Expression of Epithelial Alarmin Receptor on Innate Lymphoid Cells Type 2 in Eosinophilic Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
Highlights
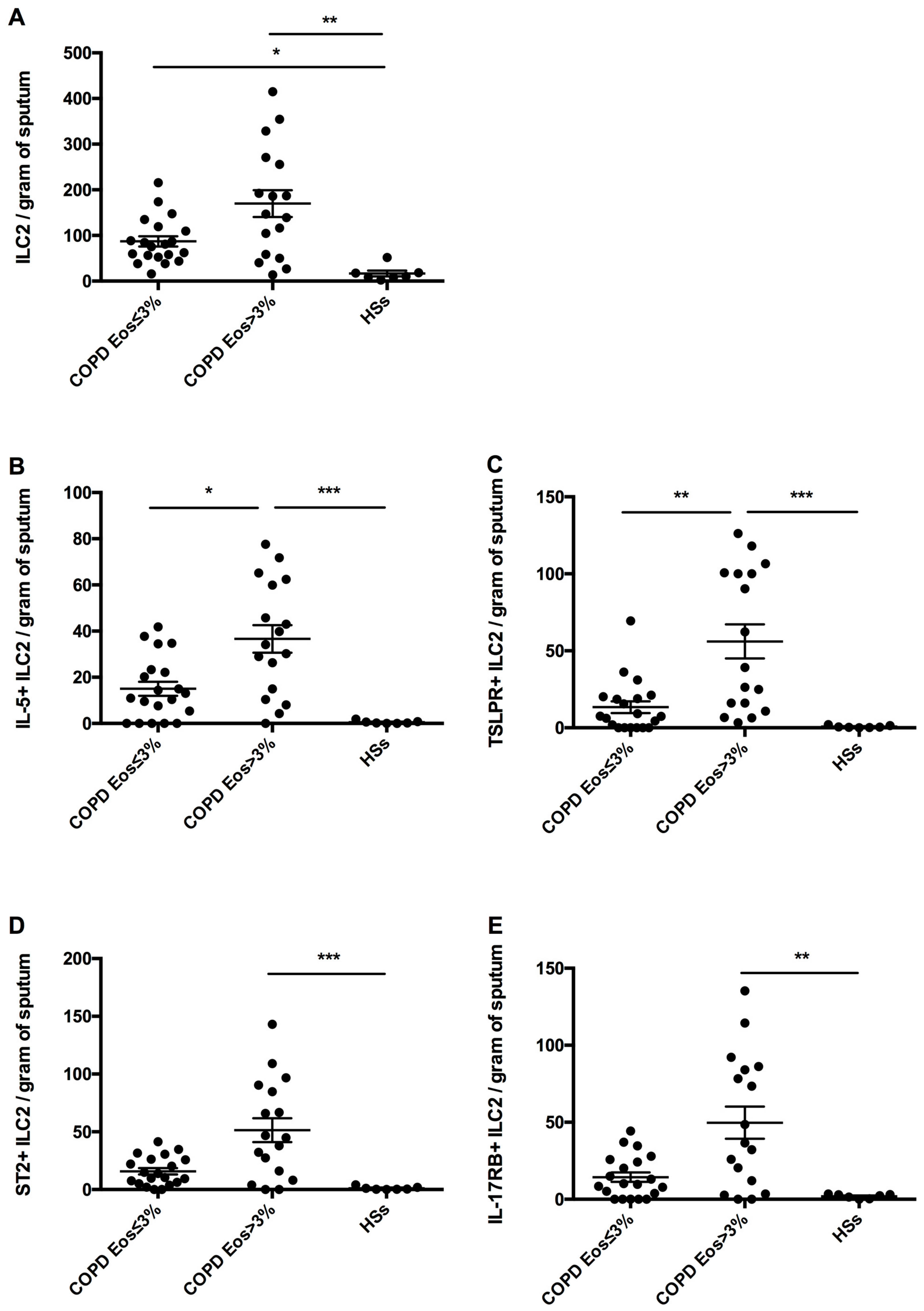
- We found an increased number of airway ILC2s expressing TSLP receptor and intracellular IL-5 in eosinophilic COPD patients compared with non-eosinophilic patients and heathy smokers.
