Preoperative Six-Minute Walking Distance as a Predictor of Postoperative Complications in Patients Undergoing Lobectomy for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Highlights
- Preoperative six-minute walking distance (6MWD) of ≤450 m was independently associated with a 5.6-fold higher risk of 30-day postoperative pulmonary complications after VATS lobectomy for non-small-cell lung cancer.
- In the logistic regression analysis focusing on pulmonary complications, the length of hospital stay was further identified as a significant factor.
- A simple, low-cost six-minute walk test (6MWT) can serve as a practical preoperative risk stratification tool, complementing routine spirometry to identify high-risk patients.
- Patients with a 6MWD of ≤450 m may benefit from targeted prehabilitation or intensified perioperative management to reduce postoperative morbidity.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haruki, T.; Takagi, Y.; Kubouchi, Y.; Kidokoro, Y.; Nakanishi, A.; Taniguchi, Y.; Nakamura, H. Current status of robot-assisted thoracoscopic surgery in Japan. J. Vis. Surg. 2020, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howington, J.A.; Blum, M.G.; Chang, A.C.; Balekian, A.A.; Murthy, S.C. Treatment of stage I and II non–small cell lung cancer: Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2013, 143, 278S–313S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Japanese Association for Thoracic Surgery. Thoracic and cardiovascular surgeries in Japan during 2023: Annual report by the Japanese Association for Thoracic Surgery. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2025, 68, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Rauniyar, R.; Yang, J.; Zhou, C.; Cai, D.; Chen-Yoshikawa, T.F.; Yutaka, Y.; Orlandi, R.; Geraci, T.C.; Lin, J.; et al. Risk stratification of postoperative pulmonary complications in elderly patients undergoing lung cancer resection: A propensity score-matched study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2023, 15, 3908–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, F.G.; Kosinski, A.S.; Burfeind, W.R.; Jacobs, J.P.; Magee, M.J.; Boffa, D.J.; Wright, C.D. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons lung cancer resection risk model: Higher quality data and superior outcomes. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 102, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunelli, A.; Charloux, A.; Bolliger, C.T.; Rocco, G.; Sculier, J.P.; Varela, G.; Licker, M.; Ferguson, M.K.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Huber, R.M.; et al. ERS/ESTS clinical guidelines on fitness for radical therapy in lung cancer patients (surgery and chemo-radiotherapy). Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskovic, A.; Lumb, A.B. Postoperative pulmonary complications. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 118, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, K.J.; Skinner, E.H.; Berney, S. Association of postoperative pulmonary complications with delayed mobilization following major abdominal surgery: An observational cohort study. Physiotherapy 2013, 99, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Funakoshi, Y.; Ohse, N.; Kusumoto, H.; Maeda, H. Postoperative pneumonia after lung cancer. J. Jpn. Assoc. Chest Surg. 2010, 24, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, F.; Cara, A.; Cassina, E.M.; Faverio, P.; Franco, G.; Libretti, L.; Pirondini, E.; Raveglia, F.; Sibilia, M.C.; Tuoro, A.; et al. Evaluation of preoperative cardiopulmonary reserve and surgical risk of patients undergoing lung cancer resection. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2024, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories. ATS statement: Guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeratichananont, W.; Thanadetsuntorn, C.; Keeratichananont, S. Value of preoperative six-minute walk test for predicting postoperative pulmonary complications. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2016, 10, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enright, P.L.; Sherrill, D.L. Reference equations for the six-minute walk in healthy adults. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 158, 1384–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japanese Respiratory Society. Respiratory Function Tests: Guidelines for Clinical Practice (2014); Japanese Respiratory Society: Tokyo, Japan, 2014. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Oken, M.M.; Creech, R.H.; Tormey, D.C.; Horton, J.; Davis, T.E.; McFadden, E.T.; Carbone, P.P. Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 1982, 5, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brierley, J.D.; Gospodarowicz, M.K.; Wittekind, C. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 8th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2017; Available online: https://www.uicc.org/resources/tnm-classification-malignant-tumours-8th-edition (accessed on 18 July 2025).
