Abstract
Identification of reliable molecular biomarkers that can complement clinical practice represents a fascinating challenge in any cancer field. Renal tumors are usually asymptomatic and incidentally identified during imaging studies undertaken for unrelated causes. However, in 25% to 30% of patients the first diagnosis is accompanied by symptoms and associated with distant metastasis. Thus, early diagnosis may reduce the risk of disease progression also avoiding side effects of inadequate treatments. Moreover, the ability to categorize patients' risk of recurrence after radical treatment, or even predict benefit from a target therapy, represents a compelling challenge. Here we review the current state-of-the-art on RCC biomarkers, particularly focusing on the new approaches of genomics, liquid biopsy, proteomics, and metabolomics.
Introduction
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the third most common urological cancer in the United States, with an estimated 44 120 new cases in 2019 [1]. Clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is the most frequent subtype, accounting for approximately 75% to 80% of these tumors, and is responsible for the majority of kidney cancer deaths [2]. In this narrative review we present the current state-of-the-art on diagnostic and prognostic RCC biomarkers, particularly focusing on the new approaches of genomics, liquid biopsy, proteomics, and metabolomics. A MEDLINE/PubMed search was performed using individual or/and different combinations of terms including “renal cell carcinoma,” “biomarker,” “diagnosis,” “prognosis,” and “survival.” Only papers with the title and abstract in the English language were screened for eligibility. The full text of included papers was analyzed.
Biomarkers in Early Detection and Diagnosis
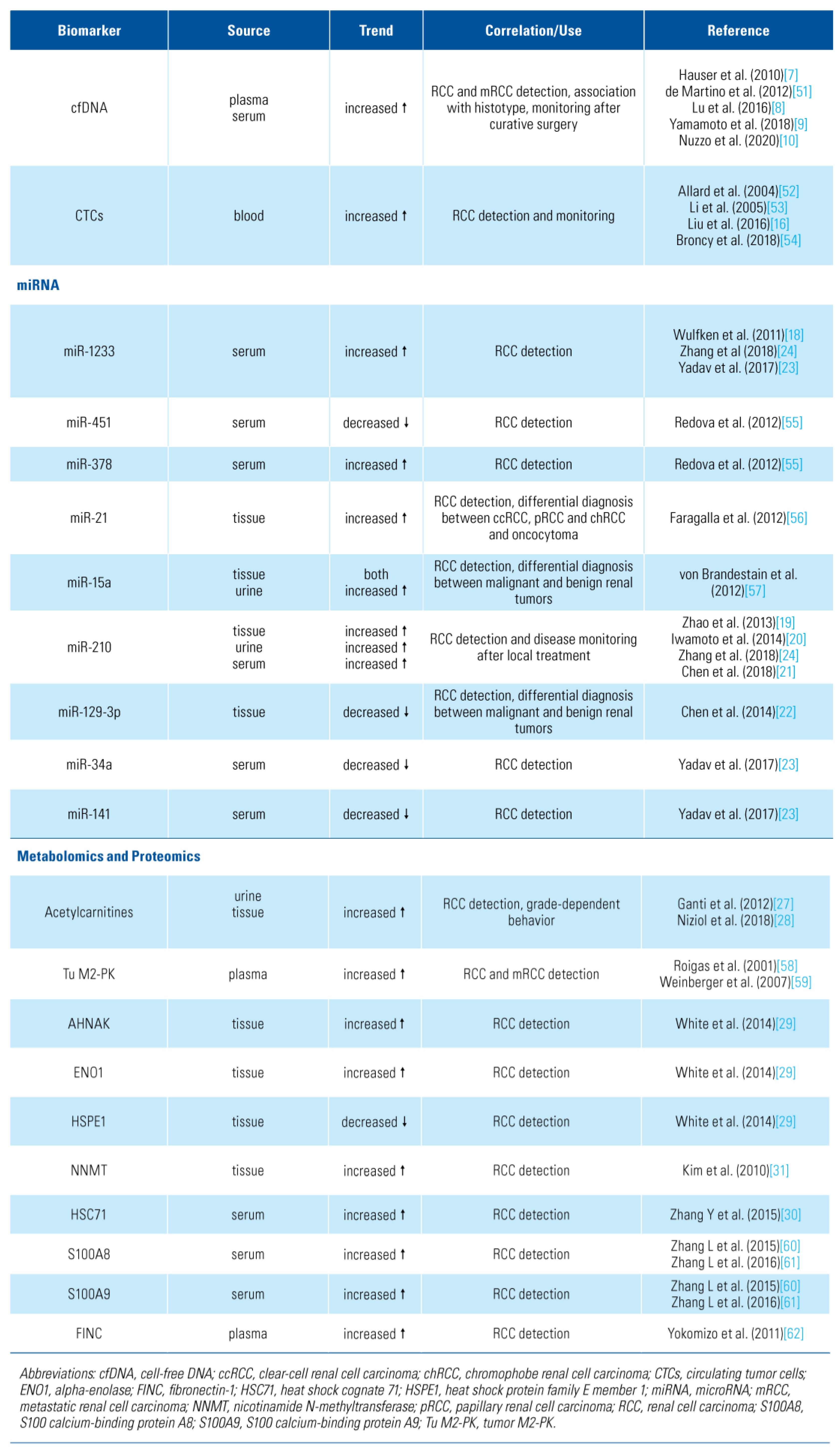
Recent advances in diagnostic techniques have increased early ccRCC detection. Mortality rates, however, remain steady [3]. Imaging studies are still unable to differentiate histology, and renal mass biopsy has a 10% to 20% non-diagnostic rate [4]. Therefore, it is highly desirable to have novel and reliable biomarkers suitable for RCC screening and early detection, ensuring that the benefits of new technologies are fully realised (Table 1).

