Abstract
Across many resting-state electroencephalography (EEG) studies, dementia is associated with changes to the power spectrum and fractal dimension. Here, we describe a novel method to examine changes in the fractal dimension over time and within frequency bands. This method, which we call fractal dimension distributions (FDD), combines spectral and complexity information. In this study, we illustrate this new method by applying it to resting-state EEG data recorded from patients with subjective cognitive impairment (SCI) or dementia. We compared the performance of FDD with the performance of standard fractal dimension metrics (Higuchi and Katz FD). FDD revealed larger group differences detectable at greater numbers of EEG recording sites. Moreover, linear models using FDD features had lower AIC and higher R2 than models using standard full time-course measures of the fractal dimension. FDD metrics also outperformed the full time-course metrics when comparing SCI with a subset of dementia patients diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease. FDD offers unique information beyond traditional full time-course fractal analyses and may help to identify dementia caused by Alzheimer’s disease and dementia from other causes.
1. Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the leading cause of dementia and the seventh most common cause of death in the United States [1]. The risk of developing AD grows with age; about 10% of adults aged 65 or older have Alzheimer’s dementia, and that percentage passes 25% for those aged 85 or older [2,3]. AD is ultimately fatal, with no cure and mostly symptomatic treatments [4]. The annual incidence of AD is projected to double by 2050 due to increasing life expectancies [5], necessitating new methods to treat and test for the disease.
Most AD patients first experience a stage of mild cognitive impairment (MCI), where memory loss and other cognitive changes are pronounced enough to register on clinical assessments, but not so extreme as to interfere with independent daily functioning. Before being diagnosed with MCI, some patients report worsening cognitive abilities despite scoring within healthy ranges on clinical assessments [6]; this condition is referred to as subjective cognitive impairment (SCI). AD is primarily diagnosed through clinical cognitive assessments [7], which may not always catch early-stage cognitive impairment or distinguish between different forms of dementia [8]. Historically, AD diagnoses were only confirmed post-mortem through an autopsy. There has been a push to incorporate more objective biomarker-based tests into clinical practice and research [9], but these tests are often invasive (e.g., a lumbar puncture) or expensive (e.g., positron emission tomography). While new plasma biomarkers have demonstrated excellent accuracy at detecting amyloid and tau pathology [10], these methods can take time to compute and may not be strongly associated with cognitive impairment. A growing body of research positions the electroencephalogram (EEG) as a fast, inexpensive, non-invasive biomarker for AD [11].
AD patients present with a number of EEG abnormalities, one of which is reduced signal complexity [12,13,14]. Complexity in brain signals arises from interacting neural circuits operating over multiple spatial and temporal scales. A variety of complexity methods have been previously used, including entropy, Hurst exponent, correlation dimension, and fractal dimension (reviewed in [13]). The fractal dimension (FD) is a nonlinear measure that expresses how the details of a self-similar form are altered by the scale at which they are measured [15]. In this study, we utilize both the Katz fractal dimension (KFD) and the Higuchi fractal dimension (HFD) methods. KFD calculates the fractal dimension by comparing distances along the waveform [16], whereas HFD approximates the box-counting dimension in time-series data by repeatedly downsampling a waveform and comparing the length of the subsampled waveforms to the downsampling factor [17]. Though KFD tends to underestimate FD, KFD is sometimes better at discriminating between different brain states than HFD [18].
Diminished HFD and KFD are observed in the EEG and magnetoencephalography (MEG) of individuals with AD and dementia [19,20,21,22,23]. While EEG signal complexity drops after age 60 even in the absence of disease, AD is associated with a decrease in FD beyond what is observed in healthy, age-matched controls [21]. HFD and KFD have been used in conjunction with machine learning algorithms to distinguish between AD and healthy controls with high accuracy and specificity, making them a prime candidate for an EEG-based AD biomarker [24,25,26]. These algorithms can be improved by computing FD within distinct frequency bands (e.g., delta, theta, alpha) rather than in broadband EEG [25,27]. For instance, Nobukawa and colleagues [22] found that the difference in a modified HFD between AD and healthy controls was greater at higher frequencies than lower frequencies.
We propose that the predictive capability of EEG could be further improved by analyzing the distribution of FD over the course of an EEG session [28,29]. A common implementation of HFD and KFD algorithms compute a single value summarizing the entire time series, meaning any changes in FD over time are lost. Some previous work calculated FD within moving windows but discarded information about potential changes in FD over time by averaging the resulting values together [23,26]. However, the distribution of FD over time may contain valuable information. Here we develop a new technique called fractal dimension distributions (FDD). Rather than assessing FD using the full EEG time-course, FDD slides a moving window across the full time-course, computes FD (HFD or KFD) within each window, and then summarizes the distribution of FD values across time windows (e.g., mean, standard deviation). We provide an initial demonstration of this approach by calculating FDD in participants with SCI or dementia. We then evaluate whether FDD carries more information about dementia than traditional full time-course metrics of FD.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
All patients were adults over the age of 55 who visited a specialty memory clinic (Pacific Brain Health Center in Santa Monica, CA, USA) for memory complaints. Adults were evaluated by a dementia specialist during their visit. Evaluations included behavioral testing and EEG recordings. Patients with SCI or dementia were selected retrospectively by reviewing charts for patients seen between July 2018 and February 2021. Full data were available from 148 adults (see Table 1 for demographic information). Groups were divided into adults diagnosed with SCI (N = 97) or dementia (N = 51). Within the dementia group, 38 individuals were diagnosed with AD. The remaining individuals were diagnosed with Lewy body dementia (n = 4), vascular dementia (n = 2), frontotemporal dementia (n = 2), Parkinson’s disease (n = 2), or unknown (n = 3). All procedures aligned with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975 and were approved by the Institutional Review Board at the St. John’s Cancer Institute. All patients provided informed consent.

Table 1.
Demographic information.
2.2. Clinical Diagnosis
Patient diagnosis was based on consensus of a panel of board-certified dementia specialists using the 2011 guidelines proposed by the National Institute of Aging and the Alzheimer’s Association (NIA-AA). Diagnoses utilized standard clinical methods for neurological examinations, cognitive testing (MMSE [30] or MoCA [31]), clinical history (e.g., depression, diabetes, head injury, hypertension), and laboratory testing (e.g., thyroid-stimulating hormone levels, rapid plasma reagin testing, vitamin B-12 levels). Cognitive impairment was diagnosed on the basis of the MMSE (or MoCA scores converted to MMSE [32]). MCI was diagnosed according to the criteria established by Langa and Levine [33], and distinguished from dementia on the basis of preserved functional abilities and independence together with a lack of significant impairment in occupational or social functioning. SCI was diagnosed based on subjective complaints without evidence of MCI.
