Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane Films for Liquid Crystal Alignment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
- γS < γLC—homeotropic alignment
- γS > γLC—homogenous alignment
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qi, H.; Hegmann, T. Impact of nanoscale particles and carbon nanotubes on current and future generations of liquid crystal displays. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 3288–3294. [Google Scholar]
- Jeng, S.-C.; Kuo, C.-W.; Wang, H.-L.; Liao, C.-C. Nanoparticles-induced vertical alignment in liquid crystal cell. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 061112. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.-J.; Jeng, S.-C.; Yang, C.-Y.; Kuo, C.-W.; Liao, C.-C. Characteristics of nanoparticle-doped homeotropic liquid crystal devices. J Phys. D 2009, 42, 025102. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, W.-Y.; Jeng, S.-C.; Ding, J.-M.; Kuo, C.-W.; Chin, W.-K. Flexible homeotropic liquid crystal displays using low-glass-transition-temperature poly(ethylene terephthalate) substrates. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 49, 010205. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.-J.; Jeng, S.-C.; Hsieh, I.-M. Nanoparticle-doped polyimide for controlling the pretilt angle of liquid crystals devices. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 16507–16512. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.H.; Kwon, D.W.; Gim, H.Y.; Jeong, K.U.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, Y.H.; Ryu, J.J.; Kim, K.H. Polymer-stabilized pretilt angle on the surface of nanoparticle-induced vertical-alignment surface for multi-domain vertical-alignment liquid-crystal display. J. SID 2011, 19, 417–422. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.-Z.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Lin, T.-H. Single-cell-gap transflective liquid-crystal display based on photo- and nanoparticle-induced alignment effects. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 2545–2547. [Google Scholar]
- Fuh, A.Y.-G.; Huang, C.-Y.; Liu, C.-K.; Chen, Y.-D.; Cheng, K.-T. Dual Liquid crystal alignment configuration based on nanoparticle-doped polymer films. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 11825–11831. [Google Scholar]
- Baney, R.H.; Itoh, M.; Sakakibara, A.; Suzuki, T. Silsesquioxanes. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 1409–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Leu, C.M.; Chang, Y.T.; Wei, K.H. Polyimide-side-chain tethered polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanocomposites for low-dielectric film applications. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 3721–3727. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, S.; Nguyen, M.; Gong, X.; Gao, Y.; Wu, H.; Moses, D.; Heeger, A.J. Stabilization of semiconducting polymers with silsesquioxane. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2003, 13, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Dong, X.-H.; Yu, X.; Guo, K.; Su, H.; Yue, K.; Wesdemiotis, C.; Cheng, S.Z.D.; Zhang, W.-B. Giant gemini surfactants based on polystyrene–hydrophilic polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane shape amphiphiles: sequential “click” chemistry and solution self-assembly. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.-A.; Choi, Y.-E.; Yoon, W.-J.; Kuo, S.-W.; Hsu, C.-H.; Huang, M.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, K.-U. Asymmetric organic−inorganic hybrid giant molecule: cyanobiphenyl monosubstituted polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanoparticles for vertical alignment of liquid crystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 6300–6306. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, K.; Ishiguro, F.; Jeon, J.-H.; Hiraoka, T.; Chujo, Y. POSS ionic liquid crystals. NPG Asia Mater. 2015, 7, e174. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Dong, X.-H.; Zou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yue, K.; Huang, M.; Liu, H.; Feng, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, W.; et al. Polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane meets “click” chemistry: Rational design and facile preparation of functional hybrid materials. Polymer 2017, 125, 303–329. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, K.; Kozuka, H.; Ueda, K.; Jeon, J.-H.; Chujo, Y. POSS-based molecular fillers for simultaneously enhancing thermal and viscoelasticity of poly(methyl methacrylate) films. Mater. Lett. 2017, 203, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Sigma-Aldrich Corp. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/ (accessed on 30 May 2017).