Table 1.
Novel potential candidates biomarkers in diagnosis and early detection of renal cell carcinoma.
Circulating cell-free DNA
Liquid biopsy assays, such as circulating tumor cells (CTCs) or circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA), constitute promising and less invasive techniques that can overcome the limits related to conventional diagnostic methods [5]. cfDNA consist mostly of double-stranded molecules that circulate as nucleoprotein complexes [6].
Hauser et al. evaluated cfDNA from patients with RCC and from healthy individuals using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Two primer sets amplifying a sequence of the actin-beta gene (ACTB) were used: ACTB-106 detects fragmented cfDNA that results from apoptosis, and ACTB-384 detects long DNA fragments released by necrosis. In this analysis, DNA fragments were significantly increased in RCC patients compared to healthy controls [7]. Lu et al. evaluated cfDNA extracted from plasma of healthy controls and 229 ccRCC patients at stages M0 and M1. The 306 base pairs fragment was lower in RCC patients than in controls. Since cfDNA fragment sizes are indicators of the integrity of cfDNA molecules, the authors showed that the ratio of longer to shorter cfDNA fragments was significantly improved in patients staged as M0 compared with those as M1 subgroup [8]. On plasma cfDNA, Yamamoto et al. showed that median levels of cfDNA and median size of fragments from RCC patients were significantly greater than those from controls. An optimal cut-off value of 2876 copies/mL was identified [9].
Nuzzo et al. performed cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq). cfMeDIP-seq is an enrichment- based method to comprehensively interrogate cfDNA methylation profile extracted from plasma and urine. The authors identified differentially methylated regions and selected the top rated between case and control samples. Samples from RCC patients were assigned a higher median methylation score than those from controls. Furthermore, the lowest methylation scores in RCC patients came from patients with small tumors. Thus the authors reported an accurate classification of patients across all stages of RCC in plasma cfDNA (AUC 0.99) and demonstrated the validity of this assay using urine cfDNA (AUC 0.86) [10].
The abundance and relative fragmentation of cfDNA in blood can be a universal marker for RCC7 yet the precise cfDNA metrics that are most clinically relevant remain controversial. Study results reported to date are limited by heterogeneity with respect to clinical stage, tumor pathology, blood sample processing, and methods of cfDNA analysis.
Circulating tumor cells
CTCs are cells that have been shed into the vasculature or lymphatics from a primary tumor. The detection and analysis of CTCs can assist in determining patient prognosis and personalized treatments, as well as initial diagnostic and monitoring procedures. Moreover, CTCs are particularly suited to interrogate functional heterogeneity by combining genetic and transcriptomic assessment of single CTC [11] or by transcriptome and epigenome analysis [12].
It is difficult to assess the diagnostic value of CTCs in RCC due to the use of different methods of CTC collection and identification across studies [13]. The different techniques include epithelial or non-epithelial marker-dependent isolation, reverse transcription PCR- based methods, and morphological- and cell size-based methods [14]. Moreover, RCC cancer cells are inclined to the loss of their epithelial antigens through epithelial- to-mesenchymal transition, in which morphological transformation leads to acquisition of mesenchymal features [15]. Other surface markers have been developed to select RCC cancer cells in the blood (eg, CAIX). Adding this new set of cell surface markers including CAIX and CD147 to the conventional detection of CTCs through epithelial markers, such as the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), has shown better results [16].
The role of microRNAs
MicroRNAs (miRs) are implicated in the regulation of processes such as proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis, and are readily detectable in tissues and bodily fluids [17].
Wulfken et al. reported that the level of miR-1233 was significantly increased in patients with RCC compared with healthy controls. Thus, miR-1233 levels were investigated in an independent cohort confirming a higher mean value in RCC patients [18]. Zhao et al. found that miR-210 levels were higher in primary RCC tissues than in normal tissue. Furthermore, the serum level of miR-210 was significantly decreased in patients 7 days after nephrectomy; consequently, a potential combined role in early detection and monitoring after radical treatment could be proposed [19]. Iwamoto et al. confirmed at the serum level that the expression of miR-210 was significantly higher in RCC patients than in healthy controls [20]. In addition, a meta-analysis conducted by Chen et al. that included 7 studies, 570 RCC patients, and 415 healthy controls showed pooled sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic OR to predict RCC of 74%, 76%, and 8.81, respectively [21].
Chen et al. evaluated the expression levels of miR- 129-3p and miR-129-5p in 69 cases of paired renal tumors, healthy tissues, and conventional RCC cell lines. MiR-129-3p and miR-129-5p are 2 mature products of miR-129-2 known for its anti-tumor effects in various malignancies. They showed that miR-129-3p, but not miR-129-5p, was widely attenuated in human ccRCC, and chRCC, yielding a 73.5% accuracy in discriminating ccRCC from normal tissues. The relative miR-129-3p expression significantly differed between malignant and benign kidney tumors [22].
In a prospective cohort, Yadav et al. found that use of serum miR-34a, miR-141, and miR-1233 was able to diagnose ccRCC with a sensitivity of 80.76%, 75%, and 93.33%, and specificity of 80%, 73.33%, and 100%, respectively, when tumor pathologic was used as the reference. Moreover, a combined approach using a panel of 2 serum miRs (miR-141 and miR-1233), allowed a diagnosis of ccRCC with 100% sensitivity and 73.3% specificity [23].
