Gd(OH)3 as Modifier of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles—Insights on the Synthesis, Characterization and Stability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Synthesis of Mag@PEG
2.2.2. Synthesis of Gd(OH)3 Nps
2.2.3. Synthesis of Mag@Gd(OH)3
2.2.4. Influence of the Biological Media: Interaction with Proteins
2.2.5. Mannose Coating Procedure: Mag@Gd(OH)3@Man
2.2.6. Stability Assays
2.3. Characterization Methods
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of Hybrid Nanosystems
3.2. Characterization of Raw and Hybrid Nanosystems Mag@Gd(OH)3
- Crystalline Pattern by XRD
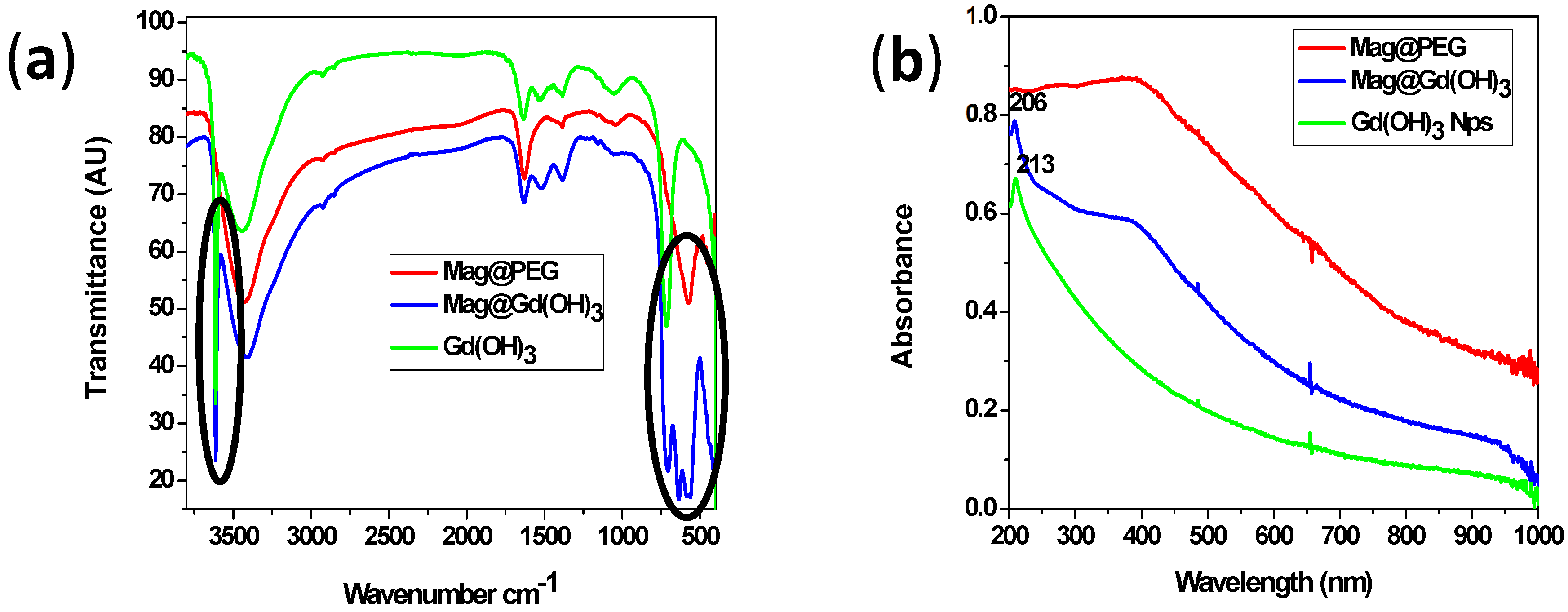
- FTIR and UV–Vis Spectroscopy
- Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Hydrodynamic Diameter
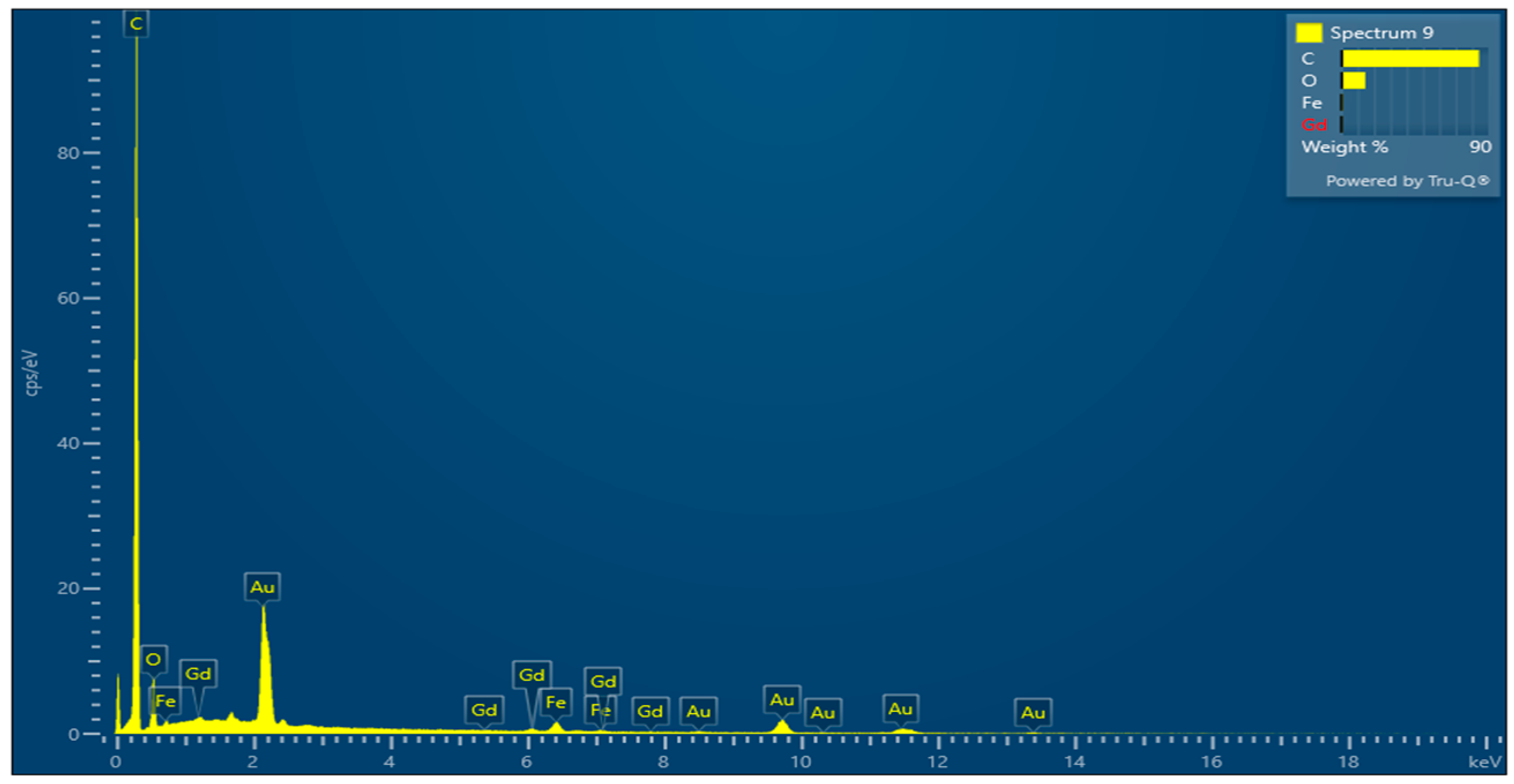
- Energy-Dispersive X-ray (SEM-EDS)
- Thermogravimetric Analysis
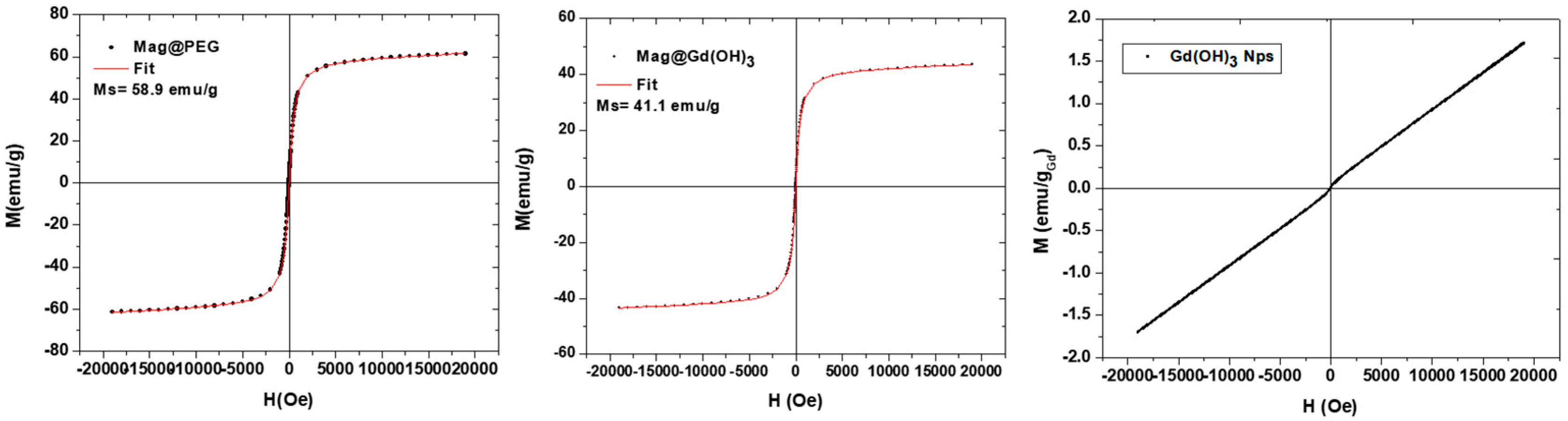
- Magnetic Measurements
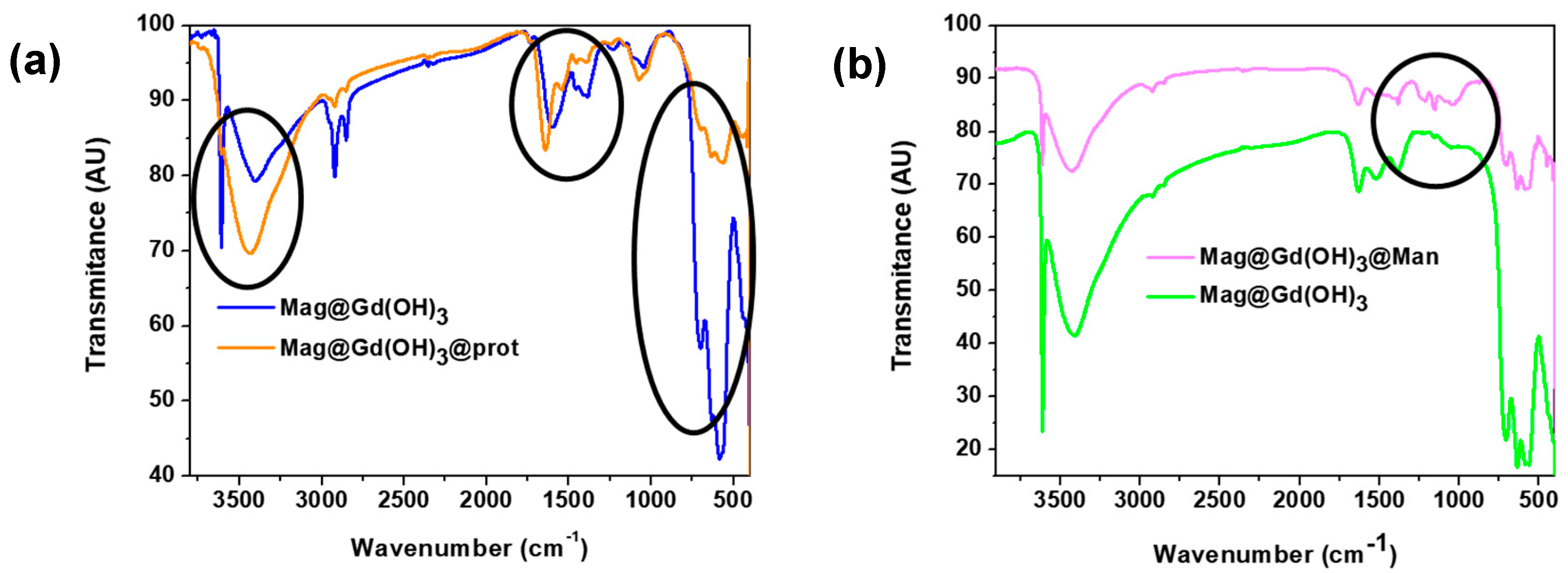
3.3. Influence of the Biological Media: Study on Protein Corona Formation
3.4. Surface Modification of Hybrid Mag@Gd(OH)3: Mannose Coating
Stability Assays
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wahsner, J.; Gale, E.M.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Caravan, P. Chemistry of MRI contrast agents: Current challenges and new frontiers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 957–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, E.; Fiorenza, D.; Torino, E.; Di Polidoro, A.C.; Cavaliere, C.; Netti, P.A.; Salvatore, M.; Aiello, M. Radiolabeled PET/MRI Nanoparticles for Tumor Imaging. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, H.S. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: A serious adverse reaction to gadolinium-1997-2006-2016. Part 1. Acta Radiol. 2016, 57, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, M.; Halbert, M.V.; Stephen, Z.R.; Zhang, M. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as T1 Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Fundamentals, Challenges, Applications, and Prospectives. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e1906539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, K.N.; Pierre, V.C. Next generation, high relaxivity gadolinium MRI agents. Bioconjug. Chem. 2005, 16, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortezazadeh, T.; Gholibegloo, E.; Alam, N.R.; Dehghani, S.; Haghgoo, S.; Ghanaati, H.; Khoobi, M. Gadolinium (III) oxide nanoparticles coated with folic acid-functionalized poly(β-cyclodextrin-co-pentetic acid) as a biocompatible targeted nano-contrast agent for cancer diagnostic: In vitro and in vivo studies. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2019, 32, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Xu, K. Comparative study on in vivo behavior of PEGylated gadolinium oxide nanoparticles and Magnevist as MRI contrast agent. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, F.; Sanavio, B.; Saccani, A.; Tang, Y.; Zucca, I.; Carney, T.M.; Mastropietro, A.; Jacob Silva, P.H.; Carney, R.P.; Schenk, K.; et al. Superparamagnetic nanoparticles as high efficiency magnetic resonance imaging T2 contrast agent. Bioconjug. Chem. 2017, 28, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, B.; Diaz-Diestra, D.; Beltran-Huarac, J.; Weiner, B.R.; Morell, G. Enhanced MRI T 2 Relaxivity in Contrast-Probed Anchor-Free PEGylated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellico, J.; Ruiz-Cabello, J.; Fernández-Barahona, I.; Gutiérrez, L.; Lechuga-Vieco, A.V.; Enríquez, J.A.; del Morales, M.P.; Herranz, F. One-step fast synthesis of nanoparticles for MRI: Coating chemistry as the key variable determining positive or negative contrast. Langmuir 2017, 33, 10239–10247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel Schneider, M.G.; Lassalle, V.L. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as novel and efficient tools for atherosclerosis diagnosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 1098–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estelrich, J.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J.; Busquets, M.A. Nanoparticles in magnetic resonance imaging: From simple to dual contrast agents. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1727–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.H.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S.; Cheon, J. Recent advances in magnetic nanoparticle-based multi-modal imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4501–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, B.; Wang, D.; Wu, H.; Xu, P.; Jiang, P.; Xia, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Q. Core-Shell Structurized Fe3O4@C@MnO2 Nanoparticles as pH Responsive T1-T2∗ Dual-Modal Contrast Agents for Tumor Diagnosis. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 3047–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Guo, S.; Zu, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Fan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Pang, X.; Ji, Z.; Cheng, J. Magnetic vortex nanoring coated with gadolinium oxide for highly enhanced T1-T2 dual-modality magnetic resonance imaging-guided magnetic hyperthermia cancer ablation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 112926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, D.; Yuan, Q. Facile and large-scale synthesis of Gd (OH) 3 nanorods for MR imaging with low toxicity w. N. J. Chem. 2012, 36, 1335–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Peng, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, W.; Li, F. Biomaterials Long-term in vivo biodistribution and toxicity of Gd(OH)3 nanorods. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel Schneider, M.G.; Martín, M.J.; Coral, D.F.; Muraca, D.; Gentili, C.; Fernández van Raap, M.B.; Lassalle, V.L. Selective contrast agents with potential to the earlier detection of tumors: Insights on synthetic pathways, physicochemical properties and performance in MRI assays. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, H.; Bordonali, L.; Lascialfari, A.; Wan, S.; Monopoli, M.P.; Lynch, I.; Laurent, S.; Mahmoudi, M. Protein corona affects the relaxivity and MRI contrast efficiency of magnetic nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.G.; Min, B.K.; Sohn, Y. Synthesis and characterization of Gd(OH)3 and Gd2O3 nanorods. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, N.; Imran, M.; Liang, K.; Yuan, C.Z.; Zeb, A.; Jiang, N.; Qazi, U.Y.; Sahar, S.; Xu, A.W. Highly dispersed ultra-small Pd nanoparticles on gadolinium hydroxide nanorods for efficient hydrogenation reactions. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 13800–13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoia, M.; Istratie, R.; Păcurariu, C. Investigation of magnetite nanoparticles stability in air by thermal analysis and FTIR spectroscopy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 125, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, X.H.; Hu, X.D.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, R.; Liu, P.D.; Zhang, H.Q. Synthesis and characteristics of nanorods of gadolinium hydroxide and gadolinium oxide. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 664, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Yeap, S.; Che, H.; Low, S. Characterization of magnetic nanoparticle by dynamic light scattering. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Lin, B.; Li, D.; Ai, H. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for MR imaging and therapy: Design considerations and clinical applications. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honary, S.; Barabadi, H.; Ebrahimi, P.; Naghibi, F.; Alizadeh, A. Development and optimization of biometal nanoparticles by using mathematical methodology: A microbial approach. J. Nano Res. 2015, 30, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caciandone, M.; Niculescu, A.G.; Roșu, A.R.; Grumezescu, V.; Negut, I.; Holban, A.M.; Oprea, O.; Vasile, B.; Ștefan; Bîrcă, A.C.; et al. PEG-Functionalized Magnetite Nanoparticles for Modulation of Microbial Biofilms on Voice Prosthesis. Antibiotics 2021, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, A.; Kalyani, S.; Ranoo, S.; Philip, J. One-step microwave-assisted synthesis of water-dispersible Fe3O4 magnetic nanoclusters for hyperthermia applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 439, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Sharma, P.; Priya, R.; Pandey, O.P. Thermal dehydration kinetics involved during the conversion of gadolinium hydroxide to gadolinium oxide. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 822, 153450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, K.; Ali, L.; Gul, I.; Rizwan, S.; Mumtaz, M. Effect of silica coating on the structural, dielectric, and magnetic properties of maghemite nanoparticles. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2014, 404, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscas, G.; Concas, G.; Cannas, C.; Musinu, A.; Ardu, A.; Orrù, F.; Fiorani, D.; Laureti, S.; Rinaldi, D.; Piccaluga, G.; et al. Magnetic properties of small magnetite nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 23378–23384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopac, T. Protein corona, understanding the nanoparticle–protein interactions and future perspectives: A critical review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalu, S.; Simon, V. Proteins adsorption to orthopaedic biomaterials: Vibrational spectroscopy evidence. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2007, 9, 3297–3302. [Google Scholar]
- Dalle Vedove, E.; Costabile, G.; Merkel, O.M. Mannose and Mannose-6-Phosphate Receptor–Targeted Drug Delivery Systems and Their Application in Cancer Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1701398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, T.; Guo, X. Catalytic pyrolysis of mannose as a model compound of hemicellulose over zeolites. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 57, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, G.N.; Piloni, R.V.; Moldenaers, P.; Iturriaga, L.B.; Ribotta, P.D. Rheological behavior of the galactomannan fraction from Gleditsia triacanthos seed in aqueous dispersion. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 132, 107848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva Kumar, D.; Chandra Babu Naidu, K.; Mohamed Rafi, M.; Prem Nazeer, K.; Ayisha Begam, A.; Ramesh Kumar, G. Structural and dielectric properties of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) stabilized by sugar solutions. Mater. Sci. Pol. 2018, 36, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcona, P.L.; Montiel Schneider, M.G.; Grünhut, M.; Lassalle, V.L. Stimuli-responsive nanotheranostics intended for oncological diseases:: In vitro evaluation of their target, diagnostic and drug release capabilities. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 2126–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Khanduri, H.; Pathak, S.; Singh, A.; Basheed, G.A.; Pant, R.P. Temperature selectivity for single phase hydrothermal synthesis of PEG-400 coated magnetite nanoparticles. Dalt. Trans. 2020, 49, 8672–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolás, P.; Saleta, M.; Troiani, H.; Zysler, R.; Lassalle, V.; Ferreira, M.L. Preparation of iron oxide nanoparticles stabilized with biomolecules: Experimental and mechanistic issues. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 4754–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanzadeh-Kouyakhi, A.; Masoudi, A.; Ardestani, M. Synthesis method of novel Gd2O3@Fe3O4 nanocomposite modified by dextrose capping agent. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 13442–13448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajaroh, F.; Setyawan, H.; Nur, A.; Lenggoro, I.W. Thermal stability of silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles prepared by an electrochemical method. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 24, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Soriano, D.; Milán-Rois, P.; Lafuente-Gómez, N.; Navío, C.; Gutiérrez, L.; Cussó, L.; Desco, M.; Calle, D.; Somoza, Á.; Salas, G. Iron oxide-manganese oxide nanoparticles with tunable morphology and switchable MRI contrast mode triggered by intracellular conditions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 613, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janko, C.; Zaloga, J.; Pöttler, M.; Dürr, S.; Eberbeck, D.; Tietze, R.; Lyer, S.; Alexiou, C. Strategies to optimize the biocompatibility of iron oxide nanoparticles–“SPIONs safe by design”. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 431, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcona, P.; López-Corral, I.; Lassalle, V. Fabrication of folic acid magnetic nanotheranostics: An insight on the formation mechanism, physicochemical properties and stability in simulated physiological media. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 537, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmer, E.; Kohl, Y.; Colquhoun, V.; Thielecke, H.; Soga, K.; Mathur, S. Probing cytotoxicity of gadolinium hydroxide nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 4358–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Hydrodynamic Diameter (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (meV) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mag@PEG | 208.8 ± 6.6 | 0.473 | −25.6 |
| Gd(OH)3 Nps | 243 | 0.045 | −17.2 |
| Mag@Gd(OH)3 | 264.6 ± 2.8 | 0.328 | −33.5 |
| Amount of Gd(OH)3 before Stability Assay * | Amount of Gd(OH)3 after Stability Assay * | % of Gd(OH)3 Reduction | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mag@Gd(OH)3 | 40 | 17.9 | 55% |
| Mag@Gd(OH)3@Man | 26.9 | 17.2 | 36.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montiel Schneider, M.G.; Rivero, P.S.; Muñoz Medina, G.A.; Sanchez, F.H.; Lassalle, V.L. Gd(OH)3 as Modifier of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles—Insights on the Synthesis, Characterization and Stability. Colloids Interfaces 2023, 7, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids7010008
Montiel Schneider MG, Rivero PS, Muñoz Medina GA, Sanchez FH, Lassalle VL. Gd(OH)3 as Modifier of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles—Insights on the Synthesis, Characterization and Stability. Colloids and Interfaces. 2023; 7(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids7010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontiel Schneider, María Gabriela, Paula Sofía Rivero, Guillermo Arturo Muñoz Medina, Francisco H. Sanchez, and Verónica Leticia Lassalle. 2023. "Gd(OH)3 as Modifier of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles—Insights on the Synthesis, Characterization and Stability" Colloids and Interfaces 7, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids7010008
APA StyleMontiel Schneider, M. G., Rivero, P. S., Muñoz Medina, G. A., Sanchez, F. H., & Lassalle, V. L. (2023). Gd(OH)3 as Modifier of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles—Insights on the Synthesis, Characterization and Stability. Colloids and Interfaces, 7(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids7010008