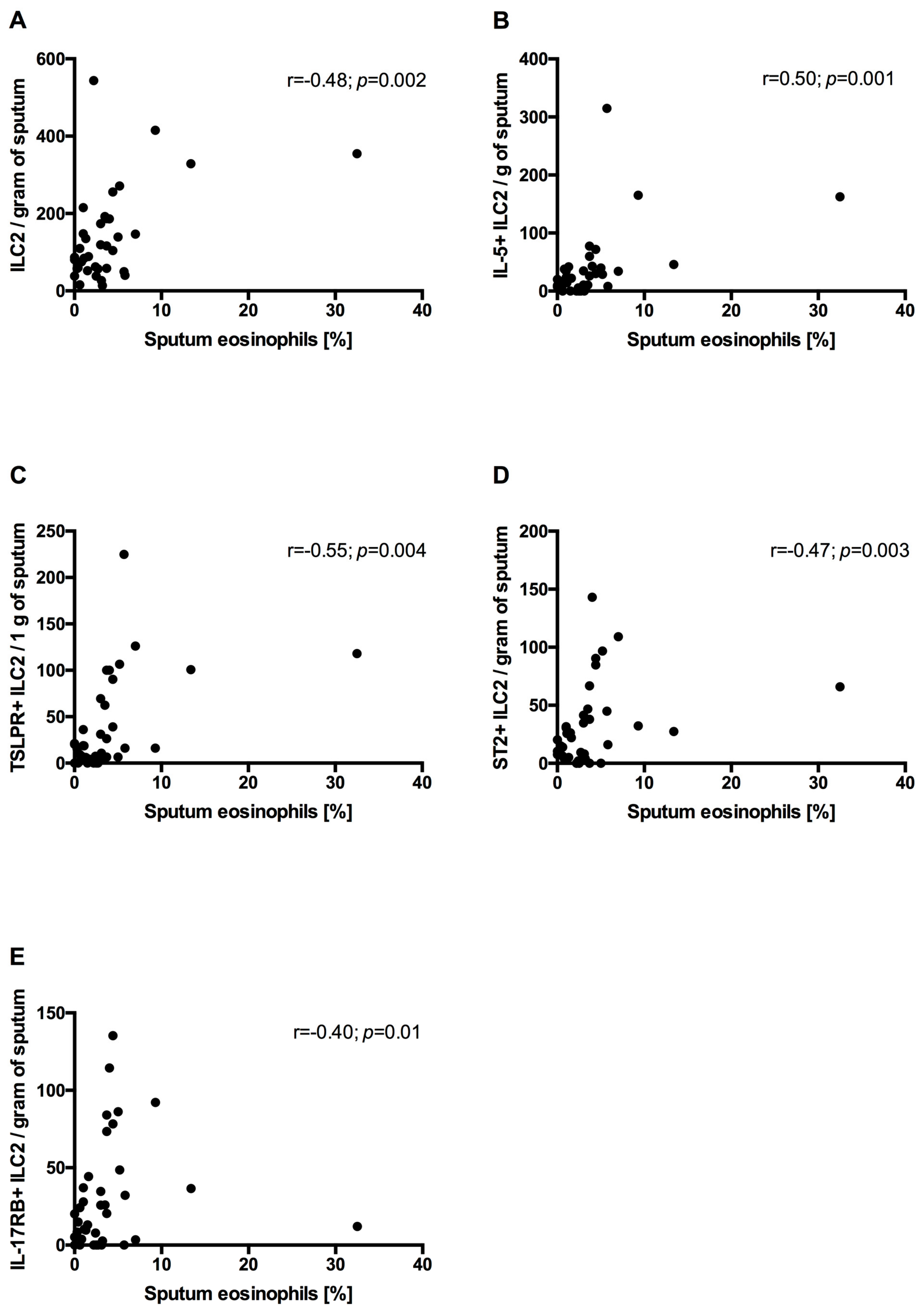
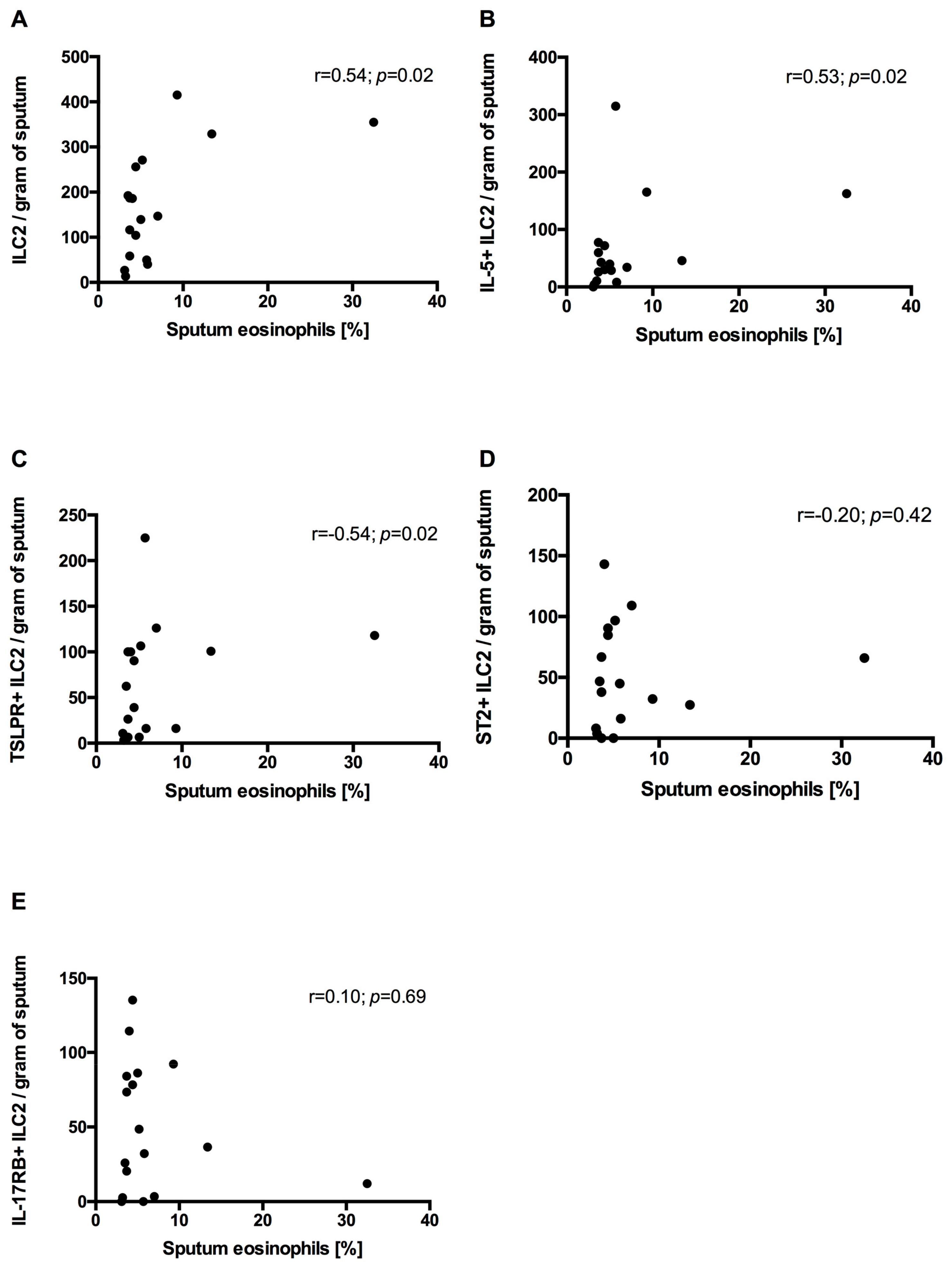
- In COPD patients’ sputum, ILC2s correlated positively with sputum eosinophilia.