Recently, Zhang et al. investigated whether miRNAs in serum exosomes can serve as biomarkers in ccRCC. Their findings showed that the expression levels of exosomal miR-210 and miR-1233 were significantly higher in RCC patients than in healthy individuals (both P < 0.01). ROC analysis demonstrated that exosomal expression levels distinguished RCC patients from healthy individuals with 70% sensitivity and 62.2% specificity for miR-210, and 81% sensitivity and 76% specificity for miR-1233 [24].
Metabolites as novel biomarkers of RCC
Metabolomic approaches have shown promising results in oncology, with the recognition of metabolic reprogramming as a hallmark of cancer. Globally, RCC metabolic signature of the tumor microenvironment is characterized by alterations in metabolites associated with energy metabolism, especially those involved in glycolysis, amino acid metabolism, and fatty acid catabolism pathways, which are essential for cell growth and proliferation [25].
Kim et al. first evaluated the utility of urine meta-bolomics analysis for metabolomic profiling. The authors identified a total of 212 molecules able to differentiate RCC presence. The rate of correct classification was 88% [26]. Ganti et al. showed differential urinary concentrations of several acylcarnitines as a surrogate of RCC status and grade, with most acylcarnitines being increased in RCC patients’ urine. Furthermore, urinary acylcarnitines were increased in a grade-dependent fashion in RCC patients and likely emanated from the tumor tissues. Acylcarnitines have both cytotoxicity and immune modulatory properties and thus may play a role in decreasing the inflammatory response and providing a mechanism by which these cells are able to evade immune surveillance [27]. In the same field, Niziol et al. showed that hydroxybutyrylcarnitine, decanoylcarnitine, propanoylcarnitine, carnitine, dodecanoylcarnitine, and norepinephrine sulfate were found in much higher concentrations in both RCC tissues (compared with the paired normal tissue) and urine of cancer patients (compared with urine of control subjects) [28].
Proteomics analysis
Proteomics offers a useful platform to study the complex molecular events of tumorigenesis. Upregulation in the glycolytic f lux is a common pathway in cancer. Therefore, using isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) White et al. identified 55 proteins significantly dysregulated in RCC. Dysregulation of alpha-enolase (ENO1), L-lactate dehydrogenase A chain (LDHA), heatshock protein beta-1, known as Hsp27, mitochondrial (HSPE1) was confirmed in 2 independent sets of patients by western blot and immunohistochemistry (IHC). The expressions of AHNAK, ENO1, and Hsp27 were found to be significantly elevated in ccRCC compared with matched normal tissues. Whereas HSPE1 was significantly downregulated in RCC patients [29]. Zhang et al. recently found 16 significantly upregulated and 14 significantly downregulated in early-stage RCC compared with healthy controls. Serum heat shock cognate 71 (HSC71) was highly elevated in the RCC group compared with control group [30]. Kim et al. showed that RCC upregulated proteins were nicotinamide-N-methyl- transferase (NNMT), secretagogin (SCGN), L-plastin, human neuron specific enolase (hNSE), nonmetastatic cell 1 (NM23A), ferritin light chain (FTL), and thioredoxin peroxidase (KIM2010). NNMT was the most commonly upregulated protein over all types of RCC, especially in comparison with normal tissues. SCGN was elevated in ccRCC samples but not in papillary, chromophobe, or normal tissue, while NM23A showed the same behavior, although the magnitude of changes was smaller than in the first 2 molecules [31].
Prognostic Biomarkers
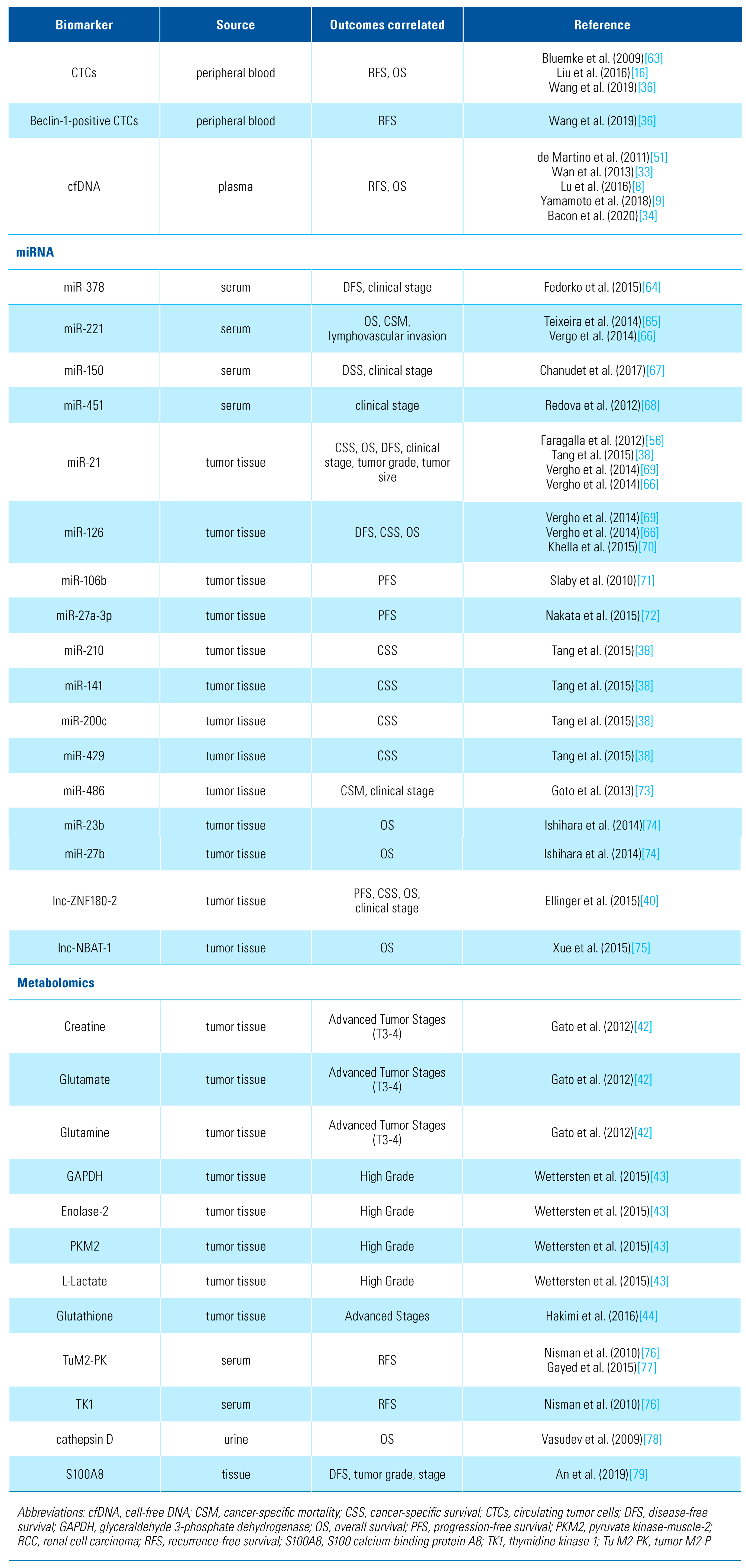
Although most biomarkers for early detection and diagnosis remain at an early stage, more advances have been made with prognostic biomarkers for RCC. To date, few biomarkers have been taken beyond single studies, thus none are yet ready for routine clinical practice. Furthermore, emerging and promising approaches can serve as new platform in which novel potential biomarkers can be found. Following any type of surgical treatment of RCC, there is a need for risk stratification aiming to enable personalized outcome prediction. The major endpoints evaluated and predicted using prognostic biomarkers across the studies referred to in the following sections of this paper are disease/ progression/recurrence-free survival (D/P/RFS), overall and cancer-specific survival (OS, CSS), and correlations with clinicopathological features that might influence the prognosis among these patients [32] (Table 2).

