Interactions in Lidocaine-Carboxylic Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Implications for Cobalt Extraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. HDES Preparation
2.3. Investigation of HDES Physicochemical Properties and Intermolecular Interactions
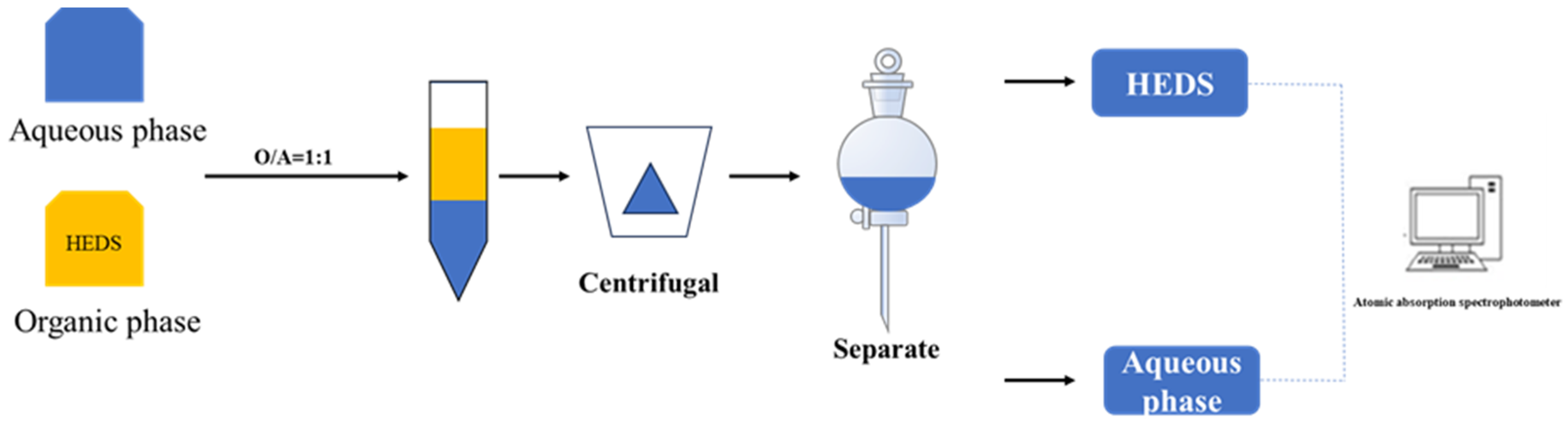
2.4. Extraction Experiment
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of HDES
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of HDES
3.2.1. Density of HDES
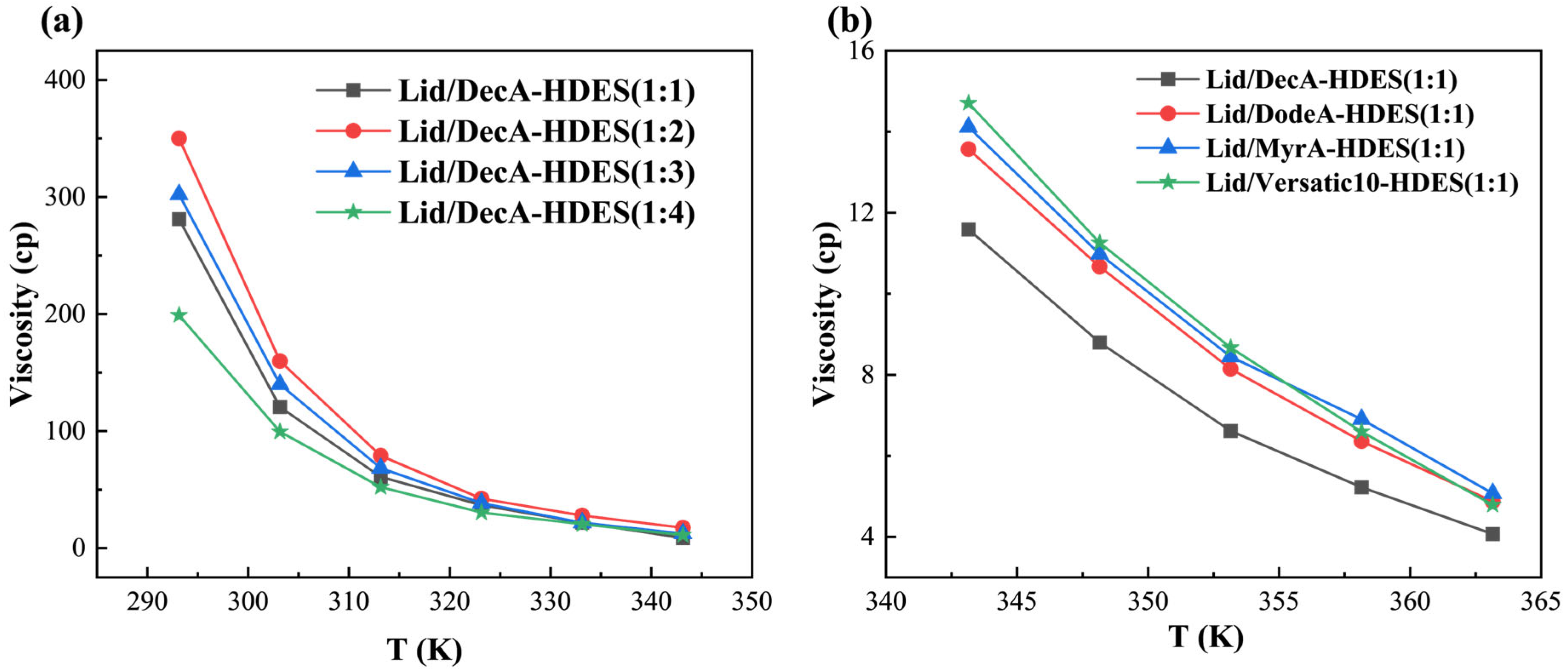
3.2.2. Viscosity of HDES
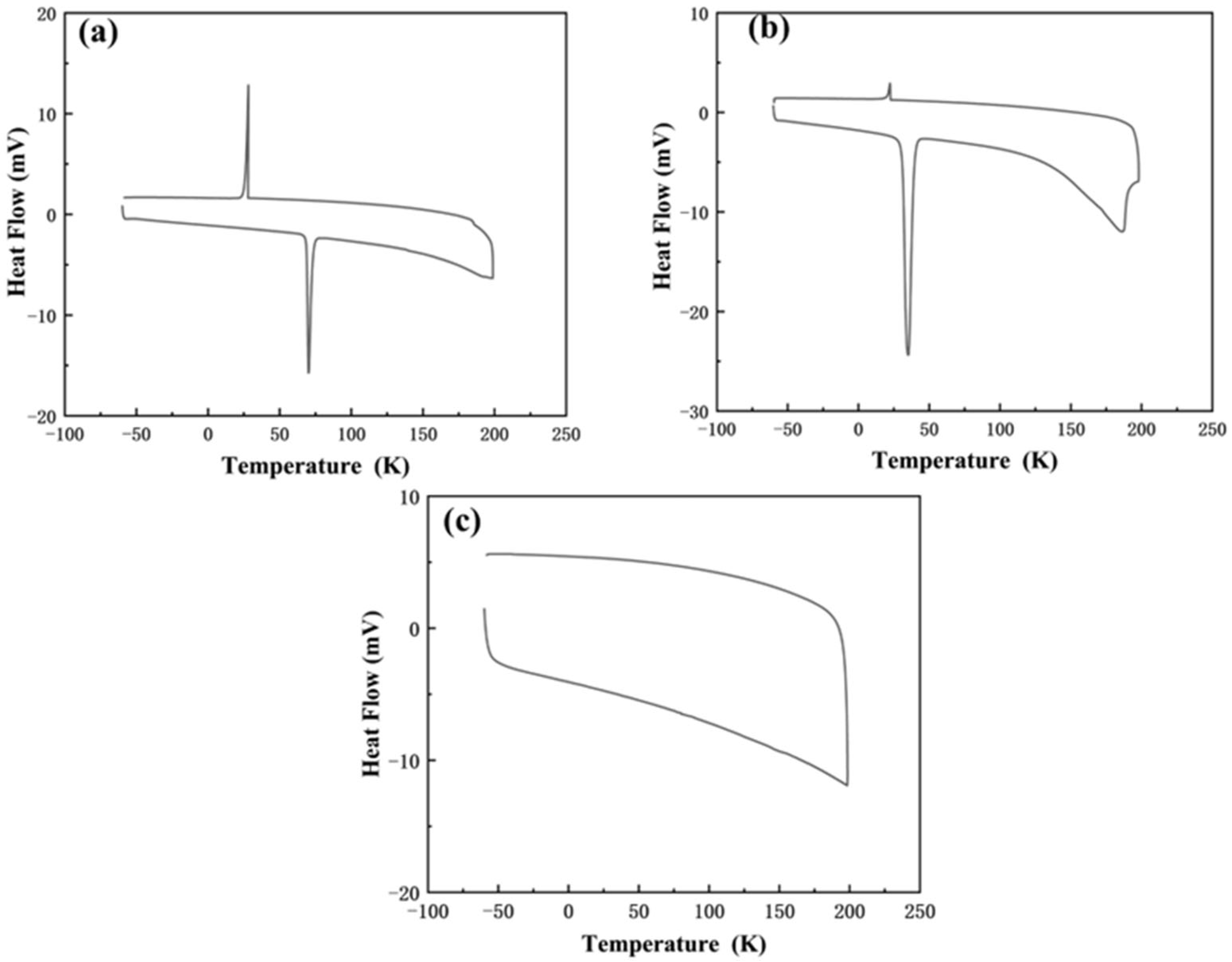
3.2.3. Thermal Stability of HDES
3.3. Investigation of Intermolecular Interactions in HDES
3.3.1. Excess Molar Volume
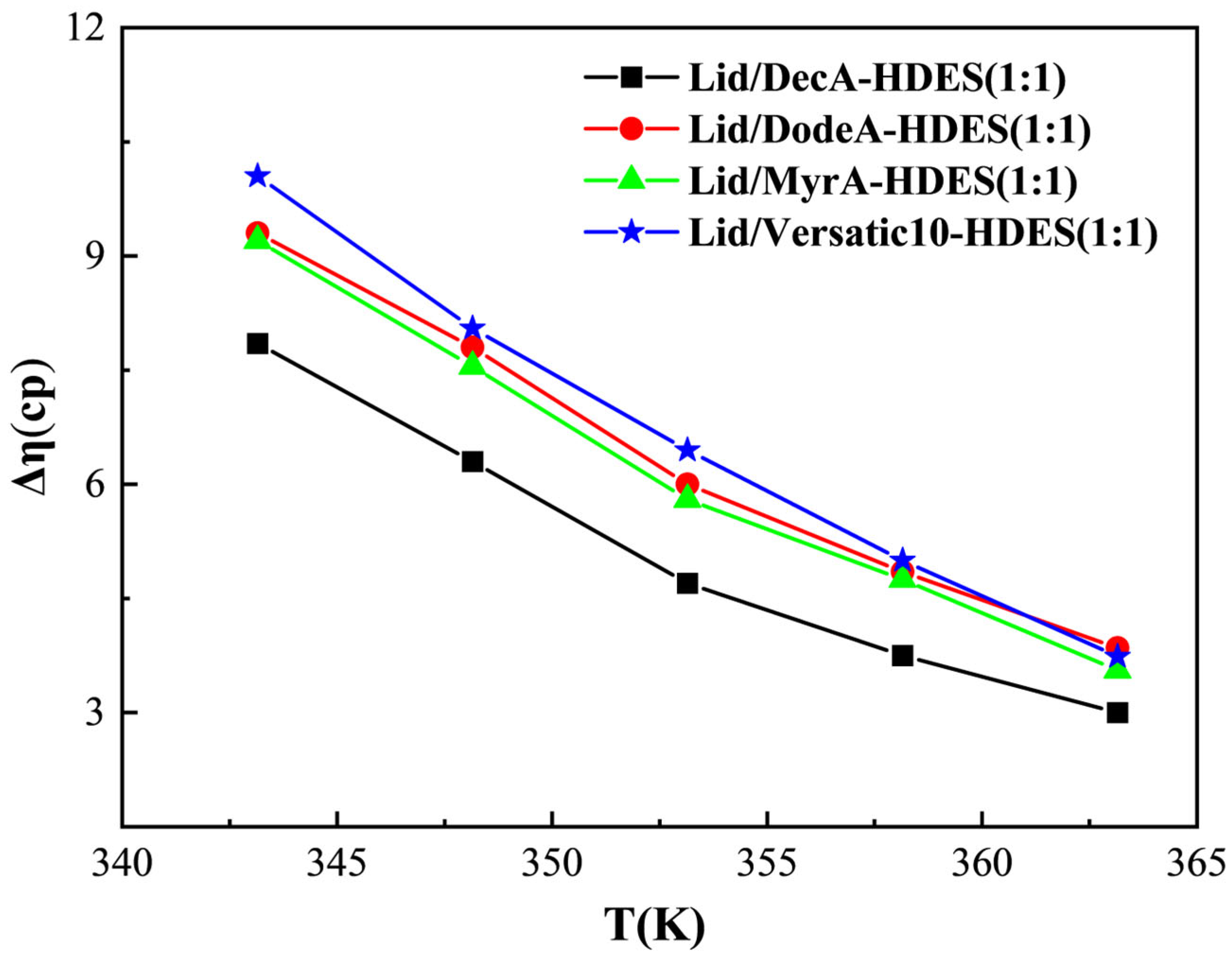
3.3.2. Viscosity Deviation and Interaction Force Parameters
3.3.3. FT-IR Analysis
3.3.4. NMR Analysis
3.4. Study on HDES Extraction of Cobalt from Aqueous Phase
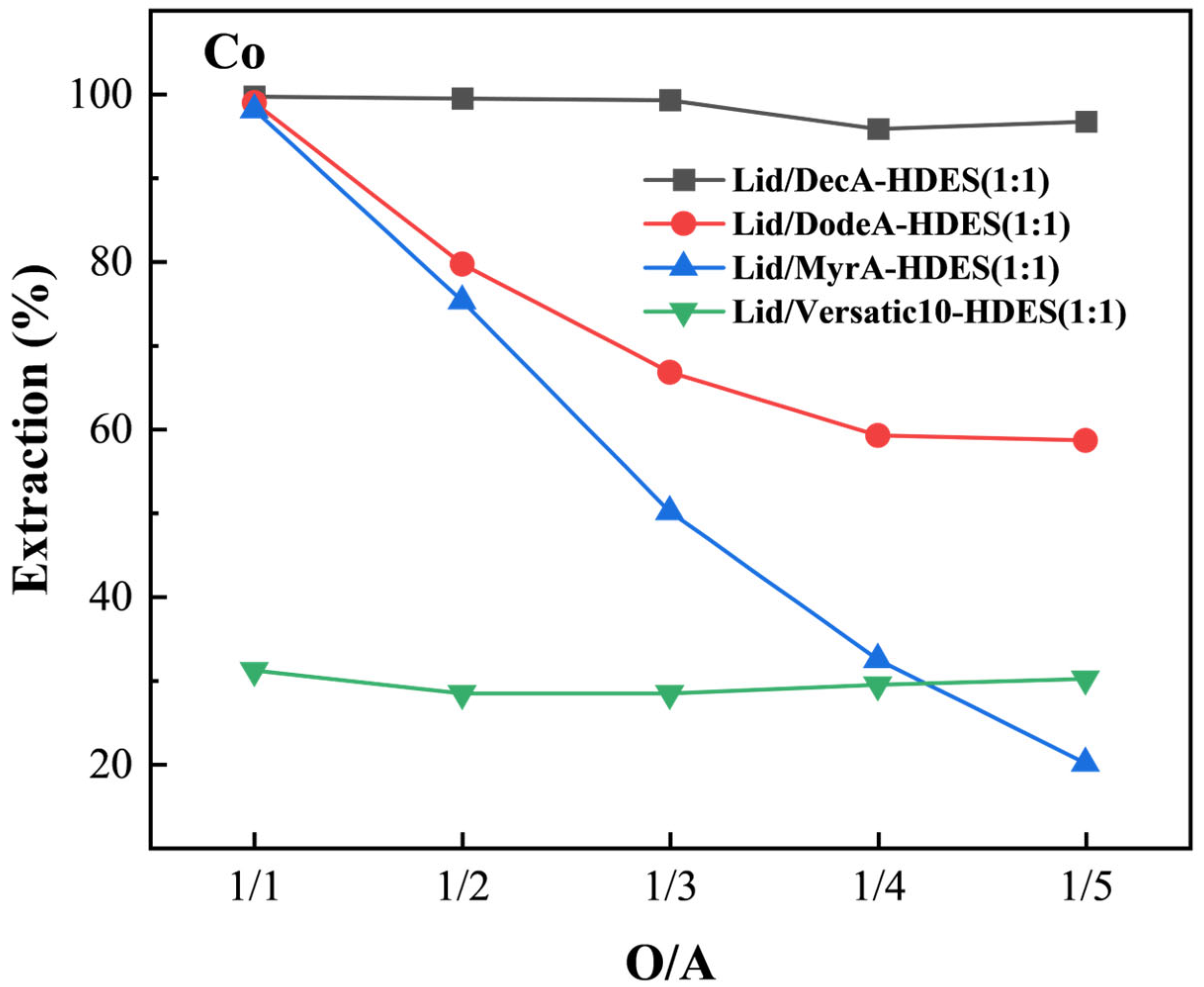
3.4.1. Effect of Hydrogen Bond Donor on HDES Extraction of Cobalt
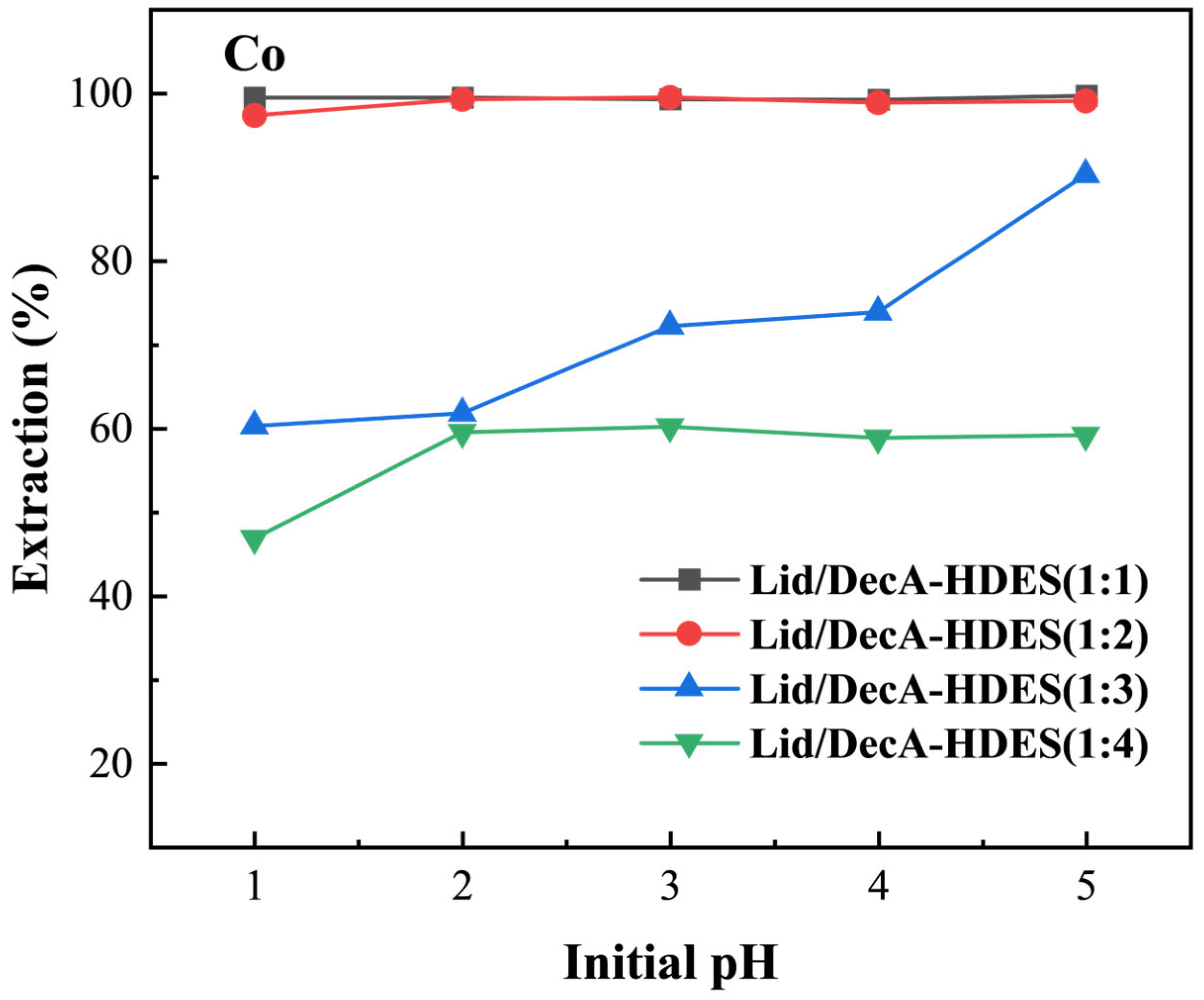
3.4.2. HBA Molar Ratio on HDES Extraction of Cobalt
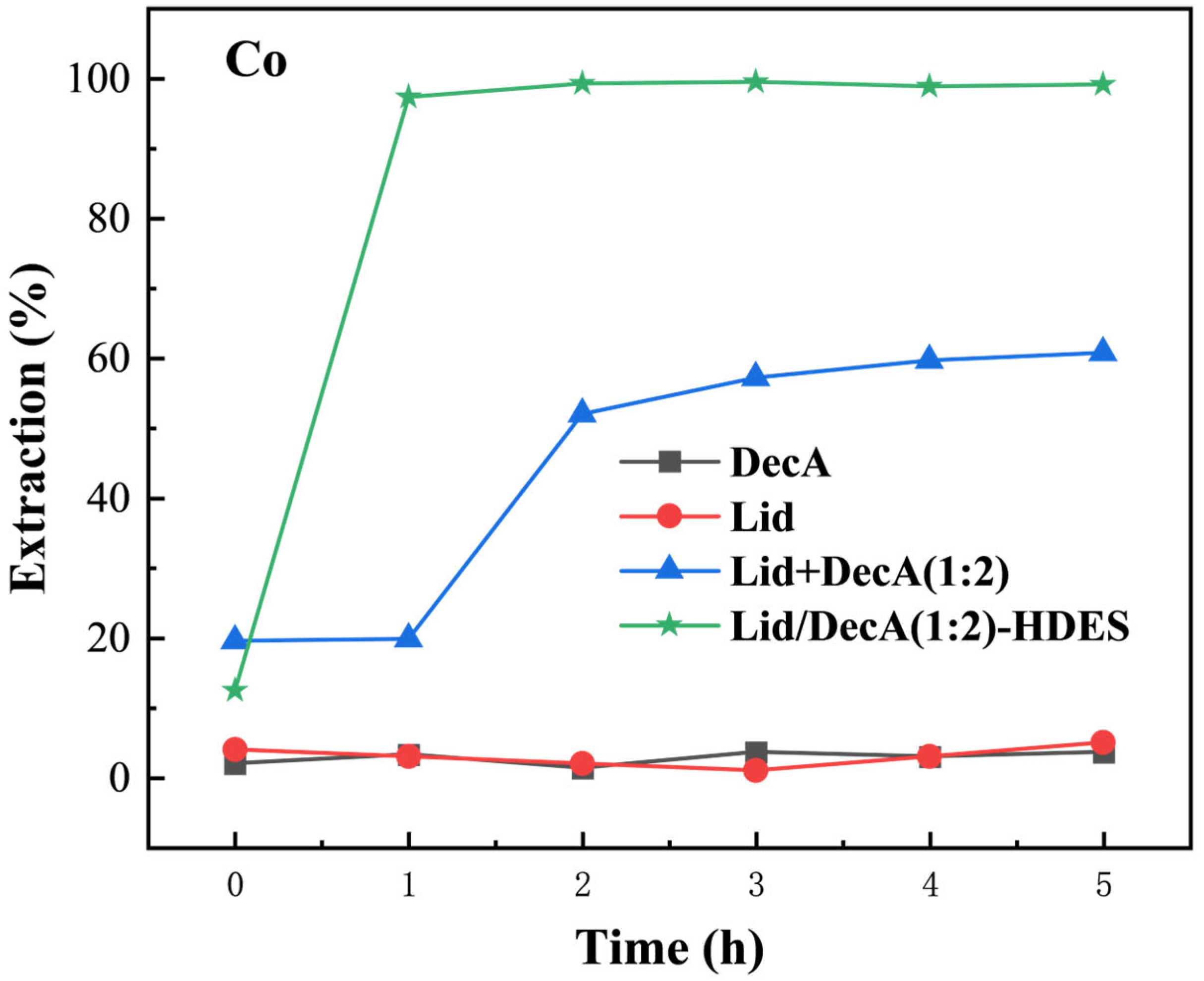
3.4.3. Regeneration Performance of HDES
3.4.4. Comparison of HDES Extraction Systems with Conventional Extraction Systems
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słupek, P.E.; Gębicki, J. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents in microextraction techniques—A review. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104384. [Google Scholar]
- Azmi, S.; Koudahi, M.F.; Frackowiak, E. Reline deep eutectic solvent as a green electrolyte for electrochemical energy storage applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 1156–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavi, P.G.; Altimari, P.; Branchi, M.; Zanoni, R.; Simonetti, G.; Navarra, M.A.; Pagnanelli, F. Selective recovery of cobalt from mixed lithium ion battery wastes using deep eutectic solvent. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal-Abidin, M.H.; Hayyan, M.; Wong, W.F. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: Current progress and future directions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 97, 142–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhune, A.; Dey, R. Green and sustainable solvents of the future: Deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 379, 121676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achkar, T.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fourmentin, S. Basics and properties of deep eutectic solvents: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Munro, H.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Preparation of novel, moisture-stable, Lewis-acidic ionic liquids containing quaternary ammonium salts with functional side chains. Chem. Commun. 2001, 19, 2010–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.Y.; Chislov, M.V.; Nechaeva, D.V.; Moskvin, L.N.; Bulatov, A.V. A new approach for microextraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from human urine samples based on in-situ deep eutectic mixture formation. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Osch, D.J.; Zubeir, L.F.; Van Den Bruinhorst, A.; Rocha, M.A.; Kroon, M.C. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as water-immiscible extractants. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4518–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, M.; Ghassab, N.; Hemmati, M.; Asghari, A. Emulsification microextraction of amphetamine and methamphetamine in complex matrices using an up-to-date generation of eco-friendly and relatively hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. J. Chromatogr. A. 2018, 1576, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, M.; Moral, R.; Thakuria, S.; Mitra, A.; Paul, S. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as greener substitutes for conventional extraction media: Examples and techniques. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 9702–9728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tereshatov, E.E.; Boltoeva, M.Y.; Folden, C.M. First evidence of metal transfer into hydrophobic deep eutectic and low-transition-temperature mixtures: Indium extraction from hydrochloric and oxalic acids. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 4616–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milevskii, N.; Zinov’eva, I.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.J.H. Separation of Li (I), Co (II), Ni (II), Mn (II), and Fe (III) from hydrochloric acid solution using a menthol-based hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 207, 105777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, K.q.A.; Rocha, F.R.; Hespanhol, M.C.J.A.S.C. Engineering, Greener route for recovery of high-purity lanthanides from the waste of nickel metal hydride battery using a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 6169–6181. [Google Scholar]
- Peeters, N.; Binnemans, K.; Riaño, S. Solvometallurgical recovery of cobalt from lithium-ion battery cathode materials using deep-eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 4210–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xue, K.; Zhu, W.; Fan, D.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhu, Z.; Cui, P. Cobalt recovery from lithium battery leachate using hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: Performance and mechanism. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 190, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, E.; Safari, H.; Rezaee, M.; Rezaei, A.; Abdollahi, H. An environmentally friendly method for extraction of cobalt and molybdenum from spent catalysts using deep eutectic solvents (DESs). Env. Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023, 30, 90243–90255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylak, M.; Koksal, M. Deep eutectic solvent microextraction of lead(II), cobalt(II), nickel(II) and manganese(II) ions for the separation and preconcentration in some oil samples from Turkey prior to their microsampling flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Osch, D.J.; Parmentier, D.; Dietz, C.H.