- Our report suggests the involvement of ILC2s in airway eosinophilic inflammatory responses in COPD.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. The COPD Assessment Test (CAT)
2.3. The Modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) Dyspnea Scale
2.4. Symptom Intensity and Risk of Exacerbations
2.5. Skin Prick Testing
2.6. Blood Sample Processing
2.7. Sputum Induction and Processing
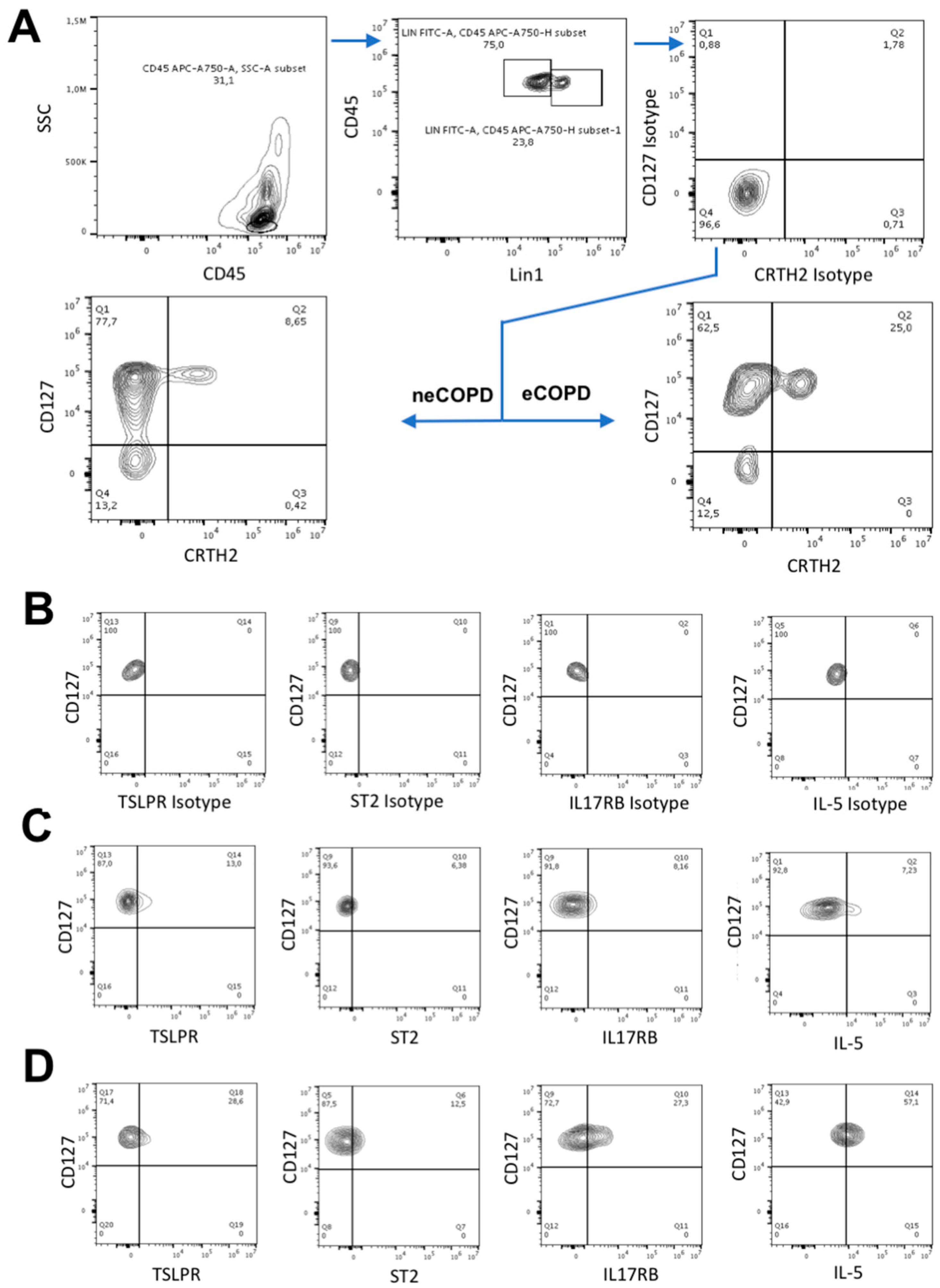
2.8. Flow Cytometry
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Circulating ILC2s
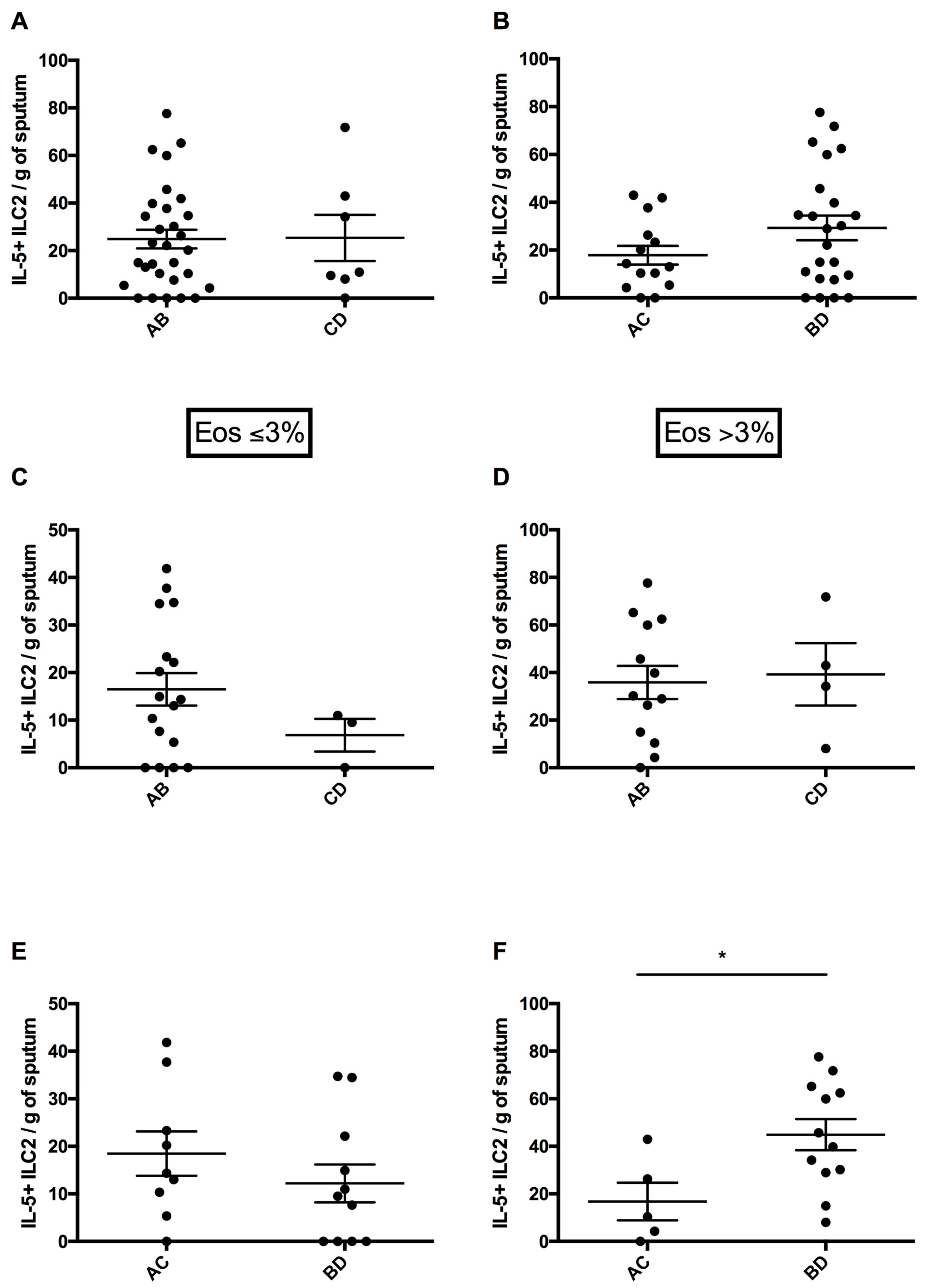
3.3. Sputum ILC2s
3.4. Circulating ILC2 Numbers According to Risk of Exacerbations and Symptom Intensity
3.5. Sputum ILC2 Numbers According to Risk of Exacerbations and Symptom Intensity
3.6. Correlation Between Sputum ILC2s and Sputum Eosinophils and mMRC and CAT
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saetta, M.; Di Stefano, A.; Maestrelli, P.; Turato, G.; Ruggieri, M.P.; Roggeri, A.; Calcagni, P.; E Mapp, C.; Ciaccia, A.; Fabbri, L.M. Airway eosinophilia in chronic bronchitis during exacerbations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 150, 1646–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzano, G.; Stefanelli, F.; Iorio, C.; DE Felice, A.; Melillo, E.M.; Martucci, M.; Melillo, G. Eosinophilic Inflammation in Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Relationship with neutrophils and airway function. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 1486–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolsum, U.; Damera, G.; Pham, T.-H.; Southworth, T.; Mason, S.; Karur, P.; Newbold, P.; Singh, D. Pulmonary inflammation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with higher blood eosinophil counts. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1181–1184.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchesne, M.; Okoye, I.; Lacy, P. Epithelial cell alarmin cytokines: Frontline mediators of the asthma inflammatory response. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 975914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zhao, J.; Shang, J.; Li, M.; Zeng, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Xie, J. Increased IL-33 expression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 308, L619–L627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tworek, D.; Majewski, S.; Szewczyk, K.; Kiszałkiewicz, J.; Kurmanowska, Z.; Górski, P.; Brzeziańska-Lasota, E.; Kuna, P.; Antczak, A. The association between airway eosinophilic inflammation and IL-33 in stable non-atopic COPD. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smelter, D.F.; Sathish, V.; Thompson, M.A.; Pabelick, C.M.; Vassallo, R.; Prakash, Y.S. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in Cigarette Smoke-Exposed Human Airway Smooth Muscle. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 3035–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camelo, A.; Rosignoli, G.; Ohne, Y.; Stewart, R.A.; Overed-Sayer, C.; Sleeman, M.A.; May, R.D. IL-33, IL-25, and TSLP induce a distinct phenotypic and activation profile in human type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, H.; Moro, K.; Koyasu, S. Innate lymphoid cells in allergic and nonallergic inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.G.; Gugilla, A.; Mukherjee, M.; Merim, K.; Irshad, A.; Tang, W.; Kinoshita, T.; Watson, B.; Oliveria, J.-P.; Comeau, M.; et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin and IL-33 modulate migration of hematopoietic progenitor cells in patients with allergic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, J.S.; Kearley, J.; Copenhaver, A.M.; Sanden, C.; Mori, M.; Yu, L.; Pritchard, G.H.; Berlin, A.A.; Hunter, C.A.; Bowler, R.; et al. Inflammatory triggers associated with exacerbations of COPD orchestrate plasticity of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in the lungs. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bal, S.M.; Bernink, J.H.; Nagasawa, M.; Groot, J.; Shikhagaie, M.M.; Golebski, K.; van Drunen, C.M.; Lutter, R.; Jonkers, R.E.; Hombrink, P.; et al. IL-1β, IL-4 and IL-12 control the fate of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in human airway inflammation in the lungs. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: www.goldcopd.org (accessed on 6 April 2024).
- Jones, P.W.; Harding, G.; Berry, P.; Wiklund, I.; Chen, W.H.; Kline Leidy, N. Development and first validation of the COPD Assessment Test. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahler, D.A.; Wells, C.K. Evaluation of Clinical Methods for Rating Dyspnea. Chest 1988, 93, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafadhel, M.; McCormick, M.; Saha, S.; McKenna, S.; Shelley, M.; Hargadon, B.; Mistry, V.; Reid, C.; Parker, D.; Dodson, P.; et al. Profiling of Sputum Inflammatory Mediators in Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Respiration 2012, 83, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartemes, K.R.; Kephart, G.M.; Fox, S.J.; Kita, H. Enhanced innate type 2 immune response in peripheral blood from patients with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 671–678.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Kolsum, U.; Brightling, C.E.; Locantore, N.; Agusti, A.; Tal-Singer, R.; ECLIPSE Investigators. Eosinophilic inflammation in COPD: Prevalence and clinical characteristics. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1697–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Tao, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, F.; Ding, J. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells participate in IL-33-stimulated Th2-associated immune response in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 3109–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grove, K.C.; Provoost, S.; Verhamme, F.M.; Bracke, K.R.; Joos, G.F.; Maes, T.; Brusselle, G.G. Characterization and Quantification of Innate Lymphoid Cell Subsets in Human Lung. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tworek, D.; Smith, S.G.; Salter, B.M.; Baatjes, A.J.; Scime, T.; Watson, R.; Obminski, C.; Gauvreau, G.M.; O’byrne, P.M. IL-25 Receptor Expression on Airway Dendritic Cells after Allergen Challenge in Subjects with Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.D.; Salter, B.M.; Oliveria, J.P.; El-Gammal, A.; Tworek, D.; Smith, S.G.; Sehmi, R.; Gauvreau, G.M.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Mitchell, P.D.; et al. IL-33 and Its Receptor ST2 after Inhaled Allergen Challenge in Allergic Asthmatics. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 176, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sajee, D.; Sehmi, R.; Hawke, T.J.; El-Gammal, A.; Howie, K.J.; Watson, R.M.; Londei, M.; Gauvreau, G.M.; O’byrne, P.M. Expression of IL-33 and TSLP and Their Receptors in Asthmatic Airways after Inhaled Allergen Challenge. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 805–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Miyata, M.; Ohba, T.; Ando, T.; Hatsushika, K.; Suenaga, F.; Shimokawa, N.; Ohnuma, Y.; Katoh, R.; Ogawa, H.; et al. Cigarette smoke extract induces thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression, leading to TH2-type immune responses and airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Shan, L.; Rahman, M.S.; Unruh, H.; Halayko, A.J.; Gounni, A.S. Constitutive and inducible thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression in human airway smooth muscle cells: Role in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2007, 293, L375–L382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.N.; Guo, Y.B.; Li, X.; Li, C.L.; Tan, W.P.; Fan, X.L.; Qin, Z.L.; Chen, D.; Wen, W.P.; Zheng, S.G.; et al. ILC2 frequency and activity are inhibited by glucocorticoid treatment via STAT pathway in patients with asthma. Allergy 2018, 73, 1860–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Verma, M.; Michalec, L.; Liu, W.; Sripada, A.; Rollins, D.; Good, J.; Ito, Y.; Chu, H.; Gorska, M.M.; et al. Steroid resistance of airway type 2 innate lymphoid cells from patients with severe asthma: The role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 141, 257–268.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.G.; Chen, R.; Kjarsgaard, M.; Huang, C.; Oliveria, J.-P.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Gauvreau, G.M.; Boulet, L.-P.; Lemiere, C.; Martin, J.; et al. Increased numbers of activated group 2 innate lymphoid cells in the airways of patients with severe asthma and persistent airway eosinophilia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 75–86.