Concomitant Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: An Updated Narrative Review
Abstract
Highlights
- Lung cancer (LC) in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) occurs more frequently compared to the general population.
- IPF and LC share common risk factors and overlapping pathobiological mechanisms.
- The coexistence of IPF and LC is particularly concerning, as it is associated with poor prognosis and a high risk of complications related to both diagnosis and treatment.
- The development of standardized management guidelines for patients with coexisting IPF and LC is essential to improve clinical outcomes.
- Novel therapeutic agents that simultaneously target the fibrotic and neoplastic pathways of IPF and LC are currently under investigation.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
2.1. Epidemiology of LC in Patients with IPF
2.2. Risk Factors for LC Development in IPF
2.3. Epidemiology of LC Concomitant with CPFE
2.4. Localization and Histologic Type of LC in IPF
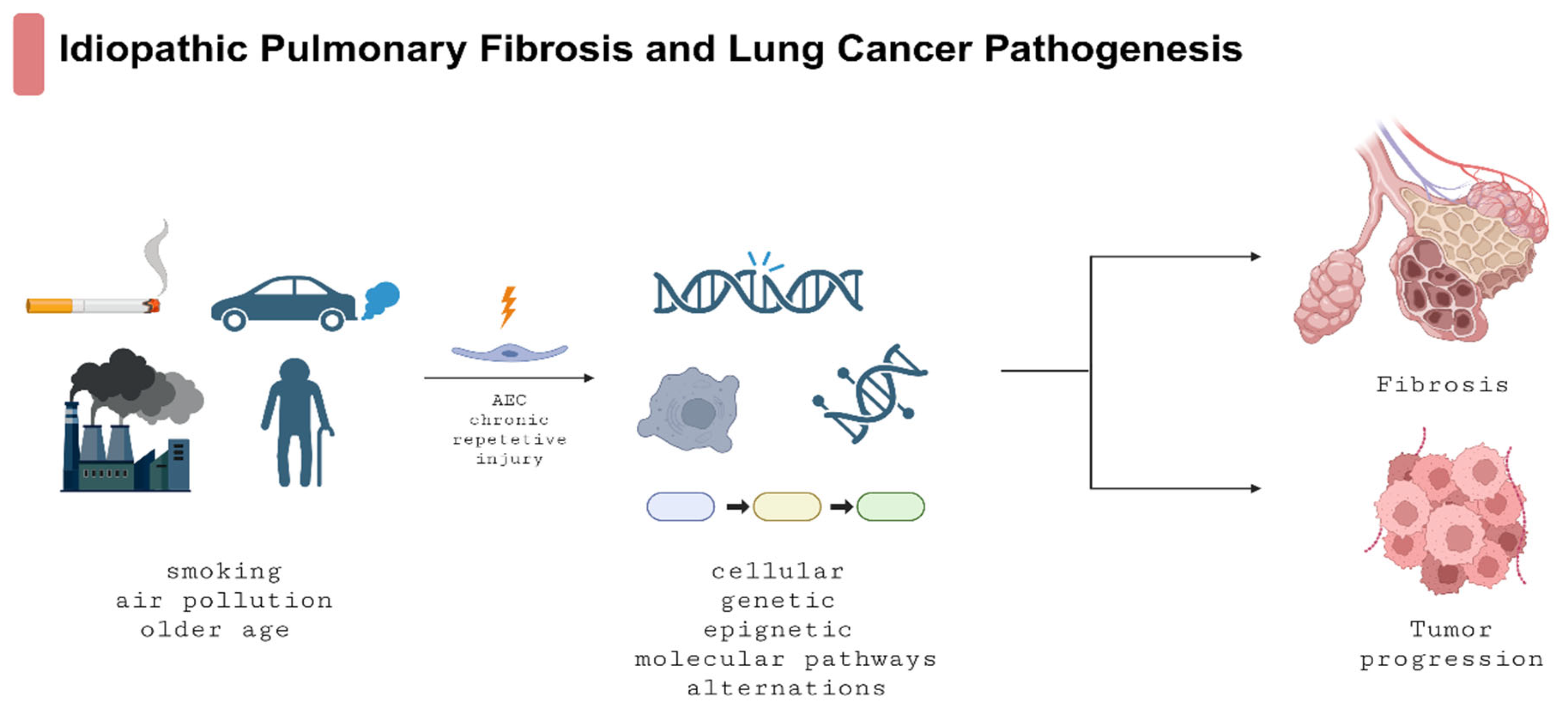
3. Common Cellular, Molecular, and Epigenetic Mechanisms in IPF and LC
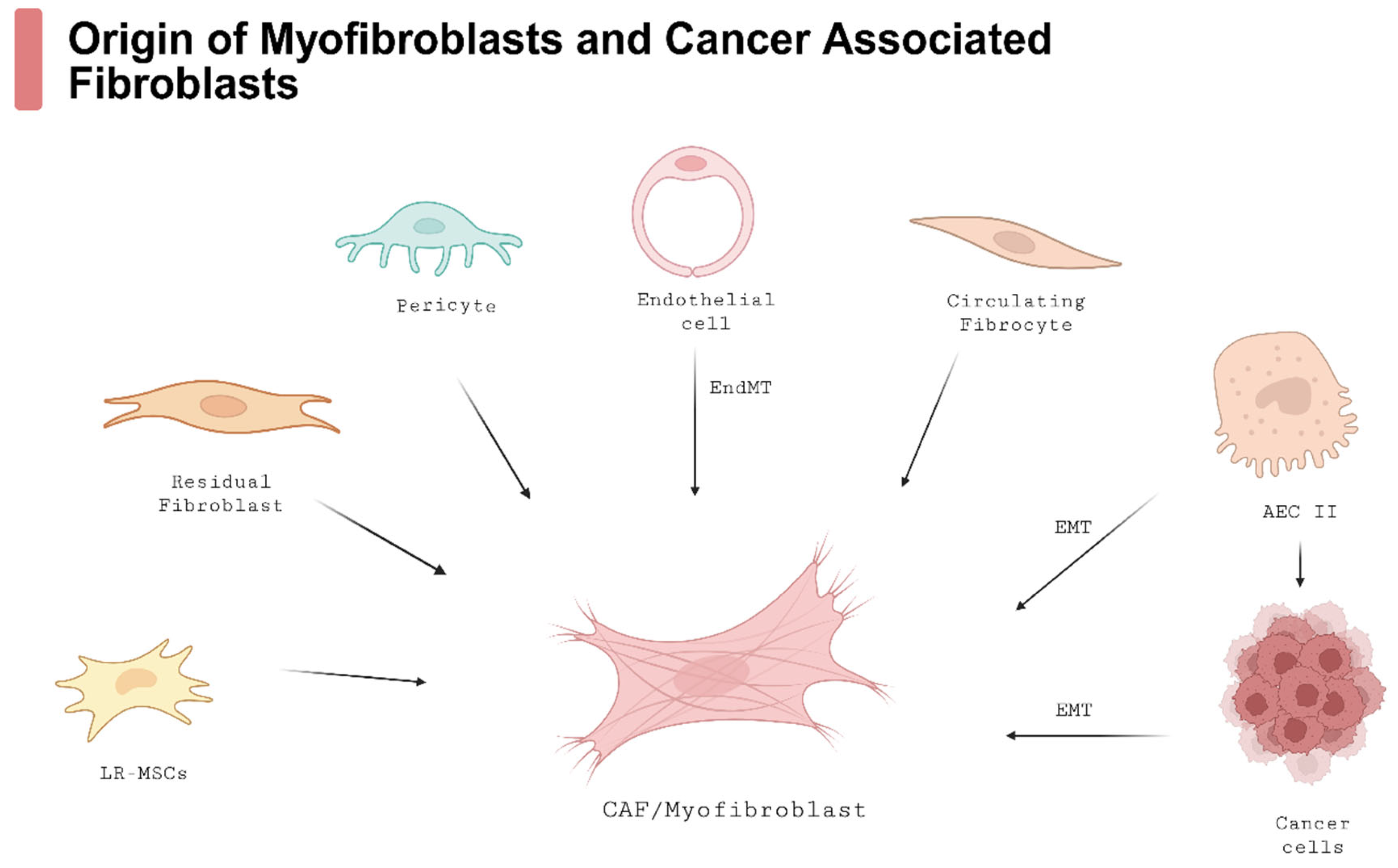
3.1. The Role of Myofibroblasts and Other Cells in IPF Development
3.2. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs)
3.3. Tissue Invasion and Cell–Cell Communication
3.4. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Unfolded Protein Response
3.5. Molecular Pathways
3.6. Germinal Mutations
3.7. Somatic Mutations
3.8. Epigenetics
3.9. Knowledge Gaps and Future Treatment Options
4. Diagnosis of LC in IPF Patients
4.1. Imaging and Management of Suspected Malignancy
4.2. Risks Related to Invasive Diagnostic Procedures of Suspected LC in Patients with IPF
5. Surgical Treatment of IPF-LC Patients
5.1. AE-IPF Risk in LC Resection Surgery
5.2. Risk Factors of Postoperative AE
5.3. Overall Survival After Surgery in IPF-LC
5.4. Prevention of Postoperative AE-IPF
6. Non-Surgical Treatment of IPF-LC Patients: Possible Options, Limitations, and Challenges
6.1. Percutaneous Ablation of Lung Tumors
6.2. Radiotherapy for Patients with IPF-LC
6.3. Chemotherapy for NSCLC
6.3.1. Chemotherapy for SCLC
6.3.2. Prevention of Chemotherapy-Induced AE
6.4. Targeted Therapies and Immunotherapy
7. The Promising Potential of Antifibrotics in Preventing LC Development in Patients with IPF
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACEs | Alveolar ephitelium cells |
| ADC | Adenocarcinoma |
| AE | Acute exacerbation |
| AKT | Protein kinase B |
| ALK | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase |
| APOBEC | Apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiology |
| BAL | Bronchoalveolar lavage |
| BALf | Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
| BRAF | B-Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CAF | Cancer-associated fibroblast |
| CSC | Cancer stem cells |
| CDKN1A | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A |
| CL13 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 13 |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| Cx43 | Connexin 43 |
| CXCL2 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 2 |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| DCR | Disease control rate |
| DLCO | Diffusing capacity of lungs for carbon monoxide |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EGF | Epithelial growth factor |
| EGFR | Epithelial growth factor receptor |
| ED | Extensive disease |
| EFS | Exacerbation-free survival |
| EMT | Epithelial-to-mesenchymal cell transition |
| EndMT | Endothelial-to-mesenchymal cell transition |
| ER | Endoplasmatic reticulum |
| FAK | Focal adhesion kinase |
| FEV1 | Forced expiratory volume in 1 s |
| FGF | Fibroblast growth factor |
| FHIT | Fragile histidine triad |
| GAP index | Genomic Age and Physiology index |
| GGO | Ground-glass opacity |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| HRCT | High-resolution computed tomography |
| ICIs | Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| IGTA | Image-guided thermal ablation |
| IIP | Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia |
| ILD | Interstitial lung disease |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1 beta |
| IL-4 | Interleukin 4 |
| IL-5 | Interleukin 5 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-12 | Interleukin 12 |
| KL-6 | Krebs von den Lungen-6 |
| KRAS | Kirsten rat sarcoma virus gene |
| LC | Lung cancer |
| Let-7d | Lethal-7d |
| LR-MSCs | Lung-resident mesenchymal stroma cells |
| MALT1 | Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 |
| MARCKS | Myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate |
| MGMT | O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase |
| miR-29 | MicroRNA-29 |
| miR-155 | MicroRNA-155 |
| miR-200 | MicroRNA-200 |
| miR-221 | MicroRNA-221 |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| MWA | Microwave ablation |
| NSCLC | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| OSA | Obstructive sleep apnea LC |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PBT | Proton-beam therapy |
| PD-1 | Programmed death-1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death-ligand 1 |
| PDGF | Platelet-derived growth factor |
| PE | Pulmonary embolism |
| PET-CT | Positron emission tomography |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| PFT | Pulmonary function test |
| PH | Pulmonary hypertension |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PLA2G7 | Phospholipase A2 group VII |
| PF | Pulmonary fibrosis |
| RAS | Rat sarcoma virus |
| RFA | Radiofrequency ablation |
| RhoA | Ras homolog family member A |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RP | Radiation pneumonitis |
| RR | Response rate |
| RTEL1 | Regulator of telomere elongation helicase 1 |
| SASP | Senescence-associated secretory phenotype |
| SBRT | Stereotactic body radiotherapy |
| SCC | Squamous cell carcinoma |
| SEMA6B | Semaphorin 6B |
| SFTPA1 | Pulmonary surfactant-associated protein A1 |
| SFTPB | Surfactant protein B |
| Shh | Sonic Hedgehog |
| SLB | Surgical lung biopsy |
| SMAD 4 | SMAD family member 4 |
| SCLC | Small-cell lung carcinoma |
| SP-D | Surfactant protein D |
| SPARC | Secreted protein acidic and cysteine-rich |
| SPP1 | Secreted phosphoprotein 1 |
| TBLC | Transbronchial lung cryobiopsy |
| TBLB | Transbronchial lung biopsy |
| TERC | Telomerase RNA component |
| TERT | Telomerase reverse transcriptase |
| TGF-α | Transforming growth factor alpha |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor beta |
| TKI | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| TLA | Three-letter acronym |
| TLC | Total lung capacity |
| TLCD2 | TLC domain containing 2 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alfa |
| TP53 | Tumor protein 53 |
| UIP | Usual interstitial pneumonia |
| UPR | Unfolded protein response |
| VC | Vital capacity |
| %VC | Percentage of predicted vital capacity |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VEGFR | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor |
| Wnt/β-catenin | Wingless/Int beta-catenin |
| YAP | Yes-associated protein |
References
- Piotrowski, W.J.; Bestry, I.; Białas, A.J.; Boros, P.W.; Grzanka, P.; Jassem, E.; Jastrzębski, D.; Klimczak, D.; Langfort, R.; Lewandowska, K.; et al. Guidelines of the Polish Respiratory Society for Diagnosis and Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Adv. Respir. Med. 2020, 88, 41–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majewski, S.; Lewandowska, K.; Martusewicz-Boros, M.; Piotrowski, W. Diagnostic and Treatment Standards in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in the Era of Antifibrotic Drugs in Poland: A Real-World Practice Survey. Adv. Respir. Med. 2020, 87, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.J.; Collard, H.R.; Pardo, A.; Raghu, G.; Richeldi, L.; Selman, M.; Swigris, J.J.; Taniguchi, H.; Wells, A.U. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, S.; Harari, S.; Caminati, A.; Zanobetti, A.; Schwartz, J.D.; Bertazzi, P.A.; Cesana, G.; Madotto, F. The Association between Air Pollution and the Incidence of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in Northern Italy. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1700397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, S.; Piotrowski, W.J. Air Pollution-An Overlooked Risk Factor for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugg, S.T.; Scott, A.; Parekh, D.; Naidu, B.; Thickett, D.R. Cigarette Smoke Exposure and Alveolar Macrophages: Mechanisms for Lung Disease. Thorax 2022, 77, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, V.; Inoue, Y.; Selman, M.; Ryerson, C.J.; Wells, A.U.; Agusti, A.; Antoniou, K.M.; Bianchi, P.; Caro, F.; Corte, T.J.; et al. Syndrome of Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Research Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, E7–E41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, M.; Koo, C.W.; Scanlon, P.D.; Ryu, J.H. Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: A Narrative Review. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2023, 98, 1685–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaki, M.; Antoniou, K.M. Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 41, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, W.; Martusewicz-Boros, M.; Białas, A.; Lewandowska, K. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)―Common Practice in Poland before the “Antifibrotic Drugs Era”. Adv. Respir. Med. 2017, 85, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, P.W.; Albera, C.; Bradford, W.Z.; Costabel, U.; Glassberg, M.K.; Kardatzke, D.; King, T.E.; Lancaster, L.; Sahn, S.A.; Szwarcberg, J.; et al. Pirfenidone in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (CAPACITY): Two Randomised Trials. Lancet 2011, 377, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, T.E.; Bradford, W.Z.; Castro-Bernardini, S.; Fagan, E.A.; Glaspole, I.; Glassberg, M.K.; Gorina, E.; Hopkins, P.M.; Kardatzke, D.; Lancaster, L.; et al. A Phase 3 Trial of Pirfenidone in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richeldi, L.; du Bois, R.M.; Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nintedanib in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majewski, S.; Białas, A.J.; Barczyk, A.; Batura-Gabryel, H.; Buchczyk, M.; Doboszyńska, A.; Górska, K.; Grabowska-Skudlarz, L.; Jagielska-Len, H.; Jarzemska, A.; et al. A Real-World Multicenter Retrospective Observational Study on Polish Experience with Nintedanib Therapy in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: The PolExNIB Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, S.; Białas, A.J.; Buchczyk, M.; Gomółka, P.; Górska, K.; Jagielska-Len, H.; Jarzemska, A.; Jassem, E.; Jastrzębski, D.; Kania, A.; et al. A Multicentre Retrospective Observational Study on Polish Experience of Pirfenidone Therapy in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: The PolExPIR Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Tsiri, P.; Sampsonas, F. Challenges in the Management of Lung Cancer in ILD. Soc. Esp. Neumol. Cir. Torac. (SEPAR) 2024, 60, S1–S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.A.W.; Dobelle, M.; Padilla, M.; Agovino, M.; Wisnivesky, J.P.; Hashim, D.; Boffetta, P. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019, 16, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, P.; Zhou, H.; Kong, H.; Xie, W. An Increased Risk of Lung Cancer in Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema Patients with Usual Interstitial Pneumonia Compared with Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Alone: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2021, 15, 17534666211017050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.; Jeong, B.H.; Chung, M.J.; Lee, K.S.; Kwon, O.J.; Chung, M.P. Risk Factors and Clinical Characteristics of Lung Cancer in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bade, B.C.; Dela Cruz, C.S. Lung Cancer 2020. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederer, D.J.; Martinez, F.J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, B.; Milara, J.; Cortijo, J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: Mechanisms and Molecular Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karampitsakos, T.; Spagnolo, P.; Mogulkoc, N.; Wuyts, W.A.; Tomassetti, S.; Bendstrup, E.; Molina-Molina, M.; Manali, E.D.; Unat, Ö.S.; Bonella, F.; et al. Lung Cancer in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Retrospective Multicentre Study in Europe. Respirology 2023, 28, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OZAWA, Y.; SUDA, T.; NAITO, T.; ENOMOTO, N.; HASHIMOTO, D.; FUJISAWA, T.; NAKAMURA, Y.; INUI, N.; NAKAMURA, H.; CHIDA, K. Cumulative Incidence of and Predictive Factors for Lung Cancer in IPF. Respirology 2009, 14, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.C. Epidemiology and Comorbidities in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Nationwide Cohort Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassetti, S.; Gurioli, C.; Ryu, J.H.; Decker, P.A.; Ravaglia, C.; Tantalocco, P.; Buccioli, M.; Piciucchi, S.; Sverzellati, N.; Dubini, A.; et al. The Impact of Lung Cancer on Survival of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 2015, 147, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, E.; Takayanagi, N.; Takaku, Y.; Kagiyama, N.; Kanauchi, T.; Ishiguro, T.; Sugita, Y. Incidence and Predictive Factors of Lung Cancer in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. ERJ Open Res. 2018, 4, 00111–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Cho, Y.J.; Yoon, H.I.; Lee, J.H.; Jheon, S.; Lee, C.T.; Park, J.S. Lung Cancer in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Clinical Characteristics and Impact on Survival. Respir. Med. 2014, 108, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Spagnolo, P.; Bonella, F.; Vancheri, C.; Tzilas, V.; Crestani, B.; Kreuter, M.; Bouros, D. Patients with IPF and Lung Cancer: Diagnosis and Management. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyldgaard, C.; Hilberg, O.; Bendstrup, E. How Does Comorbidity Influence Survival in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis? Respir. Med. 2014, 108, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Chung, M.P.; Kim, Y.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.S.; Ryu, J.S.; Lee, H.L.; Park, S.W.; Park, C.S.; Uh, S.T.; et al. Prevalence, Risk Factors and Survival of Lung Cancer in the Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Thorac. Cancer 2012, 3, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, S.A.; Toraih, E.A.; Ismail, E.A.; Hagras, A.M.; Elmorsy, E.; Fawzy, M.S. Vaping, Environmental Toxicants Exposure, and Lung Cancer Risk. Cancers 2023, 15, 4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merecz-Sadowska, A.; Sitarek, P.; Zielinska-Blizniewska, H.; Malinowska, K.; Zajdel, K.; Zakonnik, L.; Zajdel, R. A Summary of in Vitro and in Vivo Studies Evaluating the Impact of E-Cigarette Exposure on Living Organisms and the Environment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, N.; Park, C.M.; Lee, J.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, S.M.; Yim, J.J.; Yoo, C.G.; Kim, Y.W.; Han, S.K.; Lee, C.H. Lung Cancer Risk among Patients with Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema. Respir. Med. 2014, 108, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.J.; Kim, H.H.; Hyun, D.G.; Ji, W.; Choi, C.M.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, H.C. Clinical Characteristics and Outcome of Lung Cancer in Patients with Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouronte-Roibás, C.; Leiro-Fernández, V.; Fernández-Villar, A.; Botana-Rial, M.; Ramos-Hernández, C.; Ruano-Ravina, A. COPD, Emphysema and the Onset of Lung Cancer. A Systematic Review. Cancer Lett. 2016, 382, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasim, F.; Moua, T. Lung cancer in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: A large retrospective cohort analysis. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 00521–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Min, K.H.; Hur, G.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kang, K.H.; Shim, J.J. Impact and Prognosis of Lung Cancer in Patients with Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2020, 37, 7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, K.; Tanai, C.; Tanaka, Y.; Noda, H.; Ishihara, T. The Prevalence of Pulmonary Fibrosis Combined with Emphysema in Patients with Lung Cancer. Respirology 2011, 16, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yoshizawa, A.; Kawakami, S.; Asaka, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Yasuo, M.; Agatsuma, H.; Toishi, M.; Shiina, T.; Yoshida, K.; et al. The Histological Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes of Lung Cancer in Patients with Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 2721–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiftci, F.; Gülpınar, B.; Atasoy, Ç.; Kayacan, O.; Saryal, S. Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: How Does Cohabitation Affect Respiratory Functions? Adv. Med. Sci. 2019, 64, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo, K.; Perez-Rodas, N.; García-Olivé, I.; Guasch-Arriaga, I.; Centeno, C.; Serra, P.; Becker-Lejuez, C.; Sanz-Santos, J.; Andreo García, F.; Ruiz-Manzano, J. Lung Cancer in Patients With Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. A Descriptive Study in a Spanish Series. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2017, 53, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugino, K.; Ishida, F.; Kikuchi, N.; Hirota, N.; Sano, G.; Sato, K.; Isobe, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Takai, Y.; Homma, S. Comparison of Clinical Characteristics and Prognostic Factors of Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema versus Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Alone. Respirology 2014, 19, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, A.; Tsushima, K.; Sugiyama, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Soeda, S.; Togashi, Y.; Kono, Y.; Kasagi, S.; Setoguchi, Y. Histological Types and Localizations of Lung Cancers in Patients with Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema. Thorac. Cancer 2013, 4, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Duan, Y.; Lv, X.; Li, Q.; Liang, B.; Ou, X. The Impact of Lung Cancer in Patients with Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema (CPFE). J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.J.; Do, K.H.; Lee, J.B.; Alblushi, S.; Lee, S.M. Lung cancer in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Karampitsakos, T.; Gomatou, G.; Bouros, E.; Tzilas, V.; Manali, E.; Tomos, I.; Trachalaki, A.; Kolilekas, L.; Korbila, I.; et al. Lung Cancer in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. A Retrospective Multicenter Study in Greece. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 60, 101880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Zhang, Y.; Rumgay, H.; Morgan, E.; Langselius, O.; Vignat, J.; Colombet, M.; Bray, F. Estimated Worldwide Variation and Trends in Incidence of Lung Cancer by Histological Subtype in 2022 and over Time: A Population-Based Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2025, 13, 348–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakopanagiotakis, F.; Krauss, E.; Michailidou, I.; Drosos, V.; Anevlavis, S.; Günther, A.; Steiropoulos, P. Lung Cancer and Interstitial Lung Diseases. Cancers 2024, 16, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masai, K.; Tsuta, K.; Motoi, N.; Shiraishi, K.; Furuta, K.; Suzuki, S.; Asakura, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Sakurai, H.; Watanabe, S.I.; et al. Clinicopathological, Immunohistochemical, and Genetic Features of Primary Lung Adenocarcinoma Occurring in the Setting of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia Pattern. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 2141–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wu, W.; Chen, N.; Song, H.; Lu, T.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liu, L. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Lung Cancer Patients with Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 13 Studies. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 5322–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotton, C.J.; Chambers, R.C. Molecular Targets in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 2007, 132, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A. The Leading Role of Epithelial Cells in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cell Signal 2020, 66, 109482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Gomatou, G.; Bouros, E.; Trigidou, R.; Tzilas, V.; Bouros, D. Common Pathogenic Mechanisms Between Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer. Chest 2019, 156, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarelli, A.V.; Masciale, V.; Aramini, B.; Coló, G.P.; Tonelli, R.; Marchioni, A.; Bruzzi, G.; Gozzi, F.; Andrisani, D.; Castaniere, I.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms and Cellular Contribution from Lung Fibrosis to Lung Cancer Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A.; Horie, M.; Micke, P.; Nagase, T. The Role of TGF-β Signaling in Lung Cancer Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, N.; O’Connor, R.N.; Unruh, H.W.; Warren, P.W.; Flanders, K.C.; Kemp, A.; Bereznay, O.H.; Greenberg, A.H. Increased Production and Immunohistochemical Localization of Transforming Growth Factor-Beta in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1991, 5, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Goto, T. Molecular Mechanisms of Pulmonary Fibrogenesis and Its Progression to Lung Cancer: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Xiong, W.; Gu, W.; Wang, C.-Y. Macrophages: Friend or Foe in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis? Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunna, C.; Mengru, H.; Lei, W.; Weidong, C. Macrophage M1/M2 Polarization. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 877, 173090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwano, K.; Araya, J.; Hara, H.; Minagawa, S.; Takasaka, N.; Ito, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Nakayama, K. Cellular Senescence and Autophagy in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). Respir. Investig. 2016, 54, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waisberg, D.R.; Barbas-Filho, J.V.; Parra, E.R.; Fernezlian, S.; Ribeiro de Carvalho, C.R.; Kairalla, R.A.; Capelozzi, V.L. Abnormal Expression of Telomerase/Apoptosis Limits Type II Alveolar Epithelial Cell Replication in the Early Remodeling of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia/Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Caam, A.; Vonk, M.; van den Hoogen, F.; van Lent, P.; van der Kraan, P. Unraveling SSc Pathophysiology; The Myofibroblast. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zohar, R.; McCulloch, C.A. Multiple Roles of α-Smooth Muscle Actin in Mechanotransduction. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C. Cell Tracing Reveals the Transdifferentiation Fate of Mouse Lung Epithelial Cells during Pulmonary Fibrosis in Vivo. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upagupta, C.; Shimbori, C.; Alsilmi, R.; Kolb, M. Matrix Abnormalities in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 180033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewska, J.; Sadowska, A.; Wójtowicz, A.; Słyszewska, M.; Szóstek-Mioduchowska, A. Perspective on Stem Cell Therapy in Organ Fibrosis: Animal Models and Human Studies. Life 2021, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.N.; Manuel, F.; Nascimento, D.S. The Bright Side of Fibroblasts: Molecular Signature and Regenerative Cues in Major Organs. NPJ Regen. Med. 2021, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almudéver, P.; Milara, J.; De Diego, A.; Serrano-Mollar, A.; Xaubet, A.; Perez-Vizcaino, F.; Cogolludo, A.; Cortijo, J. Role of Tetrahydrobiopterin in Pulmonary Vascular Remodelling Associated with Pulmonary Fibrosis. Thorax 2013, 68, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, S.H. Genesis of the Myofibroblast in Lung Injury and Fibrosis. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2012, 9, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleaveland, K.R.; Velikoff, M.; Yang, J.; Agarwal, M.; Rippe, R.A.; Moore, B.B.; Kim, K.K. Fibrocytes Are Not an Essential Source of Type I Collagen during Lung Fibrosis. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5229–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micke, P.; Ostman, A. Exploring the Tumour Environment: Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts as Targets in Cancer Therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2005, 9, 1217–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.B.; Wakefield, L.M. The Two Faces of Transforming Growth Factor β in Carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8621–8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhurst, R.J.; Hata, A. Targeting the TGFβ Signalling Pathway in Disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 790–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caja, L.; Dituri, F.; Mancarella, S.; Caballero-Diaz, D.; Moustakas, A.; Giannelli, G.; Fabregat, I. TGF-β and the Tissue Microenvironment: Relevance in Fibrosis and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noy, R.; Pollard, J.W. Tumor-Associated Macrophages: From Mechanisms to Therapy. Immunity 2014, 41, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J.; Wynn, T.A. Protective and Pathogenic Functions of Macrophage Subsets. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugeratski, F.G.; Atkinson, S.J.; Neilson, L.J.; Lilla, S.; Knight, J.R.P.; Serneels, J.; Juin, A.; Ismail, S.; Bryant, D.M.; Markert, E.K.; et al. Hypoxic Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Increase NCBP2-AS2/HIAR to Promote Endothelial Sprouting through Enhanced VEGF Signaling. Sci. Signal 2019, 12, eaan8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Ji, J.; Shan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, X. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts from NSCLC Promote the Radioresistance in Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 7002–7008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Yang, J. Mechanical Forces: The Missing Link between Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2022, 101, 151234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A. Revealing the Pathogenic and Aging-Related Mechanisms of the Enigmatic Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Integral Model. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krtolica, A.; Parrinello, S.; Lockett, S.; Desprez, P.-Y.; Campisi, J. Senescent Fibroblasts Promote Epithelial Cell Growth and Tumorigenesis: A Link between Cancer and Aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12072–12077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, G.; Pastorino, U.; Pasini, F.; Maissoneuve, P.; Fraggetta, F.; lannucci, A.; Sonzogni, A.; De Manzoni, G.; Terzi, A.; Durante, E.; et al. Independent Prognostic Value of Fascin Immunoreactivity in Stage I Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, Y.; Niki, T.; Yamada, T.; Matsuno, Y.; Kondo, H.; Hirohashi, S. Increased Expression of Laminin-5 and Its Prognostic Significance in Lung Adenocarcinomas of Small Size. An Immunohistochemical Analysis of 102 Cases. Cancer 2001, 91, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, C.; Schmitt, E.; Candé, C.; Vahsen, N.; Parcellier, A.; Kroemer, G. HSP27 and HSP70: Potentially Oncogenic Apoptosis Inhibitors. Cell Cycle 2003, 2, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilosi, M.; Zamò, A.; Doglioni, C.; Reghellin, D.; Lestani, M.; Montagna, L.; Pedron, S.; Ennas, M.G.; Cancellieri, A.; Murer, B.; et al. Migratory Marker Expression in Fibroblast Foci of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losa, D.; Chanson, M.; Crespin, S. Connexins as Therapeutic Targets in Lung Disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2011, 15, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesen-Cummings, K. Frequent Reduction of Gap Junctional Intercellular Communication and Connexin43 Expression in Human and Mouse Lung Carcinoma Cells. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato-Salinaro, A.; Trovato-Salinaro, E.; Failla, M.; Mastruzzo, C.; Tomaselli, V.; Gili, E.; Crimi, N.; Condorelli, D.F.; Vancheri, C. Altered Intercellular Communication in Lung Fibroblast Cultures from Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erratum: Corrigendum: Comprehensive Molecular Profiling of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 514, 262. [CrossRef]
- Rashid, H.O.; Yadav, R.K.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. ER Stress: Autophagy Induction, Inhibition and Selection. Autophagy 2015, 11, 1956–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolters, P.J.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, K.D. Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2014, 9, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Ferry, C.H.; Markell, L.K.; Blazanin, N.; Glick, A.B.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Peters, J.M. The Nuclear Receptor Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-β/δ (PPARβ/δ) Promotes Oncogene-Induced Cellular Senescence through Repression of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 20102–20119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E. The Role for Autophagy in Cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Gili, E.; Fruciano, M.; Korfei, M.; Fagone, E.; Iemmolo, M.; Lo Furno, D.; Giuffrida, R.; Crimi, N.; Guenther, A.; et al. PI3K P110γ Overexpression in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Lung Tissue and Fibroblast Cells: In Vitro Effects of Its Inhibition. Lab. Investig. 2013, 93, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, J.C.; Lee, D.Y.; Waghray, M.; Keshamouni, V.G.; Thomas, P.E.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Z.; Thannickal, V.J. Activation of the Pro-Survival Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/AKT Pathway by Transforming Growth Factor-Β1 in Mesenchymal Cells Is Mediated by P38 MAPK-Dependent Induction of an Autocrine Growth Factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Fruciano, M.; Fagone, E.; Gili, E.; Caraci, F.; Iemmolo, M.; Crimi, N.; Vancheri, C. Inhibition of PI3K Prevents the Proliferation and Differentiation of Human Lung Fibroblasts into Myofibroblasts: The Role of Class I P110 Isoforms. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumarola, C.; Bonelli, M.A.; Petronini, P.G.; Alfieri, R.R. Targeting PI3K/AKT/MTOR Pathway in Non Small Cell Lung Cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 90, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilosi, M.; Poletti, V.; Zamò, A.; Lestani, M.; Montagna, L.; Piccoli, P.; Pedron, S.; Bertaso, M.; Scarpa, A.; Murer, B.; et al. Aberrant Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Activation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroux-Leprieur, E.; Costantini, A.; Ding, V.W.; He, B. Hedgehog Signaling in Lung Cancer: From Oncogenesis to Cancer Treatment Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhoff, B.; Colaluca, I.N.; D’Ario, G.; Donzelli, M.; Tosoni, D.; Volorio, S.; Pelosi, G.; Spaggiari, L.; Mazzarol, G.; Viale, G.; et al. Alterations of the Notch Pathway in Lung Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22293–22298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Zhou, X.; Lai, S.; Liu, J. Notch Signaling and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauss, E.; Gehrken, G.; Drakopanagiotakis, F.; Tello, S.; Dartsch, R.C.; Maurer, O.; Windhorst, A.; von der Beck, D.; Griese, M.; Seeger, W.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Familial Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (f-IPF). BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, N.; Giraud, V.; Picard, C.; Nunes, H.; Dastot-Le Moal, F.; Copin, B.; Galeron, L.; De Ligniville, A.; Kuziner, N.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; et al. Germline SFTPA1 Mutation in Familial Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia and Lung Cancer. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kuan, P.J.; Xing, C.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Torres, F.; Rosenblatt, R.L.; DiMaio, J.M.; Kinch, L.N.; Grishin, N.V.; Garcia, C.K. Genetic Defects in Surfactant Protein A2 Are Associated with Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropski, J.A.; Blackwell, T.S.; Loyd, J.E. The Genetic Basis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korthagen, N.M.; van Moorsel, C.H.M.; Barlo, N.P.; Kazemier, K.M.; Ruven, H.J.T.; Grutters, J.C. Association between Variations in Cell Cycle Genes and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.A.; Kim, D.; Chun, S.; Bae, S.; Song, J.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Koo, H.J.; Song, J.W.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, J.C.; et al. Genomic Profiles of Lung Cancer Associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2018, 244, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Amos, C.I.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Grossman, B.H.; Shay, J.W.; Luo, S.; Hong, W.K.; Spitz, M.R. Telomere Dysfunction: A Potential Cancer Predisposition Factor. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, M.T.; Chatterjee, N.; Yu, K.; Goldin, L.R.; Goldstein, A.M.; Rotunno, M.; Mirabello, L.; Jacobs, K.; Wheeler, W.; Yeager, M.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study of Lung Cancer Identifies a Region of Chromosome 5p15 Associated with Risk for Adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, G.; Tan, N.; Meng, C.; Li, J.; Jing, L.; Yan, M.; Jin, T.; Chen, F. Genetic Variations in TERC and TERT Genes Are Associated with Lung Cancer Risk in a Chinese Han Population. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 110145–110152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, J.D.; Hung, R.J.; Han, Y.; Zong, X.; Carreras-Torres, R.; Christiani, D.C.; Caporaso, N.E.; Johansson, M.; Xiao, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Large-Scale Association Analysis Identifies New Lung Cancer Susceptibility Loci and Heterogeneity in Genetic Susceptibility across Histological Subtypes. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, S.L.; Mulholland, S.; Al Jbour, K.; Steer, H.; Gutsche, M.; Foley, N.; Srivastava, R.; Sharp, C.; Adamali, H.I. South–West of England’s Experience of the Safety and Tolerability Pirfenidone and Nintedanib for the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.; Neuhausen, S.L.; Hunt, S.C.; Kimura, M.; Hwang, S.-J.; Chen, W.; Bis, J.C.; Fitzpatrick, A.L.; Smith, E.; Johnson, A.D.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Identifies OBFC1 as a Locus Involved in Human Leukocyte Telomere Biology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9293–9298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peljto, A.L.; Zhang, Y.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Ma, S.-F.; Garcia, J.G.N.; Richards, T.J.; Silveira, L.J.; Lindell, K.O.; Steele, M.P.; Loyd, J.E.; et al. Association Between the MUC5B Promoter Polymorphism and Survival in Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. JAMA 2013, 309, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekevian, A.; Gershwin, M.E.; Chang, C. Diagnosis and Classification of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashio, R.; Ueda, J.; Ryuge, S.; Nakashima, H.; Jiang, S.-X.; Kobayashi, M.; Yanagita, K.; Katono, K.; Satoh, Y.; Masuda, N.; et al. Diagnostic and Prognostic Significances of MUC5B and TTF-1 Expressions in Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, T.; Gomez, D.R.; Jeter, M.; Levy, L.B.; Song, Y.; Hahn, S.; Liao, Z.; Yuan, X. The Pulmonary Fibrosis Associated MUC5B Promoter Polymorphism Is Prognostic of the Overall Survival in Patients with Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Receiving Definitive Radiotherapy. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 795–798. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.J.; Guillen-Guio, B.; Oldham, J.M.; Ma, S.-F.; Dressen, A.; Paynton, M.L.; Kraven, L.M.; Obeidat, M.; Li, X.; Ng, M.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Susceptibility to Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, D.L.; Baez, W.D.; Huebner, K.; Bundschuh, R.; Schoenberg, D.R. Loss of Fragile Histidine Triad (Fhit) Protein Expression Alters the Translation of Cancer-Associated MRNAs. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uematsu, K.; Yoshimura, A.; Gemma, A.; Mochimaru, H.; Hosoya, Y.; Kunugi, S.; Matsuda, K.; Seike, M.; Kurimoto, F.; Takenaka, K.; et al. Aberrations in the Fragile Histidine Triad (FHIT) Gene in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 8527–8533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sozzi, G.; Veronese, M.L.; Negrini, M.; Baffa, R.; Cotticelli, M.G.; Inoue, H.; Tornielli, S.; Pilotti, S.; De Gregorio, L.; Pastorino, U.; et al. The FHIT Gene at 3p14.2 Is Abnormal in Lung Cancer. Cell 1996, 85, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsoukis, N.; Wang, Q.; Strauss, L.; Boussiotis, V.A. Revisiting the PD-1 Pathway. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovich, E.I.; Kapetanaki, M.G.; Steinfeld, I.; Gibson, K.F.; Pandit, K.V.; Yu, G.; Yakhini, Z.; Kaminski, N. Global Methylation Patterns in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemma Reduced Transcription of the Smad4 Gene during Pulmonary Carcinogenesis in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2008. [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.K.; Scruggs, A.M.; McEachin, R.C.; White, E.S.; Peters-Golden, M. Lung Fibroblasts from Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Exhibit Genome-Wide Differences in DNA Methylation Compared to Fibroblasts from Nonfibrotic Lung. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lan, Q.; Siegfried, J.M.; Luketich, J.D.; Keohavong, P. Aberrant Promoter Methylation of P16 and MGMT Genes in Lung Tumors from Smoking and Never-Smoking Lung Cancer Patients. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, S.M.; Kratzke, R.A.; Kelsey, K.T. Epigenetics of Lung Cancer. Transl. Res. 2015, 165, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, Y.Y.; Pardo, A.; Selman, M.; Nuovo, G.J.; Tollefsbol, T.O.; Siegal, G.P.; Hagood, J.S. Thy-1 Promoter Hypermethylation: A Novel Epigenetic Pathogenic Mechanism in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 39, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Shen, H.; Qiu, C.; Ni, Y.; Wang, L.; Dong, W.; Liao, Y.; Du, J. High Expression of MiR-21 and MiR-155 Predicts Recurrence and Unfavourable Survival in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vancheri, C. Common Pathways in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Cancer. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2013, 22, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Kaiser, R.; Mellemgaard, A.; Douillard, J.-Y.; Orlov, S.; Krzakowski, M.; von Pawel, J.; Gottfried, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Liao, M.; et al. Docetaxel plus Nintedanib versus Docetaxel plus Placebo in Patients with Previously Treated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (LUME-Lung 1): A Phase 3, Double-Blind, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.-Y.; Kim, H.; Bae, Y.; Song, J.W. Pirfenidone and Risk of Lung Cancer Development in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Eur. Respir. J. 2025, 65, 2401484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.S.; Kim, K.J.; Rhee, C.K.; Kim, Y.H. Impact of Antifibrotic Therapy on Lung Cancer Incidence and Mortality in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2024, 16, 8528–8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediavilla-Varela, M.; Boateng, K.; Noyes, D.; Antonia, S.J. The Anti-Fibrotic Agent Pirfenidone Synergizes with Cisplatin in Killing Tumor Cells and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S. Identification and Molecular Modelling of Potential Drugs Targeting the Genes Involved in the Progression of Lung Cancer in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Gene Rep. 2024, 37, 102067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galioto, F.; Palmucci, S.; Astut, G.M.; Vancheri, A.; Distefano, G.; Tiralongo, F.; Libra, A.; Cusumano, G.; Basile, A.; Vancheri, C. Complications in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Focus on Their Clinical and Radiological Features. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratella, E.; Fiorese, I.; Marrocchio, C.; Salton, F.; Cova, M.A. Imaging Review of the Lung Parenchymal Complications in Patients with IPF. Medicina 2019, 55, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, J.-E.; Kim, S.-S.; Park, T.S.; Kim, D.S.; Choi, C.-M. Evolving Early Lung Cancers Detected During Follow-Up of Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia: Serial CT Features. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.J.; Lee, K.S.; Kwon, O.J.; Rhee, C.H.; Shim, Y.M.; Han, J. Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma: Focal Area of Ground-Glass Attenuation at Thin-Section CT as an Early Sign. Radiology 1996, 199, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgalla, G.; Larici, A.R.; Golfi, N.; Calvello, M.; Farchione, A.; Del Ciello, A.; Varone, F.; Iovene, B.; Manfredi, R.; Richeldi, L. Mediastinal Lymph Node Enlargement in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Relationships with Disease Progression and Pulmonary Function Trends. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mets, O.M.; de Jong, P.A.; Chung, K.; Lammers, J.W.J.; van Ginneken, B.; Schaefer-Prokop, C.M. Fleischner Recommendations for the Management of Subsolid Pulmonary Nodules: High Awareness but Limited Conformance—A Survey Study. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 3840–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, H.; Tsukahara, Y.; Sato, S.; Ohta, H.; Kida, G.; Nakamura, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Kawabe, R.; Oba, T.; Akasaka, K.; et al. Impact of Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) in ILD Patients Complicated with Secondary Spontaneous Pneumothorax. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2022, 38, e2021042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.J.; Yun, G.; Yoon, S.H.; Song, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Park, J.S.