Physicochemical Morphological Evaluation and Stability Assessment of Nanoemulsions Containing Nutrients for Parenteral Nutrition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of NEs
2.2.2. Dynamic Light Scattering
2.2.3. Electrophoretic Light Scattering
2.2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nanoemulsion for Parental Nutrition
3.2. Physicochemical Evaluation and Stability Assessment of the Nanoemulsions
3.3. Morphological Characterization of the Nanoemulsions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACD | Automated Compounding Device |
| CΜA | Critical Material Attribute |
| CQA | Critical Quality Attribute |
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| DLVO | Derjaguin–Landau–Verwey–Overbeek Theory |
| ICU | Intensive Care Units |
| NE | Nanoemulsions |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffer Saline |
| PDI | Polydispersity Index |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| UA | Uranyl Acetate |
References
- Singh, Y.; Meher, J.G.; Raval, K.; Khan, F.A.; Chaurasia, M.; Jain, N.K.; Chourasia, M.K. Nanoemulsion: Concepts, development and applications in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 252, 28–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, P.; Gulati, N.; Makhija, M.; Purohit, D.; Dureja, H. Nanoemulsion: A Novel Drug Delivery Approach for Enhancement of Bioavailability. Recent Patents Nanotechnol. 2020, 14, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasaz, S.; Morozova, K.; Ferrentino, G.; Scampicchio, M. Encapsulation of Lipid-Soluble Bioactives by Nanoemulsions. Molecules 2020, 25, 3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzayat, A.; Adam-Cervera, I.; Álvarez-Bermúdez, O.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Nanoemulsions for synthesis of biomedical nanocarriers. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2021, 203, 111764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, V.; Capozza, M.; Panza, R.; Laforgia, N.; Baldassarre, M.E. Macronutrients and Micronutrients in Parenteral Nutrition for Preterm Newborns: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anez-Bustillos, L.; Dao, D.T.; Baker, M.A.; Fell, G.L.; Puder, M.; Gura, K.M. Intravenous Fat Emulsion Formulations for the Adult and Pediatric Patient. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2016, 31, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Cui, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, C.; Cheng, Y. Optimizing parenteral nutrition to achieve an adequate weight gain according to the current guidelines in preterm infants with birth weight less than 1500 g: A prospective observational study. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Shen, W.; Yang, Q.; Lin, R.; Tang, L.-X.; Bai, R.-M.; Yang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Yu, W.-T.; et al. Analysis of risk factors for parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis in preterm infants: A multicenter observational study. BMC Pediatr. 2023, 23, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skouroliakou, M.; Kountouri, A.M.; Hatziantoniou, S.; Koutri, K.; Chiou, A. Physicochemical stability assessment of all-in-one parenteral emulsion for neonates containing SMOFlipid. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2012, 19, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boullata, J.I.; Mirtallo, J.M.; Sacks, G.S.; Salman, G.; Gura, K.; Canada, T.; Maguire, A. the ASPEN Parenteral Nutrition Safety Committee Parenteral nutrition compatibility and stability: A comprehensive review. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2021, 46, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papandreou, P.; Gioxari, A.; Ntountaniotis, D.; Korda, O.-N.; Skouroliakou, M.; Siahanidou, T. Administration of an Intravenous Fat Emulsion Enriched with Medium-Chain Triglyceride/ω-3 Fatty Acids is Beneficial Towards Anti-Inflammatory Related Fatty Acid Profile in Preterm Neonates: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suliman, A.S.; Tom, R.; Palmer, K.; Tolaymat, I.; Younes, H.M.; Arafat, B.; Elhissi, A.M.A.; Najlah, M. Development, characterization and stability evaluation of ciprofloxacin-loaded parenteral nutrition nanoemulsions. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2020, 25, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchoud, L.; Sadeghipour, F.; Klingmüller, M.; Fonzo-Christe, C.; Bonnabry, P. Long-term physico-chemical stability of standard parenteral nutritions for neonates. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 29, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skouroliakou, M.; Matthaiou, C.; Chiou, A.; Panagiotakos, D.; Gounaris, A.; Nunn, T.; Andrikopoulos, N. Physicochemical Stability of Parenteral Nutrition Supplied as All-in-One for Neonates. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2008, 32, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berne, B.J.; Pecora, R. Dynamic Light Scattering: With Applications to Chemistry, Biology, and Physics; Dover Publications Inc: Mineola, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, M.; Dalgleish, D.G. Dynamic Light Scattering Techniques and Their Applications in Food Science. Food Biophys. 2006, 1, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllopoulou, E.; Selianitis, D.; Pippa, N.; Gazouli, M.; Valsami, G.; Pispas, S. Development of Hybrid DSPC:DOPC:P(OEGMA950-DIPAEMA) Nanostructures: The Random Architecture of Polymeric Guest as a Key Design Parameter. Polymers 2023, 15, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.J. Zeta Potential in Colloid Science: Principles and Applications; Colloid science; New paperback edition; Academic Press: London, UK; San Diego, CA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima, H. Electrophoretic Mobility of a Spherical Colloidal Particle in a Salt-Free Medium. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 248, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pispas, I.; Spiliopoulos, N.; Papagiannopoulos, A. Biocompatible Preparation of Beta-Lactoglobulin/Chondroitin Sulfate Carrier Nanoparticles and Modification of Their Colloidal and Hydropathic Properties by Tween 80. Polymers 2024, 16, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, B.; Rhodes, C. Use of the Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, and Overbeek Theory to Interpret Pharmaceutical Suspension Stability. J. Pharm. Sci. 1970, 59, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumrey, M. Small angle x-ray scattering (SAXS). In Characterization of Nanoparticles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 173–183. ISBN 978-0-12-814182-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, K.P.; Elliott, G.R.; Robertson, H.; Kumar, A.; Wanless, E.J.; Webber, G.B.; Craig, V.S.J.; Andersson, G.G.; Page, A.J. Understanding specific ion effects and the Hofmeister series. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 12682–12718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Eral, H.B.; Hatton, T.A.; Doyle, P.S. Nanoemulsions: Formation, properties and applications. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 2826–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishard, A.; Gibb, B.C. Dynamic light scattering – an all-purpose guide for the supramolecular chemist. Supramol. Chem. 2019, 31, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabín, J.; Prieto, G.; Messina, P.V.; Ruso, J.M.; Hidalgo-Alvarez, R.; Sarmiento, F. On the Effect of Ca2+ and La3+ on the Colloidal Stability of Liposomes. Langmuir 2005, 21, 10968–10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabın, J.; Prieto, G.; Ruso, J.M.; Hidalgo-Álvarez, R.; Sarmiento, F. Size and stability of liposomes: A possible role of hydration and osmotic forces. Eur. Phys. J. E 2006, 20, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabın, J.; Prieto, G.; Ruso, J.M.; Sarmiento, F. Fractal aggregates induced by liposome-liposome interaction in the presence of Ca2+. Eur. Phys. J. E 2007, 24, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzetto, G.; Barzan, D.; Marzaro, G.; Pigozzo, S.; Valenti, A. One-chamber and two-chamber parenteral nutrition admixtures for pediatric and adult patients: An evaluation of physico-chemical stability at room and cold temperature. Nutrition 2022, 106, 111891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boullata, J.I.; Gilbert, K.; Sacks, G.; Labossiere, R.J.; Crill, C.; Goday, P.; Kumpf, V.J.; Mattox, T.W.; Plogsted, S.; Holcombe, B.; et al. A.S.P.E.N. Clinical Guidelines. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 334–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klang, V.; Matsko, N.B.; Valenta, C.; Hofer, F. Electron microscopy of nanoemulsions: An essential tool for characterisation and stability assessment. Micron 2012, 43, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grapentin, C.; Barnert, S.; Schubert, R.; Bansal, V. Monitoring the Stability of Perfluorocarbon Nanoemulsions by Cryo-TEM Image Analysis and Dynamic Light Scattering. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0130674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Morrison, E.D.; Frethem, C.D.; Zasadzinski, J.A.; McCormick, A.V. Cryogenic Electron Microscopy Study of Nanoemulsion Formation from Microemulsions. Langmuir 2014, 30, 10826–10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

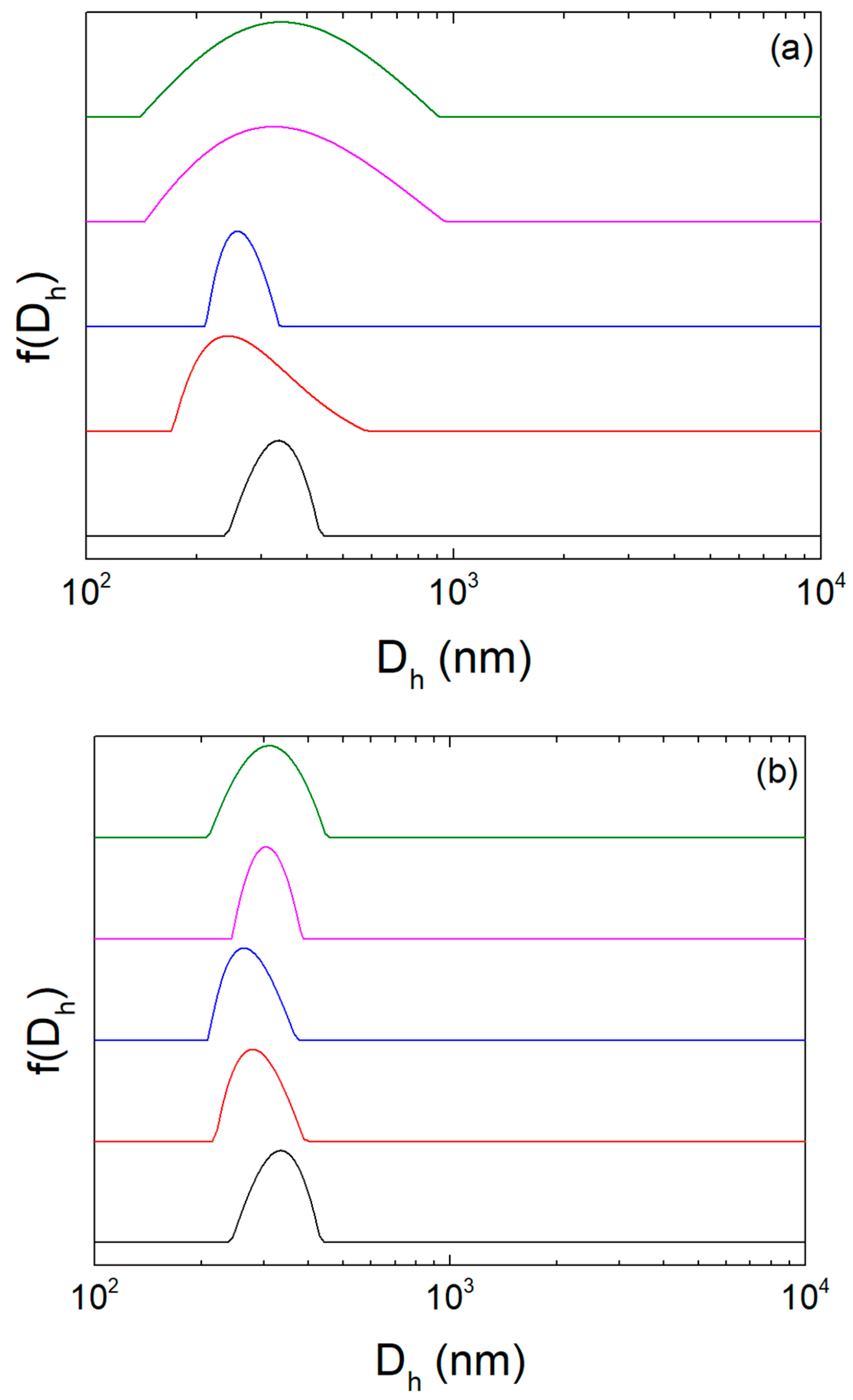
