Titanium Silicates Precipitated on the Rice Husk Biochar as Adsorbents for the Extraction of Cesium and Strontium Radioisotope Ions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of Titanium Silicates
2.3. Adsorption Experiments
2.4. Analytic Methods
3. Results and Discussion
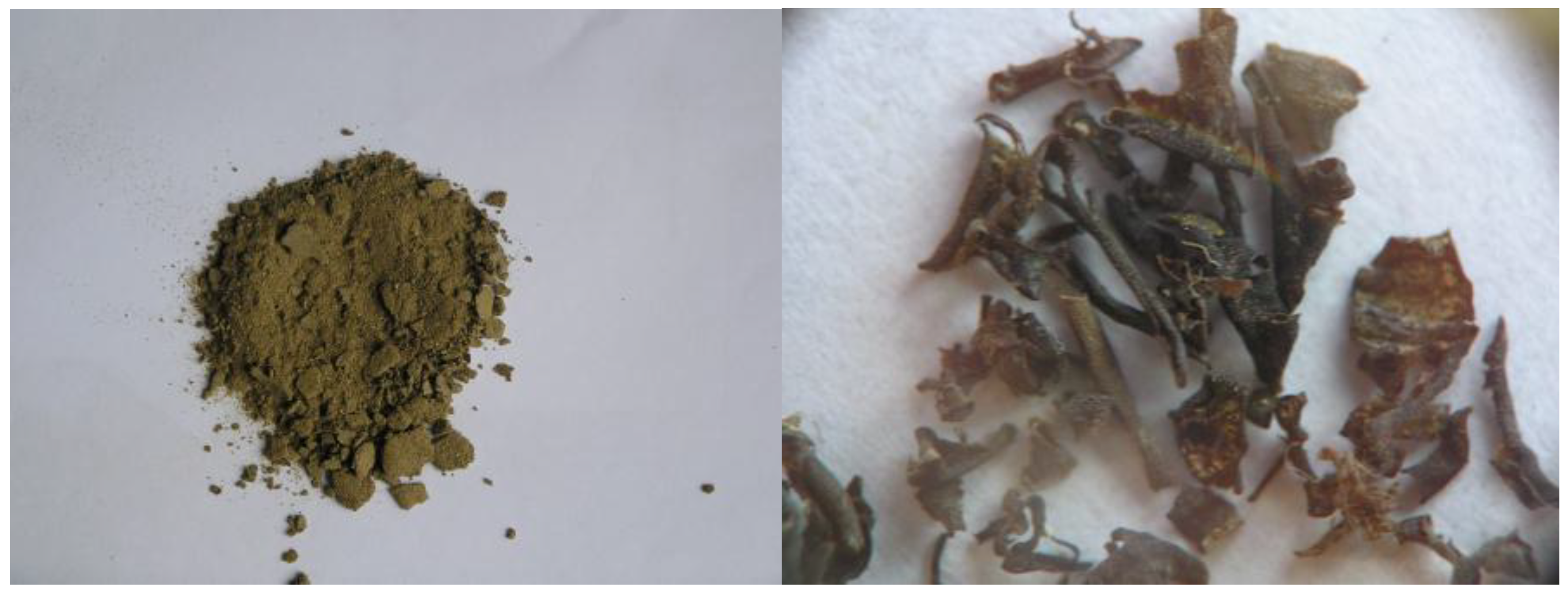
3.1. Physical-Chemical Characterization
3.2. Ion-Exchange Properties
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Health Consequences of the Chernobyl Accident. Scientific Report, 1st ed.; Souchkevitch, G.N., Tsyb, A.F., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; pp. 128–431. ISBN 5-88429-010-1. [Google Scholar]
- Clough, R.L. High-energy radiation and polymers: A Review of commercial processes and emerging applications. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 2001, 185, 8–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, S.F.; Pillay, K.K.S. Effect of Ionized Radiation on Modern Ion Exchangers Material; USDOE: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; pp. 1–23.