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Tuinier, R.; Kroon, M.C. Removal of alkali and transition metal ions from water with hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11987–11990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ola, P.D.; Matsumoto, M. Use of deep eutectic solvent as extractant for separation of Fe (III) and Mn (II) from aqueous solution. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 54, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaibuna, M.; Padinhattath, S.P.; Gardas, R.L. Efficient removal of multiple heavy metal ions from wastewater using task-specific hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: A circular approach. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 416, 126487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchel, M.; Rayaroth, M.P.; Wang, C.; Kong, L.; Khan, J.A.; Boczkaj, G. Hydrophobic (deep) eutectic solvents (HDESs) as extractants for removal of pollutants from water and wastewater–a review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 475, 144971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Su, E. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: The new generation of green solvents for diversified and colorful applications in green chemistry. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Quest for Green-Solvent Design: From Hydrophilic to Hydrophobic (Deep) Eutectic Solvents. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.-N.; Pauli, G.F. Natural deep eutectic solvents: Properties, applications, and perspectives. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A.; Hernández, A.; Khan, A.Y.; Ahmed, S. Physicochemical properties of deep eutectic solvent choline chloride: Propionic acid (ChCl/PA DES) and its binary solutions with 1-butanol as cosolvent. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 425, 127217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, N.; Nain, A.K. Volumetric, ultrasonic, viscometric and refractive index studies of molecular interactions in binary mixtures of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate with methyl acrylate at temperatures from 293.15 to 318.15 K. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 111890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, X.; He, N.; Song, F.; Zhang, X. Physical absorption and thermodynamic modeling of CO2 in new deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 402, 124752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijardar, S.P.; Singh, V.; Gardas, R.L. Revisiting the physicochemical properties and applications of deep eutectic solvents. Molecules 2022, 27, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Flammia, V.; Carvalho, T.; Viciosa, M.T.; Dionísio, M.; Barreiros, S.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Paiva, A. Properties and thermal behavior of natural deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, M.R.; Lima, A.S.; de Almeida Ribeiro Oliveira, G.; Liao, L.M.; Franceschi, E.; Silva, R.d.; Cardozo-Filho, L. Choline Chloride- and Organic Acids-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Exploring Chemical and Thermophysical Properties. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2024, 69, 3403–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarghampour, A.; Jafari, P.; Rahimpour, E.; Jouyban, A. Thermodynamic investigation on the aqueous mixtures of choline chloride/propylene glycol deep eutectic solvent at T = (293.15 to 313.15) K. BMC Chem. 2024, 18, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Alavianmehr, M.M.; Moghadasi, J. Transport properties of pure and mixture of ionic liquids from new rough hard-sphere-based model. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2016, 429, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, N.; Kumar Nain, A. Physicochemical studies of intermolecular interactions in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate + benzonitrile binary mixtures at temperatures from 293.15 to 318.15 K. Phys. Chem. Liq. 2020, 59, 358–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, N.; Nain, A.K. Densities, Ultrasonic Speeds, Viscosities, Refractive Indices, and Excess Properties of 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate + N-Methylacetamide Binary Mixtures at Different Temperatures. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 2020, 65, 1447–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidi, E.; Bakhshi, H. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents characterization and performance for efficient removal of heavy metals from aqueous media. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 57, 104680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Li, H.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, W.; Wang, C.; Wu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H. Vibrational analysis and formation mechanism of typical deep eutectic solvents: An experimental and theoretical study. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2016, 68, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Oliveira, F.S.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Fernandes, A.M.; Marrucho, I.M. Insights into the Synthesis and Properties of Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Cholinium Chloride and Carboxylic Acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wei, L.; Ren, P.; Mu, T. Efficient Dissolution of Lithium-Ion Batteries Cathode LiCoO2 by Polyethylene Glycol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents at Mild Temperature. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 11713–11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, A.; Sanjuan, A.; Bou-Ali, M.M.; Alonso, R.M.; Campanero, M.A. Physicochemical characterization of hydrophobic type III and type V deep eutectic solvents based on carboxylic acids. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 392, 123431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.; Mishra, S. Deep eutectic solvents: Physico-chemical properties and their use for recovery of metal values from waste products. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 390, 123070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






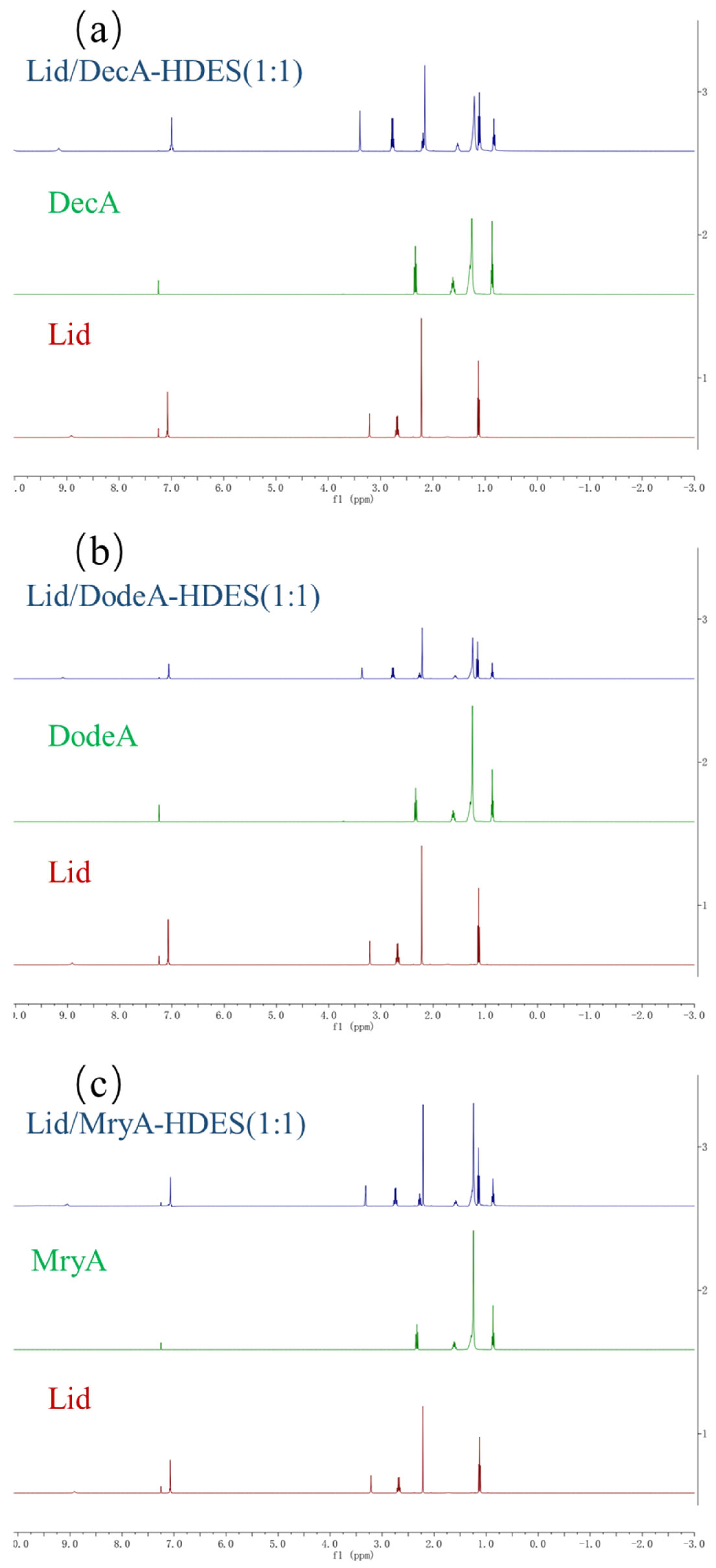
