Midterm Outcomes of Endovascular Treatment for Intracranial Atherosclerosis: High-Volume Versus Low-Volume Centres
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Brain Parenchymal Imaging Analysis and the Most Likely Stroke Mechanisms
2.3. Angiographic Analysis
2.4. Procedural Aspects
2.5. Follow-Up Data
2.6. Outcome Assessment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Procedure Characteristics
3.3. Clinical and Radiological Follow-Up
3.4. Outcome Parameters
3.5. Comparison Between High and Low-Volume Centres
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chimowitz, M.I.; Lynn, M.J.; Howlett-Smith, H.; Stern, B.J.; Hertzberg, V.S.; Frankel, M.R.; Levine, S.R.; Chaturvedi, S.; Kasner, S.E.; Benesch, C.G.; et al. Comparison of Warfarin and aspirin for symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimowitz, M.I.; Lynn, M.J.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Turan, T.N.; Fiorella, D.; Lane, B.F.; Janis, L.S.; Lutsep, H.L.; Barnwell, S.L.; Waters, M.F.; et al. Stenting versus Aggressive Medical Therapy for Intracranial Arterial Stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidat, O.O.; Fitzsimmons, B.F.; Woodward, B.K.; Wang, Z.; Killer-Oberpfalzer, M.; Wakhloo, A.; Gupta, R.; Kirshner, H.; Megerian, J.T.; Lesko, J.; et al. Effect of a Balloon-Expandable Intracranial Stent vs. Medical Therapy on Risk of Stroke in Patients with Symptomatic Intracranial Stenosis. JAMA 2015, 313, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Chebl, A.; Steinmetz, H. Critique of “Stenting Versus Aggressive Medical Therapy for Intracranial Arterial Stenosis” by Chimowitz et al in the New England Journal of Medicine. Stroke 2012, 43, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Al-Senani, F.M.; Husain, S.; Janjua, N.A.; Lanzino, G.; Lavados, P.M.; Nguyen, T.; Raymond, J.; Shah, Q.A.; Suarez, J.I.; et al. Intracranial Angioplasty and Stent Placement After Stenting and Aggressive Medical Management for Preventing Recurrent Stroke in Intracranial Stenosis (SAMMPRIS) Trial: Present State and Future Considerations. J. Neuroimaging 2012, 22, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.; Cai, Y.; Li, T.; Wu, W.; Shi, H.; He, W.; Zhu, F.; et al. China Angioplasty and Stenting for Symptomatic Intracranial Severe Stenosis (CASSISS): A new, prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled trial in China. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2015, 21, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualhasan, A.; Abd-Allah, F.; Pero, G.; Sobh, K.; Mansour, O.; El-Serafy, O.; Boccardi, E. Intracranial Stenting: Is It Still an Option for Treatment of Patients With Intracranial Atherosclerosis? Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; He, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Wang, D.; Shi, H.; Li, T.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, Y.; Wu, W.; et al. Stenting Plus Medical Therapy vs Medical Therapy Alone for Symptomatic Intracranial Artery Stenosis: Long-Term Results of a Multicentre, Randomised Controlled Trial. SSRN Preprint 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wu, H.; Bao, Y.; Jiao, L.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Hua, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; et al. Randomized Controlled Trial of Symptomatic Middle Cerebral Artery Stenosis. Stroke 2012, 43, 3284–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.J.; Zauner, A.; Chaloupka, J.C.; Baxter, B.; Callison, R.C.; Gupta, R.; Song, S.S.; Yu, W.; Feng, L.; Bonovich, D.; et al. WEAVE Trial. Stroke 2019, 50, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Sun, D.; Nguyen, T.N.; Tong, X.; Peng, G.; Liu, A.; Xu, Y.; et al. Balloon Angioplasty vs Medical Management for Intracranial Artery Stenosis. JAMA 2024, 332, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psychogios, M.; Brehm, A.; López-Cancio, E.; De Marchis, G.M.; Meseguer, E.; Katsanos, A.H.; Kremer, C.; Sporns, P.; Zedde, M.; Kobayashi, A.; et al. European Stroke Organisation guidelines on treatment of patients with intracranial atherosclerotic disease. Eur. Stroke J. 2022, 7, XLII–LXXX. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turan, T.N.; Zaidat, O.O.; Gronseth, G.S.; Chimowitz, M.I.; Culebras, A.; Furlan, A.J.; Goldstein, L.B.; Gonzalez, N.R.; Latorre, J.G.; Messé, S.R.; et al. Stroke Prevention in Symptomatic Large Artery Intracranial Atherosclerosis Practice Advisory. Neurology 2022, 98, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleindorfer, D.O.; Towfighi, A.; Chaturvedi, S.; Cockroft, K.M.; Gutierrez, J.; Lombardi-Hill, D.; Kamel, H.; Kernan, W.N.; Kittner, S.J.; Leira, E.C.; et al. 2021 Guideline for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients With Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack: A Guideline From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2021, 52, e364–e467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahab, F.; Lynn, M.J.; Kasner, S.E.; Alexander, M.J.; Klucznik, R.; Zaidat, O.O.; Chaloupka, J.; Lutsep, H.; Barnwell, S.; Mawad, M.; et al. Risk factors associated with major cerebrovascular complications after intracranial stenting. Neurology 2009, 72, 2014–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdeyn, C.P.; Fiorella, D.; Lynn, M.J.; Barnwell, S.L.; Zaidat, O.O.; Meyers, P.M.; Gobin, Y.P.; Dion, J.; Lane, B.F.; Turan, T.N.; et al. Impact of operator and site experience on outcomes after angioplasty and stenting in the SAMMPRIS trial. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2012, 5, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, O.B.; Joseph, G.J.; Lynn, M.J.; Smith, H.A.; Chimowitz, M.I. A Standardized Method for Measuring Intracranial Arterial Stenosis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2000, 21, 643–646. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shuai, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, K.; Liu, L.; Li, B.; Shi, X.; Gao, L.; et al. Thirty-Day Outcome of a Multicenter Registry Study of Stenting for Symptomatic Intracranial Artery Stenosis in China. Stroke 2015, 46, 2822–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurre, W.; Berkefeld, J.; Brassel, F.; Brüning, R.; Eckert, B.; Kamek, S.; Klein, G.E.; Knauth, M.; Liebig, T.; Maskova, J.; et al. In-Hospital Complication Rates After Stent Treatment of 388 Symptomatic Intracranial Stenoses. Stroke 2010, 41, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derdeyn, C.P.; Chimowitz, M.I.; Lynn, M.J.; Fiorella, D.; Turan, T.N.; Janis, L.S.; Montgomery, J.; Nizam, A.; Lane, B.F.; Lutsep, H.L.; et al. Aggressive medical treatment with or without stenting in high-risk patients with intracranial artery stenosis (SAMMPRIS): The final results of a randomised trial. Lancet 2013, 383, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, J.J.; Wojak, J.C.; Hoppe, B.H. The Technique of Endovascular Intracranial Revascularization. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piano, M.; Milonia, L.; Cervo, A.; Modello, B.; Macera, A.; Pero, G.; Quilici, L.; Boccardi, E.; Valvassori, L. Endovascular Treatment of Symptomatic Intracranial Vertebrobasilar Stenosis: A 10-Year Single Centre Experience Using Balloon-Expandable Coronary Artery Stents. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 105431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, M.J. Intracranial stenting for intracranial atherosclerotic disease: Still much to learn. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2012, 4, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutsep, H.L.; Lynn, M.J.; Cotsonis, G.A.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Turan, T.N.; Fiorella, D.; Janis, L.S.; Lane, B.F.; Montgomery, J.; Chimowitz, M.I. Does the Stenting Versus Aggressive Medical Therapy Trial Support Stenting for Subgroups With Intracranial Stenosis? Stroke 2015, 46, 3282–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, V.L.; Go, A.S.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Adams, R.J.; Berry, J.D.; Brown, T.M.; Carnethon, M.R.; Dai, S.; De Simone, G.; Ford, E.S.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2011 Update. Circulation 2010, 123, e18–e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Lancet: Global Burden of Disease 2019. Available online: https://www.thelancet.com/infographics-do/gbd-2019 (accessed on 16 December 2024).