- Amphlett, C.B. Inorganic Ion Exchangers; Elsevier Pub. Com: New York, NY, USA, 1964; pp. 1–141. [Google Scholar]
- Dyer, A.; Pillinger, M.; Newton, M.; Harjula, R.; Moller, T.; Amin, S. Sorption Behavior of Radionuclides on Crystalline Synthetic Tunnel Manganese Oxides. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 3798–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Attar, L.; Dyer, A.; Harjula, R. Uptake of radionuclides on microporous and layered ion exchange materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 2963–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravlev, I.; Kanibolotsky, V.; Strelko, V.; Gallios, G.; Strelko, V., Jr. Novel High Porous Spherically Granulated Ferrophosphatesilicate Gels. Mater. Res. Bull. 2004, 39, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravlev, I.; Kanibolotsky, V.; Strelko, V.; Gallios, G. Novel Spherically Granulated Inorganic Ion Exchangers Based on Aluminophosphatesilicate and Ferrophosphatesilicate Gels. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S. Sorption of the long-lived radionuclides cesium-134, strontium-85 and cobalt-60 on bentonite. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2003, 258, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehto, J.; Brodkin, L.; Harjula, R.; Tusa, E. Separation of Radioactive Strontium from Alkaline Nuclear Waste Solutions with the Highly Effective Ion Exchanger SrTreat. Nucl. Technol. 1999, 127, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Tomar, R.; Tomar, R.; Tomar, S. Sorption of homologues of radionuclides by synthetic ion exchanger. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 142, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilchi, A.; Hadjmohammadi, M.; Garmarodi, S.; Saberi, R. Studies on the adsorption behavior of trace amounts of 90Sr2+, 140La3+, 60Co2+, Ni2+and Zr4+ cations on synthesized inorganic ion exchangers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Pal, D.; Basu, S.; Nayak, D.; Lahiri, S. Synthesis of a new ion exchanger, zirconium vanadate, and its application to the separation of barium and cesium radionuclides at tracer levels. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2002, 57, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Rahman, R.; Ibrahim, H.; Hung, Y. Liquid Radioactive Wastes Treatment: A Review. Water 2011, 3, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaumik, A.; Inagaki, S. Mesoporous Titanium Phosphate Molecular Sieves with Ion-Exchange Capacity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortun, A.; Bortun, L.; Clearfield, A.; Khainakov, S.; Strelko, V.; Khryaschevskii, V.; Kvashenko, A.; Voitko, I. Synthesis and characterization of ion exchange properties of spherically granulated titanium phosphate. Solvent Extr. Ion Exchang. 1997, 15, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clearfield, A. Inorganic Ion Exchangers with Layered Structures. Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1984, 14, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clearfield, A. Role of Ion Exchange in Solid-state Chemistry. Chern. Rev. 1988, 88, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clearfield, A.; Bortun, A.; Khainakov, S.; Bortun, L.; Strelko, V.; Khryaschevskii, V. Spherically granulated titanium phosphate as exchanger for toxic heavy metals. Waste Manag. 1998, 18, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clearfield, A. Inorganic Ion Exchangers, Past, Present, and Future. Solvent Extr. Ion Exchang. 2000, 18, 655–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Pan, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, P.; Hong, C.; Pan, B.; Zhang, Q. Adsorption of Pb2+, Zn2+ and Cd2+ from waters by amorphous titanium phosphate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 318, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, K.; Sahu, B.; Das, D. A comparative study on textural characterization: Cation-exchange and sorption properties of crystalline α-zirconium(IV), tin(IV), and titanium(IV) phosphates. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 270, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravlev, I.; Kanibolotsky, V.; Strelko, V.; Bortun, A.; Bortun, L.; Khainakov, S.; Clearfield, A. Synthesis and Characterization of the Ion Exchange Properties of Spherically Granulated Sodium Aluminophosphatesilicate. Solvent Extr. Ion Exchang. 1999, 17, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharygin, L.; Kalyagina, M.; Borovkov, S. Sol-Gel Technique for Production of Spherically Granulated Zirconium(IV) Phosphate. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2005, 78, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakutevskyy, O.; Psareva, T.; Strelko, V. Sorption of U(VI) Ions on Sol-Gel-Synthesized Amorphous Spherically Granulated Titanium Phosphates. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2012, 85, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharygin, L. Preparation of Globular Zirconium(IV) Hydroxide by Sol-Gel Process. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2002, 75, 1394–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravlev, I.; Zakutevsky, O.; Psareva, T.; Kanibolotsky, V.; Strelko, V.; Taffet, M.; Gallio, G. Uranium sorption on amorphous titanium and zirconium phosphates modified by Al3+ or Fe3+ ions. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2002, 254, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaelides, P.; Gallios, G.; Sarri, S.; Zamboulis, D.; Pavlidou, E.; Kantiranis, N.; Anousis, I.; Zhuravlev, I.; Strelko, V. Separation of Uranium from Aqueous Solutions Using Al3+- and Fe3+-modified Titanium- and Zirconium Phosphates. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaelides, P.; Sarri, S.; Zamboulis, D.; Gallios, G.; Zhuravlev, I.; Strelko, V. Separation of europium from aqueous solutions using Al3+- and Fe3+-doped zirconium and titanium phosphates. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2006, 268, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubar, N.; Kanibolotskyy, V.; Strelko, V.; Gallios, G.; Samanidou, V.; Shaposhnikova, T.; Milgrandt, V.; Zhuravlev, I. Adsorption of phosphate ions on novel inorganic ion exchangers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 255, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubar, N.; Shaposhnikova, T.; Kouts, V.; Gallios, G.; Kanibolotskyy, V.; Strelko, V.; Zhuravlev, I. Adsorption of Fluoride, Chloride, Bromide, and Bromate Ions on a Novel Ion Exchanger. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 291, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strelko, V.; Milyutin, V.; Gelis, V.; Psareva, T.; Zhuravlev, I.; Shaposhnikova, T.; Milgrandt, V.; Bortun, A. Sorption of cesium radionuclides onto semicrystalline alkali metal silicotitanates. Radiochemistry 2015, 57, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Attar, L.; Dyer, A.; Paajanen, A.; Harjula, R. Purification of nuclear wastes by novel inorganic ion exchangers. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 2969–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyil, S.; Aslani, A.; Eral, M. Sorption characteristics of uranium onto composite ion exchangers. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2003, 256, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marageh, M.; Husain, S.; Khanchi, A.; Ahmady, S. Sorption Studies of Radionuclides on a New Ion Exchanger: Cerium (III) Silicate. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1996, 47, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inorganic Ion Exchangers and Adsorbents for Chemical Processing in the Nuclear Fuel Cycle. In Proceedings of the A Technical Committee Meeting, Vienna, Austria, 12–15 June 1984.