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, K.H. Accuracy and Complications of Percutaneous Transthoracic Needle Lung Biopsy for the Diagnosis of Malignancy in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 9000–9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.V.; Afraz, Z.; Huo, Y.R.; Kandel, S.; Rogalla, P. Manual Aspiration of a Pneumothorax after CT-Guided Lung Biopsy: Outcomes and Risk Factors. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20220366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundson, W.H.; Racila, E.; Allen, T.; Dincer, H.E.; Tomic, R.; Bhargava, M.; Perlman, D.M.; Kim, H.J. Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease after Procedures. Respir. Med. 2019, 150, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, H.R.; Ryerson, C.J.; Corte, T.J.; Jenkins, G.; Kondoh, Y.; Lederer, D.J.; Lee, J.S.; Maher, T.M.; Wells, A.U.; Antoniou, K.M.; et al. Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis an International Working Group Report. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyajima, M.; Watanabe, A.; Sato, T.; Teramukai, S.; Ebina, M.; Kishi, K.; Sugiyama, Y.; Kondo, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Takahashi, Y.; et al. What Factors Determine the Survival of Patients with an Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease after Lung Cancer Resection? Surg. Today 2018, 48, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishaba, T. Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Medicina 2019, 55, 499–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.W.; Hong, S.-B.; Lim, C.-M.; Koh, Y.; Kim, D.S. Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Incidence, Risk Factors and Outcome. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bando, M.; Ohno, S.; Hosono, T.; Yanase, K.; Sato, Y.; Sohara, Y.; Hironaka, M.; Sugiyama, Y. Risk of Acute Exacerbation After Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Lung Biopsy for Interstitial Lung Disease. J. Bronchology Interv. Pulmonol. 2009, 16, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plönes, T.; Osei-Agyemang, T.; Elze, M.; Palade, E.; Wagnetz, D.; Loop, T.; Kayser, G.; Passlick, B. Morbidity and Mortality in Patients with Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Pattern Undergoing Surgery for Lung Biopsy. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samejima, J.; Tajiri, M.; Ogura, T.; Baba, T.; Omori, T.; Tsuboi, M.; Masuda, M. Thoracoscopic Lung Biopsy in 285 Patients with Diffuse Pulmonary Disease. Asian Cardiovasc. Thorac. Ann. 2015, 23, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhooria, S.; Mehta, R.M.; Srinivasan, A.; Madan, K.; Sehgal, I.S.; Pattabhiraman, V.; Yadav, P.; Sivaramakrishnan, M.; Mohan, A.; Bal, A.; et al. The Safety and Efficacy of Different Methods for Obtaining Transbronchial Lung Cryobiopsy in Diffuse Lung Diseases. Clin. Respir. J. 2018, 12, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HIWATARI, N.; SHIMURA, S.; TAKISHIMA, T.; SHIRATO, K. Bronchoalveolar Lavage as a Possible Cause of Acute Exacerbation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Patients. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1994, 174, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Taniguchi, H.; Kondoh, Y.; Wakai, K.; Kimura, T.; Kataoka, K.; Hashimoto, N.; Nishiyama, O.; Hasegawa, Y. Acute Exacerbation of IPF Following Diagnostic Bronchoalveolar Lavage Procedures. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Teramukai, S.; Kondo, H.; Watanabe, A.; Ebina, M.; Kishi, K.; Fujii, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Yoshimura, M.; Maniwa, T.; et al. Impact and Predictors of Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Diseases after Pulmonary Resection for Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 1604–1611.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Hao, J.; Chen, C.; Peng, H.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Q.; Liu, L. Risk Factors for Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease Following Lung Cancer Resection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2022, 34, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.J.; Walters, G.I.; Watkins, S.; Rogers, V.; Fallouh, H.; Kalkat, M.; Naidu, B.; Bishay, E.S. Lung Cancer Resection in Patients with Underlying Usual Interstitial Pneumonia: A Meta-Analysis. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2023, 10, e001529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Huang, J.; Feng, H.; Sun, H.; Ren, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, D. Impact of Interstitial Lung Disease on Postoperative Morbidity and 90-Day Mortality after Pulmonary Resection. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzaki, M.; Kikkawa, T.; Maeda, H.; Kondo, M.; Isaka, T.; Shimizu, T.; Murasugi, M.; Onuki, T. Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias after Surgical Resection of Lung Cancer. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 13, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.; Shim, Y.; Choi, Y. Prediction of Acute Pulmonary Complications after Resection of Lung Cancer in Patients with Preexisting Interstitial Lung Disease. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 59, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniwa, T.; Isaka, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Ohde, Y.; Okumura, T.; Endo, M.; Kondo, H. Chest-Tube Drainage Is a Sign of Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Lung Cancer. Surg. Today 2013, 43, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, T.; Tajiri, M.; Baba, T.; Ogura, T.; Iwasawa, T.; Okudela, K.; Takemura, T.; Oba, M.S.; Maehara, T.; Nakayama, H.; et al. Pulmonary Resection for Lung Cancer in Patients With Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, S.; Kim, D.K.; Sim, H.J.; Lee, G.D.; Hwang, S.K.; Choi, S.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, Y.-H.; Park, S.-I. Clinical Results of Sublobar Resection versus Lobectomy or More Extensive Resection for Lung Cancer Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Karube, Y.; Nishihira, M.; Inoue, T.; Araki, O.; Maeda, S.; Sado, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Chida, M. Postoperative Pyothorax a Risk Factor for Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia Following Lung Cancer Resection. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutani, Y.; Mimura, T.; Kai, Y.; Ito, M.; Misumi, K.; Miyata, Y.; Okada, M. Outcomes after Lobar versus Sublobar Resection for Clinical Stage I Non−small Cell Lung Cancer in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 154, 1089–1096.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Ren, Y.; She, Y.; Dai, C.; Wang, T.; Su, H.; Sun, W.; Jiang, G.; Chen, C. Is Operation Safe for Lung Cancer Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease on Computed Tomography? Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2020, 14, 1753466620971137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Miyoshi, S.; Hamada, C.; Sano, Y.; Nogami, N.; Yamaguchi, O.; Hamaguchi, N. Associations between Comorbidities and Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease after Primary Lung Cancer Surgery. Acta Medica Okayama 2023, 77, 301–309. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, M.; Mimae, T.; Tsutani, Y.; Miyata, Y.; Okada, M. Complications and Survival After Lung Cancer Resection in Interstitial Lung Disease. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2023, 115, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T. Measuring Surgery Outcomes of Lung Cancer Patients with Concomitant Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Review of the Literature. Cancers 2018, 10, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, F.; Kitaguchi, Y.; Shiina, T.; Asaka, S.; Yasuo, M.; Wada, Y.; Kinjo, T.; Yoshizawa, A.; Hanaoka, M. The Interstitial Lung Disease-Gender-Age-Physiology Index Can Predict the Prognosis in Surgically Resected Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease and Concomitant Lung Cancer. Respiration 2020, 99, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Watanabe, A.; Kondo, H.; Kanzaki, M.; Okubo, K.; Yokoi, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Marutsuka, T.; Shinohara, H.; Teramukai, S.; et al. Long-Term Results and Predictors of Survival after Surgical Resection of Patients with Lung Cancer and Interstitial Lung Diseases. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 149, 64–70.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Tsutani, Y.; Wakabayashi, M.; Mizutani, T.; Aokage, K.; Miyata, Y.; Kuroda, H.; Saji, H.; Watanabe, S.; Okada, M. Sublobar Resection versus Lobectomy for Patients with Resectable Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Phase III Study Evaluating Survival (JCOG1708, SURPRISE). Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 50, 1076–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, T.; Yoshida, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Wada, H.; Nakajima, T.; Suzuki, H.; Yoshino, I. Effect of Perioperative Pirfenidone Treatment in Lung Cancer Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 102, 1905–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongiolatti, S.; Salvicchi, A.; Rosi, E.; Bargagli, E.; Mugnaini, G.; Gonfiotti, A.; Lavorini, F.; Spagnolo, P.; Dell’Amore, A.; Rea, F.; et al. Perioperative Anti-Fibrotic Treatment Prevents Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis After Lung Cancer Surgery. Life 2024, 14, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, T.; Yoshino, I.; Yoshida, S.; Ikeda, N.; Tsuboi, M.; Asato, Y.; Katakami, N.; Sakamoto, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Okami, J.; et al. A Phase II Trial Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Perioperative Pirfenidone for Prevention of Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in Lung Cancer Patients Undergoing Pulmonary Resection: West Japan Oncology Group 6711 L (PEOPLE Study). Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakairi, Y.; Yoshino, I.; Iwata, T.; Yoshida, S.; Kuwano, K.; Azuma, A.; Sakai, S.; Kobayashi, K. A Randomized Controlled Phase III Trial Protocol: Perioperative Pirfenidone Therapy in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Combined with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis to Confirm the Preventative Effect against Postoperative Acute Exacerbation: The PIII-PEOPLE Study (NEJ034). J. Thorac. Dis. 2023, 15, 1486–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.J.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Dobre, I.A.; Tait, S.; Schumacher, L.; Fintelmann, F.J.; Fingerman, L.M.; Keane, F.K.; Montesi, S.B. Management of Lung Cancer in the Patient with Interstitial Lung Disease. Oncologist 2023, 28, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graur, A.; Montesi, S.B.; Lanuti, M.; Fintelmann, F.J. Treating Lung Cancer in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease: What Do We Know? J. Thorac. Dis. 2023, 15, 1555–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, S.W.; Mortell, K.E.; Talenfeld, A.D.; Brunner, M.C. Thermal Ablation Matches Sublobar Resection Outcomes in Older Patients with Early-Stage Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 1–9.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaseda, K.; Asakura, K.; Nishida, R.; Okubo, Y.; Masai, K.; Hishida, T.; Inoue, M.; Yashiro, H.; Nakatsuka, S.; Jinzaki, M.; et al. Feasibility and Safety of Percutaneous Cryoablation under Local Anesthesia for the Treatment of Malignant Lung Tumors: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 4297–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.Z.; Bie, Z.X.; Li, Y.M.; Guo, R.Q.; Li, X.G. Safety and Efficacy of CT-Guided Percutaneous Microwave Ablation for Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Patients with Comorbid Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 4708–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.A.; Murphy, M.C.; Montesi, S.B.; Hariri, L.P.; Hallowell, R.W.; Keane, F.K.; Lanuti, M.; Mooradian, M.J.; Fintelmann, F.J. Diagnosis and Treatment of Lung Cancer in the Setting of Interstitial Lung Disease. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 60, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, D.; Lyen, S.; Kandel, S.; Shapera, S.; Le, L.W.; Lindsay, P.; Wong, O.; Bezjak, A.; Brade, A.; Cho, B.C.J.; et al. Impact of Pretreatment Interstitial Lung Disease on Radiation Pneumonitis and Survival in Patients Treated With Lung Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT). Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, e219–e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, H.; Yamashita, H.; Shioyama, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Takayama, K.; Matsuo, Y.; Miyakawa, A.; Matsushita, H.; Aoki, M.; Nihei, K.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Patients with Pulmonary Interstitial Change: High Incidence of Fatal Radiation Pneumonitis in a Retrospective Multi-Institutional Study. Cancers 2018, 10, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Dickinson, P.; Shrimali, R.K.; Salem, A.; Agarwal, S. Is Thoracic Radiotherapy an Absolute Contraindication for Treatment of Lung Cancer Patients With Interstitial Lung Disease? A Systematic Review. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 34, e493–e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Liang, S.; Xu, Y. Risk Factors for Radiation Pneumonitis in Lung Cancer Patients with Subclinical Interstitial Lung Disease after Thoracic Radiation Therapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Pyo, H.; Noh, J.M.; Lee, W.; Park, B.; Park, H.Y.; Yoo, H. Preliminary Result of Definitive Radiotherapy in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Who Have Underlying Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Comparison between X-Ray and Proton Therapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaji, N.; Tadokoro, A.; Kita, N.; Murota, M.; Ishii, T.; Takagi, T.; Watanabe, N.; Tojo, Y.; Harada, S.; Hasui, Y.; et al. Impact of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis on Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Survival. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 1855–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yang, R.; Jin, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, W. Impact of Concomitant Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis on Prognosis in Lung Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenmotsu, H.; Yoh, K.; Mori, K.; Ono, A.; Baba, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Yamaguchi, O.; Ko, R.; Okamoto, H.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. Phase II Study of Nab-paclitaxel + Carboplatin for Patients with Non-small-cell Lung Cancer and Interstitial Lung Disease. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 3738–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asahina, H.; Oizumi, S.; Takamura, K.; Harada, T.; Harada, M.; Yokouchi, H.; Kanazawa, K.; Fujita, Y.; Kojima, T.; Sugaya, F.; et al. A Prospective Phase II Study of Carboplatin and Nab-Paclitaxel in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Concomitant Interstitial Lung Disease (HOT1302). Lung Cancer 2019, 138, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuizumi, A.; Minegishi, Y.; Omori, M.; Atsumi, K.; Takano, N.; Hisakane, K.; Takahashi, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Sugano, T.; Takeuchi, S.; et al. Weekly Paclitaxel in Combination with Carboplatin for Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Complicated by Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias: A Single-Arm Phase II Study. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 24, 1543–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanibuchi, M.; Kakiuchi, S.; Atagi, S.; Ogushi, F.; Shimizu, E.; Haku, T.; Toyoda, Y.; Azuma, M.; Kondo, M.; Kawano, H.; et al. A Multicenter, Open-Label, Phase II Trial of S-1 plus Carboplatin in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease. Lung Cancer 2018, 125, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, A.; Satoh, H.; Baba, T.; Ikeda, S.; Okuda, R.; Shinohara, T.; Komatsu, S.; Hagiwara, E.; Iwasawa, T.; Ogura, T.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of S-1 in Combination with Carboplatin in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease: A Pilot Study. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, S.; Ichiyasu, H.; Ikeda, T.; Inaba, M.; Kashiwabara, K.; Sadamatsu, T.; Sato, N.; Akaike, K.; Okabayashi, H.; Saruwatari, K.; et al. Protective Effect of Bevacizumab on Chemotherapy-Related Acute Exacerbation of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Advanced Non-Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Shukuya, T.; Takahashi, F.; Mori, K.; Suina, K.; Asao, T.; Kanemaru, R.; Honma, Y.; Muraki, K.; Sugano, K.; et al. Pemetrexed for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N.; Taniguchi, H.; Kondoh, Y.; Kimura, T.; Kataoka, K.; Nishiyama, O.; Kondo, M.; Hasegawa, Y. Chemotherapy for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 19, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.J.; Lim, S.Y.; Park, J.S.; Yoon, H.I.