Low Salinity Waterflooding in Carbonate Reservoirs: Review of Interfacial Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Working Conditions
2.1. Reservoir Parameters
2.1.1. Formation Water Composition and pH
2.1.2. Initial Water Saturation
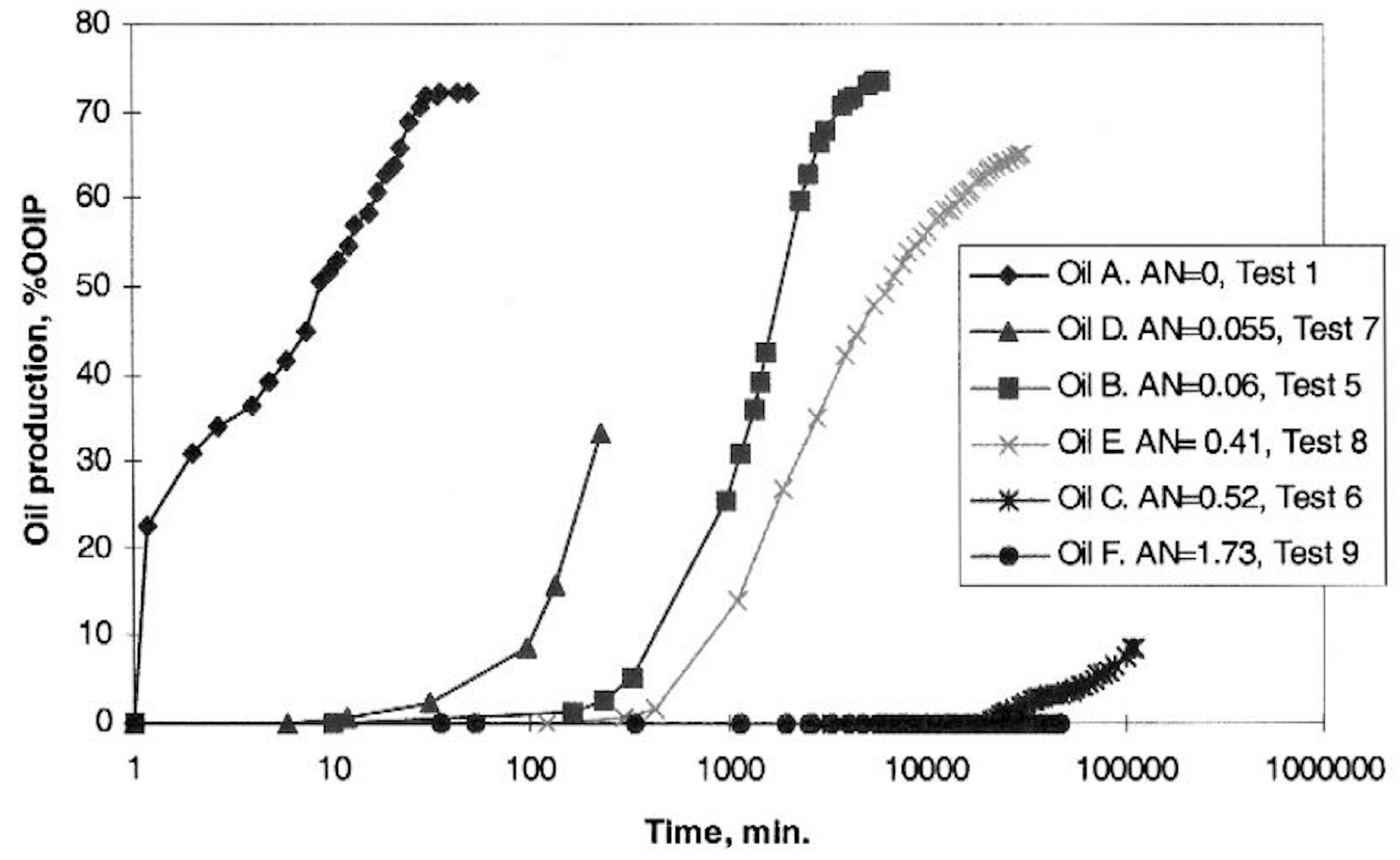
2.1.3. Crude Oil Composition
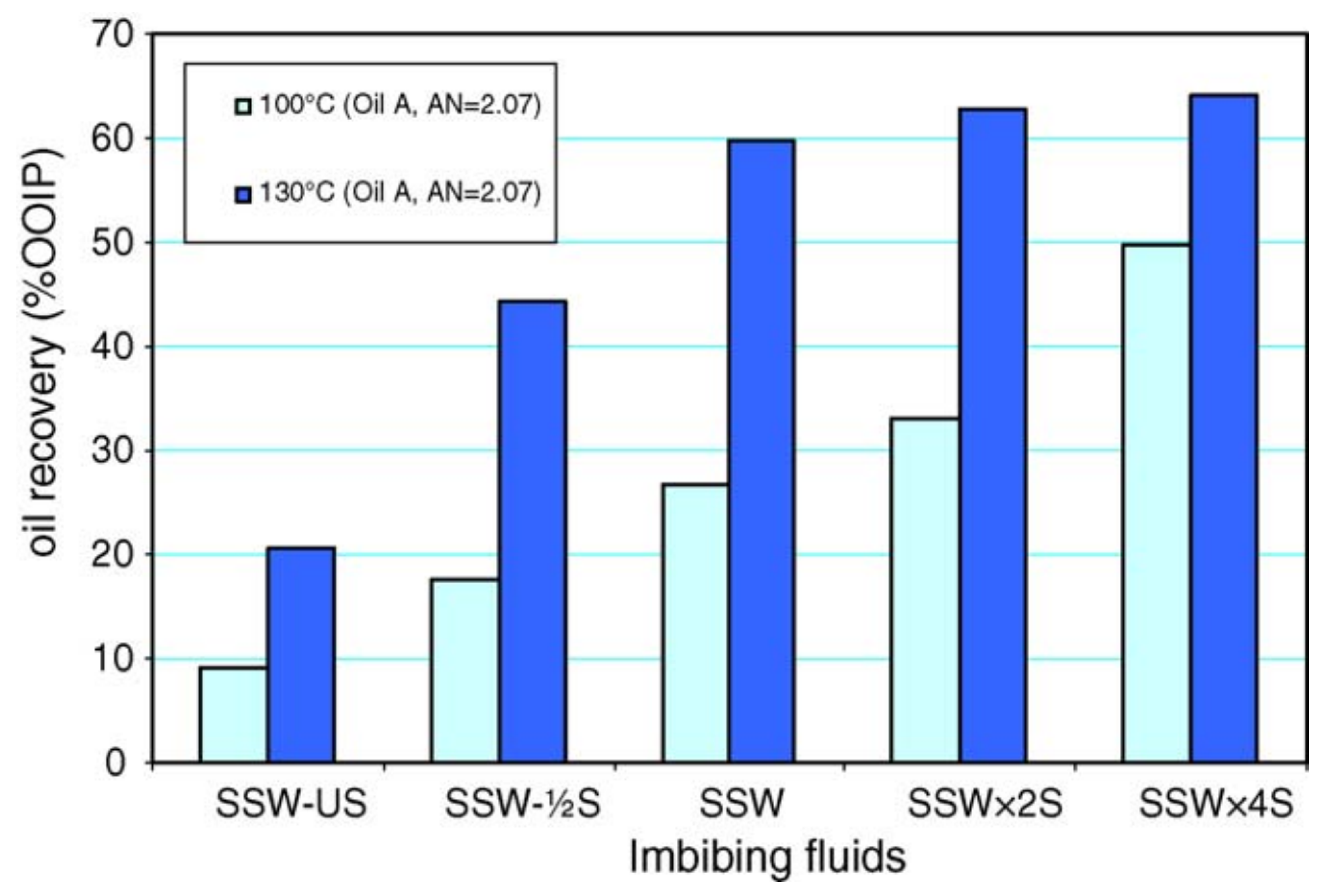
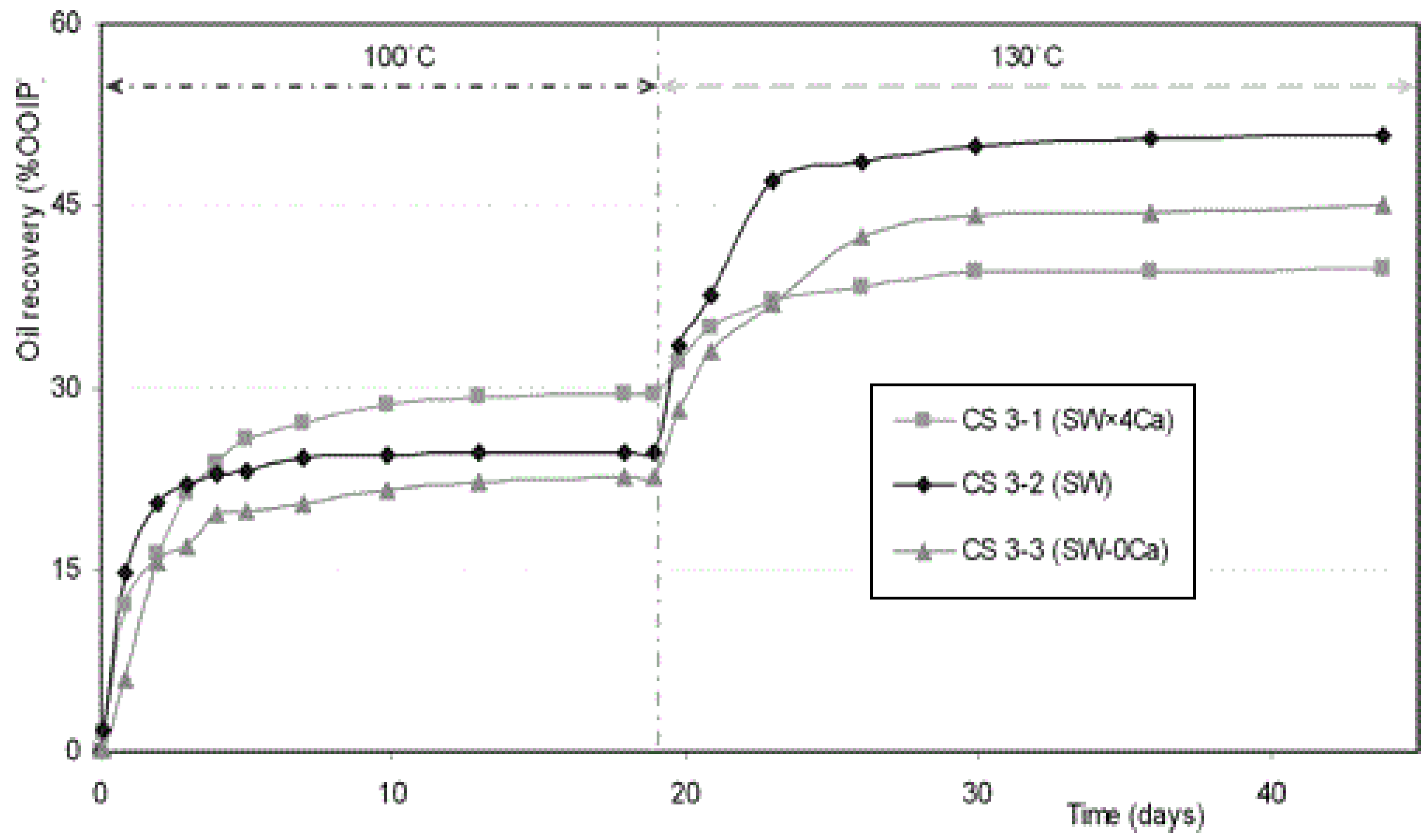
2.1.4. Aging Time, Temperature, and Pressure
2.1.5. Rock Mineralogy
2.1.6. Rock Porosity and Permeability
2.2. Injected Brine Parameters
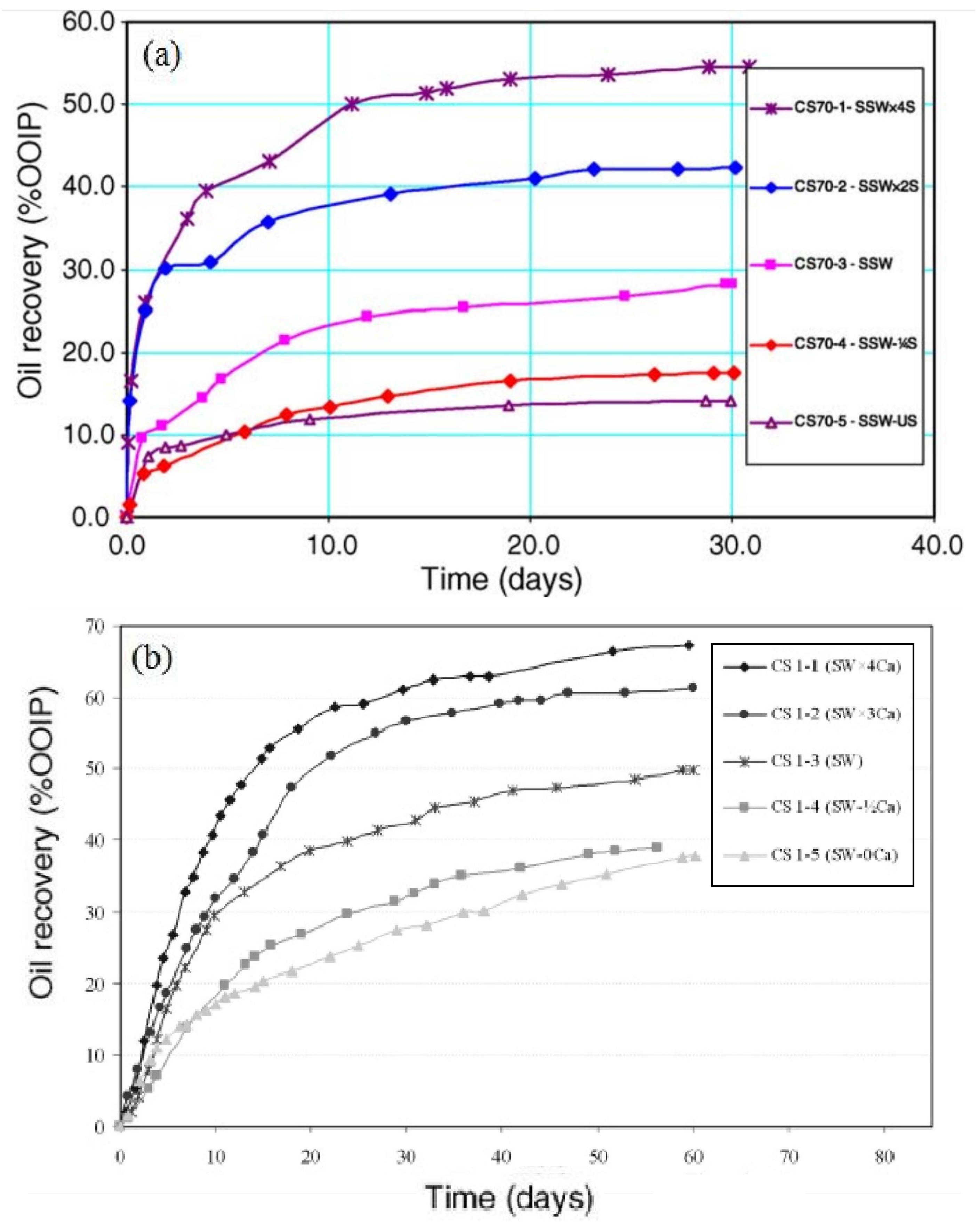
2.2.1. Ionic Composition and Temperature
2.2.2. Ionic Concentration
2.2.3. Surfactant
3. Investigation Techniques
3.1. Surface Wettability
3.1.1. Chromatographic Wettability
3.1.2. Contact Angle
3.1.3. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
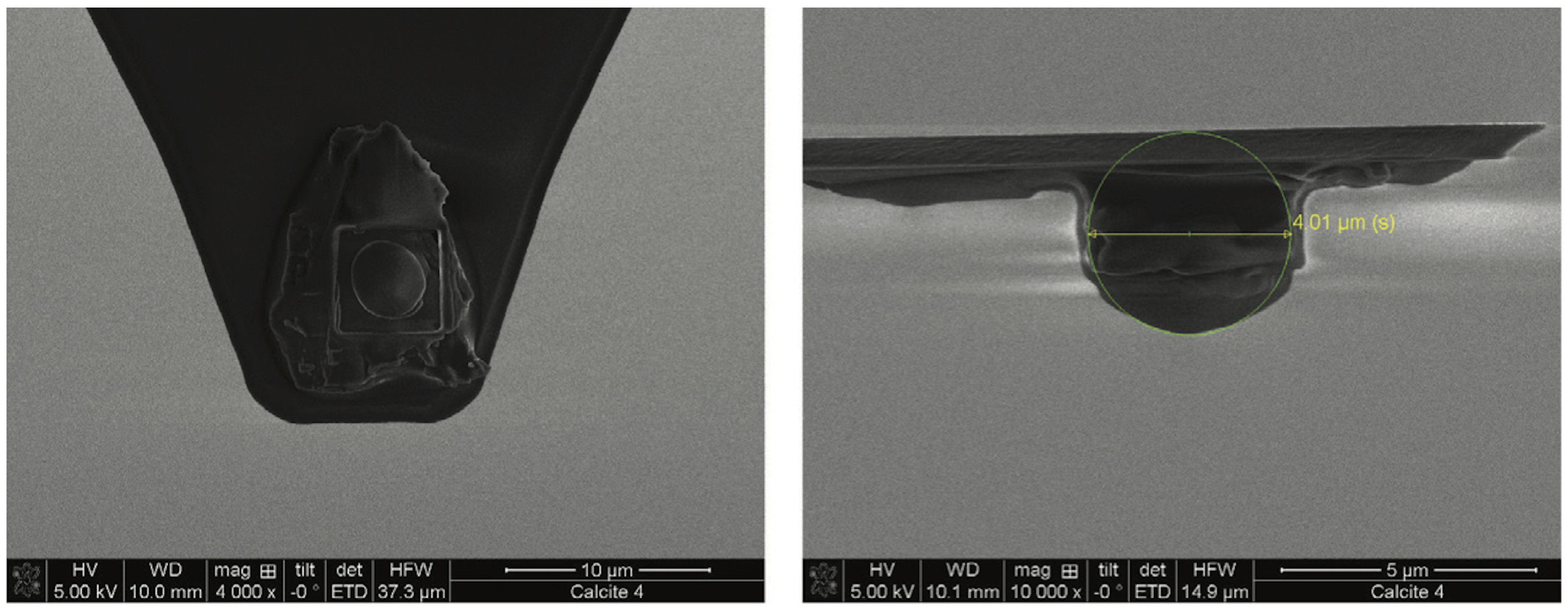
3.1.4. Atomic Force Microscopy
3.1.5. Zeta Potential
3.1.6. Surface Complexation Modelling
3.2. Interfacial Tension
3.3. Recovery Factor
3.3.1. Imbibition
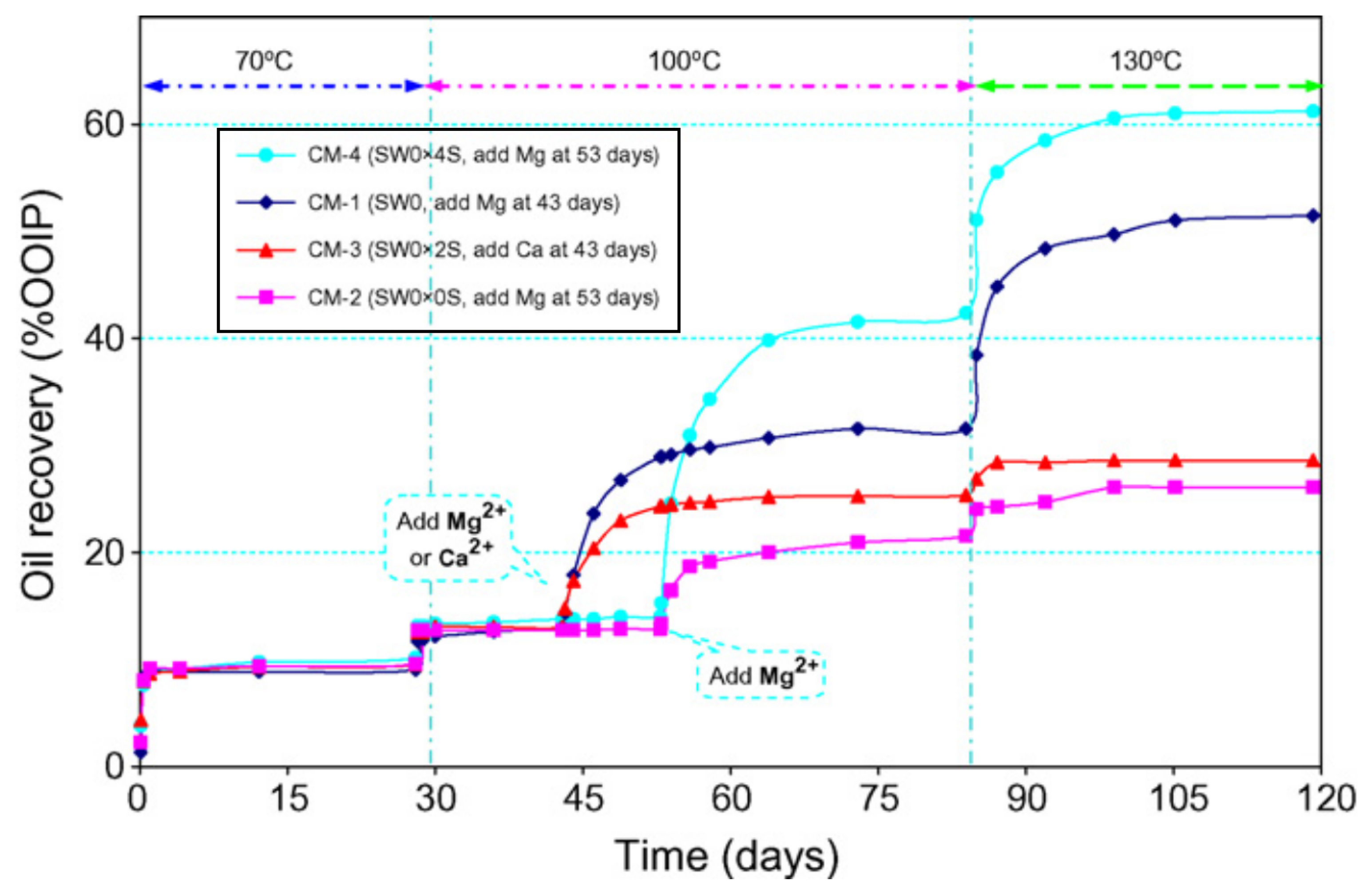
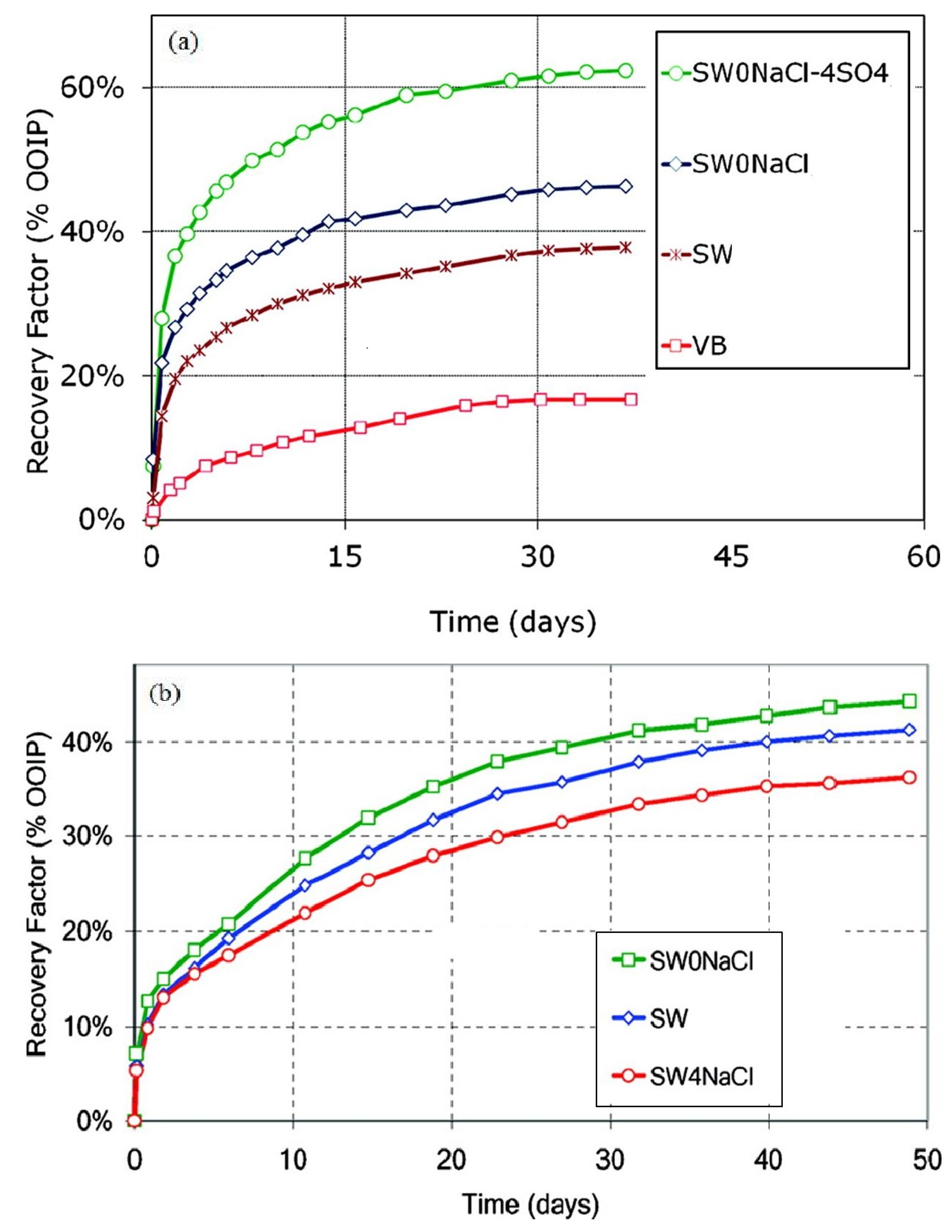
3.3.2. Coreflooding
3.3.3. Reservoir Modelling
3.4. Field Studies
4. Proposed Mechanisms
4.1. Multicomponent Ionic Exchange
4.2. Rock Dissolution
4.3. Fines Migration
4.4. Reduction of Interfacial Tension and Role of pH
4.5. Fluid–Fluid Interactions and Formation of Microemulsions
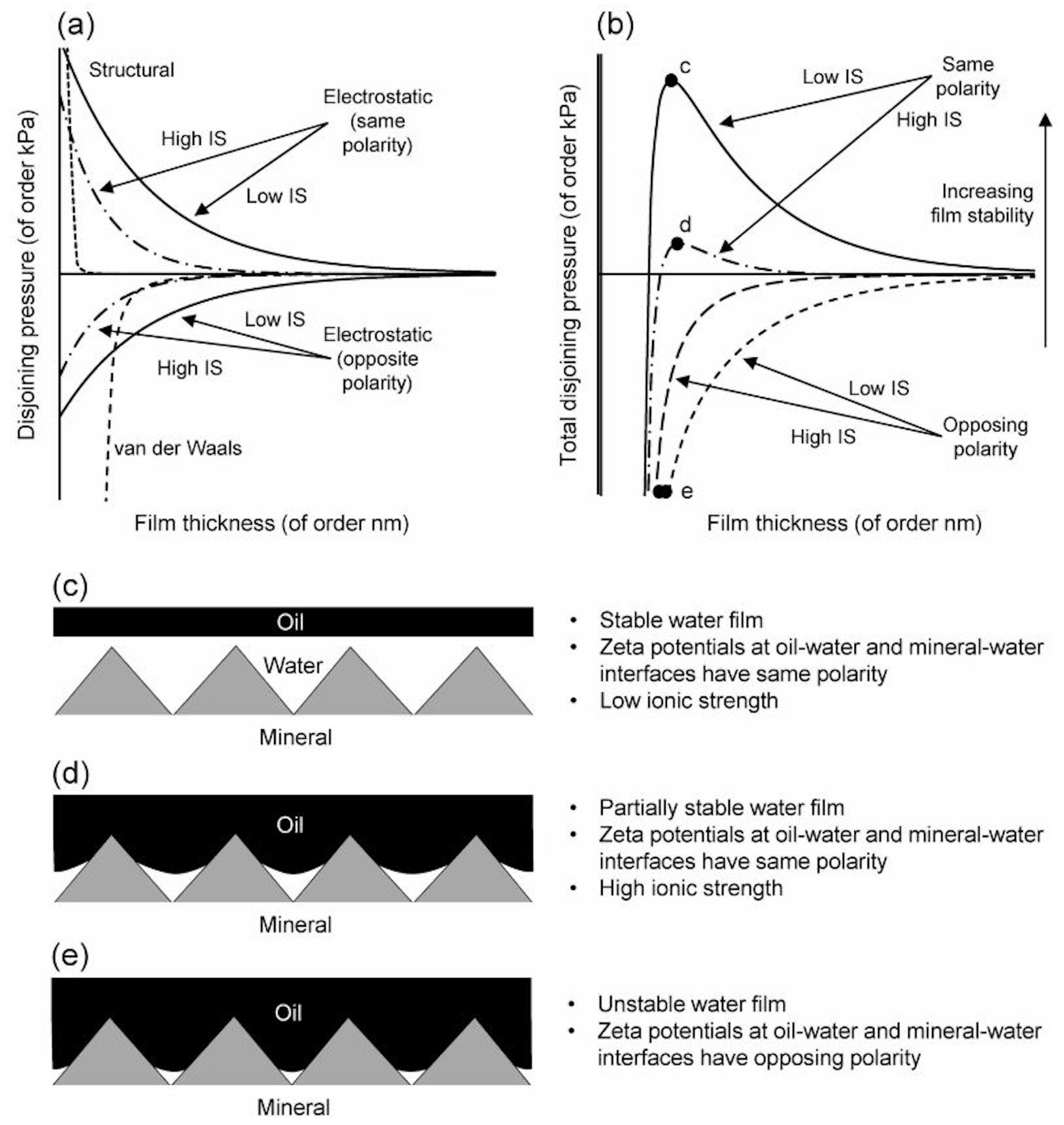
4.6. Expansion of Electric Double Layer
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kokal, S.; Al-Kaabi, A. Enhanced oil recovery: Challenges & opportunities. World Pet. Coun. Off. Publ. 2010, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Terry, R.E. Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, J. Enhanced Oil Recovery Field Case Studies; Elsevier Science: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lyons, W.C.; Plisga, G.J. Standard Handbook of Petroleum and Natural Gas Engineering; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lake, L.W. Enhanced Oil Recovery; Prentice Hall Englewood Cliffs: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, P.K. A Water-Sensitive Sandstone Flood Using Low Salinity Water. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhunandan, P.P. Effects of Brine Composition, Crude Oil, and Aging Conditions on Wettability and Oil Recovery. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Petroleum Engineering, New Mexico Institute of Mining & Technology, Socorro, NM, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhunandan, P.; Morrow, N. Spontaneous imbibition of water by crude oil/brine/rock systems. In Situ (USA) 1991, 15, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhunandan, P.; Morrow, N.R. Effect of wettability on waterflood recovery for crude-oil/brine/rock systems. Soc. Pet. Eng. Reserv. Eng. 1995, 10, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, H.O.; Morrow, N.R. Effect of brine composition on recovery of Moutray crude oil by waterflooding. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 1996, 14, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Morrow, N.R. Salinity, temperature, oil composition, and oil recovery by waterflooding. Soc. Pet. Eng. Reserv. Eng. 1997, 12, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.Q.; Morrow, N.R. Influence of brine composition and fines migration on crude oil/brine/rock interactions and oil recovery. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 1999, 24, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, K.; Black, C.; Al-Ajeel, H. Low salinity oil recovery-log-inject-log. In Proceedings of the Middle East Oil & Gas Show and Conference, 9–12 June 2003; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Manama, Bahrain, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, K.; Black, C.; Edmonds, I. Low salinity oil recovery–The role of reservoir condition corefloods. In Proceedings of the IOR 2005-13th European Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, Budapest, Hungary, 25–27 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, K.J.; Black, C.J.J.; Tjetland, G. A laboratory study investigating methods for improving oil recovery in carbonates. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Doha, Qatar, 21–23 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- McGuire, P.; Chatham, J.; Paskvan, F.; Sommer, D.; Carini, F. Low salinity oil recovery: An exciting new EOR opportunity for Alaska’s North Slope. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Western Regional Meeting, Irvine, CA, USA, 30 March–1 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, E.P. Low-Salinity Waterflooding to Improve Oil Recovery-Historical Field Evidence; Technical Report; Idaho National Laboratory (INL): Idaho Falls, ID, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lager, A.; Webb, K.J.; Collins, I.R.; Richmond, D.M. LoSal enhanced oil recovery: Evidence of enhanced oil recovery at the reservoir scale. In Society of Petroleum Engineers Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Seccombe, J.; Lager, A.; Jerauld, G.; Jhaveri, B.; Buikema, T.; Bassler, S.; Denis, J.; Webb, K.; Cockin, A.; Fueg, E. Demonstration of low-salinity EOR at interwell scale, Endicott field, Alaska. In Society of Petroleum Engineers Improved Oil Recovery Symposium; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ligthelm, D.J.; Gronsveld, J.; Hofman, J.; Brussee, N.; Marcelis, F.; van der Linde, H. Novel waterflooding strategy By manipulation Of injection brine composition. In Proceedings of the EUROPEC/EAGE Conference and Exhibition, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–11 June 2009; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nasralla, R.A.; Sergienko, E.; Masalmeh, S.K.; van der Linde, H.A.; Brussee, N.J.; Mahani, H.; Suijkerbuijk, B.M.; Al-Qarshubi, I.S. Potential of low-salinity waterflood to improve oil recovery in carbonates: Demonstrating the effect by qualitative coreflood. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 2016, 21, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasralla, R.A.; Mahani, H.; van der Linde, H.A.; Marcelis, F.H.; Masalmeh, S.K.; Sergienko, E.; Brussee, N.J.; Pieterse, S.G.; Basu, S. Low Salinity waterflooding for a carbonate reservoir: Experimental evaluation and numerical interpretation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 164, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vledder, P.; Gonzalez, I.E.; Carrera Fonseca, J.C.; Wells, T.; Ligthelm, D.J. Low salinity water flooding: Proof of wettability alteration on a field wide scale. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Tulsa, OK, USA, 24-28 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mahani, H.; Sorop, T.; Ligthelm, D.J.; Brooks, D.; Vledder, P.; Mozahem, F.; Ali, Y. Analysis of field responses to low-salinity waterflooding in secondary and tertiary mode in Syria. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers EUROPEC/EAGE Annual Conference and Exhibition, Vienna, Austria, 23–26 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mahani, H.; Menezes, R.; Berg, S.; Fadili, A.; Nasralla, R.; Voskov, D.; Joekar-Niasar, V. Insights into the impact of temperature on the wettability alteration by low salinity in carbonate rocks. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 7839–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahani, H.; Keya, A.L.; Berg, S.; Nasralla, R. Electrokinetics of carbonate/brine interface in low-salinity waterflooding: Effect of brine salinity, composition, rock type, and pH on ζ-potential and a surface-complexation model. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 2017, 22, 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Smith, G.G.; Hu, L.; Willingham, T.; Lo Cascio, M.; Shyeh, J.J.; Harris, C.R. Enhanced waterflood for carbonate reservoirs-impact of injection water composition. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Middle East Oil and Gas Show and Conference, Manama, Bahrain, 25–28 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Lu, P.; Glotzbach, R.; Hehmeyer, O. A Novel, field-representative enhanced-oil-recovery coreflood method. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 2015, 20, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, W.; Gmira, A. Wettability assessment and surface compositional analysis of aged calcite treated with dynamic water. Energy Fuels 2013, 28, 1652–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasha, A.; Al-Hashim, H.; Abdallah, W.; Taherian, R.; Sauerer, B. Effect of Ca2+, Mg2+ and SO ions on the zeta potential of calcite and dolomite particles aged with stearic acid. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 482, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hashim, H.; Kasha, A.A.; Abdallah, W.; Sauerer, B. Impact of modified seawater on zeta potential and morphology of calcite and dolomite aged with stearic acid. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 1644–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soraya, B.; Malick, C.; Philippe, C.; Bertin, H.J.; Hamon, G. Oil recovery by low-salinity brine injection: Laboratory results on outcrop and reservoir cores. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 4–7 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cissokho, M.; Bertin, H.; Boussour, S.; Cordier, P.; Hamon, G. Low salinity oil recovery on clayey sandstone: Experimental study. Petrophysics 2010, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, A.; Hadia, N.; Torsaeter, O.; Tweheyo, M.T. Laboratory investigation of low salinity waterflooding as secondary recovery process: Effect of wettability. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Oil and Gas India Conference and Exhibition, Mumbai, India, 20–22 January 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Skrettingland, K.; Holt, T.; Tweheyo, M.T.; Skjevrak, I. Snorre low-salinity-water injection–coreflooding experiments and single-well field pilot. Soc. Pet. Eng. Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2011, 14, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazankapov, N. Enhanced oil recovery in Caspian carbonates with “smart water”. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Russian Oil and Gas Exploration & Production Technical Conference and Exhibition, Moscow, Russia, 14–16 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yousef, A.A.; Al-Saleh, S.; Al-Jawfi, M.S. Improved/enhanced oil recovery from carbonate reservoirs by tuning injection water salinity and ionic content. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Tulsa, OK, USA, 14–18 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yousef, A.A.; Al-Saleh, S.; Al-Kaabi, A.U.; Al-Jawfi, M.S. Laboratory investigation of novel oil recovery method for carbonate reservoirs. In Proceedings of the Canadian Unconventional Resources and International Petroleum Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 19–21 October 2010; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shaker Shiran, B.; Skauge, A. Enhanced oil recovery (EOR) by combined low salinity water/polymer flooding. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthiesen, J.; Bovet, N.; Hilner, E.; Andersson, M.P.; Schmidt, D.; Webb, K.; Dalby, K.N.; Hassenkam, T.; Crouch, J.; Collins, I. How naturally adsorbed material on minerals affects low salinity enhanced oil recovery. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 4849–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerauld, G.R.; Webb, K.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Seccombe, J. Modeling low-salinity waterflooding. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, San Antonio, TX, USA, 24–27 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sohal, M.A.; Thyne, G.; Søgaard, E.G. Review of recovery mechanisms of ionically modified waterflood in carbonate reservoirs. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 1904–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.; Sharma, H.; Mohanty, K.K. Wettability alteration with brine composition in high temperature carbonate rocks. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dubai, UAE, 26–28 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Akbar, M.; Vissapragada, B.; Alghamdi, A.H.; Allen, D.; Herron, M.; Carnegie, A.; Dutta, D.; Olesen, J.R.; Chourasiya, R.; Logan, D. A snapshot of carbonate reservoir evaluation. Oilfield Rev. 2000, 12, 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Marathe, R.; Turner, M.L.; Fogden, A. Pore-scale distribution of crude oil wettability in carbonate rocks. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 6268–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, P.C.; Firoozabadi, A. Thin liquid films in improved oil recovery from low-salinity brine. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 20, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomari, K.R.; Hamouda, A. Effect of fatty acids, water composition and pH on the wettability alteration of calcite surface. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2006, 50, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauerer, B.; Stukan, M.; Abdallah, W.; Derkani, M.H.; Fedorov, M.; Buiting, J.; Zhang, Z.J. Quantifying mineral surface energy by scanning force microscopy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 472, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, M.; Al-Maamari, R.S.; Ayatollahi, S.; Mehranbod, N. Mechanistic study of wettability alteration of oil-wet calcite: The effect of magnesium ions in the presence and absence of cationic surfactant. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 482, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomari, K.R.; Denoyel, R.; Hamouda, A. Wettability of calcite and mica modified by different long-chain fatty acids (C18 acids). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 297, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badri, M.; El-Banbi, A.; Montaron, B. The Schlumberger commitment to carbonate reservoirs. Middle East Asia Reserv. Rev. 2009, 4–15. [Google Scholar]
