The Effort, Dyspnea, and Cooperation Scores in Mild and Moderate Post-COVID-19 Patients: Results of a Retrospective Study
Abstract
Highlights
- Post-COVID-19 patients with mild and moderate forms of the disease showed significant improvements in cooperation, effort, and dyspnea scores following a structured rehabilitation program.
- Improvements were observed across all demographic subgroups (by gender and age), although some variation in magnitude was noted.
- These results highlight the effectiveness of personalized rehabilitation in enhancing not only physical capacity but also patient engagement and respiratory comfort during post-COVID-19 recovery.
- The identified correlations and demographic patterns may guide targeted interventions and resource allocation, supporting more individualized and symptom-oriented rehabilitation strategies.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clarification of Disease Severity Classification
2.2. Functional Evaluation Protocol
- Effort was measured using the Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE) Scale [16], which allows patients subjectively rate how hard they feel they are working on a scale from 0 to 10:
- Dyspnea was assessed using the Modified Borg Dyspnea Scale [17], a validated instrument for rating perceived breathlessness. Patients were asked to rate their sensation of dyspnea on a scale from 0 to 10, with descriptive anchors as follows:
- Cooperation was assessed using the Score Five Questions (S5Q) scale [18,19], which measures how well patients cooperate during the acute and subacute stages of illness. The scale includes five simple commands, each scored as 0 (no response) or 1 (correct response).
- (a)
- Open and close your eyes!
- (b)
- Look at me!
- (c)
- Open your mouth and stick out your tongue!
- (d)
- Nod your head up and down!
- (e)
- Raise your eyebrows and hold for a count of five.
2.3. Rehabilitation Protocol
- Respiratory physiotherapy including breathing retraining, postural correction to enhance bronchial drainage, and incentive spirometry.
- Joint mobilization to preserve mobility and prevent deconditioning.
- Muscle strengthening and endurance training for both upper and lower limbs.
- Balance and coordination exercises, such as sitting, standing, and walking retraining.
- Occupational therapy adapted to each patient’s level of independence and cognitive status.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive and Comparative Analysis of Subjective Scores
3.2. Age-Stratified Comparison of Subjective Recovery Outcomes
3.3. Combined Analysis by Gender and Age
3.4. Correlations Between Baseline Subjective Scores
4. Discussion
4.1. Overall Improvements in Effort, Dyspnea, and Cooperation
4.2. Gender-Based Analysis—Subtle Differences Without Significance
4.3. Age-Related Analysis—Consistent Improvements Across Age Groups
4.4. Strong Correlation Between Effort and Dyspnea
4.5. Relationship Between Cooperation and Perceived Effort
4.6. Clinical Implications and Relevance to Rehabilitation Practice
4.7. Alignment with Existing Literature and Pathophysiological Considerations