Table 2.
Novel potential candidate biomarkers in prognosis of renal cell carcinoma.
cfDNA
One of the most promising uses of liquid biopsy is to determine the risk of recurrence after curative treatment. Wan et al. measured plasma levels of cfDNA before and after surgery for localized disease. Mean preoperative level of plasma cfDNA in patients who developed recurrent disease was significantly higher than in those with localized disease or controls [33]. Analyzing the genomic and mitochondrial cfDNA concentrations, Lu et al. developed 2 models that incorporated clinicopathological features to specific expression patterns among cfDNA fragments. Particularly, APP gene, the Alu sequences, and the mitochondrial DNA fragments showing significant correlation in terms of OS and RFS [8]. In terms of quantitative measurement, Yamamoto et al. divided their cohort into 2 subgroups according to the length of cfDNA fragments. Their results showed that cfDNA fragment size was significantly associated with progression-free survival (PFS). Although cfDNA fragmentation correlated with poorer outcomes, cfDNA plasma levels were not associated with any of survival outcomes [9]. Evaluating plasma circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) as a subset of cfDNA, Bacon et al. reported that only 33% of patients had detectable ctDNA. Among ctDNA-positive patients the most commonly mutated genes were VHL, BAP1, and PBRM1. Moreover, ctDNA-positive patients had shorter OS and PFS on first-line therapy [34].
CTCs identification
An initial experience using a RT-PCR assay to detect CTCs in peripheral blood of patients at different stages of RCC reported a different rate of positivity on localized and metastatic RCC (mRCC) [35]. Developing a new set of cell surface markers including CAIX and CD147, Liu et al. showed a significant association of CTC number/ CTC expression status of vimentin, with disease progression [16]. Wang et al. investigated the relationship of dynamic changes of CTCs and Beclin-1 expression of CTCs and RCC prognosis. CTCs were divided into epithelial, mesenchymal, and mixed phenotype-based surface biomarkers. For the metastatic group, the number of mixed CTCs at 12 months was significantly higher than mixed preoperatively and 6 months CTCs. Of note, the number of preoperative Beclin-1 positive CTCs was significantly higher in the metastatic group. Thus, variation trend of CTCs and Beclin-1 expressive CTCs was significantly associated with the onset of metastatic disease [36]. Moreover, in a prospective cohort of 60 patients who underwent surgical treatment with curative intent, Haga et al. evaluated CTCs drawn from a peripheral artery collected just before and immediately after surgery. The authors showed that open nephrectomy resulted in a significantly greater number of postoperative CTCs. At multivariate level that the surgical approach was significantly correlated with the number of postoperative CTCs (P = 0.016) and the perioperative change in CTCs (P = 0.01). Thus, especially after open surgery more cancer cells can be expelled into the bloodstream, suggesting a careful follow-up for these patients [37].
miRNA
In a comprehensive meta-analysis of 29 published studies reporting miRNA signatures in RCC, Tang et al. identified a robust meta-signature of miRNAs as a prognostic biomarker. They reported that high expression of miR-21, miR-210, and low expression of miR-141, miR-200c, and miR-429 were associated with worse CSS following RCC resection [38]. Similarly, Gu et al. conducted a meta-analysis of 27 published studies and found that elevated expression of miR-21, miR-1260b, miR-210, miR-100, miR-125b, miR-221, miR-630, and miR-497 was associated with a poor prognosis in RCC patients. Conversely, decreased expression of miR-106b, miR-99a, miR-1826, miR-215, miR-217, miR- 187, miR-129–3p, miR-23b, miR-27b, and miR-126 was associated with a worse prognosis. Importantly, the results from this meta-analysis confirmed that elevated miR-21 expression was associated with shorter OS, CSS, and DFS. The decreased expression of miR-126 was associated with shorter CSS, OS, and DFS [39].