- Clearfield, A. Inorganic Ion Exchange Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; 295p, ISBN 978-1-35-109046-9. [Google Scholar]
- Fisseha, G. Advances in Inorganic Ion Exchangers and Their Applications. A Review Article. Chem. Mater. Res. 2017, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Clearfield, A.; Bortun, L.; Bortun, A. Alkali metal ion exchange by the framework titanium silicate M2Ti2O3 SiO4 nH2O (M = H, Na). React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 43, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puziy, A. Cesium and strontium exchange by the framework potassium titanium silicate K3HTi404(SiO4)3·4H2O. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1998, 237, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clearfield, A. Structure and ion exchange properties of tunnel type titanium silicates. Solid State Sci. 2001, 3, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortun, A.; Bortun, L.; Poodjary, D.; Xiang, O.; Clearfield, A. Synthesis, Characterization, and Ion Exchange Behavior of a Framework Potassium Titanium Trisilicate K2TiSi3O9·H2O and Its Protonated Phases. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solbra, S.; Allison, N.; Waite, S.; Mikhalovsky, S.; Bortun, A.; Bortun, L.; Clearfield, A. Cesium and Strontium Ion Exchange on the Framework Titanium Silicate M2Ti2O3SiO4·H2O (M = H, Na). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watari, K.; Izawa, M. Separation of Radiocesium by Copper Ferrocyanide-Anion Exchange Resin. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 1965, 2, 321–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilchi, A.; Malek, B.; Granadi Maragheh, M.; Khanchi, A. Exchange properties of cyanide complexes Part I. Ion exchange of cesium on ferrocyanides. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2003, 258, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, T.; Vincent, C.; Guibal, E. Immobilization of Metal Hexacyanoferrate Ion-Exchangers for the Synthesis of Metal Ion Sorbents—A Mini-Review. Molecules 2015, 20, 20582–20613. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Twenty-Five Years after Chornobyl Accident: Safety for the Future National Report of Ukraine; KIM: Kyiv, Ukraine, 2011; 328p, ISBN 978-966-1547-64-2.
- Tananaev, I. Chemistry of the Ferrocyanides; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1971; p. 320. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Zhuravlev, I.; Strelko, V. Mode of Preparation of Titanium Silicate Based on Rice Husk Silica and Titanium Compounds. Patent of the Ukraine No. 99221, 22 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Babaso, P.; Sharanagouda, H. Rice Husk and Its Applications: Review. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2017, 6, 1144–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Sheng, D.; Xu, C.; Dai, X.; Silver, M.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Xiao, C.; et al. Identifying the Recognition Sitefor Selective Trapping of 99TcO4 in a Hydrolytically Stable and Radiation Resistant Cationic Metal-Organic Framework. JACS 2017, 139, 14873–14876. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Chen, L.; Sheng, D.; Yang, S.; Xiao, C.; Wang, J.; Chai, Z.; et al. Selenium Sequestration in a Cationic Layered Rare Earth Hydroxide: A Combined Batch Experiments and EXAFS Investigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8606–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Bai, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Xiao, C.; Dheng, D.; Diwu, J.; et al. Umbellate Distortions of the Uranyl Coordination Environment Result in a Stable and Porous Polycatenated Framework That Can Effectively Remove Cesium from Aqueous Solutions. JACS 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, D.; Zhu, L.; Xu, C.; Xiao, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Diwu, J.; Chen, J.; Chai, Z.; et al. Efficient and Selective Uptake of TcO4 by a Cationic Metal-Organic Framework Material with Open Ag+ Sites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3471–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Yang, Z.; Gui, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Dai, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L.; et al. Overcoming the Cristallization and Designability Issuis in the Ultrastable Zirconium Phosphonate Framework System. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Dai, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.; Xie, J.; Chen, L.; Diwu, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Ratiometric Monitoring of Thorium Contamination in Natural Water using a Dual-Emission Luminescent Europium Organic Framework. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Dai, X.; Bai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Gui, D.; et al. Highly Sensitive and Selective Uranium Detection in Natural Water Systems Using a Luminescent Mesoporous Metal-Organic