Highlights
What are the main findings?
- Ultrasonography (USG) can be used to diagnose adult pneumonia as it has excellent diagnostic performance including sensitivity and specificity.
- Bedside USG can be done in patients where pneumonia is suspected.
What is the implication of the main finding?
- 3.
- This ensures the correct and easier way of diagnosis in regions where X-ray machines are not used, such as in remote and poor areas or even in patients home.
- 4.
- The portability and the easier learning arc for non-radiologist doctors is a huge benefit in the world of diagnostics.
Abstract
Background: Pneumonia is a ubiquitous health condition with severe outcomes. The advancement of ultrasonography techniques allows its application in evaluating pulmonary diseases, providing safer and accessible bedside therapeutic decisions compared to chest X-ray and chest computed tomography (CT) scan. Because of its aforementioned benefits, we aimed to confirm the diagnostic accuracy of lung ultrasound (LUS) for pneumonia in adults. Methods: A systematic literature search was performed of Medline, Cochrane and Crossref, independently by two authors. The selection of studies proceeded based on specific inclusion and exclusion criteria without restrictions to particular study designs, language or publication dates and was followed by data extraction. The gold standard reference in the included studies was chest X-ray/CT scan or both. Results: Twenty-nine (29) studies containing 6702 participants were included in our meta-analysis. Pooled sensitivity, specificity and PPV were 92% (95% CI: 91–93%), 94% (95% CI: 94 to 95%) and 93% (95% CI: 89 to 96%), respectively. Pooled positive and negative likelihood ratios were 16 (95% CI: 14 to 19) and 0.08 (95% CI: 0.07 to 0.09). The area under the ROC curve of LUS was 0. 9712. Conclusions: LUS has high diagnostic accuracy in adult pneumonia. Its contribution could form an optimistic clue in future updates considering this condition.
1. Introduction
Pneumonia is a significant healthcare and economic issue with a massive impact on morbidity and mortality, ranking as the third leading cause of death globally [1,2,3,4,5,6]. It is a primary infectious killer and one of the most frequent causes of ER visits and hospital admissions [7,8]. In addition, it is the second-most-prevalent nosocomial infection with the greatest fatality rate, making it not only a reason for hospital admission, but also a significant healthcare-related complication [9].
In developed countries, the overall prevalence of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) varies from 1.6 to 16 cases per 1000 and about 20% of them require hospitalization, with a fatality rate as high as 48% [10]. Owing to this heavy burden, it is a continuous struggle for doctors to differentiate pneumonia from other differential diagnoses through clinical presentation alone in order to start effective treatment—especially in the backdrop of antimicrobial resistance [11,12].
A combination of suggestive clinical signs and the presence of consolidation or opacification on a chest x-ray (CXR) or computerized tomography (CT) scan of the chest is used to make the diagnosis of pneumonia [13,14]. Currently, the most common initial approach in cases of possible pneumonia is chest X-ray (CXR), especially in low–middle income countries (LMICs) [15,16,17]. However, it has many restrictions, such as that it cannot be used on pregnant women due to radiation exposure, and its requirement of both poster anterior and lateral projections in hospitalized patients, particularly in the critically ill [18,19]. Meanwhile, the gold-standard imaging method for pneumonia, the chest CT scan, has its own disadvantages, such as being more expensive, impractical and exposing patients to more radiation than CXR [19,20,21]. Both techniques are time-consuming, and radiologists have many disagreements on the interpretation of the results [22,23].
Although being previously restricted to the identification of pleural effusions, thoracentesis and biopsy-guided treatments, ultrasonography techniques have significantly advanced in recent years in evaluating pulmonary diseases such as pneumonia and pneumothorax [24,25,26,27,28]. In the last decade, LUS has grown in popularity in intensive care units and emergency departments, and has gained more acceptance as a potentially helpful diagnostic technique for community-acquired pneumonia [29,30], because it permits therapeutic decisions to be made at the bedside, is simple to repeat and prevents the patient from being exposed to ionizing radiation [26,27,28]. Thus, this study is focused on confirming the diagnostic accuracy of the LUS in diagnosing pneumonia through a systematic review and a meta-analysis that assembles several studies published in the literature.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Study Eligibility
A systematic literature search was applied to Medline, Cochrane and Crossref. The terms “ultrasound”, “ultrasonography”, “sonograph”, and “pneumonia” were used in various combinations for carrying out the literature search. Only published researches were considered without any language restriction. The search of studies was not limited on the basis of publication dates or study designs. All prospective, retrospective and cross-sectional studies were included if meeting the following criteria: (1) adult patients aged ≥ 18 years with either clinical suspicion or confirmed diagnosis of pneumonia or acute respiratory failure; (2) enrollment of patients with community-acquired or nosocomial pneumonia including VAP; (3) reference method for diagnosing pneumonia was based on clinical data, laboratory results and confirmation by chest radiology/CT scan or both; (4) ability to extract the necessary data for calculating sensitivity and specificity. We excluded studies that enrolled children [31,32], included fewer than 20 participants [33] and studies that evaluated pneumonia only based on clinical data. The literature search and data analysis were carried out in February 2023.