- Fiorella, D.; Chow, M.M.; Anderson, M.; Woo, H.; Rasmussen, P.A.; Masaryk, T.J. A 7-year experience with balloon-mounted coronary stents for the treatment of symptomatic vertebrobasilar intracranial atheromatous disease. Neurosurgery 2007, 61, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.R.; Feng, L.; Li, S.; Zhu, F.; Ji, X.; Jiao, L.; Ling, F. Treatment of symptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis with balloon-mounted stents: Long-term follow-up at a single center. Neurosurgery 2009, 64, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durst, C.R.; Geraghty, S.R.; Southerland, A.M.; Starke, R.M.; Rembold, K.; Malik, S.; Wintermark, M.; Liu, K.C.; Crowley, R.W.; Gaughen, J.; et al. Stenting of symptomatic intracranial stenosis using balloon mounted coronary stents: A single center experience. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2014, 7, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidat, O.O.; Klucznik, R.; Alexander, M.J.; Chaloupka, J.; Lutsep, H.; Barnwell, S.; Mawad, M.; Lane, B.; Lynn, M.J.; Chimowitz, M. The NIH registry on use of the Wingspan stent for symptomatic 70–99% intracranial arterial stenosis. Neurology 2008, 70, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costalat, V.; Maldonado, I.L.; Vendrell, J.F.; Riquelme, C.; Machi, P.; Arteaga, C.; Turjman, F.; Desal, H.; Sedat, J.; Bonafé, A. Endovascular treatment of symptomatic intracranial stenosis with the Wingspan stent system and Gateway PTA balloon: A multicenter series of 60 patients with acute and midterm results. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Yin, Q.; Xi, G.; Zhu, W.; Xu, G.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, M.; Jin, G.; Liu, X. Comparison of BMSs with SES for Symptomatic Intracranial Disease of the Middle Cerebral Artery Stenosis. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2010, 34, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