4.8. On the Use of Subjective Assessment Tools
4.9. Limitations and Further Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
References
- Che Mohd Nassir, C.M.N.; Hashim, S.; Wong, K.K.; Abdul Halim, S.; Idris, N.S.; Jayabalan, N.; Guo, D.; Mustapha, M. COVID-19 Infection and Circulating Microparticles—Reviewing Evidence as Microthrombogenic Risk Factor for Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 4188–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, J.; Minko, T. Recent Developments on Therapeutic and Diagnostic Approaches for COVID-19. AAPS J. 2021, 23, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, D.; Wang, C.; Crawford, T.; Holland, C. Association between COVID-19 Infection and New-Onset Dementia in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2024, 24, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, G.; Guaraldi, G. Drug Treatment of COVID-19 Infection. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2023, 29, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parasher, A. COVID-19: Current Understanding of Its Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation and Treatment. Postgrad. Med. J. 2021, 97, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ora, J.; Liguori, C.; Puxeddu, E.; Coppola, A.; Matino, M.; Pierantozzi, M.; Mercuri, N.B.; Rogliani, P. Dyspnea Perception and Neurological Symptoms in Non-Severe COVID-19 Patients. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 2671–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, A.L. Minimally Clinically Important Difference for the UCSD Shortness of Breath Questionnaire, Borg Scale, and Visual Analog Scale. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2005, 2, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tache-Codreanu, D.-L.; Bobocea, L.; David, I.; Burcea, C.-C.; Sporea, C. The Role of the Six-Minute Walk Test in the Functional Evaluation of the Efficacy of Rehabilitation Programs After COVID-19. Life 2024, 14, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarnezhadgero, A.A.; Noroozi, R.; Fakhri, E.; Granacher, U.; Oliveira, A.S. The Impact of COVID-19 and Muscle Fatigue on Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Running Kinetics in Female Recreational Runners. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 942589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherr, J.; Wolfarth, B.; Christle, J.W.; Pressler, A.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Halle, M. Associations between Borg’s Rating of Perceived Exertion and Physiological Measures of Exercise Intensity. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 113, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakefield, J.C. The Concept of Mental Disorder: Diagnostic Implications of the Harmful Dysfunction Analysis. World Psychiatry 2007, 6, 149. [Google Scholar]