2.2. Selection of Studies and Data Extraction
Two authors independently performed the search of the literature and screened the title and abstract of each article. Full-text articles that met the inclusion criteria were retrieved for this review. Any discrepancies during the entire process were resolved by consensus. The following data were extracted from each study: first author’s name, year of publication, country of origin, study design and setting, sample size, mean age and sex of the population, inclusion criteria expertise of operator, ultrasound diagnostic criteria considered in each study, and reference diagnostic standard.
2.3. Quality Assessment
The methodological quality was assessed using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS-2) criteria [34], which provides a standardized approach for grading the quality of studies included in meta-analyses of diagnostic accuracy. The risk of bias and study generalizability are categorized by QUADAS-2 as low, unclear or high. Two authors scored the QUADAS-2 checklist independently and any disagreements were resolved via consensus.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were carried out using RevMan (Review Manager, version 5.3), SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, version 20) and Excel in Stata 14. Individual study sensitivity and specificity were plotted on a Forest plot and the overall area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was calculated. The post-test probabilities were calculated using the prior probability, and the summary positive and negative likelihood ratios, evaluated using the Fagan plot analysis command in Stata 14.0.
3. Results
3.1. Flowchart of Articles Retrieved from Search of Databases
A systematic search to retrieve studies that assessed the diagnostic accuracy of LUS for pneumonia in adults was performed in the Medline, Cochrane and Crossref databases. A total of 2829 studies were identified. After the first screening stage (title, abstract and keywords), 85 relevant studies were retrieved, and their full texts were reviewed for eligibility. A total of 29 studies with 6702 participants satisfying the inclusion criteria were analyzed (Figure 1). The study characteristics are shown in Table 1.
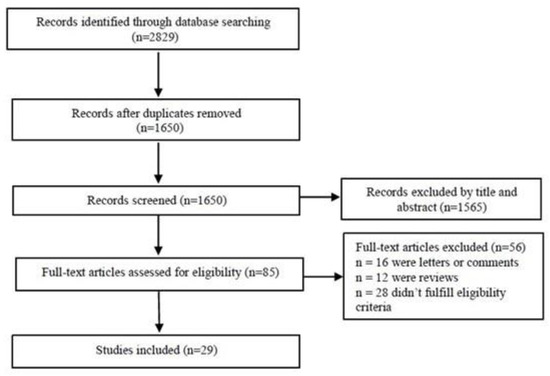
Figure 1.
Flowchart of articles retrieved from search of databases.

Table 1.
Main characteristics of the included studies.
3.2. Main Characteristics of the Included Studies
In total, 13 (44.8%) studies were carried out in Italy, 5 (17.2%) in France and the remaining studies were carried out in USA, Iran, Egypt, Germany, Denmark, Switzerland, China and Turkey. The predominant design was prospective, three studies were cross-sectional [16,46,47] and only one study was performed retrospectively [54]. Final diagnosis considering all the observed instrumental and laboratory findings was the reference standard in ten (34.5%) studies [1,7,8,38,40,45,47,49,55,56]. Three studies (10.3%) used a combination of clinical criteria and imaging [35,41,52] and 16 (55.2%) used imaging only as the reference standard; seven used chest CT scan for the diagnosis of pneumonia in the entire sample and eight used chest CT scan when the results of CXR and LUS were found to be discordant. In one study, the reference standard was only the CXR [54]. Most studies reported blinding the professionals performing ultrasound to the results of the reference standard. Only five reported the absence of blinding, and three did not clearly state whether blinding took place.
A total of 20 studies were conducted in adult patients admitted to EDs and/or medical wards, 8 studies included critically ill patients in the ICU and one in the stroke unit [16]. The participant characteristics are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Main characteristics of the included participants.
3.3. Forest Plots of Sensitivity and Specificity for Diagnosis of Pneumonia in Adults
The sensitivity and specificity of the considered studies are shown in the forest plot (Figure 2). Overall pooled sensitivity, specificity and PPV were 92% (95% CI, 91 to 93%), 94% (95% CI, 94 to 95%) and 93% (95% CI, 89 to 96%), respectively.
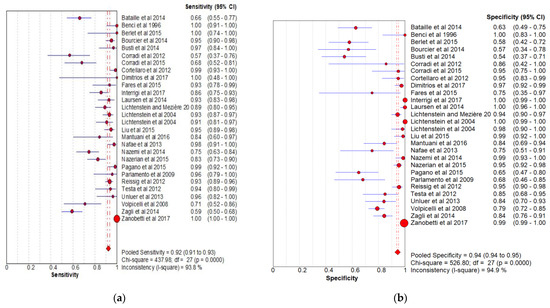
Figure 2.