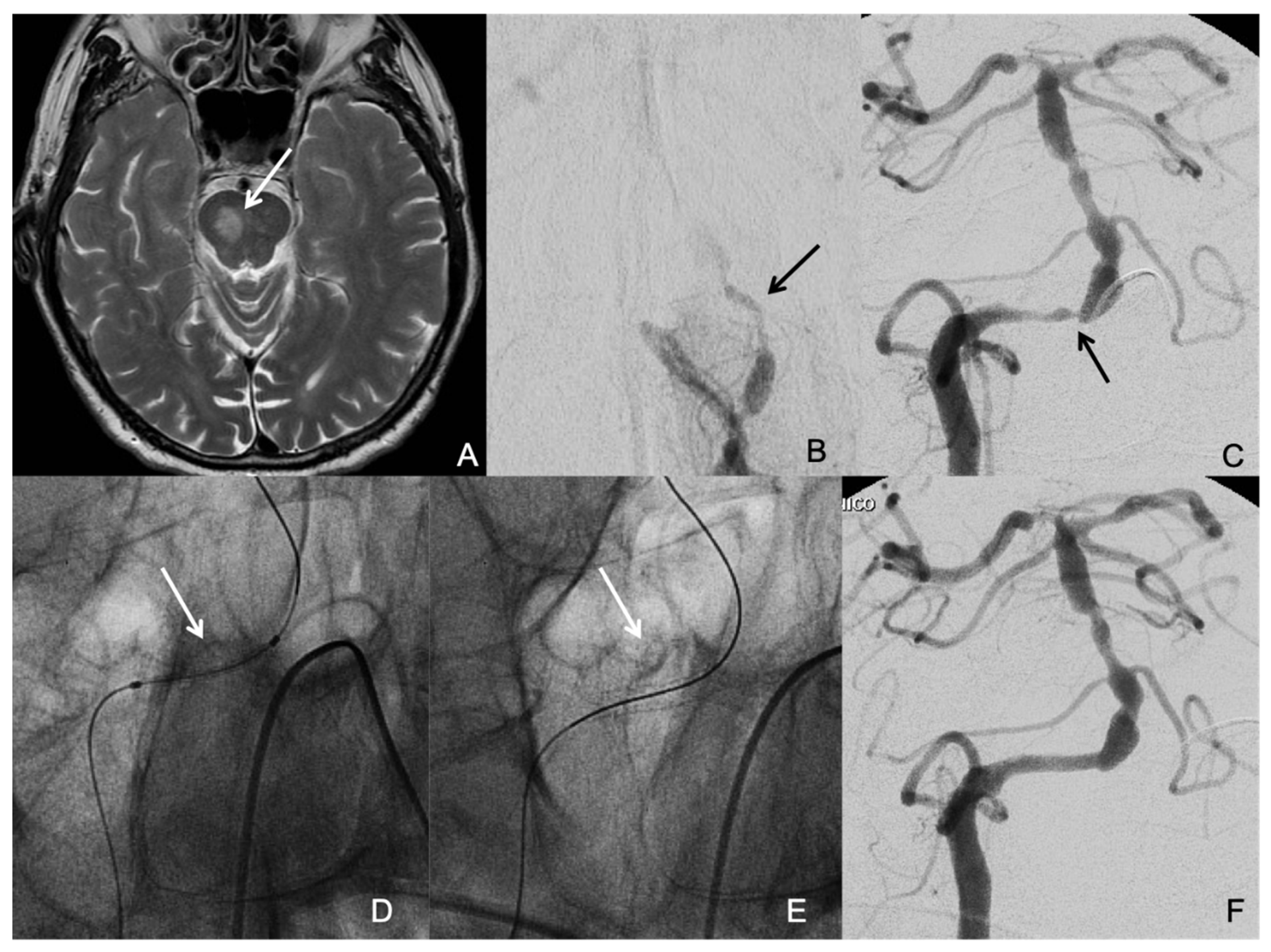
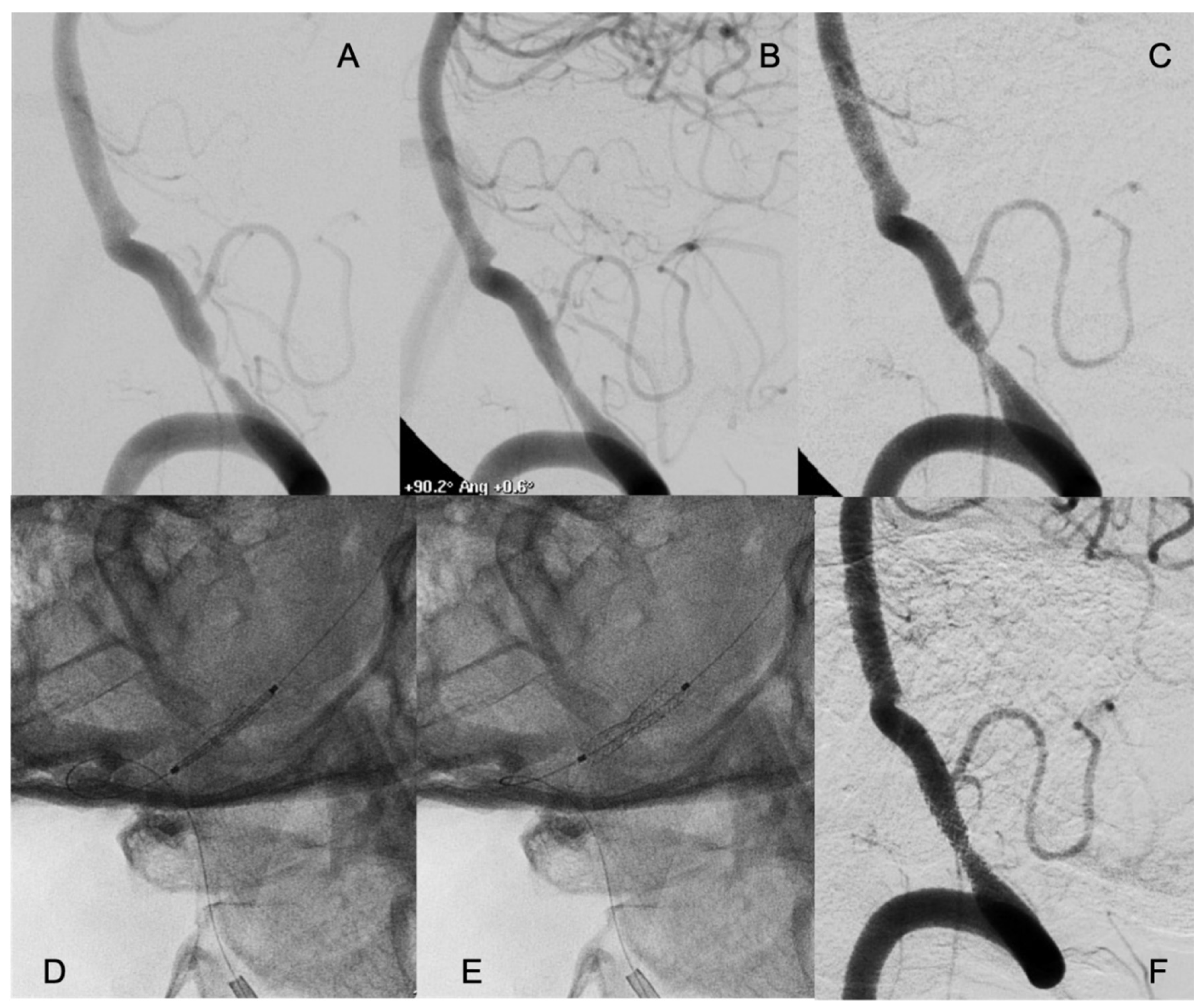
| Characteristic | LV Group (n = 18) | HV Group (n = 18) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. (%) | No. (%) | |||
| Male sex | 14 (77.8) | 15 (83.3) | 1 | |
| Hypertension | 15 (83.3) | 15 (83.3) | 1 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 8 (44.4) | 4 (22.2) | 0.157 | |
| Coronary artery disease | 4 (22.2) | 4 (22.2) | 1 | |
| Dyslipidaemia | 13 (72.2) | 11 (61.1) | 0.480 | |
| Smoking history | Never | 7 (38.9) | 11 (61.1) | 0.357 |
| Former | 1 (5.6) | 2 (11.1) | ||
| Current | 10 (55.6) | 5 (27.8) | ||
| Peripheral vascular disease | 0 | 2 (11.1) | 0.486 | |
| Obesity | 0 | 2 (11.1) | 0.486 | |
| Hyperuricaemia | 0 | 3 (16.7) | 0.229 | |
| Hyperhomocystienaemia | 0 | 2 (11.1) | 0.486 | |
| Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome | 0 | 2 (11.1) | 0.486 | |
| Qualifying event | TIA | 5 (27.8) | 8 (44.4) | 0.298 |
| Stroke | 13 (72.2) | 10 (55.6) | ||
| Previous non-qualifying cerebrovascular events | 10 (55.6) | 13 (72.2) | 0.298 | |
| stroke severity (NIHSS) | mild (<5) | 5 (27.8) | 9 (50) | 0.101 |
| moderate (5–14) | 7 (38.9) | 8 (44.4) | ||
| severe (15–24) | 6 (33.3) | 1 (5.6) | ||
| Preprocedural Functional status | mRs ≤ 3 | 14 (77.8) | 14 (77.8) | 1 |
| mRs ˃ 3 | 4 (22.2) | 4 (22.2) | ||
| Symptomatic qualifying artery | Basilar | 8 (44.4) | 7 (38.9) | 0.167 |
| Intracranial Vertebral | 4 (22.2) | 9 (50) | ||
| MCA | 3 (16.7) | 0 | ||
| Intracranial ICA | 3 (16.7) | 2 (11.1) | ||
| Most likely stroke mechanism | Artery-to-artery embolism | 7 (38.9) | 2 (11.1) | 0.124 |
| Hypoperfusion | 3 (16.7) | 7 (38.9) | ||
| Mixed | 8 (44.4) | 9 (50.0) | ||