Also, results were promising in a study by Ellinger et al. regarding specific circulating long non-coding (lnc) RNAs, defined as RNA transcripts longer than 200 nucleotides that are not transcribed into a protein. The authors next validated the expression profile of 6 lncRNAs transcripts (lnc-ACO1625, lnc-CYP4A22-2/3, lnc-PEAK1.1-1, lnc-PCYOX1L, lnc-VCAN-1, lnc-ZNF180-2) with potential prognostic interest. A significant increase of lnc-ZNF180-2 expression in advanced RCC tissue compared with localized RCC was observed. Furthermore, lnc-ZNF180-2 expression levels were an independent predictor of PFS, CSS, and OS [40]. Qu et al. built a model named RCClnc4 based on 4 lncRNAs to improve postoperative risk stratification after radical treatment. Stratifying patients into high-risk versus low-risk groups in terms of clinical outcomes, RCClnc4 remained as an independent prognostic factor, achieving a higher accuracy than clinical staging systems like TNM and SSIGN score [41].
Prognostic value of metabolomic approaches
Analyzing tumors and their matched tissue, Gao et al. studied the metabolomic RCC profile. Creatine, glutamate, and glutamine were found at higher concentrations in tissues of tumors at T3-4 stages [42]. The glycolysis-relevant metabolites are significantly increased in high-grade disease, suggesting that glucose metabolism is more prominent with increasing tumor grade. Consequently, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, enolase 2, and pyruvate kinase- muscle-2 are increased in tumor tissue as compared with normal tissues. L-lactate follows the same tendency in a grade-dependent manner. Also levels of carnitine and acyl/acetyl-carnitines were associated with grade, suggesting how the combination of these metabolites can predict the biological aggressiveness of RCC and thus influence its prognosis [43]. A study by Hakemi et al. showed increased levels of glutathione were also grade- and stage-dependent [44]. Thus, the upregulation of antioxidant capacity in adaptation to intrinsic oxidative stress is indeed a common event in RCC, especially in the advanced stages [45].
Epigenetic and DNA methylation biomarkers
Epigenetic variations play an important role in renal carcinogenesis and progression. DNA methylation is defined as a covalent addition of a methyl group to cytosines that precede a guanosine which are mainly clustered as CpG islands in the promoter region of genes bringing a functional silencing [46]. Furthermore, DNA methylation alterations are often shown to be associated with clinicopathological features and RCC patient survival or both [47]. CpG island methylation markers reflect tumor biology, allowing the identification of patients with “high epigenetic risk” who can benefit from tailored management to improve survival outcomes.
In a recent systematic review, Joosten et al. described 9 genes (SFRP1, BNC1, GREM1, RASSF1A, PCDH8, SCUBE3, GATA5, LAD1, and NEFH), associated with patient survival. Their prognostic value was independently validated in other studies [48]. To develop a 5-CpG-based assay for ccRCC prognosis, a panel composed by methylation of PITX1, FOXE3, TWF2, RIN1, and EHBP1L, was validated in 3 independent sets from China, the United States, and the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Stratifying patients into 2 groups from this 5-CpG panel, Wei et al. defined low- and high-risk categories. An important correlation between the high-risk group and poorer OS [49] was demonstrated. With the same endpoint, Chen et al. identified 7 specific prognosis-subgroups based on the DNA methylation spectrum of RCC from the TCGA database. The specific DNA methylation patterns reflected differentially in the clinical index, including TNM classification, pathological grade, clinical stage, and age. In addition, 437 CpGs corresponding to 477 genes of 151 samples were identified as specific hyper/hypomethylation sites for each specific subgroup. The authors then constructed a Bayesian classifier to determine the function of the prognosis prediction model, with 437 specific CpG sites as characters (AUC 0.95) [50].
Conclusions
Cancer biomarkers have shifted treatment and management of patients with many cancer types. Although “personalized” medicine is becoming more common in our daily practice, none of the RCC biomarkers discussed are in routine clinical use. Metabolomics and proteomics studies have shown excellent potential in terms of diagnostic accuracy, but research in these areas still appears to be hypothesis-generating. Most of publications mentioned above aimed to understand tumor biology due to the high heterogenicity of RCC.
Circulating biomarkers have attracted a lot of interest; however, the great diversity of techniques precludes any further conclusions. The growing use of liquid biopsy, popularized by the easy accessibility of samples, and the accompanying standardization of methods of analysis and quantification of CTCs, cfDNA and miRNAs will continue to provide promising results. Particularly, NGS cfDNA is a novel technology that can complement tumor tissue biopsy. It has demonstrated its potential role across the diagnostic and prognostic fields of both localized and metastatic RCC. Single molecule validations are being replaced by multipanel biomarkers to provide improved validation results. It also reflects the role of molecular biology in current clinical nomograms as a transition tool from bench to bedside.
Conflicts of Interest
None declared.