(a) Forest plot for sensitivity; (b) forest plot for specificity (LUS has an overall sensitivity of 92% (95% CI, 91–93%) and specificity of 94% (95% CI, 94–95%) in the diagnosis of pneumonia in adult).
3.4. Positive and Negative Likelihood Ratio Using Fagan Plot Analysis
Pooled positive and negative likelihood ratios were 16 (95% CI, 14 to 19) and 0.08 (95% CI, 0.07 to 0.09), respectively (Figure 3).
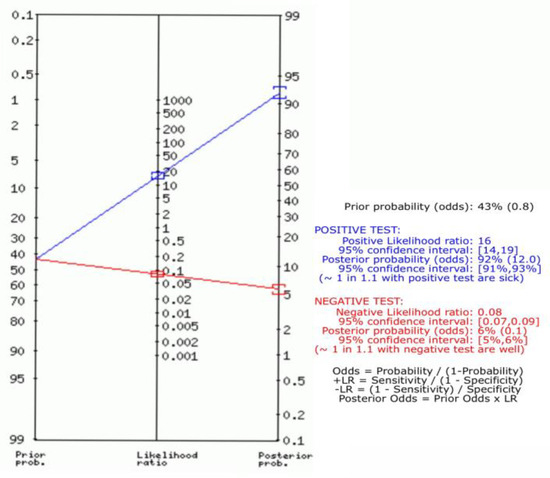
Figure 3.
Fagan plot analysis showed the prior probability is 43, the positive likelihood ratio is 16, the probability of post-test is 92, the negative likelihood ratio is 0.08, and the probability of the post-test is 6.
3.5. Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve for LUS in All Studies
The estimation of the area under the ROC curve of lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of pneumonia was 0.9712. The overall diagnostic odds ratio as per random effect model was 139.65 (57.02–342.02) (Figure 4).
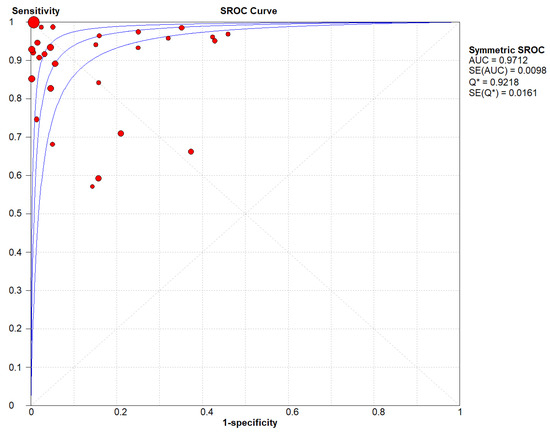
Figure 4.
Summary receiver operating characteristic curve for LUS in all studies. The area under the ROC was 0.9712. The overall diagnostic odds ratio as per random effect model was 139.65 (57.02–342.02). The red dot in the SROC plot is each individual paper with the size of the ball corresponding to the same sample of the paper and in turn the weight of the paper in the analysis. The blue lines demonstrate the SROC curve approximations.
3.6. Risk of Bias and Applicability Concerns of Included Studies
The overall quality of studies included in our meta-analysis was fair (Figure 5). The publication bias in patient selection was low in 18, unclear in 10 and high in only one paper. However, the index test was low in 22 and unclear in 7. The appraised reference standard was low in 17, high in 5 and unclear in 7. The flow and timing were low in 21 and high in 8. Applicability concerns in patient selection was low in 23, high in 3 and unclear in 3. The index test was low in 23 papers and unclear in 6, while the reference standard was low and unclear in 26 and 3, respectively.