- Soriano, J.B.; Murthy, S.; Marshall, J.C.; Relan, P.; Diaz, J.V. A Clinical Case Definition of Post-COVID-19 Condition by a Delphi Consensus. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, e102–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, S.; Siddiqi, Z.; Ukachukwu, C.; Mehkari, Z.; Khan, S.; Pamurthy, K.; Jahan, F.; Brown, A. COVID-19: Post-Recovery Manifestations. Cureus 2023, 15, e36886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimeno-Almazán, A.; Buendía-Romero, Á.; Martínez-Cava, A.; Franco-López, F.; Sánchez-Alcaraz, B.J.; Courel-Ibáñez, J.; Pallarés, J.G. Effects of a Concurrent Training, Respiratory Muscle Exercise, and Self-Management Recommendations on Recovery from Post-COVID-19 Conditions: The RECOVE Trial. J. Appl. Physiol. 2023, 134, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascella, M.; Rajnik, M.; Aleem, A.; Dulebohn, S.C.; Di Napoli, R. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19); StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, N. The Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE) Scale. Occup. Med. 2017, 67, 404–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Odah, H.; Liu, X.-L.; Wang, T.; Zhao, I.Y.; Yorke, J.; Tan, J.-Y.B.; Molassiotis, A. Modified Borg Scale (MBorg), the Numerical Rating Scale (NRS), and the Dyspnea-12 Scale (D-12): Cross-Scale Comparison Assessing the Development of Dyspnea in Early-Stage Lung Cancer Patients. Support. Care Cancer 2025, 33, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.H.; Shin, M.-J.; Shin, Y.B. Pulmonary and Physical Rehabilitation in Critically Ill Patients. Acute Crit. care 2019, 34, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Luo, L.; Wang, D.; Yu, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhang, P.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Z. Early Rehabilitation after Lung Transplantation with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) of COVID-19 Patient: A Case Report. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B.; Chen, H.J. A Comparative Study of Various Tests for Normality. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1343–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, D.; Neuhäuser, M. Wilcoxon-Signed-Rank Test. In International Encyclopedia of Statistical Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1658–1659. ISBN 3642048986. [Google Scholar]
- Wall Emerson, R. Mann-Whitney U Test and t-Test. J. Vis. Impair. Blind. 2023, 117, 99–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, S.; Haufe, S.; Dirks, M.; Scharbau, M.; Lampe, V.; Dopfer-Jablonka, A.; Tegtbur, U.; Pink, I.; Drick, N.; Kerling, A. Post-COVID-19 Syndrome: Physical Capacity, Fatigue and Quality of Life. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0292928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Chen, X.-K.; Sit, C.H.; Liang, X.; Li, M.-H.; Ma, A.C.; Wong, S.H. Effect of Physical Exercise-Based Rehabilitation on Long COVID: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2023, 56, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, E.A.K.; Mitra, A.K.; Bhuiyan, A.R. Impact of COVID-19 on Mental Health in Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alosaimi, N.; Sherar, L.B.; Griffiths, P.; Pearson, N. Clustering of Diet, Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour and Related Physical and Mental Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawes, M.T.; Szenczy, A.K.; Klein, D.N.; Hajcak, G.; Nelson, B.D. Increases