2.3. EEG Collection
EEG data were recorded using a 19-channel eVox System (Evoke Neuroscience) at the Pacific Neuroscience Institute. Electrodes were positioned in a cap according to the international 10–20 system (Fp1, Fp2, F7, F3, Fz, F4, F8, T7, C3, Cz, C4, T8, P7, P3, Pz, P4, P8, O1, and O2). Data were collected at 250 Hz while patients completed two resting-state recordings—five minutes each of eyes closed and eyes open—and a 15 min Go/No-Go task. For this study, we used only the eyes-closed resting-state data.
2.4. EEG Preprocessing
EEG data were re-referenced offline to the average of all channels using the MNE python library (version 1.0.0). Jump artifacts were defined as large deviations in global field power over a short period of time. Global field power was calculated as the standard deviation across all channels at each timepoint. Jumps were defined as global field power more than 10 standard deviations from the mean persisting across no more than 10 consecutive samples (40 ms). Wherever a jump artifact was detected, those samples were replaced with a linear interpolation between the nearest samples that were not contaminated by the jump artifact, and computed separately for each channel. Ocular artifacts were removed with the aid of Independent Component Analysis (ICA). In total 18 ICA components were extracted, then compared to templates of stereotypical ocular artifacts for horizontal and vertical eye movement. Components with a high correlation with either eye movement template were excluded, then the remaining components were projected back into sensor space.
For the broadband analysis, we filtered data with a 1–50 Hz zero-phase finite impulse response bandpass to help attenuate line noise. In the banded analysis, we applied separate bandpass filters for the delta (1–4 Hz), theta (4–8 Hz), alpha (8–13Hz), beta (13–30 Hz), and gamma (30–50 Hz) frequency bands. After filtering, we segmented the data into 1 s duration epochs, with a 0.5 s overlap.
2.5. Fractal Dimension
We calculated KFD and HFD using the AntroPy package (version 0.1.4). Katz’s method [16] calculates the sum—i.e., length (L)—and average (a) Euclidean distance between successive points in the time series, as well as the maximum distance from the first point in the time series to any other point in the time series (d). The fractal dimension of the time series (FD) is then calculated as follows:
Thus, Katz’s method relies only on the raw time series itself. However, Higuchi’s method [17] begins by subsampling a time series across progressive smaller time scales, then examining how the length of time series is related to the scaling. Given a time series ℝ with sample points and , Higuchi’s method begins by first calculating the length of a curve, , across a range of values based on initial time (m) and interval time (k). This length, , is defined as follows:
for each and . Then, the length is the average:
and HFD is the slope of the best-fit line through points .
Thus, HFD depends on both the number of sample points (N) and the parameter kmax, which sets the upper limit on the number of time intervals. Some early work suggested using kmax = 6 for time series with 40–1000 points [34]. Other approaches suggest calculating HFD across multiple kmax values and identifying the value of kmax, at which HFD plateaus [35,36]. However, HFD is not guaranteed to plateau. Recently, Wanliss and Wanliss demonstrated that an optimal kmax can be estimated algorithmically based on the length of the time series [37]. The proposed algorithm uses two sinusoids and three pairs of parameters with empirically derived distributions. We used this algorithm to estimate the optimal kmax for the length of the full time-course, and for 1 s windows (Supplementary Materials). This indicated kmax = 108 for the full sample and kmax = 25 for 1 s windows.
2.5.1. Full Time-Course Fractal Dimension
We calculated the full time-course fractal dimension by applying Katz’s method or Higuchi’s method (with kmax = 108) to the entire resting-state EEG recording. This analysis reflects the way prior studies computed FD [19,25].
2.5.2. Fractal Dimension Distributions (FDD)
For the fractal dimension distributions, we first segmented the data using 1 s moving windows, with a 0.5 s overlap (see Section 3.6 for discussion of other window sizes). We then extracted the KFD or HFD (kmax = 25) within each window. Finally, we summarized the distribution of KFD or HFD values across windows using the mean and standard deviation.
2.6. Group Differences
We sought to compare the fractal dimension measures between the SCI and dementia. We used threshold-free cluster enhancement (TFCE) to estimate the difference at each channel [38,39]. TFCE is a non-parametric technique that computes cluster-level statistics across a range of cluster-forming thresholds. The channel-level TFCE statistic incorporates both the strength of the difference at that channel and the spatial extent of any neighboring clusters that exist in the data. This approach produces one TFCE value per channel. TFCE values can then be calculated for data that have had labels permuted. The final TFCE-adjusted t-statistics are thus controlled for multiple comparisons across channels. We used 10,000 permutations as implemented in the permutation_cluster_test function in MNE. Positive and negative difference were calculated separately, using a step size of 0.2. Group differences were then visualized by projecting the t-statistics to the scalp with a bilinear interpolation in MNE, and individually significant channels were identified using alpha corresponding to corrected p < 0.05. In order to understand whether non-AD dementia and AD might be associated with different patterns of FD, we repeated this analysis comparing SCI to AD.
2.7. Logistic Regressions
The TFCE analyses test whether FD metrics in individual channels carry information about dementia. As a complementary analysis, we used logistic regressions to test how information can be combined across channels to predict dementia (or AD). We regressed cognitive status on FD metrics in all channels, using either full time-course FD or FDD features. All models included age as a covariate. Fractal scores across channels were correlated (see Supplementary Figures S1–S3), so we used regularized Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regressions as implemented in the statsmodels package (version 0.13.2). L1 regularization helps to avoid overfitting by penalizing models with higher complexity. For each set of predictors, a series of logistic regressions were fitted, with L1 penalty values (alpha) ranging from 0 to 10 in 0.05 step increments. Default values were used for all other hyperparameters. The model with the lowest Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) was selected for that set of predictors. Here, our goal was to understand how variance in group membership was related to variance in fractal features. Each model was fitted once, using data from all subjects, rather than partitioning data for validation.