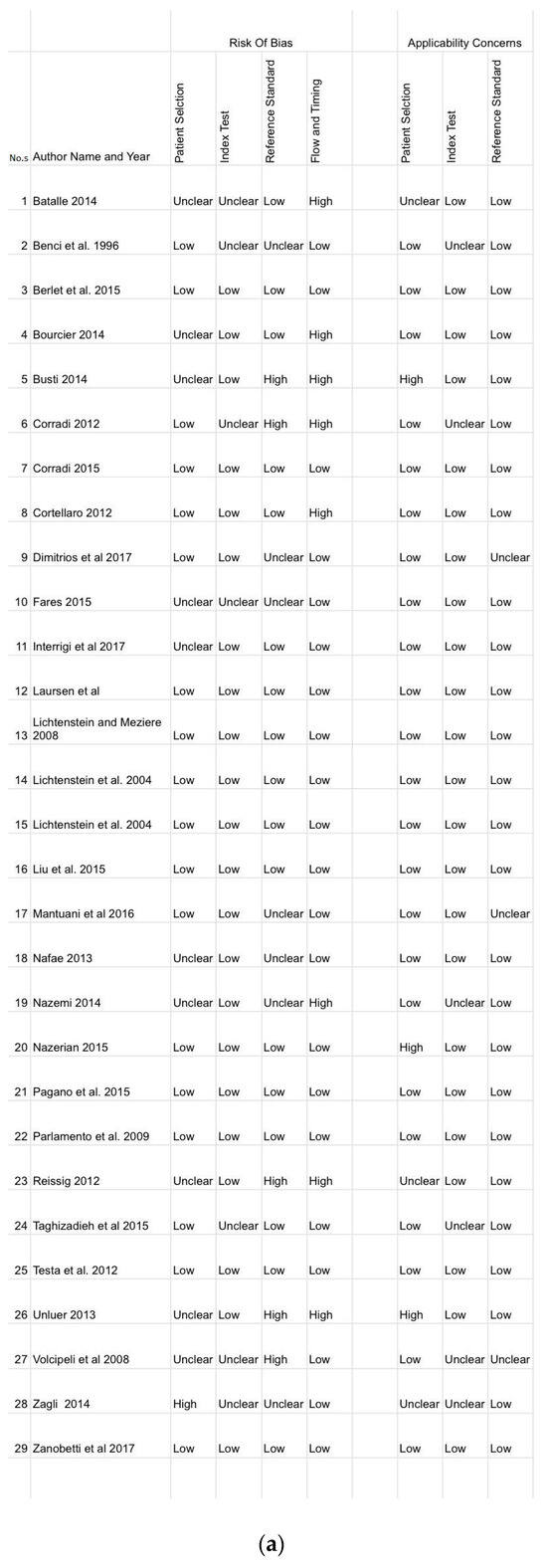
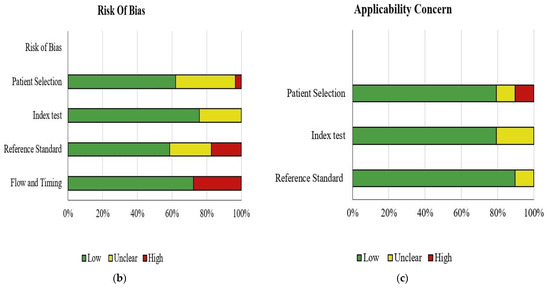
Figure 5.
Risk of bias and applicability of concern of the 29 included studies. Image (a) shows the bias of every paper while image (b,c) show the frequency of a paper having a bias and their applicability concern respectively. These images show the quality of the papers used in the analysis.
4. Discussion
LUS has only recently been appreciated by the wider medical community [57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65] because respected sources considered it to be unfit for assessing the pulmonary parenchyma [66] even though, during the past decade, LUS has been shown to be a very useful tool in the hands of intensivists and emergency physicians for the diagnosis of other thoracic conditions. Several studies have shown that bedside ultrasonography is useful for diagnosing cardiogenic pulmonary edema [67,68,69,70] is more accurate than CXR for diagnosing pneumothorax [71,72], and has applications in diagnosing pulmonary embolisms. Its use in the diagnosis of pneumonia has also been investigated in consideration of the great limitations of CXR. This is of particular importance when CXR is performed in the emergency departments, where many patients are critically ill and can be examined only in the supine position, often with bedside equipment [73].
Pneumonia commonly leads to significant pulmonary consolidation marked by a complete loss of aeration in the concerned lung region—manifesting differently in various modalities. On CXR, it is defined as a homogeneous opacity that may have effacement of blood vessel shadows and the presence of air bronchograms. Meanwhile, on LUS, consolidation is seen as an isoechoic, tissue-like pattern reminiscent of the liver, known as “hepatization”—with the aerated lung forming a boundary marked by the pleural line or an effusion if present. This potentially forms an irregular, scattered line if the consolidation is limited—specifically known as a “shred sign”—or a regular line if the whole pulmonary lobe is involved [5]. In addition, B-lines on LUS are well-defined hyperechoic comet-tail artifacts, arising from pleural lines and spreading vertically indefinitely, erasing A-lines and moving with the lung when lung sliding is present. It indicates the partial loss of lung aeration. However, consolidation is a non-specific sign of pneumonia because it is also present in lung atelectasis, and differential diagnosis could be difficult. The ultrasound sign that differentiates pneumonia from obstructive atelectasis is the presence of a dynamic air bronchogram in the former case (specificity 94% and positive predictive value 97) [32,63]. The possibility of a dynamic evaluation gives ultrasound an advantage over CXR, and possibly also over CT scan, which cannot always clearly differentiate between the two conditions [64].
Another distinct advantage of LUS in imaging pneumonia includes the better visualization of the regional pulmonary blood flow within lung consolidations in LUS with Doppler or contrast-enhanced sonography compared to CXR; thereby, providing critical information about the etiology of the disease. However, for all its benefits in detecting pneumonia in superficial lung parenchyma, LUS reliability remains doubtful in deeper alveolar lesions [57].