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, A.T.; Martinez, F.J.; Curtis, J.L.; Doerschuk, C.M.; Hansel, N.N.; Christenson, S.; Putcha, N.; E Ortega, V.; Li, X.; Barr, R.G.; et al. Association of sputum and blood eosinophil concentrations with clinical measures of COPD severity: An analysis of the SPIROMICS cohort. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| neCOPD | eCOPD | HSs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (number of M/F) | 11/9 | 10/7 | 5/5 |
| Age (years) | 62.15 ± 1.75 | 57.47 ± 1.91 | 58.50 ± 2.44 |
| Number of pack-years | 32.60 ± 3.56 | 29.12 ± 3.03 | 26.40 ± 4.02 |
| Smoking status (smoker/ex-smoker) | 16/4 | 13/4 | 10/0 |
| Sputum eosinophil count (%) | 1.3 ± 0.22 | 6.91 ± 1.71 * | 1.02 ± 0.37 |
| Sputum macrophage count (%) | 30.30 ± 3.17 | 30.45 ± 4.11 | 53.14 ± 4.61 ** |
| Sputum neutrophil count (%) | 57.44 ± 4.35 | 53.65 ± 4.79 | 38.70 ± 4.31 *** |
| Sputum lymphocyte count (%) | 3.28 ± 0.30 | 2.85 ± 0.56 | 2.37 ± 0.37 |
| Number of atopic subjects | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| PB FEV1 (% of predicted) | 71.37 ± 4.53 | 74.20 ± 8.92 | 92.36 ± 6.41 **** |
| PB FEV1%FVC | 57.29 ± 7.62 | 61.72 ± 6.85 | 75.17 ± 2.48 **** |
| mMRC (points, median (min–max)) | 1 (0–3) | 1 (0–3) | NA |
| CAT (score) | 12.40 ± 1.58 | 15.88 ± 1.93 | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Polish Respiratory Society. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Królak-Nowak, K.; Wierzbińska, M.; Żal, A.; Antczak, A.; Tworek, D. Expression of Epithelial Alarmin Receptor on Innate Lymphoid Cells Type 2 in Eosinophilic Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Adv. Respir. Med. 2024, 92, 429-443. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm92050039
Królak-Nowak K, Wierzbińska M, Żal A, Antczak A, Tworek D. Expression of Epithelial Alarmin Receptor on Innate Lymphoid Cells Type 2 in Eosinophilic Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Advances in Respiratory Medicine. 2024; 92(5):429-443. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm92050039
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrólak-Nowak, Katarzyna, Marta Wierzbińska, Aleksandra Żal, Adam Antczak, and Damian Tworek. 2024. "Expression of Epithelial Alarmin Receptor on Innate Lymphoid Cells Type 2 in Eosinophilic Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease" Advances in Respiratory Medicine 92, no. 5: 429-443. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm92050039
APA StyleKrólak-Nowak, K., Wierzbińska, M., Żal, A., Antczak, A., & Tworek, D. (2024). Expression of Epithelial Alarmin Receptor on Innate Lymphoid Cells Type 2 in Eosinophilic Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Advances in Respiratory Medicine, 92(5), 429-443. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm92050039