- Puntervold, T.; Strand, S.; Austad, T. Coinjection of seawater and produced water to improve oil recovery from fractured North Sea chalk oil reservoirs. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 2527–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaron, B. Defining the challenges of carbonate reservoirs. Middle East Asia Reserv. Rev. 2009, 9, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lager, A.; Webb, K.; Black, C. Impact of brine chemistry on oil recovery. In Proceedings of the IOR 2007-14th European Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, Cairo, Egypt, 22 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lager, A.; Webb, K.J.; Black, C.; Singleton, M.; Sorbie, K.S. Low salinity oil recovery-an experimental investigation1. Petrophysics 2008, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Seccombe, J.C.; Lager, A.; Webb, K.J.; Jerauld, G.; Fueg, E. Improving wateflood recovery: LoSalTM EOR field evaluation. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, Tulsa, Oklahoma, USA, 20–23 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Morrow, N.R. Comparison of secondary and tertiary recovery with change in injection brine composition for crude-oil/sandstone combinations. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers/DOE Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, Tulsa, OK, USA, 22–26 April 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Strand, S.; Høgnesen, E.J.; Austad, T. Wettability alteration of carbonates—Effects of potential determining ions (Ca2+ and SO) and temperature. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 275, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, S.; Austad, T.; Puntervold, T.; Høgnesen, E.J.; Olsen, M.; Barstad, S.M.F. “Smart water” for oil recovery from fractured limestone: A preliminary study. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 3126–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RezaeiDoust, A.; Puntervold, T.; Strand, S.; Austad, T. Smart water as wettability modifier in carbonate and sandstone: A discussion of similarities/differences in the chemical mechanisms. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 4479–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austad, T.; Strand, S.; Høgnesen, E.; Zhang, P. Seawater as IOR fluid in fractured chalk. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers International Symposium on Oilfield Chemistry, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 2–4 February 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Austad, T.; Shariatpanahi, S.; Strand, S.; Black, C.; Webb, K. Conditions for a low-salinity enhanced oil recovery (EOR) effect in carbonate oil reservoirs. Energy Fuels 2011, 26, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tweheyo, M.T.; Austad, T. Wettability alteration and improved oil recovery by spontaneous imbibition of seawater into chalk: Impact of the potential determining ions Ca2+, Mg2+, and SO. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 301, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, S.; Puntervold, T.; Austad, T. Effect of temperature on enhanced oil recovery from mixed-wet chalk cores by spontaneous imbibition and forced displacement using seawater. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 3222–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, S.J.; Austad, T.; Strand, S. “Smart water” as a wettability modifier in chalk: The effect of salinity and ionic composition. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2514–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, A.A.; Al-Salehsalah, S.H.; Al-Jawfi, M.S. New recovery method for carbonate reservoirs through tuning the injection water salinity: Smart waterflooding. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers EUROPEC/EAGE Annual Conference and Exhibition, Vienna, Austria, 23–26 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yousef, A.A.; Al-Saleh, S.; Al-Jawfi, M.S. The impact of the injection water chemistry on oil recovery from carbonate reservoirs. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers EOR Conference at Oil and Gas West Asia, Muscat, Oman, 16–18 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yousef, A.A.; Al-Saleh, S.H.; Al-Kaabi, A.; Al-Jawfi, M.S. Laboratory investigation of the impact of injection-water salinity and ionic content on oil recovery from carbonate reservoirs. Soc. Pet. Eng. Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2011, 14, 578–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, A.; Shapiro, A.A.; Skauge, A. Experimental studies of low salinity water flooding carbonate: A new promising approach. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Enhanced Oil Recovery Conference at Oil and Gas West Asia, Muscat, Oman, 16–18 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Winoto, W.; Loahardjo, N.; Xie, S.X.; Yin, P.; Morrow, N.R. Secondary and tertiary recovery of crude oil from outcrop and reservoir rocks by low salinity waterflooding. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Tulsa, OK, USA, 14–18 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Agbalaka, C.C.; Dandekar, A.Y.; Patil, S.L.; Khataniar, S.; Hemsath, J.R. Coreflooding studies to evaluate the impact of salinity and wettability on oil recovery efficiency. Transp. Porous Media 2009, 76, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, X.; Morrow, N.R. Waterflood performance by injection of brine with different salinity for reservoir cores. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Anaheim, CA, USA, 11–14 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nasralla, R.A.; Nasr-El-Din, H.A. Double-layer expansion: Is it a primary mechanism of improved oil recovery by low-salinity waterflooding? Soc. Pet. Eng. Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2014, 17, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivet, S.; Lake, L.W.; Pope, G.A. A coreflood investigation of low-salinity enhanced oil recovery. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Florence, Italy, 19–22 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nasralla, R.A.; Nasr-El-Din, H.A. Impact of electrical surface charges and cation exchange on oil recovery by low salinity water. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Asia Pacific Oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition, Jakarta, Indonesia, 20–22 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Austad, T.; RezaeiDoust, A.; Puntervold, T. Chemical mechanism of low salinity water flooding in sandstone reservoirs. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers improved oil recovery symposium, Tulsa, OK, USA, 24–28 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Morrow, N.; Buckley, J. Improved oil recovery by low-salinity waterflooding. J. Pet. Technol. 