Our results suggest that bedside lung ultrasound has excellent accuracy for the diagnosis of pneumonia in adults. This points towards a clearly defined application of LUS as a diagnostic tool that can be considered reliable and dependable in clinical settings; further supplemented by a weighted sensitivity and specificity of 94% and 96%, respectively, with an area under the SROC curve of 0.98 according to Chavez et al. [11]. To further aid these findings, Hu et al. obtained a DOR of 509.99 and an area under the SROC curve of 0.99; although seven of the nine analyzed studies included children and even infants, so the samples were not comparable. In fact, several pediatric studies have suggested superior diagnostic performance for chest ultrasound in children compared to adults, which may be related to the fact that children usually have a thinner chest wall and a smaller volume of lung parenchyma, as outlined pertinently in the current literature [19,57,58]. When compared to other modalities currently considered for diagnosis, LUS was found to have various advantages such as (1) shorter turnaround time—with approximately 13 min being required in the procedure [59,60], along with (2) better reproducibility, (3) low cost, (4) avoidance of exposure to ionizing radiation, and (5) a broad spectrum of use in exploring findings not clearly visualized or understood on CXR [61,62]. This results in the determination of concrete evidence favoring a specific differential that would allow effective treatment regimens to be undertaken.
However, as also very prudently pointed out in the same studies, LUS also presents with a unique set of disadvantages such as (1) its limited value in patients with subcutaneous emphysema and in obese people due to the thickness of the chest wall; (2) inability to be conducted where access to the patient’s chest is limited by large bandages, prosthetic material or skin disorders; and most notably (3) its observer-dependent nature, as it implies the need for operators with certain skills and experience.
Although it has proven benefits, the inculcation of USG with different diagnostic techniques as a supplemental aid for reaching the correct diagnosis should be further studied, especially in the context of resource-limited settings [40]. One such study established that the addition of point-of-care ultrasonography (POCUS) of the heart, lungs and deep veins to the standard initial diagnostic tests resulted in 24% more patients with respiratory complaints being given correct presumptive diagnoses four hours after admission to the emergency department—yielding 21% more patients receiving appropriate treatment. However, the proportion of advanced diagnostic tests ordered was also higher in the POCUS group, possibly making it less cost-effective.
5. Conclusions
All aspects duly considered, ultrasound as a modality promises efficiency, efficacy and prudence in reaching an early diagnosis and can be safely employed for this purpose in patients suffering from pneumonia and a spectrum of cardiorespiratory conditions of varying etiologic and epidemiological factors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.A.A., S.A.A. and T.A.M.; methodology, T.A.A., S.A.A. and T.A.M.; software, D.D., M.E.M. and T.A.M.; validation, K.M.S., E.M.S. and L.S.B.D.; data collection and analysis, D.D., A.B.S. and T.A.M.; writing—original draft preparation, K.M.S., E.M.S., A.H.M., M.E.M., T.A.M. and L.S.B.D.; writing—review and editing, K.M.S., E.M.S., A.H.M., J.R.C.D., J.O.B. and L.S.B.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
CAP, community-acquired pneumonia; CT, computerized tomography; CXR, chest X-ray; LUS, lung ultrasound; POCUS, point-of-care ultrasonography; ROC, receiver-operating-characteristic.
References
- Bataille, B.; Riu, B.; Ferre, F.; Moussot, P.E.; Mari, A.; Brunel, E.; Ruiz, J.; Mora, M.; Fourcade, O.; Genestal, M.; et al. Integrated use of bedside lung ultrasound and echocardiography in acute respiratory failure: A prospective observational study in ICU. Chest 2014, 146, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- File, T.M., Jr.; Marrie, T.J. Burden of community-acquired pneumonia in North American adults. Postgrad. Med. 2010, 122, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welte, T.; Torres, A.; Nathwani, D. Clinical and economic burden of community-acquired pneumonia among adults in Europe. Thorax 2012, 67, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiemken, T.L.; Peyrani, P.; Ramirez, J.A. Global changes in the epidemiology of community-acquired pneumonia. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 33, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.; Vos, T.; Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Flaxman, A.D.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2197–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO: The Top 10 Causes of Death. 2013. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/ (accessed on 9 December 2020).