We assessed model fit using a chi-square likelihood ratio test (LRT) comparing models with fractal features to a model with age as the only predictor. This test verifies that fractal features carry information about dementia beyond the information captured by age alone. We used the age-only model as the comparison because age is considered an import predictor of dementia [3]. The LRT is inappropriate for directly comparing models using full time-course FD to models using FDD features since they are non-nested. Instead, we used AIC, with lower AIC values indicating a better model. The LRT and AIC protect against overfitting by penalizing more complicated models. For each model we also calculated Tjur’s coefficient of determination to obtain pseudo-R2, which reflects how well the model separates the two classes of patients, with 0 reflecting no separation and 1 reflecting complete separation [40].
3. Results
Before comparing traditional full time-course FD with the novel FDD metric, we established a baseline model, using age as the only predictor. This model was a better fit to the data than an intercept-only null model (X2(1) = 7.59, p = 0.006). It served as a reference when conducting likelihood ratio tests for models using the fractal dimension values.
3.1. FDD Differentiates Dementia Better Than Full Time-Course Fractal Dimension
First, we tried to replicate previous studies by looking for differences in full time-course HFD and KFD between SCI and dementia [19]. In the broadband data, group differences in full time-course HFD and full time-course KFD were in the expected direction, but did not reach statistical significance. Three electrodes showed a trend towards lower HFD in the dementia group (Figure 1; O1 t = −1.37, p = 0.099; Pz t = −1.40, p = 0.099, and P3 t = −1.44, p = 0.089).
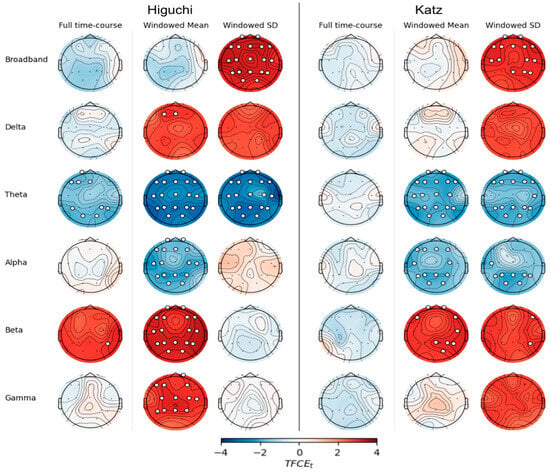
Figure 1.
EEG fractal values differ between dementia and SCI groups. Scalp plots show differences (dementia—SCI) calculated using threshold-free cluster enhancement (TFCE) for Higuchi fractal dimension (left) or Katz fractal dimension (right). Electrodes with significant differences (TFCE FEW p < 0.05) are marked with white circles.
We next examined the FDD features by calculating the mean and standard deviation of HFD and KFD across windows. In the broadband data, the mean of windowed HFD did not significantly differ between groups. In contrast, the standard deviation of windowed HFD was significantly higher in the dementia group at every electrode (smallest difference at T8, t = 1.92, p = 0.020, largest difference at T7, t = 2.89, p < 0.001). Furthermore, the standard deviation of windowed KFD was significantly higher in the dementia group at all but five electrodes (O1, O2, P3, P7, Cz; all p > 0.08).
A logistic regression model using full time-course HFD showed better performance than a model using only patients’ age, and both of these were outperformed by a model using FDD features (Table 2; ΔAIC = −16.7, ΔR2 = 0.16). Similarly, a model using FDD features based on KFD outperformed a model using the full time-course KFD (Table 3; ΔAIC = −12.7, ΔR2 = 0.24). Interestingly, the lowest AIC across models using full time-course KFD was a model in which LASSO regularization set all channel coefficients to 0, retaining only age; this indicates that KFD obtained from the full time-course did not contain enough unique information relating to dementia to be included in the model.

Table 2.
Summary of models distinguishing between dementia and SCI using Higuchi fractal information.

Table 3.
Summary of models distinguishing between dementia and SCI using Katz fractal information.
3.2. FDD Is More Informative Than Full Time-Course Fractal Dimension in Most Frequency Bands
We next compared the fractal dimensions between SCI and dementia within five frequency bands, calculating either the full time-course FD or FDD (Figure 1). In every band, more scalp locations showed significant group differences using Higuchi FDD calculated from full time-course HFD, particularly the windowed mean (Figure 1, left). There were no significant differences in any band using the full time-course KFD (all ps > 0.187). Using the Katz FDD, however, several clusters of electrodes showed significant group differences in the theta, alpha, and beta bands.
In order to visualize the extent to which FDD and full time-course FD discriminate between SCI and dementia, we plotted the absolute TFCE-t statistic averaged across channels for the full time-course FD and FDD mean and standard deviation. Figure 2 shows these values for HFD and KFD (Figure 2) for each frequency band. We then subtracted the full time-course FD values from the corresponding FDD metrics to obtain a numerical measure of the increase or decrease in the group difference at each channel—positive values indicate a larger difference using FDD features compared to full time-course FD features. We plot these relative TFCE values in each frequency band for HFD and KFD (Figure 2).
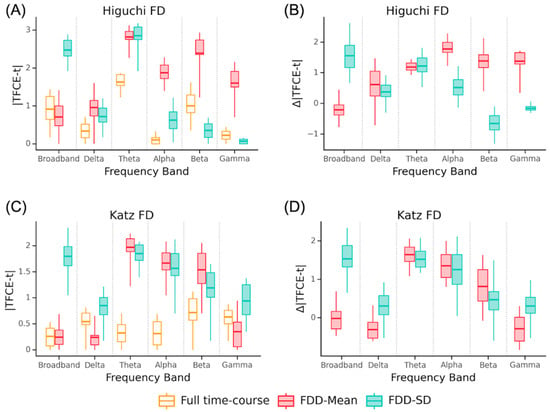
Figure 2.
Comparison of group differences for Dem-SCI with full time-course and FDD features. Absolute TFCE-t statistic averaged across channels for group differences (Dem—SCI) in each frequency band using Higuchi (A) or Katz FD (C). Difference between FDD metrics and full time-course FD in each frequency band (B,D). Box outlines show the interquartile range, central line shows the median, and whiskers extend to minimum and maximum value.
As in the broadband analysis, we then used logistic LASSO regressions to test whether using FDD features lead to more accurate models than full time-course FD. For both the Katz and Higuchi methods, the models using FDD outperformed models using full time-course FD, though the effect was stronger for HFD (Table 2; average ΔAIC = −7.9, ΔR2 = 0.15) than KFD (Table 3; average ΔAIC = −3.5, ΔR2 = 0.08). The logistic regression using FDD with Higuchi in the delta band had lower AIC but did not have higher R2 than the model using full time-course HFD (ΔAIC = −2.7, ΔR2 = −0.03). In contrast, regressions using Higuchi FDD features were universally better in the theta (ΔAIC = −15.3, ΔR2 = 0.32), alpha (ΔAIC = −15.4, ΔR2 = 0.38), and beta (ΔAIC = −6.5, ΔR2 = 0.14) bands. The model with full time-course HFD had a slightly lower AIC than the model with FDD in the gamma band (ΔAIC = 0.3, ΔR2 = −0.08).