Framework Equipped with Abundant Lewis Basic Sites: A Combined Batch, X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy, and First Principle Simulation Investigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3911–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Dai, X.; Zhu, L.; Xu, C.; Zhang, D.; Silver, M.; Li, P.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Zuo, D.; et al. 99TcO4—Remediation by a cationic polymeric network. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lujaniene, G.; Meleshevich, S.; Kanibolotskyy, V.; Sapolaite, J.; Strelko, V.; Remeikis, V.; Oleksienko, O.; Ribikaite, K.; Seiglo, T. Application of inorganic sorbents for removal of Cs, Sr, Pu and Am from contaminated solutions. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2009, 282, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
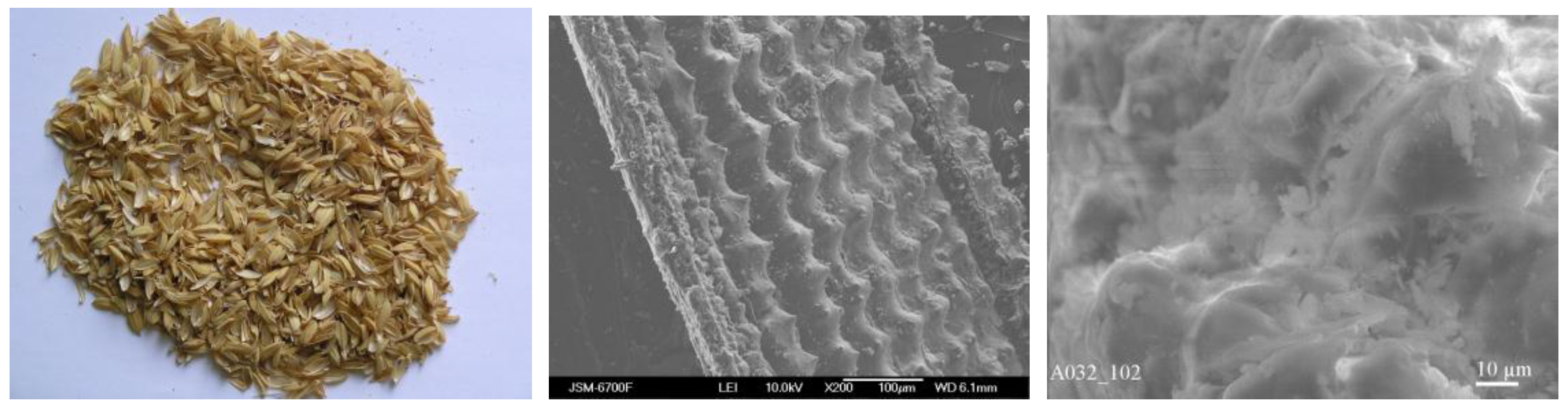
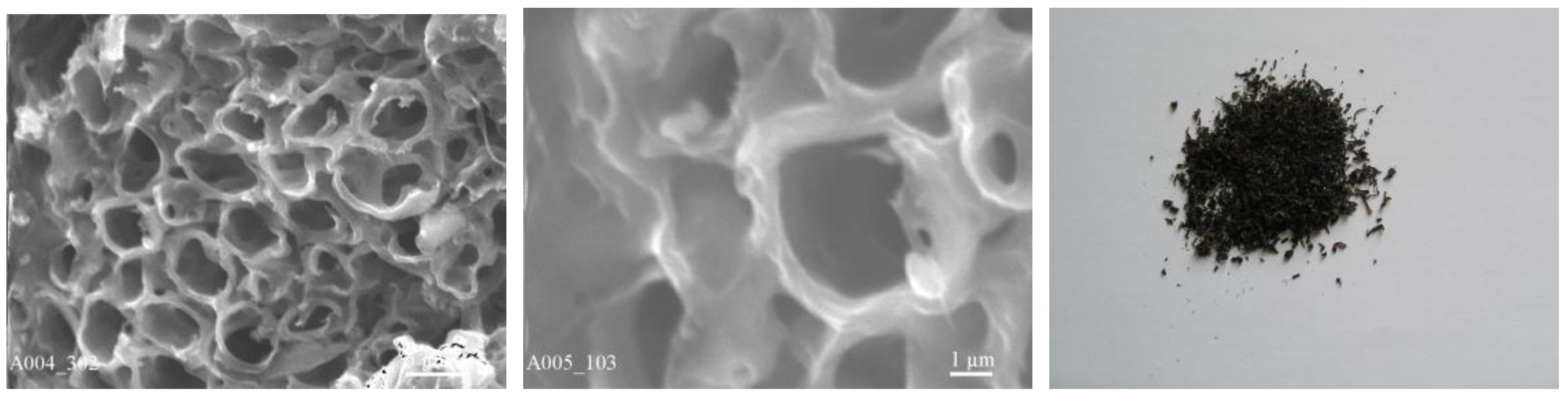

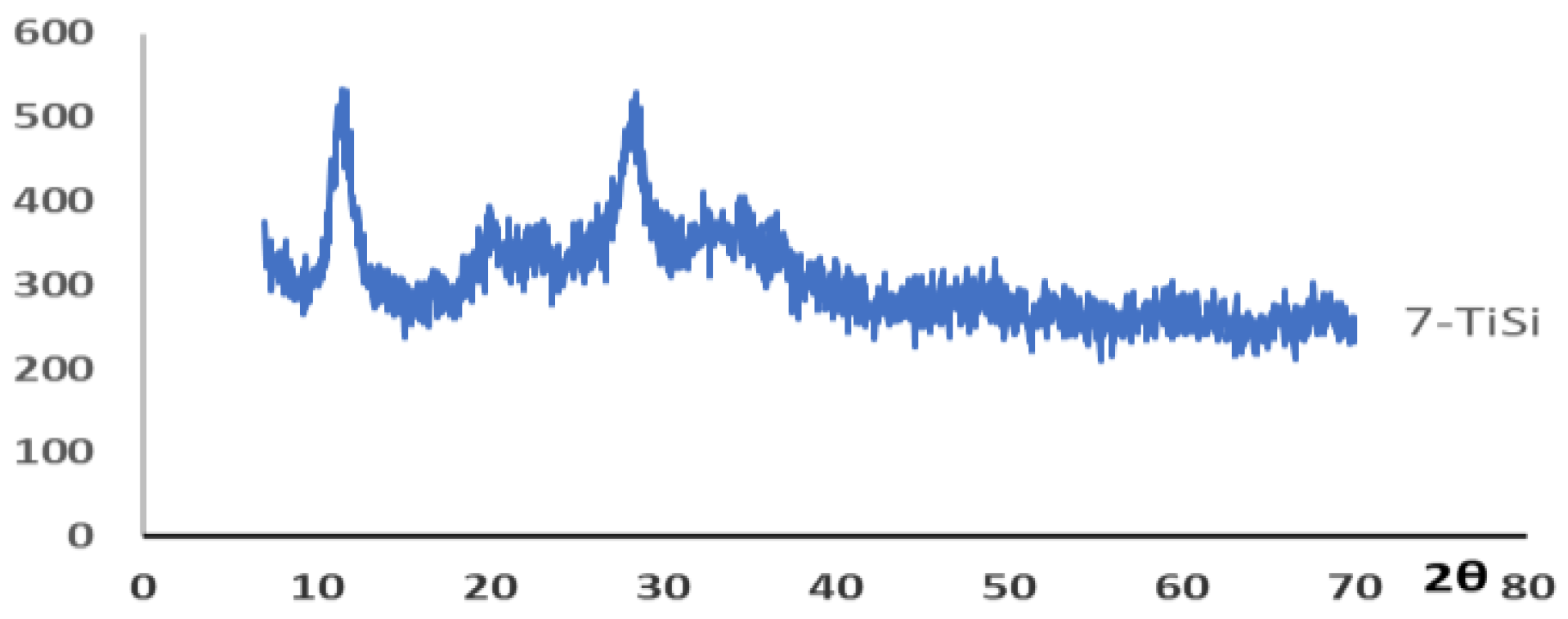
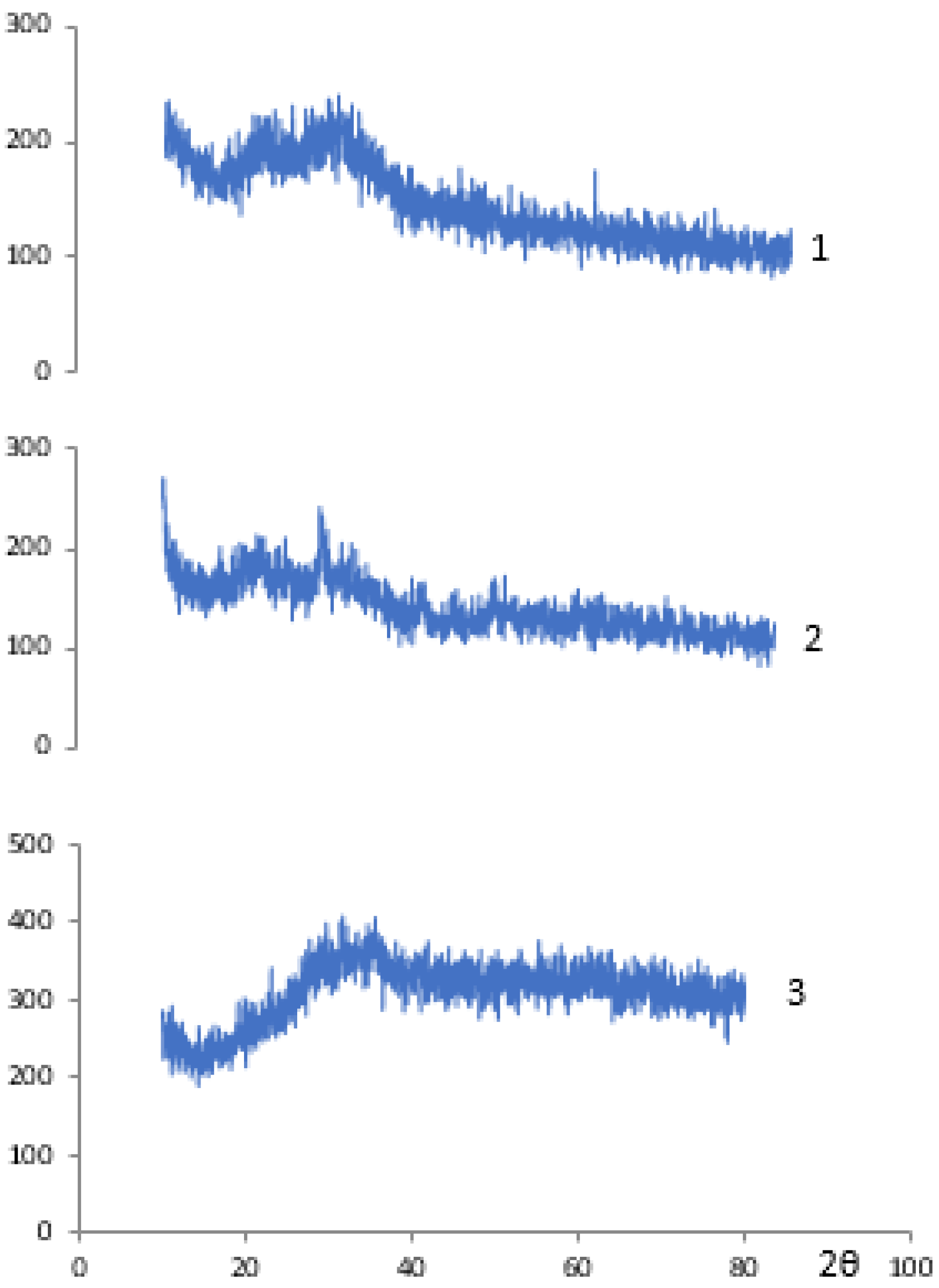
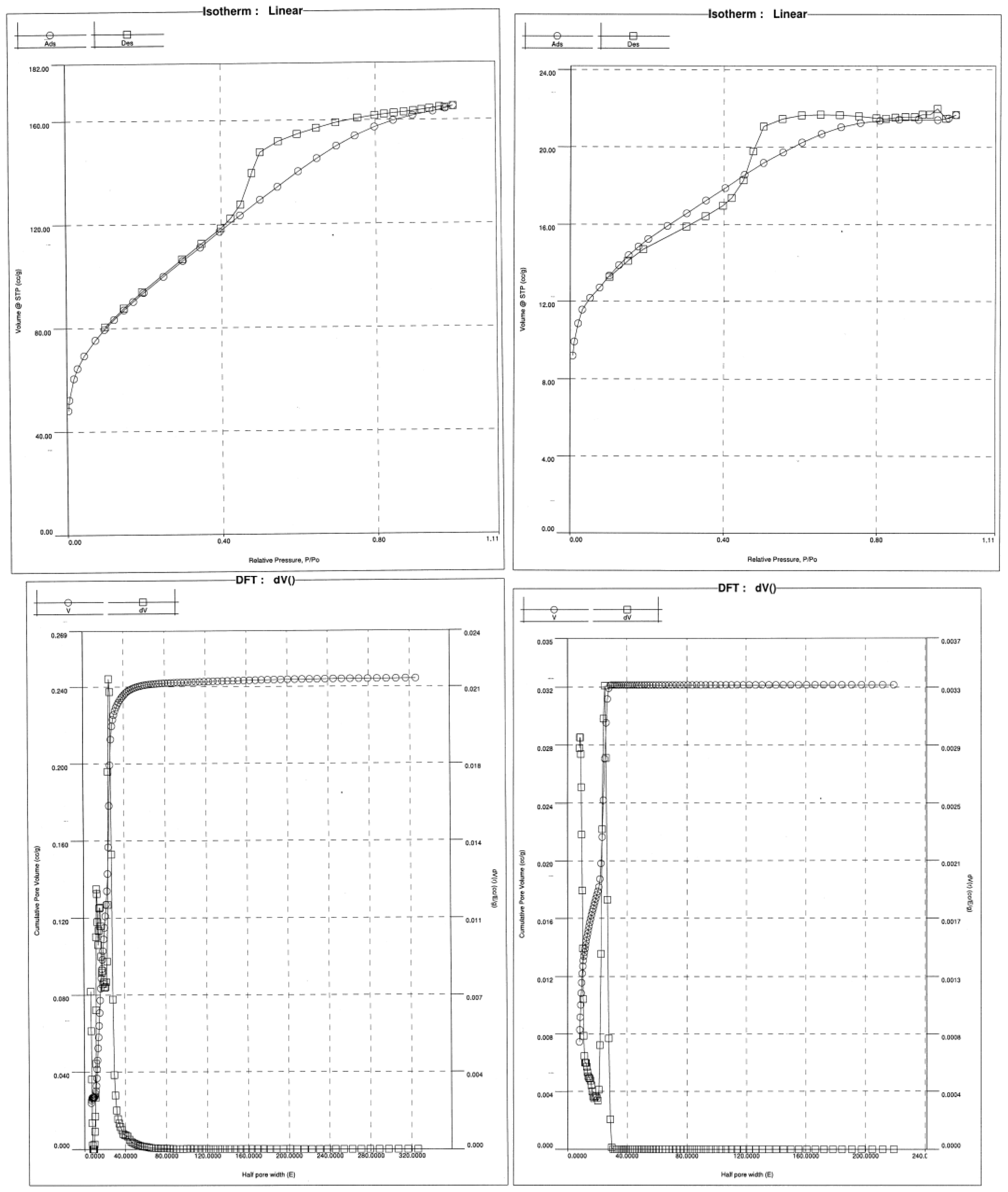
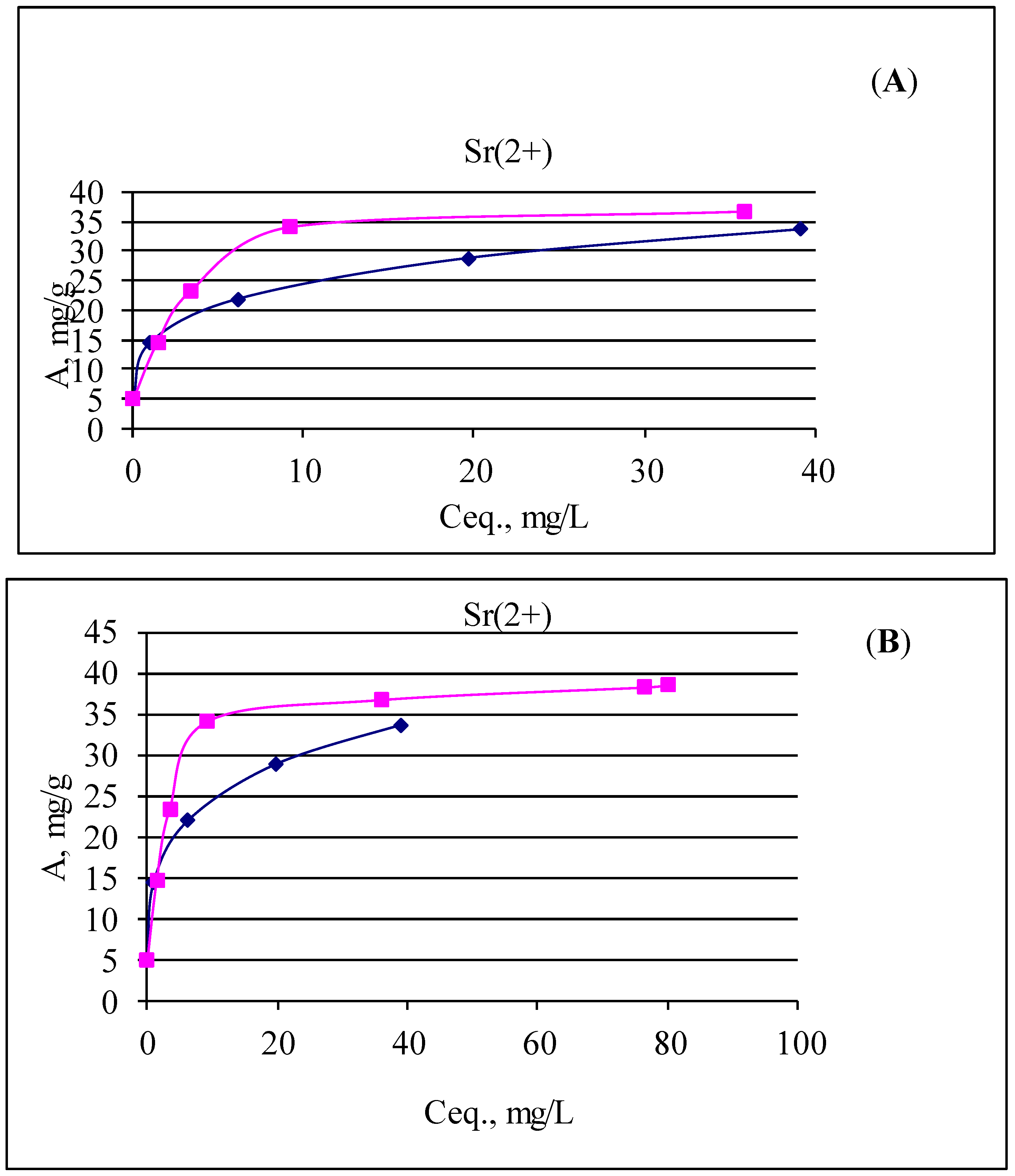
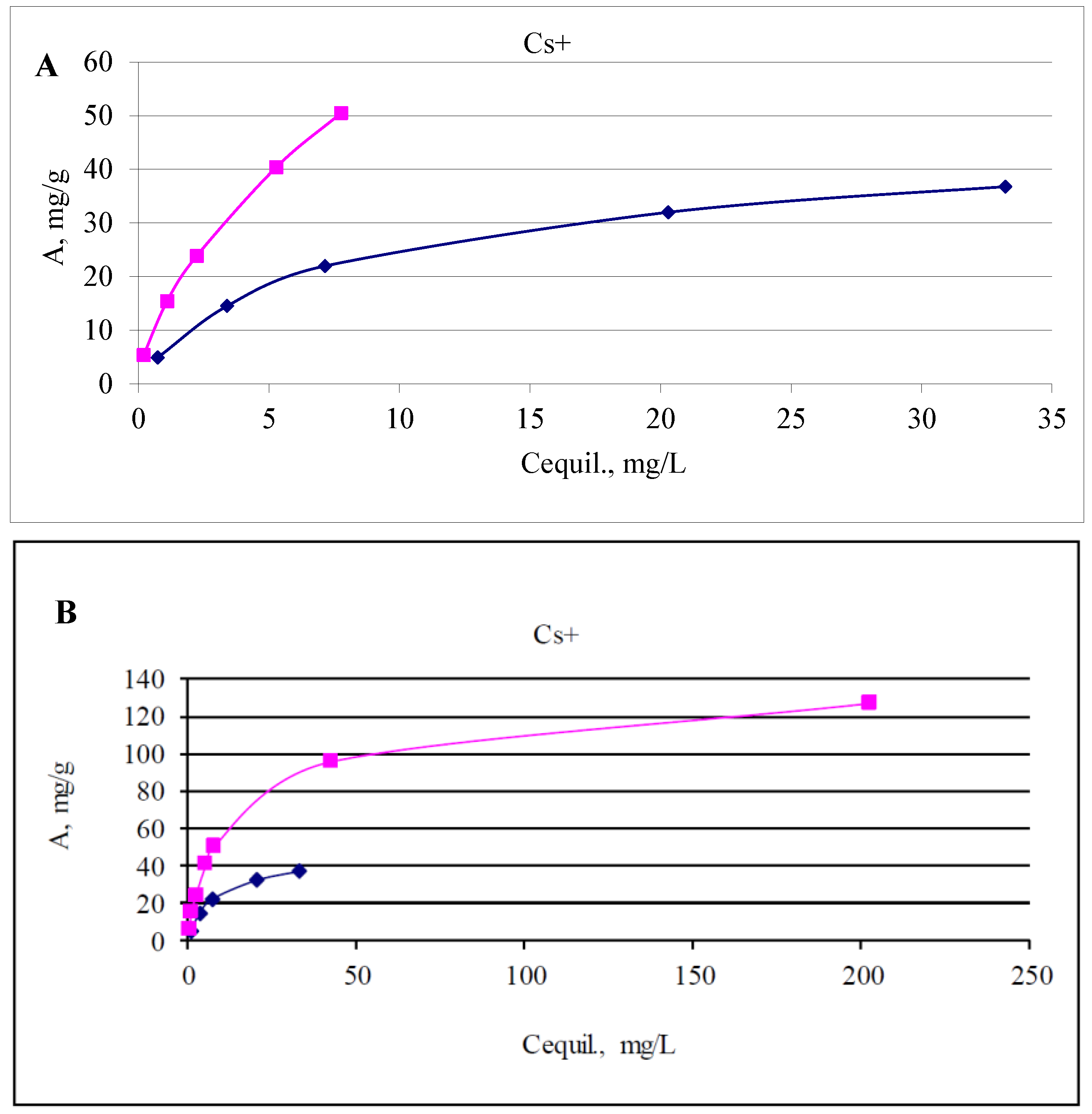
| Fraction | pH | Sr2+, mg/L | A | Kd | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Equil. | Cin. | Ceq. | ΔC | mg/g | mg-eqv./g | ||
| CarbonTiSi | 6.62 | 6.94 | 9.64 | 0.01 | 9.63 | 4.82 | 0.11 | 4.8 × 105 |
| 6.64 | 7.27 | 30.2 | 0.97 | 29.23 | 14.62 | 0.33 | 1.5 × 104 | |
| 6.37 | 7.0 | 50.5 | 6.2 | 44.3 | 22.15 | 0.51 | 3.6 × 103 | |
| 5.99 | 6.87 | 76.75 | 19.65 | 57.1 | 28.6 | 0.65 | 1.5 × 103 | |
| 6.06 | 6.74 | 107.88 | 39.1 | 68.78 | 34.4 | 0.79 | 0.9 × 103 | |