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.-H.; Chang, W.-Y.; Chen, J.-H. Measurement of the pretilt angle and the cell gap of nematic liquid crystal cells by heterodyne interferometry. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 14143–14149. [Google Scholar]
- Nastishin, Y.A.; Polak, R.D.; Shiyanovskii, S.V.; Bodnar, V.H.; Lavrentovich, O.D. Nematic polar anchoring strength measured by electric field techniques. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 4199–4213. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.J. Precise optical retardation measurement of nematic liquid crystal display using the phase-sensitive technique. J. Display Technol. 2005, 1, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Cognard, J. Alignment of nematic liquid crystals and their mixtures. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. Suppl. 1982, 1, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Geary, J.M.; Goodby, J.W.; Kmetz, A.R.; Patel, J.S. The mechanism of polymer alignment of liquid-crystal materials. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 62, 4100–4108. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, T.; Hiroshima, K. Vertically Aligned Nematic Liquid Crystal on Anodic Porous Alumina. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 43, L1004. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, T.-T.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Pan, R.-P.; Shieh, J.-M.; Pan, C.-L. Strong Vertical Alignment of Liquid Crystal on Porous Anodic Aluminum Oxide Film. J. Display Technol. 2009, 5, 350–354. [Google Scholar]
- Lueder, E. Liquid Crystal Displays: Addressing Schemes and Electro-Optical Effects; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Kim, J.-H.; Shi, Y. What aligns liquid crystals on solid substrates? The role of surface roughness anisotropy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 077803. [Google Scholar]
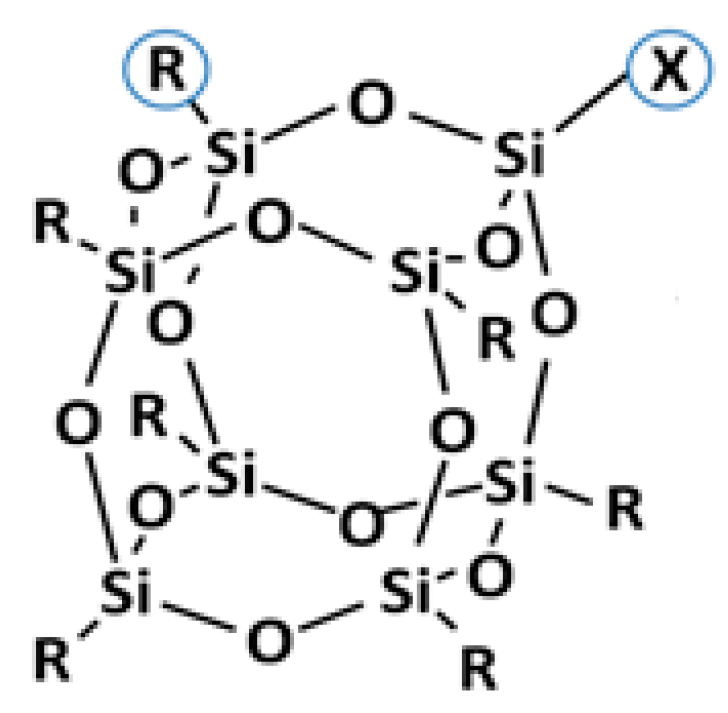
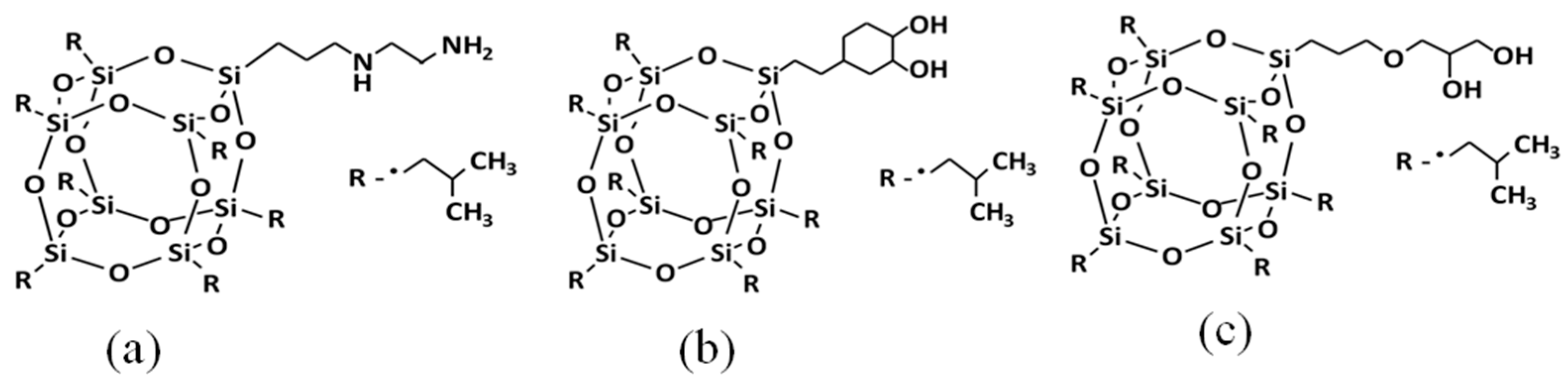

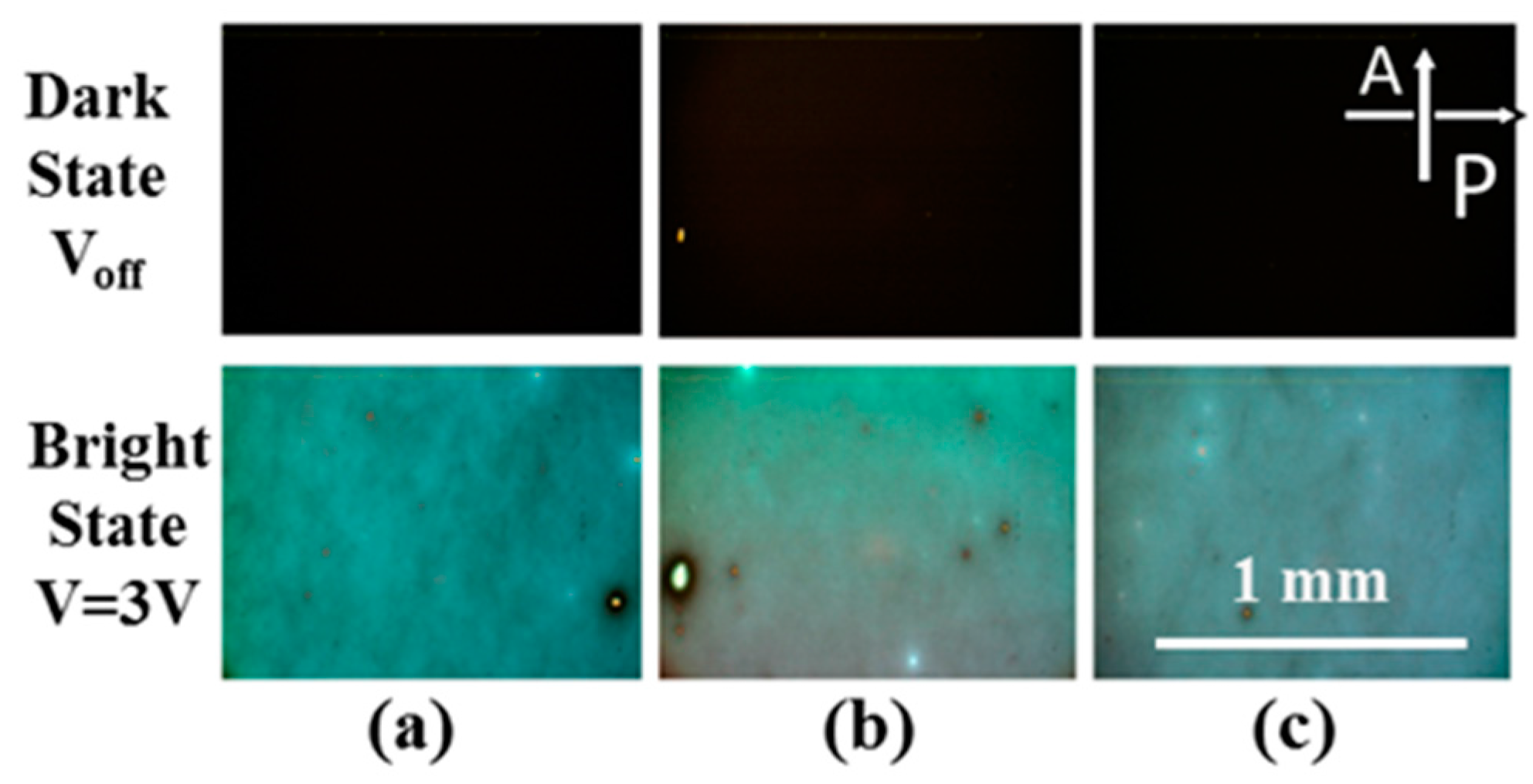
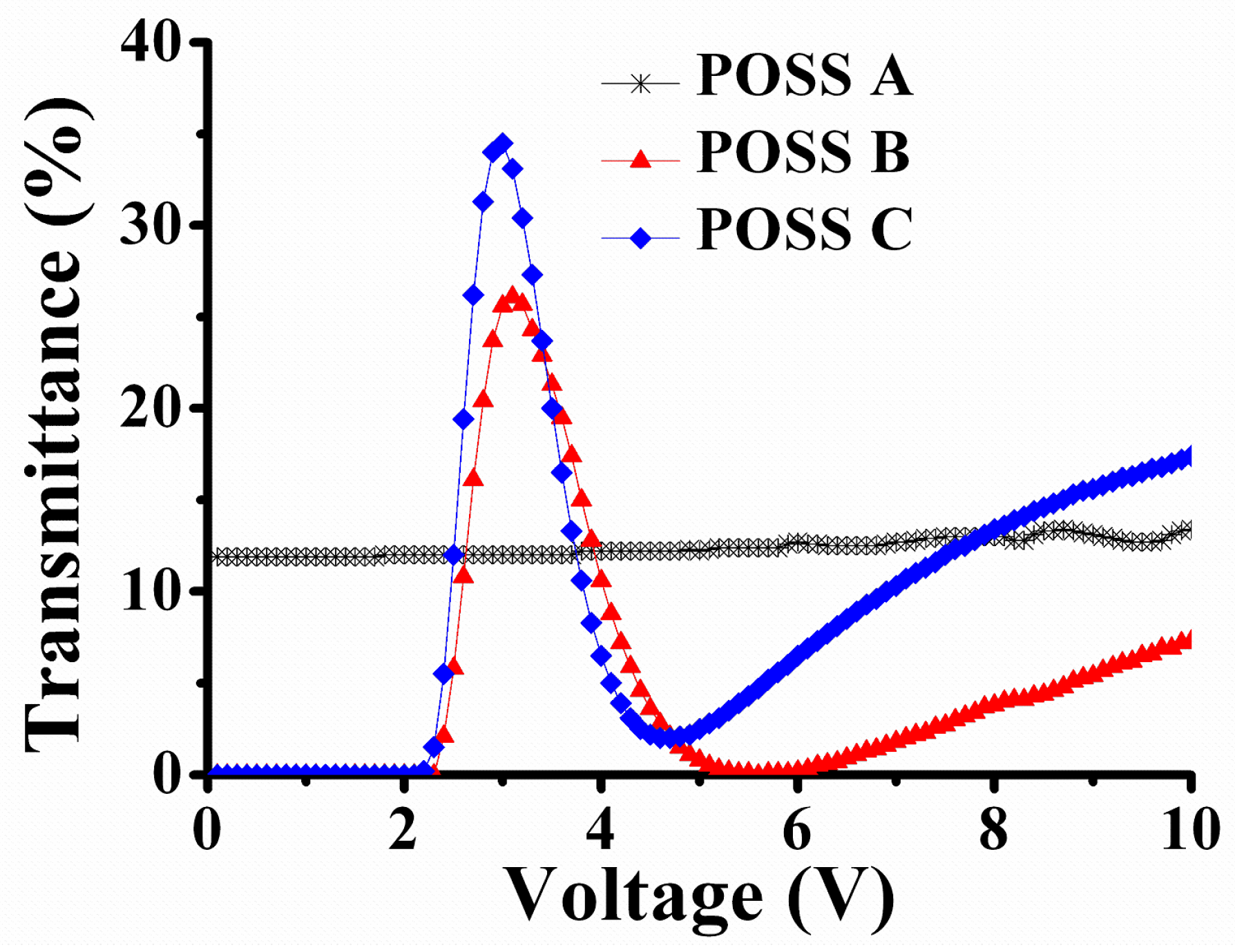