in Depression and Anxiety Symptoms in Adolescents and Young Adults during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Psychol. Med. 2022, 52, 3222–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgüç, S.; Kaplan Serin, E.; Tanriverdi, D. Death Anxiety Associated with Coronavirus (COVID-19) Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. OMEGA J. Death Dying 2024, 88, 823–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alacevich, C.; Thalmann, I.; Nicodemo, C.; de Lusignan, S.; Petrou, S. Depression and Anxiety during and after Episodes of COVID-19 in the Community. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kızılkaya, S.; Çağatay, A. Detrás Del Backstage de La Pandemia de COVID-19: Ansiedad y Trabajadores de La Salud. Cir. Cir. 2023, 91, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Ayllon, M.; Cadenas-Sánchez, C.; Estévez-López, F.; Muñoz, N.E.; Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Migueles, J.H.; Molina-García, P.; Henriksson, H.; Mena-Molina, A.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; et al. Role of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior in the Mental Health of Preschoolers, Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 1383–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, C. Enhancing Mental Health, Well-Being and Active Lifestyles of University Students by Means of Physical Activity and Exercise Research Programs. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 849093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.A.; Tortelli, L.; Motta, J.; Menguer, L.; Mariano, S.; Tasca, G.; de Bem Silveira, G.; Pinho, R.A.; Silveira, P.C.L. Effects of Aquatic Exercise on Mental Health, Functional Autonomy and Oxidative Stress in Depressed Elderly Individuals: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Clinics 2019, 74, e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C.; O’ Sullivan, R.; Caserotti, P.; Tully, M.A. Consequences of Physical Inactivity in Older Adults: A Systematic Review of Reviews and Meta-analyses. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2020, 30, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Corral, T.; Fabero-Garrido, R.; Plaza-Manzano, G.; Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Navarro-Santana, M.; López-de-Uralde-Villanueva, I. Home-Based Respiratory Muscle Training on Quality of Life and Exercise Tolerance in Long-Term Post-COVID-19: Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2023, 66, 101709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, K.; McLean, S.M.; Moffett, J.K.; Gardiner, E. Barriers to Treatment Adherence in Physiotherapy Outpatient Clinics: A Systematic Review. Man. Ther. 2010, 15, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.R.; Hoffman, M.; Jones, A.W.; Holland, A.E.; Borghi-Silva, A. Effect of Pulmonary Rehabilitation on Exercise Capacity, Dyspnea, Fatigue, and Peripheral Muscle Strength in Patients with Post-COVID-19 Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2024, 105, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNarry, M.A.; Berg, R.M.G.; Shelley, J.; Hudson, J.; Saynor, Z.L.; Duckers, J.; Lewis, K.; Davies, G.A.; Mackintosh, K.A. Inspiratory Muscle Training Enhances Recovery Post-COVID-19: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2103101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Milá, Z.; Abuín-Porras, V.; Romero-Morales, C.; Almazán-Polo, J.; Velázquez Saornil, J. Effectiveness of a Respiratory Rehabilitation Program Including an Inspiration Training Device versus Traditional Respiratory Rehabilitation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazão, M.; da Cruz Santos, A.; Silva, P.E.; de Assis Pereira Cacau, L.; Petrucci, T.R.; Assis, M.C.; de Almeida Leal, R.; Brasileiro, E.; de Moraes Forjaz, C.L.; do Socorro Brasileiro-Santos, M. Impaired Neuromuscular Efficiency and Symptom-Limited Aerobic Exercise Capacity 4 Weeks After Recovery From COVID-19 Appear to Be Associated With Disease Severity at Onset. Phys. Ther. 2023, 103, pzac167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, J.; Yu, Y.; Mao, L.; Luo, L.; Zou, L.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J.; Chen, Z. Early Physical Therapy for a Patient Affected by Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) on Awake Veno-Venous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Case Report. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.C.; Limbach, M.; Schuler, M.; Merkl, S.; Schwarzl, G.; Jakab, K.; Nowak, D.; Schultz, K. Effectiveness of a Three-Week Inpatient Pulmonary Rehabilitation Program for Patients after COVID-19: A Prospective Observational Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugazzaro, S.; Contri, A.; Esseroukh, O.; Kaleci, S.; Croci, S.; Massari, M.; Facciolongo, N.C.; Besutti, G.; Iori, M.; Salvarani, C.; et al. Rehabilitation Interventions for Post-Acute COVID-19 Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, T.; Gajić, I.; Gimigliano, F.; Backović, A.; Hrković, M.; Nikolić, D.; Filipović, A. The Role of Acute Rehabilitation in COVID-19 Patients. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2023, 59, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Vieira, A.G.S.; Pinto, A.C.P.N.; Garcia, B.M.S.P.; Eid, R.A.C.; Mól, C.G.; Nawa, R.K. Telerehabilitation Improves Physical Function and Reduces Dyspnoea in People with COVID-19 and Post-COVID-19 Conditions: A Systematic Review. J. Physiother. 2022, 68, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouliopoulou, D.V.; Macdermid, J.C.; Saunders, E.; Peters, S.; Brunton, L.; Miller, E.; Quinn, K.L.; Pereira, T.V.; Bobos, P. Rehabilitation Interventions for Physical Capacity and Quality of Life in Adults with Post–COVID-19 Condition. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2333838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyazed, T.I.A.; Alsharawy, L.A.; Salem, S.E.; Helmy, N.A.; El-Hakim, A.A.E.-M.A. Effect of Home-Based Pulmonary Rehabilitation on Exercise Capacity in Post COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trail. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2024, 21, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleguezuelos, E.; Sánchez-Nuño, S.; Del Carmen, A.; Serra-Payá, N.; Moreno, E.; Molina-Raya, L.; Robleda, G.; Benet, M.; Santos-Ruiz, S.; Garrido, A.B.; et al. Effect of Different Types of Supervised Exercise Programs on Cardiorespiratory and Muscular Fitness, Pain, Fatigue, Mental Health and Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Older Patients with Post-COVID-19 Sequelae “EJerSA-COVID-19”: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olezene, C.S.; Hansen, E.; Steere, H.K.; Giacino, J.T.; Polich, G.R.; Borg-Stein, J.; Zafonte, R.D.; Schneider, J.C. Functional Outcomes in the Inpatient Rehabilitation Setting Following Severe COVID-19 Infection. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalbandian, A.; Sehgal, K.; Gupta, A.; Madhavan, M.V.; McGroder, C.; Stevens, J.S.; Cook, J.R.; Nordvig, A.S.; Shalev, D.; Sehrawat, T.S.; et al. Post-Acute COVID-19 Syndrome. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabat, S.; Marmor, A.; Shiri, S.; Tsenter, J.; Meiner, Z.; Schwartz, I. Correlations between Disease Severity and Rehabilitation Outcomes in Patients Recovering from Covid-19 Infection. J. Rehabil. Med. 2023, 55, jrm00344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhan, C.; Ma, Y.; Guo, C.; Chen, W.; Fang, X.; Fang, L. Effect of Qigong Exercise and Acupressure Rehabilitation Program on Pulmonary Function and Respiratory Symptoms in Patients Hospitalized with Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Integr. Med. Res. 2021, 10, 100796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curci, C.; Pisano, F.; Bonacci, E.; Camozzi, D.M.; Ceravolo, C.; Bergonzi, R.; De Franceschi, S.; Moro, P.; Guarnieri, R.; Ferrillo, M.; et al. Early Rehabilitation in Post-Acute COVID-19 Patients: Data from an Italian COVID-19 Rehabilitation Unit and Proposal of a Treatment Protocol. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 56, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.J.; Baldwin, M.M.; Daynes, E.; Evans, R.A.; Greening, N.J.; Jenkins, R.G.; Lone, N.I.; McAuley, H.; Mehta, P.; Newman, J.; et al. Respiratory Sequelae of COVID-19: Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary Origins, and Approaches to Clinical Care and Rehabilitation. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 709–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asimakos, A.; Spetsioti, S.; Mentzelopoulos, S.; Vogiatzis, I.; Vassiliou, A.G.; Gounopoulos, P.; Antonoglou, A.; Spaggoulakis, D.; Pappa, S.; Zakynthinos, S.; et al. Rehabilitation Is Associated with Improvements in Post–COVID-19 Sequelae. Respir. Care 2024, 69, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Mustafaoglu, R.; Yeldan, I.; Yasaci, Z.; Erhan, B. Effect of Pulmonary Rehabilitation Approaches on Dyspnea, Exercise Capacity, Fatigue, Lung Functions, and Quality of Life in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 103, 2051–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaherian, M.; Shadmehr, A.; Keshtkar, A.; Beigmohammadi, M.T.; Dabbaghipour, N.; Syed, A.; Attarbashi Moghadam, B. Safety and Efficacy of Pulmonary Physiotherapy in Hospitalized Patients with Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia (PPTCOVID Study): A Prospective, Randomised, Single-Blind, Controlled Trial. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0268428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevei, M.; Onofrei, R.R.; Gherle, A.; Gug, C.; Stoicanescu, D. Rehabilitation of Post-COVID-19 Musculoskeletal Sequelae in Geriatric Patients: A Case Series Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harenwall, S.; Heywood-Everett, S.; Henderson, R.; Smith, J.; McEnery, R.; Bland, A.R. The Interactive Effects of Post-Traumatic Stress Symptoms and Breathlessness on Fatigue Severity in Post-COVID-19 Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waluyo, Y.; Artika, S.R.; Wahyuni, I.N.; Valen, S.D.; Sam, N. Optimizing Early Rehabilitation Intervention: Insights from Different Outcomes in 2 Patients with Severe COVID-19. Am. J. Case Rep. 2021, 22, e933329-1–e933329-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Mean ± SD | Median (IQR) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cooperation | Initial (p < 0.001 ) | 3.79 ± 0.85 | 4 (3–5) | <0.001 |
| After recovery (p < 0.001) | 4.27 ± 0.71 | 4 (4–5) | <0.01 | |
| Effort | Initial (p < 0.001) | 5.54 ± 1.35 | 6 (4–7) | <0.01 |
| After recovery (p < 0.001) | 4.55 ± 1.18 | 4.5 (4–5) | <0.01 | |
| Dyspnea | Initial (p < 0.001) | 5.62 ± 1.4 | 6 (4–7) | <0.01 |
| After recovery (p < 0.001) | 4.57 ± 1.2 | 5 (4–5) | <0.01 | |
| Women’s cooperation scores | Initial (p < 0.001) | 3.82 ± 0.86 | 4 (3–5) | <0.01 |
| After recovery (p < 0.001) | 4.25 ± 0.79 | 4 (4–5) | <0.01 | |
| Women’s effort scores | Initial (p < 0.001) | 5.4 ± 1.31 | 5 (4–6.5) | <0.01 |
| After recovery (p < 0.001) | 4.45 ± 1.15 | 4 (3–5) | <0.01 | |
| Women’s dyspnea scores | Initial (p < 0.001) | 5.48 ± 1.38 | 6 (4–7) | <0.01 |
| After recovery (p < 0.001) | 4.47 ± 1.18 | 4 (3–5) | <0.01 | |
| Men’s cooperation scores | Initial (p < 0.001) | 3.73 ± 0.82 | 3 (3–4) | <0.01 |
| After recovery (p < 0.001) | 4.3 ± 0.58 | 4 (4–5) | <0.01 | |
| Men’s effort scores | Initial (p = 0.011) | 5.76 ± 1.38 | 6 (5–7) | <0.01 |
| After recovery (p = 0.00) | 4.7 ± 1.22 | 5 (4–6) | <0.01 | |
| Men’s dyspnea scores | Initial (p = 0.006) | 5.83 ± 1.42 | 6 (5–7) | <0.01 |
| After recovery (p = 0.002) | 4.71 ± 1.22 | 5 (4–6) | <0.01 | |
| Parameter | Mean ± SD | Median (IQR) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients’ cooperation scores under 60 years old | Initial (p < 0.001) | 4.07 ± 0.84 | 4 (3–5) | <0.01 |
| After recovery (p < 0.001) | 4.49 ± 0.63 | 5 (4–5) | <0.001 | |
| Patients’ effort scores under 60 years old | Initial (p < 0.001) | 5.14 ± 1.33 | 5 (4–6) | <0.01 |
| After recovery (p < 0.001) | 4.14 ± 1.15 | 4 (3–5) | <0.01 | |
| Patients’ dyspnea scores under 60 years old | Initial (p < 0.001) | 5.24 ± 1.44 | 5 (4–6.5) | <0.01 |
| After recovery (p < 0.001) | 4.15 ± 1.18 | 4 (3–5) | <0.01 | |
| Patients’ cooperation scores ≥ 60 years | Initial (p < 0.001) | 3.47 ± 0.74 | 3 (3–4) | <0.01 |
| After recovery (p < 0.001) | 4.01 ± 0.73 | 4 (3–5) | <0.01 | |
| Patients’ effort scores ≥ 60 years | Initial (p < 0.001) | 6 ± 1.23 | 6 (5–7) | <0.01 |