2011, 63, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awolayo, A.; Sarma, H.; AlSumaiti, A.M. A laboratory study of ionic effect of smart water for enhancing oil recovery in carbonate reservoirs. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers EOR Conference at Oil and Gas West Asia, Muscat, Oman, 31 March–2 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, S.J.; Austad, T.; Strand, S. Water-based enhanced oil recovery (EOR) by “smart water”: Optimal ionic composition for EOR in carbonates. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 5173–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Sarma, H.K. Improving waterflood recovery efficiency in carbonate reservoirs through salinity variations and ionic exchanges: A promising low-cost “smart-waterflood” approach. In Proceedings of the Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Conference and Exhibition, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 11–14 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tetteh, J.T.; Rankey, E.; Barati, R. Low Salinity Waterflooding Effect: Crude Oil/Brine Interactions as a Recovery Mechanism in Carbonate Rocks. In OTC Brasil; Offshore Technology Conference: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Wang, M. Electrokinetic mechanism of wettability alternation at oil-water-rock interface. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2018, 72, 369–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afekare, D.A.; Radonjic, M. From mineral surfaces and coreflood experiments to reservoir implementations: Comprehensive review of low-salinity water flooding (LSWF). Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 13043–13062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purswani, P.; Tawfik, M.S.; Karpyn, Z.T. Factors and mechanisms governing wettability alteration by chemically tuned waterflooding: A review. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 7734–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiorth, A.; Cathles, L.; Madland, M. The impact of pore water chemistry on carbonate surface charge and oil wettability. Transp. Porous Media 2010, 85, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabtree, M.; Eslinger, D.; Fletcher, P.; Miller, M.; Johnson, A.; King, G. Fighting scale—Removal and prevention. Oilfield Rev. 1999, 11, 30–45. [Google Scholar]
- Shariatpanahi, S.F.; Strand, S.; Austad, T. Initial wetting properties of carbonate oil reservoirs: Effect of the temperature and presence of sulfate in formation water. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 3021–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanuka, J.; Hofman, J.; Ligthelm, D.J.; Suijkerbuijk, B.; Marcelis, F.; Oedai, S.; Brussee, N.; van der Linde, H.; Aksulu, H.; Austad, T. Low salinity EOR in carbonates. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Tulsa, OK, USA, 14–18 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Khatib, Z.; Salanitro, J. Reservoir souring: Analysis of surveys and experience in sour waterfloods. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, San Antonio, TX, USA, 5–8 October 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bódi, T. Direct and indirect connate water saturation determination methods in the practice of Riaes Tibor Bódi. In Proceedings of the Conference & Exhibition on Earth Sciences and Environmental Protection, Miskolc-Egyetemváros, Hungary, 27–29 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Morrow, N.R.; Xie, X. Oil recovery by spontaneous imbibition from weakly water-wet rocks. Petrophysics 2001, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Puntervold, T.; Strand, S.; Austad, T. Water flooding of carbonate reservoirs: Effects of a model base and natural crude oil bases on chalk wettability. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puntervold, T.; Strand, S.; Austad, T. New method to prepare outcrop chalk cores for wettability and oil recovery studies at low initial water saturation. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 3425–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denekas, M.; Mattax, C.; Davis, G. Effects of crude oil components on rock wettability. Soc. Pet. Eng. 1959, 216, 330–333. [Google Scholar]
- Mullins, O.C.; Sabbah, H.; Eyssautier, J.; Pomerantz, A.E.; Barré, L.; Andrews, A.B.; Ruiz-Morales, Y.; Mostowfi, F.; McFarlane, R.; Goual, L. Advances in asphaltene science and the Yen–Mullins model. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 3986–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breure, B.; Subramanian, D.; Leys, J.; Peters, C.J.; Anisimov, M.A. Modeling asphaltene aggregation with a single compound. Energy Fuels 2012, 27, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbaghi, S.; Jahanmiri, A.; Ayatollahi, S.; Shariaty Niassar, M.; Mansoori, G.A. Characterization of asphaltene using potential energy and nanocalculation. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. (IJCCE) 2008, 27, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Akbarzadeh, K.; Hammami, A.; Kharrat, A.; Zhang, D.; Allenson, S.; Creek, J.; Kabir, S.; Jamaluddin, A.; Marshall, A.G.; Rodgers, R.P. Asphaltenes—Problematic but rich in potential. Oilfield Rev. 2007, 19, 22–43. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, S.; Doe, P. Base number and wetting properties of crude oils. Soc. Pet. Eng. Reserv. Eng. 1993, 8, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Austad, T. The relative effects of acid number and temperature on chalk wettability. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers International Symposium on Oilfield Chemistry, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 2–4 February 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, S.J.; Austad, T.; Strand, S. Effect of water-extractable carboxylic acids in crude oil on wettability in carbonates. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 2587–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standnes, D.C.; Austad, T. Wettability alteration in chalk: 1. Preparation of core material and oil properties. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2000, 28, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standnes, D.C.; Austad, T. Wettability alteration in chalk: 2. Mechanism for wettability alteration from oil-wet to water-wet using surfactants. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2000, 28, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, S.J.; Austad, T.; Strand, S.; Puntervold, T. Wettability alteration in carbonates: The effect of water-soluble carboxylic acids in crude oil. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2974–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.M.; Clouse, J.A.; Longo, J.M. Adsorption of organic compounds on carbonate minerals: 1. Model compounds and their influence on mineral wettability. Chem. Geol. 1993, 109, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, P.; Thyne, G.; Rao, D. Extensive experimental wettability study in sandstone and carbonate-oil-brine systems: Part 1—Screening tool development. In Proceedings of the International Symposium of the Society of Core Analysts, Napa Valley, CA, USA, 16–19 September 2013; pp. 