- Freitas Júnior, R.; Nunes, R.D.; Martins, E.; Curado, M.P.; Freitas, N.M.A.; Soares, L.R.; Oliveira, J.C. Prognostic factors and overall survival of breast cancer in the city of Goiania, Brazil: A population-based study. Rev. Col. Bras. Cir. 2017, 44, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, B.F.A.; Souza, H.C.D.; Miranda, A.P.B.; Cipriano, F.G.; Gastaldi, A.C. Performance in the six-minute walk test and postoperative pulmonary complications in pulmonary surgery: An observational study. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2016, 20, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.W.; Watson, D.; Herndon, J.E.; Eves, N.D.; Haithcock, B.E.; Loewen, G.J.; Kohman, L. Peak oxygen consumption and long-term all-cause mortality in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 2010, 116, 4825–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, K.; Matsuda, T.; Takagi, Y.; Nagaya, M.; Inoue, T.; Nishida, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kawaguchi, K.; Fukui, T.; Ozeki, N.; et al. Preoperative six-minute walk distance is associated with pneumonia after lung resection. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2018, 26, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, T.; Jackson, A.; Sharples, L.; Groves, A.M.; Wells, F.C.; Ritchie, A.J.; Laroche, C.M. Cardiopulmonary exercise tests and lung cancer surgical outcome. Chest 2005, 127, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, A.E.; Spruit, M.A.; Troosters, T.; Puhan, M.A.; Pepin, V.; Saey, D.; McCormack, M.C.; Carlin, B.W.; Sciurba, F.C.; Pitta, F.; et al. An official European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society technical standard: Field walking tests in chronic respiratory disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1428–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanski, T.; Wnuk, D.; Bosakowski, D.; Szmuda, T.; Sawicka, W.; Rzyman, W. Patients who do not reach a distance of 500 m during the 6-min walk test have an increased risk of postoperative complications and prolonged hospital stay after lobectomy. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2015, 47, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanski, T.; Wnuk, D.; Dziedzic, R.; Ostrowski, M.; Sawicka, W.; Rzyman, W. 500 Meters Is a Result of 6-Minute Walk Test Which Differentiates Patients with High and Low Risk of Postoperative Complications after Lobectomy—A Validation Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruit, M.A.; Singh, S.J.; Garvey, C.; ZuWallack, R.; Nici, L.; Rochester, C.; Hill, K.; Holland, A.E.; Lareau, S.C.; Man, W.D.-C.