With Katz’s method, models using FDD had lower AIC and larger R2 than models using full time-course KFD in delta (ΔAIC = −7.8, ΔR2 = 0.17) and beta bands (ΔAIC = −9.2, ΔR2 = 0.14). The model using FDD features had lower AIC and slightly larger R2 in the alpha band (ΔAIC = −0.9, ΔR2 = 0.01). In the theta band, the model using FDD features produced a smaller AIC, but worse R2 (ΔAIC = −4.7, ΔR2 = −0.04). As with HFD, in the gamma band, the model using full time-course KFD outperformed the model using FDD (ΔAIC = 5.0, ΔR2 = 0.10).
Across all models comparing dementia and SCI, the two with the lowest AIC and highest R2 used Higuchi FDD features in the alpha band (AIC = 166.6, R2 = 0.644, X2(25) = 66.42, p < 0.001) or theta band (AIC = 159.6, R2 = 0.592, X2(23) = 69.44, p < 0.001).
3.3. FDD Differentiates Alzheimer’s Disease Better Than Full Time-Course Fractal Dimension
The previous analyses demonstrate that the distribution FD carries additional information about dementia beyond the information carried by standard full time-course FD. Next, we tested whether this distributional information also helps to specifically distinguish between SCI and dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease (AD). There were no significant differences between SCI and AD in full time-course HFD or KFD when estimated from broadband data (Figure 3; all p > 0.3). There were also no significant differences in mean HFD or mean KFD at any electrode (all p > 0.2). However, KFD SD was significantly higher in the AD group at F8 (t = 1.71, p = 0.037) and HFD SD was higher at left and frontal sites, including F4, Fz, F3, F7, T7, C3 and P3.
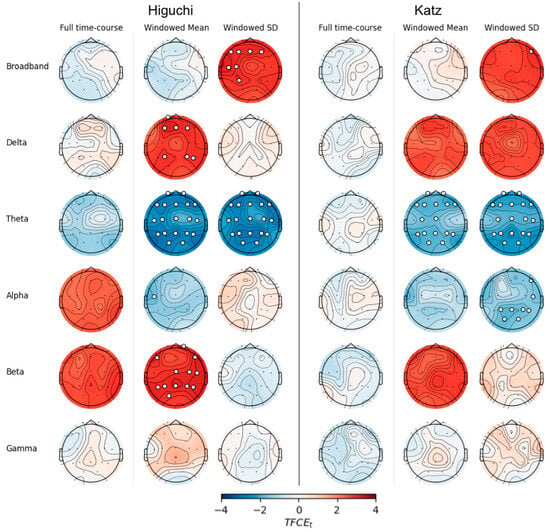
Figure 3.
EEG fractal values that differ between AD and SCI groups. Scalp plots show differences (AD—SCI) calculated using threshold-free cluster enhancement (TFCE) for Higuchi fractal dimension (left) or Katz fractal dimension (right). Electrodes with significant differences (TFCE FEW p < 0.05) are marked with white circles.
The logistic regression using age to predict AD status was a significantly better fit than the intercept-only model (X2(1) = 7.22, p = 0.007). Again, while full time-course HFD improved model fit relative to an age-only model, models with FDD features fit the data even better (Table 4; ΔAIC = −5.4, ΔR2 = 0.13). Furthermore, the model using Katz FDD features outperformed the model using full time-course KFD (ΔAIC = −10.7, ΔR2 = 0.42).

Table 4.
Summary of models distinguishing between AD and SCI using Higuchi fractal information.
3.4. FDD Is More Informative for Alzheimer’s Disease in Most Frequency Bands
Next, we examined the difference between SCI and AD when FD metrics were calculated within individual frequency bands. There were no significant differences at any electrode using full time-course estimates of HFD and KFD in the delta (all p > 0.5), alpha (all p > 0.5), beta (all p > 0.1) or gamma (all p > 0.3) bands. In the theta band, no electrodes showed significant differences in full time-course HFD (all p > 0.09).
Within the delta band, mean windowed HFD was significantly higher in the AD group at frontal and parietal electrodes (all t > 1.63, p < 0.045). The SD of windowed HFD was not significantly different between groups at any electrodes (all p > 0.1). Similarly, no electrodes showed significant group differences for either Katz FDD metric in the delta band (all p > 0.1). In the theta band, every electrode showed reduced Higuchi FDD measures in AD compared to SCI. Nearly all channels showed significantly lower KFD mean and SD. Finally, mean HFD was significantly higher in the AD group at central and posterior sites, as well as at Fp2, F7, and F8 (all t > 1.64, p < 0.049).
As with the Dem-SCI analysis, we plotted the absolute TFCE-t statistics for AD-SCI at each channel for the full time-course FD compared to TFCE-t scores obtained using FDD measures (Figure 4), as well as the difference between FDD features and the full time-course FD metrics. The most pronounced improvement was in the theta band.
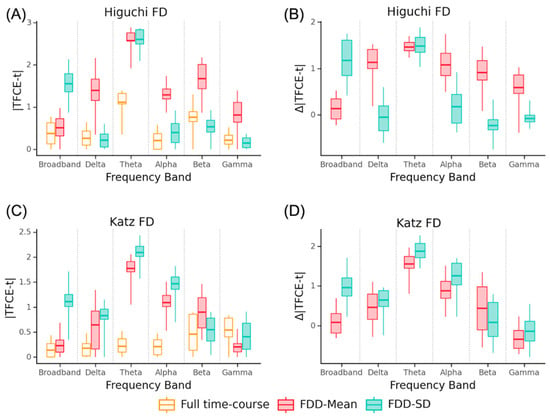
Figure 4.
Comparison of group differences for AD-SCI with full time-course and FDD features. Average channel absolute TFCE-t statistic for AD-SCI in each frequency band using Higuchi (A) or Katz (C). Difference between FDD metrics and full time-course FD in each frequency band (B,D). Whiskers extend to minimum and maximum value.