| Material | POSS A | POSS B | POSS C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C33H76N2O12Si8 | C36H78O14Si8 | C34H76O15Si8 |
| Melting Point | 108–117 °C | 121–127 °C | 117–123 °C |
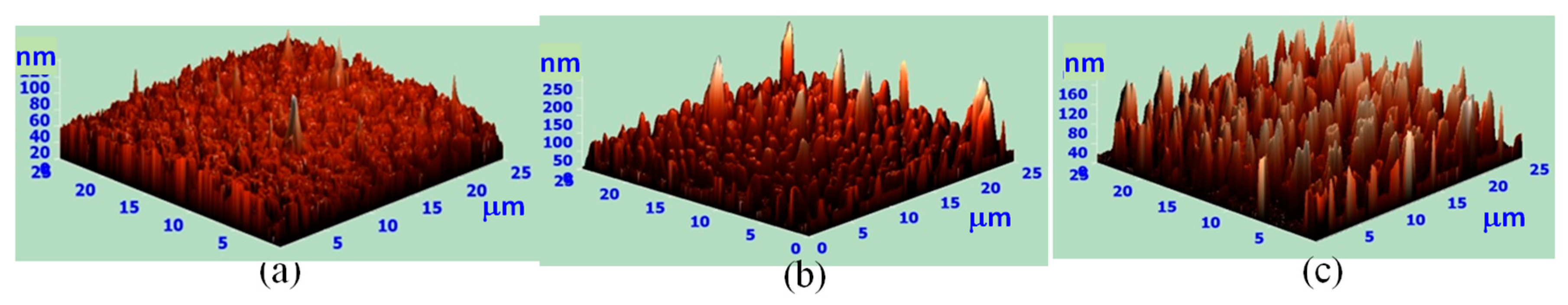
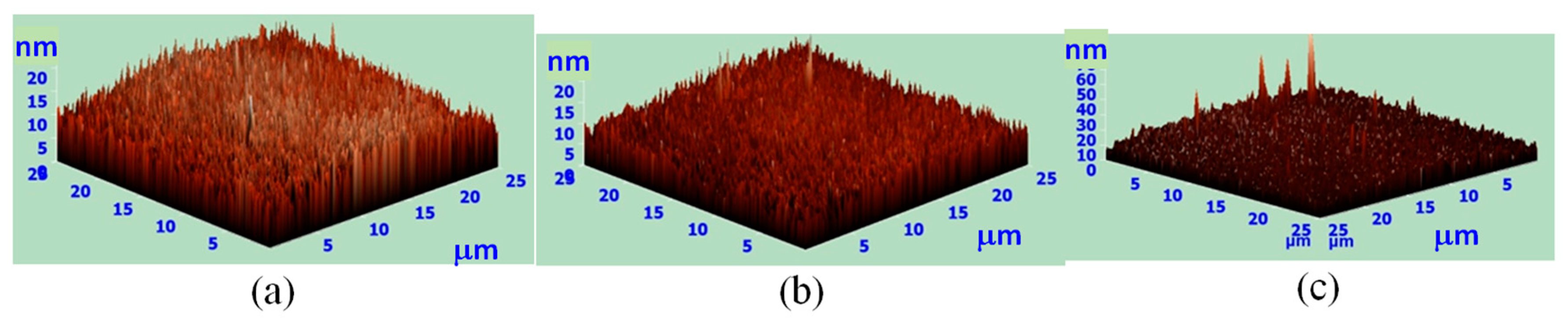
| Surface Roughness (nm) | Process I | Process II |
|---|---|---|
| POSS A | 10.1 | 1.9 |
| POSS B | 23.9 | 1.7 |
| POSS C | 33.3 | 2.2 |
| Process Material | Process I (Coating) | Process II (Melting) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O | CH2I2 | SA b | VA c | FCK | H2O | CH2I2 | SA b | VA c | FCK | |
| POSS A | 102.4 | 59.6 | 29.1 | No | No | 107.3 | 59.2 | 29.0 | Yes | Yes |
| POSS B | 73.5 | 47.1 | 42.7 | Yes | No | 103.1 | 49.9 | 34.3 | Yes | Yes |
| POSS C | 66.1 | 47.4 | 46.2 | Yes | No | 105.9 | 59.6 | 28.8 | Yes | Yes |
| H-PI d | 80.0 | 33.7 | 45.9 | |||||||
| V-PI e | 100.2 | 48.0 | 35.4 | |||||||
| ITO | 25.1 | 33.3 | 72.3 | |||||||
| Material | POSS A | POSS B | POSS C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pretilt angle | 89.7° ± 0.1° | 89.7° ± 0.2° | 89.4° ± 0.1° |
| PAE (×10−4 J/m2) | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 1.2 ± 0.2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.-W.; Jeng, S.-C. Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane Films for Liquid Crystal Alignment. Colloids Interfaces 2018, 2, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2010009
Huang C-W, Jeng S-C. Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane Films for Liquid Crystal Alignment. Colloids and Interfaces. 2018; 2(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chun-Wei, and Shie-Chang Jeng. 2018. "Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane Films for Liquid Crystal Alignment" Colloids and Interfaces 2, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2010009
APA StyleHuang, C.-W., & Jeng, S.-C. (2018). Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane Films for Liquid Crystal Alignment. Colloids and Interfaces, 2(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids2010009




