Development of PSL-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PSL-Loaded PLGA NPs Formulation
2.3. Evaluation of Physical Properties of PSL-Loaded PLGA NPs
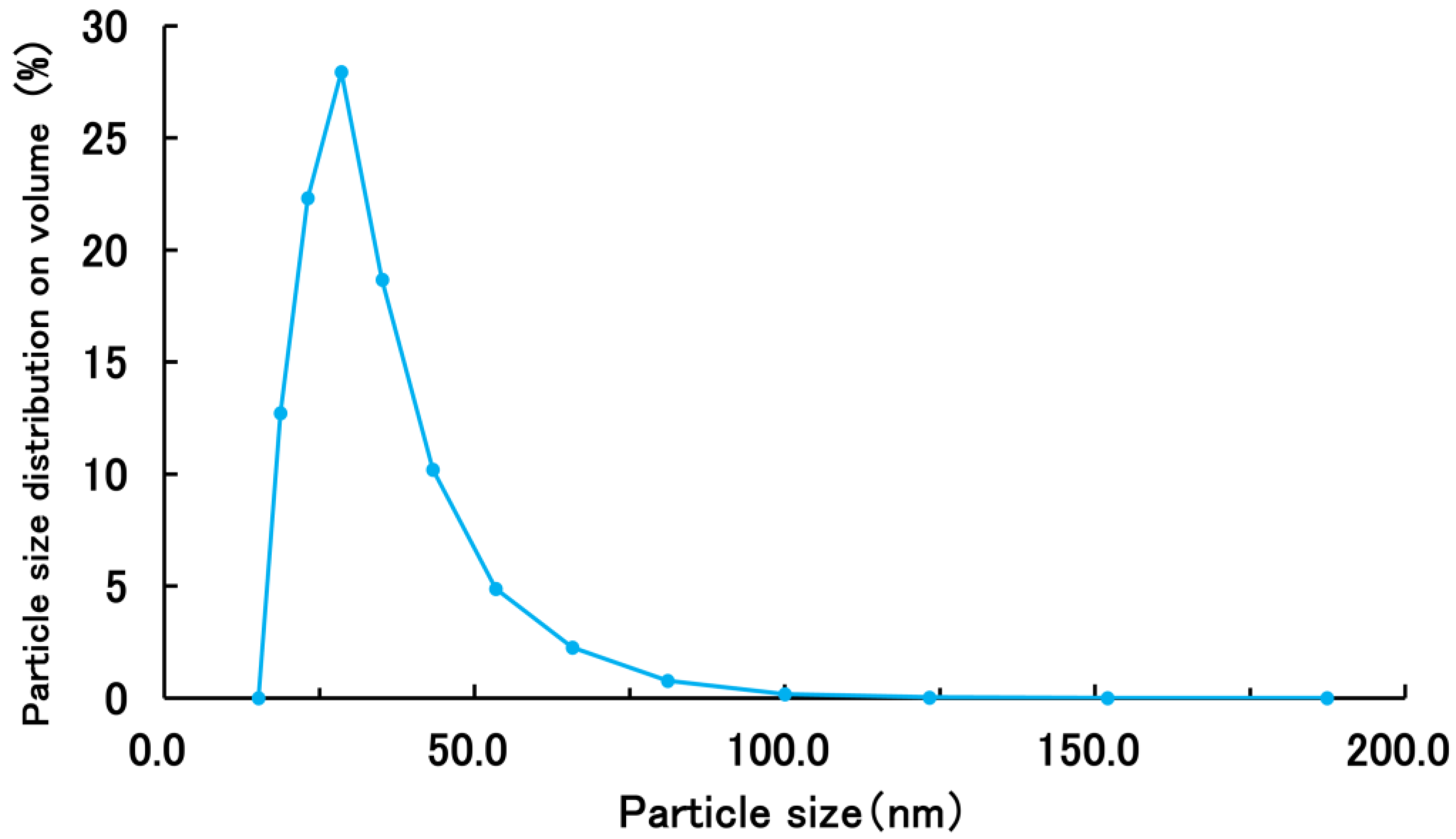
2.3.1. Particle Size Measurement
2.3.2. Loading Capacity and Content Efficiency
2.3.3. Morphological Observation
2.4. Animal Experiments
2.4.1. Preparation of CHS Model Mice
2.4.2. Treatment Experiments Using CHS Model Mice
2.4.3. Evaluation of Treatment Effect by ELISA
3. Results
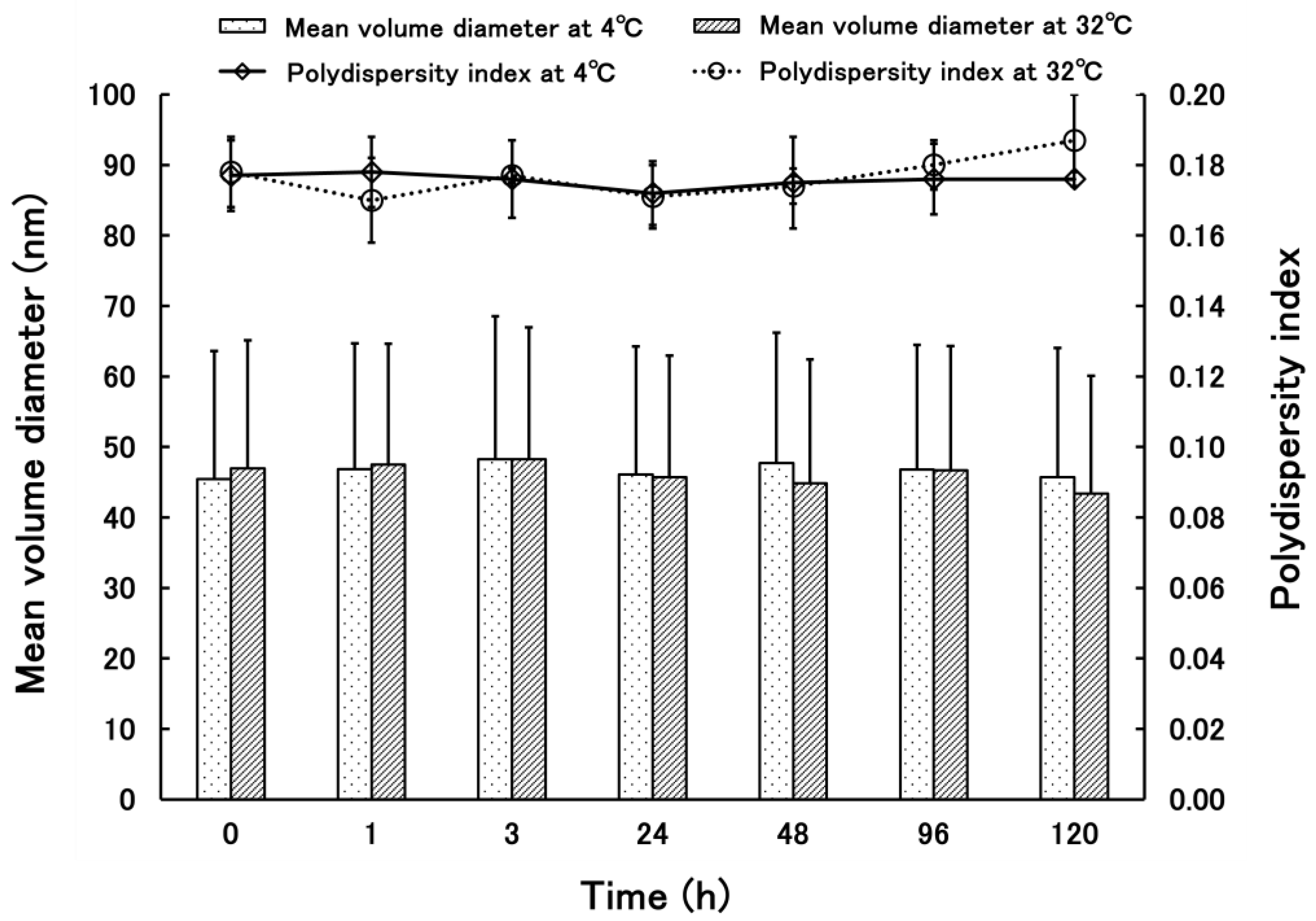
3.1. Evaluation of Physical Properties of PSL-Loaded PLGA NPs
3.1.1. Properties of PSL-Loaded PLGA NPs
3.1.2. Properties of PSL-Loaded PLGA NPs
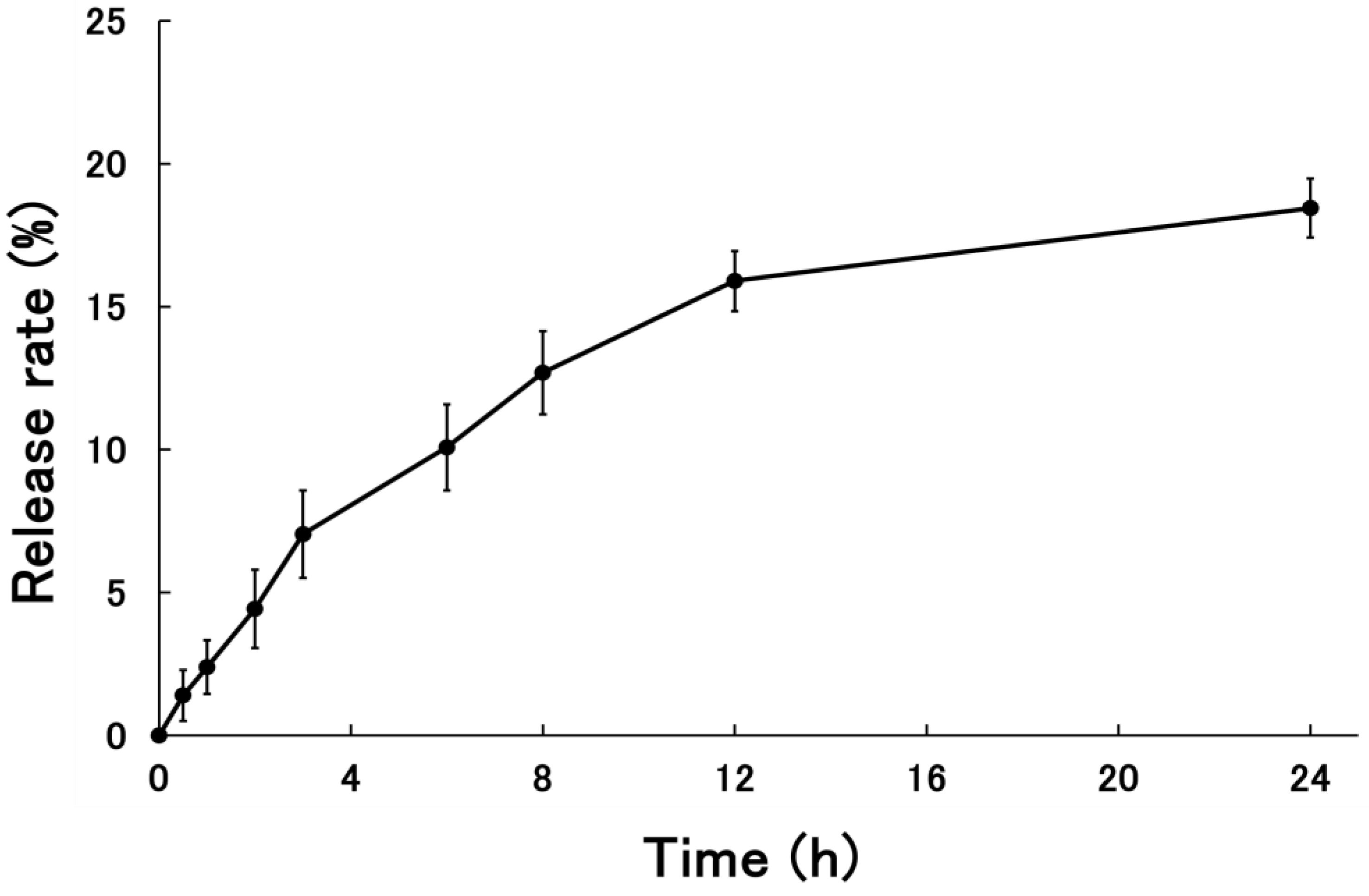
3.1.3. Release Rate of PSL-Loaded PLGA NPs
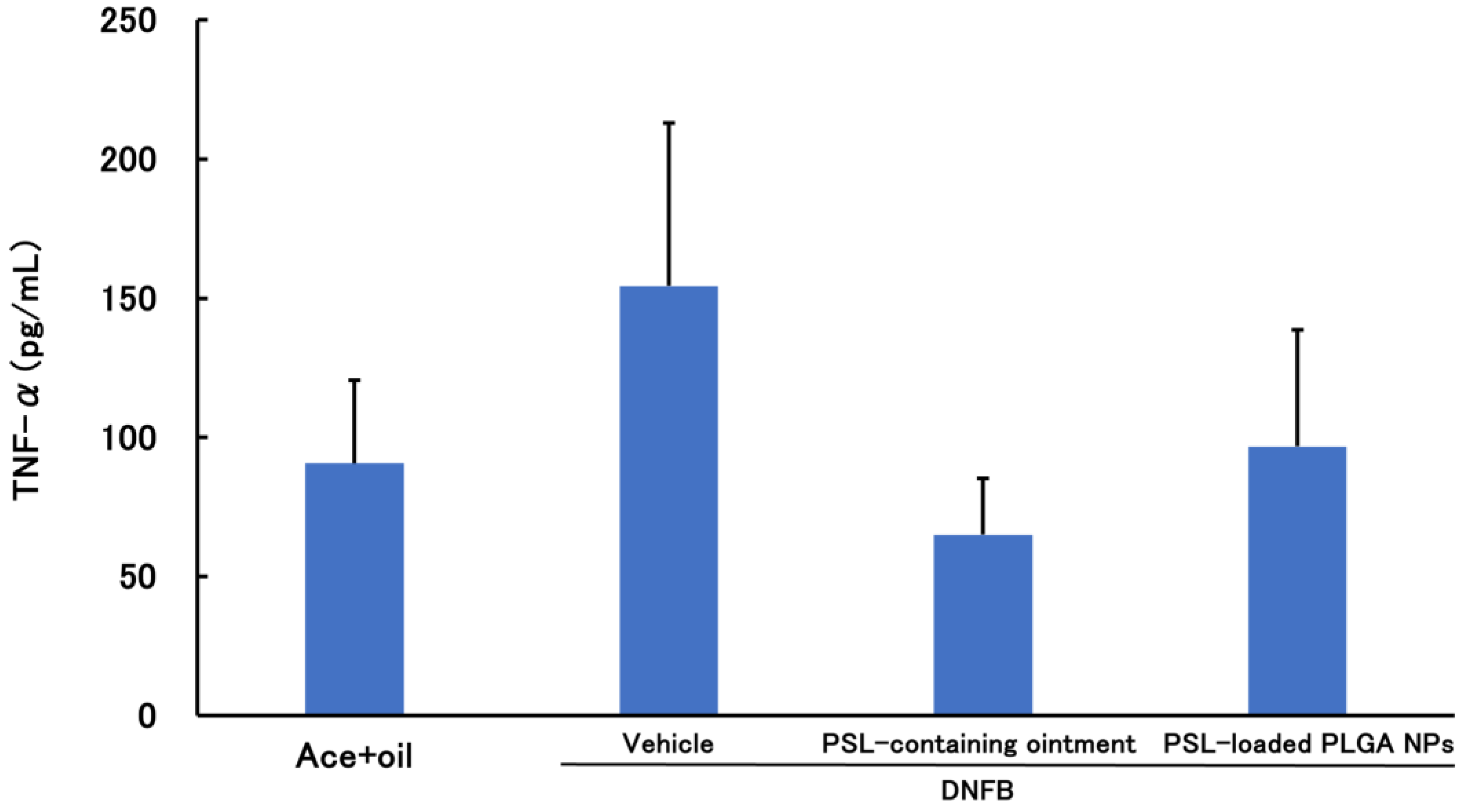
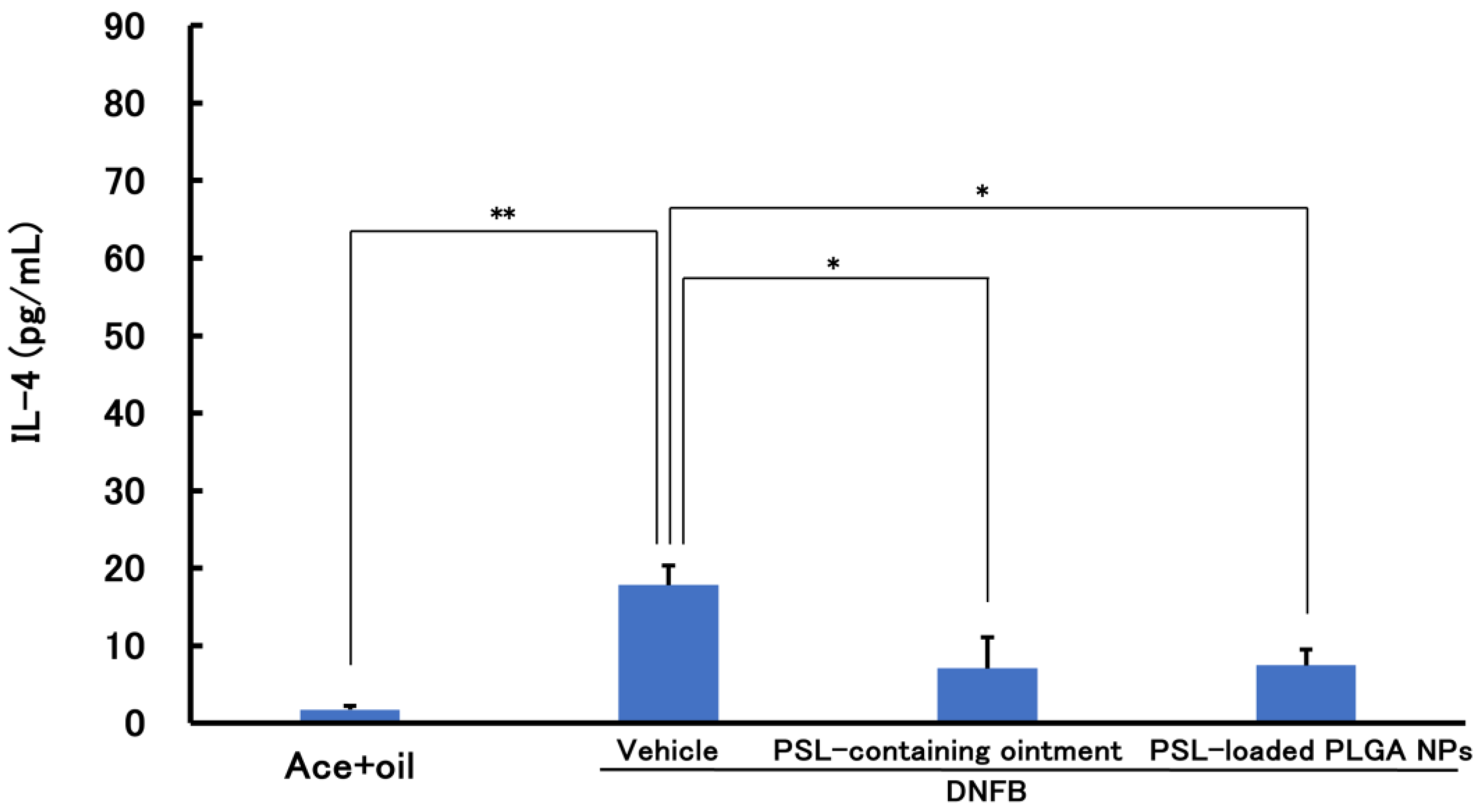
3.2. Evaluation of Therapeutic Efficacy of PSL-Loaded PLGA NPs Using CHS Model Mice
3.2.1. PSL Administered 2 h before Sensitization
3.2.2. PSL Administered 2 h after Sensitization Administration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Honda, T.; Egawa, G.; Grabbe, S.; Kabashima, K. Update of immune events in the murine contact hypersensitivity model: Toward the understanding of allergic contact dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vocanson, M.; Hennino, A.; Rozières, A.; Poyet, G.; Nicolas, J. Effector and regulatory mechanisms in allergic contact dermatitis. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 64, 1699–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, D.; Igyártó, Z.; Gaspari, A. Early immune events in the induction of allergic contact dermatitis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiser, M.; Tralau, T.; Heidler, J.; Api, A.M.; Arts, J.H.E.; Basketter, D.A.; English, J.; Diepgen, T.L.; Fuhlbrigge, R.C.; Gaspari, A.A.; et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: Epidemiology, molecular mechanisms, in vitro methods and regulatory aspects. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, H.; Popple, A.; Gellatly, N.; Maxwell, G.; Williams, J.; Friedmann, P.S.; Kimber, I.; Dearman, R.J. Anti-hapten antibodies in response to skin sensitization. Contact Dermat. 2016, 74, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coondoo, A.; Phiske, M.; Verma, S.; Lahiri, K. Side-effects of topical steroids: A long overdue revisit. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2014, 5, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.; Nadkarni, N.; Patil, S.; Godse, K.; Gautam, M.; Agarwal, S. Topical corticosteroids in dermatology. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2016, 82, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, V. Misuse of topical corticosteroids: A clinical study of adverse effects. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2014, 5, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ference, J.; Last, A. Choosing Topical Corticosteroids. Am. Fam. Physician 2009, 79, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Hengge, U.; Ruzicka, T.; Schwartz, R.; Cork, M. Adverse effects of topical glucocorticosteroids. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 54, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, R.; Smitha, P.; Sudhir, N. Topical steroid damaged skin: A clinico-epidemiological and dermatological study. J. Pak. Assoc. Dermatol. 2021, 31, 407–414. [Google Scholar]
- Lodén, M. Role of Topical Emollients and Moisturizers in the Treatment of Dry Skin Barrier Disorders. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2003, 4, 771–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makadia, H.; Siegel, S. Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brannon-Peppas, L. Recent advances on the use of biodegradable microparticles and nanoparticles in controlled drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 116, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, H.; Naylor, A.; Clegg, F.; Sammom, C. Investigation of factors influencing the hydrolytic degradation of single PLGA microparticles. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 119, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, I.; Hidaka, Y.; Oshizaka, T.; Takei, C.; Mori, K.; Sugibayashi, K.; Makino, K. Chitosan-coated PLGA nanoparticles for transcutaneous immunization: Skin distribution in lysozyme-sensitized mice. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 220, 112916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, I.; Suzuki, T.; Makino, K. Iontophoretic transdermal delivery using chitosan-coated PLGA nanoparticles for transcutaneous immunization. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 608, 125607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Khuda-Bukhsh, A. PLGA-loaded nanomedicines in melanoma treatment: Future prospect for efficient drug delivery. Indian J. Med. Res. 2016, 144, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Mittal, A.; Jain, A. Enhanced Topical Delivery of Cyclosporin-A Using PLGA Nanoparticles as Carrier. Curr. Nanosci. 2011, 7, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.; Sahoo, S. PLGA nanoparticles containing various anticancer agents and tumour delivery by EPR effect. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folle, C.; Marqués, A.M.; Díaz-Garrido, N.; Espina, M.; Sánchez-López, E.; Badia, J.; Baldoma, L.; Calpena, A.C.; García, M.L. Thymol-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: An efficient approach for acne treatment. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Macgregor, R.B., Jr.; Yan, H.; Zhang, R.X. Encapsulation and release rate to cytotoxicity in human lens epithelial cells|Enhanced Reader. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röse, L.; Schneider, C.; Stock, C.; Zollner, T.; Döcke, W. Extended DNFB-induced contact hypersensitivity models display characteristics of chronic inflammatory dermatoses. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manresa, M. Animal Models of Contact Dermatitis: 2,4-Dinitrofluorobenzene-Induced Contact Hypersensitivity. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2223, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagawa, A.; Sato, A.; Makino, K.; Takeuchi, I. Therapeutic Effects of 30 nm Cyclosporin A-Loaded Nanoparticles Using PLGA-PEG-PLGA Triblock Copolymer for Transdermal Delivery in Mouse Models of Psoriasis. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomoda, K.; Yabuki, N.; Terada, H.; Makino, K. Surfactant free preparation of PLGA nanoparticles: The combination of antisolvent diffusion with preferential solvation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 457, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, I.; Kobayashi, S.; Hida, Y.; Makino, K. Estradiol-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for improving low bone mineral density of cancellous bone caused by osteoporosis: Application of enhanced charged nanoparticles with iontophoresis. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 155, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, I.; Kagawa, A.; Makino, K. Skin permeability and transdermal delivery route of 30-nm cyclosporin A-loaded nanoparticles using PLGA-PEG-PLGA triblock copolymer. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 600, 124866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipasquale, D.; Buono, M.; Kolkhorst, F. Effect of Skin Temperature on the Cholinergic Sensitivity of the Human Eccrine Sweat Gland. Jpn. J. Physiol. 2003, 53, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, I.; Makino, K. Biocompatibility and effectiveness of paclitaxel-encapsulated micelle using phosphoester compounds as a carrier fir cancer trearment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 177, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J. TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelová, H.; Hošek, J. TNF-α signalling and inflammation: Interactions between old acquaintances. Inflamm. Res. 2013, 62, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradding, P.; Feather, I.H.; Howarth, P.H.; Mueller, R.; Roberts, J.A.; Britten, K.; Bews, J.P.; Hunt, T.C.; Okayama, Y.; Heusser, C.H. Interleukin 4 Is Localized to and Released by Human Mast Cells. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzina, I.G.; Keegan, A.D.; Heller, N.M.; Rook, G.A.; Shea-Donohue, T.; Atamas, S.P. Regulation of inflammation by interleukin-4: A review of “alternatives”. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwstra, J.; Loan Honeywell-Nguyen, P.; Gooris, G.; Ponec, M. Structure of the skin barrier and its modulation by vesicular formulations. Prog. Lipid Res. 2003, 42, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, P. Structure and function of the stratum corneum permeability barrier. Drug Dev. Res. 1988, 13, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labouta, H.; El-Khordagui, L.; Kraus, T.; Schneider, M. Mechanism and determinants of nanoparticle penetration through human skin. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4989–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küchler, S.; Radowski, M.R.; Blaschke, T.; Dathe, M.; Plendl, J.; Haag, R.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Kramer, K.D. Nanoparticles for skin penetration enhancement—A comparison of a dendritic core-multishell-nanotransporter and solid lipid nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 71, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, E.; Flanagan Linhardt’, R. Importance of Distinct Water Environments in the Hydrolysis of Poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide). Macromolecules 1994, 27, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujisawa, R.; Sakurai, R.; Oshizaka, T.; Mori, K.; Saitoh, A.; Takeuchi, I.; Sugibayashi, K. Development of PSL-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Colloids Interfaces 2024, 8, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids8030039
Fujisawa R, Sakurai R, Oshizaka T, Mori K, Saitoh A, Takeuchi I, Sugibayashi K. Development of PSL-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Colloids and Interfaces. 2024; 8(3):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids8030039
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujisawa, Ryo, Ryuse Sakurai, Takeshi Oshizaka, Kenji Mori, Akiyoshi Saitoh, Issei Takeuchi, and Kenji Sugibayashi. 2024. "Development of PSL-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Allergic Contact Dermatitis" Colloids and Interfaces 8, no. 3: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids8030039
APA StyleFujisawa, R., Sakurai, R., Oshizaka, T., Mori, K., Saitoh, A., Takeuchi, I., & Sugibayashi, K. (2024). Development of PSL-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Colloids and Interfaces, 8(3), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids8030039