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Statement: Key Concepts and Advances in Pulmonary Rehabilitation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 13–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salati, M.; Andolfi, M.; Roncon, A.; Guiducci, G.M.; Xiumè, F.; Tiberi, M.; Nanto, A.C.; Cingolani, S.; Ricci, E.; Refai, M. Does the Performance of a Six-Minute Walking Test Predict Cardiopulmonary Complications After Uniportal Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery Anatomic Lung Resection? Cancers 2024, 17, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qiu, T.; Pei, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Cui, Y.; Liang, N.; Li, S.; Chen, W.; Huang, Y. Two-Week Multimodal Prehabilitation Program Improves Perioperative Functional Capability in Patients Undergoing Thoracoscopic Lobectomy for Lung Cancer: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 131, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.W.C.; Heutlinger, O.; Dong, S.; Scott, B.; Kucera, J.; Antevil, J.L.; Trachiotis, G.D. Perioperative rehabilitation and the impact of multidisciplinary teams following video-assisted thoracoscopic pulmonary resection: A narrative review. Video-Assist. Thorac. Surg. 2025, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelli, A.; Hardavella, G.; Huber, R.M.; Berghmans, T.; Frille, A.; Rodriguez, M.; Tietzova, I.; Depypere, L.; Asteggiano, R.; Batchelor, T.; et al. European Respiratory Society and European Society of Thoracic Surgeons clinical practice guideline on fitness for curative intent treatment of lung cancer. Eur. Respir. J. 2025, 66, 2500156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Fu, L.; He, D.; Chen, X.; Chen, K. Blood Urea Nitrogen to Serum Albumin Ratio as a Potential Marker for Predicting 28-Day Mortality in Older Adults with Sepsis. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2025, 63, 56008–56016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasyanto, T.; Tridamayanti, A. Blood Urea Nitrogen as a Predictor of In-Hospital Mortality in Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients. Indones. J. Med. 2019, 4, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C.; Kushner, I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
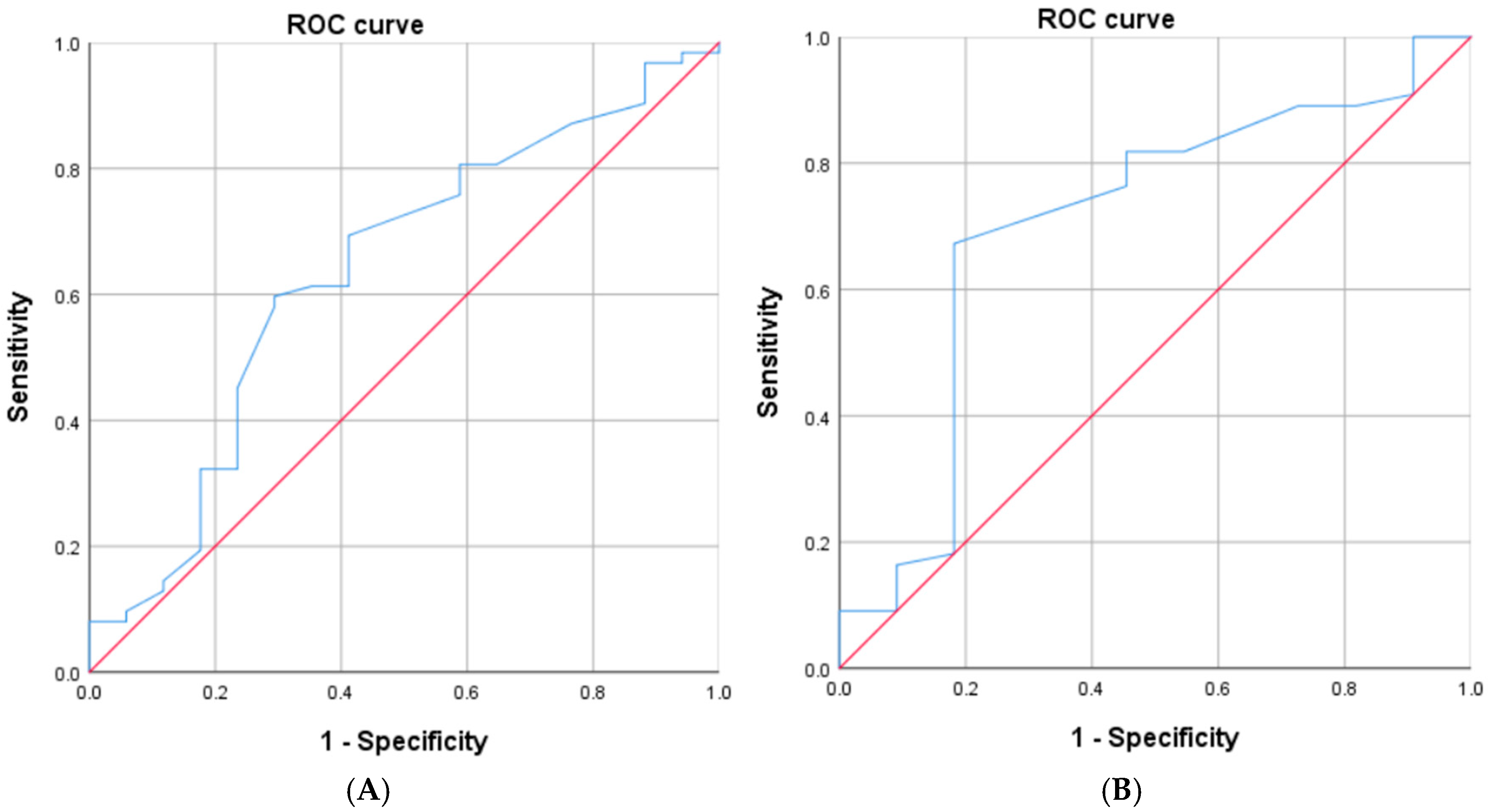
| (A) | |||
| Characteristics | PC Group (n = 20) | Non-PC Group (n = 46) | p |
| n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Age | 73 ± 4 | 68 ± 10 | 0.142 |
| Sex, Female (%) | 8 (40%) | 20 (43%) | 0.364 |
| Male (%) | 12 (60%) | 26 (57%) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25 ± 4 | 23 ± 4 | 0.018 * |
| Brinkman index (smoking) | 898 ± 770 | 490 ± 271 | 0.143 |
| Comorbidity | 0.269 | ||
| COPD | 2 (10%) | 2 (4%) | |
| Interstitial pneumonia | 2 (10%) | 1 (2%) | |
| Hypertension | 12 (60%) | 19 (41%) | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 5 (25%) | 7 (15%) | |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 0.4 ± 0.7 | 0.1 ± 0.3 | 0.048 * |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 17 ± 4 | 14 ± 4 | 0.002 ** |
| WBC (μL) | 6615 ± 1867 | 6043 ± 1580 | 0.258 |
| Alb (g/dL) | 3 ± 0.4 | 4 ± 0.4 | 0.136 |
| FVC (% predicted) | 116 ± 17 | 108 ± 23 | 0.128 |
| FEV1.0 (%predicted) | 101 ± 22 | 95 ± 26 | 0.549 |