| HBA/HBD Composition | Target Metal Ion(s) | Extraction Medium | Extraction Efficiency | Study/Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aliquat336/L-menthol (3:7) | Fe3+ Mn2+ Co2+ | HCl solution | ~99% | Milevskii et al. [14] |
| TOPO/Decanoic acid | La3+ Ce3+ | Battery acid leachate | 96–98% | Cruz et al. [15] |
| Choline chloride/Citric acid (2:1) | Co2+ | LiCoO2 | 98% | Peeters et al. [16] |
| Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate/1-butanol (2:1) | Co2+ | HCl solution | 95.64% | Liu et al. [17] |
| Polyethylene glycol 400/p-Toluene sulfonic acid (1:1) | Co2+ Mo2+ | Spent catalyst | 93% of Co/87% of Mo | Ebrahimi et al. [18] |
| Choline chloride/Urea (1:2) | Pb2+ Co2+ Ni2+ Mn2+ | Oil samples | >95% | Soylak et al. [19] |
| Abbreviation | HBA | HBD | HBD:HBA Molar Ratio | Phase State at Room Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lid/DecA-HDES(1:1) | Lidocaine (Lid) | Decanoic acid (DecA) | 1:1 | Homogeneous transparent liquid |
| Lid/DecA-HDES(1:2) | Decanoic acid (DecA) | 1:2 | Homogeneous transparent liquid | |
| Lid/DecA-HDES(1:3) | Decanoic acid (DecA) | 1:3 | Homogeneous transparent liquid | |
| Lid/DecA-HDES(1:4) | Decanoic acid (DecA) | 1:4 | Homogeneous transparent liquid | |
| Lid/DodeA-HDES(1:1) | Dodecanoic acid (DodeA) | 1:1 | Homogeneous transparent liquid | |
| Lid/DodeA-HDES(1:2) | Dodecanoic acid (DodeA) | 1:2 | Homogeneous transparent liquid | |
| Lid/DodeA-HDES(1:3) | Dodecanoic acid (DodeA) | 1:3 | Gel-like | |
| Lid/DodeA-HDES(1:4) | Dodecanoic acid (DodeA) | 1:4 | Gel-like | |
| Lid/MyrA-HDES(1:1) | Myristic acid (MyrA) | 1:1 | Homogeneous transparent liquid | |
| Lid/MyrA-HDES(1:2) | Myristic acid (MyrA) | 1:2 | Gel-like | |
| Lid/MyrA-HDES(1:3) | Myristic acid (MyrA) | 1:3 | Gel-like | |
| Lid/MyrA-HDES(1:4) | Myristic acid (MyrA) | 1:4 | Gel-like | |
| Lid/Versatic10-HDES(1:1) | Versatic 10 (Versatic10) | 1:1 | Homogeneous transparent liquid |
| A/O | Equilibrium pH | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lid/DecA-HDES(1:1) | Lid/DodeA-HDES(1:1) | Lid/MyrA-HDES(1:1) | Lid/Versatic10-HDES(1:1) | |
| 1 | 6.61 | 6.62 | 6.44 | 2.26 |
| 2 | 6.41 | 5.72 | 5.42 | 0.74 |