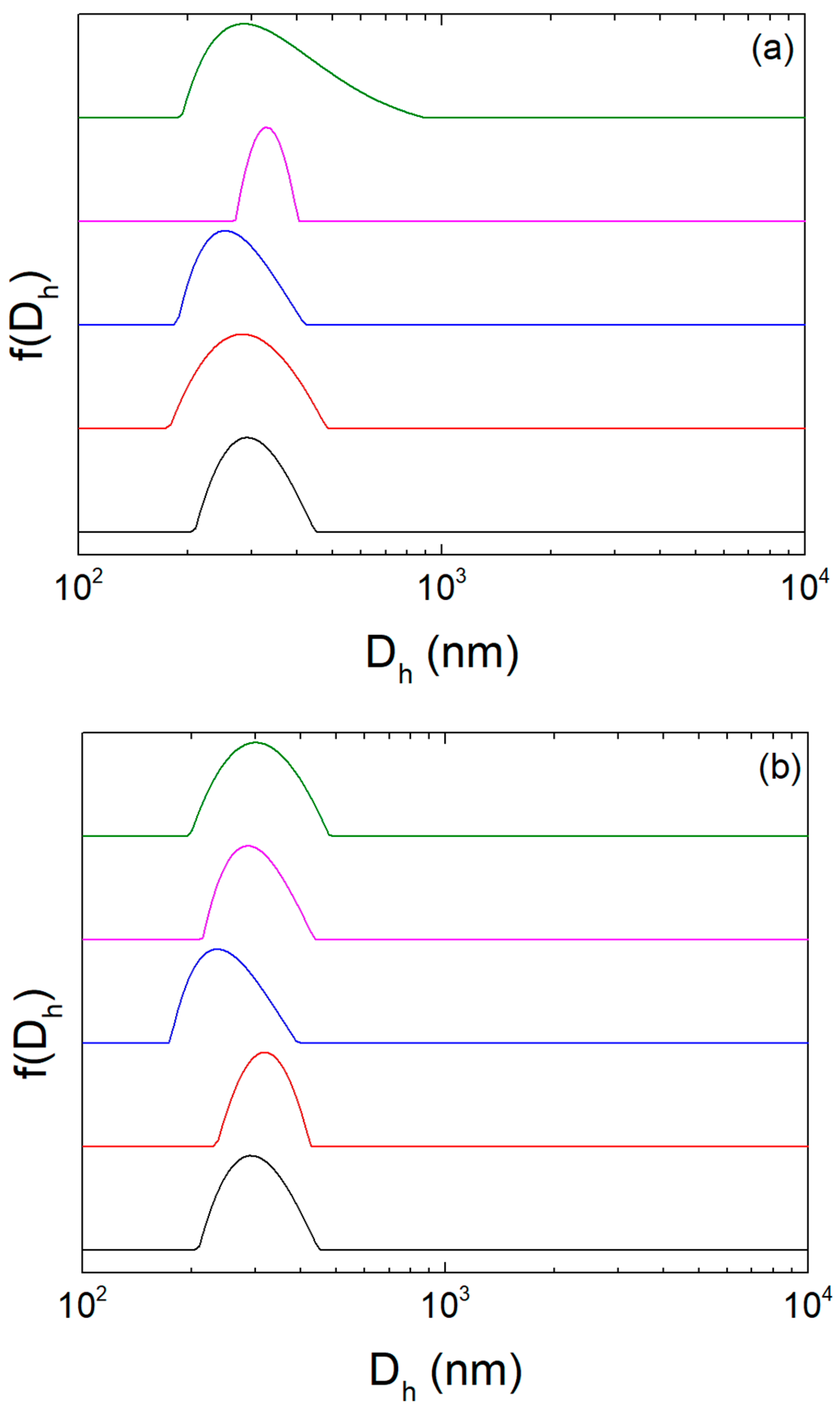


| Ingredient | Amount (mL) |
|---|---|
| Calcium gluconate 10% | 3.85 |
| Glucose 10% | 135.74 |
| Glucose 35% | 24.06 |
| Glycophos | 2.03 |
| MgSO4∙7H2O 25% | 0.15 |
| Peritrace | 1.35 |
| Potassium chloride 10% | 6.44 |
| SMOFlipid 200 mg/mL | 16.92 |
| Sodium chloride15% | 5.35 |
| Soluvit | 0.18 |
| Vamin Infant | 57.00 |
| Vitalipid Infant | 0.54 |
| Ingredient | Amount (mL) |
|---|---|
| Calcium gluconate 10% | 6.32 |
| Glucose 10% | 111.24 |
| Glucose 35% | 77.92 |
| Glycophos | 2.78 |
| MgSO4∙7H2O 25% | 1.39 |
| Peritrace | 5.25 |
| Potassium chloride 10% | 4.15 |
| SMOFlipid 200 mg/mL | 27.83 |
| Sodium chloride 15% | 2.17 |
| Soluvit | 5.25 |
| Vamin Infant | 170.44 |
| Vitalipid Infant | 5.25 |
| Amino Acids | Glucose | Fat | Energy | Non-Protein Energy | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g | g/kg | kcal | G | g/kg | kcal | g | g/kg | kcal | kcal | kcal/kg | kcal | |
| Parental nutrition | 3.72 | 0.12 | 14.89 | 22.00 | 0.73 | 74.79 | 3.38 | 0.11 | 30.46 | 120.13 | 4.00 | 105.24 |
| Micronutrients and Additives | Value per Bag | Value per kg | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca2+ | 1.69 | mEq | 0.06 | mEq/kg |
| Trace elements | 1.35 | mL | 0.05 | mL/kg |
| K+ | 8.63 | mEq | 0.29 | mEq/kg |
| Lipophilic vitamins | 0.54 | mL | 0.02 | mL/kg |
| Mg2+ | 0.30 | mEq | 0.01 | mEq/kg |
| Na+ | 17.77 | mEq | 0.59 | mEq/kg |
| Water-soluble vitamins | 0.18 | mL | 0.01 | mL/kg |
| PHO4− | 2.03 | mmol | 0.07 | mmol/kg |
| Amino Acids | Glucose | Fat | Energy | Non-Protein Energy | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g | g/kg | kcal | g | g/kg | kcal | g | g/kg | kcal | kcal | kcal/kg | kcal | |
| Parental nutrition | 10.60 | 3.53 | 42.40 | 47.70 | 15.90 | 162.18 | 5.30 | 1.77 | 47.70 | 252.28 | 84.09 | 209.88 |
| Micronutrients and Additives | Value per Bag | Value per kg | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca2+ | 2.65 | mEq | 0.88 | mEq/kg |
| Trace elements | 5.00 | mL | 1.67 | mL/kg |
| K+ | 5.30 | mEq | 1.77 | mEq/kg |
| Lipophilic vitamins | 5.00 | mL | 1.67 | mL/kg |
| Mg2+ | 2.65 | mEq | 0.88 | mEq/kg |
| Na+ | 10.60 | mEq | 3.53 | mEq/kg |
| Water-soluble vitamins | 5.00 | mL | 1.67 | mL/kg |
| PHO4− | 2.65 | mmol | 0.88 | mmol/kg |
| Sodium chloride 15% | 2.17 mL (In the bag) | |||