Averaging across frequency bands, models using FDD had a lower AIC and higher R2 than models using full time-course estimates (ΔAIC = −2.6, ΔR2 = 0.08). Models using Higuchi FDD were nearly indistinguishable but had improved class separation relative to full time-course models (Table 4; average ΔAIC = −0.2, ΔR2 = 0.08), while models using Katz FDD had lower AIC while showing a minimal increase in class separation. (Table 5; average ΔAIC = −2.6, ΔR2 = 0.01).

Table 5.
Summary of models distinguishing between AD and SCI using Katz fractal information.
Models using Higuchi FDD outperformed models using full time-course HFD in the delta (Table 4; ΔAIC = −9.8, ΔR2 = 0.05) and alpha bands (ΔAIC = −5.4, ΔR2 = 0.30). In the theta and gamma bands, the windowed model separated the classes better, but had worse expected prediction error (ΔAIC = 2.0, ΔR2 = 0.09; ΔAIC = 8.9, ΔR2 = 0.05). The model using FDD features had lower performance than the models using full time-course HFD in the beta band (ΔAIC = 3.2, ΔR2 = −0.09).
The models using KFD were similarly mixed. Models using FDD features outperformed models using full time-course FD in the delta (ΔAIC = −12.1, ΔR2 = 0.22) and gamma bands (ΔAIC = −6.8, ΔR2 = 0.23), but underperformed models using full time-course FD in the alpha (ΔAIC = 2.2, ΔR2 = −0.06) and beta bands (ΔAIC = 4.4, ΔR2 = −0.20). In the theta band, models based on FDD had lower AIC but also lower class separation (ΔAIC = −2.0, ΔR2 = −0.22).
Across all models comparing AD and SCI, the models with the lowest AIC and largest R2 used Higuchi FDD in the delta band (AIC = 144.0, R2 = 0.342, X2(17) = 51.40, p < 0.001) or Katz FDD with broadband EEG (AIC = 148.9, R2 = 0.507, X2(32) = 76.48, p < 0.001).
3.5. Features Useful for Distinguishing AD and Dementia Partially Overlap
Are the features that are useful for distinguishing between SCI and any dementia the same as the features that are useful for distinguishing between SCI and AD dementia? To answer this question, we examined the regression coefficients from each of the final models. In these LASSO regressions, L1 regularization selects variables that relate to the dependent variable and sets all other coefficients to zero. We examined which channels, frequencies, and FD analysis methods were retained in these models as non-zero coefficients. As shown in Figure 5, while the regularized logistic regression indicated that some features were useful for both models, other features were only useful in one of the models but not the other. Across the fractal variability models, dementia–SCI models used a total of 122 EEG features while AD-SCI models used 191, with 89 features appearing in both models.
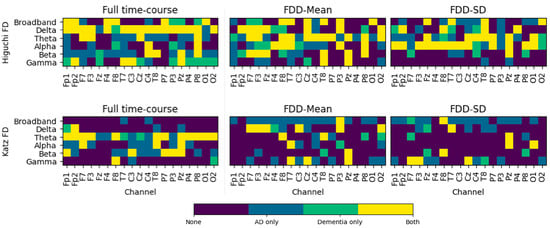
Figure 5.
Channels used in final models. Channels with non-zero coefficients in the regularized logistic regression using full time-course FD (left) or FDD (center and right) features calculated using Higuchi (top) or Katz (bottom) methods.
3.6. FDD Provides Information about Dementia across Different Window Lengths
To understand whether our results depended on the length of the window used to calculate FDD features, we repeated the analysis using three other window sizes—0.5 s, 5 s, 10 s—each with a 50% overlap. We estimated the ideal kmax = 25 for the 0.5 s and 5 s windows, and kmax = 28 for the 10 s windows. Models using FDD continued to generally outperform models using full time-course FD values, with better performance in broadband for both dementia–SCI and AD-SCI. (see Supplemental Tables S1–S4). Across analyses comparing dementia–SCI within specific frequency bands, models using FDD features calculated with 1 s windows outperformed models using full time-course FD in 8/10 cases. Similarly, using 0.5 s or 5 s windows resulted in better performance with FDD features in 9/10 cases and FDD calculated from 10 s windows produced better performance in 6/10 cases. When modeling AD-SCI, FDD with 1 s windows outperformed full time-course FD in 5/10 models. Changing the window size resulted in similar performance for 0.5 s (5/10 models), 5 s (4/10 models), or 10 s (6/10) durations.
4. Discussion
In this study, we present the FDD metric, a novel method for quantifying the distribution of the fractal dimension values over time. We then apply FDD to examine signal complexity in Alzheimer’s disease. We show that FDD carries information above and beyond the full time-course fractal dimension of a signal, and that FDD features are useful for distinguishing individuals diagnosed with dementia from individuals with SCI, as well as individuals with AD dementia from individuals with SCI. Using both Higuchi and Katz algorithms, FDD calculated from broadband EEG revealed more significant differences between groups than full time-course fractal values (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Models using FDD features were also better (as measured by lower AIC and higher R2) than models using full time-course FD (Table 2 and Table 3). FDD features also demonstrated more group differences, larger effect sizes, and better models across most frequency bands (Table 2 and Table 3; Figure 1 and Figure 2).
When comparing SCI to dementia or SCI to AD dementia, the most widespread group differences were observed in the theta band (Figure 1 and Figure 3). Theta band activity has long been associated with memory performance [41]. This is not entirely surprising, since memory loss is a hallmark of dementia. However, there are many open questions related to theta oscillations in the human neocortex, such as whether observed associations between memory function and theta power arise from focal changes in theta power or rather as an overall shift in the power spectrum [42].
A second goal of this work was to understand whether the distribution of the fractal dimension scores could also elucidate characteristics of AD dementia. FDD features again revealed more electrodes with significant AD-SCI differences than full time-course FD, both in broadband and the majority of traditional frequency bands (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Using broadband data, FDD features produced better models for both HFD and KFD (Table 4 and Table 5). Models using FDD to distinguish between AD and SCI were better in the delta band and slightly better on average.
Previous work has found lower HFD in AD [20,21,22,23]. Similarly, prior studies have examined FD separately within canonical frequency bands, and find lower KFD and HFD in AD [12,27,43]. Using FDD, we replicate this decrease in FD for the dementia and AD dementia within the theta and alpha bands. Using full time-course FD, we find non-significant trends toward decreases in FD using full time-course broadband HFD and KFD. Why do we find a non-significant trend where other studies showed a significant decrease? We compare AD dementia to SCI, whereas other work used healthy older adults recorded in a laboratory setting [12,19]. There may also be an important difference between FD calculated from EEG compared to MEG [20,21]. Moreover, as discussed above (see Section 2.3), computing HFD relies on the kmax parameter, and previous investigations of HFD in dementia did not calculate kmax using the approach based on time-course length [37]. Our proposed FDD metric did reliably identify reduced complexity, for both HFD and KFD.