| Degree of stenosis (%) | 70–79% | 5 (27.8) | 3 (16.7) | 0.830 |
| 80–89% | 6 (33.3) | 7 (38.9) | ||
| 90–99% | 7 (38.9) | 8 (44.4) | ||
| Lesion Length (mm) | <5 mm | 3 (16.7) | 3 (16.7) | 1 |
| 5–10 mm | 12 (66.7) | 13 (72.2) | ||
| >10 mm | 3 (16.7) | 2 (11.1) | ||
| Concomitant significant large artery disease > 70% | Multiple ICAD | 5 (27.8) | 8 (44.4) | 0.298 |
| Concomitant Extracranial stenosis | 3 (16.7) | 2 (11.1) | 1 | |
| Concomitant significant tandem stenosis > 70% | 2 (11.1) | 0 | 0.486 | |
| Endovascular treatment modality | Primary balloon angioplasty | 3 (16.7) | 0 | <0.001 |
| Bare metal stent | 1 (5.6) | 18 (100) | ||
| Drug-eluting stent | 5 (27.8) | 0 | ||
| Self-expanding stent | 9 (50) | 0 | ||
| Pre-stent angioplasty | 12 (66.7) | 6 (33.3) | 0.0455 | |
| Combined Treatment of other lesions | 5 (27.8) | 1 (5.6) | 0.177 | |
| Tortous Proximal Vessels (≥2 acute curve) | 10 (55.6) | 11 (61.1) | 0.735 | |
| Intermediate catheter use | 1 (5.6) | 2 (11.1) | 1 | |
| Over wire exchange | 9 (50) | 7 (38.9) | 0.502 | |
| No. of lesion pass | Single | 14 (77.8) | 16 (88.9) | 0.658 |
| Multiple | 4 (22.2) | 2 (11.1) | ||
| Intraprocedural adverse events | 1 (5.6) | 1 (5.6) | 1 | |
| Outcome Parameter | LV Group (n = 18) | HV Group (n = 18) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. (%) | No. (%) | ||
| Successful revascularization (residual stenosis < 50%) | 17 (94.4) | 18 (100.0) | 1 |
| Death, stroke, and/or TIA at 30 days | 4 (22.2) | 1 (5.6) | 0.188 |
| Target territory-related stroke and/or TIA at 30 days | 3 (16.7) | 1 (5.6) | 0.603 |
| Haemorrhagic stroke at 30 days | 1 (5.6) | 0 | 1 |
| Death, stroke, and/or TIA after 30 days | 4 (22.2) | 3 (16.7) | 1 |
| Target territory-related stroke and/or TIA after 30 days | 4 (22.2) | 2 (11.1) | 0.658 |
| Death, stroke, and/or TIA at 18 months | 7 (38.9) | 3 (16.7) | 0.137 |