Abbreviations
| ACTB | actin-beta gene |
| ccRCC | clear-cell renal cell carcinoma |
| CSS | cancer-specific survival |
| CTCs | circulating tumor cells |
| cfDNA | circulating cell-free DNA |
| miRs | microRNAs |
| OS | overall survival |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| PFS | progression-free survival |
| RCC | renal cell carcinoma |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capitanio, U.; Cloutier, V.; Zini, L.; Isbarn, H.; Jeldres, C.; Shariat, S.F.; et al. A critical assessment of the prognostic value of clear cell, papillary and chromophobe histological subtypes in renal cell carcinoma: A population-based study. BJU Int. 2009, 103, 1496–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, M.; Lucarelli, G. The role of renal surgery in the era of targeted therapy: The urologist’s perspective. Urol. J. 2015, 82, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconi, L.; Dabestani, S.; Lam, T.B.; Hofmann, F.; Stewart, F.; Norrie, J.; et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy of percutaneous renal tumour biopsy. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Casas, A.; García-Olmo, D.C.; García-Olmo, D. Further the liquid biopsy: Gathering pieces of the puzzle of genometastasis theory. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 8, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischhacker, M.; Schmidt, B. Circulating nucleic acids (CNAs) and cancer-A survey. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2007, 1775, 181–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, S.; Zahalka, T.; Ellinger, J.; Fechner, G.; Heukamp, L.C.; Von Ruecker, A.; et al. Cell-free circulating DNA: Diagnostic value in patients with renal cell cancer. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 2785–2789. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Busch, J.; Jung, M.; Rabenhorst, S.; Ralla, B.; Kilic, E.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic potential of circulating cell-free genomic and mitochondrial DNA fragments in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. Clin. Chim Acta 2016, 452, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Uemura, M.; Nakano, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Wang, C.; Ishizuya, Y.; et al. Increased level and fragmentation of plasma circulating cell-free DNA are diagnostic and prognostic markers for renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 20467–20475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, P.V.; Berchuck, J.E.; Korthauer, K.; Spisak, S.; Nassar, A.H.; Abou Alaiwi, S.; et al. Detection of renal cell carcinoma using plasma and urine cell-free DNA methylomes. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1041–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.A.; Seidl, S.; Petat-Dutter, K.; Offner, S.; Geigl, J.B.; Schmidt-Kitler, O.; et al. Combined transcriptome and genome analysis of single micrometastatic cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Hu, S.; Huo, X.; Zhang, Y. Dr. seq2, A quality control and analysis pipeline for parallel single cell transcriptome and epigenome data. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180583. [Google Scholar]
- Cimadamore, A.; Massari, F.; Santoni, M.; Mollica, V.; Di Nunno, V.; Cheng, L.; et al. Molecular characterization and diagnostic criteria of renal cell carcinoma with emphasis on liquid biopsies. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 00, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Toom, E.E.; Verdone, J.E.; Gorin, M.A.; Pienta, K.J. Technical challenges in the isolation and analysis of circulating tumor cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 62754–62766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piva, F.; Giulietti, M.; Santoni, M.; Occhipinti, G.; Scarpelli, M.; Lopez- Beltran, A.; et al. Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Renal Cell Carcinoma: Implications for Cancer Therapy. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2016, 20, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hou, S.; Hu, S.; Wu, J.; et al. Combined cell surface carbonic anhydrase 9 and CD147 antigens enable high- efficiency capture of circulating tumor cells in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 59877–59891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteller, M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulfken, L.M.; Moritz, R.; Ohlmann, C.; Holdenrieder, S.; Jung, V.; Becker, F.; et al. MicroRNAs in renal cell carcinoma: Diagnostic implications of serum miR-1233 levels. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Li, G.; Péoc’h, M.; Genin, C.; Gigante, M. Serum miR-210 as a novel biomarker for molecular diagnosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2013, 94, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, H.; Kanda, Y.; Sejima, T.; Osaki, M.; Okada, F.; Takenaka, A. Serum miR-210 as a potential biomarker of early clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Shao, S. Detection performance of circulating MicroRNA-210 for renal cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Clin. Lab. 2018, 64, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ruan, A.; Wang, X.; Han, W.; Wang, R.; Lou, N.; et al. miR-129-3p, as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for renal cell carcinoma, attenuates cell migration and invasion via downregulating multiple metastasis-related genes. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Khandelwal, M.; Seth, A.; Saini, A.K.; Dogra, P.N.; Sharma, A. Serum microRNA expression profiling: Potential diagnostic implications of a panel of serum microRNAs for clear cell renal cell cancer. Urology 2017, 104, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ni, M.; Su, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, A.; et al. MicroRNAs in serum exosomes as potential biomarkers in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. Focus 2018, 4, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catchpole, G.; Platzer, A.; Weikert, C.; Kempkensteffen, C.; Johannsen, M.; Krause, H.; et al. Metabolic profiling reveals key metabolic features of renal cell carcinoma. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Aronov, P.; Zakharkin, S.O.; Anderson, D.; Perroud, B.; Thompson, I.M.; et al. Urine metabolomics analysis for kidney cancer detection and biomarker discovery. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2009, 8, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganti, S.; Taylor, S.L.; Kim, K.; Hoppel, C.L.; Guo, L.; Yang, J.; et al. Urinary acylcarnitines are altered in human kidney cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 2791–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizioł, J.; Bonifay, V.; Ossoliñski, K.; Ossoliñski, T.; Ossoliñski, A.; Sunner, J.; et al. Metabolomic study of human tissue and urine in clear cell renal carcinoma by LC-HRMS and PLS-DA. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 3859–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, N.M.A.; Masui, O.; DeSouza, L.V.; Krakovska-Yutz, O.; Metias, S.; Romaschin, A.D.; et al. Quantitative proteomic analysis reveals potential diagnostic markers and pathways involved in pathogenesis of renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, H. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis identified HSC71 as a novel serum biomarker for renal cell carcinoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 802153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Choi, Y.P.; Kang, S.; Gao, M.Q.; Kim, B.; Park, H.R.; et al. Panel of candidate biomarkers for renal cell carcinoma. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3710–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golovastova, M.O.; Korolev, D.O.; Tsoy, L.V.; Varshavasky, V.A.; Xu, W.-H.; Vinarov, A.Z.; et al. Biomarkers of renal tumors: The current state and clinical perspectives. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, K. Monitoring of plasma cell-free DNA in predicting postoperative recurrence of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Int. 2013, 91, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, J.V.W.; Annala, M.; Soleimani, M.; Lavoie, J.-M.; So, A.; Gleave, M.E.; et al. Plasma circulating tumor DNA and clonal hematopoiesis in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin Cancer 2020, 18, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKiernan, J.M.; Buttyan, R.; Bander, N.H.; de la Taille, A.; Stifelman, M.D.; Emanuel, E.R.; et al. The detection of renal carcinoma cells in the peripheral blood with an enhanced reverse transcriptase- polymerase chain reaction assay for MN/CA9. Cancer 1999, 86, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-L.; Zhang, P.; Li, H.-C.; Yang, X.-J.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Li, Z.-L.; et al. Dynamic changes of different phenotypic and genetic circulating tumor cells as a biomarker for evaluating the prognosis of RCC. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, N.; Onagi, A.; Koguchi, T.; Hoshi, S.; Ogawa, S.; Akaihata, H.; et al. Perioperative detection of circulating tumor cells in radical or partial nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.; Xu, H. Prognostic value of meta-signature miRNAs in renal cell carcinoma: An integrated miRNA expression profiling analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Ma, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; et al. MicroRNAs as prognostic molecular signatures in renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 32545–32560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinger, J.; Alam, J.; Rothenburg, J.; Deng, M.; Schmidt, D.; Syring, I.; et al. The long non-coding RNA lnc-ZNF180-2 is a prognostic biomarker in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2799–2807. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, L.; Wang, Z.-L.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.-M.; He, H.-W.; Hsieh, J.J.; et al. Prognostic value of a long non-coding RNA signature in localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Dong, B.; Jia, J.; Zhu, H.; Diao, C.; Yan, Z.; et al. Application of ex vivo 1H NMR metabonomics to the characterization and possible detection of renal cell carcinoma metastases. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 138, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettersten, H.I.; Hakimi, A.A.; Morin, D.; Bianchi, C.; Johnstone, M.E.; Donohoe, D.R.; et al. Grade-dependent metabolic reprogramming in kidney cancer revealed by combined proteomics and metabolomics analysis. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2541–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakimi, A.A.; Reznik, E.; Lee, C.H.; Creighton, C.J.; Brannon, A.R.; Luna, A.; et al. An integrated metabolic atlas of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trachootham, D.; Alexandre, J.; Huang, P. Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical therapeutic approach? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylin, S.B. DNA methylation and gene silencing in cancer. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2005, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.R.; Latif, F. The epigenetic landscape of renal cancer. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosten, S.C.; Deckers, I.A.; Aarts, M.J.; Hoeben, A.; van Roermund, J.G.; Smits, K.M.; et al. Prognostic DNA methylation markers for renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review. Epigenomics 2017, 9, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.-H.; Haddad, A.; Wu, K.-J.; Zhao, H.-W.; Kapur, P.; Zhang, Z.-L.; et al. A CpG-methylation-based assay to predict survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, P.P.; Jiang, J.; Lin, C.; Zeng, P.; et al. DNA methylation-based classification and identification of renal cell carcinoma prognosis-subgroups. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, M.; Klatte, T.; Haitel, A.; Marberger, M. Serum cell-free DNA in renal cell carcinoma: A diagnostic and prognostic marker. Cancer 2012, 118, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, W.J.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Repollet, M.; Connelly, M.C.; Rao, C.; et al. Tumor cells circulate in the peripheral blood of all major carcinomas but not in healthy subjects or patients with nonmalignant diseases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Passebosc-Faure, K.; Gentil-Perret, A.; Lambert, C.; Genin, C.; Tostain, J. Cadherin-6 gene expression in conventional renal cell carcinoma: A useful marker to detect circulating tumor cells. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Broncy, L.; Njima BBen Méjean, A.; Béroud, C.; Romdhane, K.B.; Ilie, M.; et al. Single-cell genetic analysis validates cytopathological identification of circulating cancer cells in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 20058–20074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redova, M.; Poprach, A.; Nekvindova, J.; Iliev, R.; Radova, L.; Lakomy, R.; et al. Circulating miR-378 and miR-451 in serum are potential biomarkers for renal cell carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faragalla, H.; Youssef, Y.M.; Scorilas, A.; Khalil, B.; White, N.M.A.; Mejia-Guerrero, S.; et al. The clinical utility of miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic marker for renal cell carcinoma. J. Mol. Diagn. 