Our results also highlight the importance of distinguishing between dementia caused by AD from non-AD dementia. Particularly when using FDD, the dementia and SCI groups demonstrate significant differences across nearly the entire scalp (Figure 1). In contrast, significant differences between AD and SCI were restricted to fewer electrodes and appeared primarily in the theta band (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Moreover, while 73% of the FDD features that were retained in the dementia–SCI models were also retained in AD-SCI models (Figure 5), less than half of the features used in the AD-SCI models appeared in the dementia–SCI models (47%). In other words, while some EEG signals are generally useful for detecting cognitive impairment, our results suggest that EEG is also sensitive to additional signals which are uniquely important for detecting AD. Discovering whether FDD is useful for distinguishing between AD and non-AD dementia cases will require additional evidence with larger populations of patients with dementia.
AD is a neurodegenerative disease with a distinct progression of physical and cognitive symptoms. Its pathology is characterized by two features: extracellular deposits of beta-amyloid plaques, and intracellular accumulations of abnormally phosphorylated tau, called neurofibrillary tangles [44]. Patients with Alzheimer’s dementia exhibit widespread amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles throughout the brain, but beta-amyloid and tau start to amass long before severe cognitive symptoms appear [45]. One origin of reduced EEG complexity in AD patients may be an abnormal cortical excitation/inhibition ratio [46]; beta-amyloid is linked to neuronal hypoactivity, and tau is associated with neuronal hyperactivity [47]. Decreases in EEG complexity might also arise from general neurodegeneration, with fewer neurons and fewer interactions between neurons [48]. However, more work is needed to clarify any associations between beta-amyloid and tau abnormalities, cognitive decline, and EEG complexity.
Researchers investigating FD in EEG might also benefit from examining FDD features as a complement to full time-course FD methods. Previous work has used FD in EEG signals to identify a variety of neuropsychological and neurocognitive conditions. EEG complexity and FD in schizophrenia has been widely investigated, with studies reporting both increased and decreased FD based on symptomatology, age, and medication status [49,50,51,52]. In schizophrenia, the FD also has strong predictive power, and it has been used to distinguish individuals with schizophrenia from healthy controls with high accuracy [53]. Other work has examined FD in mood and cognitive disorders, with increased FD reported in depression [49,54,55], bipolar disorder [56], and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder [57].
Our introduction of FDD is focused on the mean and standard deviation of FD computed across multiple moving windows. However, future work could investigate other methods of assessing changes in fractal content over time. For instance, higher-order distributional summary statistics, such as skewness or kurtosis could be included. Similarly, time-sensitive measures, such as autoregressive variance, might provide additional unique information that could be used to identify or distinguish neurodegenerative conditions.
One additional potential advantage of FDD over full time-course fractal measures is that it allows for momentary artifacts to be excluded from the data. If artifacts contaminate a portion of an EEG recording, that artifact could bias estimates of FD. A windowed approach like FDD makes it trivially easy to handle events such as jump artifacts or movement artifacts—simply exclude windows with artifacts from the analysis. Thus, FDD offers the potential to recover usable EEG recordings from a broader range of patients.
While our results suggest that models trained using FDD could be a useful early screening tool in clinical settings, future studies will be required to determine optimal FDD parameters. We expect that FDD will be most useful in a clinical setting when used alongside other EEG features, such as spectral power, or combined with molecular or liquid biomarkers.
The current manuscript has several limitations. The dataset contains only 13 patients with non-AD dementia. This means we were not well positioned to directly address how well FDD might distinguish between different dementia subtypes. Moreover, our data are cross-sectional. Longitudinal studies will be needed to assess the prospective utility of FDD. Our goal was to introduce FDD, rather than propose exact parameters values. Thus, we did not exhaustively test potential values for parameters, such as window length.
5. Conclusions
We propose a novel method, FDD, to investigate the fractal dimensions within and across frequency bands in resting-state EEG data. Our results extend previous work linking differences in EEG spectral content and fractal dimension to Alzheimer’s disease dementia and dementia without Alzheimer’s disease. In broadband EEG, and within most of the traditional frequency bands, FDD revealed stronger group differences and more informative features than full time-course FD for both dementia and AD dementia. Moreover, regularized linear regressions using FDD features were better at accounting for differences between unimpaired subjects and subjects with dementia than models using full time-course fractal dimension. Overall, our findings demonstrate that FDD can provide information about cognitive status and AD diagnosis from resting-state EEG, above and beyond traditional full time-course methods.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ctn8030027/s1, Figure S1. Channel correlations for full time-course fractal dimension. Heatmap showing channel-by-channel correlations for HFD (upper right triangle) and KFD (lower left triangle). Note that all resulting correlations are positive; Figure S2. Channel correlations for windowed fractal mean. Heatmap showing channel-by-channel correlations for HFD (upper right triangle) and KFD (lower left triangle). Note that all resulting correlations are positive; Figure S3. Channel correlations for windowed fractal standard deviation. Heatmap showing channel-by-channel correlations for HFD (upper right triangle) and KFD (lower left triangle). Note that all resulting correlations are positive; Table S1. Estimates of best fitting parameters for kmax function; Table S2. Summary of models predicting Dementia vs. SCI using Higuchi fractal information with different window lengths; Table S3. Summary of models predicting Dementia vs. SCI using Katz fractal information with different window lengths; Table S4. Summary of models predicting AD vs. SCI using Katz fractal information with different window lengths; Table S5. Summary of models predicting AD vs. SCI using Katz fractal information with different window lengths.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.J.Y., C.Q. and C.L.; data curation, C.Q.; formal analysis, K.J.Y.; funding acquisition, S.G. and C.L.; methodology, K.J.Y.; resources, D.A.M. and S.G.; software, K.J.Y., G.B. and C.Q.; supervision, D.A.M. and S.G.; visualization, K.J.Y.; writing—original draft, K.J.Y.; writing—review and editing, K.J.Y., Geoffrey Brookshire, R.M.G., D.A.M., C.Q. and C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by SPARK Neuro Inc. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of the article, or the decision to submit it for publication.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board at the Saint John’s Cancer Institute (Protocol JWCI-19-1101).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Restrictions apply to the availability of these data. Data were obtained from the Pacific Neuroscience Institute [58] and can be obtained from D.A.M with permission of D.A.M.
