.; Lacombe, L.; Têtu, B.; et al. Predictive value of cell cycle markers p53, MDM2, p21, and Ki-67 in superficial bladder tumor recurrence. Clin. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 4079–4084. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Song, C.; Shin, E.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, C.-S.; Ahn, H. Do molecular biomarkers have prognostic value in primary T1G3 bladder cancer treated with bacillus Calmette-Guérin intravesical therapy? Urol. Oncol. 2013, 31, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzai, T.S.; Chow, N.H.; Lin, J.S.; Yang, W.H.; Tong, Y.C. The expression of p53 and bcl-2 in superficial bladder transitional cell carcinoma and its role in the outcome of postoperative intravesical chemotherapy. Anticancer Res. 1998, 18, 4717–4721. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.T.; Chen, J.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Huang, J.K. The role of bcl-2, p53, and ki-67 index in predicting tumor recurrence for low grade superficial transitional cell bladder carcinoma. J. Urol. 2000, 163, 758–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, R.; kamel, M.; Salem, E.A.; Salem, N.A.; Fawzy, A.; Sakr, A.; et al. The prognostic significance of p53, p63 and her2 expression in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer in relation to treatment with bacille Calmette-Guérin. Arab. J. Urol. 2015, 13, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.D.; Cho, Y.M.; Choi, G.-S.; Park, H.K.; Paick, S.H.; Kim, W.Y.; et al. Clinical significance of substaging and her2 expression in papillary nonmuscle invasive urothelial cancers of the urinary bladder. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breyer, J.; Otto, W.; Wirtz, R.M.; Wullich, B.; Keck, B.; Erben, P.; et al. ERBB2 Expression as potential risk-stratification for early cystectomy in patients with pT1 bladder cancer and concomitant carcinoma in situ. Urol. Int. 2017, 98, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breyer, J.; Gierth, M.; Shalekenov, S.; Aziz, A.; Schäfer, J.; Burger, M.; et al. Epithelial–mesenchymal transformation markers E-cadherin and survivin predict progression of stage pTa urothelial bladder carcinoma. World J. Urol. 2016, 34, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senol, S.; Yildirim, A.; Ceyran, B.; Uruc, F.; Zemheri, E.; Ozkanli, S.; et al. Prognostic significance of survivin, β-catenin and p53 expression in urothelial carcinoma. Bosn J. Basic Med. Sci. 2015, 15, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fristrup, N.; Ulhøi, B.P.; Birkenkamp-Demtröder, K.; Mansilla, F.; Sanchez-Carbayo, M.; Segersten, U.; et al. Cathepsin E, maspin, Plk1, and survivin are promising prognostic protein markers for progression in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 1824–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, N.H.; Liu, H.S.; Chan, S.H.; Cheng, H.L.; Tzai, T.S. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in primary superficial bladder cancer. Anticancer Res. 1999, 19, 4593–4597. [Google Scholar]
- Theodoropoulos, V.E.; Lazaris, A.C.; Kastriotis, I.; Spiliadi, C.; Theodoropoulos, G.E.; Tsoukala, V.; et al. Evaluation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha overexpression as a predictor of tumour recurrence and progression in superficial urothelial bladder carcinoma. BJU Int. 2005, 95, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breyer, J.; Wirtz, R.M.; Otto, W.; Erben, P.; Worst, T.S.; Stoehr, R.; et al. High PDL1 mRNA expression predicts better survival of stage pT1 non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 403–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, S.F.; Chade, D.C.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Ashfaq, R.; Isbarn, H.; Fradet, Y.; et al. Combination of multiple molecular markers can improve prognostication in patients with locally advanced and lymph node positive bladder cancer. J. Urol. 2010, 183, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariat, S.F.; Bolenz, C.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Fradet, Y.; Ashfaq, R.; Bastian, P.J.; et al. p53 expression in patients with advanced urothelial cancer of the urinary bladder. BJU Int. 2010, 105, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, E.; Eltze, E.; Bierer, S.; Köpke, T.; Görge, T.; Neumann, J.; et al. VEGF-C, VEGF-D and Flt-4 in transitional bladder cancer: Relationships to clinicopathological parameters and long-term survival. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 3127–3133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bringuier, P.P.; Umbas, R.; Schaafsma, H.E.; Karthaus, H.F.; Debruyne, F.M.; Schalken, J.A. Decreased E-cadherin immunoreactivity correlates with poor survival in patients with bladder tumors. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 3241–3245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vasala, K.; Paakko, P.; Turpeenniemi-Hujanen, T. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 immunoreactive protein as a prognostic marker in bladder cancer. Urology 2003, 62, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilari, D.; Iczkowski, K.A.; Pandya, C.; Robin, A.J.; Messing, E.M.; Guancial, E.; et al. Copper transporter-CTR1 expression and pathological outcomes in platinum-treated muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 495–502. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, P.W.; James, N.D.; Ganesan, R.; Burton, A.; Young, L.S.; Wallace, D.M. Bcl-2 expression identifies patients with advanced bladder cancer treated by radiotherapy who benefit from neoadjuvant chemotherapy. BJU Int. 2000, 85, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, M.F.; Dizdar, O.; Dincer, N.; Balci, S.; Guler, G.; Gok, B.; et al. Low ERCC1 expression is associated with prolonged survival in patients with bladder cancer receiving platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Urol. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1709–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Allen, E.M.; Mouw, K.W.; Kim, P.; Iyer, G.; Wagle, N.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; et al. Somatic ERCC2 mutations correlate with cisplatin sensitivity in muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1140–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, R.; Ashab, H.A.; Erho, N.; van Rhijn, B.W.; Winters, B.; Douglas, J.; et al. Impact of molecular subtypes in muscle-invasive bladder cancer on predicting response and survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Eur. Urol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, K.N.; Griffiths, T.R.; Robinson, M.C.; Marsh, C.; Roberts, J.T.; Hall, R.R.; et al. TP53 accumulation predicts improved survival in patients resistant to systemic cisplatin-based chemotherapy for muscle- invasive bladder cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 3500–3507. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kong, G.; Shin, K.Y.; Oh, Y.H.; Lee, J.J.; Park, H.Y.; Woo, Y.N.; et al. Bcl-2 and p53 expressions in invasive bladder cancers. Acta Oncol. 1998, 37, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadler, W.M.; Lerner, S.P.; Groshen, S.; Stein, J.P.; Shi, S.R.; Raghavan, D.; et al. Phase III study of molecularly targeted adjuvant therapy in locally advanced urothelial cancer of the bladder based on p53 status. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3443–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rödel, C.; Grabenbauer, G.G.; Rödel, F.; Birkenhake, S.; Kühn, R.; Martus, P.; et al. Apoptosis, p53, bcl-2, and Ki-67 in invasive bladder carcinoma: Possible predictors for response to radiochemotherapy and successful bladder preservation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 46, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, K.; Yoshida, S.; Koga, F.; Inoue, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Ishioka, J.; et al. High Ki-67 expression predicts favorable survival in muscle- invasive bladder cancer patients treated with chemoradiation-based bladder-sparing protocol. Clin. Genitourin Cancer 2015, 13, e243–e251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, H.; Wada, T.; Fukunaga, K.; Yoshihiro, S.; Matsuyama, H.; Naito, K. Bax to Bcl-2 ratio and Ki-67 index are useful predictors of neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy in bladder cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 34, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, A.; Nakayama, M.; Kakuta, Y.; Abe, T.; Hatano, K.; Mukai, M.; et al. Excision repair cross-complementing group 1 may predict the efficacy of chemoradiation therapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2561–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakano, S.; Ogawa, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Nishijima, J.; Miyachika, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; et al. ERCC1 and XRCC1 expression predicts survival in bladder cancer patients receiving combined trimodality therapy. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 1, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Nelson, L.D.; Teo, M.T.; Chilka, S.; Bhattarai, S.; Johnston, C.F.; et al. MRE11 expression is predictive of cause-specific survival following radical radiotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7017–7026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, N.B.; Scott, S.N.; Zabor, E.C.; Cha, E.K.; Hreiki, J.; Sfakianos, J.P.; et al. Genomic characterization of response to chemoradiation in urothelial bladder cancer. Cancer 2016, 122, 3715–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarti, A.; Winter, K.; Wu, C.L.; Kaufman, D.; Hammond, E.; Parliament, M.; et al. Expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor and Her-2 are predictors of favorable outcome and reduced complete response rates, respectively, in patients with muscle-invading bladder cancers treated by concurrent radiation and cisplatin-based chemot. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 62, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Koga, F.; Yoshida, S.; Tamura, T.; Fujii, Y.; Ito, E.; et al. Significance of ERBB2 overexpression in therapeutic resistance and cancer-specific survival in muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients treated with chemoradiation-based selective bladder- sparing approach. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelson, M.D.; Hu, C.; Pham, H.T.; Dahl, D.M.; Lee-Wu, C.; Swanson, G.P.; et al. A phase 1/2 trial of a combination of paclitaxel and trastuzumab with daily irradiation or paclitaxel alone with daily irradiation after transurethral surgery for noncystectomy candidates with muscle-invasive bladder cancer (Trial NRG Oncology RTOG 0524). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 97, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Yoshida, S.; Koga, F.; Toda, K.; Yoshimura, R.; Nakajima, Y.; et al. Impact of immunohistochemistry-based subtypes in muscle-invasive bladder cancer on response to chemoradiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urushibara, M.; Kageyama, Y.; Akashi, T.; Otsuka, Y.; Takizawa, T.; Koike, M.; et al. HSP60 may predict good pathological response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in bladder cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 37, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
This is an open access article under the terms of a license that permits non-commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. © 2021 The Authors. Société Internationale d'Urologie Journal, published by the Société Internationale d'Urologie, Canada.