2012, 14, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Brandenstein, M.; Pandarakalam, J.J.; Kroon, L.; Loeser, H.; Herden, J.; Braun, G.; et al. MicroRNA 15a, inversely correlated to PKC, is a potential marker to differentiate between benign and malignant renal tumors in biopsy and urine samples. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roigas, J.; Schulze, G.; Raytarowski, S.; Jung, K.; Schnorr, D.; Loening, S.A. Tumor M2 pyruvate kinase in plasma of patients with urological tumors. Tumor Biol. 2001, 22, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, R.; Appel, B.; Stein, A.; Metz, Y.; Neheman, A.; Barak, M. The pyruvate kinase isoenzyme M2 (Tu M2-PK) as a tumour marker for renal cell carcinoma: Original article. Eur. J. Cancer Care (Engl.) 2007, 16, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.; Xu, G.; Wen, H.; Gu, B.; Liu, J.; et al. Proteins S100A8 and S100A9 are potential biomarkers for renal cell carcinoma in the early stages: Results from a proteomic study integrated with bioinformatics analysis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 4093–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.; Xu, G.; Chu, N.; Xu, N.; Wen, H.; et al. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis reveals potential early diagnostic markers of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Biosci. Trends 2016, 10, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yokomizo, A.; Takakura, M.; Kanai, Y.; Sakuma, T.; Matsubara, J.; Honda, K.; et al. Use of quantitative shotgun proteomics to identify fibronectin 1 as a potential plasma biomarker for clear cell carcinoma of the kidney. Cancer Biomarkers 2011, 10, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluemke, K.; Bilkenroth, U.; Meye, A.; Fuessel, S.; Lautenschlaeger, C.; Goebel, S.; et al. Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood of patients with renal cell carcinoma correlates with prognosis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2009, 18, 2190–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorko, M.; Stanik, M.; Iliev, R.; Redova-Lojova, M.; Machackova, T.; Svoboda, M.; et al. Combination of MiR-378 and MiR-210 serum levels enables sensitive detection of renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 23382–23389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, A.L.; Ferreira, M.; Silva, J.; Gomes, M.; Dias, F.; Joaquina, S.; et al. Higher circulating expression levels of miR-221 associated with poor overall survival in renal cell carcinoma patients. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 4057–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergho, D.C.; Kneitz, S.; Kalogirou, C.; Burger, M.; Krebs, M.; Rosenwald, A.; et al. Impact of miR-21, miR-126 and miR-221 as prognostic factors of clear cell renal cell carcinoma with tumor thrombus of the inferior vena cava. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanudet, E.; Wozniak, M.B.; Bouaoun, L.; Byrnes, G.; Mukeriya, A.; Zaridze, D.; et al. Large-scale genome-wide screening of circulating microRNAs in clear cell renal cell carcinoma reveals specific signatures in late-stage disease. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 1730–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redova, M.; Poprach, A.; Nekvindova, J.; Iliev, R.; Radova, L.; Lakomy, R.; et al. Circulating miR-378 and miR-451 in serum are potential biomarkers for renal cell carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergho, D.; Kneitz, S.; Rosenwald, A.; Scherer, C.; Spahn, M.; Burger, M.; et al. Combination of expression levels of miR-21 and miR-126 is associated with cancer-specific survival in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khella, H.W.Z.; Scorilas, A.; Mozes, R.; Mirham, L.; Lianidou, E.; Krylov, S.N.; et al. Low expression of miR-126 Is a prognostic marker for metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaby, O.; Jancovicova, J.; Lakomy, R.; Svoboda, M.; Poprach, A.; Fabian, P.; et al. Expression of miRNA-106b in conventional renal cell carcinoma is a potential marker for prediction of early metastasis after nephrectomy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, W.; Uemura, M.; Sato, M.; Fujita, K.; Jingushi, K.; Ueda, Y.; et al. Expression of miR-27a-3p is an independent predictive factor for recurrence in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 21645–21654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Goto, K.; Oue, N.; Shinmei, S.; Sentani, K.; Sakamoto, N.; Naito, Y.; et al. Expression of miR-486 is a potential prognostic factor after nephrectomy in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 1, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ishihara, T.; Seki, N.; Inoguchi, S.; Yoshino, H.; Tatarano, S.; Yamada, Y.; et al. Expression of the tumor suppressive miRNA-23b/27b cluster is a good prognostic marker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2014, 192, 1822–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, S.; Li, Q.-W.; Che, J.-P.; Guo, Y.; Yang, F.-Q.; Zheng, J.-H. Decreased expression of long non-coding RNA NBAT-1 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 3765–3774. [Google Scholar]
- Nisman, B.; Yutkin, V.; Nechushtan, H.; Gofrit, O.N.; Peretz, T.; Gronowitz, S.; et al. Circulating tumor M2 pyruvate kinase and thymidine kinase 1 are potential predictors for disease recurrence in renal cell carcinoma after nephrectomy. Urology 2010, 76, 513–e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayed, B.A.; Gillen, J.; Christie, A.; Peña-Llopis, S.; Xie, X.-J.; Yan, J.; et al. Prospective evaluation of plasma levels of ANGPT2, TuM2PK, and VEGF in patients with renal cell carcinoma. BMC Urol. 2015, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudev, N.S.; Sim, S.; Cairns, D.A.; Ferguson, R.E.; Craven, R.A.; Stanley, A.; et al. Pre-operative urinary cathepsin D is associated with survival in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.J.; Koh, H.M.; Song, D.H. S100A8 expression may have a prognostic value in CCRCC reflecting TNM staging and Fuhrman nuclear grade. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 4681–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
This is an open access article under the terms of a license that permits non-commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. © 2021 The Authors. Société Internationale d'Urologie Journal, published by the Société Internationale d'Urologie, Canada.