| Ti-Si powder | 6.62 | 6.88 | 9.64 | 0.04 | 9.6 | 4.8 | 0.11 | 1.2 × 105 |
| 6.64 | 6.85 | 30.2 | 1.44 | 28.76 | 14.38 | 0.33 | 1.0 × 104 | |
| 6.37 | 6.74 | 50.5 | 3.44 | 47.06 | 23.5 | 0.54 | 6.8 × 103 | |
| 5.99 | 6.67 | 76.75 | 9.26 | 67.49 | 33.7 | 0.77 | 3.6 × 103 | |
| 6.06 | 6.54 | 107.88 | 35.9 | 71.98 | 36.0 | 0.82 | 1.0 × 103 | |
| 6.38 | 6.65 | 185 | 108.6 | 76.5 | 38.3 | 0.87 | 352 | |
| 6.14 | 6.48 | 373 | 293 | 80 | 40 | 0.91 | 137 | |
| Fraction | pH | Cs+, mg/L | A | Kd | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Equil. | Cin. | Ceq. | ΔC | mg/g | mg-eqv/g | ||
| Carbontisi | 6.68 | 6.87 | 10.8 | 0.74 | 10.06 | 5.03 | 0.038 | 6.8 × 103 |
| 6.79 | 7.18 | 32.3 | 3.4 | 28.9 | 14.45 | 0.109 | 4.3 × 103 | |
| 6.76 | 7.16 | 51.0 | 7.15 | 43.95 | 21.98 | 0.165 | 3.1 × 103 | |
| 6.41 | 7.13 | 85.88 | 20.3 | 65.58 | 32.8 | 0.247 | 1.6 × 103 | |
| 6.33 | 7.15 | 107.75 | 33.2 | 75.55 | 37.78 | 0.284 | 1.1 × 103 | |
| 6.68 | 6.75 | 10.8 | 0.2 | 10.6 | 5.3 | 0.04 | 2.7 × 104 | |
| Ti-Si powder | 6.79 | 6.88 | 32.3 | 1.1 | 31.2 | 15.6 | 0.117 | 1.4 × 104 |
| 6.76 | 6.90 | 51.0 | 2.24 | 48.76 | 24.4 | 0.18 | 1.1 × 104 | |
| 6.41 | 9.80 | 85.88 | 5.28 | 80.6 | 40.3 | 0.30 | 7.6 × 103 | |
| 6.33 | 6.89 | 107.75 | 7.76 | 100.99 | 50.5 | 0.38 | 6.5 × 103 | |
| 6.68 | 7.24 | 237.5 | 42.3 | 195.2 | 97.6 | 0.73 | 2.3 × 103 | |
| 6.70 | 7.01 | 463 | 202.5 | 260.5 | 130.3 | 0.98 | 6.4 × 102 | |
| 6.62 | 6.38 | 686 | 371.5 | 314.5 | 157.3 | 1.18 | 423 | |
| 6.45 | 6.32 | 968 | 623 | 345 | 172.5 | 1.30 | 277 | |
| No. | Sample | Cesium: Concentration, mg/L; Kd, mL/g, and Adsorption, mg/g | Strontium: Concentration, mg/L; Kd, mL/g; and Adsorption, mg/g | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cin. | Ceq. | A | Kd | Cin. | Ceq. | A | Kd | ||