| After recovery (p < 0.001) | 5.01 ± 1.05 | 5 (4–6) | <0.01 | |
| Patients’ dyspnea scores ≥ 60 years | Initial (p = 0.006 ) | 6.04 ± 1.23 | 6 (5–7) | <0.01 |
| After recovery (p = 0.002 ) | 5.04 ± 1.05 | 5 (4–6) | <0.01 | |
| Parameter | Mean ± SD | Median (IQR) | Mean Rank | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cooperation Scores by Gender | Female (p < 0.001 ) | 0.42 ± 0.62 | 0 (0–1) | 75.72 | 0.065 |
| Male (p < 0.001 ) | 0.57 ± 0.56 | 1 (0–1) | 87.86 | 0.065 | |
| Effort Scores by Gender | Female (p < 0.001 ) | −0.95 ± 1 | −1 (−1–0) | 81.78 | 0.639 |
| Male (p < 0.001 ) | −1.06 ± 1 | −1 (−1–0) | 78.52 | 0.639 | |
| Dyspnea Scores by Gender | Female (p < 0.001 ) | −1.01 ± 1.02 | −1 (−1–0) | 82.09 | 0.565 |
| Male (p < 0.001) | −1.11 ± 0.97 | −1 (−2–0) | 78.06 | 0.565 | |
| Cooperation Scores by Age | <60 years (p < 0.001 ) | 0.42 ± 0.56 | 0 (0–1) | 76.34 | 0.220 |
| ≥60 years (p < 0.001 ) | 0.54 ± 0.64 | 0 (0–1) | 84.21 | 0.220 | |
| Effort Scores by Age | <60 years (p < 0.001 ) | −1 ± 1.07 | −1 (−1–0) | 82.64 | 0.403 |
| ≥60 years (p < 0.001 ) | −0.97 ± 0.9 | −1 (−1–−0.75) | 76.97 | 0.403 | |
| Dyspnea Scores by Age | <60 years (p < 0.001) | −1.08 ± 1.08 | −1 (−1.5–0) | 80.84 | 0.793 |
| ≥60 years (p < 0.001) | −1 ± 0.9 | −1 (−1.25–0) | 79.04 | 0.793 | |
| Correlation | p * |
|---|---|
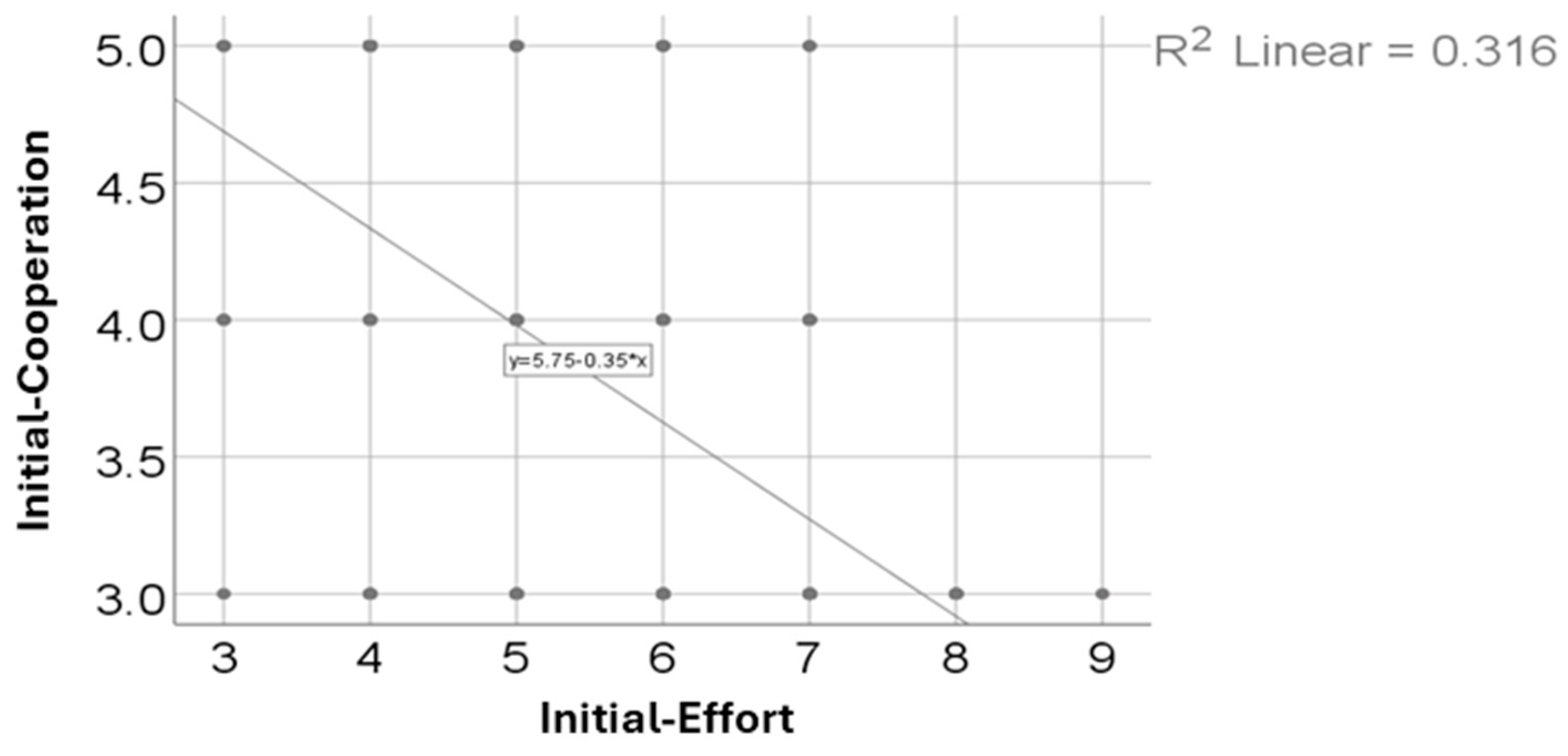
| Cooperation (p < 0.001 **) x Effort (p < 0.001 **) | <0.001, R = −0.571 |
| Correlation | p * |
|---|---|
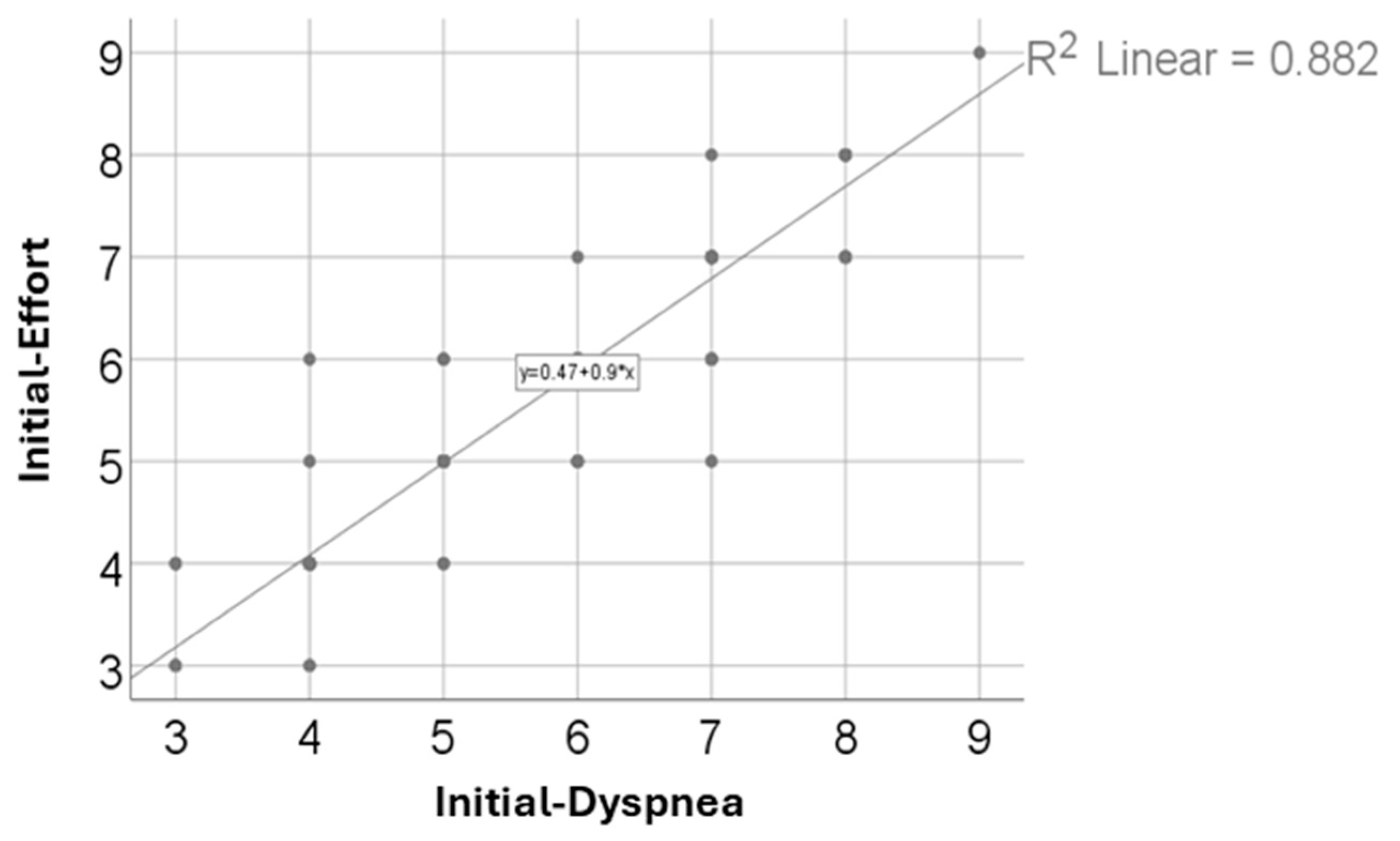
| Effort (p < 0.001 **) x Dyspnea (p < 0.001 **) | <0.001, R = 0.942 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Polish Respiratory Society. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiriac, O.C.; Sporea, C.; Miricescu, D.; Mitrea, A.R.; Vacaroiu, I.A.; Grigore, R.; Nica, A.S. The Effort, Dyspnea, and Cooperation Scores in Mild and Moderate Post-COVID-19 Patients: Results of a Retrospective Study. Adv. Respir. Med. 2025, 93, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93050043
Chiriac OC, Sporea C, Miricescu D, Mitrea AR, Vacaroiu IA, Grigore R, Nica AS. The Effort, Dyspnea, and Cooperation Scores in Mild and Moderate Post-COVID-19 Patients: Results of a Retrospective Study. Advances in Respiratory Medicine. 2025; 93(5):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93050043
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiriac, Ovidiu Cristian, Corina Sporea, Daniela Miricescu, Ana Raluca Mitrea, Ileana Adela Vacaroiu, Raluca Grigore, and Adriana Sarah Nica. 2025. "The Effort, Dyspnea, and Cooperation Scores in Mild and Moderate Post-COVID-19 Patients: Results of a Retrospective Study" Advances in Respiratory Medicine 93, no. 5: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93050043
APA StyleChiriac, O. C., Sporea, C., Miricescu, D., Mitrea, A. R., Vacaroiu, I. A., Grigore, R., & Nica, A. S. (2025). The Effort, Dyspnea, and Cooperation Scores in Mild and Moderate Post-COVID-19 Patients: Results of a Retrospective Study. Advances in Respiratory Medicine, 93(5), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93050043