Conflicts of Interest
K.J.Y., G.B., S.G., C.Q. and C.L. were employed by SPARK Neuro Inc., a medical technology company developing diagnostic aids to help clinicians identify and assess neurodegenerative diseases, during this study. The remaining authors have no competing interests to declare.
References
- Kochanek, K.D.; Murphy, S.L.; Xu, J.; Arias, E. Mortality in the United States, 2022; NCHS Data Brief; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, K.B.; Weuve, J.; Barnes, L.L.; McAninch, E.A.; Wilson, R.S.; Evans, D.A. Population Estimate of People with Clinical Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment in the United States (2020–2060). Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, 1966–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manly, J.J.; Jones, R.N.; Langa, K.M.; Ryan, L.H.; Levine, D.A.; McCammon, R.; Heeringa, S.G.; Weir, D. Estimating the Prevalence of Dementia and Mild Cognitive Impairment in the US: The 2016 Health and Retirement Study Harmonized Cognitive Assessment Protocol Project. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, M.; Silvestre, S. Alzheimer’s Disease: Recent Treatment Strategies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 887, 173554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, L.E.; Beckett, L.A.; Scherr, P.A.; Evans, D.A. Annual Incidence of Alzheimer Disease in the United States Projected to the Years 2000 Through 2050. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2001, 15, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisberg, B.; Prichep, L.; Mosconi, L.; John, E.R.; Glodzik-Sobanska, L.; Boksay, I.; Monteiro, I.; Torossian, C.; Vedvyas, A.; Ashraf, N.; et al. The Pre–Mild Cognitive Impairment, Subjective Cognitive Impairment Stage of Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2008, 4, S98–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The Diagnosis of Dementia Due to Alzheimer’s Disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association Workgroups on Diagnostic Guidelines for Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arevalo-Rodriguez, I.; Smailagic, N.; Figuls, M.R.i.; Ciapponi, A.; Sanchez-Perez, E.; Giannakou, A.; Pedraza, O.L.; Cosp, X.B.; Cullum, S. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) for the Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias in People with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 3, 1–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmand, B.; Eikelenboom, P.; van Gool, W.A.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Value of Neuropsychological Tests, Neuroimaging, and Biomarkers for Diagnosing Alzheimer’s Disease in Younger and Older Age Cohorts. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2011, 59, 1705–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therriault, J.; Vermeiren, M.; Servaes, S.; Tissot, C.; Ashton, N.J.; Benedet, A.L.; Karikari, T.K.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Brum, W.S.; Lussier, F.Z.; et al. Association of Phosphorylated Tau Biomarkers With Amyloid Positron Emission Tomography vs Tau Positron Emission Tomography. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, P.M.; Di Iorio, R.; Vecchio, F.; Anfossi, M.; Babiloni, C.; Bozzali, M.; Bruni, A.C.; Cappa, S.F.; Escudero, J.; Fraga, F.J.; et al. Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease: The Role of Biomarkers Including Advanced EEG Signal Analysis. Report from the IFCN-Sponsored Panel of Experts. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 1287–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nuaimi, A.H.H.; Jammeh, E.; Sun, L.; Ifeachor, E. Complexity Measures for Quantifying Changes in Electroencephalogram in Alzheimer’s Disease. Complexity 2018, 2018, 8915079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, B.; Niu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Fan, C.; Zhang, N.; Xue, J.; Wei, J.; Xiang, J. Complexity Analysis of EEG, MEG, and fMRI in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review. Entropy 2020, 22, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.C.; Wang, S.-J.; Lai, K.-L.; Tsai, C.-F.; Yang, C.-H.; Hwang, J.-P.; Lo, M.-T.; Huang, N.E.; Peng, C.-K.; Fuh, J.-L. Cognitive and Neuropsychiatric Correlates of EEG Dynamic Complexity in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 47, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandelbrot, B. How Long Is the Coast of Britain? Statistical Self-Similarity and Fractional Dimension. Science 1967, 156, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, M.J. Fractals and the Analysis of Waveforms. Comput. Biol. Med. 1988, 18, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, T. Approach to an Irregular Time Series on the Basis of the Fractal Theory. Phys. Nonlinear Phenom. 1988, 31, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, Z.J.; Pham, T.; Chen, S.H.A.; Makowski, D. Brain Entropy, Fractal Dimensions and Predictability: A Review of Complexity Measures for EEG in Healthy and Neuropsychiatric Populations. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2022, 56, 5047–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Nuaimi, A.H.H.; Jammeh, E.; Sun, L.; Ifeachor, E. Higuchi Fractal Dimension of the Electroencephalogram as a Biomarker for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 11–15 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 2320–2324. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, C.; Hornero, R. Entropy and Complexity Analyses in Alzheimer’s Disease: An MEG Study. Open Biomed. Eng. J. 2010, 4, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, C.; Mediavilla, Á.; Hornero, R.; Abásolo, D.; Fernández, A. Use of the Higuchi’s Fractal Dimension for the Analysis of MEG Recordings from Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobukawa, S.; Yamanishi, T.; Nishimura, H.; Wada, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Takahashi, T. Atypical Temporal-Scale-Specific Fractal Changes in Alzheimer’s Disease EEG and Their Relevance to Cognitive Decline. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2019, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, F.M.; Porcaro, C.; Cottone, C.; Cancelli, A.; Rossini, P.M.; Tecchio, F. Electroencephalographic Fractal Dimension in Healthy Ageing and Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadlou, M.; Adeli, H.; Adeli, A. Fractality and a Wavelet-Chaos-Methodology for EEG-Based Diagnosis of Alzheimer Disease. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2011, 25, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; Mammone, N.; Morabito, F.C.; Marino, S.; Adeli, H. A Novel Methodology for Automated Differential Diagnosis of Mild Cognitive Impairment and the Alzheimer’s Disease Using EEG Signals. J. Neurosci. Methods 2019, 322, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staudinger, T.; Polikar, R. Analysis of Complexity Based EEG Features for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 2033–2036. [Google Scholar]