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Jung, J.Y.; Kang, Y.A.; Park, M.S.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. Prognosis of Small Cell Lung Cancer with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Assessment According to GAP Stage. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, N.; Iwai, Y.; Nagai, Y.; Aoshiba, K.; Nakamura, H. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in Small Cell Lung Cancer as a Predictive Factor for Poor Clinical Outcome and Risk of Its Exacerbation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, A.; Michimae, H.; Nakahara, Y.; Akagawa, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Minegishi, Y.; Ogura, T.; Hontsu, S.; Date, H.; Takahashi, K.; et al. Acute Exacerbation Predicting Poor Outcomes in Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia and Advanced Lung Cancer Patients Undergoing Cytotoxic Chemotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Minegishi, Y.; Higa, K.; Fukuizumi, A.; Onda, N.; Takeuchi, S.; Miyanaga, A.; Gemma, A.; Seike, M. Carboplatin in Combination with Etoposide for Advanced Small Cell Lung Cancer Complicated with Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia: A Single-Arm Phase II Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2025, 25, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Yano, Y.; Kuge, T.; Okabe, F.; Ishijima, M.; Uenami, T.; Kanazu, M.; Akazawa, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Mori, M. Safety and Effectiveness of Pirfenidone Combined with Carboplatin-based Chemotherapy in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 3317–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makiguchi, T.; Tanaka, H.; Okudera, K.; Taima, K.; Tasaka, S. Safety and Feasibility of Carboplatin and Paclitaxel in Combination with Nintedanib for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Prospective Pilot Study. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2023, 12, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsubo, K.; Kishimoto, J.; Ando, M.; Kenmotsu, H.; Minegishi, Y.; Horinouchi, H.; Kato, T.; Ichihara, E.; Kondo, M.; Atagi, S.; et al. Nintedanib plus Chemotherapy for Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Randomised Phase 3 Trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2200380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, S.; Ogura, T.; Kato, T.; Kenmotsu, H.; Agemi, Y.; Tokito, T.; Ito, K.; Isomoto, K.; Takiguchi, Y.; Yoneshima, Y.; et al. Nintedanib plus Chemotherapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer with Comorbid Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2024, 21, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, C.H.; Kim, K.W.; Pyo, J.; Hatabu, H.; Nishino, M. The Incidence of ALK Inhibitor-Related Pneumonitis in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lung Cancer 2019, 132, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, Y.; Uchida, Y.; Ando, K.; Manabe, R.; Tanaka, A.; Sagara, H. Risk Factors for Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Respir. Investig. 2024, 62, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudoh, S.; Kato, H.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Fukuoka, M.; Nakata, K.; Ichinose, Y.; Tsuboi, M.; Yokota, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Suga, M.; et al. Interstitial Lung Disease in Japanese Patients with Lung Cancer. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 1348–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzuto, A.; Ricci, A.; Palermo, T.; Salvucci, C.; Pelosi, G.; Stirpe, F.; Gallippi, A.; Pace, I.; Chichi, E.; Carico, E. Discrepancy between Clinical and Radiological Responses in Non-Infectious Pneumonia during Immunotherapy: A Case Report. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2025, 29, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanai, O.; Kim, Y.H.; Demura, Y.; Kanai, M.; Ito, T.; Fujita, K.; Yoshida, H.; Akai, M.; Mio, T.; Hirai, T. Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Preexisting Interstitial Lung Disease. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, Y.; Masuda, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Horimasu, Y.; Nakashima, T.; Miyamoto, S.; Tsutani, Y.; Iwamoto, H.; Fujitaka, K.; et al. Pre-Existing Interstitial Lung Abnormalities Are Risk Factors for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Interstitial Lung Disease in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Respir. Investig. 2019, 57, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasaka, Y.; Honda, T.; Nishiyama, N.; Tsutsui, T.; Saito, H.; Watabe, H.; Shimaya, K.; Mochizuki, A.; Tsuyuki, S.; Kawahara, T.; et al. Non-Inferior Clinical Outcomes of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease. Lung Cancer 2021, 155, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Nintedanib: A Review of Its Use as Second-Line Treatment in Adults with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer of Adenocarcinoma Histology. Target. Oncol. 2015, 10, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Cottin, V.; du Bois, R.M.; Selman, M.; Kimura, T.; Bailes, Z.; Schlenker-Herceg, R.; Stowasser, S.; Brown, K.K. Nintedanib in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Combined Evidence from the TOMORROW and INPULSIS® Trials. Respir. Med. 2016, 113, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, Y.; Saito, T.; Tanaka, T.; Takoi, H.; Yatagai, Y.; Inomata, M.; Nei, T.; Saito, Y.; Gemma, A.; Azuma, A. Reduced Incidence of Lung Cancer in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treated with Pirfenidone. Respir. Investig. 2018, 56, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author | Published Year | Reference | Number of Patients, n | IPF-LC n (%) | Median Time to LC Diagnosis (Months) | Men (%) | Age at IPF Diagnosis | Average Pack-Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ozawa | 2009 | [25] | 103 | 21 (20) | 120 | 95.23 | NA | 73.1 |
| Lee | 2012 | [30] | 1685 | 114 (6.8) | 17 | 94.7 | 68.5 | 44.3 |
| Hyldgaard | 2014 | [28] | 121 | 7 (6) | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Tomassetti | 2015 | [27] | 181 | 23 (13) | 30 | 82.6 | 66.9 | 36.7 |
| Kato | 2018 | [29] | 632 | 70 (11.1) | NA | 94.3 | 66.8 | 46.4 |
| Yoo | 2019 | [20] | 938 | 135 (14.5) | 38 | 94.8 | 69 | 41.7 |
| Tzouvelekis | 2020 | [31] | 1016 | 102 (10) | 33 | 94.1 | 71.4 | NA |
| Karampitsakos | 2022 | [24] | 3178 | 324 (10.2) | 28 | 90.4 | 71 | NA |
| Lee | 2023 | [26] | 21,111 | 706 (3.3) | NA | 87.54 | 70.5 | NA |
| Original Articles | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author | Reference | Published Year | Number of Patients, n | Number of AEs, n (%) | Number of AE Deaths, n (%) |
| Kanazaki | [163] | 2010 | 40 | 12 (30) | 3 (25) |
| Park | [164] | 2011 | 100 | 28 (28) | 13 (46.7) |
| Maniwa | [165] | 2013 | 89 | 8 (9) | 1 (12.5) |
| Sato | [159] | 2014 | 1763 | 164 (9.4) | 72 (43.9) |
| Omori | [166] | 2015 | 103 | 5 (4.90) | 3 (60) |
| Joo | [167] | 2016 | 80 | 6 (7.5) | NA |
| Kobayashi | [168] | 2016 | 137 | 17 (12.4) | 7(41.2) |
| Tsutani | [169] | 2017 | 107 | 6 (5.6) | NA |
| Shao | [162] | 2019 | 97 | 7(6.2) | 5 (83.3) |
| Tang | [170] | 2020 | 156 | 7 (4.5) | 5 (71.4) |
| Kato | [171] | 2023 | 68 | 8 (11.8) | 1 (12.5) |
| Fujiwara | [172] | 2023 | 91 | 14 (15.4) | 9 (64) |
| Meta-analysis | |||||
| Hao | [160] | 2022 | 2655 | 258 (9.7) | NA |
| Patel | [161] | 2023 | 2202 | 322 (14.6) | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Polish Respiratory Society. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czyżak, B.; Majewski, S. Concomitant Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: An Updated Narrative Review. Adv. Respir. Med. 2025, 93, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93040031
Czyżak B, Majewski S. Concomitant Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: An Updated Narrative Review. Advances in Respiratory Medicine. 2025; 93(4):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93040031
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzyżak, Bartłomiej, and Sebastian Majewski. 2025. "Concomitant Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: An Updated Narrative Review" Advances in Respiratory Medicine 93, no. 4: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93040031
APA StyleCzyżak, B., & Majewski, S. (2025). Concomitant Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: An Updated Narrative Review. Advances in Respiratory Medicine, 93(4), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm93040031