- Berlet, T.; Etter, R.; Fehr, T.; Berger, D.; Sendi, P.; Merz, T.M. Sonographic patterns of lung consolidation in mechanically ventilated patients with and without ventilator-associated pneumonia: A prospective cohort study. J. Crit. Care 2015, 30, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourcier, J.E.; Paquet, J.; Seinger, M.; Gallard, E.; Redonnet, J.P.; Cheddadi, F.; Garnier, D.; Bourgeois, J.M.; Geeraerts, T. Performance comparison of lung ultrasound and chest X-ray for the diagnosis of pneumonia in the ED. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 32, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.L.; Rello, J.; Marshall, J.; Silva, E.; Anzueto, A.; Martin, C.D.; Moreno, R.; Lipman, J.; Gomersall, C.; Sakr, Y.; et al. International study of the prevalence and outcomes of infection in intensive care units. JAMA 2009, 302, 2323–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llop, C.J.; Tuttle, E.; Tillotson, G.S.; LaPlante, K.; File, T.M., Jr. Antibiotic treatment patterns, costs, and resource utilization among patients with community acquired pneumonia: A US cohort study. Hosp. Pract. 2017, 45, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, M.A.; Shams, N.; Ellington, L.E.; Naithani, N.; Gilman, R.H.; Steinhoff, M.C.; Santosham, M.; Black, R.E.; Price, C.; Gross, M.; et al. Lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of pneumonia in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busti, C.; Agnelli, G.; Duranti, M.; Orlandi, C.; Marcucci, M.; Paciaroni, M. Lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of stroke-associated pneumonia. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2014, 9, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandell, L.A.; Wunderink, R.G.; Anzueto, A.; Bartlett, J.G.; Campbell, G.D.; Dean, N.C.; Dowell, S.F.; File, T.M., Jr.; Musher, D.M.; Niederman, M.S.; et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2007, 44, S27–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodhead, M.; Blasi, F.; Ewig, S.; Garau, J.; Huchon, G.; Ieven, M.; Ortqvist, A.; Schaberg, T.; Torres, A.; van der Heijden, G.; et al. Guidelines for the management of adult lower respiratory tract infections--full version. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, E1–E59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortellaro, F.; Colombo, S.; Coen, D.; Duca, P.G. Lung ultrasound is an accurate diagnostic tool for the diagnosis of pneumonia in the emergency department. Emerg. Med. J. 2012, 29, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auf, F.; Abo-Naglh, A.H.M.E.D.; Moustafa Zedan, M.D. Role of transthoracic ultrasound in detection of pneumonia in ICU patients. Med. J. Cairo Univ. 2015, 83, 307–314. [Google Scholar]
- Gallard, E.; Redonnet, J.P.; Bourcier, J.E.; Deshaies, D.; Largeteau, N.; Amalric, J.M.; Chedaddi, F.; Bourgeois, J.M.; Garnier, D.; Geeraerts, T. Diagnostic performance of cardiopulmonary ultrasound performed by the emergency physician in the management of acute dyspnea. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 33, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brent, R.L. The effect of embryonic and fetal exposure to X-ray, microwaves, and ultrasound: Counseling the pregnant and nonpregnant patient about these risks. Semin. Oncol. 1989, 16, 347–368. [Google Scholar]
- Syrjälä, H.; Broas, M.; Suramo, I.; Ojala, A.; Lähde, S. High-resolution computed tomography for the diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 1998, 27, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, J.R.; Aldrich, J.; Muller, N.L.; Fleischner Society. Radiation exposure at chest CT: A statement of the Fleischner Society. Radiology 2003, 228, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.J.; Hall, E.J. Computed tomography--an increasing source of radiation exposure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2277–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaum, M.N.; Hill, L.C.; Murphy, M.; Li, Y.H.; Fuhrman, C.R.; Britton, C.A.; Kapoor, W.N.; Fine, M.J. Interobserver reliability of the chest radiograph in community-acquired pneumonia. PORT Investigators. Chest 1996, 110, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Self, W.H.; Courtney, D.M.; McNaughton, C.D.; Wunderink, R.G.; Kline, J.A. High discordance of chest X-ray and computed tomography for detection of pulmonary opacities in ED patients: Implications for diagnosing pneumonia. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 31, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; Shen, Y.; Yang, J.; He, X.; Zhang, M. Diagnosis of pneumothorax by radiography and ultrasonography: A meta-analysis. Chest 2011, 140, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpicelli, G.; Elbarbary, M.; Blaivas, M.; Lichtenstein, D.A.; Mathis, G.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Melniker, L.; Gargani, L.; Noble, V.E.; Via, G.; et al. International Liaison Committee on Lung Ultrasound (ILC-LUS) for International Consensus Conference on Lung Ultrasound (ICC-LUS). International evidence-based recommendations for point-of-care lung ultrasound. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagaman, J.T.; Rouan, G.W.; Shipley, R.T.; Panos, R.J. Admission chest radiograph lacks sensitivity in the diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 337, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maughan, B.C.; Asselin, N.; Carey, J.L.; Sucov, A.; Valente, J.H. False-negative chest radiographs in emergency department diagnosis of pneumonia. Rhode Isl. Med. J. 2014, 97, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hayden, G.E.; Wrenn, K.W. Chest radiograph vs. computed tomography scan in the evaluation for pneumonia. J. Emerg. Med. 2009, 36, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, D.A. Ultrasound examination of the lungs in the intensive care unit. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 10, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reissig, A.; Copetti, R.; Mathis, G.; Mempel, C.; Schuler, A.; Zechner, P.; Aliberti, S.; Neumann, R.; Kroegel, C.; Hoyer, H. Lung ultrasound in the diagnosis and follow-up of community-acquired pneumonia: A prospective, multicenter, diagnostic accuracy study. Chest 2012, 142, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiulo, V.A.; Gargani, L.; Caiulo, S.; Fisicaro, A.; Moramarco, F.; Latini, G.; Picano, E.; Mele, G. Lung ultrasound characteristics of community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2013, 48, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copetti, R.; Cattarossi, L. Ultrasound diagnosis of pneumonia in children. Radiol. Med. 2008, 113, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Button, K.S.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Mokrysz, C.; Nosek, B.A.; Flint, J.; Robinson, E.S.; Munafò, M.R. Power failure: Why small sample size undermines the reliability of neuroscience. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Bossuyt, P.M.; QUADAS-2 Group. QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benci, A.; Caremani, M.; Menchetti, D.; Magnolfi, A.L. Sonographic diagnosis of pneumonia and bronchopneumonia. Eur. J. Ultrasound 1996, 4, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradi, F.; Ball, L.; Brusasco, C.; Vargas, M.; Garlaschi, A.; Altomonte, F. Lung ultrasonography fails detection of non-subpleural community acquired pneumonia. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, S238. [Google Scholar]
- Corradi, F.; Brusasco, C.; Garlaschi, A.; Paparo, F.; Ball, L.; Santori, G.; Pelosi, P.; Altomonte, F.; Vezzani, A.; Brusasco, V. Quantitative analysis of lung ultrasonography for the detection of community-acquired pneumonia: A pilot study. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 868707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanagnou, D.; Secko, M.; Gullett, J.; Stone, M.; Zehtabchi, S. Clinician-Performed Bedside Ultrasound in Improving Diagnostic Accuracy in Patients Presenting to the ED with Acute Dyspnea. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 18, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Interrigi, M.C.; Trovato, F.M.; Catalano, D.; Trovato, G.M. Emergency thoracic ultrasound and clinical risk management. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2017, 13, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, C.B.; Sloth, E.; Lassen, A.T.; Christensen Rd Lambrechtsen, J.; Madsen, P.H.; Henriksen, D.P.; Davidsen, J.R.; Rasmussen, F. Point-of-care ultrasonography in patients admitted with respiratory symptoms: A single-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, D.A.; Mezière, G.A. Relevance of lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of acute respiratory failure: The BLUE protocol. Chest 2008, 134, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, D.; Goldstein, I.; Mourgeon, E.; Cluzel, P.; Grenier, P.; Rouby, J.J. Comparative diagnostic performances of auscultation, chest radiography, and lung ultrasonography in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Anesthesiology 2004, 100, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, D.A.; Lascols, N.; Mezière, G.; Gepner, A. Ultrasound diagnosis of alveolar consolidation in the critically ill. Intensive Care Med. 2004, 30, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.L.; Lian, R.; Tao, Y.K.; Gu, C.D.; Zhang, G.Q. Lung ultrasonography: An effective way to diagnose community-acquired pneumonia. Emerg. Med. J. 2015, 32, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantuani, D.; Frazee, B.W.; Fahimi, J.; Nagdev, A. Point-of-Care Multi-Organ Ultrasound Improves Diagnostic Accuracy in Adults Presenting to the Emergency Department with Acute Dyspnea. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 17, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nafae, R.; Eman, S.R.; Mohamad, N.A.; El-Ghamry, R.; Ragheb, A.S. Adjuvant role of lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of pneumonia in intensive care unit-patients. Egypt. J. Chest Dis. Tuberc. 2013, 62, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazemi, S.; Farokhnia, M.; Pirouzi, M.; Najarion, O.; Ahmadipour, H. Accuracy of ultrasound as a diagnostic tool of pneumonia for admitted patients in Infectious Disease Section of Afzalipour Hospital. Jam. J. Sci. Tech. 2014, 25, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Nazerian, P.; Volpicelli, G.; Vanni, S.; Gigli, C.; Betti, L.; Bartolucci, M.; Zanobetti, M.; Ermini, F.R.; Iannello, C.; Grifoni, S. Accuracy of lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of consolidations when compared to chest computed tomography. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 33, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, A.; Numis, F.G.; Visone, G.; Pirozzi, C.; Masarone, M.; Olibet, M.; Nasti, R.; Schiraldi, F.; Paladino, F. Lung ultrasound for diagnosis of pneumonia in emergency department. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2015, 10, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlamento, S.; Copetti, R.; Di Bartolomeo, S. Evaluation of lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of pneumonia in the ED. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2009, 27, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadieh, A.; Ala, A.; Rahmani, F.; Nadi, A. Diagnostic Accuracy of Chest X-ray and Ultrasonography in Detection of Community Acquired Pneumonia; a Brief Report. Emergency 2015, 3, 114–116. [Google Scholar]