- Puri, D.V.; Nalbalwar, S.; Nandgaonkar, A.; Wagh, A. Alzheimer’s Disease Detection from Optimal EEG Channels and Tunable Q-Wavelet Transform. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2022, 25, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, K.J.; Brookshire, G.; Gerrol, S.; Quirk, C.; Lucero, C. Identifying and Differentiating Dementias with EEG Fractal Dimension Distributions. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, e079732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, K.J.; Brookshire, G.; Gerrol, S.; Quirk, C.; Lucero, C. Differential Diagnosis of Lewy Body Dementias Using Multivariate EEG Classifiers. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, e080264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-Mental State”. A Practical Method for Grading the Cognitive State of Patients for the Clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A Brief Screening Tool For Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, D.; Flynn, K.; Verret, L.; Poulin, S.; Bouchard, R.W.; Bocti, C.; Fülöp, T.; Lacombe, G.; Gauthier, S.; Nasreddine, Z.; et al. Multicenter Validation of an MMSE-MoCA Conversion Table. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 65, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langa, K.M.; Levine, D.A. The Diagnosis and Management of Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Clinical Review. JAMA 2014, 312, 2551–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accardo, A.; Affinito, M.; Carrozzi, M.; Bouquet, F. Use of the Fractal Dimension for the Analysis of Electroencephalographic Time Series. Biol. Cybern. 1997, 77, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, T.L.A.; Dugan, E.L.; Humphries, B.; Newton, R.U. Discriminating between Elderly and Young Using a Fractal Dimension Analysis of Centre of Pressure. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2004, 1, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajnsztejn, R.; de Carvalho, T.D.; Garner, D.M.; Raimundo, R.D.; Vanderlei, L.C.M.; Godoy, M.F.; Ferreira, C.; Valenti, V.E.; Abreu, L.C. de Higuchi Fractal Dimension Applied to RR Intervals in Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Hum. Growth Dev. 2016, 26, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wanliss, J.A.; Wanliss, G.E. Efficient Calculation of Fractal Properties via the Higuchi Method. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 109, 2893–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensen, A.; Khatami, R. Advanced EEG Analysis Using Threshold-Free Cluster-Enhancement and Non-Parametric Statistics. NeuroImage 2013, 67, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Nichols, T.E. Threshold-Free Cluster Enhancement: Addressing Problems of Smoothing, Threshold Dependence and Localisation in Cluster Inference. NeuroImage 2009, 44, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjur, T. Coefficients of Determination in Logistic Regression Models—A New Proposal: The Coefficient of Discrimination. Am. Stat. 2009, 63, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimesch, W. EEG Alpha and Theta Oscillations Reflect Cognitive and Memory Performance: A Review and Analysis. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 29, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herweg, N.A.; Solomon, E.A.; Kahana, M.J. Theta Oscillations in Human Memory. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2020, 24, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.E.; Gopakumar, K. Automated Diagnosis of Encephalopathy Using Fractal Dimensions of EEG Sub-Bands. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Recent Advances in Intelligent Computational Systems (RAICS), Thiruvananthapuram, India, 6–8 December 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, J.L. Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanseeuw, B.J.; Betensky, R.A.; Jacobs, H.I.L.; Schultz, A.P.; Sepulcre, J.; Becker, J.A.; Cosio, D.M.O.; Farrell, M.; Quiroz, Y.T.; Mormino, E.C.; et al. Association of Amyloid and Tau With Cognition in Preclinical Alzheimer Disease: A Longitudinal Study. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauterborn, J.C.; Scaduto, P.; Cox, C.D.; Schulmann, A.; Lynch, G.; Gall, C.M.; Keene, C.D.; Limon, A. Increased Excitatory to Inhibitory Synaptic Ratio in Parietal Cortex Samples from Individuals with Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, K.G.; Verma, P.; Cai, C.; Xie, X.; Kudo, K.; Gao, X.; Lerner, H.M.; Mizuiri, D.; Strom, A.; Iaccarino, L.; et al. Abnormal Neural Oscillations Depicting Excitatory-inhibitory Imbalance Are Distinctly Associated with Amyloid and Tau Depositions in Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, e055588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauwels, J.; Srinivasan, K.; Ramasubba Reddy, M.; Musha, T.; Vialatte, F.-B.; Latchoumane, C.; Jeong, J.; Cichocki, A. Slowing and Loss of Complexity in Alzheimer’s EEG: Two Sides of the Same Coin? Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 2011, 539621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akar, S.A.; Kara, S.; Latifoğlu, F.; Bilgiç, V. Investigation of the Noise Effect on Fractal Dimension of EEG in Schizophrenia Patients Using Wavelet and SSA-Based Approaches. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2015, 18, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Gómez, C.; Hornero, R.; López-Ibor, J.J. Complexity and Schizophrenia. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 45, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavendra, B.S.; Dutt, D.N.; Halahalli, H.N.; John, J.P. Complexity Analysis of EEG in Patients with Schizophrenia Using Fractal Dimension. Physiol. Meas. 2009, 30, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeti, M.; Katebi, S.; Boostani, R. Entropy and Complexity Measures for EEG Signal Classification of Schizophrenic and Control Participants. Artif. Intell. Med. 2009, 47, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshvarpour, A.; Goshvarpour, A. Schizophrenia Diagnosis Using Innovative EEG Feature-Level Fusion Schemes. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, M.; Päeske, L.; Kalev, K.; Aarma, K.; Lehtmets, A.; Ööpik, P.; Lass, J.; Hinrikus, H. Methods for Classifying Depression in Single Channel EEG Using Linear and Nonlinear Signal Analysis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 155, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čukić, M.; Stokić, M.; Radenković, S.; Ljubisavljević, M.; Simić, S.; Savić, D. Nonlinear Analysis of EEG Complexity in Episode and Remission Phase of Recurrent Depression. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 29, e1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, B.; Seyedsadjadi, R.; Babadi, B.; Noroozian, M. Brain Complexity Increases in Mania. NeuroReport 2005, 16, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, M.R.; Khaleghi, A.; Nasrabadi, A.M.; Rafieivand, S.; Begol, M.; Zarafshan, H. EEG Classification of ADHD and Normal Children Using Non-Linear Features and Neural Network. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2016, 6, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathi, A.S.; Glatt, R.M.; Bookheimer, T.H.; Popa, E.S.; Ingemanson, M.L.; Richards, C.J.; Hodes, J.F.; Pierce, K.P.; Slyapich, C.B.; Iqbal, F.; et al. Differentiation of Subjective Cognitive Decline, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Dementia Using qEEG/ERP-Based Cognitive Testing and Volumetric MRI in an Outpatient Specialty Memory Clinic. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 90, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).