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Gomari, K.R.; Hamouda, A.; Davidian, T.; Fargland, D. Study of the effect of acidic species on wettability alteration of calcite surfaces by measuring partitioning coefficients, IFT and contact angles. Contact Angle Wettabil. Adhes. 2006, 4, 351–367. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, D.N. Wettability effects in thermal recovery operations. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers/DOE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Tulsa, OK, 21–24 April 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Shimoyama, A.; Johns, W.D. Formation of alkanes from fatty acids in the presence of CaCO3. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1972, 36, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M.A.; Habibi, A.; Ayatollahi, S.; Masihi, M.; Ashoorian, S. Effect of time and temperature on crude oil aging to do a right surfactant flooding with a new approach. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference-Asia, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 25–28 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Tweheyo, M.T.; Austad, T. Wettability alteration and improved oil recovery in chalk: The effect of calcium in the presence of sulfate. Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 2056–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal, M.A.; Kucheryavskiy, S.; Thyne, G.; Søgaard, E.G. Study of ionically modified water performance in the carbonate reservoir system by multivariate data analysis. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 2414–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, J. Asphaltene precipitation and crude oil wetting. Soc. Pet. Eng. Adv. Technol. Ser. 1995, 3, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austad, T.; Strand, S.; Puntervold, T.; Ravari, R.R. New method to clean carbonate reservoir cores by seawater. Presented at the SCA2008-15 International Symposium of the Society of Core Analysts, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 29 October–2 November 2008; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, S.J.; Austad, T.; Strand, S.; Frank, S.; Mogensen, K. Evaluation of EOR potentials in an offshore limestone reservoir: A case study. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Symposium on Reservoir Wettability, Calgary, AB, Canada, 6–8 September 2010; pp. 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ravari, R.R. Water-Based EOR in Limestone by Smart Water: A Study of Surface Chemistry. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Stavanger, Stavanger, Norway, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shariatpanahi, S.; Strand, S.; Austad, T.; Aksulu, H. Wettability restoration of limestone cores using core material from the aqueous zone. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2012, 30, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernø, M.; Grønsdal, R.; Åsheim, J.; Nyheim, A.; Berge, M.; Graue, A. Use of sulfate for water based enhanced oil recovery during spontaneous imbibition in chalk. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Xie, X.; Yin, P.; Morrow, N.R. Application of coalbed methane water to oil recovery from Tensleep sandstone by low salinity waterflooding. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, Tulsa, OK, USA, 20–23 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Korsnes, R.; Strand, S.; Hoff, ∅.; Pedersen, T.; Madland, M.; Austad, T. Does the chemical interaction between seawater and chalk affect the mechanical properties of chalk. In Multiphysics Coupling and Long Term Behaviour in Rock Mechanics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 427–434. [Google Scholar]
- Puntervold, T. Waterflooding of Carbonate Reservoirs: EOR by Wettability Alteration. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Stavanger, Stavanger, Norway, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Korsnes, R.; Madland, M.; Austad, T. Impact of brine composition on the mechanical strength of chalk at high temperature. In Eurock, Proceedings of the International Symposium of the International Society for Rock Mechanics, Liège, Belgium, 9–12 May 2006; Taylor & Francis/Balkema: Ghent, Belgium, 2006; pp. 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Austad, T. Wettability and oil recovery from carbonates: Effects of temperature and potential determining ions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 279, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, S.; Standnes, D.; Austad, T. New wettability test for chalk based on chromatographic separation of SCN− and SO. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2006, 52, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hognesen, E.J.; Strand, S.; Austad, T. Waterflooding of preferential oil-wet carbonates: Oil recovery related to reservoir temperature and brine composition. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Europec/EAGE Annual Conference, Madrid, Spain, 13–16 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Austad, T.; Strand, S.; Puntervold, T. Is wettability alteration of carbonates by seawater caused by rock dissolution? In Proceedings of the SCA International Symposium, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 27–30 September 2009; p. 2009-43. [Google Scholar]
- Shehata, A.M.; Alotaibi, M.B.; Nasr-El-Din, H.A. Waterflooding in carbonate reservoirs: Does the salinity matter? Soc. Pet. Eng. Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2014, 17, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, P.V.; Thyne, G. Functional wettability in carbonate reservoirs. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 9217–9225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, S.J.; Austad, T.; Strand, S. Water-based enhanced oil recovery (EOR) by “smart water” in carbonate reservoirs. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Enhanced Oil Recovery Conference at Oil and Gas West Asia, Muscat, Oman, 16–18 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, W.; Haroun, M.; Sarma, H.; Adeoye, J.; Aras, P.; Punjabi, S.; Rahman, M.; Al Kobaisi, M. A novel approach of using phosphate-spiked smart brines to alter wettability in mixed oil-wet carbonate reservoirs. In Proceedings of the Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition and Conference, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 9–12 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sohal, M.A.; Thyne, G.; Søgaard, E.G. Novel application of the flotation technique to measure the wettability changes by ionically modified water for improved oil recovery in carbonates. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 6306–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, M.B.; Azmy, R.; Nasr-El-Din, H.A. Wettability challenges in carbonate reservoirs. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Tulsa, Oklahoma, USA, 24–28 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nasralla, R.A.; Sergienko, E.; Masalmeh, S.K.; van der Linde, H.A.; Brussee, N.J.; Mahani, H.; Suijkerbuijk, B.; Alqarshubi, I. Demonstrating the potential of low-salinity waterflood to improve oil recovery in carbonate reservoirs by qualitative coreflood. In Proceedings of the Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition and Conference, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 10–13 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Al Harrasi, A.; Al-maamari, R.S.; Masalmeh, S.K. Laboratory investigation of low salinity waterflooding for carbonate reservoirs. In Proceedings of the Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Conference and Exhibition, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 11–14 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Attar, H.H.; Mahmoud, M.Y.; Zekri, A.Y.; Almehaideb, R.; Ghannam, M. Low-salinity flooding in a selected carbonate reservoir: Experimental approach. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2013, 3, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standnes, D.C.; Nogaret, L.A.; Chen, H.L.; Austad, T. An evaluation of spontaneous imbibition of water into oil-wet carbonate reservoir cores using a nonionic and a cationic surfactant. Energy Fuels 2002, 16, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrahian, K.; Seiedi, O.; Sheykhan, M.; Sefti, M.V.; Ayatollahi, S. Wettability alteration of carbonate rocks by surfactants: A mechanistic study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 410, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirasaki, G.; Zhang, D.L. Surface chemistry of oil recovery from fractured, oil-wet, carbonate formations. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 2004, 9, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Lee, T.R. Contact angle and wetting properties. In Surface Science Techniques; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 3–34. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, W. Wettability Literature survey-part 1: Rock/oil/brine interactions and the effects of core handling on wettability. J. Pet. Technol. 1986, 1125–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, A.A.; Rezaei Gomari, K.A. Influence of temperature on wettability alteration of carbonate reservoirs. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers/DOE Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, Tulsa, OK, USA, 22–26 April 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kafili Kasmaei, A.; Rao, D. Is wettability alteration the main cause for enhanced recovery in low-salinity waterflooding? In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Tulsa, Oklahoma, USA, 12–16 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Butt, H.J.; Cappella, B.; Kappl, M. Force measurements with the atomic force microscope: Technique, interpretation and applications. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2005, 59, 1–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Hilal, N.; Langston, P.; Starov, V. Interaction forces between colloidal particles in liquid: Theory and experiment. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 134, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.D.; Al-Mahrouqi, D.; Vinogradov, J. Zeta potential in oil-water-carbonate systems and its impact on oil recovery during controlled salinity water-flooding. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, H.J.; Jaschke, M.; Ducker, W. Measuring surface forces in aqueous electrolyte solution with the atomic force microscope. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1995, 38, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiedi, O.; Rahbar, M.; Nabipour, M.; Emadi, M.A.; Ghatee, M.H.; Ayatollahi, S. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) investigation on the surfactant wettability alteration mechanism of aged mica mineral surfaces. Energy Fuels 2010, 25, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargari, S.; Ostvar, S.; Niazi, A.; Ayatollahi, S. Atomic force microscopy and wettability study of the alteration of mica and sandstone by a biosurfactant-producing bacterium Bacillus thermodenitrificans. J. Adv. Microsc. Res. 2010, 5, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducker, W.A.; Senden, T.J.; Pashley, R.M. Direct measurement of colloidal forces using an atomic force microscope. Nature 1991, 353, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigil, G.; Xu, Z.; Steinberg, S.; Israelachvili, J. Interactions of silica surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1994, 165, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, P.G.; Larson, I.; Scales, P.J. Electrokinetic and direct force measurements between silica and mica surfaces in dilute electrolyte solutions. Langmuir 1997, 13, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toikka, G.; Hayes, R.A. Direct measurement of colloidal forces between mica and silica in aqueous electrolyte. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 191, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Masliyah, J. Studies on bitumen-silica interaction in aqueous solutions by atomic force microscopy. Langmuir 2003, 19, 3911–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedeva, E.; Senden, T.; Knackstedt, M.; Morrow, N. Improved Oil Recovery from Tensleep Sandstone–Studies of Brine-Rock Interactions by Micro-CT and AFM. In Proceedings of the IOR 2009-15th European Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, Paris, France, 27–29 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Karoussi, O.; Skovbjerg, L.L.; Hassenkam, T.; Stipp, S.S.; Hamouda, A.A. AFM study of calcite surface exposed to stearic and heptanoic acids. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 325, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, M.; Segura, J.J.; Erickson, B.W.; Fantner, G.; Stellacci, F.; Voïtchovsky, K. Growth and dissolution of calcite in the presence of adsorbed stearic acid. Langmuir 2015, 31, 7563–7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomari, K.R.; Hamouda, A.; Denoyel, R. Influence of sulfate ions on the interaction between fatty acids and calcite surface. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 287, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei Gomari, K.A.; Karoussi, O.; Hamouda, A.A. Mechanistic study of interaction between water and carbonate rocks for enhancing oil recovery. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Europec/EAGE Annual Conference and Exhibition, Vienna, Austria, 12–15 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Alroudhan, A.; Vinogradov, J.; Jackson, M. Zeta potential of intact natural limestone: Impact of potential-determining ions Ca, Mg and SO4. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 493, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfared, A.D.; Ghazanfari, M.; Jamialahmadi, M.; Helalizadeh, A. Adsorption of silica nanoparticles onto calcite: Equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic and DLVO analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 281, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mahrouqi, D.; Vinogradov, J.; Jackson, M.D. Zeta potential of artificial and natural calcite in aqueous solution. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 240, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihajlović, S.R.; Vučinić, D.R.; Sekulić, Ž.T.; Milićević, S.Z.; Kolonja, B.M. Mechanism of stearic acid adsorption to calcite. Powder Technol. 2013, 245, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyström, R.; Lindén, M.; Rosenholm, J.B. The influence of Na+, Ca2+, Ba2+, and La3+ on the ζ potential and the yield stress of calcite dispersions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 242, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahani, H.; Keya, A.L.; Berg, S.; Bartels, W.B.; Nasralla, R.; Rossen, W.R. Insights into the mechanism of wettability alteration by low-salinity flooding (LSF) in carbonates. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 1352–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, K.; Araujo, M. Temperature and pressure effects on zeta potential values of reservoir minerals. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 300, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotaibi, M.B.; Nasr-El-Din, H.A.; Fletcher, J.J. Electrokinetics of limestone and dolomite rock particles. Soc. Pet. Eng. Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2011, 14, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahani, H.; Keya, A.L.; Berg, S.; Nasralla, R. The effect of salinity, rock type and ph on the electrokinetics of carbonate-brine interface and surface complexation modeling. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Reservoir Characterisation and Simulation Conference and Exhibition, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 14–16 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, S. Sensitivity of surface complexation modeling to the surface site density parameter. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1991, 145, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiorth, A.; Cathles, L.; Kolnes, J.; Vikane, O.; Lohne, A.; Madland, M. A chemical model for the seawater-CO2-carbonate system–aqueous and surface chemistry. In Proceedings of the Wettability Conference, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 29 October–2 November 2008; pp. 27–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hiorth, A.; Cathles, L.; Kolnes, J.; Vikane, O.; Lohne, A.; Madland, M. Chemical modelling of wettability change in carbonate rocks. Presented at the 10th Wettability Conference, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 7–28 October 2008; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Heberling, F.; Trainor, T.P.; Lützenkirchen, J.; Eng, P.; Denecke, M.A.; Bosbach, D. Structure and reactivity of the calcite–water interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 354, 843–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, L.; Duan, X.; Puerto, M.; Chapman, W.G.; Biswal, S.L.; Hirasaki, G.J. Surface complexation modeling of calcite zeta potential measurements in brines with mixed potential determining ions (Ca2+, CO, Mg2+, SO) for characterizing carbonate wettability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 506, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotaibi, M.; Nasr-El-Din, H. Effect of brine salinity on reservoir fluids interfacial tension. EUROPEC/EAGE Annual Conference and Exhibition, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–11 June 2009. Pap. Soc. Pet. Eng. 2009, 121569, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lashkarbolooki, M.; Ayatollahi, S.; Riazi, M. Effect of salinity, resin, and asphaltene on the surface properties of acidic crude oil/smart water/rock system. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 6820–6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Miyauchi, T.E.; Firoozabadi, A.; Fuller, G.G. Nonmonotonic elasticity of the crude oil–brine interface in relation to improved oil recovery. Langmuir 2016, 32, 2192–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado, V.; Garcia-Olvera, G.; Manrique, E. Considerations of adjusted brine chemistry for waterflooding in offshore environments. In Proceedings of the OTC Brasil, Offshore Technology Conference, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 27–29 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vijapurapu, C.S.; Rao, D.N. Effect of brine dilution and surfactant concentration on spreading and wettability. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Oilfield Chemistry, Houston, TX, USA, 5–7 February 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Okasha, T.M.; Alshiwaish, A. Effect of brine salinity on interfacial tension in Arab-D carbonate reservoir, Saudi Arabia. In Proceedings of the Middle East Oil and Gas Show and Conference, Manama, Bahrain, 15–18 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Alameri, W.; Teklu, T.W.; Graves, R.M.; Kazemi, H.; AlSumaiti, A.M. Wettability alteration during low-salinity waterflooding in carbonate reservoir cores. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Asia Pacific Oil & Gas Conference and Exhibition, Adelaide, Australia, 14–16 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W. Experimental Investigation of Dynamic Interfacial Interactions at Reservoir Conditions. Master’s Thesis, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, X.; Morrow, N.; Zhou, X. Characterization of wettability from spontaneous imbibition measurements. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 1999, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masalmeh, S. Impact of capillary forces on residual oil saturation and flooding experiments for mixed to oil-wet carbonate reservoirs. In Proceedings of the International Symposium of the Society of Core Analysts held in Aberdeen (SCA2012-11), Scotland, UK, 27–30 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Evje, S.; Kleppe, H.; Karstad, T.; Fjelde, I.; Skjaeveland, S.M. Analysis of the Wettability alteration process during seawater imbibition into preferentially oil-wet chalk cores. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, Tulsa, OK, USA, 20–23 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Al-adasani, A.; Bai, B.; Wu, Y.S. Investigating low salinity waterflooding recovery mechanisms in carbonate reservoirs. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Enhanced Oil Recovery Conference at Oil and Gas West Asia, Muscat, Oman, 16–18 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Al Shalabi, E.W.; Sepehrnoori, K.; Delshad, M. Mechanisms behind low salinity water injection in carbonate reservoirs. Fuel 2014, 121, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shalabi, E.W.; Sepehrnoori, K.; Delshad, M. Does the double layer expansion mechanism contribute to the LSWI effect on hydrocarbon recovery from carbonate rocks? In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Reservoir Characterization and Simulation Conference and Exhibition, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 16–18 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, C.; Li, L.; Johns, R.T.; Xu, J. A mechanistic model for wettability alteration by chemically tuned water flooding in carbonate reservoirs. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 27–29 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sylte, J.; Hallenbeck, L.; Thomas, L. Ekofisk formation pilot waterflood. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Houston, TX, USA, 2–5 October 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Hallenbeck, L.; Sylte, J.; Ebbs, D.; Thomas, L. Implementation of the Ekofisk field waterflood. Soc. Pet. Eng. Form. Eval. 1991, 6, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Filoco, P. Effect of brine salinity and crude-oil properties on oil recovery and residual saturations. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 2000, 5, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbalaka, C.C.; Dandekar, A.Y.; Patil, S.L.; Khataniar, S.; Hemsath, J. The effect of wettability on oil recovery: A review. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Asia Pacific Oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition, Perth, Australia, 20–22 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Austad, T. Waterflooding in chalk–relationship between oil recovery, new wettability index, brine composition and cationic wettability modifier (Society of Petroleum Engineers94209). In Proceedings of the 67th EAGE Conference & Exhibition, Madrid, Spain, 13–16 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Austad, T.; Strand, S.; Madland, M.V.; Puntervold, T.; Korsnes, R.I. Seawater in chalk: An EOR and compaction fluid. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Dubai, UAE, 4–6 December 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Standnes, D.C. Enhanced Oil Recovery from Oil-Wet Carbonate Rock by Spontaneous Imbibition of Aqueous Surfactant Solutions. Ph.D. Thesis, Dibrugarh University, Assam, India, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, H.; Xie, X.; Yin, P.; Morrow, N.R. Low-salinity waterflooding and mineral dissolution. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Florence, Italy, 19–22 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, G.G. Effect of floodwater salinity on recovery of oil from cores containing clays. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers California Regional Meeting, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 26–27 October 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Emadi, A.; Sohrabi, M. Visual investigation of oil recovery by lowsalinity water injection: Formation of water micro-dispersions and wettabilityalteration. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 30 September–2 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mahzari, P.; Sohrabi, M. Crude oil/brine interactions and spontaneous formation of micro-dispersions in low salinity water injection. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Tulsa, OK, USA, 12–16 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sohrabi, M.; Mahzari, P.; Farzaneh, S.A.; Mills, J.R.; Tsolis, P.; Ireland, S. Novel insights into mechanisms of oil recovery by use of low-salinity-water injection. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 2017, 22, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, V.; Moradi Bidhendi, M.; Garcia-Olvera, G.; Morin, B.; Oakey, J.S. Interfacial visco-elasticity of crude oil-brine: An alternative EOR mechanism in smart waterflooding. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, Tulsa, OK, USA, 12–16 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sandengen, K.; Kristoffersen, A.; Melhuus, K.; Jøsang, L.O. Osmosis as mechanism for low-salinity enhanced oil recovery. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 2016, 21, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura, K.; Chow, R.S. The electric properties of the bitumen/water interface Part II. Application of the ionizable surface-group model. Colloids Surf. 1985, 15, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shalabi, E.; Sepehrnoori, K.; Pope, G.; Mohanty, K. A Fundamental model for predicting oil recovery due to low salinity water injection in carbonate rocks. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers Energy Resources Conference, Port of Spain, Spain, 9–11 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
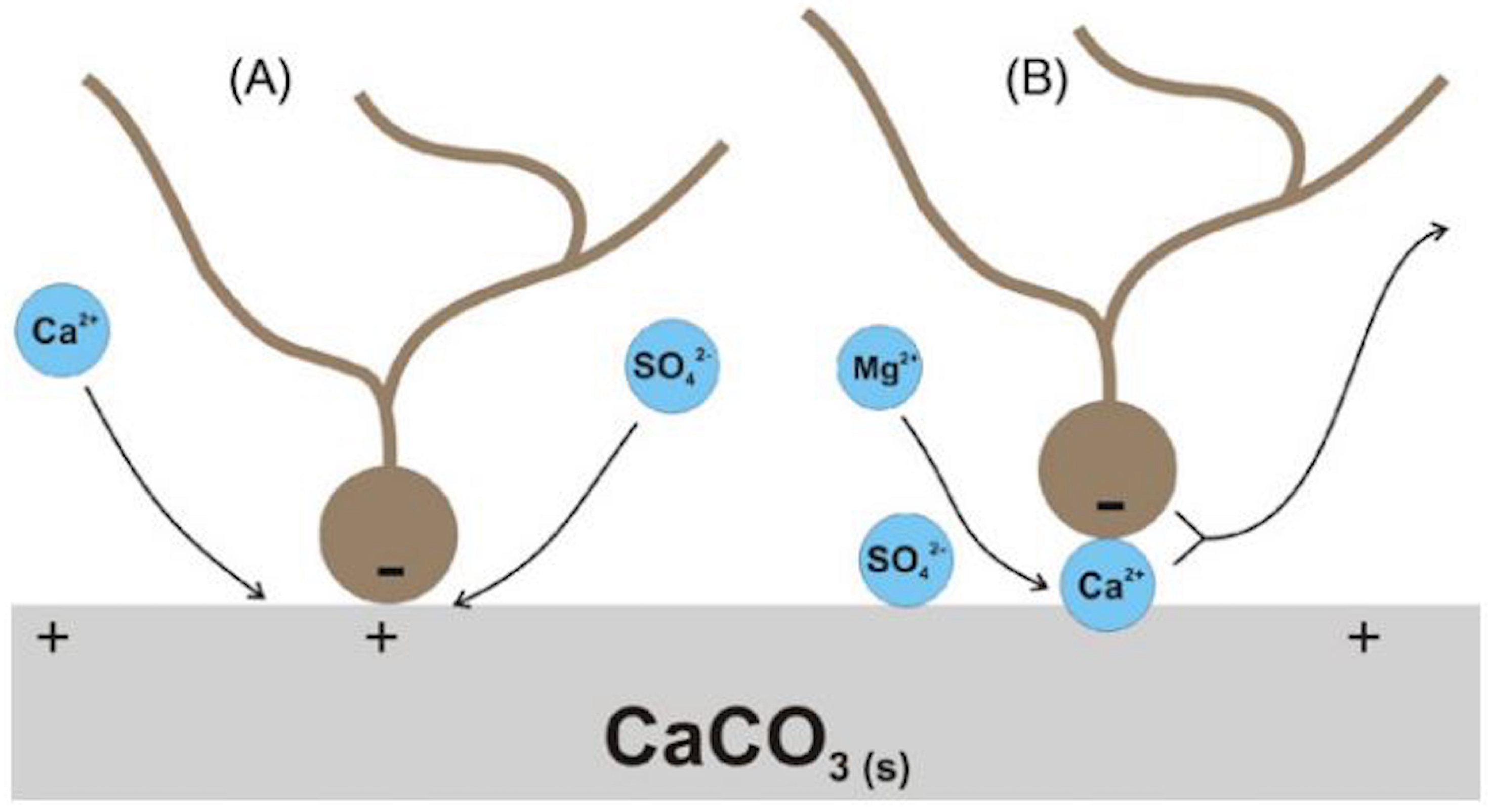
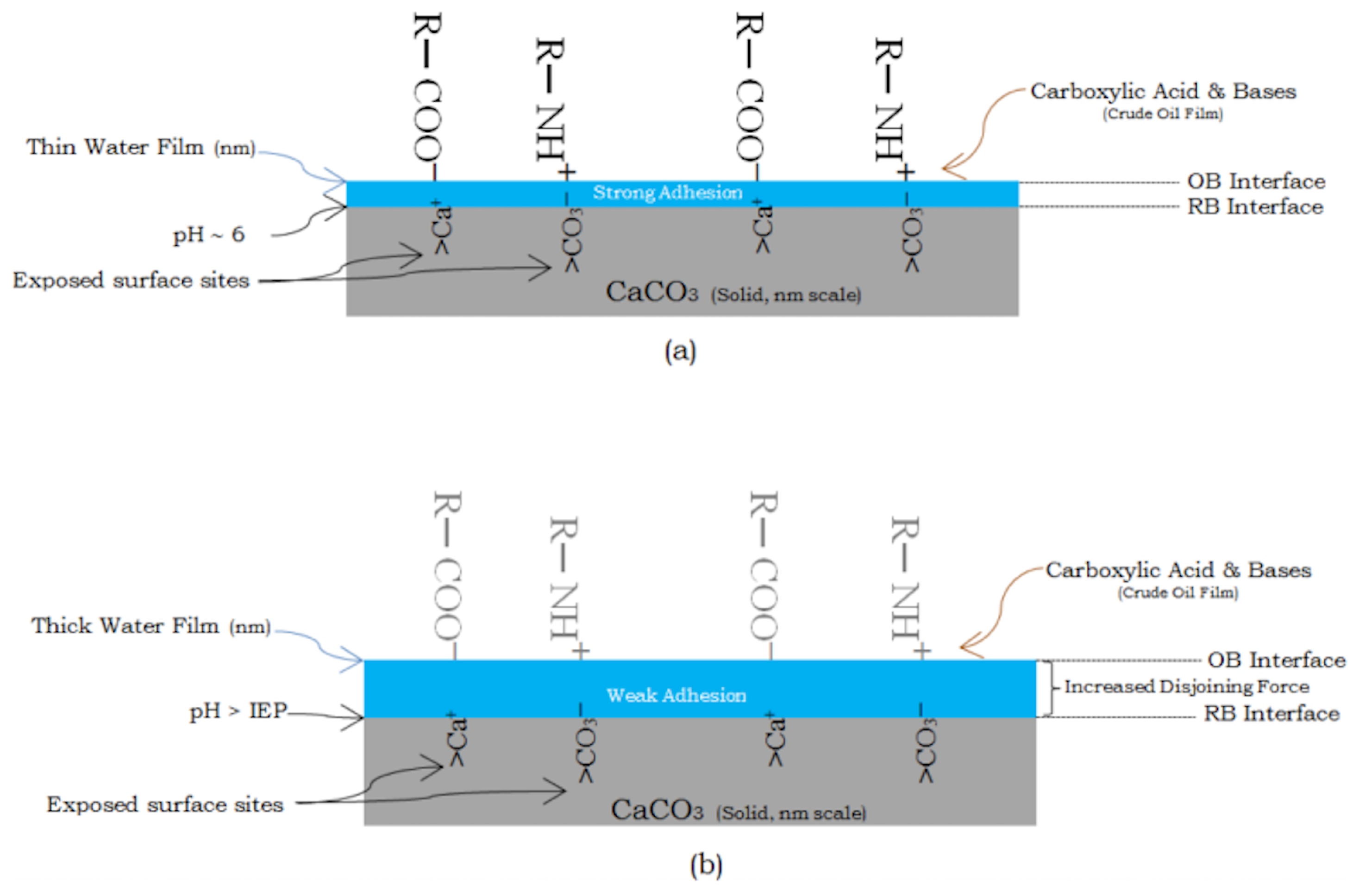
| Type | Seawater (ppm) | Formation Water (ppm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ionic Composition | Persian Gulf | Ekofisk | Common | Persian Gulf | Ekofisk | Common |
| Na+ | 18,040 | 10,345 | 10,890 | 59,491 | 15,745 | 31,275 |
| K+ | 0 | 390 | 460 | 0 | 0 | 654 |
| Ba2+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 269 |
| Ca2+ | 650 | 521 | 428 | 19,040 | 9258 | 5038 |
| Mg2+ | 2160 | 1093 | 1368 | 2439 | 607 | 379 |
| Sr2+ | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 771 |
| SO | 4450 | 2305 | 2960 | 350 | 0 | 0 |
| Cl− | 31,810 | 18,719 | 19,766 | 132,060 | 42,437 | 60,412 |
| CO | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| HCO | 120 | 122 | 0 | 354 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 57,270 | 33,497 | 35,872 | 213,734 | 68,050 | 98,798 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Derkani, M.H.; Fletcher, A.J.; Abdallah, W.; Sauerer, B.; Anderson, J.; Zhang, Z.J. Low Salinity Waterflooding in Carbonate Reservoirs: Review of Interfacial Mechanisms. Colloids Interfaces 2018, 2, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2020020
Derkani MH, Fletcher AJ, Abdallah W, Sauerer B, Anderson J, Zhang ZJ. Low Salinity Waterflooding in Carbonate Reservoirs: Review of Interfacial Mechanisms. Colloids and Interfaces. 2018; 2(2):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleDerkani, Maryam H., Ashleigh J. Fletcher, Wael Abdallah, Bastian Sauerer, James Anderson, and Zhenyu J. Zhang. 2018. "Low Salinity Waterflooding in Carbonate Reservoirs: Review of Interfacial Mechanisms" Colloids and Interfaces 2, no. 2: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2020020
APA StyleDerkani, M. H., Fletcher, A. J., Abdallah, W., Sauerer, B., Anderson, J., & Zhang, Z. J. (2018). Low Salinity Waterflooding in Carbonate Reservoirs: Review of Interfacial Mechanisms. Colloids and Interfaces, 2(2), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2020020