- Testa, A.; Soldati, G.; Copetti, R.; Giannuzzi, R.; Portale, G.; Gentiloni-Silveri, N. Early recognition of the 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) pneumonia by chest ultrasound. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unluer, E.; Karagoz, A.; Senturk, G.; Karaman, M.; Olow, K.; Bayata, S. Bedside lung ultrasonography for diagnosis of pneumonia. Hong Kong J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 20, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli, G.; Caramello, V.; Cardinale, L.; Mussa, A.; Bar, F.; Frascisco, M.F. Detection of sonographic B-lines in patients with normal lung or radiographic alveolar consolidation. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2008, 14, CR122–CR128. [Google Scholar]
- Zagli, G.; Cozzolino, M.; Terreni, A.; Biagioli, T.; Caldini, A.L.; Peris, A. Diagnosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia: A pilot, exploratory analysis of a new score based on procalcitonin and chest echography. Chest 2014, 146, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanobetti, M.; Scorpiniti, M.; Gigli, C.; Nazerian, P.; Vanni, S.; Innocenti, F.; Stefanone, V.T.; Savinelli, C.; Coppa, A.; Bigiarini, S.; et al. Point-of-Care Ultrasonography for Evaluation of Acute Dyspnea in the ED. Chest 2017, 151, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.J.; Shen, Y.C.; Jia, L.Q.; Guo, S.J.; Long, H.Y.; Pang, C.S.; Yang, T.; Wen, F.Q. Diagnostic performance of lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of pneumonia: A bivariate meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Mantel, N.; Haenszel, W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1959, 22, 719–748. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pereda, M.A.; Chavez, M.A.; Hooper-Miele, C.C.; Gilman, R.H.; Steinhoff, M.C.; Ellington, L.E.; Gross, M.; Price, C.; Tielsch, J.M.; Checkley, W. Lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of pneumonia in children: A meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2015, 135, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanobetti, M.; Poggioni, C.; Pini, R. Can chest ultrasonography replace standard chest radiography for evaluation of acute dyspnea in the ED? Chest 2011, 139, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouhemad, B.; Zhang, M.; Lu, Q.; Rouby, J.J. Clinical review: Bedside lung ultrasound in critical care practice. Crit. Care 2007, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medford, A.R.; Entwisle, J.J. Indications for thoracic ultrasound in chest medicine: An observational study. Postgrad. Med. J. 2010, 86, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, D.; Mezière, G.; Seitz, J. The dynamic air bronchogram. A lung ultrasound sign of alveolar consolidation ruling out atelectasis. Chest 2009, 135, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, D.; Peyrouset, O. Is lung ultrasound superior to CT? The example of a CT occult necrotizing pneumonia. Intensive Care Med. 2006, 32, 334–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckh, S.; Bölcskei, P.L.; Lessnau, K.D. Real-time chest ultrasonography: A comprehensive review for the pulmonologist. Chest 2002, 122, 1759–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhlbrigge, A.L.; Choi, A.K. Diagnostic Procedures in Respiratory Disease. In Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, 20th ed.; Jameson, J., Fauci, A.S., Kasper, D.L., Hauser, S.L., Longo, D.L., Loscalzo, J., Eds.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Available online: https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=2129§ionid=186950213 (accessed on 12 April 2024).
- Agricola, E.; Bove, T.; Oppizzi, M.; Marino, G.; Zangrillo, A.; Margonato, A.; Picano, E. “Ultrasound comet-tail images”: A marker of pulmonary edema: A comparative study with wedge pressure and extravascular lung water. Chest 2005, 127, 1690–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpicelli, G.; Mussa, A.; Garofalo, G.; Cardinale, L.; Casoli, G.; Perotto, F.; Fava, C.; Frascisco, M. Bedside lung ultrasound in the assessment of alveolar-interstitial syndrome. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2006, 24, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, D.; Mezière, G. A lung ultrasound sign allowing bedside distinction between pulmonary edema and COPD: The comet-tail artifact. Intensive Care Med. 1998, 24, 1331–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reissig, A.; Kroegel, C. Transthoracic sonography of diffuse parenchymal lung disease: The role of comet tail artifacts. J. Ultrasound Med. Off. J. Am. Inst. Ultrasound Med. 2003, 22, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaivas, M.; Lyon, M.; Duggal, S. A prospective comparison of supine chest radiography and bedside ultrasound for the diagnosis of traumatic pneumothorax. Acad. Emerg. Med. Off. J. Soc. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2005, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.H.; Yang, J.X.; Gan, J.X.; Xu, S.W.; You, X.D.; Jiang, G.Y. Rapid detection of pneumothorax by ultrasonography in patients with multiple trauma. Crit. Care 2006, 10, R112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esayag, Y.; Nikitin, I.; Bar-Ziv, J.; Cytter, R.; Hadas-Halpern, I.; Zalut, T.; Yinnon, A.M. Diagnostic value of chest radiographs in bedridden patients suspected of having pneumonia. Am. J. Med. 2010, 123, 88.e1–88.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).