| Soluvit | 5.25 mL (In the bag) | |||
| Vamin Infant | 170.44 mL (In the bag) | |||
| Vitalipid Infant | 5.25 mEq (In the bag) | |||
| Sample | Diluent | Dh (nm) | PDI | ζ-Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HPLC grade water | 328 | 0.1 | −36 |
| 2 | HPLC grade water | 299 | 0.1 | −33 |
| 1 | PBS | 299 | 0.1 | - |
| 2 | PBS | 309 | 0.132 | - |
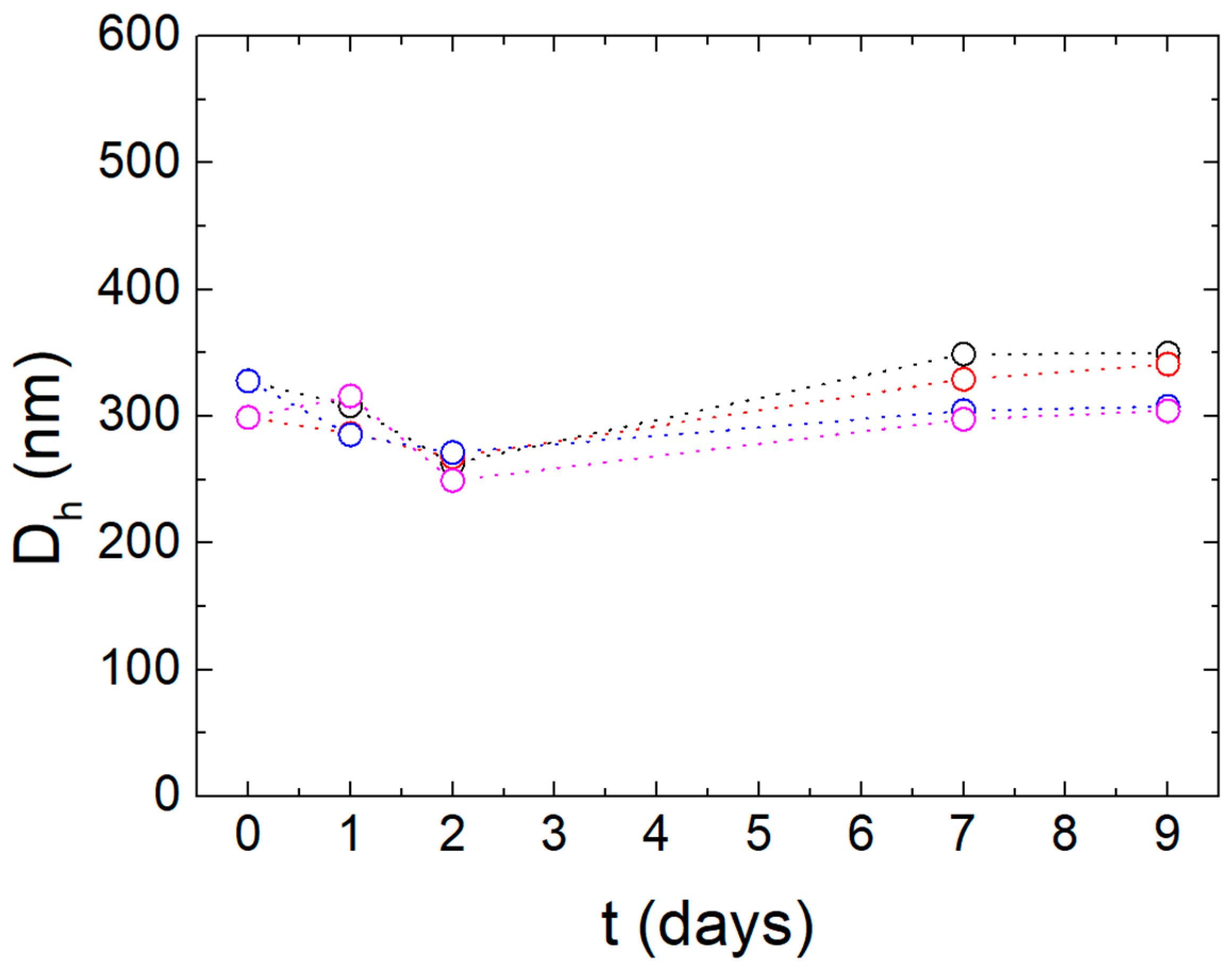
| Sample | Storage Conditions | Time from Preparation (Days) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 9 | |||||||
| Dh | PDI | Dh | PDI | Dh | PDI | Dh | PDI | Dh | PDI | ||
| 1 | 25 °C | 328 | 0.1 | 308 | 0.2 | 263 | 0.2 | 349 | 0.2 | 350 | 0.2 |
| 4 °C | - | - | 285 | 0.1 | 271 | 0.1 | 304 | 0.1 | 308 | 0.1 | |
| 2 | 25 °C | 299 | 0.1 | 286 | 0.1 | 268 | 0.1 | 329 | 0.1 | 341 | 0.2 |
| 4 °C | - | - | 316 | 0.1 | 249 | 0.2 | 298 | 0.1 | 304 | 0.1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papandreou, P.; Triantafyllopoulou, E.; Pispas, I.; Havaki, S.; Papagiannopoulos, A.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Pippa, N. Physicochemical Morphological Evaluation and Stability Assessment of Nanoemulsions Containing Nutrients for Parenteral Nutrition. Colloids Interfaces 2025, 9, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9050064
Papandreou P, Triantafyllopoulou E, Pispas I, Havaki S, Papagiannopoulos A, Gorgoulis VG, Pippa N. Physicochemical Morphological Evaluation and Stability Assessment of Nanoemulsions Containing Nutrients for Parenteral Nutrition. Colloids and Interfaces. 2025; 9(5):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9050064
Chicago/Turabian StylePapandreou, Panos, Efstathia Triantafyllopoulou, Ioannis Pispas, Sophia Havaki, Aristeidis Papagiannopoulos, Vassilis G. Gorgoulis, and Natassa Pippa. 2025. "Physicochemical Morphological Evaluation and Stability Assessment of Nanoemulsions Containing Nutrients for Parenteral Nutrition" Colloids and Interfaces 9, no. 5: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9050064
APA StylePapandreou, P., Triantafyllopoulou, E., Pispas, I., Havaki, S., Papagiannopoulos, A., Gorgoulis, V. G., & Pippa, N. (2025). Physicochemical Morphological Evaluation and Stability Assessment of Nanoemulsions Containing Nutrients for Parenteral Nutrition. Colloids and Interfaces, 9(5), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9050064