| FEV1.0 % | 71 ± 9 | 73 ± 10 | 0.402 |
| DLCO (% predicted) | 102 ± 34 | 105 ± 34 | 0.686 |
| LVEF | 51 ± 12 | 53 ± 15 | 0.257 |
| Histology Adenocarcinoma | 12 (60%) | 33 (71%) | 0.608 |
| Squamous cell Carcinoma | 6 (30%) | 10 (22%) | |
| Others | 2 (10%) | 3 (7%) | |
| Grip strength (kg) | 30 ± 11 | 26 ± 9 | 0.126 |
| 6MWT (m) | 454 ± 65 | 503 ± 77 | 0.011 * |
| Days to ambulation (days) | 6 ± 11 | 3 ± 3 | 0.341 |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | 11 ± 13 | 9 ± 1 | <0.01 ** |
| ECOG-PS: 0 | 17 (85%) | 44 (95%) | 0.397 |
| 1 | 3 (15%) | 2 (5%) | |
| 2, 3, 4 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Whole tumor size (mm) | 32 ± 14 | 29 ± 13 | 0.118 |
| Resected lobes Upper Middle Lower | 9 (45%) 0 (0%) 11 (55%) | 23 (50%) 2 (4%) 21 (46%) | 0.551 |
| Operative time (min) | 223 ± 62 | 293 ± 447 | 0.346 |
| Estimated blood loss (mL) | 56 ± 78 | 70 ± 165 | 0.835 |
| Pathological stage | 0.463 | ||
| IA·IB | 13 (65%) | 32 (70%) | |
| IIA~IIIB | 7 (35%) | 14 (30%) | |
| (B) | |||
| Characteristics | PC Group (n = 11) | Non-PC Group (n = 55) | p |
| n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Age | 72 ± 5 | 70 ± 10 | 0.959 |
| Sex, Female (%) | 4 (36%) | 24 (44%) | 0.482 |
| Male (%) | 7 (64%) | 31 (56%) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26 ± 5 | 23 ± 3 | 0.027 * |
| Brinkman index (smoking) | 950 ± 1137 | 547 ± 675 | 0.216 |
| Comorbidity | 0.269 | ||
| COPD | 1 (9%) | 3 (5%) | |
| Interstitial pneumonia | 2 (17%) | 1 (1%) | |
| Hypertension | 8 (70%) | 23 (42%) | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 3 (22%) | 9 (16%) | |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.294 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 17 ± 4 | 15 ± 4 | 0.046 |
| WBC (μL) | 6691 ± 1839 | 6022 ± 3085 | 0.095 |
| Alb (g/dL) | 4 ± 0.3 | 4 ± 0.5 | 0.511 |
| FVC (% predicted) | 114 ± 12 | 109 ± 23 | 0.530 |
| FEV1.0 (%predicted) | 103 ± 19 | 96 ± 26 | 0.294 |
| FEV1.0 % | 74 ± 8 | 72 ± 10 | 0.282 |
| DLCO (% predicted) | 90 ± 36 | 107 ± 33 | 0.111 |
| LVEF | 50 ± 11 | 53 ± 15 | 0.468 |
| Histology Adenocarcinoma | 7 (64%) | 38 (69%) | 0.237 |
| Squamous cell Carcinoma | 3 (27%) | 13 (23%) | |
| Others | 1 (9%) | 4 (8%) | |
| Grip strength (kg) | 30 ± 10 | 27 ± 9 | 0.234 |
| 6MWT (m) | 449 ± 77 | 496 ± 75 | 0.034 |
| Days to ambulation (days) | 7 ± 14 | 3 ± 2 | 0.732 |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | 14 ± 23 | 9 ± 2 | <0.01 ** |
| ECOG-PS: 0 | 8 (73%) | 53 (96%) | 0.199 |
| 1 | 3 (27%) | 2 (4%) | |
| 2, 3, 4 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Whole tumor size (mm) | 35 ± 15 | 30 ± 13 | 0.245 |
| Resected lobes Upper Middle Lower | 3 (27%) 0 (0%) 8 (73%) | 29 (53%) 2 (4%) 24 (43%) | 0.199 |
| Operative time (min) | 243 ± 74 | 278 ± 410 | 0.624 |
| Estimated blood loss (mL) | 69 ± 101 | 65 ± 152 | 0.812 |
| Pathological stage | 0.287 | ||
| IA·IB | 6 (55%) | 39 (71%) | |
| IIA~IIIB | 5 (45%) | 16 (29%) | |
| Patients (N = 66) n (%) | |