| Target territory-related stroke and/or TIA at 18 months | 7 (38.9) | 3 (16.7) | 0.137 |
| Restenosis (≥50%) at 12 month | 3 (16.7) | 1 (5.6) | 0.603 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Swiss Federation of Clinical Neuro-Societies. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abualhasan, A.; Pero, G.; Quilici, L.; Piano, M.; Valvassori, L.; Sobh, K.; Mansour, O.; Elbassiony, A.; El-Serafy, O.; Boccardi, E.; et al. Midterm Outcomes of Endovascular Treatment for Intracranial Atherosclerosis: High-Volume Versus Low-Volume Centres. Clin. Transl. Neurosci. 2025, 9, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn9010006
Abualhasan A, Pero G, Quilici L, Piano M, Valvassori L, Sobh K, Mansour O, Elbassiony A, El-Serafy O, Boccardi E, et al. Midterm Outcomes of Endovascular Treatment for Intracranial Atherosclerosis: High-Volume Versus Low-Volume Centres. Clinical and Translational Neuroscience. 2025; 9(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn9010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbualhasan, Ahmed, Guglielmo Pero, Luca Quilici, Mariangela Piano, Luca Valvassori, Khaled Sobh, Ossama Mansour, Ahmed Elbassiony, Omar El-Serafy, Edoardo Boccardi, and et al. 2025. "Midterm Outcomes of Endovascular Treatment for Intracranial Atherosclerosis: High-Volume Versus Low-Volume Centres" Clinical and Translational Neuroscience 9, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn9010006
APA StyleAbualhasan, A., Pero, G., Quilici, L., Piano, M., Valvassori, L., Sobh, K., Mansour, O., Elbassiony, A., El-Serafy, O., Boccardi, E., & Abd-Allah, F. (2025). Midterm Outcomes of Endovascular Treatment for Intracranial Atherosclerosis: High-Volume Versus Low-Volume Centres. Clinical and Translational Neuroscience, 9(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn9010006