| 1 | 200 °C TiSi powder autoclave 10 h | 10.8 | 0.2 | 5.3 | 27,000 | 9.64 | 0.04 | 4.8 | 120,000 |
| 2 | Blowing steam TiSi powder 150 °C, 2 h | 10.18 | 3.01 | 3.59 | 1200 | 7.2 | 0.04 | 3.58 | 90,000 |
| 3 | Blowing steam TiSi powder 400 °C, 2 h | 10.66 | 2.77 | 3.95 | 1424 | 8.38 | 0.002 | 4.19 | 2,095,000 |
| 4 | Blowing steam TiSi powder 600 °C, 2 h | 10.66 | 3.56 | 3.55 | 1000 | 8.38 | 0.003 | 4.19 | 1,396,000 |
| 5 | Blowing steam TiSi powder 800 °C, 2 h | 10.66 | 4.79 | 2.94 | 613 | 8.38 | 0.05 | 4.17 | 83,300 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuravlev, I. Titanium Silicates Precipitated on the Rice Husk Biochar as Adsorbents for the Extraction of Cesium and Strontium Radioisotope Ions. Colloids Interfaces 2019, 3, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3010036
Zhuravlev I. Titanium Silicates Precipitated on the Rice Husk Biochar as Adsorbents for the Extraction of Cesium and Strontium Radioisotope Ions. Colloids and Interfaces. 2019; 3(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuravlev, Igor. 2019. "Titanium Silicates Precipitated on the Rice Husk Biochar as Adsorbents for the Extraction of Cesium and Strontium Radioisotope Ions" Colloids and Interfaces 3, no. 1: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3010036
APA StyleZhuravlev, I. (2019). Titanium Silicates Precipitated on the Rice Husk Biochar as Adsorbents for the Extraction of Cesium and Strontium Radioisotope Ions. Colloids and Interfaces, 3(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids3010036