|---|---|
| Pneumonia | 3 (4.5%) |
| Atelectasis | 1 (1.5%) |
| ARDS | 2 (3.0%) |
| Lung fistula | 2 (3.0%) |
| IP exacerbation | 2 (3.0%) |
| Bronchopleural fistula | 1 (1.5%) |
| Pleuritis | 1 (1.5%) |
| Ischemic bronchitis | 1 (1.5%) |
| AF | 7 (10.6%) |
| Urinary tract infection | 1 (1.5%) |
| Intestinal bleeding | 1 (1.5%) |
| Others | 6 (9.0%) |
| (A) | |||
| Independent Variables | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p |
| BUN | 1.187 | 1.000–1.409 | 0.050 |
| 6MWT (≤450 m) † | 4.765 | 1.307–17.366 | 0.018 * |
| 6MWT (m) † | 0.992 | 0.984–1.001 | 0.096 |
| BMI | 1.164 | 0.964–1.404 | 0.114 |
| CRP | 1.968 | 0.638–6.069 | 0.239 |
| (B) | |||
| Independent Variables | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p |
| BUN | 1.387 | 0.514–1.155 | 0.066 |
| 6MWT (≤450 m) † | 5.674 | 1.206–26.684 | 0.028 * |
| 6MWT (m) † | 0.996 | 0.981–1.011 | 0.601 |
| BMI | 1.146 | 0.913–1.438 | 0.241 |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | 1.856 | 1.004–3.434 | 0.049 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Polish Respiratory Society. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maki, N.; Yanagihara, T.; Wijesinghe, A.I.; Sugai, K.; Kawamura, T.; Saeki, Y.; Kitazawa, S.; Kobayashi, N.; Kikuchi, S.; Goto, Y.; et al. Preoperative Six-Minute Walking Distance as a Predictor of Postoperative Complications in Patients Undergoing Lobectomy for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Adv. Respir. Med. 2025, 93, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93060052
Maki N, Yanagihara T, Wijesinghe AI, Sugai K, Kawamura T, Saeki Y, Kitazawa S, Kobayashi N, Kikuchi S, Goto Y, et al. Preoperative Six-Minute Walking Distance as a Predictor of Postoperative Complications in Patients Undergoing Lobectomy for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Advances in Respiratory Medicine. 2025; 93(6):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93060052
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaki, Naoki, Takahiro Yanagihara, Ashoka Indranatha Wijesinghe, Kazuto Sugai, Tomoyuki Kawamura, Yusuke Saeki, Shinsuke Kitazawa, Naohiro Kobayashi, Shinji Kikuchi, Yukinobu Goto, and et al. 2025. "Preoperative Six-Minute Walking Distance as a Predictor of Postoperative Complications in Patients Undergoing Lobectomy for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer" Advances in Respiratory Medicine 93, no. 6: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93060052
APA StyleMaki, N., Yanagihara, T., Wijesinghe, A. I., Sugai, K., Kawamura, T., Saeki, Y., Kitazawa, S., Kobayashi, N., Kikuchi, S., Goto, Y., Sakamoto, H., Taniguchi, K., Ichimura, H., & Sato, Y. (2025). Preoperative Six-Minute Walking Distance as a Predictor of Postoperative Complications in Patients Undergoing Lobectomy for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Advances in Respiratory Medicine, 93(6), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93060052