| 4 | 6.21 | 5.6 | 5.21 | 0.75 |
| 4 | 6.04 | 5.52 | 4.14 | 0.82 |
| 5 | 5.89 | 5.2 | 2.1 | 0.86 |
| pH | Equilibrium pH | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lid/DecA-HDES(1:1) | Lid/DecA-HDES(1:2) | Lid/DecA-HDES(1:3) | Lid/DecA-HDES(1:4) | |
| 1 | 6.4 | 6.17 | 5.25 | 4.56 |
| 2 | 6.45 | 6.48 | 5.44 | 5.05 |
| 4 | 6.61 | 6.41 | 5.47 | 5.24 |
| 4 | 6.58 | 6.46 | 5.62 | 5.40 |
| 5 | 6.60 | 6.46 | 5.74 | 5.48 |
| Lid/DecA-HDES(1:1) | Lid/DecA-HDES(1:2) | Lid/DecA-HDES(1:3) | Lid/DecA-HDES(1:4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extraction/% | 99.74 | 99.61 | 92.11 | 60.41 |
| Stripping/% | 27.46 | 76.21 | 84.4 | 90.85 |
| Regeneration/% | 99.44 | 98.98 | 91.24 | 59.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Z.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Qu, C.; Wang, X.; Cong, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L. Interactions in Lidocaine-Carboxylic Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Implications for Cobalt Extraction. Colloids Interfaces 2025, 9, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9030040
Dong Z, Zhang R, Chen J, Qu C, Wang X, Cong C, Liu Y, Wang L. Interactions in Lidocaine-Carboxylic Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Implications for Cobalt Extraction. Colloids and Interfaces. 2025; 9(3):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9030040
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Zaichao, Rong Zhang, Jiyan Chen, Chenghao Qu, Xin Wang, Chen Cong, Yang Liu, and Lingyun Wang. 2025. "Interactions in Lidocaine-Carboxylic Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Implications for Cobalt Extraction" Colloids and Interfaces 9, no. 3: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9030040
APA StyleDong, Z., Zhang, R., Chen, J., Qu, C., Wang, X., Cong, C., Liu, Y., & Wang, L. (2025). Interactions in Lidocaine-Carboxylic Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents: Implications for Cobalt Extraction. Colloids and Interfaces, 9(3), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9030040







